1. Introduction
P versus NP problem is one of the most important
unresolved issues of the millennium. [
1] Does
the speed of solving a problem have a direct relationship with the speed of recognizing
the correctness of the answer to that problem? The main point lies in the
problem itself. What is the relationship between the nature of time and
information? Accordingly, the equivalence between information and energy
examines the interrelationship of time and processing of a problem. [
2,
3] Due to the existence of two types of mass and
two types of energy, two forms of information can be introduced [
4]. Compressed information and extensive
information over time are an effective issue in processing speed [
5,
6]. Examining mathematical problems from the
perspective of physics does not seem logical. But the mathematical structure of
nature provides the possibility that the laws of nature are reflected and
manifested in the language of laws(math) [
7].
Examining masses of information over time can be useful in information
processing. Masses of information or compressed information are like a
gravitational field in the dimensions of time. A problem seeks an answer. And
every issue moves over time. But the answer to a problem does not depend on
time. Movement in the real dimension of time raises issues such as acceleration
and... over time, which leads to the evolution of an integrated theory [
7,
8]. Accordingly, the structure of mathematics can
be rewritten based on the laws of nature. The objects of mathematics are
numbers. And the wave function of each number has an extension in time.
Equivalence between compresses information and inertial mass better describes
phenomena such as entanglement. On the basis that compressed information over
time is like white holes that effect inertial mass in space-time [
9]. This article presents an alternative approach
that involves shifting from current problem-solving methods and adjusting the
mathematical framework according to brain activity. [
10,
11,
12]
introducing a metric for the information field, this article presents a
different view of information and information processing in six-dimensions
space-time. This type of information processing exists in the structure of the
cells of living and microscopic organisms. which can be called the way of
eating protein or different hereditary information and... This type of
information processing represents the factor of self-awareness in living
beings. This study explores the P versus NP problem from a perspective that
does not depend on the passage of time, definition the independence of
calculations from temporal constraints in the three dimension of time.
2. Methodology
Structure of number:
Numbers are the building blocks of information.
These blocks change over time. Accordingly, new definitions are expressed in
the field of information. Every real number is an infinite product of equations
between different numbers in the past. And it becomes another infinite number
in the future.
Accordingly, we consider a wave function for each
number. (2.1)
Each number in the present tense has a wave
function extended over time. (2.2)
The four main operations of addition, subtraction,
multiplication, and division can form states of the wave function. (2.3) The
probability amplitude for each number can determine the future and past state
of a number.
Based on this, operators and operators for numbers
can be determined. For example, the operator A specifies the state of the wave
function in a certain range. (2.4)
Numbers make up the world's main fact blocks.
Therefore, each number has unique properties. Different sets define the
characteristics of each group. Even numbers, odd numbers, rational numbers,
dumb numbers, real numbers, prime numbers, etc. have deep connections. Numbers
over time are products of ratios. Therefore, any number can be defined
trigonometrically in the complex space. (2.5)
The presence of each number indicates the
eccentricity of the ellipse for a set. This eccentricity of the ellipse
establishes the relationship between different sets. (2.6)
Based on this, fields can be defined for numbers.
Each field has properties related to that set. These fields are defined over
time. According to this definition, distance is essential for numbers. (2.7)
Density is the result of mathematical operations on a geometrical basis over
time. Based on this, it seems that time also originates from the geometric
potential difference. Therefore, the geometric metric expresses the field
equations over time. (2.7) r and a are two important factors to determine the characteristics
of a set in the field.
The definition of time in mathematics is very
simple. Time is geometric potential difference. Geometric potential difference
causes movement in physics. And in mathematics, the passage of time means
creating a balance between different sets of numbers. (2.8) The connection
between the Riemann zeta function and the geometric potential difference is
clear.
According to the Mobius space and repeating properties of numbers, it is expressed along a wave tensor set. The wave tensor describes the characteristics of a field over time. (2.9)
According to the mathematical definition of density, which is the result of geometric potential difference. Mass and energy also have geometric definitions. (2.10)
3. P=NP
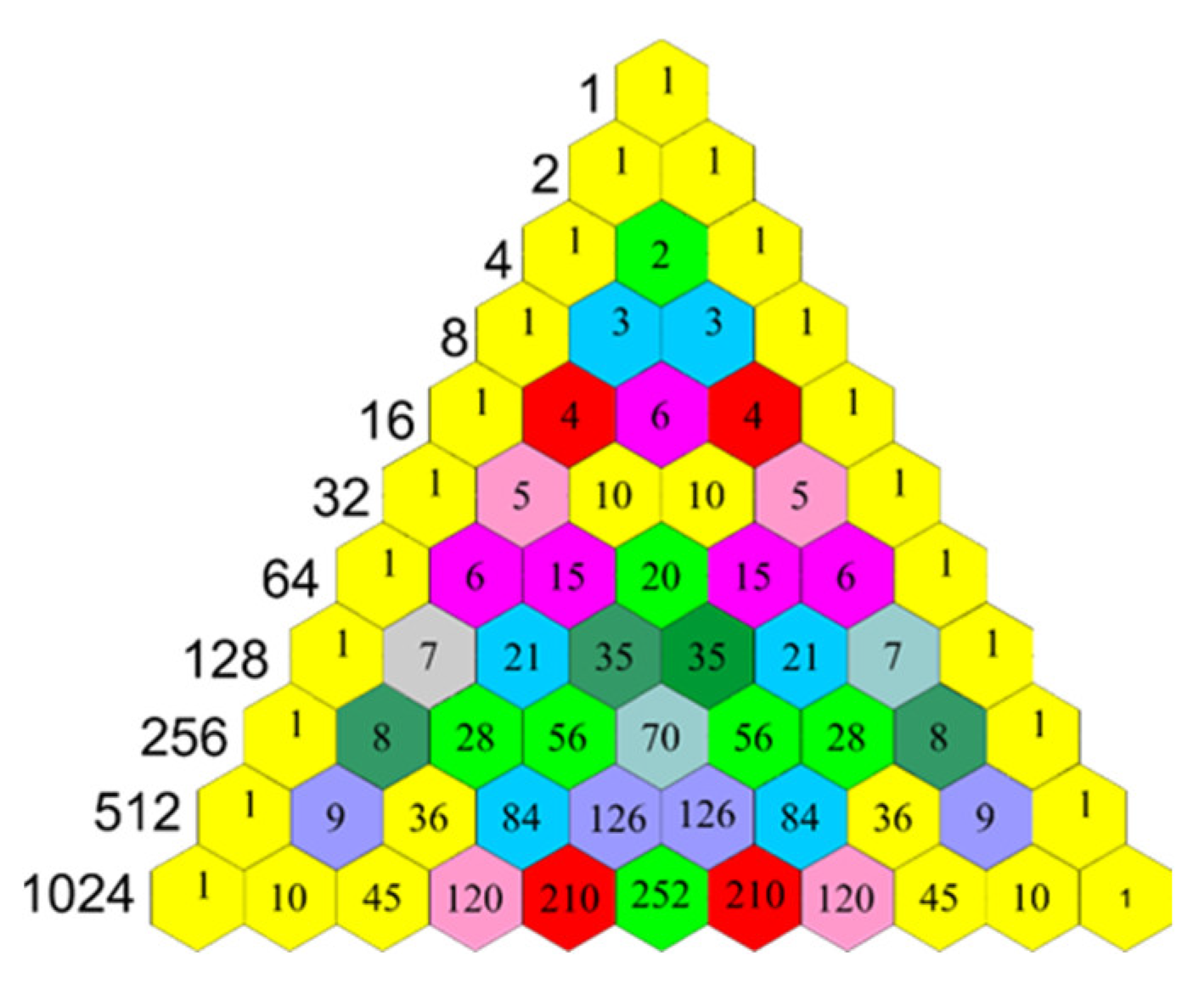
Each number has different digits. Based on Pascal Khayyam's binomial expansion, groups of numbers with the same properties are determined. Figure1. (3.1) Although these numbers seem unrelated to each other. But this method is very useful for designing algorithms without time complexity.
Figure 1.
Binomial expansion can be the basis of polynomial expansion.
Figure 1.
Binomial expansion can be the basis of polynomial expansion.
Also, the relation between prime numbers and wave function is defined by binomial expansion.
Table 1
Based on this, we can study the properties of prime numbers. (3.2)
There are many complex relations for generating prime numbers, all of which have problems. The cause of these problems is the lack of categorization of different sets of prime numbers. We mention some of them. (3.2)
The important point of these equations is the role of five prime numbers to generate other prime numbers. (3.3)
Based on this, it is possible to express the important factor of generating prime numbers. (3.4)
Table 2.
3.4
Therefore, every real number consists of the square of complex numbers. And the real part of each complex number is also composed of the complex square of other complex numbers. The number of dimensions in a field expresses this decomposition. (3.4)
Results
4.1
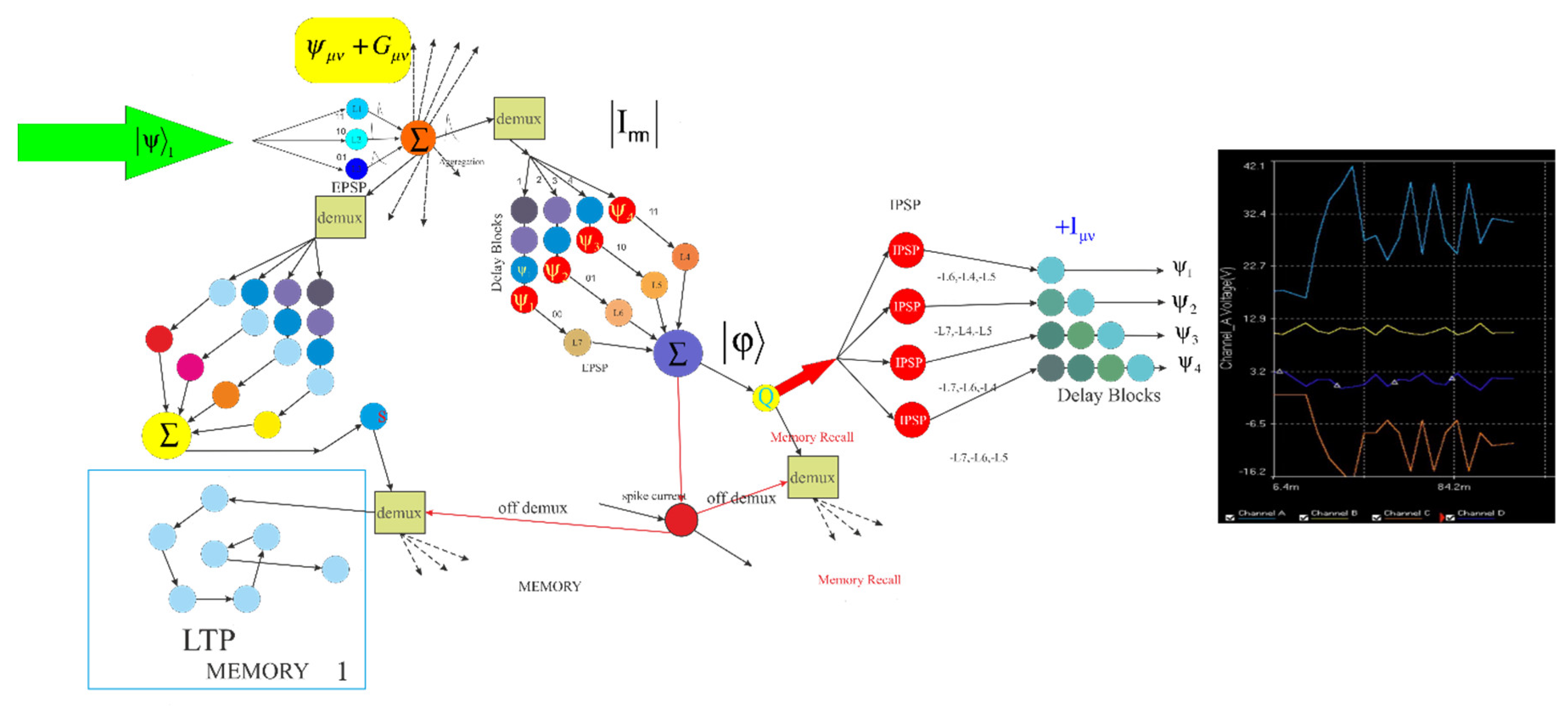
Based on the information analysis method in this study, defines into the P versus NP problem. By leveraging a prompt solution in the time domain for a problem belonging to the P class, it becomes feasible to develop straightforward algorithms for intricate problems through the periodic expansion of small polynomial blocks. Furthermore, compression big data of information into a singular spike pulse possessing attributes of smaller components allows for the classification and analogical decoding of the NP problem using Comparison of ANNs, resulting to its positioning in the P class. Information fields have unique properties. And every collection follows fields properties based on to be enter these fields. A comparison of these properties can be considered for decoding and compression. The human brain can roughly predict complex issues by comparing input information with information classified in memory based on time. The reason for the approximation is related to the lack of complete decoding of information in the brain. Based on this, the algorithm is designed to equalize it against NP. Each compressed pulse has two dimensions in time (reactance=I, C). (3.5)
Figure 2. A lot of information is compressed into a spike pulse. These pulses are quickly decoded. Small parts are simultaneously decoded from this pulse. And like the pieces of a puzzle, these parts are placed next to each other after comparison and coding.
According to natural laws, numbers can be categorized in a meaningful way based on their characteristics.
Table 3
4.2
As a result, other numbers also have the properties of this set. The strength and weakness of the properties of each number has a direct relationship with the distance from the center of the field. (4.1)
This method has many drawbacks. As a result, the definition of the time dimension of each number specifies the exact location of each number in a field. (4.2) For example, the number 21 belongs to the set 3. But it also has its own characteristics. (4.2) For example, number 21 belongs to set 3. But it also has the characteristics of its constructive digits. (4.2)
Designing an algorithm that can quickly find other features is a bit complicated. Accordingly, according to the structure of Mobius space and building blocks of the wave function, relativistic simulation is suggested. (4.3)
If we consider inertial mass to be analogous to compressed information and equate the mass of the object to other accumulated information over time, the information field becomes a combination of both types of information. (4.4) Accordingly, Mobius space indicates the existence of fractal structures and time loops in different sets membership of numbers collections.
Acknowledgments
The author expresses gratitude Dr. L.Razzazi and their professors for their helpful discussions and the book and valuable comments.
References
- Cook, S. (2000). The P versus NP problem. Clay Mathematics Institute, 2(6), 3. https://www.claymath.org/.
- Achimowicz, Jerzy Zbigniew. "Information in the Three Dimensions of Time." (2024). [CrossRef]
- Vopson, M. M. (2019). The mass-energy-information equivalence principle. AIP Advances, 9(9). [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S. K. (2024). Time Real 3_Dimensional, a Mirror Imaginary for Reflecting Information Physical World. Qeios. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y., Mandt, S., & Theis, L. (2023). An introduction to neural data compression. Foundations and Trends® in Computer Graphics and Vision, 15(2), 113-200. [CrossRef]
- Chiarot, G., & Silvestri, C. (2023). Time series compression survey. ACM Computing Surveys, 55(10), 1-32. [CrossRef]
- Levi, M. (2023). The mathematical mechanic: using physical reasoning to solve problems.
- Mousavi, S. K. (2024). General Balance in the Six-Dimensions of Space-Time. Qeios. doi, 10. [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S. K. (2023). Information Transfer Based on Brains Entanglement. Qeios. [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S. K. (2024). Artificial Self-Awareness In Over Time. Qeios. [CrossRef]
- mousavi, seyed kazem. “Compression And Decoding Of Data In The Spike Current.” SSRN Electronic Journal (2024): n. pag. [CrossRef]
- mousavi, S. K. Six Dimension for Proof of Riemann Hypothesis. Preprints 2024, 2024081612. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).