Submitted:
28 August 2024
Posted:
28 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Controlled Drug Delivery Systems
3. A pH-Independent Controlled Drug Delivery System
3.1. Advantages of pH-Independent Controlled Drug Delivery System
3.2. Disadvantages of pH-Independent Controlled Drug Delivery System
3.3. Factors That Influence the pH-Independent Controlled Drug Delivery System
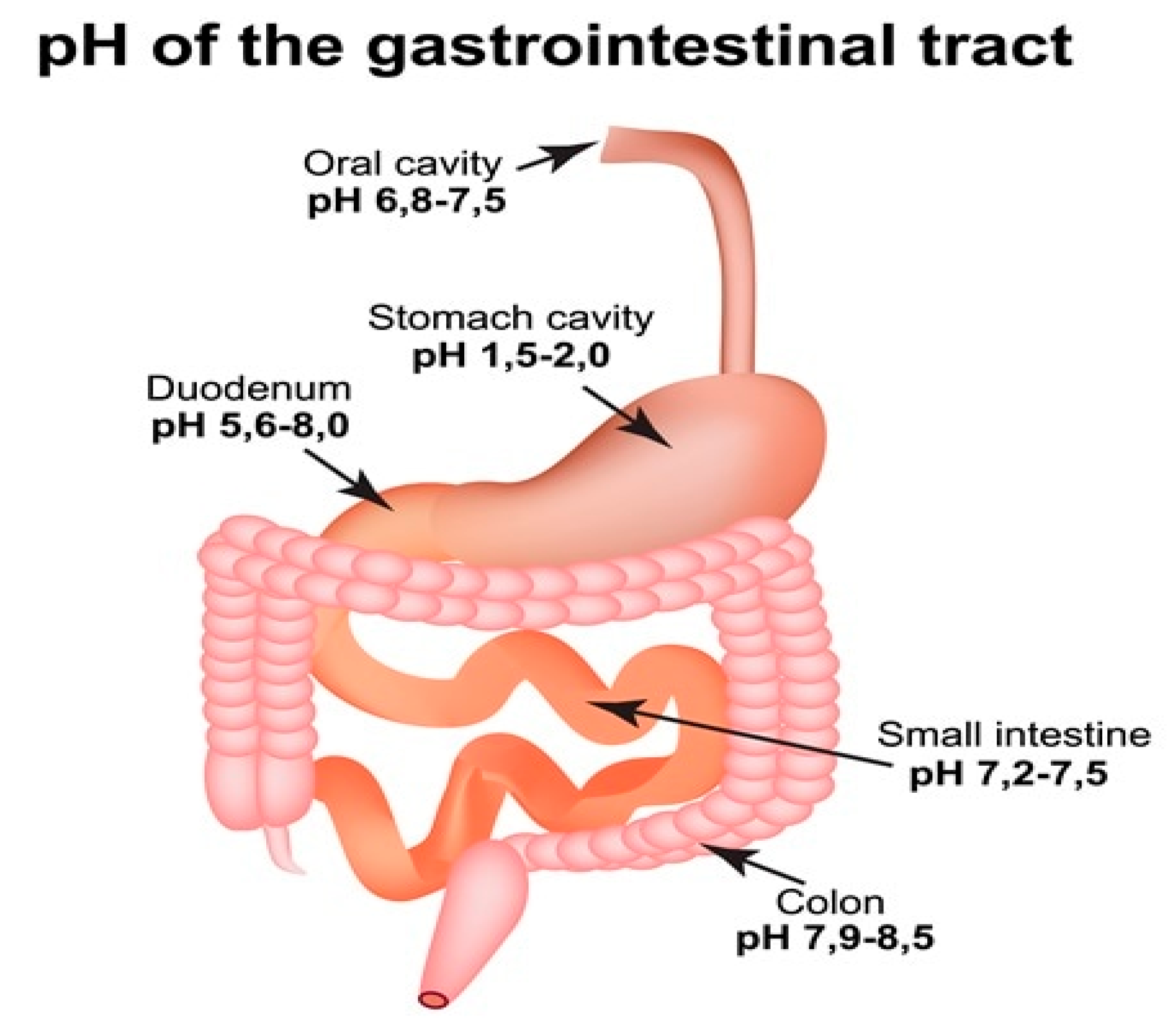
3.3.1. The pH of the Stomach
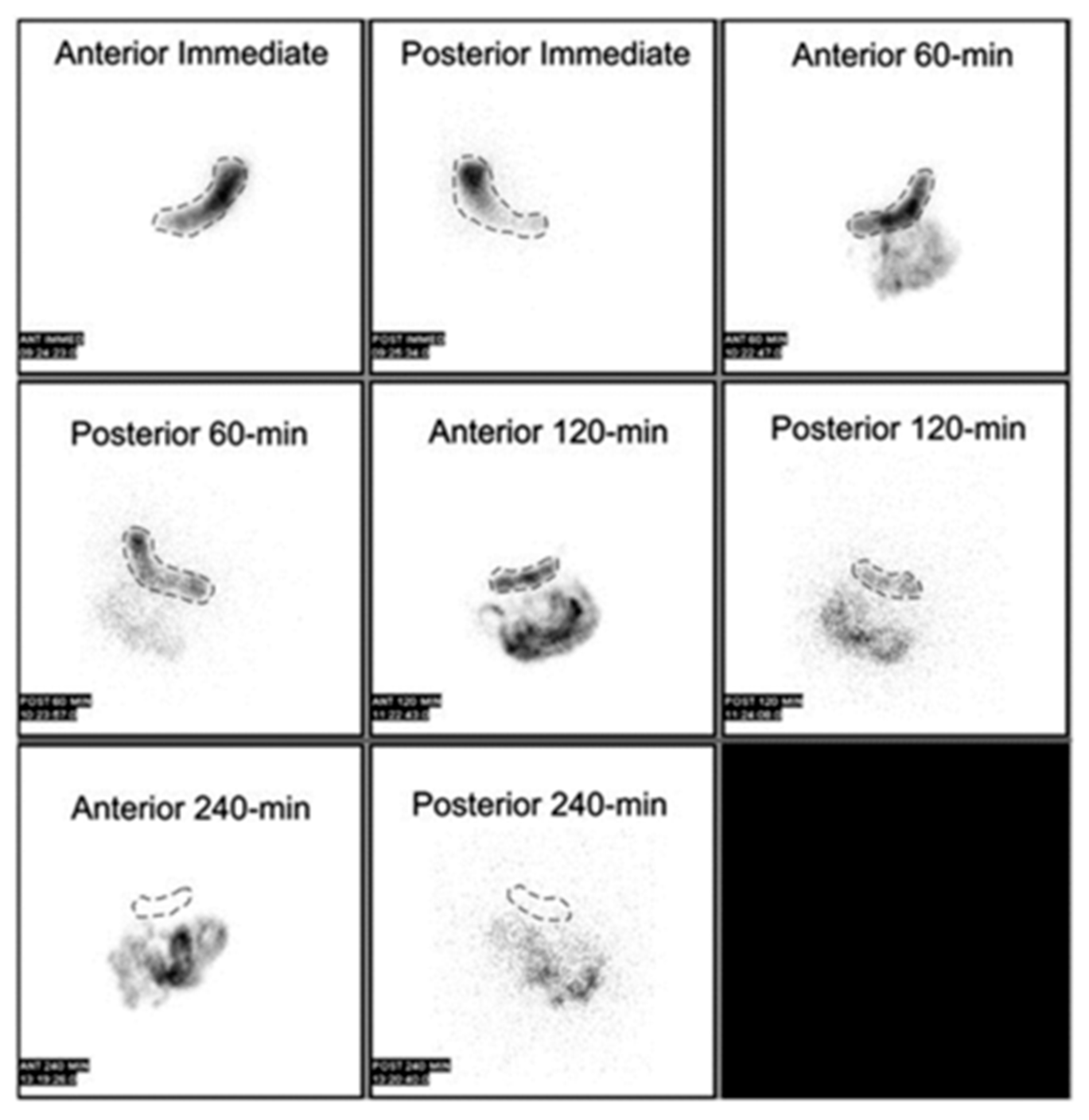
3.3.2. The Gastric Emptying
3.3.3. Drug Structure
3.3.4. Drug’s Nature
4. Suitable Drug Candidate for pH Independent Controlled Release Drug Delivery System
- Drugs that are soluble in a pH-dependent manner
- Drugs with a moderate level of basicity
- Incompletely absorbed as a result of a relatively limited absorption window in the gastrointestinal tract
- Drug precipitation occurs when a solid substance forms from a solution due to various factors. This phenomenon can have significant implications in pharmaceutical formulations and drug delivery systems. Understanding the mechanisms and conditions that lead to drug precipitation is crucial for ensuring the stability and efficacy of medications. By investigating the physicochemical properties of drugs and
- A highly potent pharmaceutical compound.
- Long-term treatment necessitates the use of medications.
- Therapeutic agents with a low half-life
5. Disease Targeting pH Independent Controlled Release Drug Delivery System
6. Approaches of pH Independent Drug Delivery Techniques
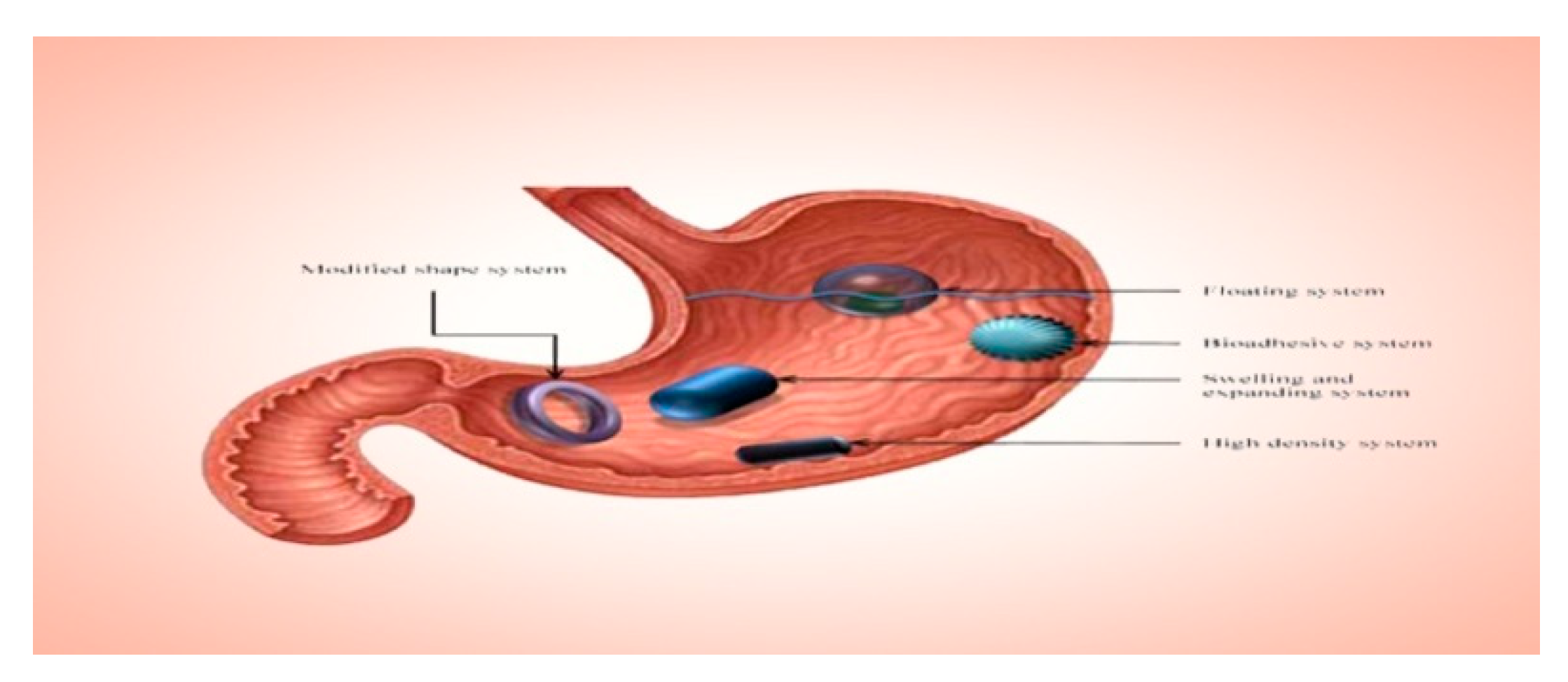
6.1. Floating Drug Delivery Systems Demonstrate the Following Characteristics
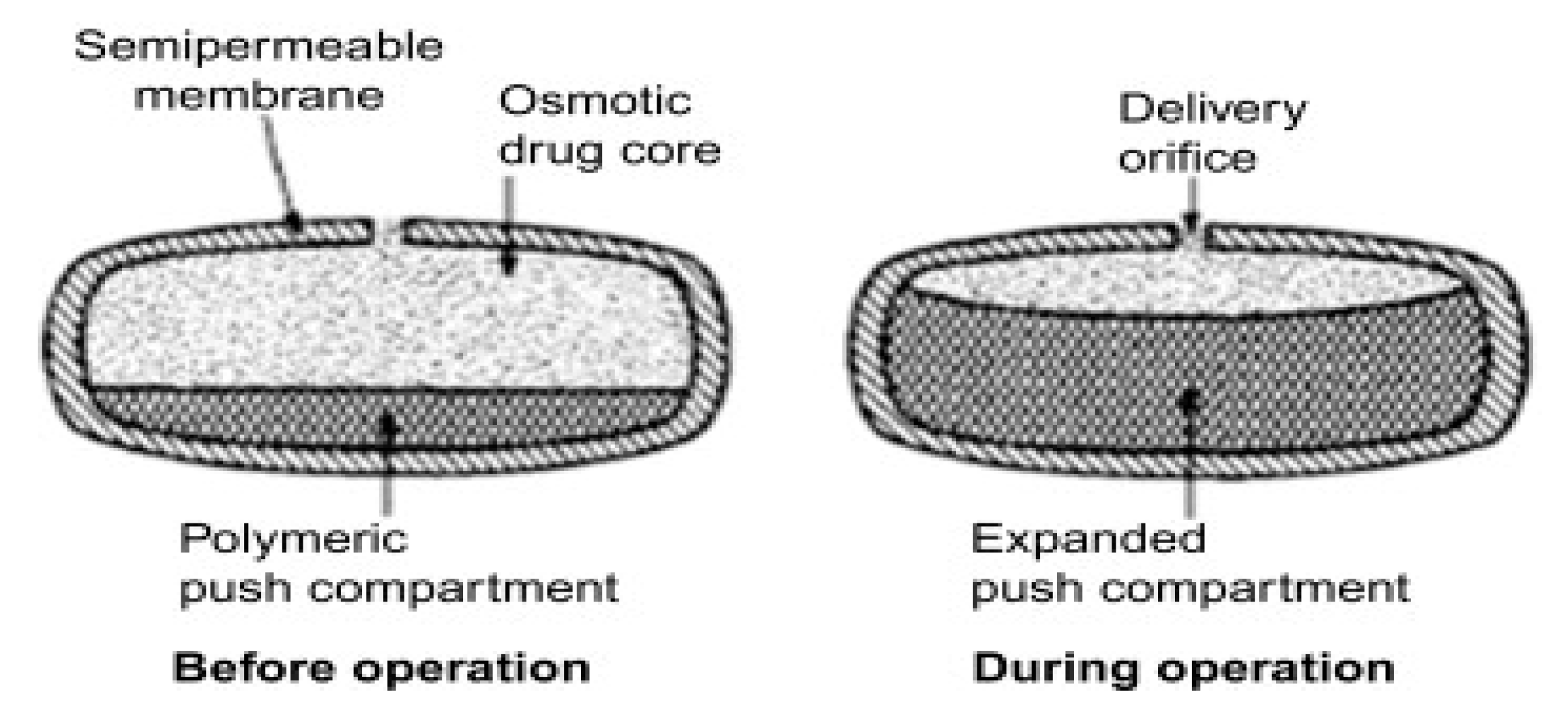
6.2. Osmotic Drug Delivery System
Limitations
- i.
- Several parameters, such as the thickness of the membrane, osmotic pressure, the type of membrane and its characteristics, and solubility, play a crucial role in this context.
- ii.
- Drugs that possess high permeability, lack an absorption window, and do not undergo significant first-pass metabolism are more likely to succeed when formulated in osmotic drug delivery systems. Ideally, these drugs should also exhibit dose-proportional and linear pharmacokinetic profiles.
6.3. pH Modifiers
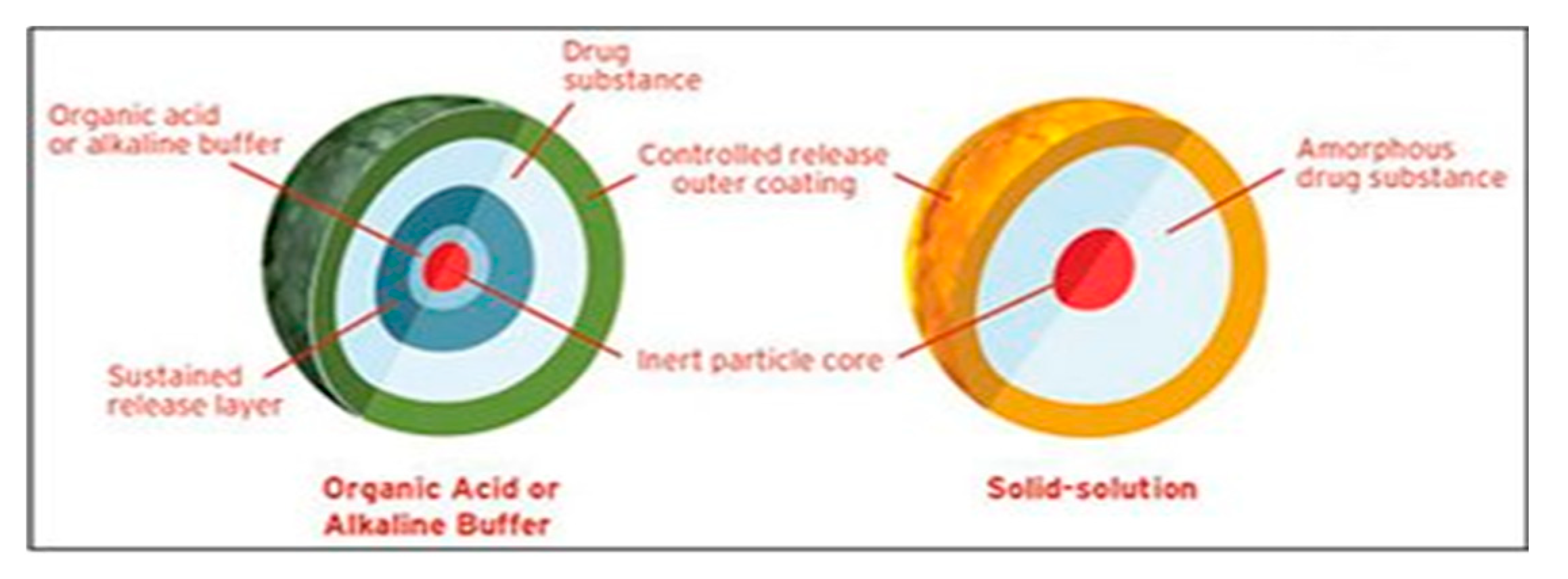
6.3.1. Organic Acids
6.3.2. Alkalizers
Limitations
6.4. By Using Enteric Polymers
6.5. Combination of Non-Ionic and Anionic Polymers
Limitations
6.6. Supersaturation That Is Independent of Ph
Limitations
6.7. Diffcore Technology
6.8. Diffucaps® Technology
7. Novel Dosage Forms and Its Applications in pH Independent Dosage Delivery Systems
Challenges and Future Prospective
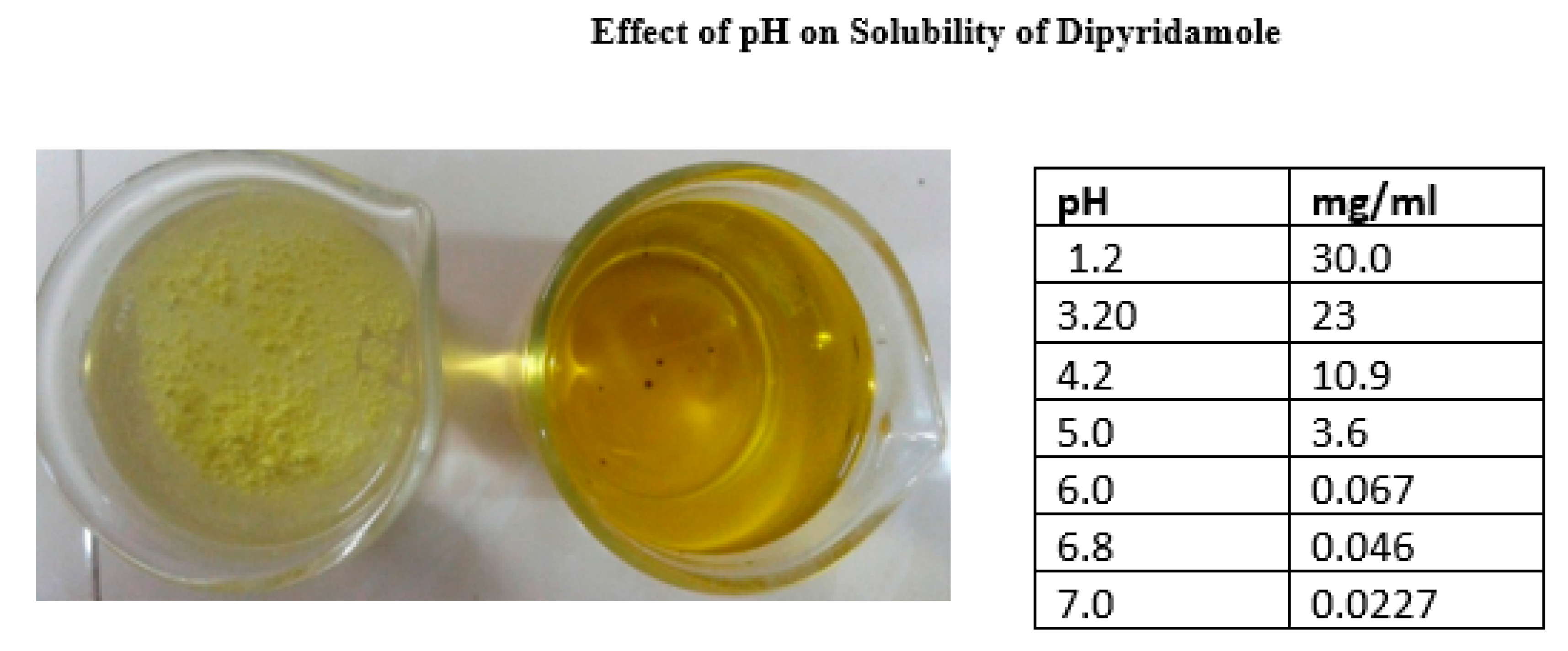
- Formulating drugs with weakly basic pH-dependent soluble drugs, such as Ondansetron HCl and Dipyridamole, presents several significant challenges. According to the literature, the major challenges can be explained as follows.
- Several drugs, such as weakly acidic and basic drugs, exhibit solubility that varies depending on the pH of the gastrointestinal tract. The rate of dissolution of a drug in a medium is directly proportional to its solubility in that medium. Consequently, the solubility of a substance varies depending on the pH of the gastrointestinal tract, resulting in varying rates of dissolution in different parts of the tract[98].
- The solubility of the drug is affected by pH, which poses challenges for conventional dosage. When the drug comes into contact with stomach fluid (which has a low pH), it easily dissolves. However, when it is transferred to the small intestine with a higher pH, it precipitates out due to its low solubility. These precipitates do not easily dissolve at the intestinal pH. Therefore, it becomes necessary to absorb the entire drug from the stomach itself, which is not feasible according to the pH partition theory. On the other hand, when this drug is included in an extended-release dosage form, the unabsorbed drug interacts with the pH of the gastrointestinal fluids, which gradually change as the dosage is processed. Therefore, the impact of GI fluid pH on drug release from the dosage form is not substantial while it resides in the stomach[99,100].
- However, as the dosage form is transferred to the intestine, the drug release is observed to decrease.
- The solubility variations caused by the drug’s pH dependence can result in either sub-therapeutic doses or toxic doses of certain potent drugs.
- The solubility patterns of pH dependent soluble drugs exhibit variations that have an impact on their absorption and, consequently, their bioavailability.
- Inter-subject variability is a phenomenon that is often observed in scientific studies. It refers to the differences or variations that exist among individuals who are part of a study or experiment. This variability can arise from a variety of factors, such as genetic differences, environmental influences, or even random chance. Understanding and accounting
- ‘Inadequate correlation between in-vitro and in-vivo data;
- Sub-therapeutic doses have no therapeutic action.
- Variation in diseased conditions
Future Directions
- Based on future perspectives, the following recommendations are proposed.
- Extensive research is required for the development of pH independent extended-release formulations for different categories of drugs. These formulations show great potential for pH dependent weakly soluble drugs. It is imperative to develop a novel technique for non pH modulating agents in order to address the limitations of current pH modulating agents.
- There has been a surge of interest in the development of pH independent extended release (ER) drug delivery systems. These systems have garnered attention for their versatility and potential in creating complex formulations, particularly for oral tablet dosage forms of pH dependent soluble drugs. There are no concerns regarding the scale-up process for the production of pH-independent extended-release tablets.
- There is potential for developing formulations utilising various multifunctional polymers, both individually and in combination. Further investigation is required to explore the impact of factors such as pH medium, polymer ratio, tablets geometric, and other formulation parameters
- It is imperative to develop methods for scaling up that can be applied in an industrial setting.
- It is essential to develop in-vitro models that can accurately replicate the in-vivo performance of pH independent controlled release tablets. An innovative compression coating technique was effectively employed and optimisation was also carried out. Therefore, further research is required in this field.
- The design and fabrication of novel extended-release formulations of Dipyridamole, which are not affected by changes in pH, have been thoroughly investigated. The study successfully implemented compression coating technology to maintain the controlled release of pH dependent soluble drugs. In order to attain optimal desirability values during the process of formulation development, it is imperative to utilise advanced tabletting equipment. This will effectively minimise both within batch and batch-batch variations, resulting in superior outcomes.
8. Conclusions
References
- Rathbone, M.J., et al., Modified-release drug delivery technology. Vol. 1. 2003: Marcel Dekker New York.
- Sastry, S.V., J.R. Nyshadham, and J.A. Fix, Recent technological advances in oral drug delivery–a review. Pharmaceutical science & technology today, 2000. 3(4): p. 138-145.
- Langer, R.S. and D.L. Wise, Medical applications of controlled release. 2019: CRC Press LLC Boca Raton, FL, USA:.
- Siepmann, J., R.A. Siegel, and M.J. Rathbone, Fundamentals and applications of controlled release drug delivery. Vol. 3. 2012: Springer.
- Silvestri, L.J. and H.R. Pyle, Sustained release dosage form. 1991, Google Patents.
- Welling, P.G. and M. Dobrinska, Dosing considerations and bioavailability assessment of controlled drug delivery systems. Chapter, 1987. 7: p. 254.
- Bhat, B.B., et al., Controlled release technologies for chronotherapy: current status and future perspectives. Current Pharmaceutical Design, 2023. 29(14): p. 1069-1091.
- Adepu, S. and S. Ramakrishna, Controlled drug delivery systems: current status and future directions. Molecules, 2021. 26(19): p. 5905.
- Freichel, O.L. and B.C. Lippold, A new oral erosion controlled drug delivery system with a late burst in the release profile. European journal of pharmaceutics and biopharmaceutics, 2000. 50(3): p. 345-351.
- Keskar, S. and V. Kumar, Journal of Population Therapeutics & Clinical Pharmacology.
- BODKE, V., et al., PULSATILE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS THE NOVEL APPROACH. 2024.
- Negut, I. and B. Bita, Polymeric micellar systems—a special emphasis on “smart” drug delivery. Pharmaceutics, 2023. 15(3): p. 976.
- Smith, A.A., A.K. Muthu, and R. Manavalan, Formulation development and evaluation of ondansetron hydrochloride sustained release matrix tablets. J. Pharma Sci. & Res, 2009. 1(4): p. 48-54.
- Streubel, A., et al., pH-independent release of a weakly basic drug from water-insoluble and-soluble matrix tablets. Journal of controlled release, 2000. 67(1): p. 101-110.
- Savjani, K.T., A.K. Gajjar, and J.K. Savjani, Drug solubility: importance and enhancement techniques. International Scholarly Research Notices, 2012. 2012(1): p. 195727.
- Siepmann, J. and N.A. Peppas, Modeling of drug release from delivery systems based on hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC). Advanced drug delivery reviews, 2012. 64: p. 163-174.
- Indurkhya, A., et al., Influence of drug properties and routes of drug administration on the design of controlled release system, in Dosage form design considerations. 2018, Elsevier. p. 179-223.
- Hoare, T.R. and D.S. Kohane, Hydrogels in drug delivery: Progress and challenges. polymer, 2008. 49(8): p. 1993-2007.
- Kopeček, J., Smart and genetically engineered biomaterials and drug delivery systems. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2003. 20(1): p. 1-16.
- Pillai, A., D. Bhande, and V. Pardhi, Controlled Drug Delivery System, in Advanced Drug Delivery: Methods and Applications. 2023, Springer. p. 267-289.
- Tang, B., et al., Development of solid self-emulsifying drug delivery systems: preparation techniques and dosage forms. Drug discovery today, 2008. 13(13-14): p. 606-612.
- Nakamura, K., E. Nara, and Y. Akiyama, Development of an oral sustained release drug delivery system utilizing pH-dependent swelling of carboxyvinyl polymer. Journal of controlled release, 2006. 111(3): p. 309-315.
- Wenande, E., R.R. Anderson, and M. Haedersdal, Fundamentals of fractional laser-assisted drug delivery: an in-depth guide to experimental methodology and data interpretation. Advanced drug delivery reviews, 2020. 153: p. 169-184.
- Fassihi, R.A. and W.A. Ritschel, Multiple-layer, direct-compression, controlled-release system: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. Journal of pharmaceutical sciences, 1993. 82(7): p. 750-754.
- Lee, P.I. and J.X. Li, Evolution of oral controlled release dosage forms. Oral controlled release formulation design and drug delivery: theory to practice, 2010: p. 21-31.
- Higuchi, T., Mechanism of sustained-action medication. Theoretical analysis of rate of release of solid drugs dispersed in solid matrices. Journal of pharmaceutical sciences, 1963. 52(12): p. 1145-1149.
- Amidon, G.L., et al., A theoretical basis for a biopharmaceutic drug classification: the correlation of in vitro drug product dissolution and in vivo bioavailability. Pharmaceutical research, 1995. 12: p. 413-420.
- Dressman, J.B., et al., Dissolution testing as a prognostic tool for oral drug absorption: immediate release dosage forms. Pharmaceutical research, 1998. 15: p. 11-22.
- Kesisoglou, F., S. Panmai, and Y. Wu, Nanosizing—oral formulation development and biopharmaceutical evaluation. Advanced drug delivery reviews, 2007. 59(7): p. 631-644.
- Lindenberg, M., S. Kopp, and J.B. Dressman, Classification of orally administered drugs on the World Health Organization Model list of Essential Medicines according to the biopharmaceutics classification system. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics, 2004. 58(2): p. 265-278.
- Ghebre-Sellassie, I., et al., Pharmaceutical extrusion technology. 2003: CRC Press.
- Qiu, Y. , et al., Developing solid oral dosage forms: pharmaceutical theory and practice. 2016: Academic press.
- Huang, Y. and W.-G. Dai, Fundamental aspects of solid dispersion technology for poorly soluble drugs. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, 2014. 4(1): p. 18-25.
- Charman, W. and V. Stella, Transport of lipophilic molecules by the intestinal lymphatic system. Advanced drug delivery reviews, 1991. 7(1): p. 1-14.
- Dahan, A. and A. Hoffman, Rationalizing the selection of oral lipid based drug delivery systems by an in vitro dynamic lipolysis model for improved oral bioavailability of poorly water soluble drugs. Journal of controlled release, 2008. 129(1): p. 1-10.
- Singh, B.N. and K.H. Kim, Floating drug delivery systems: an approach to oral controlled drug delivery via gastric retention. Journal of Controlled release, 2000. 63(3): p. 235-259.
- Hwang, S.-J., H. Park, and K. Park, Gastric retentive drug-delivery systems. Critical Reviews™ in Therapeutic Drug Carrier Systems, 1998. 15(3).
- Menon, A., W.A. Ritschel, and A. Sakr, Development and evaluation of a monolithic floating dosage form for furosemide. Journal of pharmaceutical sciences, 1994. 83(2): p. 239-245.
- Sathish, D., et al., Floating drug delivery systems for prolonging gastric residence time: a review. Current drug delivery, 2011. 8(5): p. 494-510.
- Oprea, T.I., Current trends in lead discovery: are we looking for the appropriate properties? Molecular diversity, 2000. 5: p. 199-208.
- Veber, D.F., et al., Molecular properties that influence the oral bioavailability of drug candidates. Journal of medicinal chemistry, 2002. 45(12): p. 2615-2623.
- Hansch, C., J. Björkroth, and A. Leo, Hydrophobicity and central nervous system agents: on the principle of minimal hydrophobicity in drug design. Journal of pharmaceutical sciences, 1987. 76(9): p. 663-687.
- Dobetti, L., Fast-melting tablets: Developments and technologies. Pharmaceutical technology, 2001: p. 44-44.
- Lipinski, C.A., et al., Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Advanced drug delivery reviews, 1997. 23(1-3): p. 3-25.
- Kalantzi, L., et al., Characterization of the human upper gastrointestinal contents under conditions simulating bioavailability/bioequivalence studies. Pharmaceutical research, 2006. 23: p. 165-176.
- Dressman, J.B., et al., Upper gastrointestinal (GI) pH in young, healthy men and women. Pharmaceutical research, 1990. 7: p. 756-761.
- Avdeef, A., Absorption and drug development: solubility, permeability, and charge state. 2012: John Wiley & Sons.
- Akiyama, Y., et al., Prediction of oral drug absorption in rats from in vitro data. Pharmaceutical Research, 2023. 40(2): p. 359-373.
- Khalid, G.M., EXTEMPORANEOUS PREPARATIONS IN PERSONALIZED THERAPY: THE DESIGN OF ORODISPERSIBLE DOSAGE FORMS. 2021.
- dos Santos, J., et al., Eudragit®: A Versatile Family of Polymers for Hot Melt Extrusion and 3D Printing Processes in Pharmaceutics. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1424. 2021, s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published.
- Kim, C.-j., Advanced pharmaceutics: physicochemical principles. 2004: CRC press.
- Robinson, J.R., Sustained and controlled release drug delivery systems. (No Title), 1978.
- Aulton, M.E. and K. Taylor, Aulton’s pharmaceutics: the design and manufacture of medicines. 2013: Elsevier Health Sciences.
- Teruel, A.H., et al., New insights of oral colonic drug delivery systems for inflammatory bowel disease therapy. International journal of molecular sciences, 2020. 21(18): p. 6502.
- Wang, L., et al., Porous and responsive hydrogels for cell therapy. Current Opinion in Colloid & Interface Science, 2018. 38: p. 135-157.
- Li, W., et al., Polyelectrolyte-based physical adhesive hydrogels with excellent mechanical properties for biomedical applications. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2018. 6(29): p. 4799-4807.
- Bahadır, E.B. and M.K. Sezgintürk, Poly (amidoamine)(PAMAM): An emerging material for electrochemical bio (sensing) applications. Talanta, 2016. 148: p. 427-438.
- Bindu, H.A., G. Bhavya, and K. Padmalatha, Floating drug delivery system: an overview. 2021.
- Si, X., et al., Hypoxia-sensitive supramolecular nanogels for the cytosolic delivery of ribonuclease A as a breast cancer therapeutic. Journal of Controlled Release, 2020. 320: p. 83-95.
- Gupta, P., P.K. Gnanarajan, and P. Kothiyal, Floating drug delivery system: a review. International Journal of Pharma Research & Review, 2015. 4(8): p. 37-44.
- Kumar, M.R., et al., A comprehensive review on gastro retentive drug delivery system. Acta Chimica Pharmaceutica Indica, 2013. 3(2): p. 149-164.
- Azevedo, C., et al., The effect of hypergravity in intestinal permeability of nanoformulations and molecules. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics, 2021. 163: p. 38-48.
- Siepe, S., et al., Microenvironmental pH and microviscosity inside pH-controlled matrix tablets: an EPR imaging study. Journal of controlled release, 2006. 112(1): p. 72-78.
- Company, D.C., Methocel cellulose ethers technical handbook. 2002, Dow Chemical Co Midland, MI.
- Brahmankar, D. and S.B. Jaiswal, Biopharmaceutics and pharmacokinetics. 2019: Vallabh prakashan.
- Gaber, M., et al., Protein-polysaccharide nanohybrids: Hybridization techniques and drug delivery applications. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics, 2018. 133: p. 42-62.
- JS, P., et al., Inclusion complex system; a novel technique to improve the solubility and bioavailability of poorly soluble drugs: A review. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res, 2010. 2: p. 29-34.
- Bharate, S.S., S.B. Bharate, and A.N. Bajaj, Interactions and incompatibilities of pharmaceutical excipients with active pharmaceutical ingredients: a comprehensive review. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Excipients, 2016. 1(3).
- Loftsson, T. and M.E. Brewster, Pharmaceutical applications of cyclodextrins: basic science and product development. Journal of pharmacy and pharmacology, 2010. 62(11): p. 1607-1621.
- Narasimhan, B., Macromolecular dynamics during polymer dissolution: Molecular modeling and experimental characterization. 1996, Purdue University.
- Rashid, M., et al., Bioavailability enhancement of poorly soluble drugs: the holy grail in pharma industry. Current Pharmaceutical Design, 2019. 25(9): p. 987-1020.
- Anilkumar, A., T.E.G. Krishna Murthy, and A.P. Rani, Design and development of ondansetron hydrochloride pH independent control released matrix tablets. Pakistan Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2020. 33(2).
- Chen, L. and Y. Chien, Development of a skin permeation cell to simulate clinical study of iontophoretic transdermal delivery. Drug development and industrial pharmacy, 1994. 20(6): p. 935-945.
- Ron, E., et al., Controlled release of polypeptides from polyanhydrides. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 1993. 90(9): p. 4176-4180.
- Al-Zoubi, N., et al., Optimization of pH-independent chronotherapeutic release of verapamil HCl from three-layer matrix tablets. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 2015. 494(1): p. 296-303.
- Liechty, W.B., et al., Polymers for drug delivery systems. Annual review of chemical and biomolecular engineering, 2010. 1(1): p. 149-173.
- Taniguchi, C., et al., Novel formulations of dipyridamole with microenvironmental pH-modifiers for improved dissolution and bioavailability under hypochlorhydria. International journal of pharmaceutics, 2012. 434(1-2): p. 148-154.
- Tran, P.H.-L., et al., Dissolution-modulating mechanism of pH modifiers in solid dispersion containing weakly acidic or basic drugs with poor water solubility. Expert opinion on drug delivery, 2010. 7(5): p. 647-661.
- Kandukuri, J.M., et al., Pelletization techniques for oral drug delivery. Int J Pharm Sci Drug Res, 2009. 1(2): p. 63-70.
- Mehta, D.M., et al., Investigation of the drug release modulating effect of acidifiers in modified release oral formulation of cinnarizine. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2012. 7(3).
- Jayanthi, R.M., et al., pH-independent controlled release swellable matrix tablets. IJRAP, 2011. 2: p. 577-80.
- Williams, H.D., et al., Strategies to address low drug solubility in discovery and development. Pharmacological reviews, 2013. 65(1): p. 315-499.
- Sutton, S.C., Role of physiological intestinal water in oral absorption. The AAPS journal, 2009. 11: p. 277-285.
- Siewert, M., et al., FIP/AAPS guidelines to dissolution/in vitro release testing of novel/special dosage forms. Aaps Pharmscitech, 2003. 4: p. 43-52.
- Bose, A., T.W. Wong, and N. Singh, Formulation development and optimization of sustained release matrix tablet of Itopride HCl by response surface methodology and its evaluation of release kinetics. Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal, 2013. 21(2): p. 201-213.
- Nagendrakumar, D., G. Keshavshetti, and A. Shardor, An overview: Matrix tablets as sustained release. Recent Research in Science and Technology, 2014. 5(4).
- Carlert, S., Investigation and prediction of small intestinal precipitation of poorly soluble drugs: a study involving in silico, in vitro and in vivo assessment. 2012, Acta Universitatis Upsaliensis.
- Nikam, V.K., et al., Eudragit a versatile polymer: a review. Pharmacologyonline, 2011. 1(5): p. 152-164.
- Deguchi, S., et al., Solvent Dependence of Optical Rotation of (S)-N-[1-(2-Fluorophenyl)-3, 4, 6, 7-tetrahydro-4-oxo-pyrrolo-[3, 2, 1-jk][1, 4] benzodiazepine-3-yl]-1 H-indole-2-carboxamide. Journal of pharmaceutical sciences, 1993. 82(7): p. 734-736.
- Kranz, H., V. Le Brun, and T. Wagner, Development of a multi particulate extended release formulation for ZK 811 752, a weakly basic drug. International journal of pharmaceutics, 2005. 299(1-2): p. 84-91.
- Schoen, J.C., K.M. Erlandson, and P.L. Anderson, Clinical pharmacokinetics of antiretroviral drugs in older persons. Expert opinion on drug metabolism & toxicology, 2013. 9(5): p. 573-588.
- Ching, A.L., et al., Modifying matrix micro-environmental pH to achieve sustained drug release from highly laminating alginate matrices. European journal of pharmaceutical sciences, 2008. 33(4-5): p. 361-370.
- Alderman, D., A review of cellulose ethers in hydrophilic matrices for oral controlled-release dosage forms. Int J Pharm Tech Prod Mfr, 1984. 5(3): p. 1-9.
- Prausnitz, M.R. and R. Langer, Transdermal drug delivery. Nature biotechnology, 2008. 26(11): p. 1261-1268.
- Lecomte, F., et al., pH-sensitive polymer blends used as coating materials to control drug release from spherical beads: elucidation of the underlying mass transport mechanisms. Pharmaceutical research, 2005. 22: p. 1129-1141.
- Lawrence, M.J. and G.D. Rees, Microemulsion-based media as novel drug delivery systems. Advanced drug delivery reviews, 2000. 45(1): p. 89-121.
- Amsden, B., A model for osmotic pressure driven release from cylindrical rubbery polymer matrices. Journal of controlled release, 2003. 93(3): p. 249-258.
- Li, N. and L.S. Taylor, Tailoring supersaturation from amorphous solid dispersions. Journal of Controlled Release, 2018. 279: p. 114-125.
- Hsieh, Y.-L., et al., pH-induced precipitation behavior of weakly basic compounds: determination of extent and duration of supersaturation using potentiometric titration and correlation to solid state properties. Pharmaceutical research, 2012. 29: p. 2738-2753.
- Huang, S., et al., Solubility advantage (and disadvantage) of pharmaceutical amorphous solid dispersions. Journal of pharmaceutical sciences, 2016. 105(12): p. 3549-3561.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




