1. Introduction
Around 77% of the global elderly population, aged 65 and above, suffer from chronic diseases like stroke, hypertension, asthma, diabetes, and cognitive impairment [
1]. In the United States, 95% of individuals over 60 years old suffer from at least one chronic illness, while 80% grapple with multiple conditions [
2]. Even the elderly population in Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA), comprising 3% of the overall population, [
3,
4], is vulnerable to health-related issues. At the same time, the provision of basic, high-quality, and affordable healthcare has posed a universal dilemma. The growing elderly population significantly impacts their societies and families [
5,
6], and inadequately staffed healthcare facilities pose challenges in accommodating all patients [
7].
The recent COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of home-based care [
8,
9], prompting the integration of the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) to support healthcare stakeholders both within and outside healthcare settings. The progression of sensor technologies and mobile devices has accelerated the adoption of IoMT [
10] with smartphones being integrated into IoMT for telemedicine applications due to their affordability and sensor availability, enabling non-invasive vital parameters monitoring, communication, and healthy behavior encouragement.
However, the implementation of IoMT faces challenges concerning the privacy and security of patient data [
9,
11,
12] yet IoT systems cater for both technical and non-technical users [
13], but most end users, including elderly individuals, lack technological proficiency and are unlikely to implement security measures, making them susceptible to potential attacks [
14]. At the same time, the development of security protocols often fails to account for the health issues prevalent in older populations [
15,
16] yet when it comes to authentication, [
17] indicate that elderly users have their authenticator preferences.
Although smartphones are commonly utilized for authentication purposes, there is little empirical support regarding their effectiveness across various age demographics [
5]. Despite ongoing research on suitable authentication techniques [
1], there is a lack of extensive research on the practicality of authentication technologies for senior citizens and individuals with disabilities [
18]. Therefore, research on smartphone-based user authentication mechanisms for the elderly is crucial.
This research aims to improve usable-security by developing and implementing an Android based adaptive authentication system for elderly IoMT users .
The primary objectives are as follows:
i) Examine various Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) user authentication methodologies and evaluate their appropriateness in the context of authenticating elderly individuals in SSA,
ii) Develop a Naive Bayes Android-based adaptive authentication app for IoMT hardware and software that considers elderly users’ medical conditions and risk scores for suitable authenticators, and
iii) Assess the efficacy of the proposed model in authenticating the elderly users.
The selection of an Android device was predicated on its widespread availability in the SSA region, with a substantial market share of 83.6%, in stark contrast to Apple’s 14.35% [
19].
The rest of the paper is organised as follows:
Section 2 analyses the various authenticators available and their strengths and weaknesses. Related work is discussed in
Section 3. The details of our proposed framework are discussed in
Section 4. The results and findings are presented in
Section 5. Discussion of results is presented in
Section 6. Finally
Section 7 concludes and provides future work.
2. Analysis of Various Authenticators
Despite widespread recognition, there is a lack of proactive measures to address emerging threats on IoMTs, hindering the implementation of effective mHealth applications. Around 60% of smartphone users don’t use security measures, and mobile platforms often use explicit authentication [
20]. Elderly individuals with chronic conditions like arthritis, Parkinson’s, and osteoporosis face challenges in utilizing authentication systems [
20,
21], making them more susceptible to security breaches [
22]. Authentication is a critical component in maintaining network security [
23], acting as the initial defense against potential attacks. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) combines knowledge-based, physiological, and behavioral candidate authenticators, requiring attackers to have to break another barrier if one factor is compromised [
24].
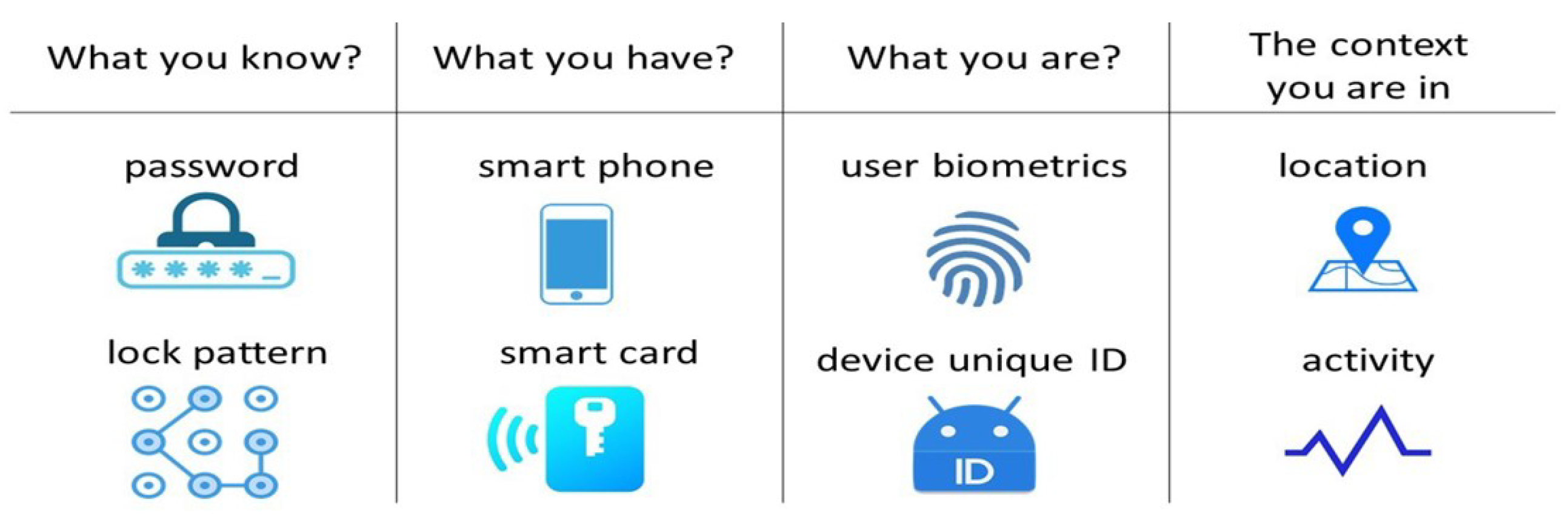
Figure 1 shows examples of factors used in MFA.
We now examine the appropriateness of the following authenticators for elderly users.
2.1. Knowledge Based Authenticators
PIN
The Personal Identification Number (PIN) is an old, secure, maskable, and quick authentication method that uses a combination of four or six numbers [
25]. It is liked by the elderly [
17], can defeat shoulder surfing, but it is easily forgotten, making it less suitable for the elderly.
Textual Password
This old authentication mechanism, which can contain special and alphanumeric symbols, is more resistant to brute force attacks than PINs [
26]. However, elderly individuals often struggle with password input due to arthritis, early-stage dementia [
5], deteriorating vision [
21], frustration [
25], and lack of prior technology exposure [
27].
Graphical Password
Images, instead of alphanumeric characters, are utilized for memory stimulation and are easier to remember than text [
25], making them more accessible to elderly users.
Face Recognition
Faces serve as a verification system for senior citizens, allowing easier memory retention and selection from a set of saved faces.
Pattern Lock
Users draw recognizable patterns on a 3 by 3 grid, which is usable and less time-consuming than PIN, but may be frustrating for dexterity-deficient adults [
25] and susceptible to side channel attacks. Fingertips can leave a distinctive trace on the screen.
Musipass
Musi pass, easy to remember, allows users to choose their preferred music as their password [
27], but may not be suitable for elderly individuals with typing difficulties.
2.2. Biometric Authenticators
Biometrics identify living individuals’ physiological or behavioral attributes for authentication [
28]. Biometric traits are widely used as authenticators in mobile devices combining the "what you have" and "what you are" dimensions [
9]. Most IoT devices are improving their sensorial abilities, enabling user data collection for authentication [
9], with success significantly influenced by user experience [
29].
2.2.1. Physiological Based Biometric Authenticators
Human motion behavior feature extraction uses machine vision and sensor-based methods, but the former is complex and susceptible to environmental factors, while the latter is low-cost and non- susceptible to environmental factors [
30].
Fingerprint/Palm
Although older users prefer fingerprint authentication [
20], they are less likely to successfully authenticate using it. Off-the-shelf smart devices now offer scanner capture technology [
31], but factors like aging, moisture, gender, medical, and occupation can hinder its effectiveness [
29].
Ocular /Eye Scanner Scanning
The eye, through the iris or retina can be used for authentication. The scanner is costly and less common, and its authentication process may be impeded by factors like spectacles [
31], age, and environmental light intensity [
29].
Voice Recognition
Most devices come with built-in microphones that can be utilized for voice capture and authentication. The user’s state or age can significantly impact the outcome of voice capture, potentially leading to a Denial of Service. Despite being user-friendly, they are more susceptible to spoofing attacks than facial recognition systems [
31] so they must be combined with other authenticators to enhance security.
Facial Recognition
This camera-based technique compares user’s image with database but requires good lighting and not suitable for low-cost wearable devices [
20]. Factors like glasses, facial expressions, age, poses, and lighting influence results [
29].
2.2.2. Behaviour Based Authentication
These models use Machine Learning (ML) to authenticate users by learning their previous access patterns. This authentication mechanism is beneficial for tracking user behavior over a specific period [
31] but requires time to observe, and algorithm design is complex. Older individuals’ use of behavior is difficult to capture due to their limited activities. Examples of authentication mechanisms are explained below.
Gait based authentication
Modern mobile devices can effectively capture gait patterns for authentication [
32], but older adults face more challenges due to walking challenges [
1].
Heart Rate Biometric Identification
Heart rate signals are unique and consistent over time [
33], and while smartphones with integrated sensors offer heart rate biometric authentication, research on its use in elderly individuals is still limited.
2.3. Smartphones and Wearables
Wearables have gained popularity for their use in health monitoring and authentication. However, most health-related signal proposals are based on high-end medical equipment datasets that may not accurately represent widely available devices. Smartphones and tablets are popular portable devices in the IoT [
34], although they are not always considered essential components. They have the expected capabilities of traditional IoT, and they interact with IoT devices.
2.4. Adaptive Authentication
Adaptive security is a self-monitoring security method that prevents network attacks by altering its behavior and controlling the conditions under observation [
23]. It reduces monotonous selection of the same authentication factors and identifies risks more effectively than the one-size-fits-all approach [
35].
2.4.1. Risk-based Authentication
This is an adaptive authentication method that calculates user activity risk using contextual and historical data, calculating the risk score in real time using specific rules [
36]. There has been a lot of research done on adaptive authentication, but not much of it has produced real-world, workable solutions [
37].
3. Related Work
3.1. IoMT Authentication
Authors [
38] proposed a secure lightweight authentication scheme (LAS) for IoMT-based healthcare systems, enhancing security in healthcare systems. The proposed system required device registration and central authority approval, but allowed peer-to-peer communication without central intervention during authentication and communication phases while outperforming other lightweight schemes. However,only the technical part of the scheme was evaluated. A graphical-password-based user authentication scheme for the IoMT to improve security and user experience during the COVID-19 pandemic was proposed in [
39]. The proposed scheme, implemented via an Android application, was assessed for system, information, and interface quality using the Post-Study System Usability Questionnaire (PSSUQ) tool, demonstrating its potential to enhance user authentication experiences in healthcare. Similarly, authors [
40] proposed an improved lightweight user authentication scheme for the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) in which the hash function and XOR operation are used for operation in low-spec healthcare IoT sensors. The proposed scheme outperformed other protocols in terms of security and performance, but did not deal with smartphone sensors. Protection of patient information’s confidentiality in IoT gadgets was proposed in [
41] who used decentralized identifiers (DIDs) and verifiable credentials (VCs) together with OAuth based authorization framework. The proposed framework demonstrated enhanced privacy and security through a smart pill despenser, thereby streamlining access control administration. The work, however, mainly focused on the technical part of the model than the user part. A study [
42] proposed a multifactor authentication system for IoT-based Wireless Medical Sensor Networks, enhancing security, scalability, and effectiveness in patient care. The proposed system, while offering enhanced functionality and resistance to common attacks, did not include smartphones. The use of artificial intelligence to enhance authentication of IoMT through the design of a framework which uses bioelectrical signals for authentication and artificial intelligence with contextual data was proposed in [
43]. The framework enhances security in healthcare, maintains user trust and data integrity, balances usability and security and is adaptable to various devices. Their work,however, was only restricted to bioelectrical signals.
Most works on IoMT involving the elderly looks at applications that monitor their health and maintain their well-being without looking at authentication. We will now look at other works in the realm of IoMT that do not necessarily look at the elderly authentication.
Authors [
44] suggested an assessment framework to offer trustworthy and safe authentication procedures based on authentication features for Internet of Health Things (IoHT) devices. Using a hybrid multicriteria decision-making methodology, the framework assesses authentication aspects and determines which authentication scheme or method is best. The work, though adaptive, does not consider the elderly users. A biometric based authentication scheme for hospital environments where patients interact with smart surroundings without explicit gadgets was proposed in [
45]. The scheme can resist various well-known attacks showing that biometric keys are crucial for identification and authentication, but the work generalises security and does not focus on the elderly. A novel, low-complexity, and resilient remote user authentication system for Internet of Things-enabled healthcare applications was presented in [
46]. A formal verification proved the security of the scheme and its applicability in real-world healthcare applications. The exploration of authentication techniques for IoT-enabled healthcare systems at different network levels and a taxonomy of attacks was conducted in [
47]. Their work focused on user and device verification but does not focus on the elderly users.
3.2. Adaptive Authentication
Bayesian probability in Context Aware Scalable Authentication (CASA) proposed in [
48] selects active authentication methods based on passive factors and location contexts to lock the screen based on PIN and password. The model, while reducing usability, forms the foundation for modern adaptive authentication. Author [
49] introduced CYOA, allowing users to choose their authentication scheme based on their inclinations, capabilities, and usage context, but restricting flexibility and introducing delays, especially for elderly users. A proposed smartphone adaptation adjusts lock functionality between vocal sound recognition, facial scan, and fingerprint based on usability was proposed in [
50], but disregards security due to its focus on usability. In conclusion, there is no universally applicable solution for IoMT security, and thus the various authentication mechanisms can be used in conjunction to improve security at the elderly users’ convenience [
51].
4. Research Method
The proposed Adaptive Authentication model analyzes user interaction with an Android application to create a risk profile using the Naive Bayes Machine Learning algorithm. During authentication, an assessment of the context is executed to estimate the risk associated with the login request. The outcome will be categorized as a Propensity Score, which will determine the level of authentication difficulty and the authenticators to be used. The goal is to create an authentication solution that is tailored to the user’s visual, mental, and physical medical condition providing a user-friendly authentication experience while ensuring the security of their medical information. The steps follow the MAPE-KHMT framework.
4.1. Naïve Bayes Machine Learning Algorithm
This supervised machine learning algorithm employs probabilistic and statistical methods for classification. The derivation of the Naïve Bayes probability from the simple Bayes Theorem is written as follows:
where X =
(,,……….,) represent the user’s context. Expanding using the chain rule gives
and since the denominator does not change, the equation is simplified as
Let
P(y |,…,) be represented by
P(u) for simplicity purposes. The verification stage compares the user’s illegitimacy probability
P(u) to a predefined threshold
, if it’s 1, access is denied, otherwise, multiclasses are used. The following formula is used to calculate the categorization decision rule:
4.1.1. Proposed System Overview
The researchers utilized Android smartphones with Android version 12 or higher, equipped with sensors for context identification and authentication. The smartphone functions as a lightweight information processor, sensing and actuating, and sending data to the cloud for further processing and storage. The research introduces a new feature - human-machine collaboration, which is integrated into the framework’s monitoring, analysis, and execution. This work introduces novel aspects that include assigning authenticators based on risk, user medical conditions, available authenticators, and testing outside the lab environment. Algorithm 1 shows the steps followed from clicking of the login button to authorisation.
|
Algorithm1. Adaptive Authentication for elderly users. |
| Input: |
Mobile_Browser, Mobile_OS, IPAddress, Network_Type, |
| |
GPS_Coordinates, Access_Time, Knowledge_based data, |
| |
Biometric_data. |
| Output: |
Risk Score, Trust Score, Age and Authentication Result. |
| Assumption: |
The usability of authenticators is significantly influenced by age |
| |
and medical condition. |
Start Adaptive App by clicking icon.
-
Get User Verification Information:
-
Define partial conditional probabilities as weights using Naïve Bayes Theorem:
-
Calculate first level weighted risk score:
If account is verified on device, request adaptive authentication PIN or password
else
Invoke other available and usable verification methods.
-
Calculate second level weighted risk score:
If user and device match, invoke one usable authenticator and update trust score
else
Invoke other available and usable authenticators.
-
Iterate Through User Profiles:
Begin: While Trust Score < Threshold
-
Display Results:
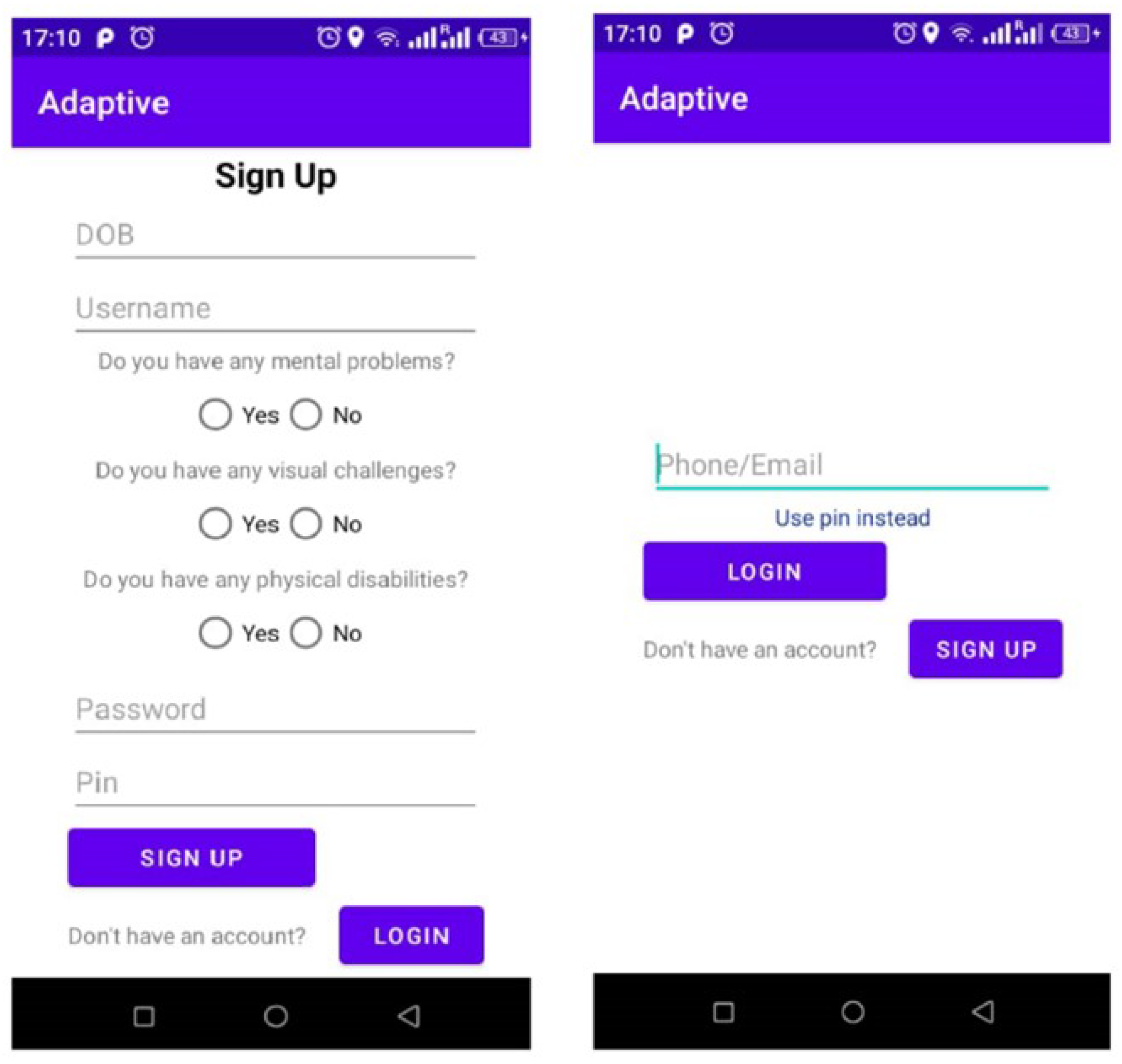
Figure 2 shows the signup and login screens.
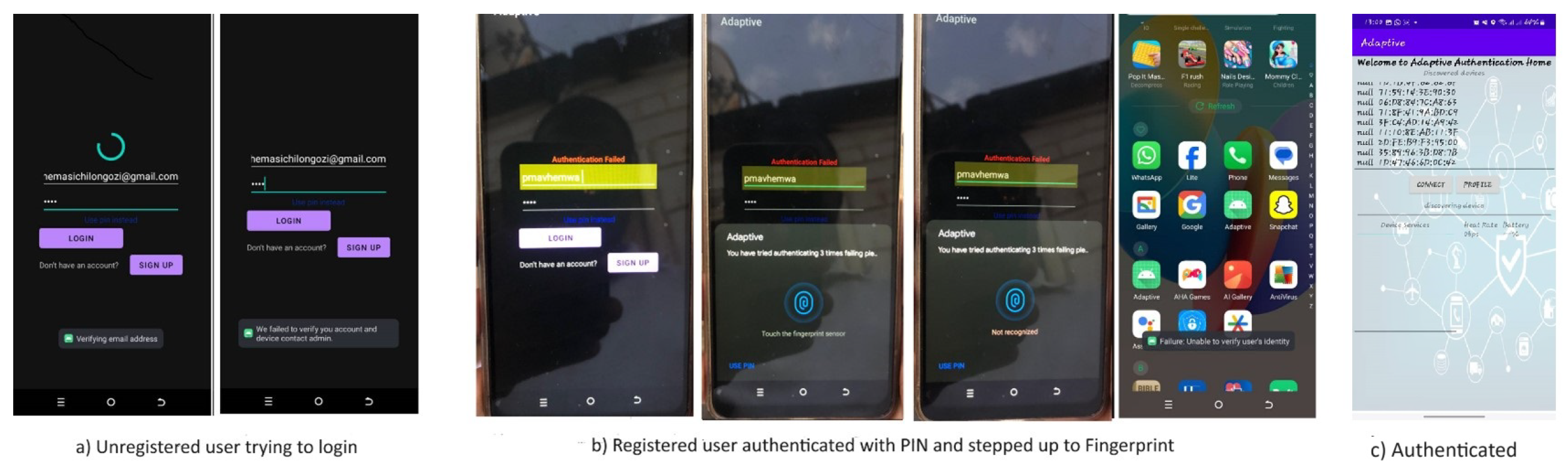
Figure 3 shows cases of failed login where a) shows an unregistered user being unrecognized and b) a registered user who fails the initial knowledge-based authentication before biometric fingerprint is invoked which is again, failed before a failure message is displayed signaling the end of the session. Part c) shows the successful authentication screen where the system starts searching for nearby bluetooth devices that can also be used for authentication.
The same occurs if there are changes in any other contextual factors.
Pre-Study Survey
Previous study [
17] analyzed user demographics, ICT backgrounds, disabilities, security awareness, and preferred authentication methods to aid in prototype development. The study utilized participants over 18 years of age in a pre-study survey to identify age-related differences in the above parameters. The information gathering stage did not involve comparison with the actual survey due to the varying outcomes and changes in participants.
Study Setup
Participants were interviewed using smartphones at workplaces, hospitals, or homes, starting with the enrollment phase where they registered, provided information, and created models. The usability of their smartphones was assumed to be enhanced due to their familiarity with them.
Tasks
Participants were instructed to assume to be logging into their health portal, primarily for authentication purposes, rather than accessing the actual portal.
4.2. Participants
4.2.1. Population
This study focused on patients over the age of fifty (50) years, assuming they are not active and are not technologically savvy, implying the need for static authentication.
4.2.2. Sample Size
Fifty-three (53) participants comprising twenty-five(25) women and twenty-eight(28) participated in the research. Seven(7) participants did not respond giving an 88% response rate.
4.2.3. Sampling Technique
The research utilized stratified systematic sampling to represent both rural and urban populations.
4.2.4. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
The study, following the Belmont Report [
52], analyzed elderly users, excluding the upper age limit, and using smartphone ownership as an inclusion criterion. The study excluded participants under the age of 50 and the elderly without a smartphone.
4.3. Data Collection
The data was collected through the app’s registration form and user logins, with an average of five trials per participant.
5. Results
The adaptive authentication app collected data on users’ contexts, medical conditions, risk scores, and authentication status after their interaction. The analysis utilized various metrics, including confusion matrices for various segments of the adaptive authentication model. The results were analyzed using R Studio.The study aimed to identify patterns in authentication difficulty or ease among elderly participants using our proposed model, focusing on successful or failed authentication.
5.1. Confusion Matrix and Statistics for Overall Authorisation
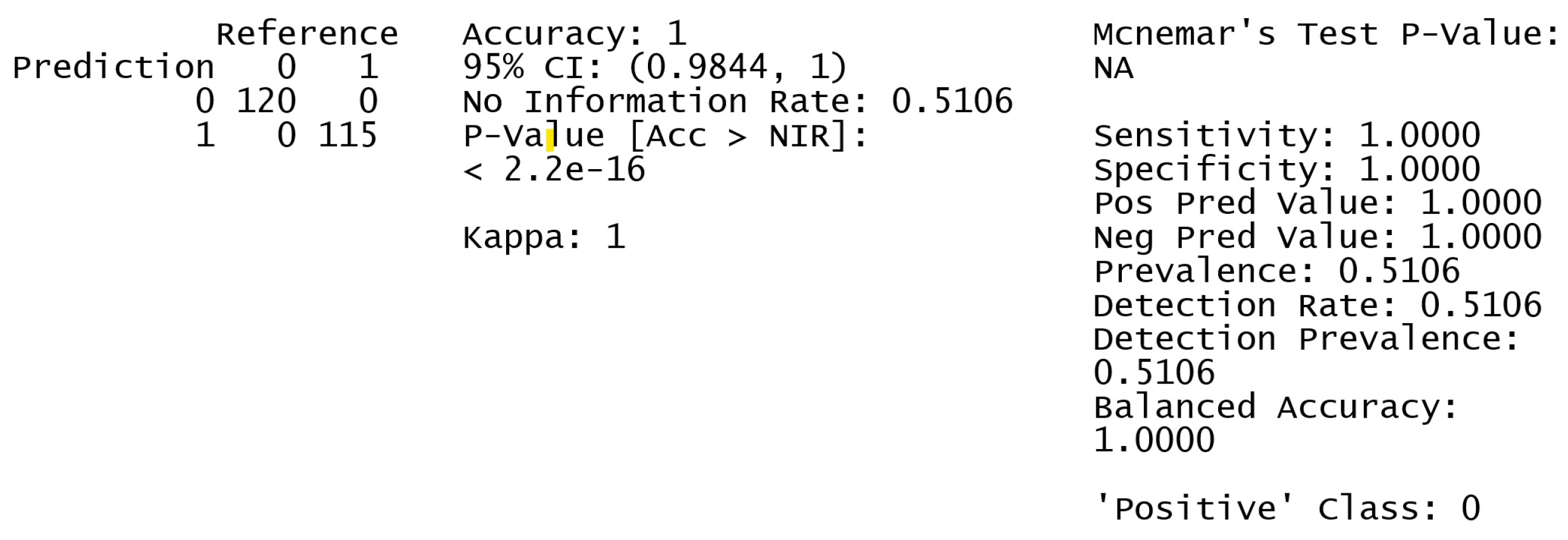
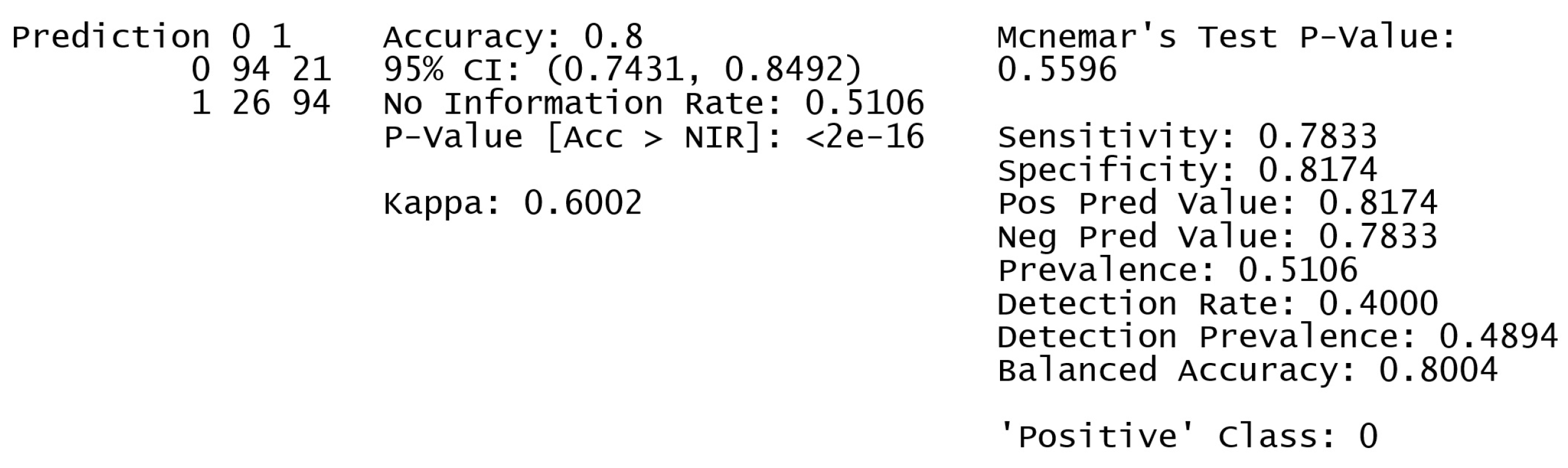
Figure 4 shows the confusion matrix and statistics for the authentication to authorisation process.
The model accurately classified every instance in the dataset, with a 95% confidence interval indicating 100% accuracy. The model’s low p-value suggests superior performance compared to the baseline, with a true accuracy of at least 98.44%. The No Information Rate indicates that an estimate about the most prevalent class could be accurate 51.06% of the time. Together, these measures provide compelling evidence that the model works remarkably well on the provided data, accurately categorising every event with no errors. Other metrics used include balanced accuracy, prevalence, detection rate, positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value (NPV), specificity, sensitivity, and McNemar’s test findings. The model accurately identified true positives and negatives when both sensitivity and specificity are at 1. The dataset’s balanced accuracy of 1 indicates similar functionality in both groups, with equal prevalence, detection rate, and detection prevalence aligning with the actual class distribution. To ensure the model’s success in generalizing and not overfitting the training data, it is crucial to confirm its performance using unexplored test data.
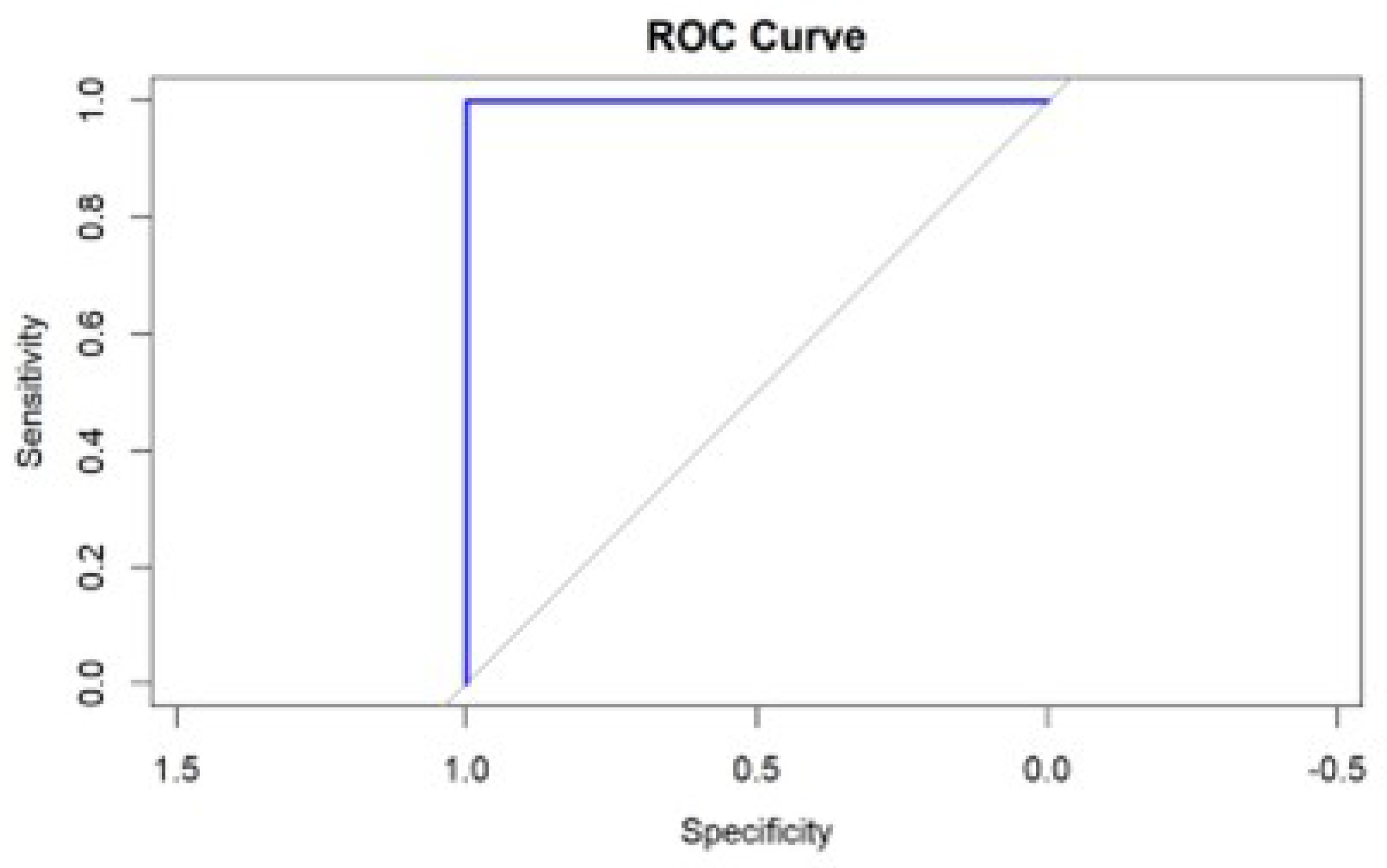
Our model demonstrated perfect discrimination capacity between the positive and negative classes with the Area Under the ROC Curve (AUC) value of 1. The model consistently scored positive instances higher than negative instances for randomly selected positive and negative instances.
Figure 5 shows the ROC curve for authentication and authorisation with the Area under the Curve (AUC) of 1.
The results of combining the AUC with additional performance indicators are shown in
Table 1.
The adaptive authentication model with no false positives or negatives, accurately recognizes all positive and negative classifications, accurately predicting data distributions. The model accurately predicts the dataset’s class distributions and consistently ranks positive examples higher than negative ones, demonstrating a flawless AUC. However, since these results may indicate overfitting we further performed cross-validation. False Positive Rate (FPR) and False Negative Rate (FNR) were calculated with results of zero (0) for each. For the given dataset, a false positive rate and false negative rate of 0 bolster the model’s accuracy and reliability.
5.2. Usability Evaluation
False Acceptance and Rejection Rates were used for measuring usability of the model.
Table 2 shows the evaluation metrics.
The authentication paradigm exhibits high security and usability, with zero false acceptance and rejection rates, demonstrating its exceptional performance. The model’s authentication decisions are accurate and consistent, ensuring users’ authenticated state is accurately matched.
5.3. User Health Impact on Authentication
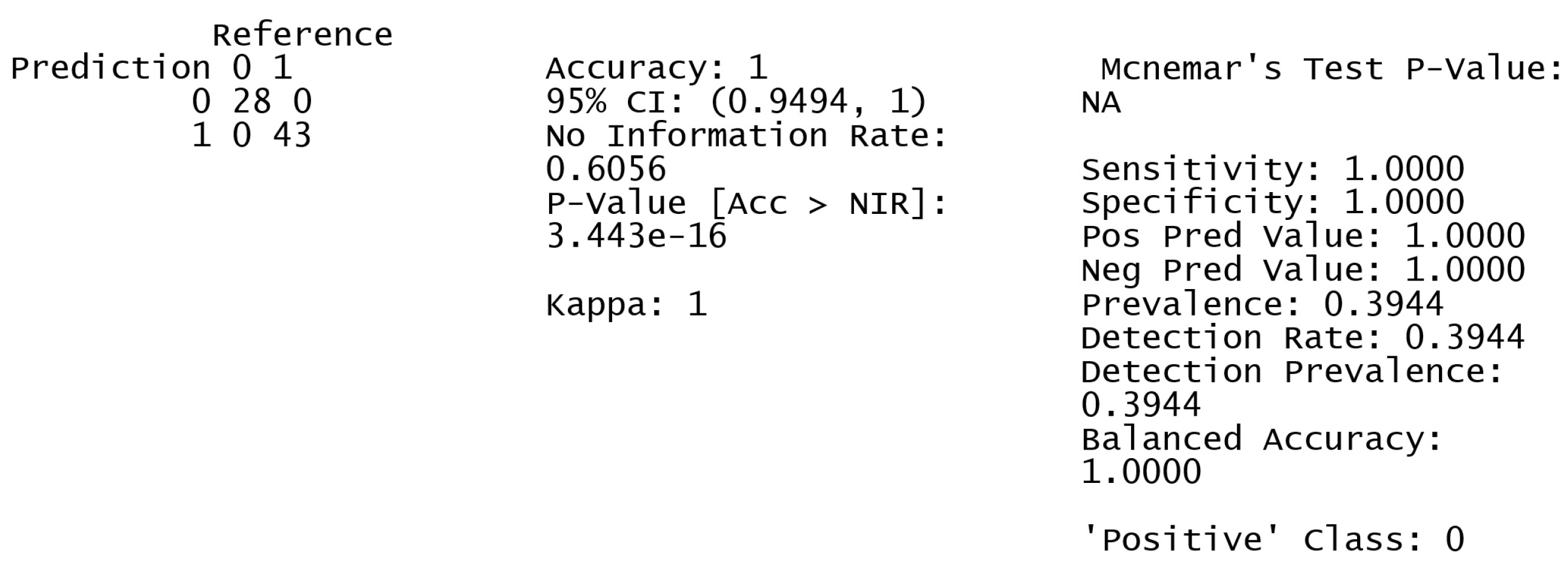
Our model accurately predicted 80% of the cases, with an overall accuracy of 80%. The system accurately detects positive situations in class 0 (positive cases), as evidenced by its high recall and precision. The model’s strong specificity indicates its ability to accurately identify instances of class 1 (negative cases).
Figure 6 shows the confusion matrix and statistics for health impact on authentication.
Further analysis and investigation may be necessary to identify the most significant predictor features and their impact on model performance. Cross validation was also required to validate the model on independent datasets.
5.4. Train Test Split and Cross-Validation
The model underwent further validation through train test split and cross-validation, utilizing Confusion Matrix and Statistics results as shown in the tables.
5.4.1. Train Test Split
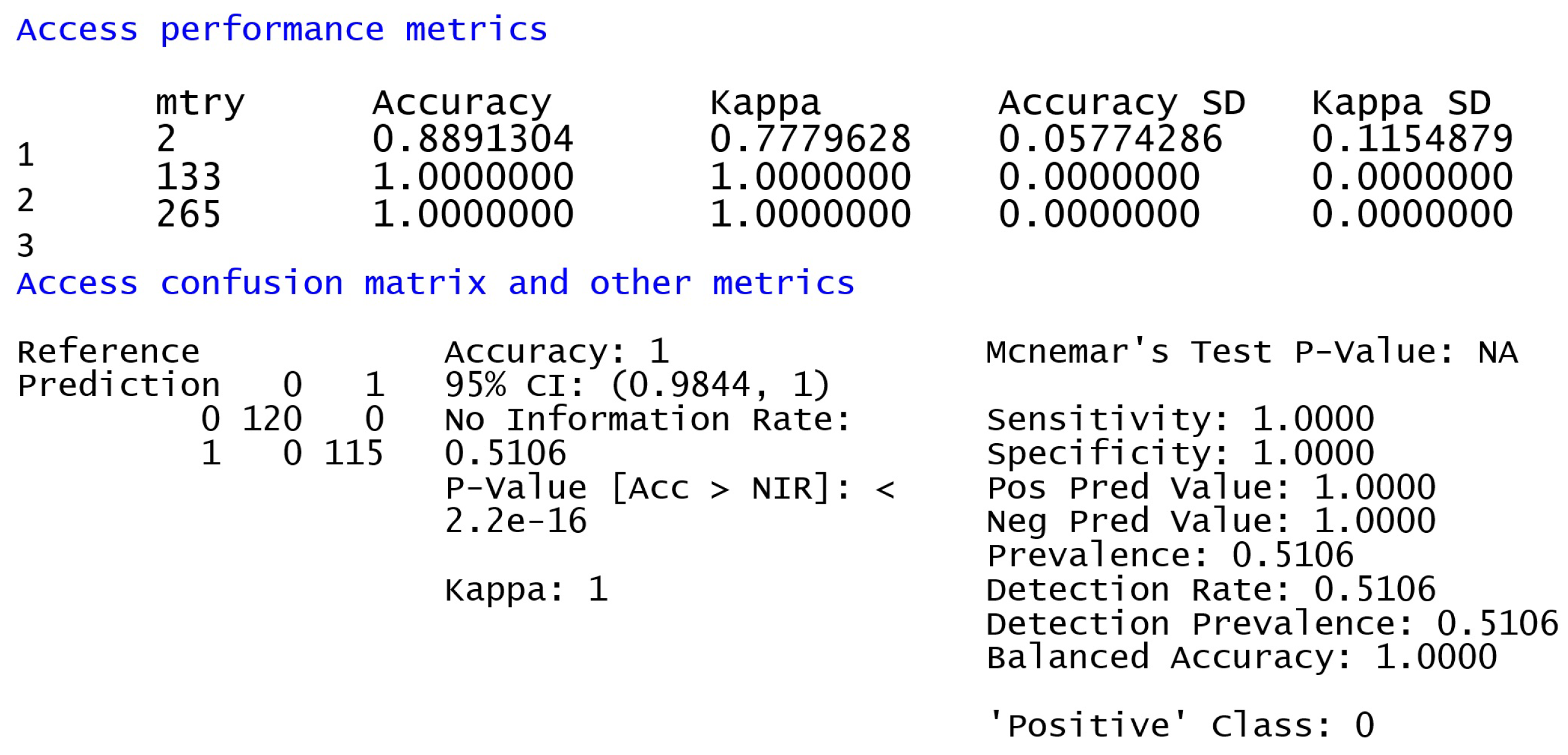
Figure 7 shows the confusion matrix and statistics for the train test split option.
The model demonstrated perfect sensitivity and specificity in accurately predicting all occurrences in the test set, detecting both positive and negative cases. The Kappa, Precision, and Negative Predictive Values indicate that all forecasts for each class were accurate, confirming the initial results. The model effectively generalizes to the test data, as indicated by the findings.
5.5. Cross Validation
The Random Forest classifier was used for cross-validation with 235 samples, 26 predictors, and 2 classes to analyze access performance metrics and confusion matrix.
Figure 8 shows the performance metrics.
The model shows high accuracy and kappa in both train-test split and cross-validation results, indicating its ability to effectively generalize to unknown data.
5.6. Distance Analysis
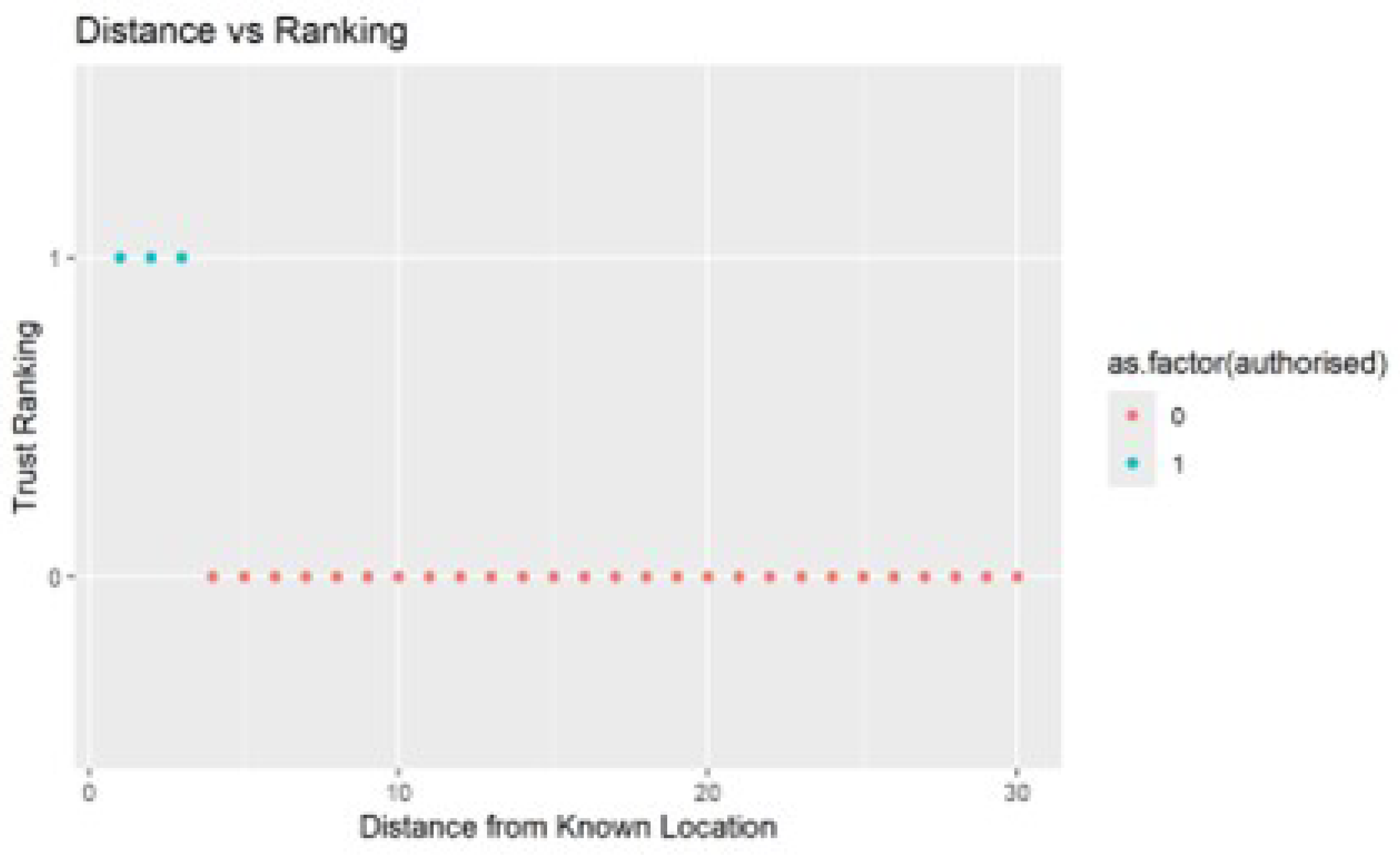
We performed distance analysis to determine the effect of location on authentication. The research emphasized the significance of location as it determined the distance a user, assumed to be always with their smartphone, would have moved from a known location. This is shown in
Figure 9.
The linear regression analysis reveals a significant negative correlation between
Dist from epicenter and
authorised. The likelihood of obtaining authorization decreases as the distance from the epicentre increases. The relationship is statistically significant due to the significant variability in the authorized variable.
Figure 10 shows a graphical illustration of the distance analysis.
The results indicate that our model has a tolerance for radius from a known location, raising suspicion when the radius exceeds the threshold. Our model’s user-friendliness is evident, particularly for the elderly users.
Effectiveness
The model’s effectiveness in predicting user access was assessed using the confusion matrix and related metrics. The success-ratio was measured to ensure the model’s reliability and usability in real-world scenarios.
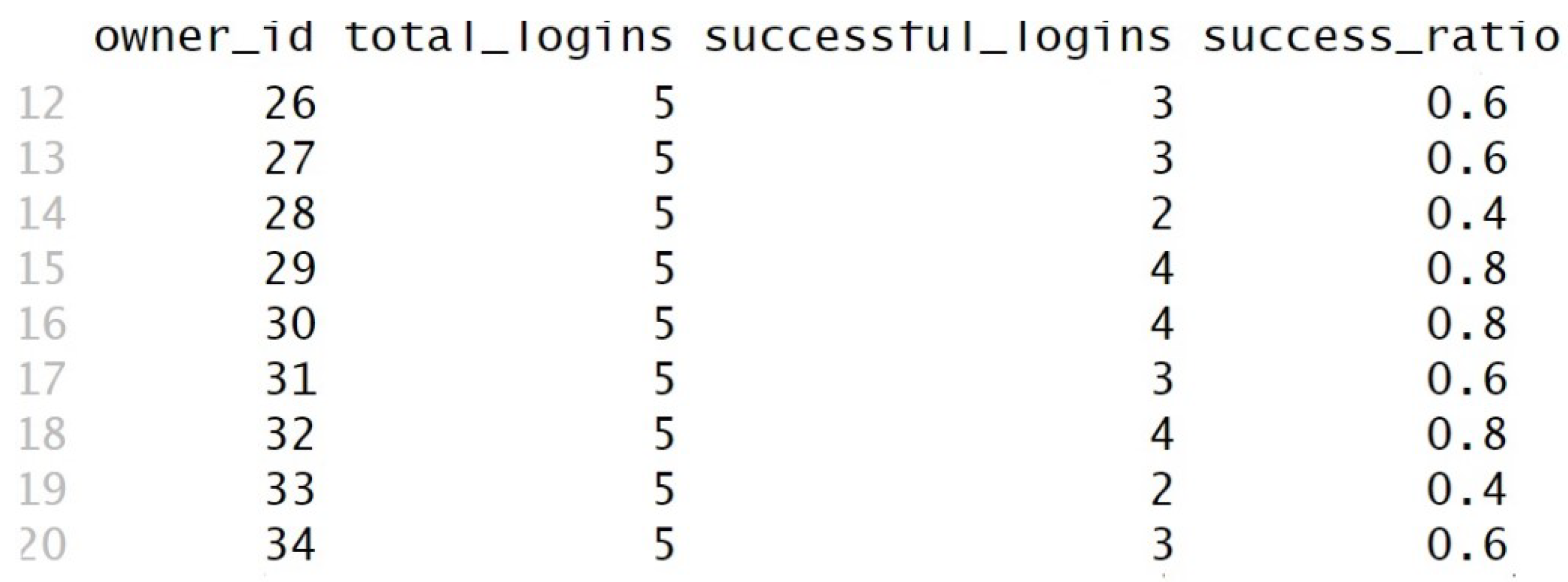
Figure 11 shows part of the success-ratio results.
The snapshot shows a success-ratio between 0.4 and 0.8, with successful logins generally exceeding failed logins.
Efficiency
The efficiency of our model was assessed through the FRR and FAR measurements, both of which had zero values indicating efficient classification. The study analyzed various factors such as trust ranking, success rate, completion rate, average success ratio, overall completion rate, and average success ratio. The overall values are as shown in
Table 3.
6. Discussion
We implemented an adaptive user authentication model for IoMT users with particular focus on improving usable-security. The model, which was implemented on Android smartphones, demonstrated promising results in terms of accuracy, precision, recall, and overall performance. The model calculates the initial risk score by utilizing various features like user ID, device ID, network, location, and habits and goes to perform a stepwise authentication guided by the hardware of the device. The model has demonstrated high accuracy (1.0) in identifying authorized and unauthorized access attempts during cross-validation, indicating effective risk calculation. These ideal outcomes, however, could not always be practical and might point to possible problems like overfitting, particularly given that the evaluation was mostly focused on training data rather than a distinct test set. To ensure the model maintains its excellent performance in real-world scenarios, it is crucial to maintain consistency in its performance on unobserved test data. The Kappa value of 1 indicates a perfect agreement between the model’s predictions and the actual values after adjusting for chance. The risk calculation mechanism accurately detects anomalies and legitimate and fraudulent access attempts, with a 1.0 sensitivity and specificity, ensuring no false positives or negatives. Combining the AUC with additional performance indicators showed that our model accurately recognizes all positive and negative classifications, accurately predicting data distributions. The results suggest that there may be overfitting, which may necessitate cross-validation. The authentication paradigm, which has zero false acceptance and rejection rates, exhibits high security and usability. Although these results are ideal,the model’s performance in real-world scenarios and against different user types is crucial for ensuring its robustness and generalizability.
The health impacts accuracy rate is 80%, indicating accurate detection of positive situations with high recall and precision. Further analysis and investigation may be necessary to identify the most significant predictor features and their impact on model performance. In evaluating using the train test split, the model’s Kappa, Precision, and NPV show accurate forecasts for each class, indicating good generalization to test data. The study found a mix of high and low trust users, with a median trust value of 0.5, influenced by contextual factors. Health conditions, age and location data in this case were significant predictors of trust score. At the same time, distance from the known location has a significant negative impact on authorization, which is consistent with the model’s logic that increased distance reduces trust. To enhance the validity of the study, it is recommended to incorporate more predictors, examine multicollinearity and non-linear relationships. The confusion matrix shows 100% accuracy in training, but 80% cross validation results suggest room for improvement in final authorization decision based on trust score and risk assessment. The high Kappa value indicates a strong agreement between the predicted and actual classes. The model was tested for usability considering health conditions and distance from known locations, ensuring fair treatment for elderly users with certain medical conditions and appropriate authentication methods. However, this is limited to the hardware on a particular smartphone. Average and overall success ratios validate [
20,
21] who assert that age and illness have a bearing on user authentication success amongst the elderly.
7. Conclusion and Future Work
The model exhibits exceptional performance in calculating risk, trust, and authorization decisions. The system effectively integrates user behavior, environmental context, and health conditions to provide adaptive and secure user authentication. However,the model’s accuracy difference between training and cross-validation indicates the need for further testing and tuning on diverse data to ensure its generalizability across various scenarios. Low success ratios may also be attributed to several factors like user experience, network, and medical conditions. In order to capture more complex user behaviours and environmental changes, future work will require diversifying the training data to cover a wider range of user behaviours and situations. It will also involve exploring additional features. Additionally, it’s important to keep track of the users’ health status and modify authentication procedures as needed to accommodate any changes. To ensure optimal performance, we will also routinely adjust the model’s parameters and validate them using fresh data.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.M.M.; methodology, P.M.M and M.Z; software, P.M.M.; validation, P.M.M., and P.N.; formal analysis, F.N.; investigation, X.X.; resources, X.X.; data curation, P.M.M.; writing—original draft preparation, P.M.M.; writing—review and editing, M.Z.; visualization, P.M.M.; supervision, M.Z.,P.N., and F.N.;. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.”
Funding
“The APC was funded by PASET-RSIF”.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Review Board (or Ethics Committee) of University of Rwanda’s College of Medicine and Health Sciences’ Institutional Review Board (IRB) Reference Number 102/CMHS IRB/2023/ of 31/01/2023.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study. The data collected did not directly identify participants, so obtaining written consent was not necessary.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author due to ethical reasons
Acknowledgments
This work was jointly supported by the African Centre of Excellence in Internet of Things (ACEIoT) from College of Science and Technology, University of Rwanda, and the Regional Innovation Scholarship Fund (RSIF).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| SSA |
Sub-Saharan Africa |
| IoMT |
Internet of Medical Things |
| IoHT |
Internet of Health Things |
| IoT |
Internet of Things |
| MFA |
Multi-Factor Authentication |
| LAS |
Lightweight Authentication Scheme |
| PSSUQ |
Post-Study System Usability Questionnaire |
| DID |
Decentralised identifier |
| VC |
Verifiable Credentials |
| CASA |
Context Aware Scalable Authentication |
| CYOA |
Choose Your Own Authenticator |
| AUC |
Area Under the Curve |
| PPv |
Positive Predictive Value |
| NPV |
Negative Predictive Value |
| FPR |
False Positive Rate |
| FNR |
False Negative Rate |
| FRR |
False Rejection Rate |
| FAR |
False Acceptance Rate |
References
- Sun, F.; Zang, W.; Gravina, R.; Fortino, G.; Li, Y. Gait-based identification for elderly users in wearable healthcare systems. Information Fusion 2020, 53, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ncoa. The Top 10 Most Common Chronic Conditions in Older Adults, 2023.
- United Nations. World Population Ageing 2019 Highlights. Technical report, United Nations, 2019. [CrossRef]
- The World Bank. Population ages 65 and above (% of total population) - Sub-Saharan Africa | Data, 2021.
- Ten Brink, R.N.; Scollan, R.I.; Bedford, M.A. Usability of Biometric Authentication Methods for Citizens with Disabilities. IRS-TPC 2019, September, 40.
- Kante, M.; Ndayizigamiye, P. Internet of medical things, policies and geriatrics: An analysis of the national digital health strategy for South Africa 2019–2024 from the policy triangle framework perspective. Scientific African 2021, 12, e00759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mtonga, K.; Kumaran, S.; Mikeka, C.; Jayavel, K. Machine Learning-Based Patient Load Prediction and IoT Integrated Intelligent Patient Transfer Systems. Future Internet 2019, 11, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jyotheeswari, P.; Jeyanthi, N. An Adaptive Authentication Scheme based on the User Mobility in Medical-IoT. International Journal of Engineering and Advanced Technology (IJEAT) 2019, Volume-9 I, 2708–2713. [CrossRef]
- Hazratifard, M.; Gebali, F.; Mamun, M. Using Machine Learning for Dynamic Authentication in Telehealth: A Tutorial. Sensors 2022, 22, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana-Mancilla, P.C.; Anido-Rifon, L.E.; Contreras-Castillo, J.; Buenrostro-Mariscal, R. Heuristic evaluation of an IoMT system for remote health monitoring in senior care. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2020, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-zubaidie, M.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J. RAMHU: A New Robust Lightweight Scheme for Mutual Users Authentication in Healthcare Applications. Security and Communication Networks 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkomo, D.; Brown, R. Hybrid Cyber Security Framework for the Internet of Medical Things. In Blockchain and Clinical Trial, Advanced Sciences and Technologies for Security Applications; IEEE Xplore, 2019; pp. 211–229.
- Michael, T.O.; Amunga, O.B.; Rajasvaran, L. Usability Evaluation Criteria for Internet of Things. International Journal of Information Technology and Computer Science 2016, 8, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blythe, J.M.; Johnson, S.D. The Consumer Security Index for IoT: A protocol for developing an index to improve consumer decision making and to incentivize greater security provision in IoT devices. IEEE Explore 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Das, S.; Kim, A.; Jelen, B.; Huber, L.L.; Camp, L.J. Non-Inclusive Online Security: Older Adults’ Experience with Two-Factor Authentication. In Proceedings of the 54th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences (HICSS 2021), 2021.
- Meli, S.; Nasabeh, S.; Luj, S. MoSIoT: Modeling and Simulating IoT Healthcare-Monitoring Systems for People with Disabilities. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2021, 18, 6357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavhemwa, P.M.; Zennaro, M.; Nsengiyumva, P.; Nzanywayingoma, F. User-Centred Design of Machine Learning Based Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) Adaptive User Authentication Using Wearables and Smartphones. Artificial Intelligence Application in Networks and Systems; Silhavy, R., Silhavy, P., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2023; pp. 783–799. [Google Scholar]
- Powell, A.Y. Ensuring biometrics work for everyone - Raconteur. https://www.raconteur.net/hr/diversity-inclusion/ensuring-biometrics-work-for-everyone/, 2021. Accessed: 2021-04-23.
- O’Dea, S. Mobile OS share in Africa 2018-2021 | Statista. https://www.statista.com/statistics/1045247/share-of-mobile-operating-systems-in-africa-by-month/, 2021. Accessed: 2022-01-16.
- Grindrod, K.; Khan, H.; Hengartner, U.; Ong, S.; Logan, A.G.; Vogel, D.; Gebotys, R.; Yang, J. Evaluating authentication options for mobile health applications in younger and older adults. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0189048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.; Grindrod, K. Evaluating Smartphone Authentication Schemes with Older Adults. In Proc. of SOUPS 2016, 2016.
- Silva, H.L.S.R.P.D.; Wittebron, D.C.; Lahiru, A.M.R.; Madumadhavi, K.L.; Rupasinghe, L.; Abeywardena, K.Y. AuthDNA : An Adaptive Authentication Service for any Identity Server. International Conference on Advancements in Computing (ICAC) December 5-6, 2019. Malabe, Sri Lanka, 2019.
- Gebrie, M.T.; Abie, H. Risk-Based Adaptive Authentication for Internet of Things in Smart Home eHealth. Proceedings of ECSA’17, September 11–15, 2017, Canterbury, United Kingdom, 7 pages., 2017. [CrossRef]
- Azmi, K.; Bakar, A.; Daud, N.I. Adaptive Authentication: A Case Study for Unified Authentication Platform. CS and IT-CSCP 2015, 2015, pp. 61–72. [Google Scholar]
- Ehatisham-ul Haq, M.; Azam, M.A.; Loo, J.; Shuang, K.; Islam, S.; Naeem, U.; Amin, Y. Authentication of smartphone users based on activity recognition and mobile sensing. Sensors (Switzerland) 2017, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, N.; Li, J.; Mondal, S.; Chen, F.; Pan, Y. On overcoming the identified limitations of a usable pin entry method. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 124366–124378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Kam, Y.H.s. Usable Authentication Methods for Seniors. International Journal of Recent Technology and Engineering (IJRTE) 2019, 8, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoobi, M.M. Keystroke Dynamics Authentication based on Naïve Bayes Classifier. Iraqi Journal of Science 2015, 56, 1176–1184. [Google Scholar]
- Grassi, P.A.; Fenton, J.L.; Newton, E.M.; Perlner, R.A.; Regenscheid, A.R.; Burr, W.E.; Richer, J.P.; Lefkovitz, N.B.; Danker, J.M.; Choong, Y.Y.; Greene, K.K.; Theofanos, M.F. Digital identity guidelines: authentication and lifecycle management. Technical report, National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg, MD, 2017. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Pan, T.; Song, Y. Development of Human Action Feature Recognition Using Sensors. Information Technology Journal 2022, 21, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ometov, A.; Petrov, V.; Bezzateev, S.; Andreev, S.; Koucheryavy, Y.; Gerla, M. INTERNET OF THINGS FOR SMART CITITES : Challenges of Multi-Factor Authentication for Securing Advanced IoT Applications. IEEE Network 2019, 33, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Liu, J.; Liu, H.; Chen, Y. Smart User authentication through actuation of daily activities leveraging WiFi-enabled IoT. Proceedings of the International Symposium on Mobile Ad Hoc Networking and Computing (MobiHoc), 2017, Vol. Part F1291. [CrossRef]
- Batool, S.; Saqib, N.A.; Khattack, M.K.; Hassan, A. Identification of remote IoT users using sensor data analytics; Vol. 69, Springer International Publishing, 2020; pp. 328–337. [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-manzano, L.; Fuentes, J.M.D.E.; Ribagorda, A. Leveraging User-related Internet of Things for Continuous Authentication: A Survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2019, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, D.; Roy, A.; Nag, A. Toward the design of adaptive selection strategies for multi-factor authentication. Computers and Security 2016, 63, 85–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hintze, D.; Koch, E.; Scholz, S.; Mayrhofer, R. Location-based risk assessment for mobile authentication. Proceedings of the 2016 ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing: Adjunct; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias-cabarcos, P. A Survey on Adaptive Authentication. ACM Comput. Surv. 2019, 52, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- V, P.; G., R.M.L.; Mathews, M.M.; Justine, S. A Provably Secure,Privacy-Preserving Lightweight Authentication Scheme for Peer-to-Peer Communication in Healthcare Systems based on Internet of Medical Things. Computer Communications 2023, 212, 284–297. [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Din, I.U.; Almogren, A. Securing Access to Internet of Medical Things Using a Graphical-Password-Based User Authentication Scheme. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5207–5207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Ryu, J.; Lee, Y.; Won, D. An Improved Lightweight User Authentication Scheme for the Internet of Medical Things. Sensors 2023, 23, 1122–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhan, M.; Salih, A.; Butt, U. Enhancing Secure Access and Authorization in Healthcare IoT through an Innovative Framework: Integrating OAuth, DIDs, and VCs. Proceedings of the 2023 6th International Conference on Information Science and Systems; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2023; ICISS ’23, p. 254–261. [CrossRef]
- Bali, M.; Yenkikar, A., IOT-BASED SECURE WIRELESS MEDICAL SENSOR NETWORKS USINGMULTIFACTOR AUTHENTICATION. In Futuristic Trends in IOT Volume 3 Book 2; IIP Edited Book Series, 2024; pp. 146–162. [CrossRef]
- Enamamu, T.S., Intelligent Authentication Framework for Internet of Medical Things (IoMT). In Illumination of Artificial Intelligence in Cybersecurity and Forensics; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2022; pp. 97–121. [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.; Ali, Y.; Khan, F. A Features-Based Privacy Preserving Assessment Model for Authentication of Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) Devices in Healthcare. Mathematics 2023, 11, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, T.; Braeken, A.; Liyanage, M.; Ylianttila, M. Identity Privacy Preserving Biometric Based Authentication Scheme for Naked Healthcare Environment. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), 2017. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Singh, G. , Robust User Authentication Scheme for IoT-Based Healthcare applications. In Recent Advancements in Smart Remote Patient Monitoring, Wearable Devices, and Diagnostics Systems; IGI Global, 2023; pp. 170–182. [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Ud Din, I.; Majali, T.; Kim, B.S. A Survey of Authentication in Internet of Things-Enabled Healthcare Systems. Sensors 2022, 22, 9089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, E.; Hong, J.; Das, S.; Amini, S.; Oakley, I. CASA : Context - Aware Scalable Authentication. Symposium on Usable Privacy and Security (SOUPS) 2013, July 24–26, 2013, Newcastle, UK., 2013, pp. 1–10.
- Forget, A.; Chiasson, S.; Biddle, R. Choose Your Own Authentication. NSPW, 2015.
- Wójtowicz, A.; Chmielewski, J. Model for adaptable context-based biometric authentication for mobile devices. Pers Ubiquit Comput 2016, 20, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias-Cabarcos, P.; Krupitzer, C. On the design of distributed adaptive authentication systems. Proceedings of the 13th Symposium on Usable Privacy and Security (SOUPS 2017) 2017.
- Department of Health, Education, and Welfare. The Belmont Report, 1979. A foundational document in the field of bioethics.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).