Submitted:
26 August 2024
Posted:
27 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Background
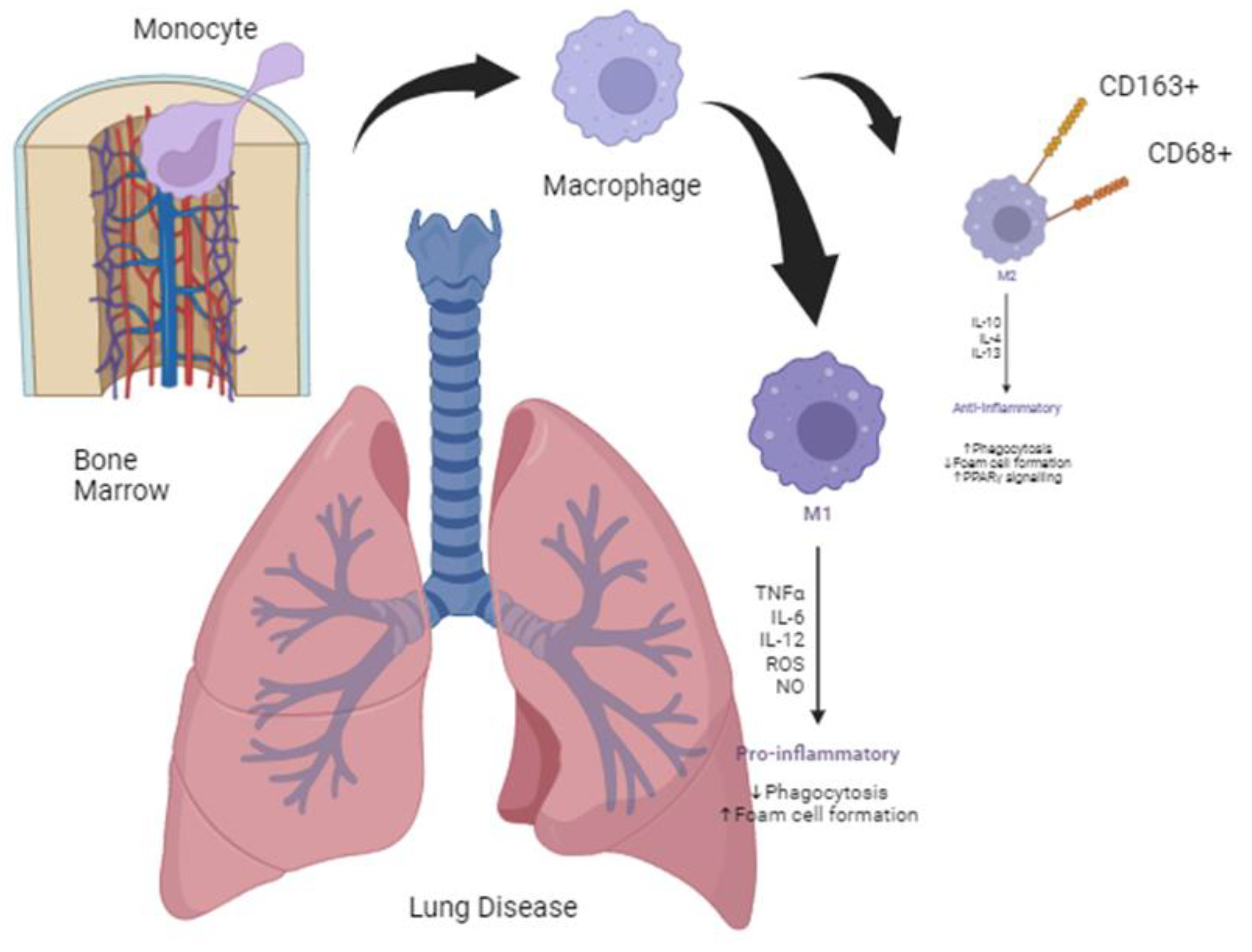
2. Lung Epithelial Cells and the Status of Common Lung Diseases Associated with M1/M2
Alveolar Macrophages and Interstitial Macrophages
3. Sequence–Structure–Function of Antigens and the Application of Macrophage Epitopes in Various Diseases, Including Lung Disease
4. Lung Disease: Focusing on PRRSV
5. Therapeutic Effects of Changes in Macrophage Status through ROS Scavenging through Nanoparticles
5.1. Effects of Nanoparticle Treatment on the Human Body
6. Macrophages and Lung Diseases in the Veterinary Field
7. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Schluger, N.W. and R. Koppaka, Lung disease in a global context. A call for public health action. Annals of the American Thoracic Society, 2014. 11(3): p. 407-416. [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y., et al., An overview of COVID-19. Journal of Zhejiang University. Science. B, 2020. 21(5): p. 343.
- Deem, S.L., et al., Canine distemper in terrestrial carnivores: a review. Journal of Zoo and Wildlife medicine, 2000. 31(4): p. 441-451.
- Chae, C., Commercial PRRS modified-live virus vaccines. Vaccines, 2021. 9(2): p. 185.
- Reinero, C.R., Advances in the understanding of pathogenesis, and diagnostics and therapeutics for feline allergic asthma. The Veterinary Journal, 2011. 190(1): p. 28-33. [CrossRef]
- Arora, S., et al., Macrophages: Their role, activation and polarization in pulmonary diseases. Immunobiology, 2018. 223(4-5): p. 383-396.
- Byrne, A.J., et al., Pulmonary macrophages: key players in the innate defence of the airways. Thorax, 2015. 70(12): p. 1189-1196.
- Shi, T., et al., Alveolar and lung interstitial macrophages: Definitions, functions, and roles in lung fibrosis. Journal of Leukocyte Biology, 2021. 110(1): p. 107-114.
- Liegeois, M., et al., The interstitial macrophage: A long-neglected piece in the puzzle of lung immunity. Cellular immunology, 2018. 330: p. 91-96.
- Soriano, J.B., et al., Prevalence and attributable health burden of chronic respiratory diseases, 1990–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. The Lancet Respiratory Medicine, 2020. 8(6): p. 585-596.
- Barnes, P.J., Alveolar macrophages as orchestrators of COPD. COPD: Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, 2004. 1(1): p. 59-70.
- Fricker, M.and P.G. Gibson, Macrophage dysfunction in the pathogenesis and treatment of asthma. European Respiratory Journal, 2017. 50(3). [CrossRef]
- Strzelak, A., et al., Tobacco Smoke Induces and Alters Immune Responses in the Lung Triggering Inflammation, Allergy, Asthma and Other Lung Diseases: A Mechanistic Review. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2018. 15(5).
- Saradna, A., et al., Macrophage polarization and allergic asthma. Translational Research, 2018. 191: p. 1-14.
- Lu, H.-L., et al., Activation of M1 macrophages plays a critical role in the initiation of acute lung injury. Bioscience reports, 2018. 38(2): p. BSR20171555.
- Biswas, S.K.and A. Mantovani, Macrophage plasticity and interaction with lymphocyte subsets: cancer as a paradigm. Nature immunology, 2010. 11(10): p. 889-896.
- Covarrubias, A. Byles, and T. Horng, ROS sets the stage for macrophage differentiation. Cell research, 2013. 23(8): p. 984-985.
- Gordon, S. and P.R. Taylor, Monocyte and macrophage heterogeneity. Nature reviews immunology, 2005. 5(12): p. 953-964.
- Tsai, C.-F., et al., Regulatory effects of quercetin on M1/M2 macrophage polarization and oxidative/antioxidative balance. Nutrients, 2021. 14(1): p. 67.
- Kwon, D.H., et al., Glutathione induced immune-stimulatory activity by promoting M1-like macrophages polarization via potential ROS scavenging capacity. Antioxidants, 2019. 8(9): p. 413.
- Griess, B., et al., Scavenging reactive oxygen species selectively inhibits M2 macrophage polarization and their pro-tumorigenic function in part, via Stat3 suppression. Free Radical Biology and Medicine, 2020. 147: p. 48-60.
- Hao, Y., et al., Critical Role of the Sulfiredoxin-Peroxiredoxin IV Axis in Urethane-Induced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Antioxidants, 2023. 12(2): p. 367.
- Fathi, M., et al., Functional and morphological differences between human alveolar and interstitial macrophages. Experimental and molecular pathology, 2001. 70(2): p. 77-82.
- Whisstock, J.C. and A.M. Lesk, Prediction of protein function from protein sequence and structure. Quarterly reviews of biophysics, 2003. 36(3): p. 307-340.
- Wrapp, D., et al., Cryo-EM structure of the 2019-nCoV spike in the prefusion conformation. Science, 2020. 367(6483): p. 1260-1263.
- Choi, K. Han, and S.J. Kim, A systematic review of chromogranin A (CgA) and its biomedical applications, unveiling its structure-related functions. Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 2021. 78: p. 427-441.
- Etzerodt, A., et al., Structural basis for inflammation-driven shedding of CD163 ectodomain and tumor necrosis factor-α in macrophages. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2014. 289(2): p. 778-788. [CrossRef]
- Ma, H., et al., The crystal structure of the fifth scavenger receptor cysteine-rich domain of porcine CD163 reveals an important residue involved in porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus infection. Journal of Virology, 2017. 91(3): p. 10.1128/jvi. 01897-16.
- Kweon, C.-h., et al., Isolation of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) in Korea. Korean Journal of Veterinary Research, 1994. 34(1): p. 77-83.
- Meulenberg, J., PRRSV, the virus. Veterinary research, 2000. 31(1): p. 11-21.
- Wensvoort, G., et al., Mystery swine disease in the Netherlands: the isolation of Lelystad virus. 1993.
- Collins, J.E., et al., Isolation of swine infertility and respiratory syndrome virus (isolate ATCC VR-2332) in North America and experimental reproduction of the disease in gnotobiotic pigs. Journal of Veterinary Diagnostic Investigation, 1992. 4(2): p. 117-126.
- Dokland, T., The structural biology of PRRSV. Virus research, 2010. 154(1-2): p. 86-97.
- Su, C.-M. R.R. Rowland, and D. Yoo, Recent advances in PRRS virus receptors and the targeting of receptor–ligand for control. Vaccines, 2021. 9(4): p. 354.
- Wills, R.W., et al., Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus: routes of excretion. Veterinary microbiology, 1997. 57(1): p. 69-81. [CrossRef]
- Prieto, C. and J.M. Castro, Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus infection in the boar: a review. Theriogenology, 2005. 63(1): p. 1-16.
- Beyer, J. , et al., Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV): kinetics of infection in lymphatic organs and lung. Journal of Veterinary Medicine, Series B, 2000. 47(1): p. 9-25.
- Bochev, I., Porcine respiratory disease complex (PRDC): A review. I. Etiology, epidemiology, clinical forms and pathoanatomical features. Bulgarian Journal of Veterinary Medicine, 2007. 10(3): p. 131-146.
- Pejsak, Z. Stadejek, and I. Markowska-Daniel, Clinical signs and economic losses caused by porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus in a large breeding farm. Veterinary microbiology, 1997. 55(1-4): p. 317-322.
- Prieto, C., et al., Semen changes in boars after experimental infection with porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome (PRRS) virus. Theriogenology, 1996. 45(2): p. 383-395.
- Ruedas-Torres, I., et al., The jigsaw of PRRSV virulence. Veterinary Microbiology, 2021. 260: p. 109168.
- Guo, B., et al., Chinese and Vietnamese strains of HP-PRRSV cause different pathogenic outcomes in United States high health swine. Virology, 2013. 446(1-2): p. 238-250.
- Balka, G., et al., Genetic diversity of PRRSV 1 in Central Eastern Europe in 1994–2014: origin and evolution of the virus in the region. Scientific Reports, 2018. 8(1): p. 7811.
- Jakab, S., et al., Genetic diversity of imported PRRSV-2 strains, 2005–2020, Hungary. Frontiers in Veterinary Science, 2022. 9: p. 986850.
- Pileri, E. and E. Mateu, Review on the transmission porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus between pigs and farms and impact on vaccination. Veterinary research, 2016. 47(1): p. 108.
- Haynes, J., et al., Temporal and morphologic characterization of the distribution of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) by in situ hybridization in pigs infected with isolates of PRRSV that differ in virulence. Veterinary pathology, 1997. 34(1): p. 39-43.
- Piras, F., et al., Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome (PRRS) virus-specific interferon-γ+ T-cell responses after PRRS virus infection or vaccination with an inactivated PRRS vaccine. Viral immunology, 2005. 18(2): p. 381-389.
- Silva, G.S., et al., Development and validation of a scoring system to assess the relative vulnerability of swine breeding herds to the introduction of PRRS virus. Preventive veterinary medicine, 2018. 160: p. 116-122.
- Han, K., et al., Comparative pathogenesis of type 1 (European genotype) and type 2 (North American genotype) porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus in infected boar. Virology journal, 2013. 10: p. 1-9.
- Beyer, J., et al., Arterivirus PRRSV: experimental studies on the pathogenesis of respiratory disease. Coronaviruses and Arteriviruses, 1998: p. 593-599.
- Van Gorp, H., et al., Sialoadhesin and CD163 join forces during entry of the porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. Journal of General Virology, 2008. 89(12): p. 2943-2953. [CrossRef]
- Choi, C. and C. Chae, Expression of tumour necrosis factor-α is associated with apoptosis in lungs of pigs experimentally infected with porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. Research in Veterinary Science, 2002. 72(1): p. 45-49.
- Mateu, E. and I. Díaz, The challenge of PRRS immunology. The Veterinary Journal, 2008. 177(3): p. 345-351.
- Tong, J. , et al., Hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis involves in anti-viral ability through regulation of immune response in piglets infected by highly pathogenic porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. BMC veterinary research, 2018. 14: p. 1-7.
- Wahyuningtyas, R., et al., Recombinant antigen of type 2 porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV-2) promotes M1 repolarization of porcine alveolar macrophages and Th1 type response. Vaccines, 2021. 9(9): p. 1009. [CrossRef]
- Gong, X., et al., Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus modulates the switch of macrophage polarization from M1 to M2 by upregulating moDC-released sCD83. Viruses, 2023. 15(3): p. 773.
- Sharpe, E. Andreescu, and S. Andreescu, Artificial nanoparticle antioxidants, in Oxidative stress: diagnostics, prevention, and therapy. 2011, ACS Publications. p. 235-253.
- Malhotra, S., et al., In vitro and in vivo antioxidant, cytotoxic, and anti--chronic inflammatory arthritic effect of selenium nanoparticles. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B: Applied Biomaterials, 2016. 104(5): p. 993-1003.
- Battin, E.E. and J.L. Brumaghim, Antioxidant activity of sulfur and selenium: a review of reactive oxygen species scavenging, glutathione peroxidase, and metal-binding antioxidant mechanisms. Cell biochemistry and biophysics, 2009. 55(1): p. 1-23.
- Medhe, S. Bansal, and M.M. Srivastava, Enhanced antioxidant activity of gold nanoparticle embedded 3, 6-dihydroxyflavone: a combinational study. Applied Nanoscience, 2014. 4: p. 153-161.
- Okamoto, S., et al., Poly (γ-glutamic acid) nano-particles combined with mucosal influenza virus hemagglutinin vaccine protects against influenza virus infection in mice. Vaccine, 2009. 27(42): p. 5896-5905.
- Sun, M., et al., Toward innovative veterinary nanoparticle vaccines. Animal Diseases, 2024. 4(1): p. 14.
- Yang, J., et al., An oral nano-antioxidant for targeted treatment of inflammatory bowel disease by regulating macrophage polarization and inhibiting ferroptosis of intestinal cells. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023. 465: p. 142940.
- Soh, M., et al., Ceria–Zirconia nanoparticles as an enhanced multi--antioxidant for sepsis treatment. Angewandte Chemie, 2017. 129(38): p. 11557-11561.
- Fang, H., et al., Macrophage-targeted hydroxychloroquine nanotherapeutics for rheumatoid arthritis therapy. ACS applied materials & interfaces, 2022. 14(7): p. 8824-8837.
- Eapen, M.S., et al., Abnormal M1/M2 macrophage phenotype profiles in the small airway wall and lumen in smokers and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Scientific reports, 2017. 7(1): p. 13392.
- Jackute, J., et al., Distribution of M1 and M2 macrophages in tumor islets and stroma in relation to prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer. BMC immunology, 2018. 19: p. 1-13.
- Lee, J.-W., et al., The role of macrophages in the development of acute and chronic inflammatory lung diseases. Cells, 2021. 10(4): p. 897.
- Almatroodi, S.A., et al., Characterization of M1/M2 tumour-associated macrophages (TAMs) and Th1/Th2 cytokine profiles in patients with NSCLC. Cancer Microenvironment, 2016. 9: p. 1-11.
- Wang, L., et al., Manipulation of macrophage polarization by peptide-coated gold nanoparticles and its protective effects on acute lung injury. Journal of nanobiotechnology, 2020. 18: p. 1-16.
- Schweer, D., et al., Tumor-associated macrophages and ovarian cancer: implications for therapy. Cancers, 2022. 14(9): p. 2220.
- Yang, Z., et al., Albumin-mediated biomineralization of shape-controllable and biocompatible ceria nanomaterials. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017. 9(8): p. 6839-6848.
- Girodet, P.-O., et al., Alternative macrophage activation is increased in asthma. American journal of respiratory cell and molecular biology, 2016. 55(4): p. 467-475.
- Vlahos, R. and S. Bozinovski, Role of alveolar macrophages in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Frontiers in immunology, 2014. 5: p. 435.
- Braga, T.T. S.H. Agudelo, and N.O.S. Camara, Macrophages during the fibrotic process: M2 as friend and foe. Frontiers in immunology, 2015. 6: p. 602.
- Gibaud, S., et al., Increased bone marrow toxicity of doxorubicin bound to nanoparticles. European Journal of Cancer, 1994. 30(6): p. 820-826.
- Anselmo, A.C., et al., Delivering nanoparticles to lungs while avoiding liver and spleen through adsorption on red blood cells. ACS nano, 2013. 7(12): p. 11129-11137.
- Drozdov, A.S. I. Nikitin, and J.M. Rozenberg, Systematic review of cancer targeting by nanoparticles revealed a global association between accumulation in tumors and spleen. International journal of molecular sciences, 2021. 22(23): p. 13011.
- Demoy, M., et al., Spleen capture of nanoparticles: influence of animal species and surface characteristics. Pharmaceutical research, 1999. 16: p. 37-41.
- Den Haan, J.M. and G. Kraal, Innate immune functions of macrophage subpopulations in the spleen. Journal of innate immunity, 2012. 4(5-6): p. 437-445.
- Mulder, R. Banete, and S. Basta, Spleen-derived macrophages are readily polarized into classically activated (M1) or alternatively activated (M2) states. Immunobiology, 2014. 219(10): p. 737-745.
- Venosa, A., et al., Protective role of spleen-derived macrophages in lung inflammation, injury, and fibrosis induced by nitrogen mustard. American Journal of Physiology-Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology, 2015. 309(12): p. L1487-L1498.
- Adams, H., et al., Altered splenic [89Zr] Zr-rituximab uptake in patients with interstitial lung disease not responding to rituximab: could this indicate a splenic immune-mediated mechanism? American Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging, 2020. 10(4): p. 168.
- Newairy, A., et al., The hepatoprotective effects of selenium against cadmium toxicity in rats. Toxicology, 2007. 242(1-3): p. 23-30. [CrossRef]
- Messarah, M., et al., Hepatoprotective role and antioxidant capacity of selenium on arsenic-induced liver injury in rats. Experimental and toxicologic pathology, 2012. 64(3): p. 167-174.
- Holm, B. Notter, and J. Finkelstein, Surface property changes from interactions of albumin with natural lung surfactant and extracted lung lipids. Chemistry and physics of lipids, 1985. 38(3): p. 287-298.
- Choi, S.H., et al., Inhalable self-assembled albumin nanoparticles for treating drug-resistant lung cancer. Journal of controlled release, 2015. 197: p. 199-207.
- Ma, H., et al., Structural comparison of CD163 SRCR5 from different species sheds some light on its involvement in porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus-2 infection in vitro. Veterinary Research, 2021. 52: p. 1-17.
- Barros, M.H.M., et al., Macrophage polarisation: an immunohistochemical approach for identifying M1 and M2 macrophages. PloS one, 2013. 8(11): p. e80908.

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




