Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has markedly transformed a diverse array of sectors, including education and biotechnology. Within education, AI enhances personalized learning, offers real-time feedback through tutoring systems, and aids in the development of educational content (Mavroudi et al. 2018; Holmes et al. 2019; Zawacki-Richter et al. 2019). In biotechnology, AI plays a crucial role in analyzing complex biological data, enhancing drug efficacy predictions, and designing synthetic biological pathways (Libbrecht & Noble 2015; Ching et al. 2018; da Silva, 2024; Hutson 2024).
AI's impact is particularly notable in molecular biology, where it excels in predicting protein structures. This is exemplified by the AlphaFold system developed by DeepMind, which has resolved numerous complex protein structures, thus offering deep insights into their functions and interactions—key aspects for drug development and biological research (Tunyasuvunakool, et al. 2021).
Additionally, AI contributes to the automation of experimental processes through autonomous experimentation systems. These systems, also known as "self-driving labs" or "materials acceleration platforms," enhance the iterative Design-Build-Test-Learn cycle, crucial in bioengineering and biomedical research (Liao et al. 2022). They are instrumental in drug discovery, enabling the screening of thousands of chemical combinations with high efficiency and precision, thereby speeding up the discovery of new materials and therapeutic compounds (Libbrecht & Noble 2015; da Silva, et al., 2024). Overall, AI is revolutionizing molecular biology by equipping scientists with powerful tools for predicting molecular structures, deciphering genetic regulation, and streamlining research and experimental processes (Tunyasuvunakool et al. 2021; Zarnack et al. 2023).
In this study, we investigated the effectiveness of AI systems in teaching and training laboratory researchers. Our goal was to determine whether individuals with limited prior laboratory experience could acquire a specific molecular biology skill set solely through the use of AI, as compared to traditional instruction by a human expert.
Traditional lab training methods often rely on shadowing an experienced colleague, allowing trainees to observe and gradually participate in procedures under close supervision. While this hands-on approach provides immediate feedback and helps build confidence in complex techniques, it can be time-consuming and dependent on the availability of skilled mentors.
To evaluate the AI systems, we focused on molecular cloning, often simply referred to as DNA cloning, a fundamental laboratory technique in molecular biology that enables the creation of multiple copies of a specific DNA segment. The process involves isolating a desired DNA fragment, inserting it into a vector (such as a plasmid), and introducing this recombinant DNA into a host cell (often bacteria). The host cells replicate, producing many copies of the inserted DNA. This technique is essential for genetic engineering, enabling researchers to study genes, express proteins, or create genetically modified organisms (Sambrook & Russell 2001; Stemmer & Morris 1992).
To ensure the training remains focused and well-structured for the purpose of this study, we concentrated on a specific DNA cloning technique known as subcloning, which entails transferring a particular DNA fragment from one vector to another. The wide availability of commercial kits and reagents make DNA subcloning a fairly simple skill to acquire for experienced laboratory technicians. However, those with limited laboratory experience can find it challenging, even with proper hands-on training. These include difficulties in designing and executing cloning strategies, managing contamination, and troubleshooting unexpected results (Ausubel et al. 2003). Sambrook and Russell (2001) outline common issues such as vector preparation and insert screening that can be particularly challenging for novices. AI can potentially mitigate some of these challenges given records of prior success of teaching capabilities in the educational field (Mavroudi et al. 2018; Holmes et al. 2019; Zawacki-Richter et al. 2019).
Our study compared the instructional capabilities of two AI platforms: Gemini Advanced (powered by Gemini Ultra 1.0) and ChatGPT (GPT-4o). With our designated project of inserting the eGFP gene into the pcDNA3.1 vector backbone, we sought to determine if AI could properly deliver step-by-step instructions while being able to provide real-time troubleshooting. We also tracked if it could warn about common laboratory mistakes and cover all bases, specifically those that may be considered common knowledge to more experienced researchers. The AI model comparison will focus on metrics such as accuracy, ease of use, and recall. Through this evaluation, the goal was to identify whether AI can be utilized for such a purpose in a laboratory setting and compare the effectiveness of specific AI models for the learning proficiency of novice researchers. Throughout the process, the AI models provided step-by-step guidance, troubleshooting, and real-time feedback. Observations on task accuracy, time taken, and user feedback were recorded to evaluate the effectiveness of Gemini and GPT-4o in guiding novices through the DNA subcloning process.
Materials and Methods
There were two participants or trainees in this study, who are also the co-first authors on this manuscript. Trainee 1 is a 19 year old female college sophomore. Trainee 2 is a 17 year old female high school senior. We both have taken science courses such as AP Biology and AP Chemistry, and have had preliminary experience doing experiments in a controlled school environment, either as part of curriculum or from science fairs. Both of us had very limited knowledge in molecular biology prior to the start of this study.
The AI systems used for this study are either Gemini Advanced (powered by Gemini Ultra 1.0), or ChatGPT (GPT-4o). Trainee 1 strictly utilized Gemini while trainee 2 strictly utilized GPT-4o. SnapeGene (GSL Biotech LLC) was used for DNA sequence analyses.
DNA plasmids and sequences:
pcDNA™3.1(+) is a mammalian expression vector (ThermoFisher Scientific); eGFP amino acid sequence is from Cormack BP et al. (1996). PCR primer oligos were synthesized by Azenta.
Reagents and kits:
For Gibson Assembly we used NEBuilder® HiFi DNA Assembly Master Mix (E2621S). Competent cells were NEB® 10-beta Competent E. coli (C3019H). Q5® High-Fidelity 2X Master Mix (M0492S) was used for PCR. Monarch® DNA Gel Extraction Kit (T1020S) was used for purification of PCR fragments. All from New England Biolabs. Agarose gels were stained with SYBR Safe DNA Gel Stain (ThermoFisher) and the DNA fragments were visualized with bluelight.
Results
The study began with the principle investigator (PI), the senior author of this study, laying out the specific objectives and ground rules in the study:
The two trainees will use AI systems exclusively (except where noted below) to learn DNA subcloning, with a specific test case as defined by the PI.
The test case is insertion of the eGFP gene into the pcDNA3.1 backbone vector.
AI systems will be used as a firstline for all inquiries regarding the project (i.e. from conceptual understanding of molecular biology to actual hands-on laboratory work).
Trainee 1 will exclusively use Gemini while trainee 2 will exclusively use GPT-4o. AI systems will be asked the same exact questions to ensure standardization.
The PI will take a ‘hands-off’ approach, and only intervene if the PI sees inaccuracies (i.e. hallucinations) in the AI output. In these situations, the PI will instruct the trainees to keep querying the AIs to obtain more accurate results. The PI may also redirect from the AI output according to the available reagents or laboratory equipment.
We first informed the respective AI programs of the scope of our project and our objectives, then through iterative questions and follow ups, relied on the AI as the sole source of general information as well as detailed instructions on how to perform DNA subcloning, specifically to insert eGFP into the pcDNA3.1 backbone vector.
Since both of us have had limited conceptual knowledge of molecular biology and lab work, we spent the first four days interacting with our respective AI programs to obtain the necessary conceptual and practical knowledge. We met with the PI daily to review our progress and to help us assess when we were ready to start the hands-on laboratory work. Both AI programs were able to provide us with the necessary conceptual information, as assessed by our PI, and there were no major differences between the two at this stage.
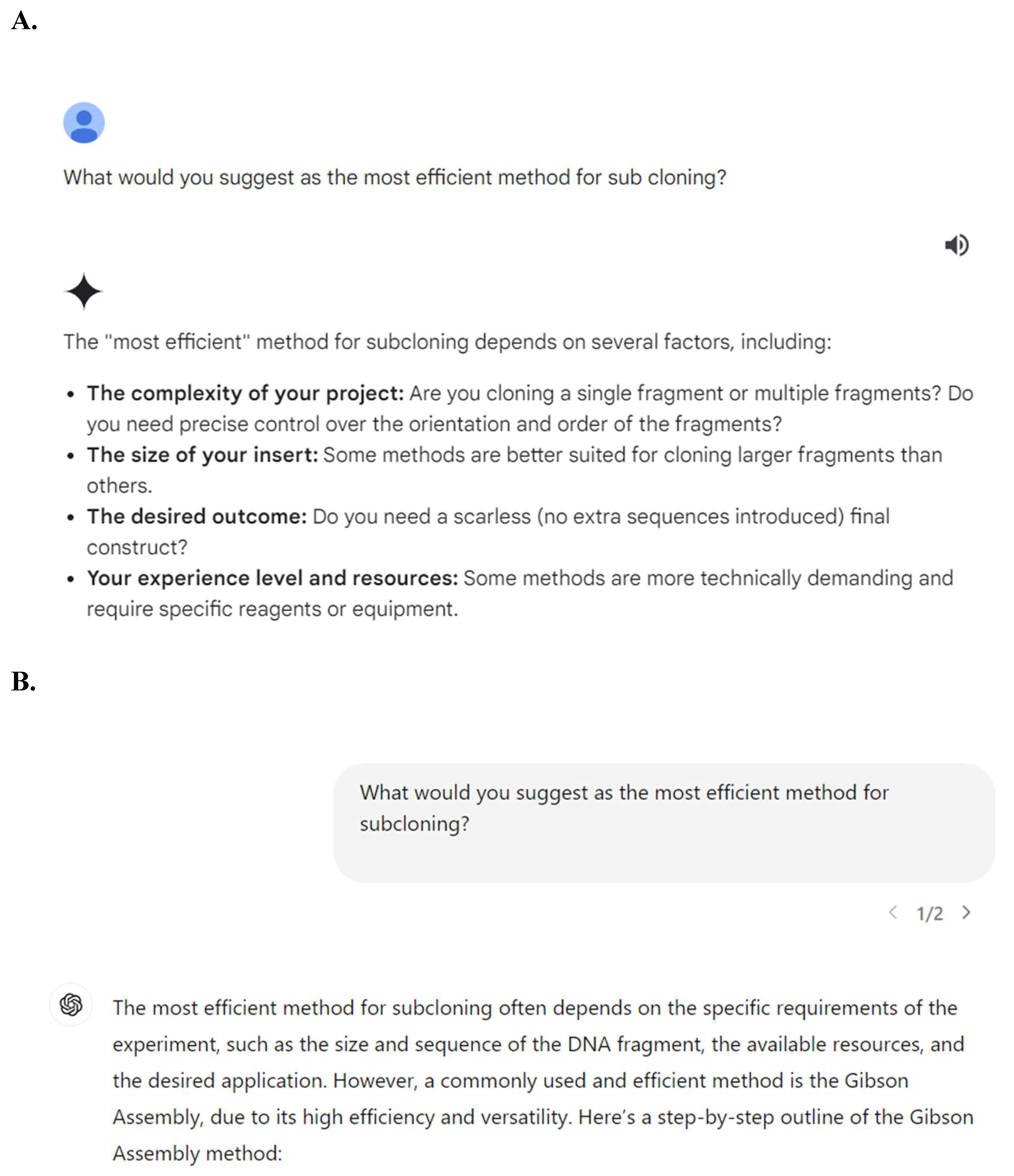
However, upon querying the AI for step-by-step instructions on proceeding with the actual subcloning process, we found various differences between the two programs that impacted the effectiveness and reliability of the AI as a training tool. It was observed that Gemini would give answers that weren’t as straightforward as GPT-4o’s. For example, when asked for the “most efficient method for subcloning,” Gemini would list multiple methods and note that it depended on the DNA size, experience level, etc. (
Figure 1A). Even when asked follow up questions to restate only one method, Gemini continued to state that it differed based on the situation. In comparison, GPT-4o would respond with one direct answer (
Figure 4B): Gibson Assembly. We found this difference, passive (Gemini) vs direct (GPT-4o) response consistently throughout the process of querying the AIs for instructions (more below).
At this point, we informed both AI models that the Gibson Assembly would be used for this project and to provide detailed instructions. Both AIs were able to provide us with instructions, and when prompted, suggestions on available commercial kits and reagents to use. Both AIs recommended the NEBuilder HiFi DNA Assembly Cloning Kit (New England Biolabs), although GPT-4o was more direct and also better at providing instructions that matched more closely with the manufacturer's instructions.
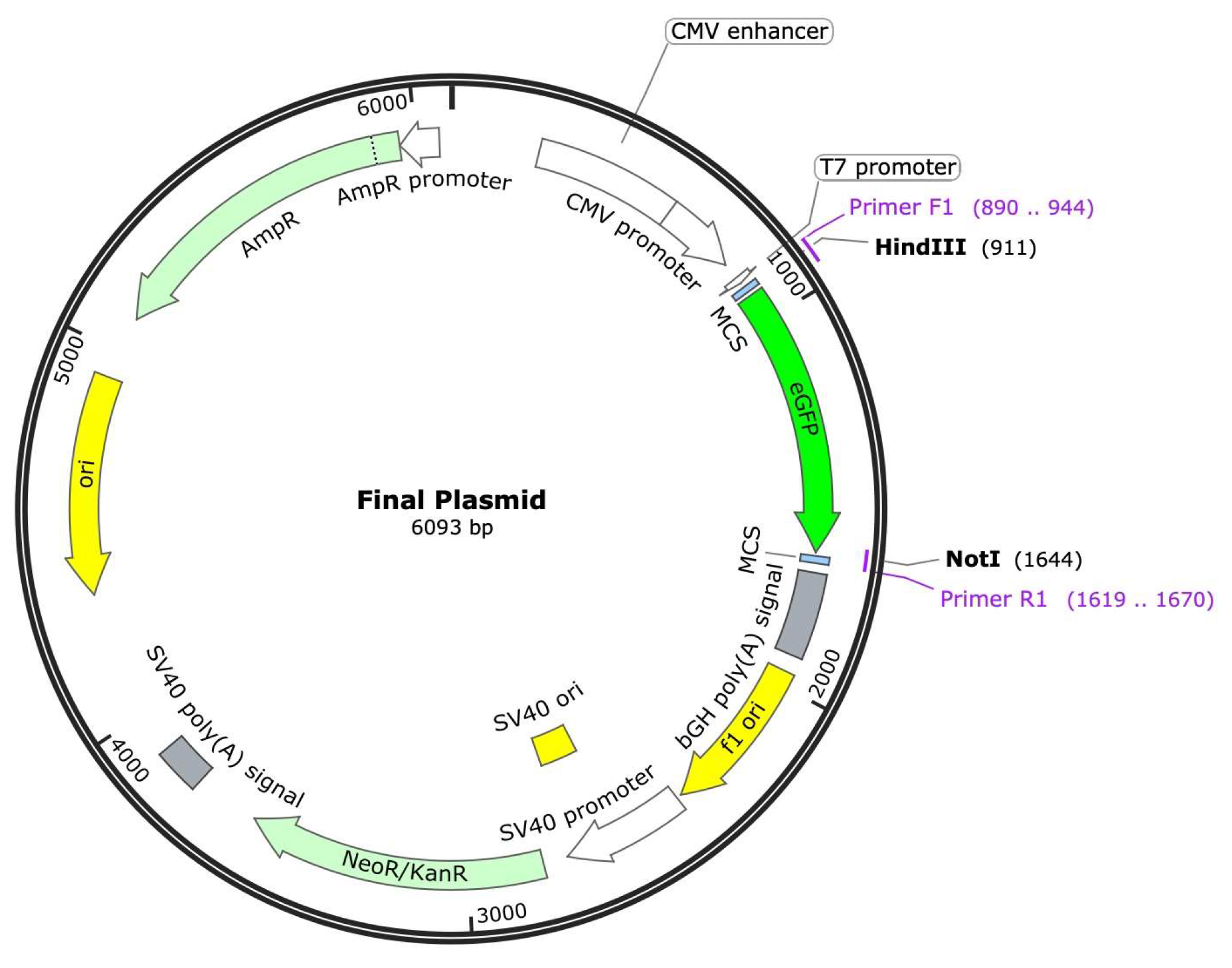
We next asked the AI to recommend the best DNA analysis programs to help us with DNA sequence analysis and primer design etc. Both AIs suggested SnapGene (GSL Biotech LLC), and were able to respond with detailed instructions regarding how to use the software. However, instructions differed although the prompts were the same. In this case, we found that GPT-4o responded with more complex instructions while Gemini’s method was simpler and also effective. Notwithstanding this difference, both AI models were able to help us piece together the expected sequence of the desired product, eGFP inserted into pcDNA3.1 (
Figure 2). From there both AI models were able to help us use SnapGene to design primers for PCR to generate the eGFP insert.
Both AI models were able to provide us with similar general outlines for the Gibson Assembly method as summarized below.
-
Prepare DNA fragments:
pcDNA3.1 vector, cut with appropriate restriction enzymes to linearize.
eGFP, design primers and PCR from an existing template.
Purify DNA fragments, gel electrophoresis and extraction of DNA fragments.
Prepare the Gibson assembly reaction.
Transform into competent E coli cells.
Plate on selective media and screen for positive clones.
We followed the AIs’ instructions to set up the PCR reactions. Both AI models were able to provide detailed protocols for setting up the PCR reactions, and recommending subsequent thermal cycling settings. Interestingly, GPT-4o seemed to have a much higher memory retention when moving through different steps. If told we were using a certain kit, it would answer with protocols for following steps based on that information while Gemini’s protocol would tend to be inaccurate and would need to be told again in order to correct itself. Furthermore, GPT-4o consistently recommended NEB reagents (e.g. Q5 DNA Polymerase), since, as we noted earlier, both AIs were told NEBuilder® HiFi DNA Assembly Master Mix would be used. Gemini, on the other hand, recommended many different manufacturers.
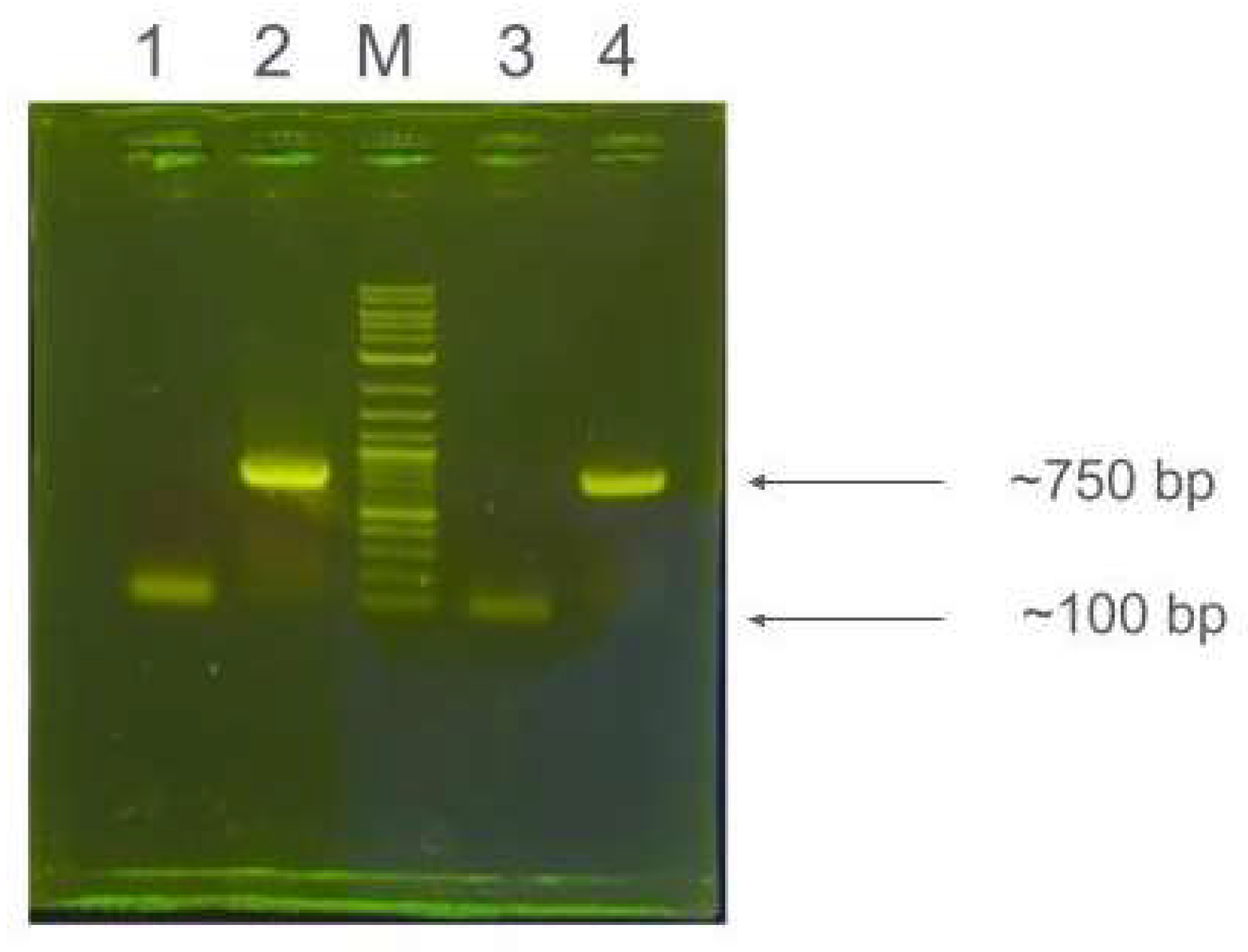
Figure 3 shows an agarose gel electrophoresis image of PCR reactions for eGFP fragments. The image of the gel was uploaded to both Gemini and GPT-4o, and the AI models were asked for interpretations of the bands. Interestingly, we found that both AI models were able to recall memories from previous inputs. At the start of the study we uploaded the sequence of the eGFP and pcDNA3.1 DNA sequences we were using, to the respective AI programs. Both AI models were able to recognize that the ~750 bp band (lanes 2 & 4) corresponded to eGFP. Curiously, both AIs initially did not comment on the faint bands (lanes 1 & 3) at ~100bp. However, when prompted for suggestions on what these bands could be, both AI models recognized that these were primer dimers, demonstrating their ability to be able to analyze images uploaded by the user.
We next followed the AIs’ detailed instructions for excision and purification of the eGFP DNA fragment, including suggestions for links to instructional videos for these processes. Here again, GPT-4o was more direct in guiding us to use the DNA Gel Extraction Kit from NEB, to purify the eGFP DNA fragment.
We next proceeded with the Gibson assembly using the NEBuilder® HiFi DNA Assembly Master Mix. Both AIs were able to provide detailed protocols, however, as mentioned previously, GPT-4o instructions more closely matched those from NEB’s manual.
After Gibson Assembly was performed, we proceeded with transformation of the reaction mix into competent
E. coli cells, using protocols provided by the AIs. Here the AI outputs followed the previous pattern whereby GPT-4o gave instructions to use NEB competent cells, whereas Gemini gave a list of options from different vendors. After transformation the cells were plated onto LB agar plates containing the antibiotic ampicillin, since our backbone vector pcDNA3.1 carried the ampicillin resistance gene. We should note here that both AI models failed to mention that ampicillin was needed on the agar plates for appropriate selection. This error was caught by the PI, who then instructed us to prompt the AIs for more clarifications with respect to selection requirements.
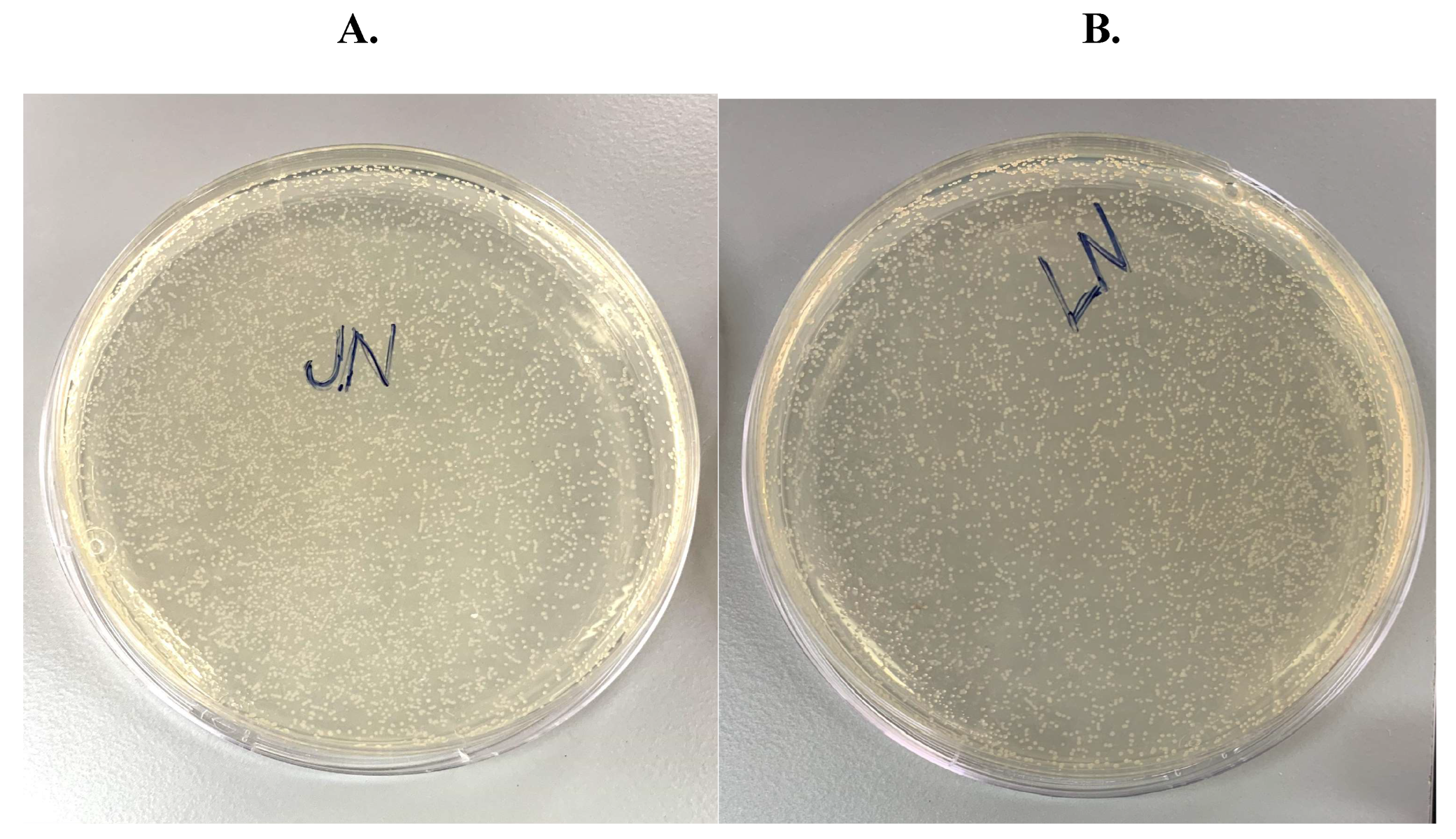
Figure 4. show the results of the colony growth after overnight incubation at 37 C.
Finally, we proceeded to the screening step, to identify the correct clone(s). Both AI models provided us with similar suggestions as to which method to use for screening, including PCR, restriction enzyme analysis and DNA sequencing. Based on recommendations from both AI models and inputs from the PI, we decided to go with DNA sequencing for screening. After picking 4 colonies each and starting culture growth for miniprep scale DNA preparations, we submitted the purified DNA for Sanger sequencing, using primers that flank the insertion site of the eGFP gene. The sequencing results indicate that 3 of the 4 clones from each of us yielded the correct sequence that matched our expected final plasmid as described in
Figure 1. The DNA subcloning project was successfully concluded, with a 75% success rate in obtaining the desired clones. Notably, this entire process, from initial planning to final confirmation, was accomplished in under three weeks.
Discussion
Throughout the study, both AI models demonstrated notable strengths and limitations in their utility as a research laboratory training tool. Gemini provided images and diagrams, offering users a thorough understanding of each DNAsubcloning step. However, Gemini's occasional inaccuracies in material quantities and procedural steps as the experiment progressed indicated a need for more robust error-checking mechanisms. GPT-4o, on the other hand, excelled in providing real-time, interactive support. Moreover, its ability to answer questions dynamically and offer detailed explanations was highly beneficial. This adaptability was particularly useful for troubleshooting and immediate problem resolution. Despite issues with image functionality that required manual intervention, GPT-4o’s guidance remained accurate and effective overall. The system's ability to analyze gel images and provide feedback on primer dimers and band locations deomstrated its potential to offer practical, lab-specific insights.
GPT-4o seemed to have a much higher memory retention when moving through different steps. If told the participant was using a certain kit, it would answer with protocol for following steps based on that information while Gemini’s protocol would be inaccurate and would need to be told again in order to correct itself. GPT-4o also consistently recommended reagents from New England Biolabs, once it understood what was frequently being utilized, while Gemini consistently offered a list of different manufacturers.
Gemini proactively included images in its responses, which enhanced the user experience during lab preparations. In contrast, GPT-4o only generated images when specifically prompted, often resulting in a lack of visual aids that could have been helpful, such as images of successful colony growth after transformation.
We do note that while minor errors, such as recommending incorrect reagent concentrations, occasionally required intervention from the PI, more significant mistakes also occurred. For example, Gemini miscalculated buffer volumes during Gibson Assembly, recommending adding 100 microliters for a reagent when only 20 microliters were needed, potentially causing the reactions to fail. GPT-4o, for its part, included a potentially disastrous method of microwaving cells as an option for heat-shocking during the transformation process.
The findings from this study will prove invaluable as AI systems like Gemini and GPT-4o continue to integrate into various sectors, including scientific research and education. These AI tools have the potential to revolutionize training methodologies by promoting standardization, ensuring precision in procedural steps and material quantities, and ultimately minimizing variability in experimental techniques. More importantly, they will also facilitate more hands-off training, as trainees can consult the AI models for immediate answers to questions that arise throughout the process. As online education becomes more popular, AI can significantly enhance the learning process by providing detailed information on lab equipment and the initial steps of various procedures, making complex topics more accessible to a broader audience.
Furthermore, the success of this study suggests that more extensive research can be conducted to explore the full potential of these tools, and to apply it for training in other areas of science. Future experiments could test the limits of Gemini, GPT-4o, and other emerging AI models, and identify areas for improvement and new applications. For instance, integrating advanced image recognition and analysis features could further enhance AI's ability to interpret experimental results accurately (Lecun et al. 2015; Topol 2019). Additionally, expanding AI training datasets with diverse and complex biological scenarios could improve the robustness and reliability of these systems.
In conclusion, the integration of AI in biotechnology education and research holds great promise for the future. These tools can transform traditional training methods, making them more efficient, standardized, and accessible (Russell & Norvig, 2016). As AI technology continues to evolve, its applications in scientific research and education will likely expand, driving innovation and improving outcomes in various fields (Topol 2019). The insights gained from this study provide a solid foundation for further exploration and development of AI-driven educational tools in molecular biology and beyond.
References
- Ausubel, F.M.; Brent, R.; Kingston, R.E.; et al. Current protocols in molecular biology. Wiley-Interscience. 2003.
- Ching, T.; Himmelstein, D.S.; Beaulieu-Jones, B.K.; et al. Opportunities and obstacles for deep learning in biology and medicine. J R Soc Interface. 2018, 15, 20170387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cormack, B.P.; Valdivia, R.H.; Falkow, S. FACS-optimized mutants of the green fluorescent protein (GFP). Gene. 1996, 173, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, R.G.L. The advancement of artificial intelligence in biomedical research and health innovation: challenges and opportunities in emerging economies. Global Health. 2024, 20, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, W.; Bialik, M.; Fadel, C. Artificial intelligence in education. Boston (MA): Center for Curriculum Redesign; 2019.
- Hutson, M. How AI is being used to accelerate clinical trials. Nature 2024, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lecun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature. 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libbrecht, M.W.; Noble, W.S. Machine learning applications in genetics and genomics. Nat Rev Genet. 2015, 16, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Ma, H.; Tang, Y.J. Artificial intelligence: a solution to involution of design-build-test-learn cycle. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2022, 75, 102712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavroudi, E.; Holmes, W. The role of AI in facilitating science education. Research in Science Education 2018, 50, 907–925. [Google Scholar]
- Russell, S.; Norvig, P. Artificial intelligence: a modern approach, 3rd ed.Pearson, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Sambrook, J.; Russell, D.W. Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 3rd ed.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Stemmer, W.P.; Morris, S.K. Enzymatic inverse PCR: a simple method for subcloning. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1992, 89, 10732–10736. [Google Scholar]
- Topol, E.J. High-performance medicine: the convergence of human and artificial intelligence. Nat Med. 2019, 25, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Jumper, J.; Baek, M.; et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarnack, K.; Eyras, E. Artificial intelligence and machine learning in RNA biology. Brief Bioinform. 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zawacki-Richter, O.; Marín, V. I.; Bond, M.; Gouverneur, F. Systematic review of research on artificial intelligence applications in higher education – where are the educators? 2019.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).