Submitted:
26 August 2024
Posted:
27 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains and Culture Conditions
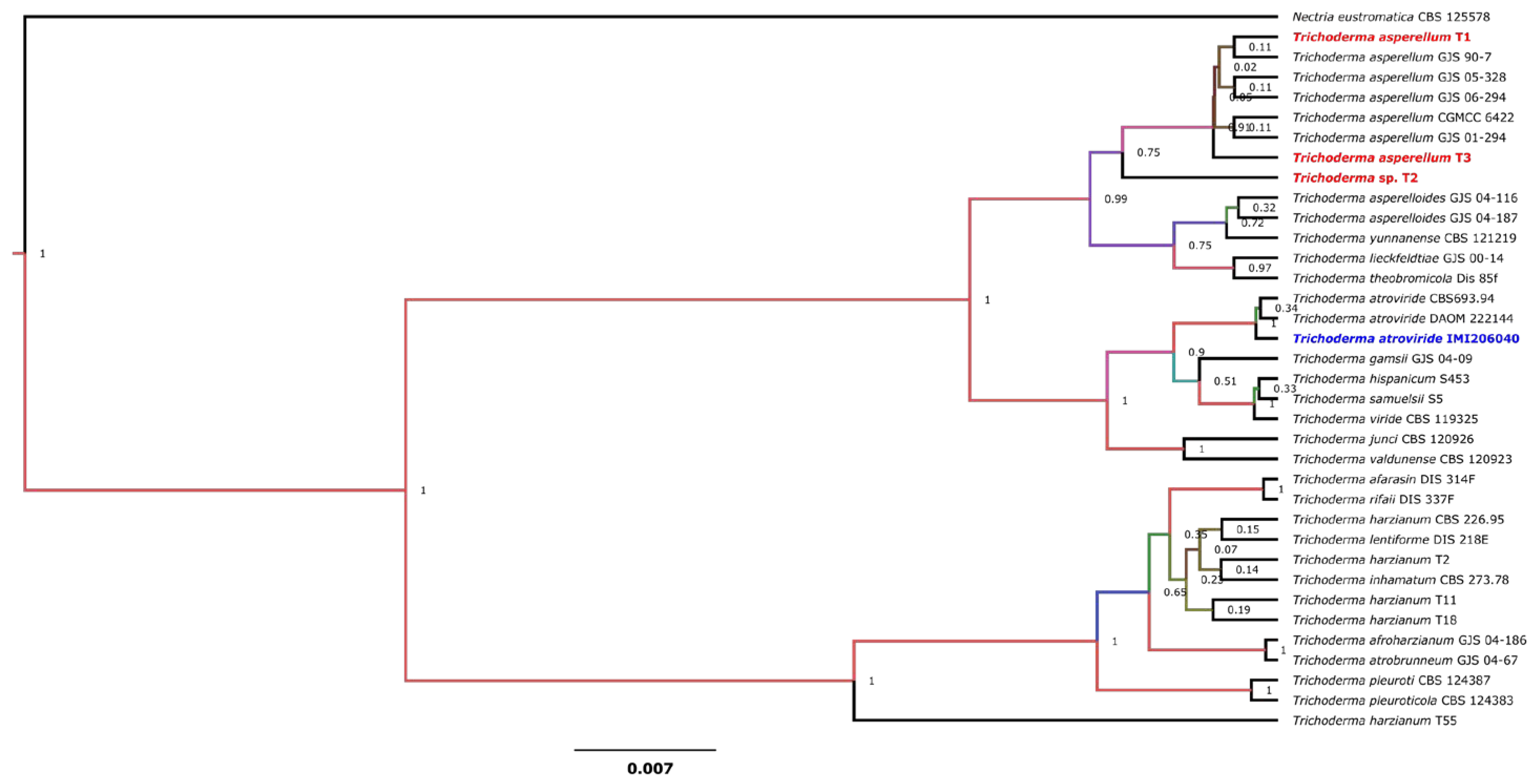
2.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of Trichoderma Strains
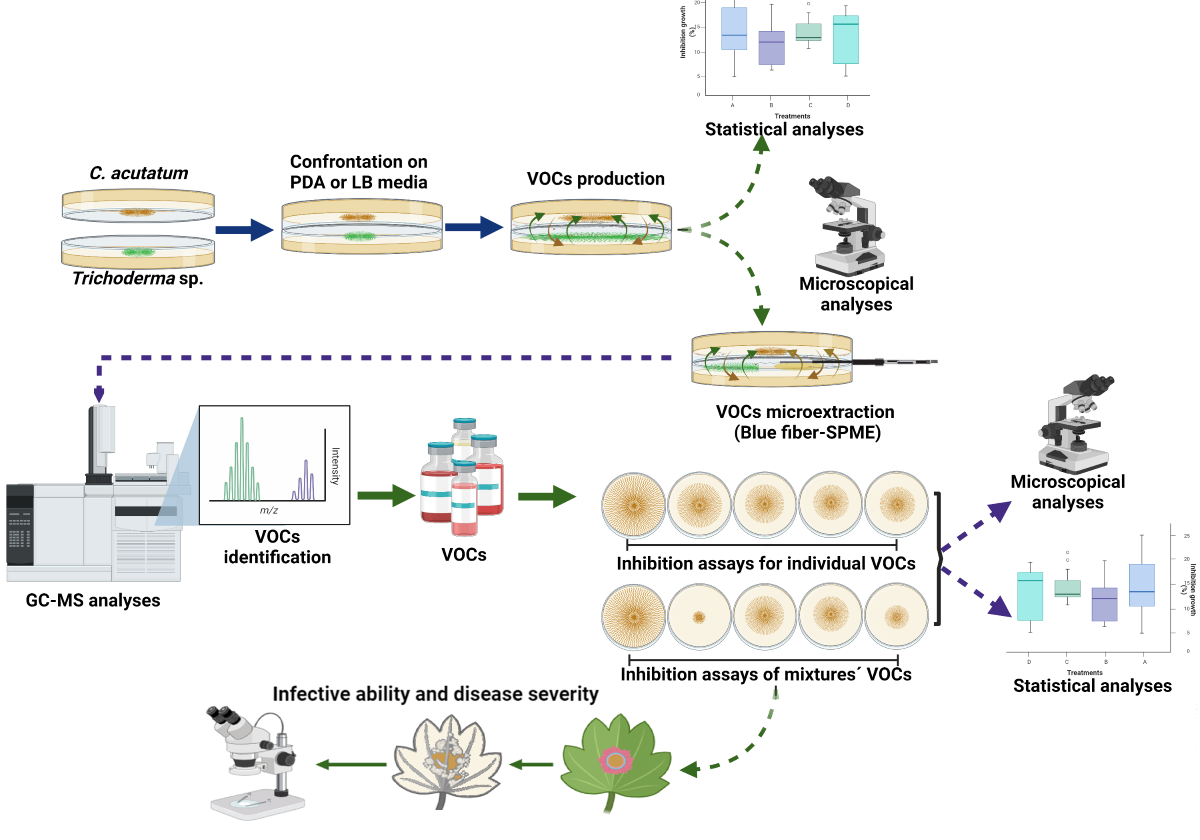
2.3. Antagonistic Activity of VOCs Produced by Trichoderma Strains against C. acutatum in Two Culture Media
| Microorganism | Strain | GenBank accession number | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trichoderma atroviride | IMI206040 | AF278795 | [20] |
| Trichoderma atroviride | CBS693.94 | KF576214 | [21] |
| Trichoderma atroviride | DAOM 222144 | AF456916 | Unpublished (Dodd, S. L., Lieckfeldt, E., and Samuels, G. J.) |
| Trichoderma afarasin | DIS 314F | FJ442259 | Unpublished (Chaverri, P., Samuels, G. J., and Evans, H. C.) |
| Trichoderma atrobrunneum | GJS 04-67 | FJ442273 | |
| Trichoderma lentiforme | DIS 218E | FJ442220 | |
| Trichoderma afroharzianum | GJS 04-186 | FJ442265 | |
| Trichoderma rifaii | DIS 337F | FJ442621 | |
| Trichoderma asperelloides | GJS 04-187 | JN133553 | [23] |
| Trichoderma asperelloides | GJS 04-116 | GU198301 | [24] |
| Trichoderma asperellum | GJS 05-328 | GU198318 | |
| Trichoderma asperellum | GJS 06-294 | GU198307 | |
| Trichoderma asperellum | GJS 90-7 | GU198317 | |
| Trichoderma yunnanense | CBS 121219 | GU198302 | |
| Trichoderma asperellum | GJS 01-294 | EU856297 | [25] |
| Trichoderma asperellum | CGMCC 6422 | KF425754 | [26] |
| Trichoderma gamsii | GJS 04-09 | DQ315459 | [27] |
| Trichoderma harzianum | T55 | MW857216 | Unpublished (Tang,G. and Gong,G.) |
| Trichoderma harzianum | T18 | MW857216 | [28] |
| Trichoderma harzianum | T2 | OR794127 | Unpublished (Alamr, A., Omar, A. F. and Hamed, K. E.) |
| Trichoderma harzianum | CBS 226.95 | AY605713 | Unpublished (Druzhinina, I. S., Bissett, J., and Kubicek, C. P. |
| Trichoderma harzianum | T11 | MT940829 | Benouzza, S) |
| Trichoderma hispanicum | S453 | JN715595 | [29] |
| Trichoderma samuelsii | S5 | JN715596 | |
| Trichoderma inhamatum | CBS 273.78 | MH861134 | [30] |
| Trichoderma pleuroti | CBS:124387 | MH863369 | |
| Trichoderma pleuroticola | CBS:124383 | MH863368 | |
| Nectria eustromatica | CBS:125578 | MH863715 | |
| Trichoderma junci | CBS 120926 | FJ860761 | [31] |
| Trichoderma valdunense | CBS 120923 | NR_134418 | [32] |
| Trichoderma viride | CBS 119325 | NR_138441 | |
| Trichoderma lieckfeldtiae | GJS 00-14 | DQ109528 | [33] |
| Trichoderma theobromicola | Dis 85f | DQ109525 | |
| Trichoderma asperellum | T1 | PQ043841 | This work |
| Trichoderma sp. | T2 | PQ043842 | |
| Trichoderma asperellum | T3 | PQ043843 |
2.4. Identification of VOCs
2.5. Analysis of the Antifungal Activity of the Synthetic VOCs Identified against C. acutatum
2.6. Bioassays of Synthetic VOCs Mixtures on the Growth and Development of C. acutatum
2.7. Analysis of the Infectivity of the Mycelium of C. acutatum Exposed to Synthetic VOCs
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Molecular Identification of Trichoderma Strains
3.2. Antagonistic Activity of VOCs Produced by Trichoderma Strains against C. acutatum
3.3. Identification of VOCs
3.4. Antifungal Activity of Synthetic VOCs against C. acutatum
3.4.1. Antifungal Activity of Synthetic VOCs Individually Assessed against C. acutatum In Vitro
3.4.2. Antifungal Activity of Synthetic VOCs Mixtures against C. acutatum In Vitro
3.5. Analysis of the Infectivity of the Mycelium of C. acutatum Exposed to the α-P+DD+2-P Mixture
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jayawardena, R.S.; Hyde, K.D.; Chen, Y.J.; Papp, V.; Palla, B.; Papp, D.; Bhunjun, C.S.; Hurdeal, V.G.; Senwanna, C.; Manawasinghe, I.S.; et al. One stop shop IV: taxonomic update with molecular phylogeny for important phytopathogenic genera: 76–100 (2020). Fungal Divers 2020, 103, 87–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.O.; Savi, D.C.; Gomes, F.B.; Gos, F.M.W.R.; Silva, G.J.; Glienke, C. Identification of Colletotrichum species associated with postbloom fruit drop in Brazil through GAPDH sequencing analysis and multiplex PCR. Eur J Plant Pathol 2017, 147, 731–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wharton, P.S.; Diéguez-Uribeondo, J. The biology of Colletotrichum acutatum. Anales del Jardín Botánico de Madrid 2004, 61, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Lio, D.; Cobo-DÍaz, J.F.; Masson, C.; Chalopin, M.; Kebe, D.; Giraud, M.; Verhaeghe, A.; Nodet, P.; Sarrocco, S.; Le Floch, G.; et al. Combined Metabarcoding and Multi-locus approach for Genetic characterization of Colletotrichum species associated with common walnut (Juglans regia) anthracnose in France. Sci Rep 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, R.; Van Kan, J.A.L.; Pretorius, Z.A.; Hammond-Kosack, K.E.; Di Pietro, A.; Spanu, P.D.; Rudd, J.J.; Dickman, M.; Kahmann, R.; Ellis, J.; et al. The Top 10 fungal pathogens in molecular plant pathology. Mol Plant Pathol 2012, 13, 414–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, A. An Overview of Distribution, Biology and the Management of Common Bean Anthracnose. J Plant Pathol Microbiol 2013, 04. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segaran, G.; Sathiavelu, M. Fungal endophytes: A potent biocontrol agent and a bioactive metabolites reservoir. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 2019, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolopoulou-Stamati, P.; Maipas, S.; Kotampasi, C.; Stamatis, P.; Hens, L. Chemical Pesticides and Human Health: The Urgent Need for a New Concept in Agriculture. Front Public Health 2016, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabouvette, C.; Olivain, C.; Steinberg, C. Biological control of plant diseases: The European situation. Eur J Plant Pathol 2006, 114, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inayati, A.; Sulistyowati, L.; Aini, L.Q.; Yusnawan, E. Antifungal activity of volatile organic compounds from Trichoderma virens. In Proceedings of the AIP Conference Proceedings; American Institute of Physics Inc., 2019; Vol. 2120, pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Gajera, H.; Domadiya, R.; Patel, S.; Kapopara, M.; Golakiya, B. Molecular mechanism of Trichoderma as bio-control agents against phytopathogen system-a review. Curr Res Microbiol Biotechnol 2013, 1, 133–142. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Jud, W.; Ghirardo, A.; Antritter, F.; Benz, J.P.; Schnitzler, J.P.; Rosenkranz, M. Sniffing fungi – phenotyping of volatile chemical diversity in Trichoderma species. New Phytologist 2020, 227, 244–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Ghirardo, A.; Weber, B.; Schnitzler, J.P.; Philipp Benz, J.; Rosenkranz, M. Trichoderma species differ in their volatile profiles and in antagonism toward ectomycorrhiza Laccaria bicolor. Front Microbiol 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gualtieri, L.; Monti, M.M.; Mele, F.; Russo, A.; Pedata, P.A.; Ruocco, M. Volatile Organic Compound (VOC) Profiles of Different Trichoderma Species and Their Potential Application. Journal of Fungi 2022, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouy, M.; Guindon, S.; Gascuel, O. Sea view version 4: A multiplatform graphical user interface for sequence alignment and phylogenetic tree building. Mol Biol Evol 2010, 27, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouckaert, R.; Vaughan, T.G.; Barido-Sottani, J.; Duchêne, S.; Fourment, M.; Gavryushkina, A.; Heled, J.; Jones, G.; Kühnert, D.; De Maio, N.; et al. BEAST 2.5: An advanced software platform for Bayesian evolutionary analysis. PLoS Comput Biol 2019, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J.; Xie, D.; Baele, G.; Suchard, M.A. Posterior summarization in Bayesian phylogenetics using Tracer 1.7. Syst Biol 2018, 67, 901–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barakat, F.M.; Abada, K.A.; Abou-Zeid, N.M.; El-Gammal, Y.H.E. Effect of volatile and non-volatile compounds of Trichoderma spp. on Botrytis fabae the causative agent of faba bean chocolate spot. American Journal of Life Sciences 2014, 2, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emanuel, R.V.; César Arturo, P.U.; Lourdes Iveth, M.R.; Homero, R. de la C.; Mauricio Nahuam, C.A. In vitro growth of Colletotrichum gloeosporioides is affected by butyl acetate, a compound produced during the co-culture of Trichoderma sp. and Bacillus subtilis. 3 Biotech 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubicek, C.P.; Herrera-Estrella, A.; Seidl-Seiboth, V.; Martinez, D.A.; Druzhinina, I.S.; Thon, M.; Zeilinger, S.; Casas-Flores, S.; Horwitz, B.A.; Mukherjee, P.K.; et al. Comparative genome sequence analysis underscores mycoparasitism as the ancestral life style of Trichoderma. Genome Biol 2011, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoneczny, D.; Oskiera, M.; Szczech, M.; Bartoszewski, G. Genetic diversity of Trichoderma atroviride strains collected in Poland and identification of loci useful in detection of within-species diversity. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 2015, 60, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanafy, A.M.; Al-Mutairi, A.A.; Al-Reedy, R.M.; Al-Garni, S.M. Phylogenetic affiliations of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens isolates produced by a bacteriocin-like substance in goat milk. Journal of Taibah University for Science 2016, 10, 631–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaverri, P.; Samuels, G.J. Evolution Of Habitat Preference And Nutrition Mode In A Cosmopolitan Fungal Genus With Evidence Of Interkingdom Host Jumps And Major Shifts In Ecology. Evolution (N Y) 2013, 67, 2823–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuels, G.J.; Ismaiel, A.; Bon, M.C.; De Respinis, S.; Petrini, O. Trichoderma asperellum sensu lato consists of two cryptic species. Mycologia 2010, 102, 944–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuels, G.J.; Ismaiel, A. Trichoderma evansii and T. lieckfeldtiae: two new T. hamatum-like species. Mycologia 2009, 101, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J. ze; Ojaghian, M.R.; Hyde, K.D. Antagonistic interaction between Trichoderma asperellum and Phytophthora capsici in vitro. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 2016, 17, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuels, G.J.; Dodd, S.; Lu, B.S.; Petrini, O.; Schroers, H.J.; Druzhinina, I.S. The Trichoderma koningii aggregate species. Stud Mycol 2006, 56, 67–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benttoumi, N.; Colagiero, M.; Sellami, S.; Boureghda, H.; Keddad, A.; Ciancio, A. Diversity of nematode microbial antagonists from algeria shows occurrence of nematotoxic Trichoderma spp. Plants 2020, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaklitsch, W.M.; Stadler, M.; Voglmayr, H. Blue pigment in Hypocrea caerulescens sp. Nov. And two additional new species in sect. Trichoderma. Mycologia 2012, 104, 925–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, D.; Groenewald, M.; de Vries, M.; Gehrmann, T.; Stielow, B.; Eberhardt, U.; Al-Hatmi, A.; Groenewald, J.Z.; Cardinali, G.; Houbraken, J.; et al. Large-scale generation and analysis of filamentous fungal DNA barcodes boosts coverage for kingdom fungi and reveals thresholds for fungal species and higher taxon delimitation. Stud Mycol 2019, 92, 135–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaklitsch, W.M. European species of Hypocrea Part I. The green-spored species. Stud Mycol 2009, 63, 1–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbertse, B.; Strope, P.K.; Chaverri, P.; Gazis, R.; Ciufo, S.; Domrachev, M.; Schoch, C.L. Improving taxonomic accuracy for fungi in public sequence databases: applying “one name one species” in well-defined genera with Trichoderma/Hypocrea as a test case. Database (Oxford) 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuels, G.J.; Suarez, C.; Solis, K.; Holmes, K.A.; Thomas, S.E.; Ismaiel, A.; Evans, H.C. Trichoderma theobromicola and T. paucisporum: two new species isolated from cacao in South America. Mycol Res 2006, 110, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Luna, F.M.; López-Bucio, J.; Altamirano-Hernández, J.; Valencia-Cantero, E.; De La Cruz, H.R.; Macías-Rodríguez, L. Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria modulate root-system architecture in Arabidopsis thaliana through volatile organic compound emission. Symbiosis 2010, 51, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, M.S.; Diamont, D.P.; Gutiérrez, B. Nota técnica de tinción de estructuras fúngicas con colorantes vegetales como una alternativa no contaminante; 2011; Vol. 23.
- Saint-Vincent, P.M.B.; Ridout, M.; Engle, N.L.; Lawrence, T.J.; Yeary, M.L.; Tschaplinski, T.J.; Newcombe, G.; Pelletier, D.A. Isolation, characterization, and pathogenicity of two Pseudomonas syringae pathovars from Populus trichocarpa seeds. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, X.; Guo, H.; Zhang, K.; Zhao, M.; Ruan, J.; Chen, J. Trichoderma and its role in biological control of plant fungal and nematode disease. Front Microbiol 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Marco, S.; Metruccio, E.G.; Moretti, S.; Nocentini, M.; Carella, G.; Pacetti, A.; Battiston, E.; Osti, F.; Mugnai, L. Activity of Trichoderma asperellum Strain ICC 012 and Trichoderma gamsii Strain ICC 080 Toward Diseases of Esca Complex and Associated Pathogens. Front Microbiol 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siameto, E.N.; Okoth, S.; Amugune, N.O.; Chege, N.C. Antagonism of Trichoderma farzianum isolates on soil borne plant pathogenic fungi from Embu District, Kenya. J Yeast Fungal Res 2010, 1, 47–54. [Google Scholar]
- Bautista-Ortega, P.I.; Hernández-Hernández, I.; Pérez-Pérez, R.; Soria-Leal, S.-L.L.Y.; Chávez-Avilés, M.N. Modulación diferencial de la actividad enzimática lítica de la pared celular entre Trichoderma sp. y Bacillus subtilis durante el biocontrol de Colletotrichum gloeosporioides in vitro. Ciencia Latina Revista Científica Multidisciplinar 2022, 6, 732–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oo, M.M.; Oh, S.-K. Chilli anthracnose (Colletotrichum spp.) disease and its management approach. Korean Journal of Agricultural Science 2016, 43, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baroncelli, R.; Talhinhas, P.; Pensec, F.; Sukno, S.A.; Floch, G. Le; Thon, M.R. The Colletotrichum acutatum species complex as a model system to study evolution and host specialization in plant pathogens. Front Microbiol 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wang, M.; Damm, U.; Crous, P.W.; Cai, L. Species boundaries in plant pathogenic fungi: A Colletotrichum case study. BMC Evol Biol 2016, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kefialew, Y.; Ayalew, A. Postharvest biological control of anthracnose (Colletotrichum gloeosporioides) on mango (Mangifera indica). Postharvest Biol Technol 2008, 50, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazie, S.; Ayalew, A.; Woldetsadik, K. Integrated management of postharvest banana anthracnose (Colletotrichum musae) through plant extracts and hot water treatment. Crop Protection 2014, 66, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanchaichaovivat, A.; Ruenwongsa, P.; Panijpan, B. Screening and identification of yeast strains from fruits and vegetables: Potential for biological control of postharvest chilli anthracnose (Colletotrichum capsici). Biological Control 2007, 42, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebailly, P.; Vigreux, C.; Godard, T.; Sichel, F.; Bar, E.; Letalaer, J.Y.; Henry-Amar, M.; Gauduchon, P.; 1772, E.A. Assessment of DNA damage induced in vitro by etoposide and ž / two fungicides carbendazim and chlorothalonil in human lymphocytes with the comet assay. Mutat Res 1997, 375, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, D.R. Biological Control by Microorganisms. In Encyclopedia of Life Sciences; Wiley, 2006.
- Sinuco León, D.C.; Pérez Cortés, A.C.; Moreno Sarmiento, N.C. Evaluación de la actividad fungicida e identificación de compuestos orgánicos volátiles liberados por Trichoderma viride. Rev Colomb Biotecnol 2017, 19, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, F.F.; Henning, A.A.; Hungria, M. Phytohormones and antibiotics produced by Bacillus subtilis and their effects on seed pathogenic fungi and on soybean root development. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 2005, 21, 1639–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achimón, F.; Krapacher, C.R.; Jacquat, A.G.; Pizzolitto, R.P.; Zygadlo, J.A. Carbon sources to enhance the biosynthesis of useful secondary metabolites in Fusarium verticillioides submerged cultures. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 2021, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalage Don, S.M.; Gambetta, J.M.; Steel, C.C.; Schmidtke, L.M. Elucidating the interaction of carbon, nitrogen, and temperature on the biosynthesis of Aureobasidium pullulans antifungal volatiles. Environ Microbiol Rep 2021, 13, 482–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Hernández, K.M.; Pérez-Pérez, R.; Orozco-Montes, S.; Chávez-Avilés, M.N. Análisis de la actividad antagónica de Trichoderma sp. sobre Fusarium graminearum, agente causal de fusariosis en trigo Triticum aestivum. In Ciencia transdisciplinar para el desarrollo y la supervivencia de la humanidad; 2021; pp. 184–195 ISBN 978-958-53278-4-9.
- Sezonov, G.; Joseleau-Petit, D.; D’Ari, R. Escherichia coli physiology in Luria-Bertani broth. J Bacteriol 2007, 189, 8746–8749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, A.; Wheatley Ron, E.; Humphris, S.N.; Hackett, C.A.; Florence, M.E.J. Production of Volatile Organic Compounds by Trichoderma in media containing different amino acids and their effect on selected wood decay fungi. Holzforschung 2000, 54, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, L.; Zhao, Y.; Tu, Y.; Yang, C.; Ma, W.; Feng, S.; Lu, L.; Zhang, J. The inhibitory effect of volatile organic compounds produced by Bacillus subtilis CL2 on pathogenic fungi of wolfberry. J Basic Microbiol 2021, 61, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havenga, W.; Jager, D.; Korsten, L. Factors affecting biocontrol efficacy of Bacillus subtilis against Colletotrichum gloeosporioides; 1999; Vol. 22.
- da Silva, L.R.; Inglis, M.C.V.; Moraes, M.C.B.; Magalhães, D.M.; Sifuentes, D.N.; Martins, I.; de Mello, S.C.M. Morphological and protein alterations in Sclerotinia sclerotiorum (Lib.) de Bary after exposure to volatile organic compounds of Trichoderma spp. Biological Control 2020, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, I.; Baroncelli, R.; Hermosa, R.; Monte, E.; Vannacci, G.; Sarrocco, S. Role and genetic basis of specialised secondary metabolites in Trichoderma ecophysiology. Fungal Biol Rev 2022, 39, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Tang, C.; Deng, C.; Wang, Y. Involvement of a response regulator VdSsk1 in stress response, melanin biosynthesis and full virulence in verticillium dahlia. Front Microbiol 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pöhlmann, J.; Risse, C.; Seidel, C.; Pohlmann, T.; Jakopec, V.; Walla, E.; Ramrath, P.; Takeshita, N.; Baumann, S.; Feldbrügge, M.; et al. The Vip1 Inositol Polyphosphate Kinase Family Regulates Polarized Growth and Modulates the Microtubule Cytoskeleton in Fungi. PLoS Genet 2014, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y. chao; Zeng, X. guo; Guo, C.; Zhang, Q. hua; Chen, F. ying; Ren, L.; Chen, W. dong; Qin, L. Reproduction response of Colletotrichum fungi under the fungicide stress reveals new aspects of chemical control of fungal diseases. Microb Biotechnol 2022, 15, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagrouh, F.; Dakka, N.; Bakri, Y. The antifungal activity of Moroccan plants and the mechanism of action of secondary metabolites from plants. J Mycol Med 2017, 27, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marei, G.I.K.; Abdel Rasoul, M.A.; Abdelgaleil, S.A.M. Comparative antifungal activities and biochemical effects of monoterpenes on plant pathogenic fungi. Pestic Biochem Physiol 2012, 103, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. hong; Sun, H. long; Chen, S. yang; Zeng, L.I.; Wang, T. tao Anti-fungal activity, mechanism studies on α-Phellandrene and Nonanal against Penicillium cyclopium. Bot Stud 2017, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, R.; Sharma, P.; Bose, D.; Singh, M. Synergistic potential of α-Phellandrene combined with conventional antifungal agents and its mechanism against antibiotic resistant Candida albicans. CABI Agriculture and Bioscience 2024, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.T.; Lee, C.C.; Leu, W.M.; Wu, J.J.; Huang, Y.C.; Meng, M. Fungicidal activity of volatile organic compounds emitted by burkholderia gladioli strain bbb-01. Molecules 2021, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphris, S.N.; Bruce, A.; Buultjens, E.; Wheatley, R.E. The effects of volatile microbial secondary metabolites on protein synthesis in Serpula lacrymans. FEMS Microbiol Lett 2002, 210, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yin, X.; Wang, Q.; Peng, Y.; Ma, Y.; Liu, P.; Shi, J. Antagonistic activities of volatiles produced by two Bacillus strains against Monilinia fructicola in peach fruit. J Sci Food Agric 2018, 98, 5756–5763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Yuan, J.; E, Y.; Raza, W.; Shen, Q.; Huang, Q. Effects of volatile organic compounds from Streptomyces albulus NJZJSA2 on growth of two fungal pathogens. J Basic Microbiol 2015, 55, 1104–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakami, K.; Kazuo, K.; Fujisawa, T.; Morita, C.; Suzuki, T. US20070191395A1 2007, 1–79.
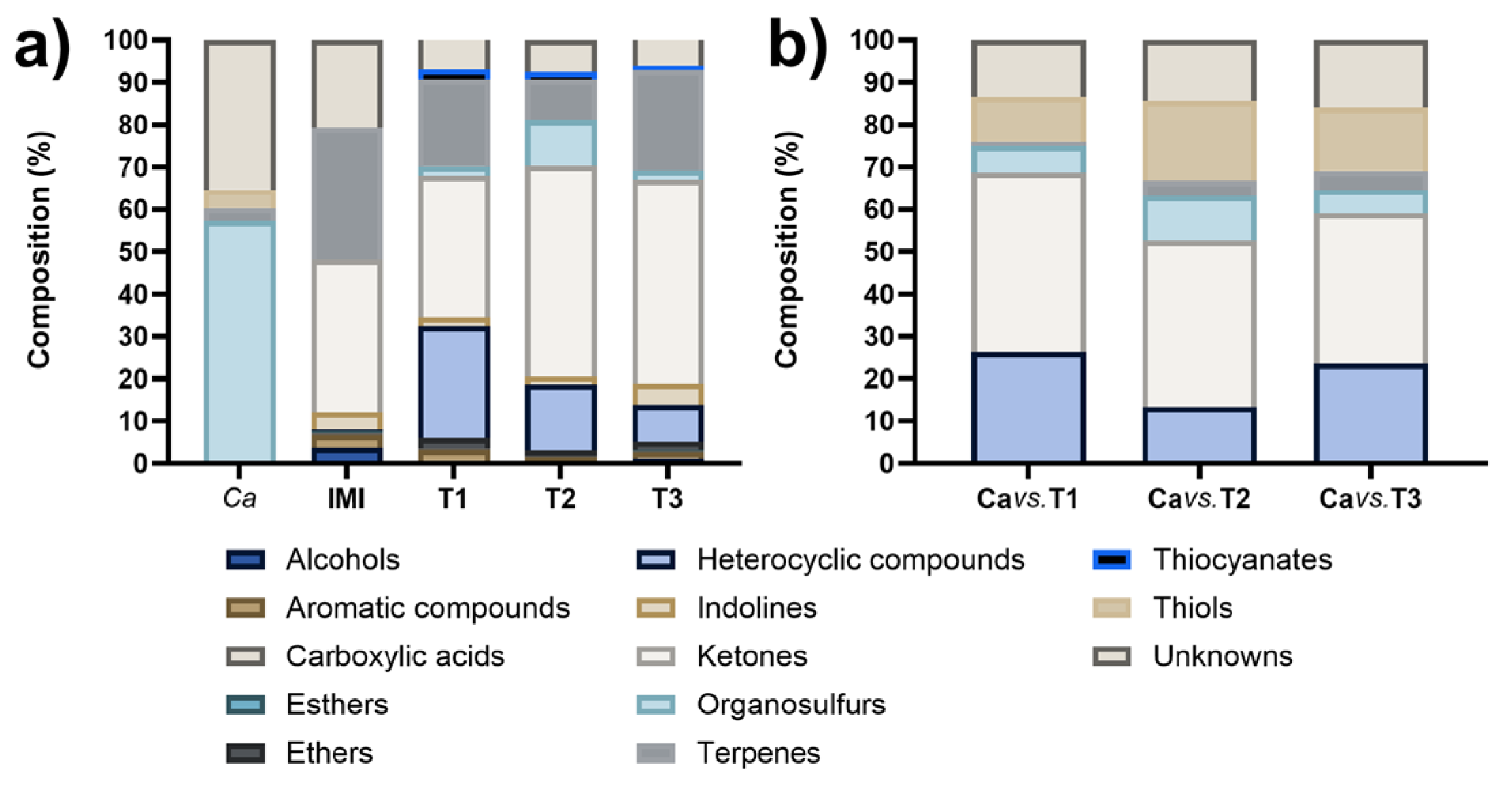
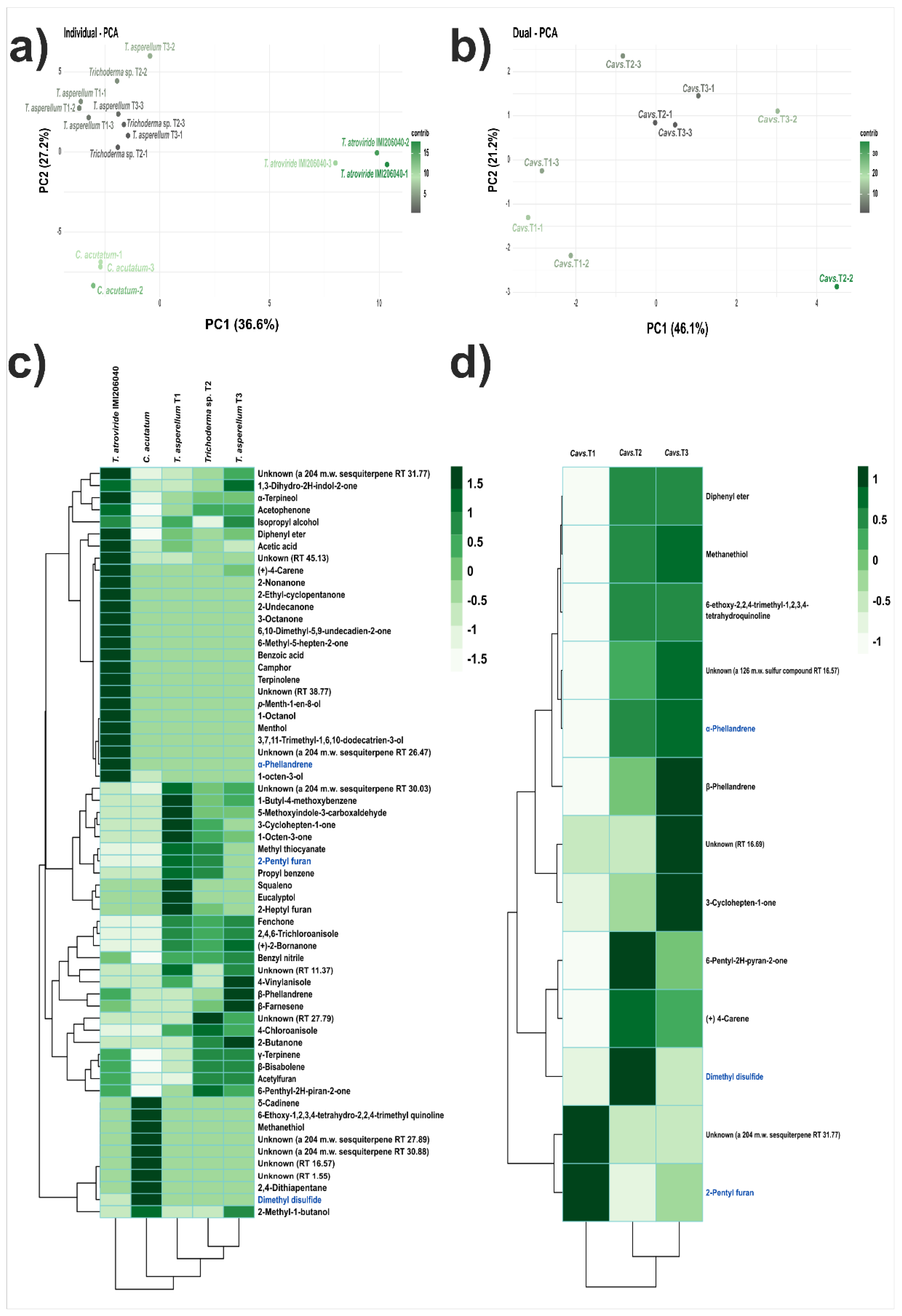
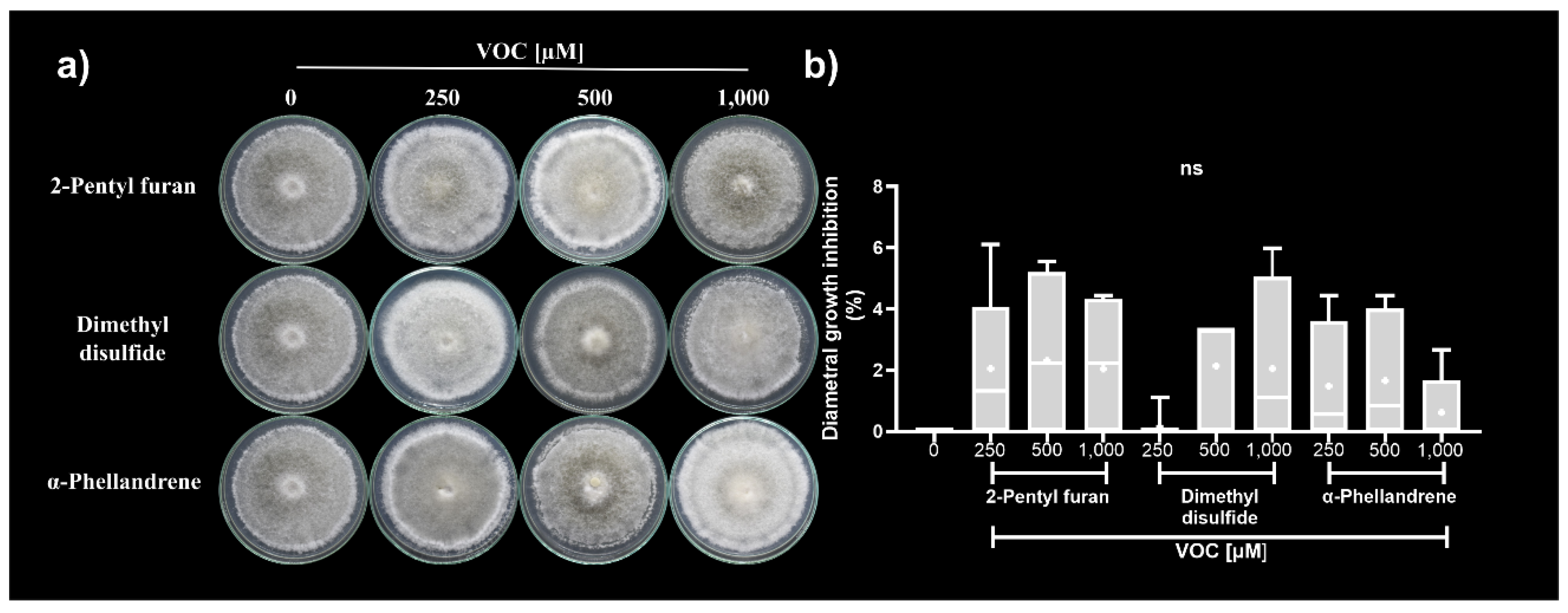
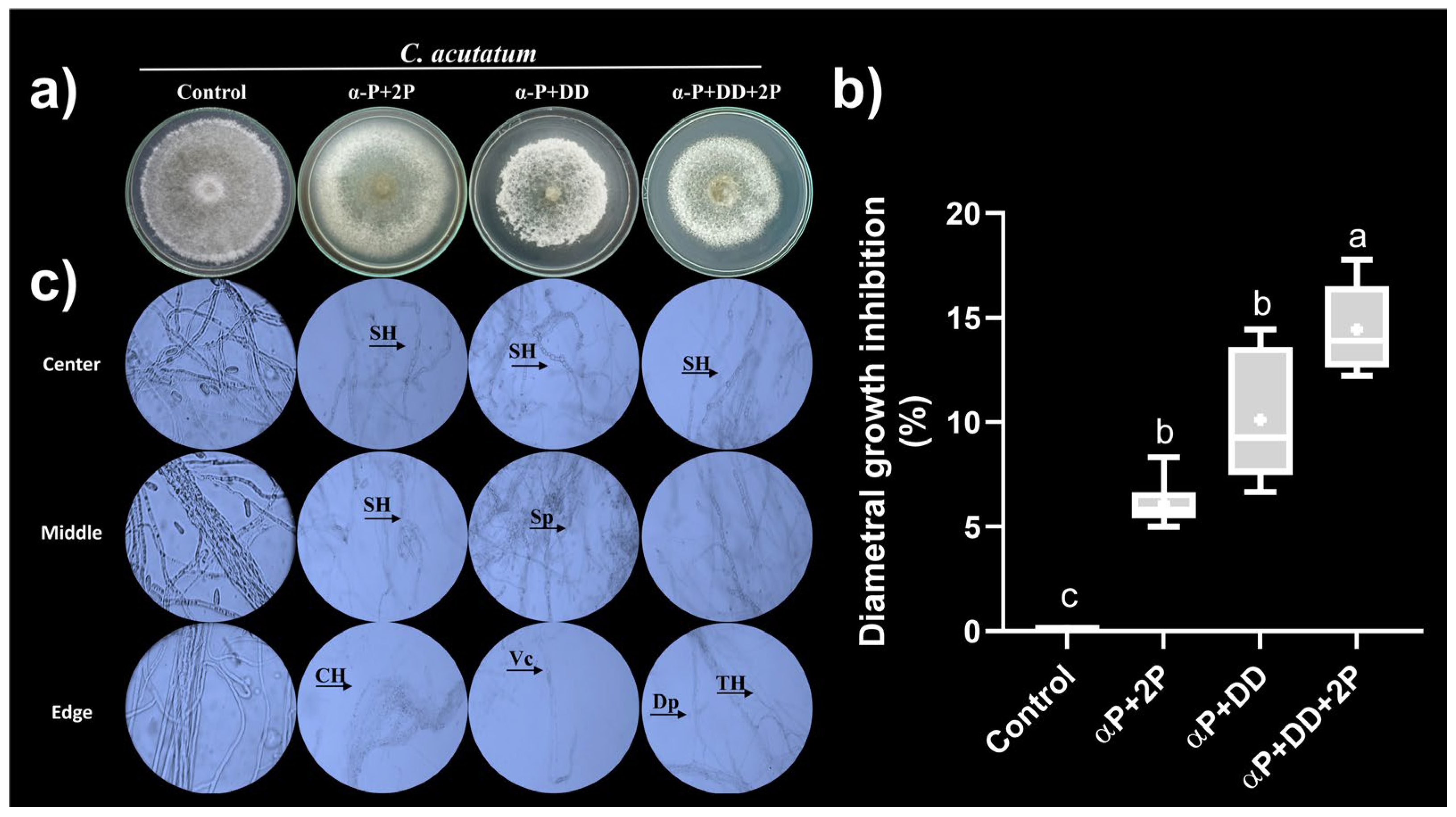
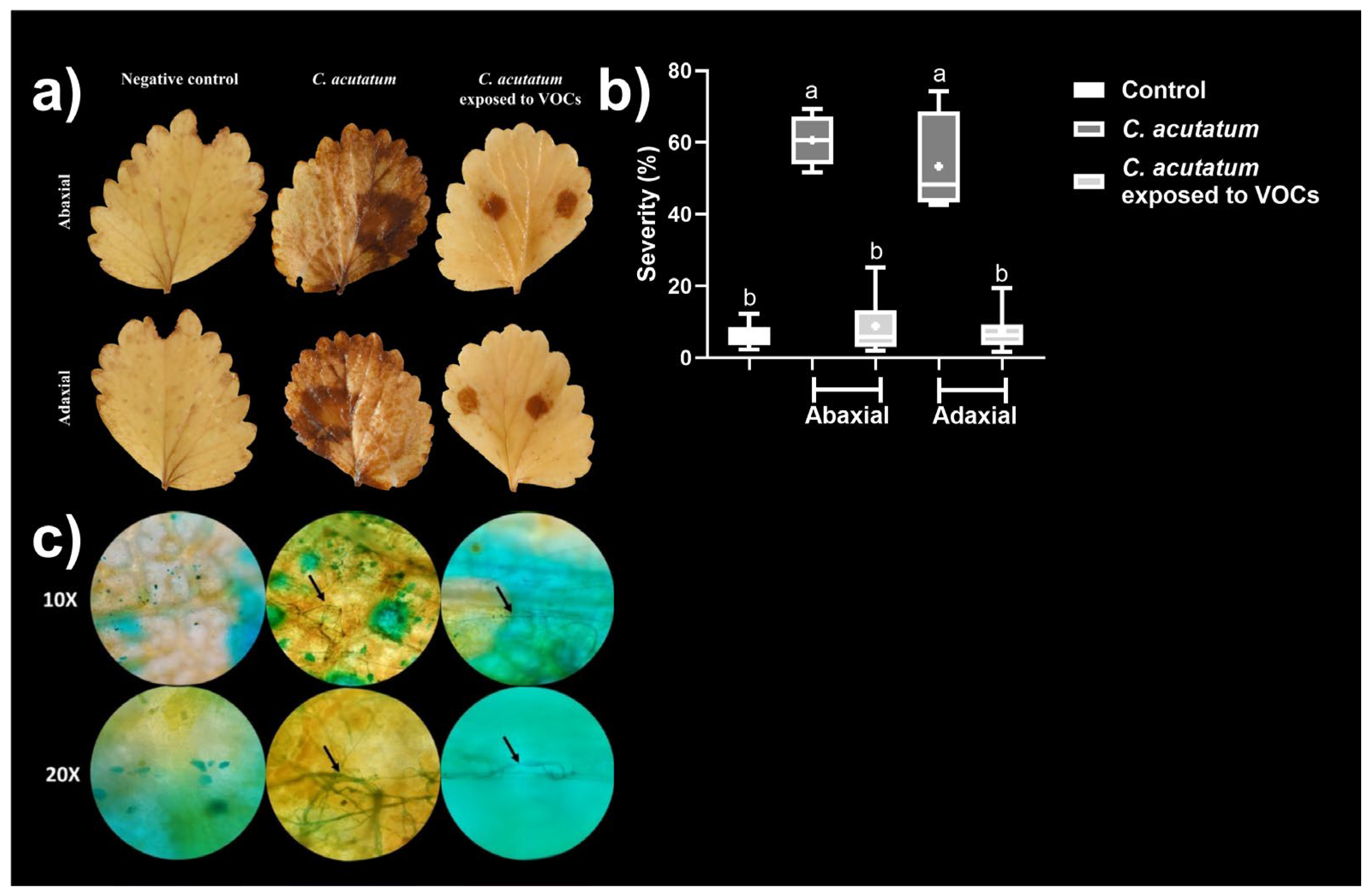
| Bioassay | C. acutatum diametral growth inhibition (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Media | ||
| PDA | LB | |
| Control | 3.94 ± 3.35c | 1.23 ± 5.55c |
| T. atroviride IMI206040 | 47.41 ± 5.77a | 49.94 ± 1.66a |
| T. asperellum T1 | 42.14 ± 4.72a | 33.96 ± 9.23b |
| Trichoderma sp. T2 | 25.46 ± 4.75b | 56.86 ± 2.60a |
| T. asperellum T3 | 12.82 ± 3.71c | 51.85 ± 3.31a |
| Compound | Retention Time (min) |
Abundance relative (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
C. acutatum vs. T. asperellum T1 (Cavs.T1) |
C. acutatum vs. Trichoderma sp. T2 (Cavs.T2) |
C. acutatum vs. T. asperellum T2 (Cavs.T3) |
||
| Methanethiol | 0.93 | 10.62 | 18.78 | 14.98 |
| 3-Cyclohepten-1-one | 2.73 | 0.80 | 1.23 | 3.11 |
| Dimethyl disulfide | 5.40 | 6.23 | 10.48 | 5.56 |
| α-Phellandrene | 8.53 | - | 1.26 | 1.49 |
| (+)-4-Carene | 9.16 | - | 1.89 | 2.00 |
| β-Phellandrene | 10.27 | - | 0.41 | 0.98 |
| 2-Pentylfuran | 11.84 | 20.44 | 3.47 | 7.81 |
| Unknown (a 126 m.w. sulfur compound) | 16.57 | 4.27 | 5.60 | 5.02 |
| Unknown | 19.69 | 9.15 | 8.85 | 10.90 |
| Unknown (a 204 m.w. sesquiterpene) | 31.77 | 1.02 | - | - |
| 6-ethoxy-2,2,4-trimethyl-1,2,3,4- tetrahydroquinoline |
37.30 | 5.92 | 9.32 | 14.95 |
| Diphenyl ether | 41.68 | - | 0.55 | 0.76 |
| 6-Pentyl-2H-pyran-2-one | 46.90 | 41.55 | 38.16 | 32.44 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





