1. Introduction
The electronics industry exerts a profound environmental impact, particularly through substantial CO2 emissions and the generation of electronic waste (e-waste) during the production and disposal of devices [
1]. The United Nations has identified e-waste as the fastest-growing waste stream globally, with an estimated 50 million tons produced annually, containing hazardous materials that pose significant risks to human health and the environment if not properly managed [
2,
3]. The manufacturing processes associated with electronic devices contribute to approximately 2% of global greenhouse gas emissions, further exacerbated by the energy consumption during the device’s operational lifespan [
4,
5]. For instance, the production of a single laptop generates an estimated 283.4 kg of CO2, while a cell phone contributes 50.5 kg [
6].
Improving the reliability of electronic products is crucial not only for enhancing the profitability of manufacturing but also for mitigating their negative environmental impact. The adoption of Industry 4.0 (I4.0) advanced tools has driven significant advancements in monitoring and optimizing assembly processes, reflecting a broader industry shift towards sustainability [
7,
8,
9,
10,
11]. Standards such as IPC-A-610 mandate the assurance of component quality and freedom from defects, yet there remains a lack of effective in-line verification methods to ensure compliance with these requirements [
12]. Although various I4.0 tools and research methodologies are employed for failure analysis and process optimization [
13,
14,
15,
16], the prevailing approach to component management—relying on procurement from trusted suppliers without thorough quality verification—falls short in addressing the root causes of failures. It is estimated that approximately 80% of failures within the electronics industry stem from faulty components [
17].
The environmental implications of component failures are significant. The malfunction of electronic components not only increases scrap rates, thereby amplifying emissions and e-waste, but also shortens product lifespans, further exacerbating the waste stream. This research aims to quantify this phenomenon, particularly by measuring the impact of component quality on product lifespan through Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF). Reliability prediction methodologies, such as the Telcordia Method and MIL-HBK-217f, utilize statistical models and failure rate data to estimate component lifespans and predict overall circuit board MTBF [
18]. Estimating MTBF enables the calculation of the environmental and economic costs associated with the failure of individual components concerning the produc
t’s expected lifespan.
This paper presents a case study illustrating how defective components (see examples in
Figure 1) significantly influence product lifespan and the associated environmental consequences. We argue that the higher-than-expected failure rates observed in the industry are primarily due to the use of suboptimal electronic components. We propose that transitioning to the exclusive use of rigorously qualified components could achieve the lower failure rates projected by reliability models. Given the inherently random occurrence of faulty components, traditional sampling methods are insufficient for ensuring component quality [
17,
19,
20,
21]. A comprehensive solution requires the 100% inspection of all components, a capability that current methodologies lack.
Moreover, this paper introduces an innovative approach—a reliable in-line visual authentication and qualification system during the assembly process—designed to reduce the failure rate and extend the longevity of electronic products [
17,
21,
22]. This system detects visual defects, corrosion, and counterfeit components in real-time, addressing the root causes of failures and minimizing the environmental footprint of the electronics industry. The proposed solution involves either the disqualification of entire reels upon detecting a significant number of defective components or the selective removal of individual defective instances post-processing.
2. The Environmental Impact of Electronic Devices
The production, usage, and disposal of electronic devices have a substantial environmental footprint, primarily manifested in the form of electronic waste (e-waste) and CO2 emissions [
6,
23]. E-waste is particularly concerning as it contains hazardous materials, including lead, mercury, and flame retardants, which pose severe risks to human health and the environment if not properly managed [
24]. The electronics industry contributes approximately 2% of global greenhouse gas emissions, with the energy consumption of electronic devices during their operational phase further exacerbating their carbon footprint [
6,
23,
24,
25,
26,
27,
28].
Pollution from electronic devices is generated at various stages of their lifecycle, including raw material extraction, manufacturing, transportation, usage, and disposal. Each stage presents distinct challenges and contributes to the overall environmental burden. For instance, the manufacturing process of printed circuit boards (PCBs) involves the use of chemicals like copper sulfate, ferric chloride, and ammonium persulfate, all of which are hazardous to both human health and the environment [
24,
27]. Additionally, during the operational phase, the energy consumption of electronic devices, primarily driven by electricity generation, accounts for up to 60% of the total CO2 emissions associated with these products. This underscores the need to not only focus on the environmental impact during the production stage but also to consider the operational efficiency of the devices throughout their lifecycle.
Conventional strategies to mitigate the environmental impact of electronic devices have predominantly focused on enhancing waste management practices and increasing the use of renewable energy sources for electricity generation [
6,
27,
29,
30,
31]. These approaches, while valuable, address only a portion of the problem. They often overlook the root causes of pollution, particularly the role of product reliability and longevity in contributing to e-waste. Electronic devices that fail prematurely require replacement, which in turn leads to the consumption of additional raw materials, energy, and water, and the generation of more pollutants. This cycle not only exacerbates the environmental burden but also highlights the inefficiency of current waste management practices in tackling the issue of sustainability at its core.
The sustainability of electronic products is intrinsically linked to their reliability and lifespan. Products that are designed and manufactured with a focus on longevity and durability not only reduce the frequency of replacements but also contribute to a significant reduction in e-waste and associated emissions. Therefore, it is crucial to shift the focus towards enhancing the quality and reliability of components used in electronic devices. By ensuring that products are built to last longer and perform reliably over time, we can make a substantial impact on reducing the overall environmental footprint of the electronics industry.
In the following sections, we will delve into the methodologies for accurately estimating the lifespan of electronic products and explore how defective components can drastically influence this critical factor. Understanding the relationship between component quality and product lifespan is essential for developing strategies that not only improve product reliability but also contribute to the broader goal of environmental sustainability.
3. Factors Impacting MTBF: Practical Real-World Insights
3.1. Overview of MTBF Calculation in Electronics
The MTBF calculation assumes that all components are in perfect condition and operating under optimal conditions, which may not reflect real-world scenarios. In reality, electronic components can degrade over time due to various factors, such as environmental conditions, aging, or manufacturing defects. These factors can impact the reliability and longevity of the product and can significantly reduce the expected MTBF. Furthermore, the failure rate of electronic components can vary significantly depending on the environmental conditions in which they are used. For example, components used in harsh or extreme conditions, such as high temperature, high humidity, or high vibration environments, may have a shorter lifespan than components used in more moderate conditions. This can result in a significant reduction in the overall MTBF of the product. Therefore, while MTBF calculation is a useful tool for evaluating the reliability of electronic products, it is important to keep in mind that the calculation is based on assumptions that may not reflect real-world conditions. To improve the accuracy of the MTBF calculation, it is necessary to consider the impact of realistic conditions and the potential degradation of components over time. By doing so, manufacturers can better predict the reliability of their products and make more informed decisions about design improvements or replacement schedules.
3.2. The Reality of Component Quality
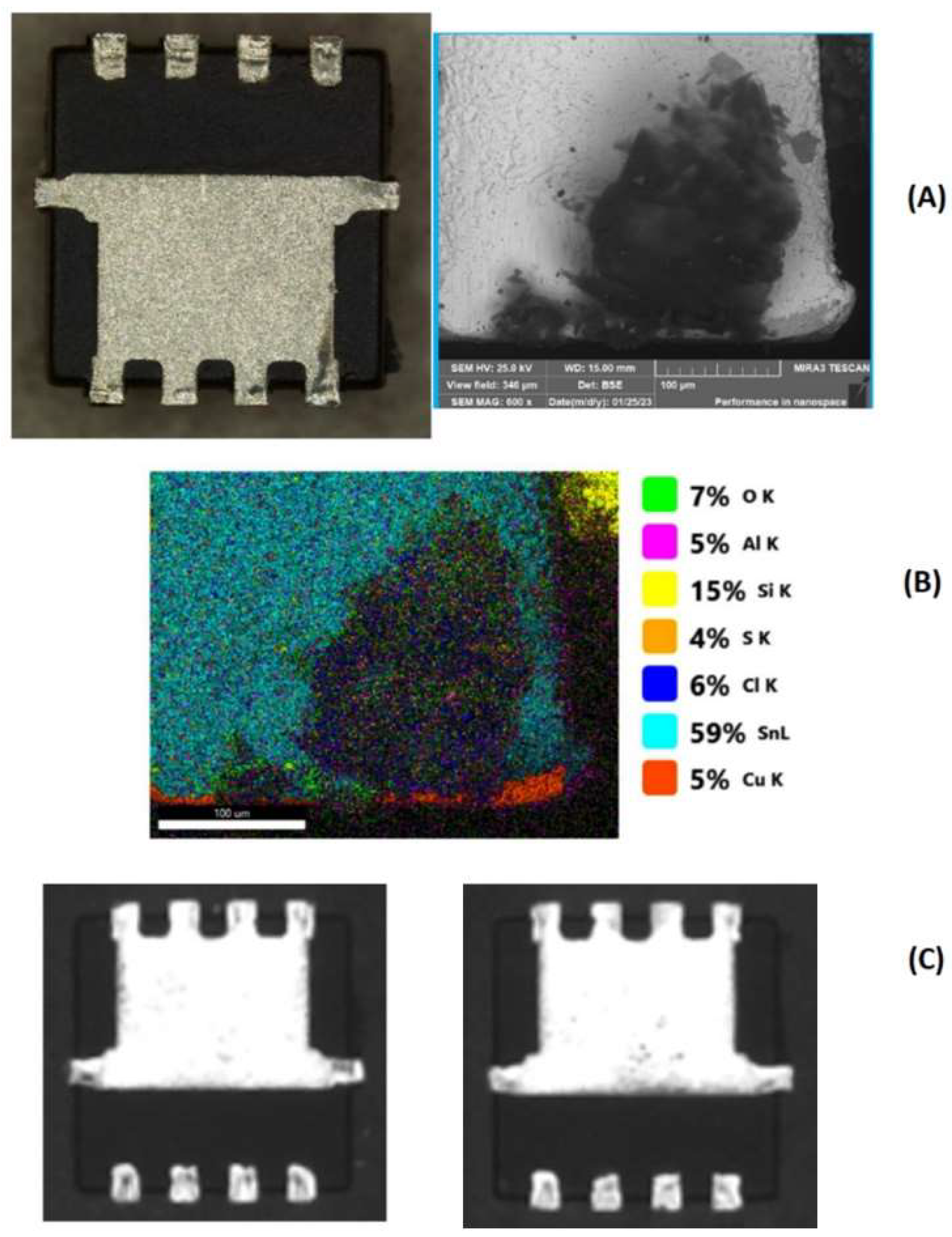
In the real world, electronic components are rarely perfect, and their quality at the time of assembly has a profound effect on their eventual lifespan. Factors such as manufacturing processes, handling, storage, and environmental exposure can all contribute to component degradation before they are even incorporated into a product. It is estimated that the defect rate in electronic components is around 150 parts per million (ppm) [
17,
19,
20], with an additional 200 ppm of components potentially affected by corrosion or mold during storage or transportation (see examples in
Figure 1 and
Figure 2). These imperfections, though statistically small, can have a significant impact on the overall reliability of the product.
The initial quality of each component plays a crucial role in determining its longevity. Even components that pass initial quality checks and are not considered defective at the time of assembly can degrade during the assembly process or over time due to operational stresses. This degradation is often compounded by external factors such as exposure to moisture, temperature fluctuations, and mechanical stress, which can accelerate the wear and tear on components. If these factors are not accounted for during the MTBF calculation, the resulting predictions may be overly optimistic, leading to an underestimation of the risk of premature failure.
To address this, it is vital to integrate the initial conditions of all components into the MTBF calculation. Failing to do so can result in inaccurate predictions of product lifespan, leading to unexpected failures, increased warranty claims, and costly recalls. A more accurate approach involves assessing the quality of components at the time of assembly and considering their individual lifespans in the MTBF calculation. This proactive approach can help manufacturers avoid the pitfalls of relying on idealized assumptions and instead base their predictions on the realities of component degradation.
Table 1.
Baseline example BOM and MTBF values for an example board.
Table 1.
Baseline example BOM and MTBF values for an example board.
| Type |
Amount |
Office |
Automotive |
Degradation factor |
| Capacitor |
97 |
0.000051 |
0.1499814 |
1 |
| Resistor |
97 |
0.00037 |
0.550378 |
1 |
| IC |
5 |
0.017 |
0.277 |
1 |
| IC |
5 |
0.01 |
0.152 |
1 |
| IC |
5 |
0.00196 |
0.047648 |
1 |
3.3. Calculating the Real Lifespan of a Product
Accurately estimating the real lifespan of a product requires a detailed understanding of how each component on the board may degrade over time. This includes factors such as corrosion, mold, cracks, defects, counterfeit materials, and the natural aging process of components. Each of these factors contributes to the overall degradation of the component, which in turn affects the MTBF of the entire product.
To achieve a more realistic assessment of product lifespan, these degradation factors must be quantified and applied to each component. This involves multiplying the expected lifespan of each component by its respective degradation factor and then integrating these factors across all components on the board. By doing so, manufacturers can develop a more accurate prediction of the product’s effective lifespan, which better reflects the conditions it will face in the real world.
In practice, the real MTBF is often validated through experimental testing under various conditions, providing a more reliable estimate of product longevity. These tests allow manufacturers to observe how products perform in different environments and under different stressors, offering insights into potential weaknesses and areas for improvement. Although this study does not delve into the quantitative estimation of degradation factors, it focuses on illustrating the mechanisms through which these factors influence product reliability, as demonstrated through a practical test case example.
4. The Influence of Component Degradation on MTBF
This section explores how degraded components affect the Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) of electronic products, particularly under varying environmental conditions. We differentiate between ground benign (GB) conditions, typically found in controlled environments like server rooms, and ground mobile (GM) conditions, which include more demanding environments such as those encountered in the automotive industry. For this analysis, GB conditions are assumed to represent server room environments, while GM conditions are modeled as a combination of 80% GM and 20% GB conditions (see
Figure 3 for a projected failure rate of an assembled PCB under GB conditions).
Figure 3.
Projected failure rate of an assembled PCB’s in GB conditions (server room) of the BOM presented in Table I-III. The predicted MTBF is shown for the baseline PCB with no faulty components with examples od various levels of defects in the board.
Figure 3.
Projected failure rate of an assembled PCB’s in GB conditions (server room) of the BOM presented in Table I-III. The predicted MTBF is shown for the baseline PCB with no faulty components with examples od various levels of defects in the board.
Figure 4.
Projected failure rate of an assembled PCB’s in automotive conditions of the BOM presented in Table I-III. The predicted MTBF is shown for the baseline PCB with no faulty components with examples od various levels of defects in the board.
Figure 4.
Projected failure rate of an assembled PCB’s in automotive conditions of the BOM presented in Table I-III. The predicted MTBF is shown for the baseline PCB with no faulty components with examples od various levels of defects in the board.
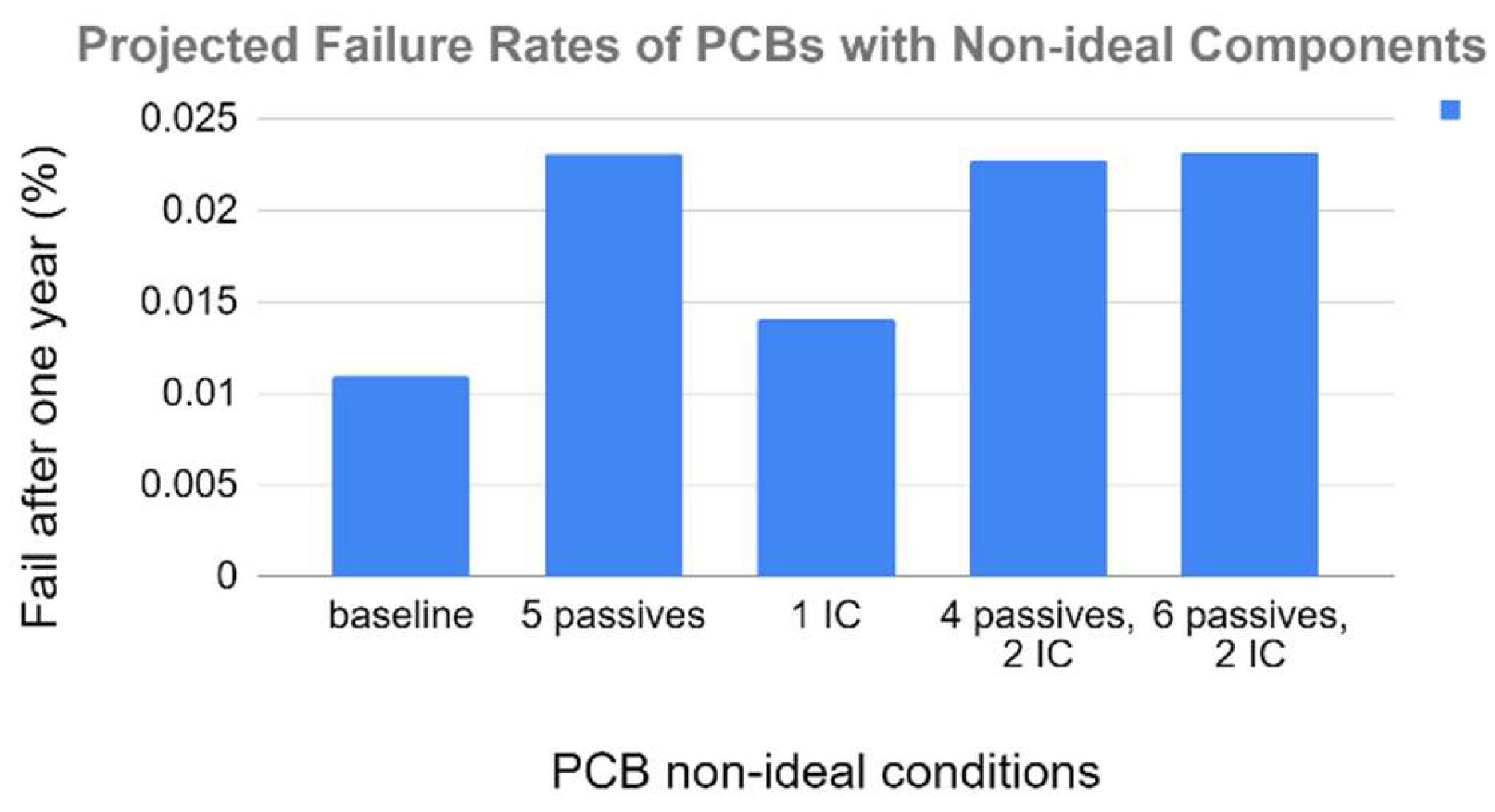
To illustrate the impact, we analyze a specific case involving a board with five types of components as outlined in the Bill of Materials (BOM): 100 Multi-Layer Ceramic Capacitors (MLCCs), 100 chip resistors, 5 Analog to Digital Converters (ADCs), 5 regulators, and 5 EEPROMs. Under ideal conditions, a conventional MTBF calculation for this board in a server room environment predicts a failure rate of 0.164% after one year, while under automotive conditions, the failure rate is expected to rise to 1.094% (refer to Table I and
Figure 3). This significant increase in failure rate under automotive conditions is attributed to the heightened environmental stress compared to office environments.
When introducing degraded components into the analysis—where the lifespan of a component is reduced by a factor of 10 for minor degradation or 50 for severe degradation—the failure rates increase dramatically. Table II presents MTBF calculations for a board with degraded components, and Table III shows the estimated MTBF for both office and automotive environments. As demonstrated, the failure rate of a board with degraded components increases to 0.41% after one year of operation in a server room, compared to 0.164% with ideal components. In an automotive environment, the failure rate jumps from 1.094% to 2.32%.
For a practical illustration, consider the following scenarios: If a single Analog to Digital Converter (ADC) undergoes degradation, the projected failure rate under server room conditions becomes 0.304%, escalating to 1.406% under automotive conditions (see
Figure 1). If a Multi-Layer Ceramic Capacitor (MLCC) experiences degradation, the failure rate after a year will rise to 0.166% under GB conditions and 1.160% under automotive conditions. Similarly, the degradation of a single chip resistor (see
Figure 2) results in a failure rate of 0.180% in server room conditions and 1.337% in automotive settings.
It is important to emphasize that these degraded components are often undetectable during production stage testing, as their failure rates typically manifest only after extended use. However, these components significantly influence the statistical calculation of the product’s MTBF and its real-world failure rate, particularly under conditions of environmental stress.
In office environments, the industry-standard failure rate of approximately 1.5% within a year is primarily due to the presence of degraded components. The theoretical failure rate of 0.164% suggests that the observed 1.5% failure rate already incorporates the impact of these degraded components. By implementing rigorous material quality control measures during production, manufacturers can reduce the incidence of degraded components, thereby improving the overall MTBF and reliability of the product.
Table 2.
BOM and MTBF values for a degraded board. The degradation factor reduces the life of the component by a factor of 10 or 50 as an example.
Table 2.
BOM and MTBF values for a degraded board. The degradation factor reduces the life of the component by a factor of 10 or 50 as an example.
| Type |
Amount |
Office |
Automotive |
Degradation factor |
| Capacitor |
97 |
0.000051 |
0.1499814 |
1 |
| Resistor |
97 |
0.00037 |
0.550378 |
1 |
| IC |
5 |
0.017 |
0.277 |
1 |
| IC |
4 |
0.01 |
0.152 |
1 |
| IC |
4 |
0.00196 |
0.047648 |
1 |
| Capacitor |
2 |
0.00051 |
0.010444 |
10 |
| Capacitor |
1 |
0.00255 |
0.07731 |
50 |
| Resistor |
2 |
0.0037 |
0.11348 |
10 |
| Resistor |
1 |
0.0185 |
0.2837 |
50 |
| IC |
1 |
0.17 |
0.394 |
10 |
| IC |
1 |
0.098 |
0.5956 |
50 |
Table 3.
MTBF estimation for degraded boards in office and automotive environments.
Table 3.
MTBF estimation for degraded boards in office and automotive environments.
| |
Office |
Automotive |
| MTBF (million hours) |
2.122 |
0.377 |
| MTBF (years) |
242.292 |
43.052 |
| Fail after year (%) |
0.41% |
2.32% |
5. Economic and Ecological Consequences
The intersection of economic performance and environmental sustainability is increasingly recognized as crucial in the electronics industry. The reliability of electronic products is intrinsically linked to the quality of components used in their production. As highlighted in the previous sections, unchecked components can drastically reduce the Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF), leading to significant economic and ecological repercussions.
5.1. Economic Impact
Degraded components contribute to higher-than-expected failure rates, impacting the economy by driving up costs associated with product returns, warranty claims, and recalls. Approximately 1.5% of products fail within the first year of operation, primarily due to faulty components. These failures result in significant economic losses, not only from the direct costs of replacing defective products but also from the potential damage to a brand’s reputation and customer trust. By implementing rigorous quality control measures, manufacturers can potentially reduce the occurrence of degraded components by over 50%, significantly lowering the number of returns and recalls. This proactive approach is not merely a cost-saving measure but also a strategic investment in long-term reliability and customer satisfaction. Moreover, extending the lifespan of products through higher-quality components aligns with circular economy principles, reducing the need for frequent replacements and conserving resources.
5.2. Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of degraded components extends far beyond the manufacturing process. Electronic waste (e-waste) is a growing global concern, with the United Nations estimating that 50 million tons of e-waste are generated annually, much of which ends up in landfills, leading to soil and water contamination. The manufacturing of electronic devices also contributes to around 2% of global greenhouse gas emissions. These environmental costs are further exacerbated when products fail prematurely due to poor-quality components, necessitating additional production cycles to replace or repair faulty devices.
To illustrate the environmental consequences of component failure, consider the following scenarios. In the first scenario, a product is entirely scrapped due to a faulty component, resulting in both e-waste and the need for a replacement product. Studies estimate that the production of electronic devices, such as laptops, emits an average of 283.4 kg of CO2 per unit and generates 6.08 kg of e-waste [
23,
25,
27,
29,
32,
33]. These figures are represented in Table IV, with columns showing the total embodied CO2 and e-waste. In the second scenario, where poor-quality components reduce the produc
t’s lifespan, the environmental impact is depicted in columns 3 and 4 of the table.
During production, electronic components are often supplied on reels containing thousands of units of a single type. Statistically, around 150 ppm of these components may exhibit defects, while 200 ppm could be compromised by corrosion or mold. This means that even within a single reel, some degraded components are almost inevitable. If such compromised components are not identified early, they can lead to a reduction in the overall MTBF of the product. For instance, a reel contaminated with corrosion was detected during production (see
Figure 1 and ). While the corrosion might not severely impact solderability, it is likely to contribute to an increased failure rate in real-world conditions, as discussed in Section IV.
To quantify the environmental savings, consider that early detection and removal of a corroded reel, containing 10,000 components and used in 2,000 circuit boards, could prevent the emission of 91.2 kg of CO2 and 0.32 kg of e-waste per laptop (see Table IV). This would amount to a theoretical total of 188.8 tons of CO2 emissions and significant e-waste savings from a single faulty reel. The degradation mechanism in this case, driven by corrosion propagation due to thermal cycling and humidity exposure, leads to a 33% reduction in the life expectancy of the products assembled with the contaminated reel.
However, it’s essential to recognize that this estimation represents a maximum-case scenario. In reality, not all failures would result in complete product scrapping. Nevertheless, this calculation serves as a valuable benchmark for understanding the potential environmental impact of component degradation. By addressing these issues early in the production process, manufacturers can significantly reduce both economic losses and environmental harm, aligning with sustainability goals and regulatory pressures.
6. Advanced Inspection and Sorting: Enhancing Reliability and Sustainability
The challenge of detecting defects such as corrosion and cracks in electronic components during assembly has traditionally been formidable due to the often subtle and inconspicuous nature of these flaws. However, recent technological advancements, particularly in the realms of big data and artificial intelligence (AI), have opened new avenues for addressing these issues with heightened precision and efficiency.
The proposed solution leverages state-of-the-art AI algorithms integrated into the assembly line’s pick-and-place machines. These systems are equipped with high-resolution cameras that capture images of electronic components in real-time as they are placed onto the boards (see Figure 5). The AI-driven analysis scrutinizes these images for minute visual cues that may indicate defects, such as discoloration, oxidation, surface degradation, and even the early signs of crack formation. This capability allows the system to differentiate between normal surface variations and genuine defects, facilitating a comprehensive and accurate assessment of component quality. By identifying compromised units early in the production process, this approach not only ensures immediate quality control but also mitigates the risk of more severe failures that could manifest later in the product lifecycle.
Moreover, this defect detection methodology plays a pivotal role in preventing the progression of latent defects, such as those stemming from environmental factors like moisture and thermal stress. Although the optical method is primarily designed to detect surface-level anomalies, it provides crucial early warnings for internal failures that may develop over time, such as broken wire bonds or internal chip damage. For example, the presence of surface corrosion or mold is often a precursor to crack propagation in components like Multi-Layer Ceramic Capacitors (MLCCs). By detecting these issues before they escalate, the system not only addresses the immediate defect but also prevents the future development of related failures, thereby extending the lifespan of the product and enhancing its overall reliability.
The sustainability benefits of this advanced inspection process are significant. By catching defects early, the system reduces the likelihood of entire products being scrapped due to failures that could have been prevented, thus conserving valuable resources and minimizing waste. In cases where defective components are detected, the system can either disqualify entire reels—if a significant proportion of components are found to be compromised—or selectively remove defective units from the assembly line post-placement. This ensures that only the highest quality components are integrated into the final product, aligning with the principles of sustainable manufacturing by reducing the environmental impact associated with the disposal of faulty products.
Furthermore, the inspection process can be deployed at multiple stages throughout the production line. Components can be analyzed as they are introduced into the line, or after they have been mounted onto the printed circuit board (PCB). Post-inspection, components can be categorized based on a reliability score, which is calculated by assessing various attributes such as authenticity, corrosion, mold, and cracks. This ranking system allows manufacturers to estimate the projected lifespan of the product under different environmental conditions, offering a predictive insight into how the product will perform over time.
For instance, consider a production line utilizing a reel of 1,000 capacitors. After inspection, it is discovered that 10% of the capacitors exhibit some form of degradation, leading to a reduced MTBF for the entire batch. By identifying and removing these degraded capacitors before they are integrated into the final product, the inspection system ensures that only components of the highest quality are used. This process not only improves the reliability of the final product but also supports sustainability by preventing the use of substandard materials, reducing waste, and lowering the carbon footprint associated with product failures and replacements.
In summary, the integration of AI-driven inspection and sorting systems within the electronic component assembly process offers a dual benefit: it enhances product reliability while significantly contributing to environmental sustainability. By ensuring that only high-quality components are used, manufacturers can extend the lifespan of their products, reduce e-waste, and minimize the ecological impact of their operations.
7. Conclusion
The reliability and Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) of electronic products are pivotal factors that determine their quality, longevity, and environmental impact. Our study reveals that degraded components can significantly reduce the MTBF of electronic products, highlighting the inadequacies of conventional MTBF calculations that assume all components are in perfect condition. Through our simulated analysis of a board with 215 components, we have demonstrated that even a small number of degraded passive components can drastically reduce the lifespan of a product—by 149% in a server room environment and 211% in an automotive setting. Importantly, these degraded components often evade detection during production-stage testing, underscoring the necessity for a 100% inspection of all components to ensure product reliability.
From an economic perspective, the unchecked use of degraded components substantially increases product costs. By improving component quality control, returns due to component failures could be reduced by over 50%, and costly recalls could be largely avoided. The environmental implications are equally profound: the reduced lifespan of products caused by a single contaminated reel of components could theoretically result in an additional 188.8 tons of CO2 emissions. This underscores the need for stringent quality control to mitigate environmental harm.
To safeguard both the economic and environmental viability of electronic products, it is imperative to implement a comprehensive inspection regime using advanced technologies such as AI and big data. Ensuring that only high-quality components are utilized in the production process will enhance the reliability and MTBF of electronic products, yielding significant cost savings and environmental benefits. The adoption of such practices should become a standard across the electronics industry, fostering a more sustainable and reliable future.
References
- C. Xin, T. Zhang, S.-B. Tsai, Y.-M. Zhai, and J. Wang, “An empirical study on greenhouse gas emission calculations under different municipal solid waste management strategies,” Applied Sciences, vol. 10, no. 5, p. 1673, 2020. [CrossRef]
- V. Forti, C. P. Baldé, R. Kuehr, and G. Bel, “The global e-waste monitor 2020,” United Nations University (UNU), International Telecommunication Union (ITU) & International Solid Waste Association (ISWA), Bonn/Geneva/Rotterdam, vol. 120, 2020.
- V. Forti, K. Baldé, and R. Kuehr, “E-waste statistics: guidelines on classifications, reporting and indicators,” 2018.
- V. Forti, C. P. Baldé, R. Kuehr, and G. Bel, “The global e-waste monitor 2020,” United Nations University (UNU), International Telecommunication Union (ITU) & International Solid Waste Association (ISWA), Bonn/Geneva/Rotterdam, vol. 120, 2020.
- J. Liu, D. Yang, B. Lu, and J. Zhang, “Carbon footprint of laptops for export from China: empirical results and policy implications,” J Clean Prod, vol. 113, pp. 674–680, 2016. [CrossRef]
- N. Singh and O. A. Ogunseitan, “Disentangling the worldwide web of e-waste and climate change co-benefits,” Circular Economy, vol. 1, no. 2, p. 100011, Dec. 2022. [CrossRef]
- T. Zheng, M. Ardolino, A. Bacchetti, and M. Perona, “The applications of Industry 4.0 technologies in manufacturing context: a systematic literature review,” Int J Prod Res, vol. 59, no. 6, pp. 1922–1954, 2021. [CrossRef]
- V. A. Wankhede and S. Vinodh, “State of the art review on Industry 4.0 in manufacturing with the focus on automotive sector,” International Journal of Lean Six Sigma, vol. 13, no. 3, pp. 692–732, 2022. [CrossRef]
- B. Bártová and V. Bína, “A novel data mining approach for defect detection in the printed circuit board manufacturing process,” Engineering Management in Production and Services, vol. 14, no. 2, pp. 13–25, 2022. [CrossRef]
- S. Sahoo and C.-Y. Lo, “Smart manufacturing powered by recent technological advancements: A review,” J Manuf Syst, vol. 64, pp. 236–250, 2022. [CrossRef]
- J. Wang, C. Xu, J. Zhang, and R. Zhong, “Big data analytics for intelligent manufacturing systems: A review,” J Manuf Syst, vol. 62, pp. 738–752, 2022. [CrossRef]
- “IPC-A-610 Acceptability of Electronic Assemblies,” 2017. [Online]. Available: www.ipc.org.
- Mzougui and Z. El Felsoufi, “A modified method to improve failure analysis,” International Journal of System Assurance Engineering and Management, vol. 12, no. 2, pp. 231–244, Apr. 2021. [CrossRef]
- R. Gadekar, B. Sarkar, and A. Gadekar, “Model development for assessing inhibitors impacting Industry 4.0 implementation in Indian manufacturing industries: an integrated ISM-Fuzzy MICMAC approach,” International Journal of System Assurance Engineering and Management, 2022. [CrossRef]
- J. Bhadu, P. Kumar, J. Bhamu, and D. Singh, “Lean production performance indicators for medium and small manufacturing enterprises: modelling through analytical hierarchy process,” International Journal of System Assurance Engineering and Management, vol. 13, no. 2, pp. 978–997, 2022. [CrossRef]
- S. Malhotra, V. Agarwal, and P. K. Kapur, “Hierarchical framework for analysing the challenges of implementing industrial Internet of Things in manufacturing industries using ISM approach,” International Journal of System Assurance Engineering and Management, vol. 13, no. 5, pp. 2356–2370, 2022. [CrossRef]
- E. Weiss, “AI Detection of Body Defects and Corrosion on Leads in Electronic Components, and a study of their Occurrence,” in 2022 IEEE International Symposium on the Physical and Failure Analysis of Integrated Circuits (IPFA), IEEE, 2022, pp. 1–6.
- K. Choudhary and P. Sidharthan, “Reliability prediction of Electronic Power Conditioner (EPC) using MIL-HDBK-217 based parts count method,” in 2015 International Conference on Computer, Communication and Control (IC4), IEEE, 2015, pp. 1–4.
- E. Weiss, “Revealing Hidden Defects in Electronic Components with an AI-Based Inspection Method: A Corrosion Case Study,” IEEE Trans Compon Packaging Manuf Technol, 2023. [CrossRef]
- E. Weiss, “Preventing Corrosion-related Failures in Electronic Assembly: A Multi-case Study Analysis,” IEEE Trans Compon Packaging Manuf Technol, May 2023. [CrossRef]
- E. Weiss, “Electronic component solderability assessment algorithm by deep external visual inspection,” in 2020 IEEE Physical Assurance and Inspection of Electronics (PAINE), IEEE, 2020, pp. 1–6.
- E. Weiss and Z. Efrat, “System and method for nondestructive assessing of solderability of electronic components,” P-603537-PC, 2021.
- V. Forti, C. P. Balde, R. Kuehr, and G. Bel, “The Global E-waste Monitor 2020: Quantities, flows and the circular economy potential,” 2020.
- S. H. Woo, D. S. Lee, and S. Lim, “Potential resource and toxicity impacts from metals in waste electronic devices,” Integr Environ Assess Manag, vol. 12, no. 2, pp. 364–370, 2016. [CrossRef]
- S. O’Connell and M. Stutz, “Product carbon footprint (PCF) assessment of Dell laptop-Results and recommendations,” in Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE international symposium on sustainable systems and technology, IEEE, 2010, pp. 1–6.
- L. Sun, Z. Li, M. Fujii, Y. Hijioka, and T. Fujita, “Carbon footprint assessment for the waste management sector: A comparative analysis of China and Japan,” Frontiers in Energy, vol. 12, pp. 400–410, 2018. [CrossRef]
- V. Forti, K. Baldé, and R. Kuehr, “E-waste statistics: guidelines on classifications, reporting and indicators,” 2018.
- J. Liu, D. Yang, B. Lu, and J. Zhang, “Carbon footprint of laptops for export from China: empirical results and policy implications,” J Clean Prod, vol. 113, pp. 674–680, 2016. [CrossRef]
- Esfandyari, S. Härter, T. Javied, and J. Franke, “A lean based overview on sustainability of printed circuit board production assembly,” Procedia CIRP, vol. 26, pp. 305–310, 2015. [CrossRef]
- Yang, J. Li, Q. Tan, L. Liu, and Q. Dong, “Green process of metal recycling: coprocessing waste printed circuit boards and spent tin stripping solution,” ACS Sustain Chem Eng, vol. 5, no. 4, pp. 3524–3534, 2017. [CrossRef]
- V. Tripathi, S. Chattopadhyaya, A. K. Mukhopadhyay, S. Sharma, C. Li, and G. Di Bona, “A Sustainable Methodology Using Lean and Smart Manufacturing for the Cleaner Production of Shop Floor Management in Industry 4.0,” Mathematics, vol. 10, no. 3, Feb. 2022. [CrossRef]
- C. Xin, T. Zhang, S.-B. Tsai, Y.-M. Zhai, and J. Wang, “An empirical study on greenhouse gas emission calculations under different municipal solid waste management strategies,” Applied Sciences, vol. 10, no. 5, p. 1673, 2020. [CrossRef]
- W. K. C. Yung, S. S. Muthu, and K. Subramanian, “Carbon footprint analysis of printed circuit board,” in Environmental Carbon Footprints: Industrial Case Studies, Elsevier, 2017, pp. 365–431. [CrossRef]
- S. E. Harpe et al., “Method 208, solderability,” MIL-STD, no. 2, 2015. [CrossRef]
- E. e Oliveira, V. L. Miguéis, and J. L. Borges, “Automatic root cause analysis in manufacturing: an overview & conceptualization,” J Intell Manuf, vol. 34, no. 5, pp. 2061–2078, 2023. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).