1. Introduction
The skin prick test (SPT) is a relatively simple and easy-to-perform immediate reading test for immunoglobulin E (IgE)-mediated reactions, but its accuracy can be limited by the need for human interpretation [
1,
2]. The measurements of the wheal dimensions appearing on the skin after the puncture are made manually, which can cause different types of errors due parallax, instrument resolution and human error. In this way, the evaluation of the allergic reaction depends on the examiner [
3]. Since the wheal area is proportional to the degree of sensitization (i.e., the stronger the immune response, the larger the wheal), this parameter is considered the main indicator for diagnosing an SPT [
4,
5]. A positive diagnosis is typically based on a wheal diameter 3 mm larger than the negative control and greater than half the diameter of the histamine response [
6].
Subjectivity in wheal assessment arises from variations in its geometric contour, leading to inconsistent readings by different examiners or even by the same examiner at different times [
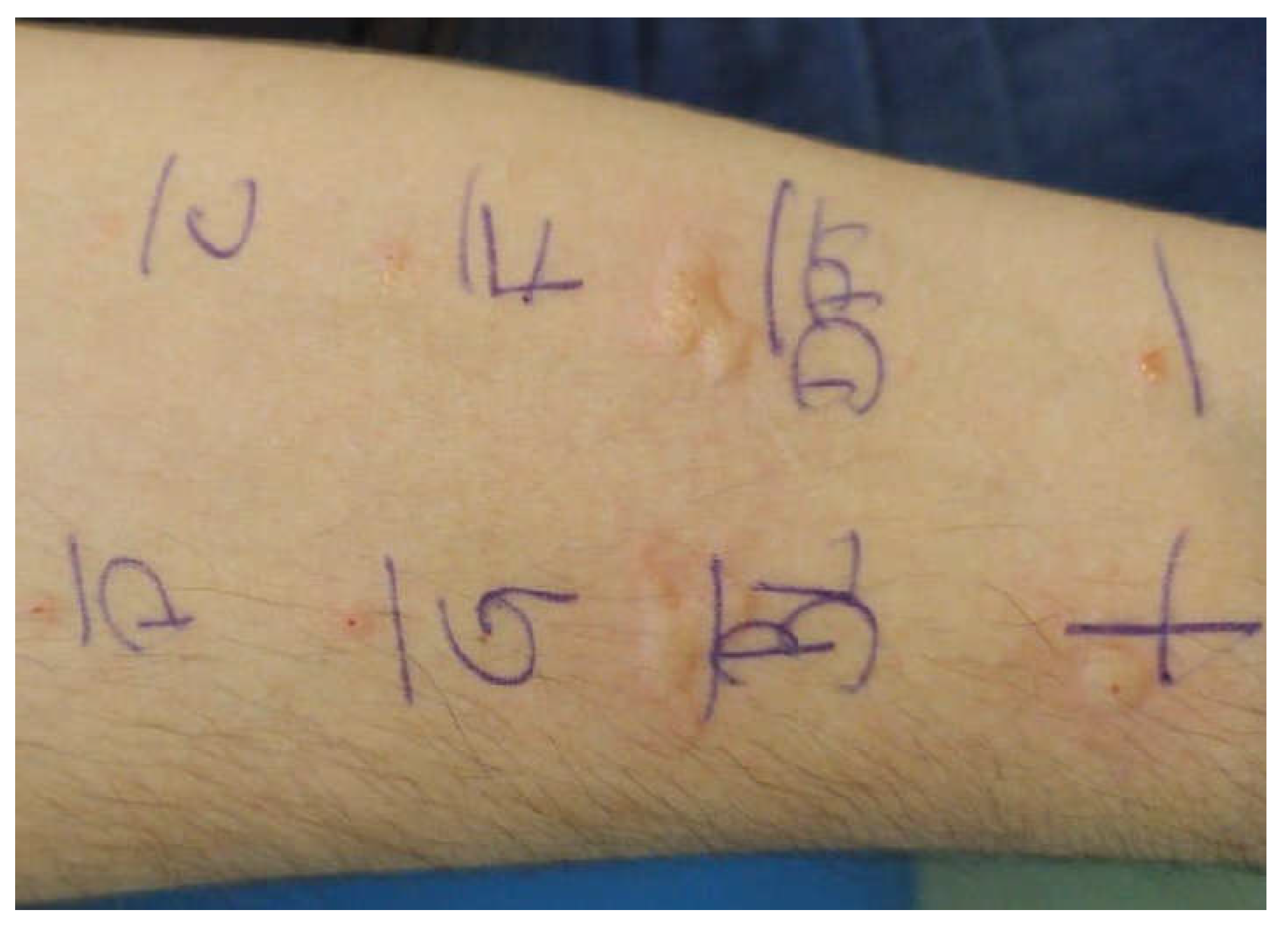
3]. As illustrated in
Figure 1, wheals can exhibit irregular geometric contours, further contributing to interpretation challenges [
7]. Skin pigmentation presents another complication, making it difficult to identify the reaction outline [
8]. Additionally, wheal location (e.g., volar vs. infrascapular region) can influence the result [
9].
Standardized methods are necessary to address subjectivity in wheal assessment and improve diagnostic consistency. Several approaches have been proposed utilizing cameras, thermographic cameras, and computer-aided color analysis [
7,
8,
10,
11,
12,
13,
14]. However, all these proposed techniques require specialized high-cost equipment, limiting their widespread adoption in clinical practice.
Machine learning techniques and deep learning algorithms have emerged as powerful tools for image-based clinical diagnostics. Studies have shown that machine learning-generated classifier models outperform human evaluators in determining geometric parameters from images, such as area, radius, perimeter, and measures of shape complexity (compactness, smoothness, concavity) [
15,
16]. Semantic image segmentation is a machine learning technique utilizing deep learning algorithms (specifically artificial neural networks), which is particularly suitable for this application. It infers models to identify patterns in the image and classify pixels into predefined segments (or labels), allowing an accurate segmentation of the wheal area, which is a crucial requirement in SPT diagnosis [
17].
This work aimed to develop a computational protocol based on deep learning to apply the image segmentation technique in test reading to improve SPT measurement techniques.
2. Methods
2.1. Acquisition of Skin Prick Test Photos
SPT photos, used to compose the training/testing dataset, were acquired from volunteer patients who agreed to participate in this research after signing informed consent. 1461 photos were acquired using smartphones of different brands/models, camera configurations, or operating systems. The SPT was performed according to the established method by European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology [
6]. Immediately after 15 minutes of puncture application:
i) a square-shaped tag in chroma key color, named as reference tag (RT) and with known dimensions (3 cm × 3 cm), was placed on the forearm or upper back near the formed wheals;
ii) the smartphone was positioned in parallel to test region at a distance which varied between 10 cm to 30 cm;
iii) the focus set-up was performed and then;
iv) the photo was captured.
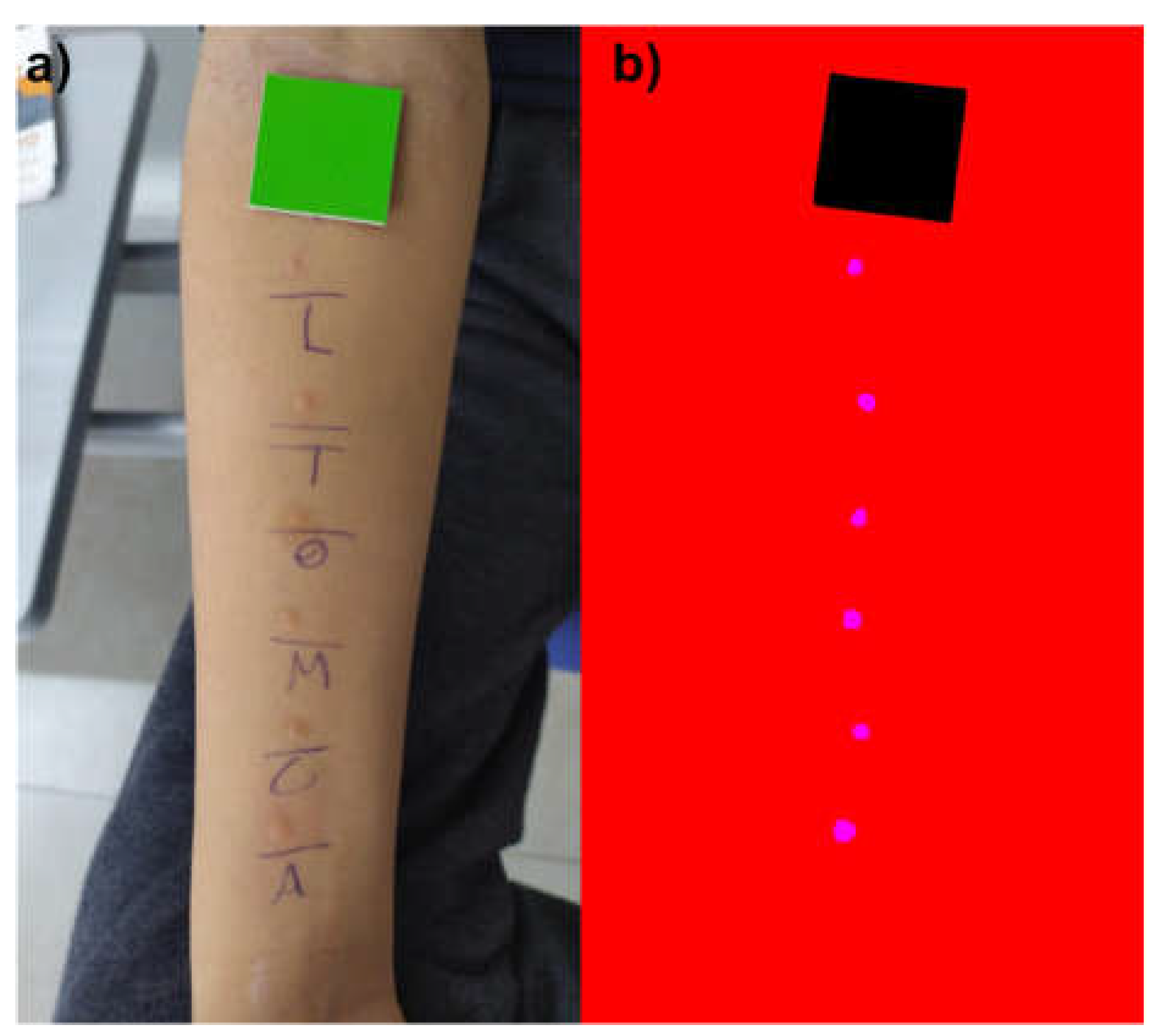
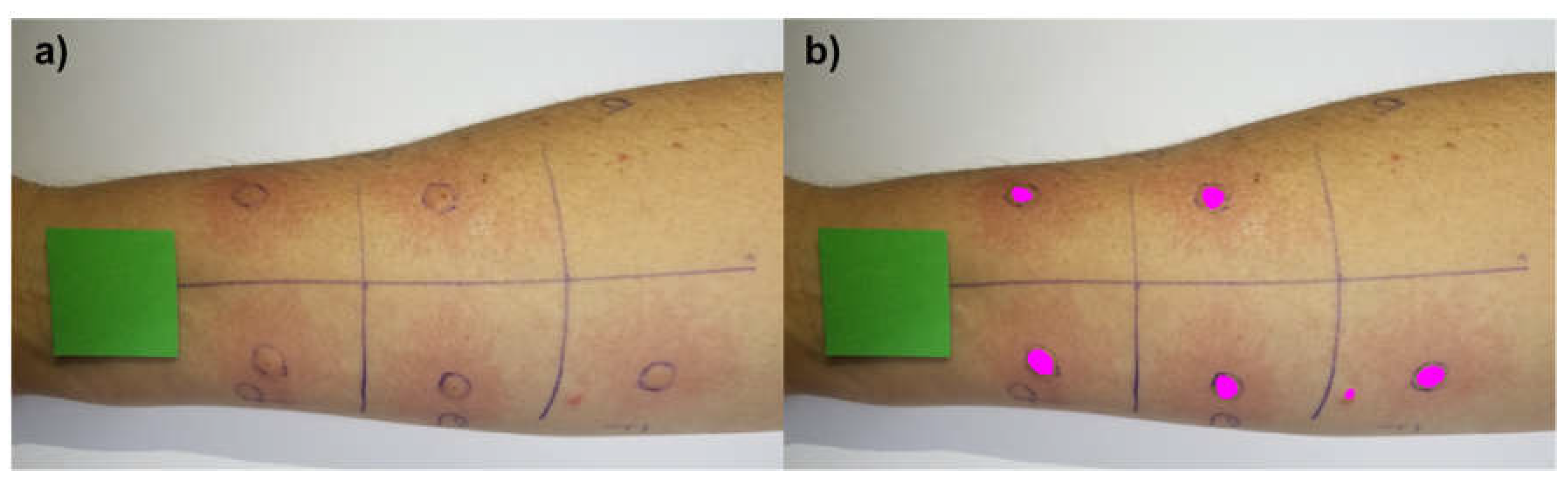
Figure 2(a) illustrates a sample of photo acquired using this method.
2.2. Dataset Standardization
The SPT photos were edited using Corel Photo-Paint and Inkscape software to create segments (or labels) in magenta color (R = 255, G = 0, B = 255) for the pixels corresponding to the wheal area, in black (R = 0, G = 0, B = 0) for the pixels corresponding to the RT and in red (R = 255, G = 0, B = 0) for the other pixels of the image.
Figure 2(b) shows an example of labeled SPT. In addition, ImageMagic software [
18] was used to resize the images to a size of (640 × 480) pixels in order to standardize the dataset and reduce the computational cost of image processing.
In machine learning models, overfitting occurs when a model becomes too specialized to the training data and performs poorly on unseen data. To enrich the dataset further and potentially reduce the overfitting of the deep learning model, a technique called data augmentation was employed using the ImageMagic software [
18,
19,
20]. Geometric transformations were applied to the SPT images to make deep learning model independent to changes in images position and orientation. For this purpose, each image underwent a sequential transformation process:
i) horizontal mirroring,
ii) 180° rotation, and finally,
iii) another horizontal mirroring. This process effectively quadrupled the dataset size, resulting in 5844 images used for model training.
2.3. Machine Learning Model Training and Wheal Clustering
A generic and extensible fully convolutional neural network (CNN) developed by [
21] was used to train the
ML model for wheals segmentation. The CNN was implemented in Python environment using the TensorFlow library [
19] and this network is based on the VGG-16 architecture [
20]. A Python algorithm was developed using Open Source Computer Vision Library (OpenCV) [
21] to determine the area of each wheal after the segmentation. The algorithm first performs the pixel clustering of the instances classified as wheal by the
ML model. Finally, the clustered pixels are used to estimate the individual wheal area using a simple proportion between the number of pixels of a wheal and the number of pixels of the RT, which has known area.
2.4. Evaluation of the Machine Learning Model Performance
An independent validation dataset consisting of 30 images containing 150 wheals was established to evaluate the performance of the proposed computational protocol. The images were obtained and segmented following the same procedures described in sections 2.1 and 2.2, with one key difference: a qualified allergist marked the contours of the wheal with a pen, which was used as a guide for the images manually labeling. This process, here referred to as assisted image segmentation (AIS), provided a reliable reference for assessing the ML model performance.
Two types of accuracy were determined for the deep learning model evaluation:
Detection accuracy and
Segmentation accuracy.
Detection accuracy was determined using equation (1). In equation (1), the
Type I error means the detection of non-existing wheals. The
Segmentation accuracy was evaluated from the variables of a confusion matrix determined by a cluster of pixels around the wheal (described in section 2.3). The expected labels used in these analyses are those generated by the
AIS method. The choice of a cluster evaluation (and not for the whole image) was due to the large number of non-wheal pixels in the images, leading to overestimating the
ML model segmentation accuracy. The model’s segmentation performance was determined as the mean of the segmentation accuracies of the 144 correctly detected wheals.
The agreement between the inferred model (
ML) and the standard medical method (largest diameter of the wheal,
Medical LD, and its perpendicular diameter,
Medical PD, measured by a professional) was evaluated based on the concordance analysis proposed by Bland and Altman [
22]. In order to compare the methods, we estimated the wheal area values from the
Medical LD and
Medical PD using equation (2) and equation (3), where,
MA1 and
MA2 are two different ways to compute the wheal area. Paired Wilcoxon signed rank tests [
23] and correlation tests were also performed between the area values obtained by each method. Finally, the cumulative distribution function was determined for the areas estimated using the four methods (
ML,
AIS,
MA1 and
MA2).
All these analyses were performed using the R software (version 4.2.2, R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria) [
24] and Python3 (version 3.9, Python Software Foundation) [
25].
2.5. Comparison of Area Estimates for Regular and Irregular Geometric Shapes Using Different Methods
Previous studies have demonstrated that computationally assisted methods can deviate from the standard protocol for measuring wheal dimensions, particularly when dealing with irregularly shaped wheals [
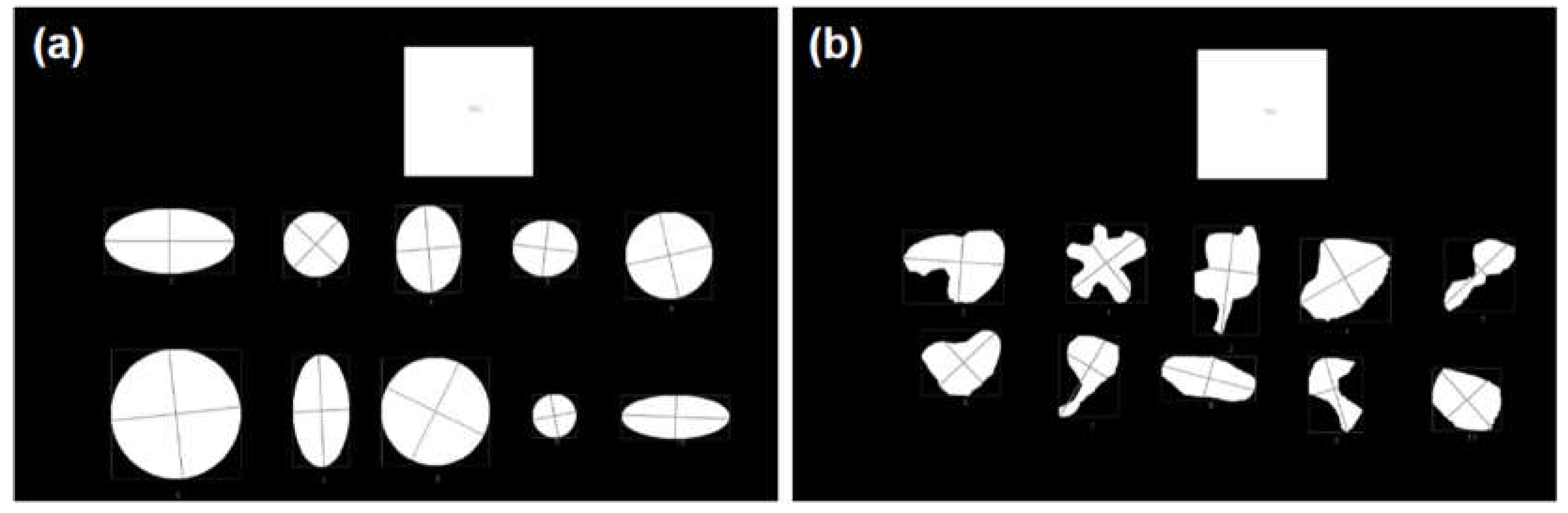
26]. To evaluate these potential divergences, two distinct groups of segmented images were created. The first group (Group 1 – Regular Shapes) consists solely of shapes with regular outlines, which can be approximated by circles or ellipses. The second group (Group 2 – Irregular Shapes) is comprised exclusively of shapes with highly irregular geometric contours.
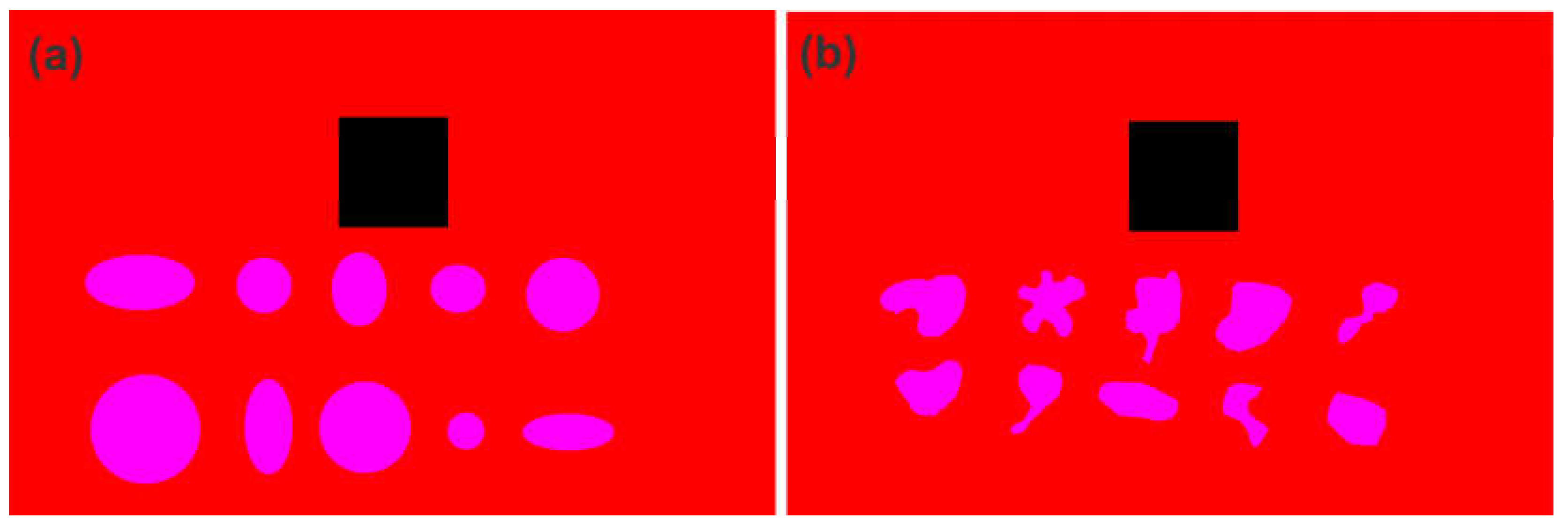
Figure 3 presents a sample of each group here described. In all images, a square with known dimensions (3 cm × 3 cm), similar to the RT, was inserted to provide a scale for determining the shapes diameters and areas.
The image files from Group 1 – Regular Shapes and Group 2 – Irregular Shapes contain 10 different segmented shapes (as shown in
Figure 3). Each group was comprised a total of 15 images files, resulting in 150 shapes for Group 1 and 150 shapes for Group 2. The shape pixels in each image were clustered using the protocol proposed in this study (see section 2.3). This procedure allowed us to estimate the shape areas in a similar way to
ML and
AIS methods. Additionally, the largest diameter (
Computational LD) and diameter perpendicular to the largest diameter (
Computational PD) were computationally determined. With these parameters, the shape areas were also estimated by the mean diameter (similar to equation (2)) and the product of half the diameters (similar to equation (3)). We also assessed the area of the figures using the function “pixel distribution histogram”, available in Corel Photo-Paint software, here referred to as
Corel Area. The percentage deviation between the methods was calculated and used to evaluate their performance in predicting the areas of shapes with regular and irregular geometric contours.
3. Results
The proposed
ML protocol was able to segment and cluster wheals in SPT images. The area of each wheal was estimated using a simple proportion between the number of pixels from RT (with a known area) and from the segmented wheal.
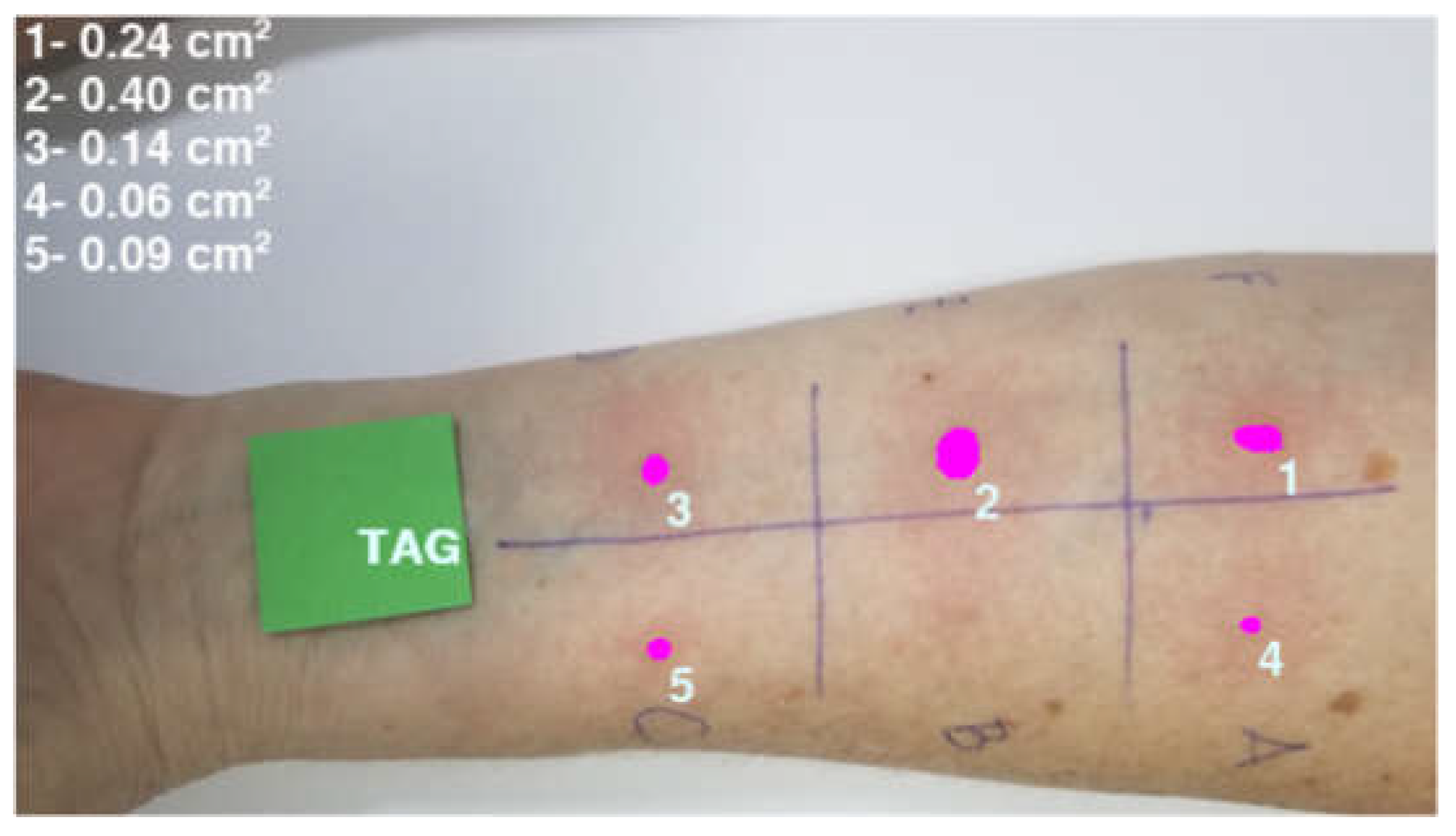
ML protocol generated an image containing the segmented wheals, each one identified with a number, accompanied by a report in the upper left corner summarizing the wheal areas in cm².
Figure 4 shows an example of an SPT image segmentation performed by the
ML protocol.
The ML model for wheals segmentation had its performance measured on a validation dataset with 30 different images and 150 wheals. In this dataset, 9 wheals were not correctly detected, with 3 detections of non-existing wheals (Type I error) and 6 wheals that existed but were not detected (Type II error), which resulted in a Detection accuracy of 94.12%. Segmentation accuracy on the remaining 144 wheals was determined using the confusion matrix variables, and the average accuracy measured for the validation dataset was 85.88%.
The paired Wilcoxon signed rank test showed a statistically significant difference between the areas
MA1,
MA2,
AIS, and
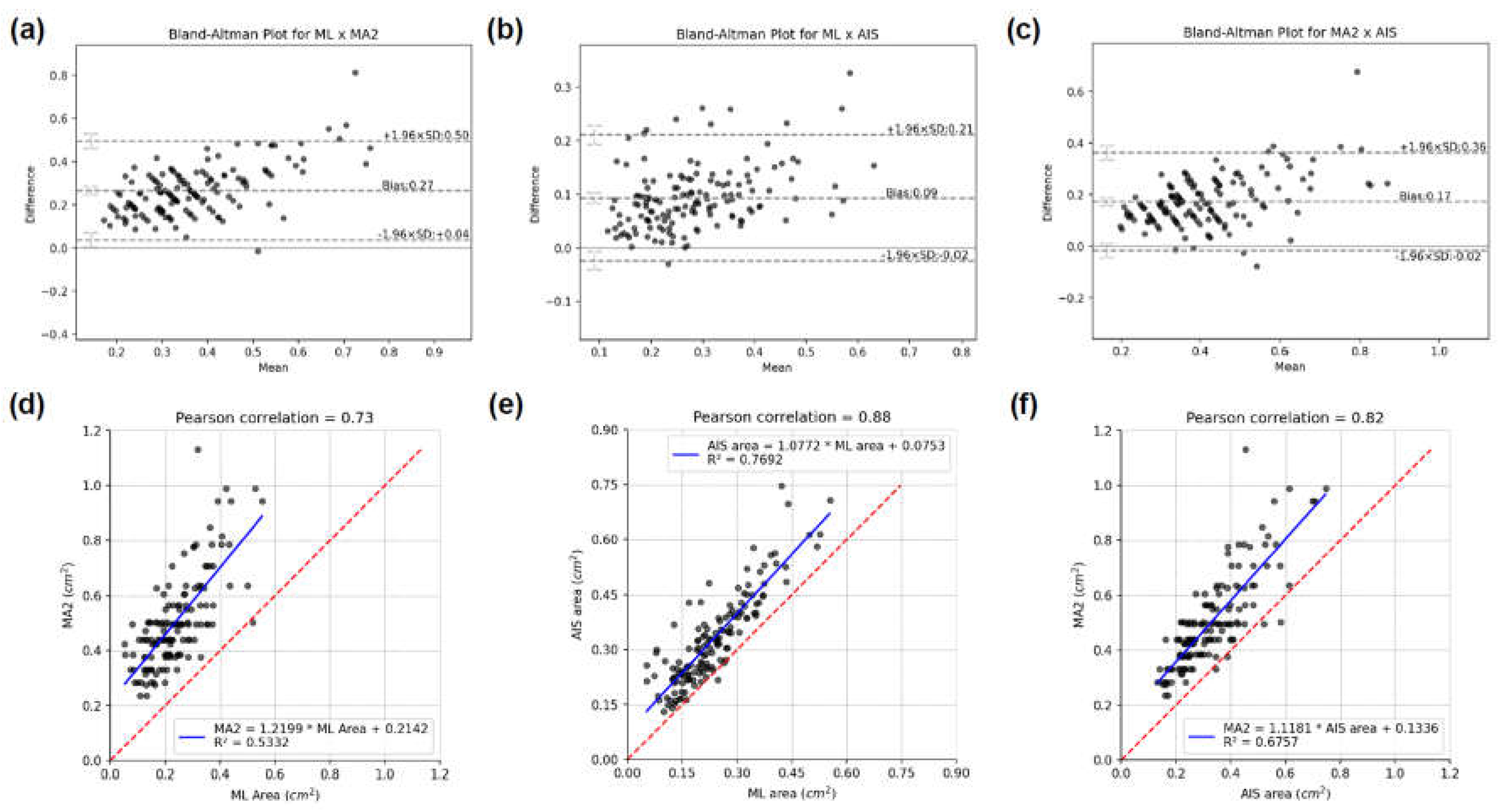
ML (p-value < 0.001 in all tests). Despite this result, the Bland-Altman analyses (
Figure 5) indicated that the difference between the measurement methods is concentrated around a bias (mean difference), indicating no correlation between the difference obtained between the measurement methods and the magnitude of the variable area.
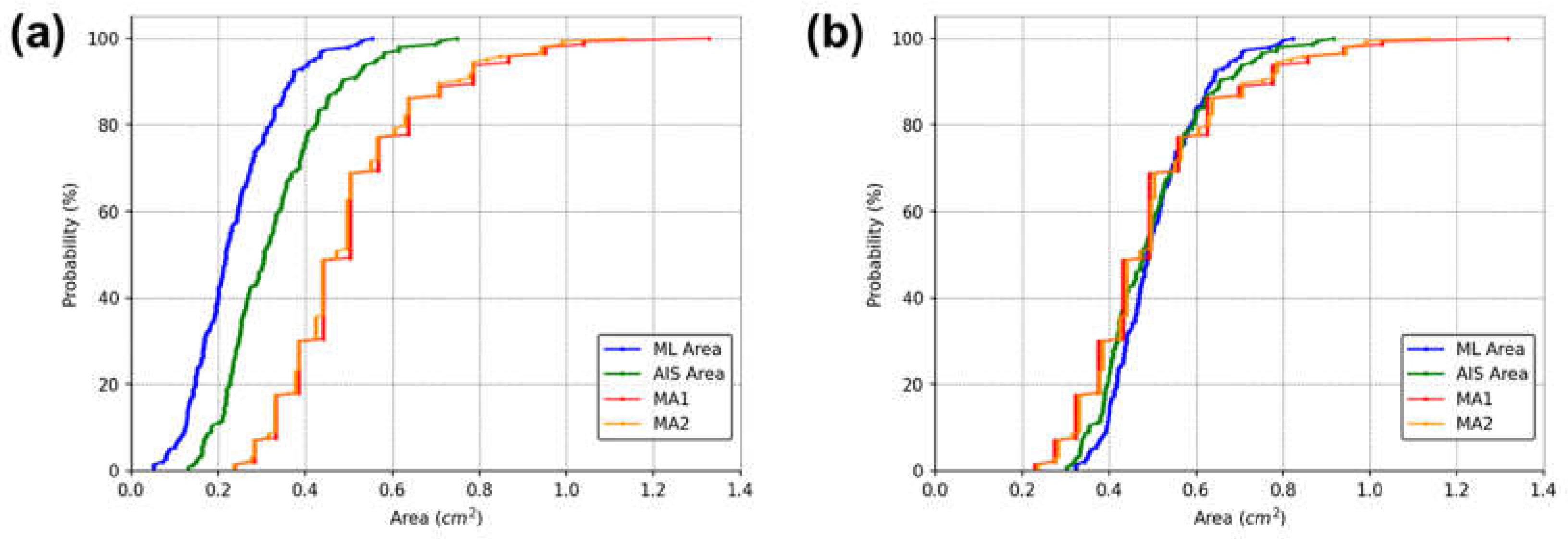
We also determined the cumulative distribution function of the areas estimated by the four methods
ML,
AIS,
MA1 and
MA2 (
Figure 6). This analysis confirmed the statistically significant difference observed in the paired Wilcoxon signed rank test, also clarified that the distributions can be superimposed by shifting the curves in the bias value. Thus, biases can be used to relate the areas obtained by different methods. Furthermore, the different methods can also be related using linear equations.
It can be noted in
Figure 5 and
Figure 6 that there is a uniform pattern in the scatter of points in all analysis performed for
MA1 or
MA2, and it should be clarified that this does not represent a bias in the dataset. This pattern occurred because the
MA1 and
MA2 were determined using a measuring instrument with precision of 1 mm. As a result, the graphical representation of these values (or the direct analyses performed with them) tends to show a pattern of points discretization. However, this pattern was not observed for the
ML and
AIS methods. This difference can be explained by the fact that the computational variables used to determine the area of the wheals were declared as floating types (i.e., real numbers), which have a precision of 10
-8. This precision is relatively high, so the graphs for the results from
ML and
AIS methods did not show point discretization This consideration is important because it highlights that the conventional method of determining wheal dimensions has an accuracy limited by the precision of the measuring instrument used for the SPT (not to mention other possible sources of error). In contrast, the computational method performs a pixel-by-pixel analysis, in which the accuracy is limited by the image resolution. Generally, any current smartphone can capture images with sufficient resolution to surpass the accuracy obtained using the
MA1 and
MA2 methods.
The following results show the performance of the methods evaluated in this study to determine the
PD,
LD and area of shapes with regular geometric contours (circles or ellipses) and irregular geometric contours (corresponding to pseudopods). The proposed method for determining
Computational LD and
Computational PD values yielded results that closely matched the mathematically expected
LD and
PD values for the regular images.
Figure 7 illustrates an example of an image from each group (regular shapes and irregular shapes) where
Computational LD and
Computational PD were calculated. For the regular shapes in
Figure 7(a), the mean percentage deviations
Computational LD and
Computational PD were 0.3754% and 0.5410%, respectively. The minor deviations observed in the regular shapes are likely due to the fact that the images represent circles and ellipses rather than ideal mathematical objects. Since our computational method for determining the diameter is invariant to the geometric shape and relies solely on the estimate of the geometric center (easily determined by averaging the coordinates of the shape), we believe that this method provides accurate estimates of
Computational LD and
Computational PD for the irregular dataset. This accuracy is further confirmed visually.
The
LD and
PD are required parameters for evaluating the accuracy of the standard medical protocol (
MA1) used to infer wheal dimensions.
MA1 assumes that the wheal contour can be approximated as an ellipse, where
LD represents the major axis and
PD represents the minor axis. Thus, the area of the wheal can be estimated as describe in the equation (2). In cases where
LD ≈
PD, the ellipse then has approximately the shape of a circle and the area can be calculated by the equation A = π*(
LD/2)
2. However, in this study, we propose that approximating wheal area as an ellipse may be inaccurate, particularly for wheals with irregular contours. Instead, we suggest that using a simple proportion between the pixels count from RT and pixels count from wheal may provide more accurate results regardless of the shape of the wheal. To support the proposed statement, the results for two distinct groups of shapes are presented below: Group 1 – Regular shapes and Group 2 – Irregular shapes. The cumulative distribution of the area values estimated by the different methods and the boxplots of the percentage deviation values between the methods were determined for both groups, and the analyses are shown in
Figure 8 and
Figure 9.
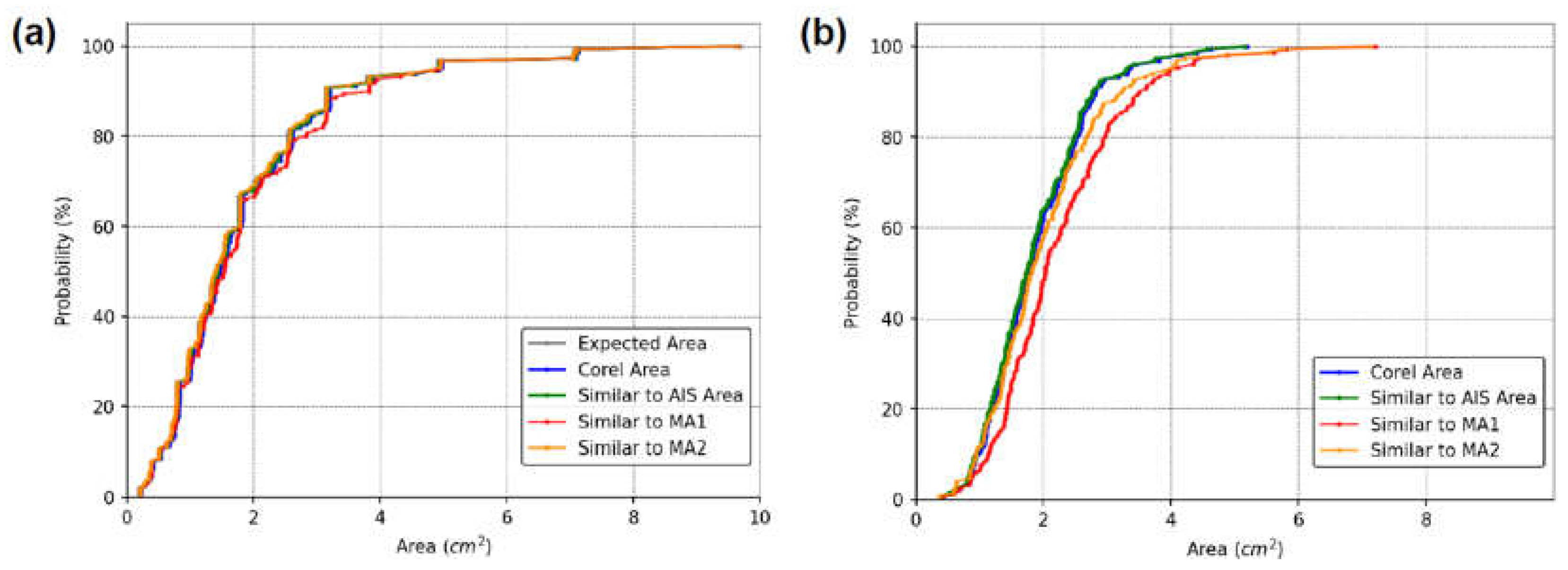
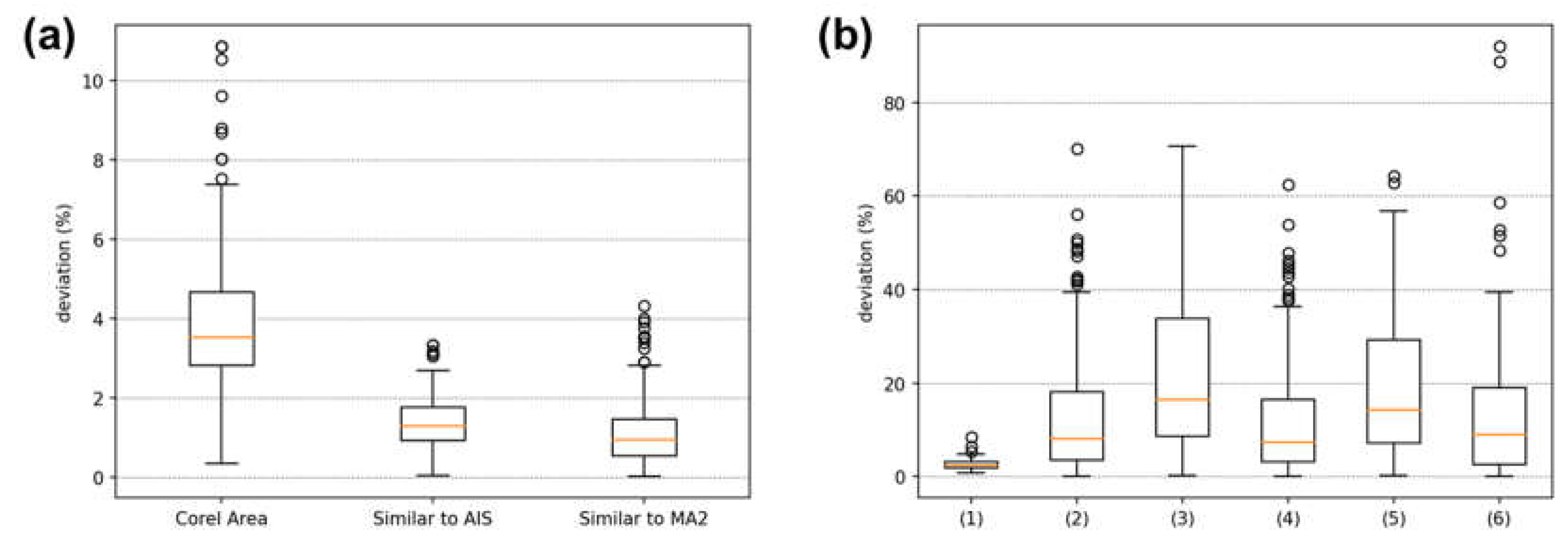
In Group 1 - Regular Shapes, the mean percentage deviations of the Corel Area, Similar to AIS, and Similar to MA2 values relative to the Expected Area were 3.82% ± 1.97%, 1.38% ± 0.64%, and 1.18% ± 0.94%, respectively. It is noteworthy that although the mean deviation of values calculated similarly to AIS is slightly higher than that calculated similarly to MA2, the maximum deviation for values similar to MA2 is greater (4.31% compared to 3.33%). Overall, all methods performed well in estimating the area of regular shapes, among them the least effective were Corel Area and similar to MA1.
The area calculation method similar to
AIS (simple proportion using an RT) is invariant to the geometric shape of the figure and showed low deviations from the expected areas in Group 1 – Regular Shapes. Therefore, we used this method as a reference for analyzing irregular figures, as we had no mathematical means of determining their expected areas. In
Figure 9-(b), it can be seen that the order of adherence to the area values calculated similarly to
AIS was in decreasing order:
Corel Area, Similar to
MA2, and Similar to
MA1 (boxplots (1), (2), and (3)). This result is consistent because, although the areas calculated using Corel Photo-Paint pixel distribution histogram function exhibited larger deviations than methods similar to
AIS and similar to
MA2 in regular figures, this method is also invariant to geometric shape and seems to have maintained the magnitude of its deviations relative to values calculated similarly to
AIS. In contrast,
MA1 and
MA2 are approximations highly dependent on the geometric shape of the figure, resulting in larger deviations from the expected area values. What should be emphasized in these results is that for figures with irregular contours, the standard medical protocol can lead to large deviations from the expected area values, thus compromising the quality of the diagnosis.
4. Discussion
Regarding the three instances that presented type I errors in the validation dataset, it was observed that two puncture marks in the negative control were detected as wheals. The third type I error is shown in
Figure 10 and refers to a small reddish mole on the patient’s arm that was segmented by the
ML model. The light conditions used to take the picture, the patient’s skin color, or the small size of the wheal were possible causes of type II errors. Although the detection accuracy was considered satisfactory, both error types tend to decrease with the increment of the number of instances (images) in the training dataset, which can be performed and evaluated in future studies. In addition, for clinical uses of the
ML approach, it is expected that the wheal segmentation performed by the
ML model will always be interpreted and validated by a health professional since the developed protocol aims to provide a tool to support humans to perform a faster and more accurate diagnosis, and not replace them.
The cumulative distribution functions confirm that the ML method produces measures closer to the AIS distribution than the MA1 and MA2. Moreover, the values obtained by the ML method have a more continuous distribution than those obtained by the Medical Diameters, which may indicate a higher analysis resolution. This characteristic probably occurred because the Medical Diameters has its resolution linked to the graduation of the instrument used to measure the wheal diameter (usually a ruler or caliper). In contrast, the ML and AIS methods perform a pixel-by-pixel analysis.
The Pearson correlation coefficients between the measurement methods are shown in
Figure 5. A strong correlation was found between the areas inferred through the
ML and
AIS methods (ρ=0.88), which was considerably more significant than the correlation between the
AIS and
MA1 (ρ=0.80) and
MA2 (ρ=0.82) and was consistent with the results of Bland-Altman’s analysis. In previous studies carried out by our group [
26], we determined a statistically significant Pearson correlation coefficient between skin temperature variation in the wheal (during the SPT) and the area determined by a similar
AIS method. Since the
ML method had a strong correlation with the
AIS method, it is reasonable to assume that the
ML method is also associated with the wheal temperature during the skin sensitization reaction, which is a characteristic known to be proportional to the intensity of sensitivity to the antigen.
Some patients with high levels of sensitization to an antigen may be more susceptible to developing wheals with irregular contours and the formation of pseudopods [
27]. In these cases, approaches that use medical diameters to infer sensitization may not be the most appropriate. These methods approximate wheal areas using only the values of
LD and
PD (or by calculating the mean of both diameters) [
4,
6]. In other words, the method for determining the area of the wheals approximates the sensitization area by assuming an elliptical shape, in which the major axis corresponding to
LD and the minor axis to
PD, or alternatively, by using a circle with a diameter equal to the average of
LD and
PD. However, for irregular shapes, such as pseudopods, this approximation may differ significantly from the real area of the wheals, as our results suggest. Moreover, the standard protocol to infer skin sensitization can be associated with other problems, such as parallax error, which may further reduce diagnostic accuracy.
It should be highlighted that the standard medical protocol for inferring the area of skin sensitization was developed based on the measurement tools that were available and feasible at the time the protocol was defined. These instruments are essentially tools for measuring linear dimensions, such as rulers or calipers. However, our results, along with findings from other studies, indicate that new technologies can be used to more accurately determine the area of skin sensitization. All of exposed here points to the need to review and update the standard prick test protocol to improve diagnostic accuracy.
In this study we propose that segmentation techniques using deep learning or other computationally assisted methods can be applied to determine the wheal areas. These techniques can be fully automated, making the prick test diagnosis entirely objective and independent of the professional’s experience or interpretation when measuring the wheal dimensions. Additionally, the need for manual measurement using tools such as rulers or calipers is eliminated, saving time for both the professional and the patient. The proposed methodology can also expedite patient care, potentially leading to significant cost savings for healthcare services performing the SPT. Furthermore, it can be easily integrated into hospital information systems, facilitating the generation of reports and medical records that include SPT images and patient history.
5. Conclusions
The results show that the measurements performed by the developed ML method were consistent with those from the other evaluated methods (AIS and Medical Diameters). Specifically, for figures with irregular contours, the proposed method for calculating the area provides more accurate estimates compared to methods based on medical diameters. These findings suggest that the proposed protocol has the potential to automate the reading of the SPT reaction and can be used objectively in clinical practice. However, further extensive studies are needed, primarily to standardize the use of area values for diagnosing antigen sensitization during the SPT. These results highlight the need to review the prick test protocol in light of the new technological tools currently available.
6. Patents
The method presented in this paper resulted in a computer program registered at Brazil’s National Institute of Industrial Property (INPI) (Process No.: BR512021000570-8).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Ramon Hernany Martins Gomes, Edson Luiz Pontes Perger and Rafael Plana Simões; Data curation, Ramon Hernany Martins Gomes, Edson Luiz Pontes Perger, Lucas Hecker Vasques, Elaine Gagete Miranda Da Silva and Rafael Plana Simões; Formal analysis, Ramon Hernany Martins Gomes, Elaine Gagete Miranda Da Silva and Rafael Plana Simões; Funding acquisition, Rafael Plana Simões; Investigation, Ramon Hernany Martins Gomes, Edson Luiz Pontes Perger, Lucas Hecker Vasques, Elaine Gagete Miranda Da Silva and Rafael Plana Simões; Methodology, Ramon Hernany Martins Gomes, Edson Luiz Pontes Perger, Lucas Hecker Vasques, Elaine Gagete Miranda Da Silva and Rafael Plana Simões; Project administration, Edson Luiz Pontes Perger and Rafael Plana Simões; Resources, Edson Luiz Pontes Perger, Elaine Gagete Miranda Da Silva and Rafael Plana Simões; Software, Ramon Hernany Martins Gomes, Edson Luiz Pontes Perger, Lucas Hecker Vasques and Rafael Plana Simões; Supervision, Rafael Plana Simões; Validation, Ramon Hernany Martins Gomes, Elaine Gagete Miranda Da Silva and Rafael Plana Simões; Writing – original draft, Ramon Hernany Martins Gomes and Edson Luiz Pontes Perger; Writing – review & editing, Ramon Hernany Martins Gomes and Rafael Plana Simões.
Funding
The APC was funded by Sao Paulo State University (UNESP).
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of Botucatu Medical School, UNESP (Document number 30680320.2.0000.5411). The study protocol conforms to the ethical guidelines of the 1975 Declaration of Helsinki as reflected in a priori approval by the institution’s human research committee.
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent has been obtained from the patients to publish this paper.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon request to the corresponding author. (The data are not publicly available due to privacy and ethical constraints.)
Acknowledgments
This research was also supported by resources supplied by the Center for Scientific Computing (NCC/GridUNESP) of the São Paulo State University (UNESP), Brazil.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Frati, F.; Incorvaia, C.; Cavaliere, C.; Di Cara, G.; Marcucci, F.; Esposito, S.; Masieri, S. The Skin Prick Test. Journal of biological regulators and homeostatic agents 2018, 32, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Knight, V.; Wolf, M.L.; Trikha, A.; Curran-Everett, D.; Hiserote, M.; Harbeck, R.J. A Comparison of Specific IgE and Skin Prick Test Results to Common Environmental Allergens Using the HYTECTM 288. Journal of Immunological Methods 2018, 462, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topal, S.; Karaman, B.; Aksungur, V. Variables Affecting Interpretation of Skin Prick Test Results. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 2017, 83, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Valk, J.P.M.; Gerth Van Wijk, R.; Hoorn, E.; Groenendijk, L.; Groenendijk, I.M.; De Jong, N.W. Measurement and Interpretation of Skin Prick Test Results. Clin Transl Allergy 2015, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haahtela, T.; Burbach, G.J.; Bachert, C.; Bindslev-Jensen, C.; Bonini, S.; Bousquet, J.; Bousquet-Rouanet, L.; Bousquet, P.J.; Bresciani, M.; Bruno, A.; et al. Clinical Relevance Is Associated with Allergen-specific Wheal Size in Skin Prick Testing. Clin Experimental Allergy 2014, 44, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinzerling, L.; Mari, A.; Bergmann, K.-C.; Bresciani, M.; Burbach, G.; Darsow, U.; Durham, S.; Fokkens, W.; Gjomarkaj, M.; Haahtela, T.; et al. The Skin Prick Test – European Standards. Clinical and Translational Allergy 2013, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Justo, X.; Díaz, I.; Gil, J.J.; Gastaminza, G. Medical Device for Automated Prick Test Reading. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics 2018, 22, 895–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Justo, X.; Díaz, I.; Gil, J.J.; Gastaminza, G. Prick Test: Evolution towards Automated Reading. Allergy 2016, 71, 1095–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, H.H.; Lundgaard, A.C.; Petersen, A.S.; Hauberg, L.E.; Sharma, N.; Hansen, S.D.; Elberling, J.; Arendt-Nielsen, L. The Lancet Weight Determines Wheal Diameter in Response to Skin Prick Testing with Histamine. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrugo, A.G.; Romero, L.A.; Pineda, J.; Vargas, R.; Altamar-Mercado, H.; M.d, J.M.; Meneses, J. Toward an Automatic 3D Measurement of Skin Wheals from Skin Prick Tests. In Proceedings of the Dimensional Optical Metrology and Inspection for Practical Applications VIII; International Society for Optics and Photonics, May 13 2019; Vol. 10991, p. 1099104.
- Pineda, J.; Vargas, R.; Romero, L.A.; Marrugo, J.; Meneses, J.; Marrugo, A.G. Robust Automated Reading of the Skin Prick Test via 3D Imaging and Parametric Surface Fitting. PLOS ONE 2019, 14, e0223623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rok, T.; Rokita, E.; Tatoń, G.; Guzik, T.; Śliwa, T. Thermographic Assessment of Skin Prick Tests in Comparison with the Routine Evaluation Methods. Postepy Dermatol Alergol 2016, 33, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svelto, C.; Matteucci, M.; Pniov, A.; Pedotti, L. Skin Prick Test Digital Imaging System with Manual, Semiautomatic, and Automatic Wheal Edge Detection and Area Measurement. Multimed Tools Appl 2018, 77, 9779–9797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svelto, C.; Matteucci, M.; Resmini, R.; Pniov, A.; Pedotti, L.; Giordano, F. Semi-and-Automatic Wheal Measurement System for Prick Test Digital Imaging and Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Imaging Systems and Techniques (IST); October 2016; pp. 482–486. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, A.S.; Marcon, M.; Ghafoor, S.; Wurnig, M.C.; Frauenfelder, T.; Boss, A. Deep Learning in Mammography: Diagnostic Accuracy of a Multipurpose Image Analysis Software in the Detection of Breast Cancer. Invest Radiol 2017, 52, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehteshami Bejnordi, B.; Veta, M.; Johannes van Diest, P.; van Ginneken, B.; Karssemeijer, N.; Litjens, G.; van der Laak, J.A.W.M.; the CAMELYON16 Consortium; Hermsen, M. ; Manson, Q.F.; et al. Diagnostic Assessment of Deep Learning Algorithms for Detection of Lymph Node Metastases in Women With Breast Cancer. JAMA 2017, 318, 2199–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully Convolutional Networks for Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR); IEEE: Boston, MA, USA, June, 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar]
- ImageMagick Studio LLC ImageMagick 2023.
- Abadi, M.; Barham, P.; Chen, J.; Chen, Z.; Davis, A.; Dean, J.; Devin, M.; Ghemawat, S.; Irving, G.; Isard, M.; et al. TensorFlow: A System for Large-Scale Machine Learning. In Proceedings of the 12th USENIX Symposium on Operating Systems Design and Implementation (OSDI 16); 2016; pp. 265–283. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition. arXiv:1409.1556 [cs] 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bradski, G. The OpenCV Library. Dr. Dobb’s Journal of Software Tools, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Martin Bland, J.; Altman, DouglasG. STATISTICAL METHODS FOR ASSESSING AGREEMENT BETWEEN TWO METHODS OF CLINICAL MEASUREMENT. The Lancet 1986, 327, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcoxon, F. Individual Comparisons by Ranking Methods. Biometrics Bulletin 1945, 1, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
-
R Core Team R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021.
- Van Rossum, G.; Drake, F.L. Python 3 Reference Manual; CreateSpace: Scotts Valley, CA, 2009; ISBN 1-4414-1269-7. [Google Scholar]
- Almeida, A.L.M.; Perger, E.L.P.; Gomes, R.H.M.; Sousa, G. dos S.; Vasques, L.H.; Rodokas, J.E.P.; Olbrich Neto, J.; Simões, R.P. Objective Evaluation of Immediate Reading Skin Prick Test Applying Image Planimetric and Reaction Thermometry Analyses. Journal of Immunological Methods 2020, 112870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serota, M.; Portnoy, J.; Jacobs, Z. Are Pseudopods On Skin Prick Testing Reproducible? Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2012, 129, AB239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Prick Test photography illustrating different wheal areas.
Figure 1.
Prick Test photography illustrating different wheal areas.
Figure 2.
Illustration of: (a) the original photograph and (b) the respective labeled image (manually segmented).
Figure 2.
Illustration of: (a) the original photograph and (b) the respective labeled image (manually segmented).
Figure 3.
Sample of a segmented image containing only: (a) shapes with regular geometric contour; (b) shapes with irregular geometric contour. The shapes are colored magenta and the RT is colored black.
Figure 3.
Sample of a segmented image containing only: (a) shapes with regular geometric contour; (b) shapes with irregular geometric contour. The shapes are colored magenta and the RT is colored black.
Figure 4.
An example of an image containing the segmented wheals identified by a number and a report in the upper left subtitle containing the wheal areas in cm2.
Figure 4.
An example of an image containing the segmented wheals identified by a number and a report in the upper left subtitle containing the wheal areas in cm2.
Figure 5.
Bland-Altman analyzes for: (a) ML × MA2, (b) ML × AIS, and (c) MA2 × AIS. Correlation plots between: (d) ML and MA2, (e) ML and AIS, and (f) MA2 and AIS. It should be noted that the slope of the lines is close to 1.0 while the intercepts are close to the Bland-Altman bias value, especially in the line relating the AIS and ML methods. The results for MA1 and MA2 are similar and, for simplicity, the graphs for MA1 are not presented in this figure.
Figure 5.
Bland-Altman analyzes for: (a) ML × MA2, (b) ML × AIS, and (c) MA2 × AIS. Correlation plots between: (d) ML and MA2, (e) ML and AIS, and (f) MA2 and AIS. It should be noted that the slope of the lines is close to 1.0 while the intercepts are close to the Bland-Altman bias value, especially in the line relating the AIS and ML methods. The results for MA1 and MA2 are similar and, for simplicity, the graphs for MA1 are not presented in this figure.
Figure 6.
Cumulative distribution functions for the areas estimated by the four methods for the: (a) original data, and (b) adding the bias between ML, AIS, MA1 and MA2.
Figure 6.
Cumulative distribution functions for the areas estimated by the four methods for the: (a) original data, and (b) adding the bias between ML, AIS, MA1 and MA2.
Figure 7.
Computational LD and
Computational PD determined for the
(a) regular and
(b) irregular geometric shapes of the segmented images presented in
Figure 3. This figure demonstrates that the computationally determined diameters serve as reliable estimates of
LD and
PD.
Figure 7.
Computational LD and
Computational PD determined for the
(a) regular and
(b) irregular geometric shapes of the segmented images presented in
Figure 3. This figure demonstrates that the computationally determined diameters serve as reliable estimates of
LD and
PD.
Figure 8.
Cumulative distribution functions for the areas estimated by different methods. In (a) Group 1 – Regular shapes; in (b) Group 2 – Irregular shapes. The Expected Area was calculated from the axes defined to create the ellipses and circles, the Corel Area was determined using the pixel distribution histogram function available in the Corel Photo-Paint software and similar to the AIS Area, MA1 and MA2 were calculated similarly to the AIS (or also to the ML area), MA1 and MA2, respectively. Note that for similar to MA1 and similar to MA2 the computationally determined diameter was used.
Figure 8.
Cumulative distribution functions for the areas estimated by different methods. In (a) Group 1 – Regular shapes; in (b) Group 2 – Irregular shapes. The Expected Area was calculated from the axes defined to create the ellipses and circles, the Corel Area was determined using the pixel distribution histogram function available in the Corel Photo-Paint software and similar to the AIS Area, MA1 and MA2 were calculated similarly to the AIS (or also to the ML area), MA1 and MA2, respectively. Note that for similar to MA1 and similar to MA2 the computationally determined diameter was used.
Figure 9.
Boxplot for percentage deviations of area values between different methods for: (a) Group 1 – Regular shapes and (b) Group 2 – Irregular shapes. In (a) the values obtained by the different methods were compared with the Expected Area. The boxplot for Similar to MA1 was omitted for clarity; its minimum, mean, and maximum values were 0.02%, 5.65% ± 13.04%, and 96.10%, respectively. In (b) the boxplot names were coded for better illustration, and their meanings are: (1) similar to AIS x Corel Area; (2) similar to AIS x similar to MA2; (3) similar to AIS x similar to MA1; (4) Corel Area x similar to MA2; (5) Corel Area x similar to MA1; and (6) similar to MA2 x similar to MA1.
Figure 9.
Boxplot for percentage deviations of area values between different methods for: (a) Group 1 – Regular shapes and (b) Group 2 – Irregular shapes. In (a) the values obtained by the different methods were compared with the Expected Area. The boxplot for Similar to MA1 was omitted for clarity; its minimum, mean, and maximum values were 0.02%, 5.65% ± 13.04%, and 96.10%, respectively. In (b) the boxplot names were coded for better illustration, and their meanings are: (1) similar to AIS x Corel Area; (2) similar to AIS x similar to MA2; (3) similar to AIS x similar to MA1; (4) Corel Area x similar to MA2; (5) Corel Area x similar to MA1; and (6) similar to MA2 x similar to MA1.
Figure 10.
(a) Patient’s arm 15 minutes after the punctures. (b) ML model segmentation where a type I error was identified.
Figure 10.
(a) Patient’s arm 15 minutes after the punctures. (b) ML model segmentation where a type I error was identified.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).