1. Introduction
One of the central events to Alzheimer’s disease (AD) pathology is the aberrant processing of amyloid precursor protein (APP), resulting in the generation of various Aβ peptides. The Aβ40 and Aβ42 are considered predominant species, with the elevated Aβ42/40 ratio playing a pivotal role in the AD disease pathogenesis [
1]. Presenilin 1 (PS1) is a catalytic subunit of the γ-secretase complex that cleaves APP within the transmembrane domain, influencing Aβ species production through distinct "open" and "closed" conformational states of PS1 [
2,
3,
4]
Increased epileptiform activity (seizures or subclinical manifestation) is frequently associated with AD. About 15–20% of AD patients experience seizures, and 20–40% show abnormal epileptiform discharges on EEG, both associated with severe cognitive decline [
11,
12,
13]. There is increasing recognition that epilepsy can occur not just concurrently with but precedes cognitive decline [
7,
8,
9,
10]. Remarkably, PS1/2 mutation carriers exhibit epileptiform activity more often than sporadic AD patients, implicating presenilins in pathways related to epilepsy [
16,
17,
18]. Further, recent trials with anti-epileptic drugs have shown promise in reducing cognitive decline in AD patients with epilepsy [
19], underscoring the significance of neuronal hyperexcitability in AD pathogenesis. However, a better understanding of the mechanism(s) underlying the link between AD pathology and hyperactivity is needed.
Glutamate transporter 1 (GLT-1, a.k.a. EAAT2), a major glutamate transporter in the brain, regulates synaptic glutamate levels, and is crucial for maintaining glutamate homeostasis. Dysregulation of GLT-1-mediated glutamate transport precedes amyloid plaque formation, neuronal dysfunction, and accelerates neurodegeneration in AD mouse models [
21,
22,
23]. GLT-1 dysfunction exacerbates cognitive deficits and accelerates disease progression in AD animal models , influencing Aβ metabolism and glutamatergic signaling pathways critical to AD pathogenesis . However, how GLT-1 impacts PS1/γ-secretase and Aβ pathology remains elusive. Further, we found that GLT-1 directly interacts with PS1 in the brain, bringing out its potential role in AD [
31]. Understanding the dynamics of GLT-1/PS1 interaction is essential for elucidating Aβ accumulation mechanisms and exploring GLT-1 as a potential therapeutic target for AD.
The current study investigates the intricate interplay between GLT-1, PS1/γ-secretase, and Aβ. We reveal the impact GLT-1 and its binding to PS1 have on Aβ levels, Aβ42/40 ratio, PS1 conformation, and γ-secretase activity, potentially guiding new therapeutic strategies in AD. Utilizing previously validated cell-permeable peptides (CPPs) to disrupt the GLT-1/PS1 interaction [
32], we uncover the impact of direct binding between GLT-1 and PS1 on regulation of Aβ levels.
By unraveling the significance of GLT-1/PS1 interaction, this study deepens our understanding of AD pathogenesis and pave the way for therapeutic interventions that might potentially target both Aβ and excitotoxicity.
2. Materials and Methods
Chemicals and Antibodies
Following reagents were used in this study: DMSO (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO), DAPT (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO), Penicillin (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA), and Geneticin (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO). Following antibodies were used in this study: anti-GLT-1 (ab41621, Abcam, Cambridge, MA), anti-β-actin (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA), PS1 N-terminal (ab15456, Abcam, Cambridge, MA, USA), PS1 C-terminal (#5643, Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA), APP (#802802, BioLegend, San Diego, CA), GAPDH (#2118, Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA).
Cell Culture
Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) PS70 cells, kindly gifted by Selkoe lab (BWH, Boston, MA), that stably expresses hPS1 and hAPP, were cultured in Opti-MEM (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA) supplemented with 5% FBS (Atlanta Biologicals Inc., Flowery branch, GA). The medium for CHO PS70 cells, was supplemented with puromycin (2.5 µg/mL) and geneticin (200 µg/mL). Cells were maintained in an incubator at 37°C, 5% CO2.
Primary cortical neurons from 14 –16-day-old embryos were enzymatically dissociated using papain (Worthington Biochemical Corporation, Lakewood, NJ) and cultured in Neurobasal medium (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA) supplemented with 2% B27, 1% GlutaMax, and 1% penicillin/streptomycin (Thermo Fisher Scientific) at 37°C with 5% CO2. All procedures involving mice were conducted in compliance with NIH guidelines for animal experimentation and were approved by the Massachusetts General Hospital Animal Care and Use Committee.
Expression Constructs and Transfections
Cells were transiently transfected with DNA using Lipofectamine 3000 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s protocol.
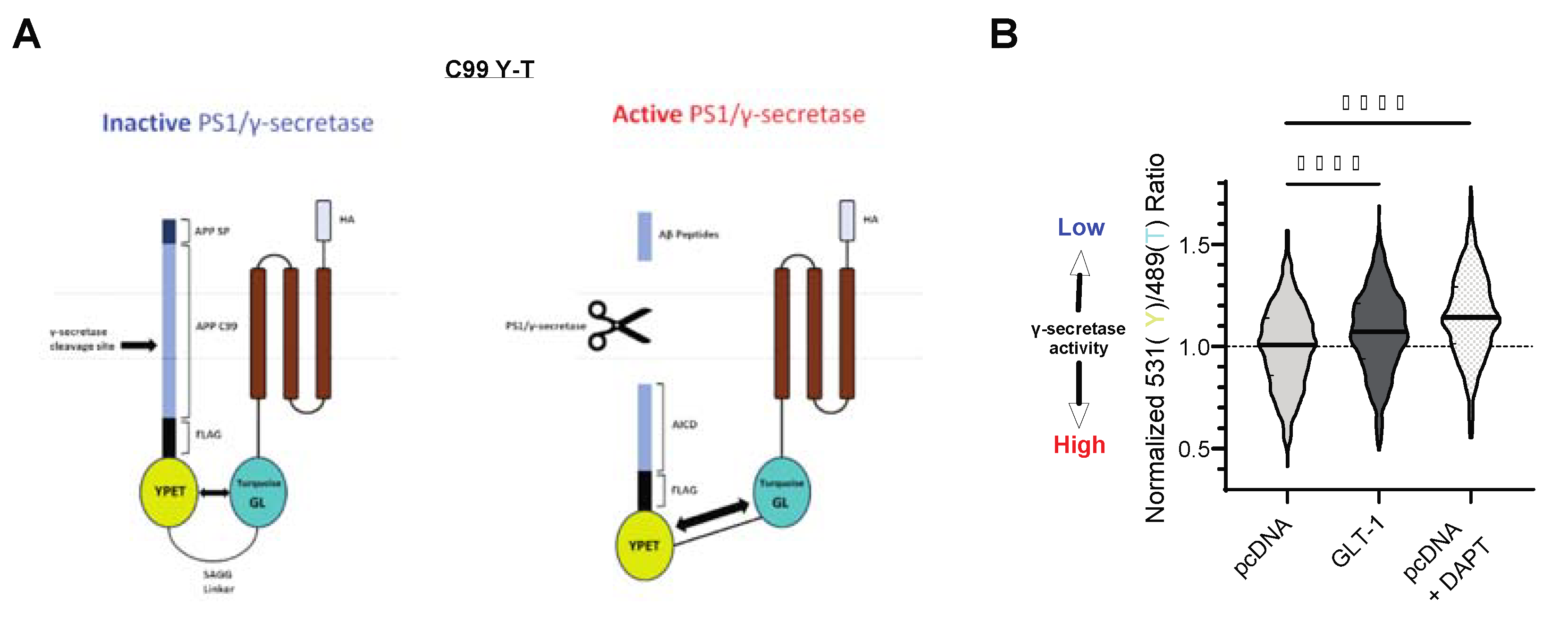
Following plasmids were used for transfection: pcDNA (empty vector), GLT-1 clonned into pcDNA, APP C99 YPet-mTurquoise-GL (C99 YT) biosensor. C99 YT (developed by [
35] contains APP C99 as an immediate substrate for γ-secretase, and two fluorescent proteins, YPet and Turquoise-GL, connected by an 80 amino-acid linker that serve as FRET donor and acceptor fluorophores, respectively.
ELISA for Aβ Species
Secreted Aβ levels from CHO PS70 cells were measured in the culture media using the Wako Human Amyloid (1–40) and Human Amyloid (1–42) ELISA kits according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Immuno-Biological Laboratories, Minneapolis, MN).
Primary neurons (12–14DIV) were treated with CPPs (5μM; 2h); the culture media was collected afterwards and concentrated five times using Amicon® Ultra Centrifugal Filter, 3 kDa MWCO (UFC9003, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) before performing Aβ ELISA.
Cytotoxicity Assay
Roche cytotoxicity detection kit (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) was used to measure lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) content according to the manufacturer's instructions. Wallac 1420 Victor2 Multilabel Microplate Reader (PerkinElmer, Waltham, MA) was used to measure the absorbance at 490 nm.
Western Blotting
Cells were lysed in RIPA lysis buffer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA) supplemented with protease and phosphatase inhibitor cocktail (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA). Total protein concentration was determined using the Pierce BCA Protein Assay Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) per manufacturer’s instructions. Subsequently, 30 µg of protein was loaded onto NuPAGE™ 4-12% Bis-Tris Protein gels (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA) and transferred to nitrocellulose membranes (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA) using the iBLOT2™ dry electroblotting system (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA). Membranes were probed with specific primary antibodies, followed by corresponding IRDye 680 RD or 800 CW-conjugated secondary antibodies (LI-COR Biosciences, Lincoln, NE, USA). Visualization of protein bands was performed using the LI-COR Odyssey CLx Infrared Imaging System (LI-COR Biosciences, Lincoln, NE, USA).
Spectral Förster Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET) analysis of γ-secretase activity
CHO PS70 cells, transiently transfected with the C99 YT biosensor, were maintained in a 37°C heating chamber with 4% CO2 using a Tokai-Hit STX-Co2 Digital CO2 Gas Mixing System (STFX model). Olympus FV3000RS Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope with a 10x objective was used for imaging. Excitation at 405 nm activated mTurquoise-GL within the biosensor, with simultaneous detection of emitted fluorescence at 470±10 nm for mTurquoise-GL and 530±10 nm for YPet. ImageJ software was used for background fluorescence reduction by subtracting median fluorescence intensity across entire images. Average fluorescence intensities per cell were measured in each channel. FRET efficiency, quantified as the Y/T ratio, was calculated by dividing YPet emission intensity by mTurquoise-GL emission intensity. MATLAB software was utilized for generating pseudocolored images based on Y/T ratios, facilitating spatial visualization and interpretation of γ-secretase activity via changes in FRET efficiency.
Immunocytochemistry
Cells cultured in 8-well chamber slides (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) were washed with PBS -/- (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA), and incubated with 1.5% normal donkey serum (Jackson ImmunoResearch Labs, West Grove, PA) for one hour to minimize non-specific binding. Following this, cells were incubated overnight at 4°C with specific primary antibodies. After thorough washing, cells were exposed to corresponding Alexa Fluor 488- or Cy3-conjugated secondary antibodies for 45 minutes at room temperature. Finally, coverslips were mounted on the slides using Vectashield mounting medium (Vector Laboratories, Inc., Burlingame, CA).
Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging Microscopy (FLIM)
The FLIM assay, as described previously by [
34], was conducted using an Olympus FV3000RS Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope equipped with a femtosecond-pulsed Spectra-Physics Mai Tai laser (Spectra-Physics, Milpitas, CA). Two-photon excitation at 850 nm was utilized to excite fluorophores, and the lifetime of donor fluorescence was measured by employing a microchannel plate-photomultiplier tube R3809 (Hamamatsu, Bridgewater, NJ, USA) and SPC-830 time-correlated single photon counting FLIM module (Becker & Hickl, Berlin, Germany). In SPC Image software (Becker & Hickl, Berlin, Germany), baseline lifetime (t1) of the Alexa 488 donor fluorophore was calculated from images of cells stained with PS1 N-terminal antibody only (used as a negative control). Raw data from cells stained with PS1 N- and C-termini antibodies were fitted to multiple decay curves to determine donor fluorophore lifetime (t2) values in the presence of Cy3 acceptor fluorophore. Based on these values, FRET efficiency was calculated and expressed as a percentage [(t1-t2) / t1] * 100.
Statistics
GraphPad Prism 9 software (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA) was used for all statistical analyses. Normality was assessed with the D’Agostino-Pearson omnibus K2 or Kolmogorov-Smirnov tests. Data normalization was done with either one-sample t-tests or Wilcoxon signed-rank tests relative to a control (mean of 1). Since each experiment tested a single independent factor, repeated-measures one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s or Friedman tests with Dunn’s post hoc comparisons analyzed matched experimental conditions. Significance was set at p < 0.05. All experiments were replicated 3–6 times. Imaging analyses used 50–100 cells per condition, with results reported as mean ± SEM or median (25th percentile; 75th percentile).
3. Results
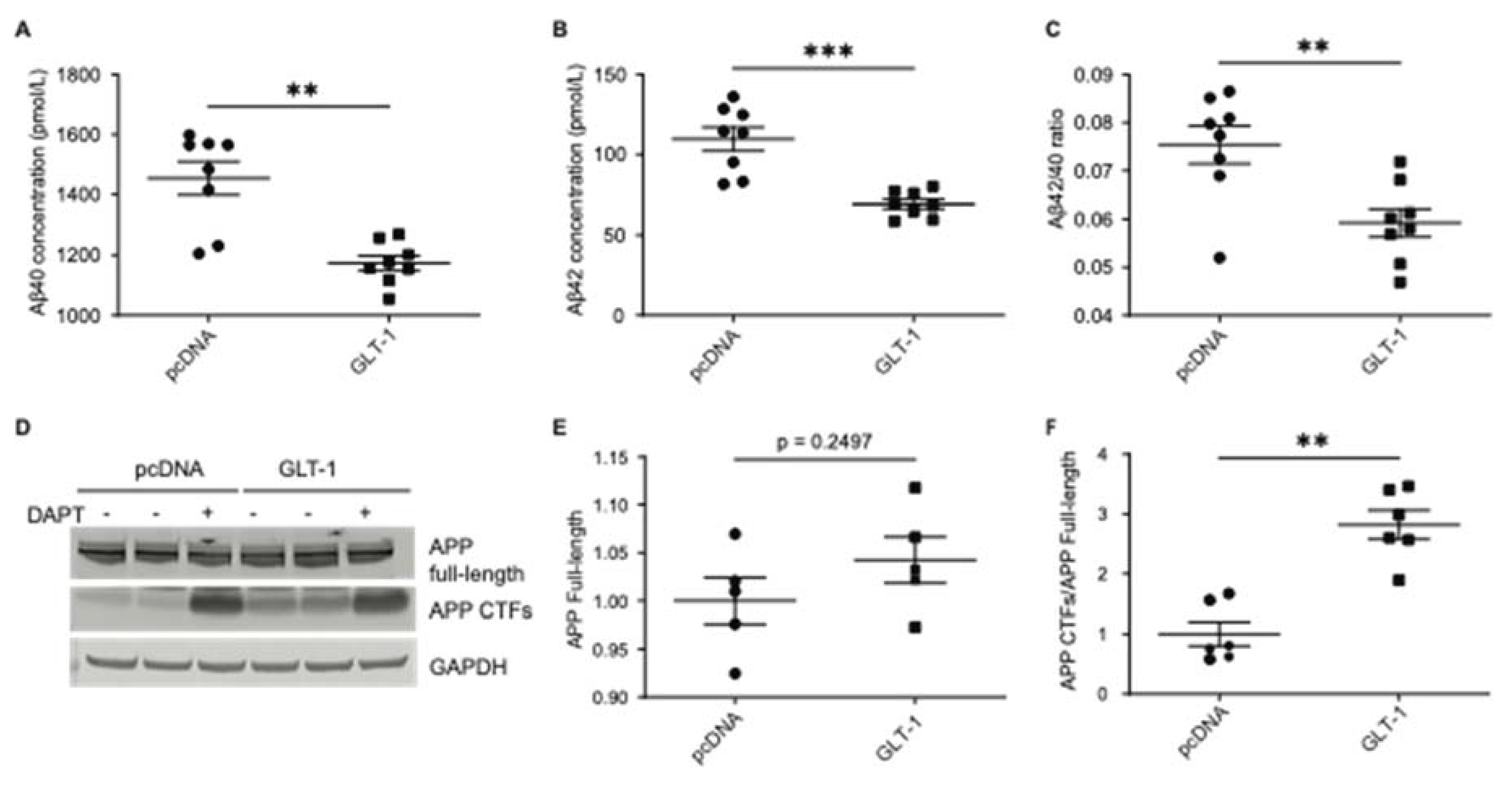
3.1. GLT-1 Overexpression Reduces Aβ40 and Aβ42 Production
To investigate the impact of GLT-1 on APP processing, CHO PS70 cells stably expressing human APP and PS1 were transfected with either GLT-1 or pcDNA (empty vector) as a control. After 48 hours, conditioned media was collected, and levels of Aβ40 and Aβ42 were measured using ELISA. Cells treated with N-[N-(3, 5-difluorophenacetyl)-l-alanyl]-s-phenylglycinet-butyl ester (DAPT) γ-secretase inhibitor 24 hours post-transfection served as a negative control. Overexpression of GLT-1 led to a significant reduction in both Aβ40 and Aβ42 levels compared to that in pcDNA (
Figure 1A and 1B). Quantitative analysis revealed a decrease of about 26% in Aβ40 (
p=0.0006) and 40% in Aβ42 (
p=0.0002) levels following GLT-1 overexpression. Given the significance of the Aβ42/40 ratio in AD pathogenesis [
33], we checked whether GLT-1 overexpression impacts this ratio. We observed a significant decrease in the Aβ42/40 ratio following GLT-1 overexpression, as depicted in
Figure 1C (48% decrease;
p=0.0047). To check whether GLT-1 affected APP expression or processing, western blotting was performed to assess the levels of total APP and APP C-terminal fragments (CTFs) (
Figure 1D). No significant change in total APP levels was observed (
Figure 1E), while an expected accumulation of APP CTFs was detected (
Figure 1F). To assess whether GLT-1 overexpression reduced Aβ production by inducing cell death, a lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) toxicity assay was conducted. Results from Supplementary
Figure 1A indicated no significant increase in cell death upon transfection with GLT-1. Transfection efficiency was confirmed by western blot analysis of GLT-1 expression (Supplementary
Figure 1B).
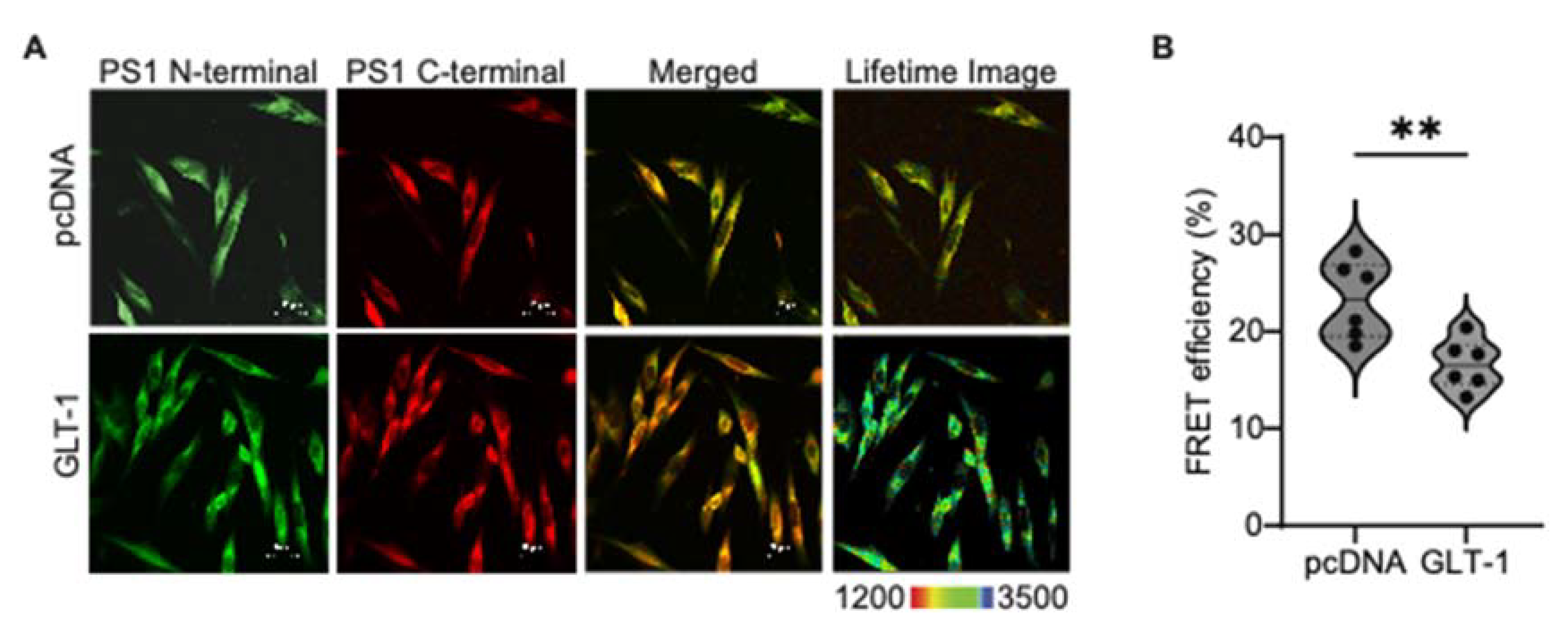
3.2. GLT-1 Promotes “Open” PS1 Conformation
Lower Aβ42/40 ratio is associated with the relaxed, "open" conformation of PS1/γ-secretase . To explore if GLT-1 overexpression induced an "open" PS1 conformation, CHO PS70 cells were transfected with pcDNA or GLT-1 and stained with PS1 N-terminal and C-terminal antibodies followed by AF488- and Cy3-fluorescently labelled secondary antibodies, respectively (
Figure 2A). PS1 conformational states were assessed by the efficiency of Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET) using fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy (FLIM). Cells stained with AF488/PS1 N-terminal antibody only served as FRET negative control. We detected lower FRET efficiency between the fluorescently labeled PS1 N- and C-termini in GLT-1 transfected cells (24% decrease;
p=0.02) compared to pcDNA transfected cells, consistent with PS1 adopting the "open" conformation in GLT-1 expressing cells (
Figure 2B).
3.3. GLT-1 Overexpression Reduces APP Processing by γ-Secretase
Based on our findings of reduced Aβ production and APP CTFs’ accumulation in cells expressing GLT-1, we hypothesized that GLT-1 by binding to PS1/γ-secretase may influence APP C99 processing. To investigate this, we employed previously characterized C99YT biosensor to assess APP C99 cleavage by γ-secretase in cells [
35]. CHO PS70 cells were co-transfected with C99YT (schematic shown in
Figure 3A) and either pcDNA or GLT-1, and C99 cleavage by γ-secretase was analyzed using spectral FRET. Imaging revealed a higher Y/T ratio in GLT-1-transfected cells (7% increase; p<0.0001), suggesting reduced γ-secretase activity compared to controls (
Figure 3B). pcDNA transfected cells treated with DAPT (γ-secretase inhibitor) served as a negative control. Data analysis indicated significant reduction in γ-secretase activity in these cells as evident by even higher Y/T ratio (11% increase; p<0.0001).
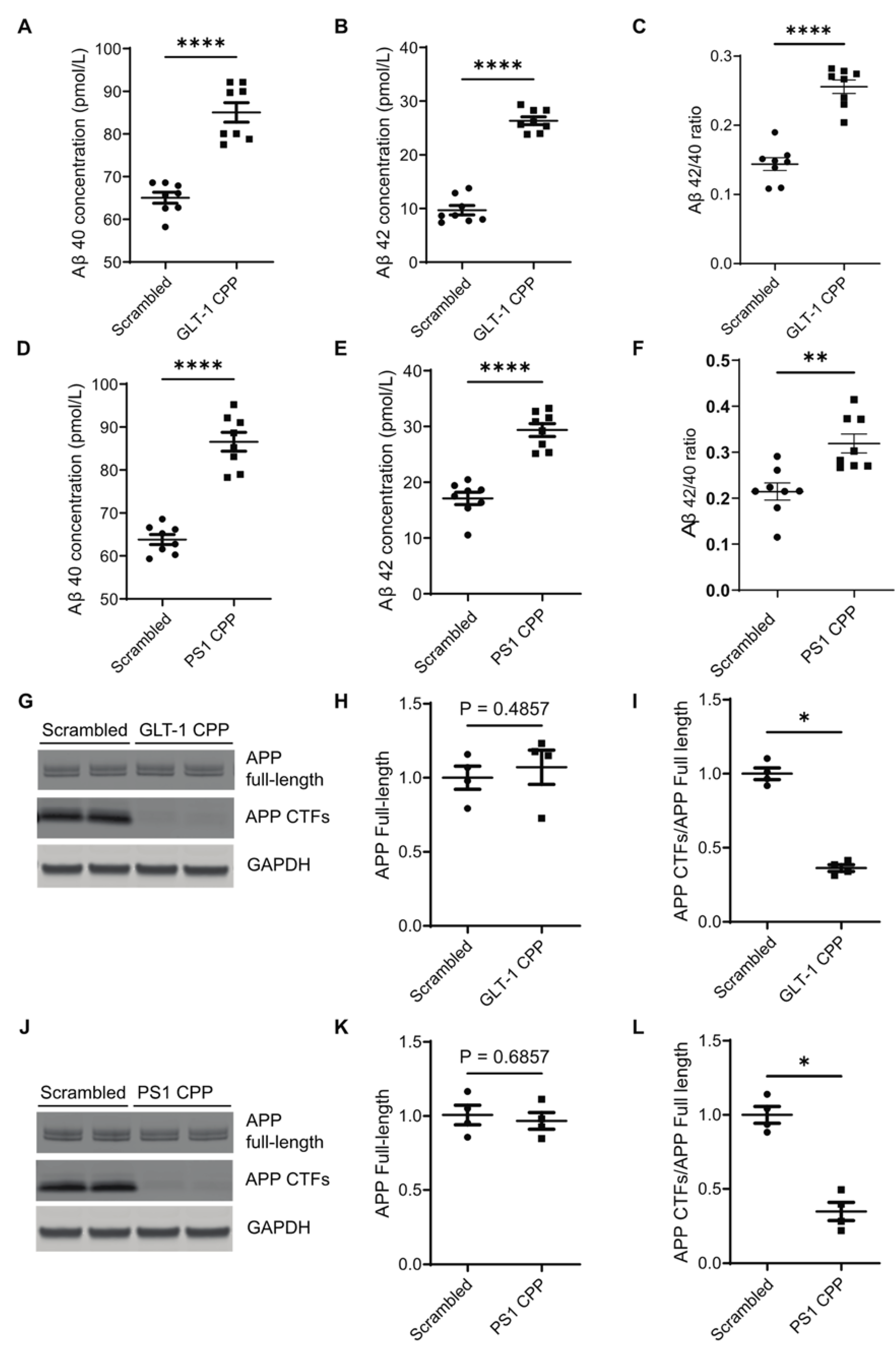
3.4. Disruption of the GLT-1/PS1 Interaction Increases Aβ Production
To investigate the mechanism underlying GLT-1-mediated effects on Aβ generation, we utilized previously characterized cell-permeable peptides (CPPs) to disrupt the interaction between endogenously expressed GLT-1 and PS1 in primary neurons [
32]. Specifically, the CPP with GLT-1 sequence involved in binding to PS1 was designated as "GLT-1 CPP," with its scrambled counterpart termed "GLT-1 Scrambled." Similarly, the CPP with PS1 sequence binding to GLT-1 was denoted as "PS1 CPP," and its scrambled form "PS1 Scrambled." Primary neurons (12–14 days
in vitro; DIV) were treated with CPPs at a concentration of 5 µM for 2 hours, or with their respective scrambled peptides. Conditioned media was collected for Aβ estimation using ELISA, while neurons were lysed for western blot analysis to assess full-length APP and APP CTFs. Conditioned media from neurons treated with either GLT-1 CPP or PS1 CPP exhibited elevated levels of both Aβ40 (
Figure 4A and 4D, respectively) and Aβ42 (
Figure 4B and 4E, respectively) compared to those treated with their scrambled counterparts. Furthermore, the Aβ42/40 ratio also increased after the CPPs treatment (
Figure 4C and 4F). Western blotting data showed a reduction in APP CTFs following CPPs treatment (
Figure 4G–4L), indicating more APP CTFs’ cleavage concomitant with higher Aβ production after CPP treatment.
Discussion
In this study, we found a novel role glutamate transporter-1 GLT-1 may play in the brain: negative regulation of Aβ production. Specifically, GLT-1 overexpression reduces both Aβ40 and Aβ42 levels and decreases the Aβ42/40 ratio by promoting an "open" PS1 conformation. To explore the cause of reduced Aβ, we investigated the effect of GLT-1 overexpression on γ-secretase activity and observed accumulation of APP CTFs and increased ratiometric FRET signal, indicating reduced APP C99 processing by PS1/γ-secretase. Using CPPs to disrupt the GLT-1/PS1 interaction, we confirmed that the GLT-1/PS1 binding is necessary for the GLT-1-mediated effects on Aβ levels, implicating the relevance of GLT-1/PS1 interaction in AD.
GLT-1 regulates glutamate homeostasis in the brain by maintaining optimal glutamate levels, thus mitigating excitotoxicity and neurodegeneration. Previous studies showed reduced Aβ deposition in animal models by utilizing transgenic or pharmacological approaches to restore GLT-1 expression , although without providing a mechanistic link between the GLT-1 and Aβ. Our study is consistent with these findings, demonstrating that GLT-1 overexpression decreases levels of both Aβ40 and Aβ42, and uncovers that reduced PS1/γ-secretase processing of APP C99 substrate is responsible for the decrease in Aβ. It is plausible that GLT-1 binding to PS1/γ-secretase may allosterically modify its conformation (per our FLIM data, Fig.2) in a way that hinders C99 access to the catalytic core for processing, leading to reduced total Aβ generation while also shifting the proportion of cleaved Aβ40 vs. Aβ42.
The correlation between a reduced Aβ42/40 ratio and PS1 conformation has been well established. Familial Alzheimer’s disease (fAD) PS1 mutations cause a pathogenic “closed” conformation, while gamma-secretase modulators (GSMs) that reduce the Aβ42/40 ratio induce a more relaxed “open” PS1 conformation . Our study revealed that GLT-1 induces a more "open" PS1 conformation, associated with a reduced Aβ42/40 ratio. This suggests that GLT-1 exerts a GSM-like allosteric effect on PS1, mitigating neurotoxic Aβ species production.
Unlike the conventional GSMs, pharmacological compounds that “stabilize” the γ-secretase/APP-CTF complex to process Aβ into shorter forms , GLT-1 presents a unique instance of a protein endogenously expressed in the brain modulating processivity of another protein. Indeed, acting as a GSM-like agent, GLT-1 might prove to be beneficial for AD patients, reducing aggregation-prone Aβ42 specie (and likely Aβ43) as well as Aβ40. This novel insight into GLT-1’s modulation of PS1 and Aβ production could lead to new therapeutic strategies targeting Aβ pathology in Alzheimer's disease.
Interestingly, GLT-1 expression is higher in the brain of individuals with AD pathology but without dementia compared to those with AD pathology and dementia, indicating the involvement of GLT-1 in cognitive resilience . Additionally, we have recently discovered that GLT-1/PS1 interaction is reduced in sporadic AD brains [
44] and with aging (unpublished data), suggesting that weakening of the GLT-1/PS1 interaction could promote Aβ deposition. Consistent with this possibility, our results indicate that disruption of the GLT-1/PS1 interaction by CPPs leads to an increase in Aβ load. These findings further support the hypothesis that enhancing GLT-1 expression and/or promoting GLT-1/PS1 interaction may be beneficial for AD patients.
In conclusion, this study advances our understanding of the intricate interplay between GLT-1-mediated glutamatergic signaling and Aβ metabolism in AD and uncovers new role glutamate transporter-1 may play in the brain. By identifying GLT-1/PS1 interaction as a potential modulator of these processes, this study opens new avenues for therapeutic interventions aimed at slowing down or halting the progression of AD pathology.
Limitations of the Study
While the study provides valuable insights into mechanistic link between the two key players in AD implicated in glutamate homeostasis and Aβ metabolism, several questions remain. Further elucidation of the precise molecular mechanisms by which GLT-1 modulates γ-secretase activity and PS1 conformation, is needed. Although blocking the PS1/GLT-1 binding by CPPs is a crucial tool supporting the conclusion of the study, unfortunately, no pharmacological agents (or genetic factors) that could stabilize the interaction are currently known/available to further test our hypothesis. In addition to being able to stabilize the interaction, in vivo studies would be necessary to validate these findings and further explore the translational potential of targeting GLT-1/PS1 interaction in AD treatment.
Supplemental information titles and legends
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org. GLT-1 overexpression does not cause cytotoxicity. (A): Empty vector pcDNA or GLT-1 was overexpressed in CHO PS70 cells, and lactate dehydrogenase concentration was measured from the conditioned media. Relative cytotoxicity was calculated, and there was no significant difference between the two groups (n=6). (B): Western blots were performed after lysing cells transfected with pcDNA or GLT-1 and probed with GLT-1 and β-actin (loading control) to confirm GLT-1 transfection.
Author Contributions
Priyanka Sinha: Writing – original draft, review & editing, Validation, Methodology, Investigation, Visualization, Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Data curation, Project administration. Yuliia Turchyna: Writing – original draft, review & editing, Validation, Methodology, Investigation, Visualization, Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Data curation. Shane Patrick Clancy Mitchell: Writing – review & editing, Validation, Methodology, Investigation, Formal analysis, Data curation. Michael Sadek: Writing – review & editing, Validation, Methodology, Investigation, Visualization. Nigar Gokce Armagan: Data curation, Validation. Florian Perrin: Writing – review & editing, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Conceptualization, Methodology. Masato Maesako: Resources. Oksana Berezovska: Conceptualization, Supervision, Project administration, Investigation, Funding acquisition, Data curation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
This work was funded by the National Institute of Health grants NIA AG044486 (OB) and AG015379 (OB)
Declaration of Generative AI and AI-Assisted Technologies
Not applicable
Declaration of Interests
The authors declare no competing interests regarding this research.
References
- Hardy, J., and Selkoe, D.J. (2002). The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer's disease: progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science 297, 353-356. [CrossRef]
- Sato, C., Morohashi, Y., Tomita, T., and Iwatsubo, T. (2006). Structure of the catalytic pore of gamma-secretase probed by the accessibility of substituted cysteines. J Neurosci 26, 12081-12088. [CrossRef]
- Uemura, K., Farner, K.C., Nasser-Ghodsi, N., Jones, P., and Berezovska, O. (2011). Reciprocal relationship between APP positioning relative to the membrane and PS1 conformation. Mol Neurodegener 6, 15. [CrossRef]
- Elad, N., De Strooper, B., Lismont, S., Hagen, W., Veugelen, S., Arimon, M., Horré, K., Berezovska, O., Sachse, C., and Chávez-Gutiérrez, L. (2015). The dynamic conformational landscape of gamma-secretase. J Cell Sci 128, 589-598. [CrossRef]
- Yang, F., Chen, L., Yu, Y., Xu, T., Chen, L., Yang, W., Wu, Q., and Han, Y. (2022). Alzheimer's disease and epilepsy: An increasingly recognized comorbidity. Front Aging Neurosci 14, 940515. [CrossRef]
- Chen, L., Yang, W., Yang, F., Yu, Y., Xu, T., Wang, D., Zhao, Q., Wu, Q., and Han, Y. (2024). The crosstalk between epilepsy and dementia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Epilepsy Behav 152, 109640. [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.C., Kim, B.K., Kang, K., Lee, W.W., Yoo, I., Kim, Y.S., and Lee, J.J. (2023). Aphasic Status Epilepticus Associated with Alzheimer's Disease: Clinical and Electrographic Characteristics. J Epilepsy Res 13, 55-58. [CrossRef]
- Nous, A., Seynaeve, L., Feys, O., Wens, V., De Tiège, X., Van Mierlo, P., Baroumand, A.G., Nieboer, K., Allemeersch, G.J., Mangelschots, S., et al. (2024). Subclinical epileptiform activity in the Alzheimer continuum: association with disease, cognition and detection method. Alzheimers Res Ther 16, 19. [CrossRef]
- Vicente, M., Addo-Osafo, K., and Vossel, K. (2024). Latest advances in mechanisms of epileptic activity in Alzheimer's disease and dementia with Lewy Bodies. Front Neurol 15, 1277613. [CrossRef]
- Kalyvas, A.C., Dimitriou, M., Ioannidis, P., Grigoriadis, N., and Afrantou, T. (2024). Alzheimer's Disease and Epilepsy: Exploring Shared Pathways and Promising Biomarkers for Future Treatments. J Clin Med 13. [CrossRef]
- Lam, A.D., Sarkis, R.A., Pellerin, K.R., Jing, J., Dworetzky, B.A., Hoch, D.B., Jacobs, C.S., Lee, J.W., Weisholtz, D.S., Zepeda, R., et al. (2020). Association of epileptiform abnormalities and seizures in Alzheimer disease. Neurology 95, e2259-e2270. [CrossRef]
- Shea, Y.F., Chu, L.W., Chan, A.O., Ha, J., Li, Y., and Song, Y.Q. (2016). A systematic review of familial Alzheimer's disease: Differences in presentation of clinical features among three mutated genes and potential ethnic differences. J Formos Med Assoc 115, 67-75. [CrossRef]
- Vossel, K.A., Tartaglia, M.C., Nygaard, H.B., Zeman, A.Z., and Miller, B.L. (2017). Epileptic activity in Alzheimer's disease: causes and clinical relevance. Lancet Neurol 16, 311-322. [CrossRef]
- Kazim, S.F., Seo, J.H., Bianchi, R., Larson, C.S., Sharma, A., Wong, R.K.S., Gorbachev, K.Y., and Pereira, A.C. (2021). Neuronal Network Excitability in Alzheimer's Disease: The Puzzle of Similar versus Divergent Roles of Amyloid β and Tau. eNeuro 8. [CrossRef]
- Palop, J.J., and Mucke, L. (2009). Epilepsy and cognitive impairments in Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol 66, 435-440. [CrossRef]
- Minkeviciene, R., Rheims, S., Dobszay, M.B., Zilberter, M., Hartikainen, J., Fülöp, L., Penke, B., Zilberter, Y., Harkany, T., Pitkänen, A., and Tanila, H. (2009). Amyloid beta-induced neuronal hyperexcitability triggers progressive epilepsy. J Neurosci 29, 3453-3462. [CrossRef]
- Vossel, K.A., Beagle, A.J., Rabinovici, G.D., Shu, H., Lee, S.E., Naasan, G., Hegde, M., Cornes, S.B., Henry, M.L., Nelson, A.B., et al. (2013). Seizures and epileptiform activity in the early stages of Alzheimer disease. JAMA Neurol 70, 1158-1166. [CrossRef]
- Vossel, K.A., Ranasinghe, K.G., Beagle, A.J., Mizuiri, D., Honma, S.M., Dowling, A.F., Darwish, S.M., Van Berlo, V., Barnes, D.E., Mantle, M., et al. (2016). Incidence and impact of subclinical epileptiform activity in Alzheimer's disease. Ann Neurol 80, 858-870. [CrossRef]
- Vossel, K., Ranasinghe, K.G., Beagle, A.J., La, A., Ah Pook, K., Castro, M., Mizuiri, D., Honma, S.M., Venkateswaran, N., Koestler, M., et al. (2021). Effect of Levetiracetam on Cognition in Patients With Alzheimer Disease With and Without Epileptiform Activity: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Neurol 78, 1345-1354. [CrossRef]
- Gautam, D., Naik, U.P., Naik, M.U., Yadav, S.K., Chaurasia, R.N., and Dash, D. (2023). Glutamate Receptor Dysregulation and Platelet Glutamate Dynamics in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's Diseases: Insights into Current Medications. Biomolecules 13. [CrossRef]
- Busche, M.A., Chen, X., Henning, H.A., Reichwald, J., Staufenbiel, M., Sakmann, B., and Konnerth, A. (2012). Critical role of soluble amyloid-β for early hippocampal hyperactivity in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109, 8740-8745. [CrossRef]
- Palop, J.J., and Mucke, L. (2016). Network abnormalities and interneuron dysfunction in Alzheimer disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 17, 777-792. [CrossRef]
- Hascup, K.N., and Hascup, E.R. (2015). Altered neurotransmission prior to cognitive decline in AβPP/PS1 mice, a model of Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis 44, 771-776. [CrossRef]
- Bragina, L., Melone, M., Fattorini, G., Torres-Ramos, M., Vallejo-Illarramendi, A., Matute, C., and Conti, F. (2006). GLT-1 down-regulation induced by clozapine in rat frontal cortex is associated with synaptophysin up-regulation. J Neurochem 99, 134-141. [CrossRef]
- Mookherjee, P., Green, P.S., Watson, G.S., Marques, M.A., Tanaka, K., Meeker, K.D., Meabon, J.S., Li, N., Zhu, P., Olson, V.G., and Cook, D.G. (2011). GLT-1 loss accelerates cognitive deficit onset in an Alzheimer's disease animal model. J Alzheimers Dis 26, 447-455. [CrossRef]
- Huffels, C.F.M., Middeldorp, J., and Hol, E.M. (2023). Aß Pathology and Neuron-Glia Interactions: A Synaptocentric View. Neurochem Res 48, 1026-1046. [CrossRef]
- Meeker, K.D., Meabon, J.S., and Cook, D.G. (2015). Partial Loss of the Glutamate Transporter GLT-1 Alters Brain Akt and Insulin Signaling in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease. J Alzheimers Dis 45, 509-520. [CrossRef]
- Gao, J., Liu, L., Liu, C., Fan, S., Liu, L., Liu, S., Xian, X.H., and Li, W.B. (2020). GLT-1 Knockdown Inhibits Ceftriaxone-Mediated Improvements on Cognitive Deficits, and GLT-1 and xCT Expression and Activity in APP/PS1 AD Mice. Front Aging Neurosci 12, 580772. [CrossRef]
- Scimemi, A., Meabon, J.S., Woltjer, R.L., Sullivan, J.M., Diamond, J.S., and Cook, D.G. (2013). Amyloid-β1-42 slows clearance of synaptically released glutamate by mislocalizing astrocytic GLT-1. J Neurosci 33, 5312-5318. [CrossRef]
- Bukke, V.N., Archana, M., Villani, R., Romano, A.D., Wawrzyniak, A., Balawender, K., Orkisz, S., Beggiato, S., Serviddio, G., and Cassano, T. (2020). The Dual Role of Glutamatergic Neurotransmission in Alzheimer's Disease: From Pathophysiology to Pharmacotherapy. Int J Mol Sci 21. [CrossRef]
- Zoltowska, K.M., Maesako, M., Meier, J., and Berezovska, O. (2018). Novel interaction between Alzheimer's disease-related protein presenilin 1 and glutamate transporter 1. Sci Rep 8, 8718. [CrossRef]
- Perrin, F., Sinha, P., Mitchell, S.P.C., Sadek, M., Maesako, M., and Berezovska, O. (2024). Identification of PS1/gamma-secretase and glutamate transporter GLT-1 interaction sites. J Biol Chem 300, 107172. [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, S., Delaby, C., Boursier, G., Catteau, C., Ginestet, N., Tiers, L., Maceski, A., Navucet, S., Paquet, C., Dumurgier, J., et al. (2018). Relevance of Aβ42/40 Ratio for Detection of Alzheimer Disease Pathology in Clinical Routine: The PLM(R) Scale. Front Aging Neurosci 10, 138. [CrossRef]
- Uemura, K., Lill, C.M., Li, X., Peters, J.A., Ivanov, A., Fan, Z., DeStrooper, B., Bacskai, B.J., Hyman, B.T., and Berezovska, O. (2009). Allosteric modulation of PS1/gamma-secretase conformation correlates with amyloid beta(42/40) ratio. PLoS One 4, e7893. [CrossRef]
- Houser, M.C., Hou, S.S., Perrin, F., Turchyna, Y., Bacskai, B.J., Berezovska, O., and Maesako, M. (2020). A Novel NIR-FRET Biosensor for Reporting PS/γ-Secretase Activity in Live Cells. Sensors (Basel) 20. [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K., Kong, Q., Lin, Y., Stouffer, N., Schulte, D.A., Lai, L., Liu, Q., Chang, L.C., Dominguez, S., Xing, X., et al. (2015). Restored glial glutamate transporter EAAT2 function as a potential therapeutic approach for Alzheimer's disease. J Exp Med 212, 319-332. [CrossRef]
- Mi, D.J., Dixit, S., Warner, T.A., Kennard, J.A., Scharf, D.A., Kessler, E.S., Moore, L.M., Consoli, D.C., Bown, C.W., Eugene, A.J., et al. (2018). Altered glutamate clearance in ascorbate deficient mice increases seizure susceptibility and contributes to cognitive impairment in APP/PSEN1 mice. Neurobiol Aging 71, 241-254. [CrossRef]
- Berezovska, O., Lleo, A., Herl, L.D., Frosch, M.P., Stern, E.A., Bacskai, B.J., and Hyman, B.T. (2005). Familial Alzheimer's disease presenilin 1 mutations cause alterations in the conformation of presenilin and interactions with amyloid precursor protein. J Neurosci 25, 3009-3017. [CrossRef]
- Cai, T., Morishima, K., Takagi-Niidome, S., Tominaga, A., and Tomita, T. (2019). Conformational Dynamics of Transmembrane Domain 3 of Presenilin 1 Is Associated with the Trimming Activity of γ-Secretase. J Neurosci 39, 8600-8610. [CrossRef]
- Olsson, F., Schmidt, S., Althoff, V., Munter, L.M., Jin, S., Rosqvist, S., Lendahl, U., Multhaup, G., and Lundkvist, J. (2014). Characterization of intermediate steps in amyloid beta (Aβ) production under near-native conditions. J Biol Chem 289, 1540-1550. [CrossRef]
- Szaruga, M., Munteanu, B., Lismont, S., Veugelen, S., Horré, K., Mercken, M., Saido, T.C., Ryan, N.S., De Vos, T., Savvides, S.N., et al. (2017). Alzheimer's-Causing Mutations Shift Aβ Length by Destabilizing γ-Secretase-Aβn Interactions. Cell 170, 443-456.e414. [CrossRef]
- Masliah, E., Alford, M., DeTeresa, R., Mallory, M., and Hansen, L. (1996). Deficient glutamate transport is associated with neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's disease. Ann Neurol 40, 759-766. [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, E., Nakano, M., Kubota, K., Himuro, N., Mizoguchi, S., Chikenji, T., Otani, M., Mizue, Y., Nagaishi, K., and Fujimiya, M. (2018). Activated forms of astrocytes with higher GLT-1 expression are associated with cognitive normal subjects with Alzheimer pathology in human brain. Sci Rep 8, 1712. [CrossRef]
- Perrin, F., Anderson, L.C., Mitchell, S.P.C., Sinha, P., Turchyna, Y., Maesako, M., Houser, M.C.Q., Zhang, C., Wagner, S.L., Tanzi, R.E., and Berezovska, O. (2023). PS1/gamma-secretase acts as rogue chaperone of glutamate transporter EAAT2/GLT-1 in Alzheimer's disease. Res Sq. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).