1. Introduction
Febrile seizures represent the most prevalent form of childhood seizure, occurring between the ages of six months and five years [
1]. Approximately 30% of seizures are prolonged, lasting more than 15 minutes. Such seizures have the potential to induce irreversible alterations in the developing brain, thereby elevating the probability of developing temporal lobe epilepsy in adulthood [
2,
3]. In addition to the epileptic process occurring in the brain, febrile seizures have been linked to the onset of subsequent neuropsychiatric disorders and cognitive impairment [
4]. Nevertheless, the underlying mechanisms of pathological changes resulting from febrile seizures remain poorly understood.
A variety of experimental models have been employed to examine the pathogenesis of febrile seizures, the subsequent development of epilepsy and the potential for neuropsychiatric complications. One validated model of febrile convulsions is the heating of 10-11-day-old rats with warm air [
5]. In this model, animals develop a prolonged convulsive seizure, which can lead to alterations in the expression of a number of genes. Reverse transcription followed by quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) is a widely employed methodology for the analysis of gene expression in a range of experimental models. The accurate normalization of data is essential for the successful implementation of a qualitative gene expression analysis, and this process requires the application of stably expressed reference genes [
6]. The use of unstable housekeeping genes as reference genes may impact the precision of the relative expression estimation of the genes of interest, potentially leading to erroneous and inconsistent results [
7,
8,
9,
10,
11]. The stability of expression of commonly used housekeeping genes may vary considerably depending on the experimental model, therefore it is desirable to ascertain the stability of reference genes for specific experimental conditions. In order to ensure the reliability of the results, it is essential that the set of housekeeping genes included in the test comprises a minimum of eight genes. [
12]. In the present study, eight housekeeping genes that are most commonly employed as reference genes were selected for analysis [
6]:
Actb (beta-actin),
Gapdh (glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase),
B2m (beta-2 microglobulin),
Rpl13a (ribosomal protein L13A),
Ppia (peptidylprolyl isomerase A),
Hprt1 (hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase 1),
Pgk1 (phosphoglycerate kinase 1),
Ywhaz (tyrosine-3-monooxygenase/tryptophan-5-monooxygenase activation protein).
The expression of housekeeping genes can be modified in response to alterations in experimental conditions [
13]. Furthermore, the onset of febrile seizures occurs at an early developmental stage when the brain is still undergoing maturation [
14]. The expression of housekeeping genes may also change with advancing age; however, the age-related dynamics of their expression have not been previously investigated. This study aimed to assess the stability of gene expression in a panel of housekeeping genes across various brain regions in rats following prolonged neonatal febrile seizures. It is known that specific regions of the brain are more susceptible to damage than others in the event of a seizure. In particular, vulnerable structures include the dorsal and ventral hippocampus, as well as the temporal and medial prefrontal cortex [
15,
16,
17]. The present study investigated the aforementioned brain regions.
3. Discussion
In the present study, we analyzed the stability of expression of eight reference genes (Actb, Gapdh, B2m, Rpl13a, Ppia, Hprt1, Pgk1, Ywhaz) in the dorsal and ventral areas of hippocampus, temporal and medial prefrontal cortex of rats that had suffered prolonged febrile seizures at an early age. Furthermore, the age-dependent expression dynamics of selected genes were investigated.
The gene with the most stable expression was identified as
Ppia. The stable genes for each brain region differed; however,
Ppia demonstrated high stability in the medial prefrontal cortex and both the dorsal and ventral hippocampus. Similarly, Swijsen and colleagues (2012) demonstrated that
Rpl13a,
Ppia, and
Tbp exhibited the greatest stability of expression in the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus using a febrile seizure model [
18]. These findings are in accordance with our results, which indicate that in the dorsal region of the hippocampus,
Rpl13a and
Ppia exhibited the greatest stability. Additionally, these genes demonstrated high stability in the rat hippocampus, as reported by Bonefeld and colleagues [
19]. As previously demonstrated, the
Ppia gene exhibited considerable stability following pentylenetetrazole-induced seizures in different rat brain regions [
17]. A lithium-pilocarpine model of epilepsy also demonstrated that
Ppia, but not
Rpl13a, exhibited consistent expression in the dorsal and ventral regions of the hippocampus [
13]. However, in an experiment utilizing the same model but with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory therapy, the
Ppia gene demonstrated instability in expression in the dorsal hippocampus [
20]. This discrepancy is likely due to the influence of the pharmacological agents administered to the experimental animals, underscoring the importance of selecting optimal reference genes for specific experimental conditions.
The expression of
Hprt1 and
Pgk1 genes was stable only in the medial prefrontal cortex of rats after febrile seizures, whereas we have previously shown that in other seizure models the mRNA expression of these genes is quite stable [
13,
17]. The fact that febrile seizures are induced at an earlier age may underlie this discrepancy.
Development of the central nervous system is known to continue into the postnatal period [
21,
22]. Early adverse effects, such as seizures, can disrupt normal brain development and lead to severe consequences in adulthood [
23]. Differential gene expression is characteristic of both normal brain development and pathological conditions [
24]. Therefore, it is important to consider that housekeeping gene expression patterns may also change during ontogeny when studying gene expression. The analysis of the expression dynamics of unstably expressed genes performed in this study showed that the mRNA production of many housekeeping genes changes with age in the brain regions studied (
Figure 3,
Figure 4,
Figure 5 and
Figure 6). This is the first time such an analysis has been performed in rats of different ages. These changes in housekeeping gene expression are a key factor to consider when assessing the expression of genes of interest in the dynamics of this model. For example, the
Gapdh gene, which is often used as a reference [
6], showed high stability in the temporal cortex and ventral, but not dorsal, hippocampus. In the dorsal hippocampal region (
Figure 3), an increase in expression of this gene was detected by postnatal day 50, which may be one of the reasons for the very low stability of
Gapdh expression. Similar data have been obtained in mice, where the level of
Gapdh gene expression in the brain varies with age [
24].
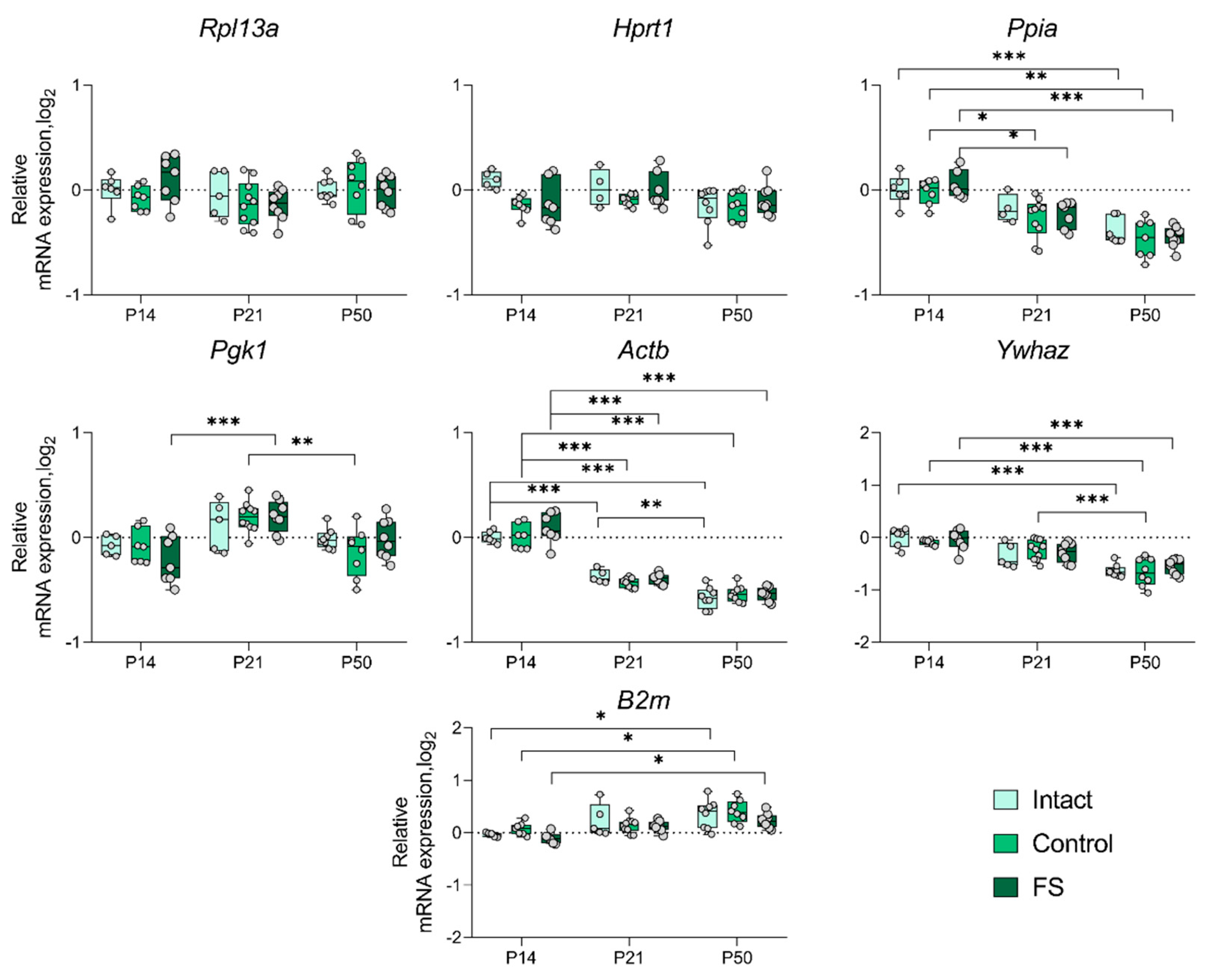
We found that febrile seizures led to increased expression of the
Rpl13a gene in the medial prefrontal cortex of rats on postnatal day 14 (
Figure 6) and in the ventral hippocampus on postnatal day 21 (
Figure 4). This gene encodes the ribosomal protein L13a [
18], and the increase in its expression may be an indication of an intensification of protein synthesis. This alteration is also characteristic of the latent phase of the lithium-pilocarpine model of epilepsy [
13] and, according to proteomic data, is observed in human epileptic brain tissue [
25]. However, in the pentylenetetrazole single seizure model, the
Rpl13a gene is highly stable in different brain regions [
17]. This may suggest that increased
Rpl13a mRNA expression may be a characteristic feature of chronic epileptic processes in the brain. Probably the medial prefrontal cortex and the ventral hippocampus are more vulnerable in febrile seizures, whereas in the dorsal hippocampus
Rpl13a is one of the most stably expressed genes. The mRNA expression of the other housekeeping genes examined did not change in the brain of rats exposed to febrile seizures.
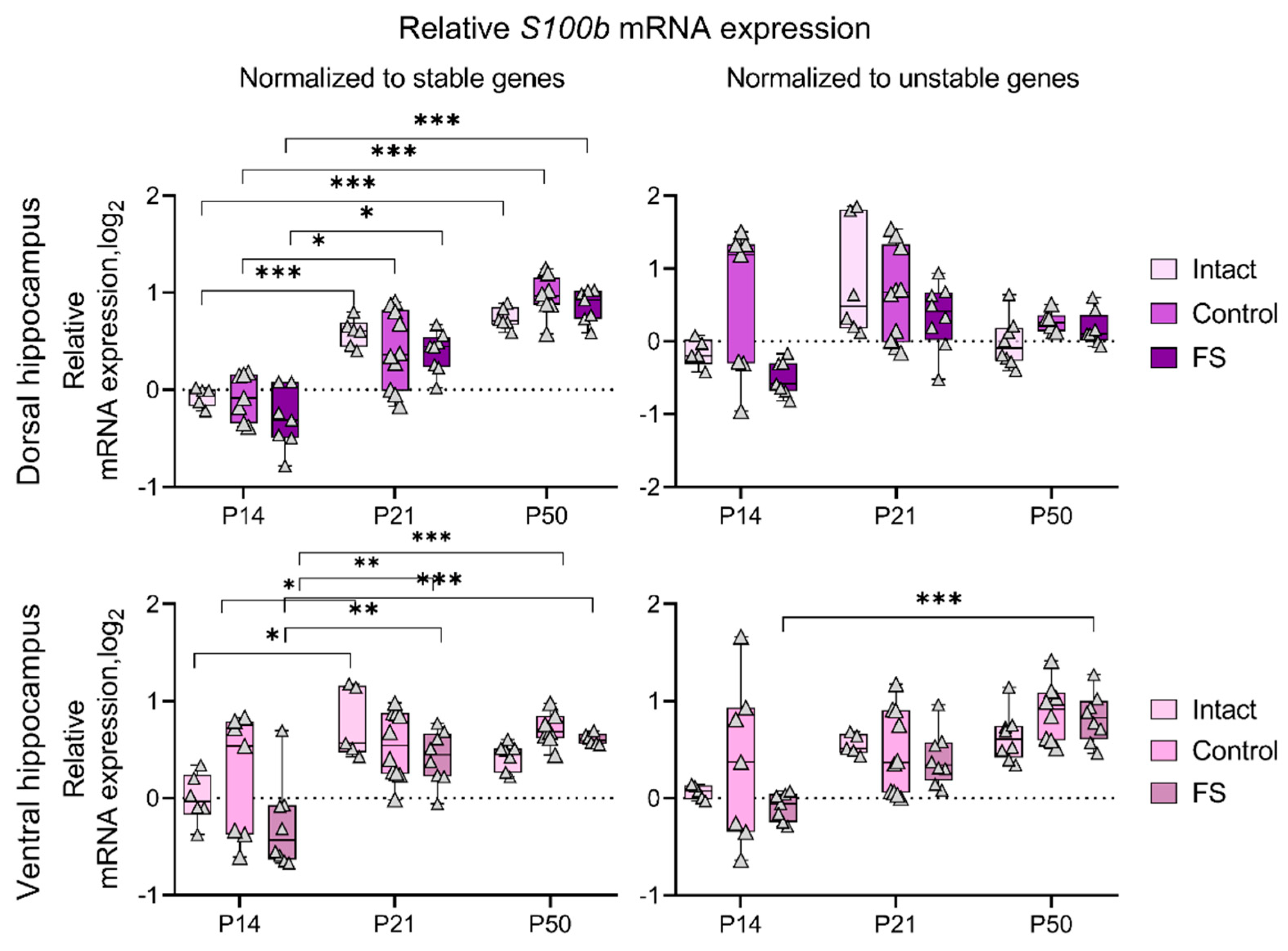
When working with RT-qPCR data, it is important to consider that normalization for unstable genes may lead to erroneous results. We demonstrated this with the example of the expression of the astrocyte marker gene
S100b (
Figure 7). It is known that in rats, mRNA expression of this gene increases by the third week of life and is maintained at this level throughout adult life [
26]. In our work, this is confirmed: when normalized to the most stably expressed genes for the dorsal and ventral hippocampus, there is an increase in
S100b expression at P21, which is maintained at P50. However, when normalized to
Gapdh in the dorsal hippocampus and
Hprt1 in the ventral hippocampus, which are the most unstable for these regions, no clear age-related changes are observed.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
The study was conducted on 70 male Wistar rats in accordance with the Rules of Animal Care and Use Committee of the Sechenov Institute of Evolutionary Physiology and Biochemistry of the RAS and the EU Directive 2010/63/EU. The animals were maintained in standard conditions with unrestricted access to water and feed. The rats were randomly assigned to groups.
4.2. Febrile Seizure Model
Febrile seizures were induced on postnatal day 11 (P11) (
Figure 8). The rats were placed at the bottom of a glass chamber, the temperature of the air within which was maintained at 45–46 °C. The rectal temperature of the animals was also monitored at the same time. Prior to the commencement of the experiment, the mean temperature of the rats was recorded at 31–33 °C. At the onset of the seizures, the temperature was observed to have risen to 38–39 °C. Following the onset of seizures, the temperature was monitored at two-minute intervals to prevent it from exceeding 41 °C [
27]. In the event of a rise in temperature above this threshold, the rats were removed from the chamber and relocated to a cooler surface until their body temperature returned to 38 °C, then they were returned to the chamber. The experiment lasted 30 minutes, during which the total duration of the seizures was a minimum of 15 minutes. To serve as a control, rats from the same litter that remained intact and rats that were weaned from the female and littermates for a similar period (30 minutes) but not heated were included in the study.
The brains were isolated for subsequent biochemical analysis on the 14th, 21st and 50th day of the rat’s life. According to the rat brain atlas [
28] the following brain structures were obtained using an OTF5000 microtome-cryostat (Bright Instrument, Luton, UK): the dorsal and ventral hippocampus, medial prefrontal and temporal cortex.
4.3. Reverse Transcription
Total RNA was extracted using the ExtractRNA reagent (Evrogen, Moscow, Russia) in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions. The resulting RNA precipitate was stored in 75% ethanol at a temperature of -20°C.
The potential genomic DNA contamination was eliminated from the samples through the use of RQ1 DNAase (Promega, Madison, WI, USA; 1 unit per sample). The RNA was resuspended in an 8 M LiCl solution for a period of 24 hours at -20 °C. Subsequently, the sample tubes were subjected to centrifugation, after which the RNA precipitate was washed on two occasions with 75% ethanol.
The precipitates were dissolved in 15 µl of water for injection. The concentration and purity of RNA in the solution were evaluated using a NanoDrop Lite spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). Absorbance at 260 nm wavelength was used to determine the concentration, while the absorbance ratio at 260/280 nm wavelengths was employed to assess the purity.
Reverse transcription was performed according to the manufacturer’s protocol in a total volume of 20 µl containing 1 µg of total RNA, 0.5 µg of oligo-dT primers, 0.25 µg of 9-mer random primers (DNA-Synthesis, Moscow, Russia) and 100 units of M-MLV reverse transcriptase (Promega). The cDNA solution was then diluted 10-fold and stored at -20 °C until the real-time PCR was initiated.
4.4. Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
Real-time PCR was performed in a total volume of 6 µl containing 0.8 µl of cDNA, 0.5 units of TaqM polymerase (Alkor Bio, Saint Petersburg, Russia) and 3.5 mM MgCl
2. The primer and probe sequences have been previously described in our research [
17,
29]. The primers and probe for the
S100b gene were also sourced from our previous work [
30]. The reactions were performed in quadruplicate.
PCR was conducted on a CFX384 Real-Time System amplifier (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA) employing the following programme: ‘hot start’ at 95°C for 15 minutes to activate the polymerase, followed by 45 to 50 cycles comprising 5 seconds at 95°C (DNA matrix denaturation) and 10 seconds at 60 to 62°C (primer annealing and elongation) with fluorescence recording.
4.5. Analysis of Gene Expression Stability
PCR data were analyzed using CFX Manager software (Bio-Rad). The cycles of quantification (Cq) were determined through the application of regression. Samples with standard deviations of Cq greater than 0.35 were excluded from further analysis. The unprocessed mean Cqs were imported into the web interface of the RefFinder
® online tool (
https://blooge.cn/RefFinder/ (accessed on 27 May 2024)). The RefFinder
® [
31] generates a stability ranking based on the geometric mean of the stability ranks obtained by four widely used algorithms: NormFinder [
32], comparative deltaCt [
33], GeNorm [
12], and BestKeeper [
34].
4.6. Relative Gene Expression Analysis
Relative gene expression was calculated using the 2
−ΔΔCt method [
35]. The data were normalized against a single stable gene or the geometric mean for the few most stable reference genes, which were determined for each individual structure.
4.7. Relative Gene Expression Analysis
The data were processed using GraphPad Prism 8.0.1 (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA) and IBM SPSS Statistics 23 (IBM, Armonk, NY, USA). The normality of the data distribution was evaluated through the implementation of the Shapiro-Wilk test. The equality of variance was checked using the Leven’s test. The exclusion of outliers was conducted through the implementation of the quartile method. Data were analyzed using two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s post hoc test. The level of significance was set at p ≤ 0.05.
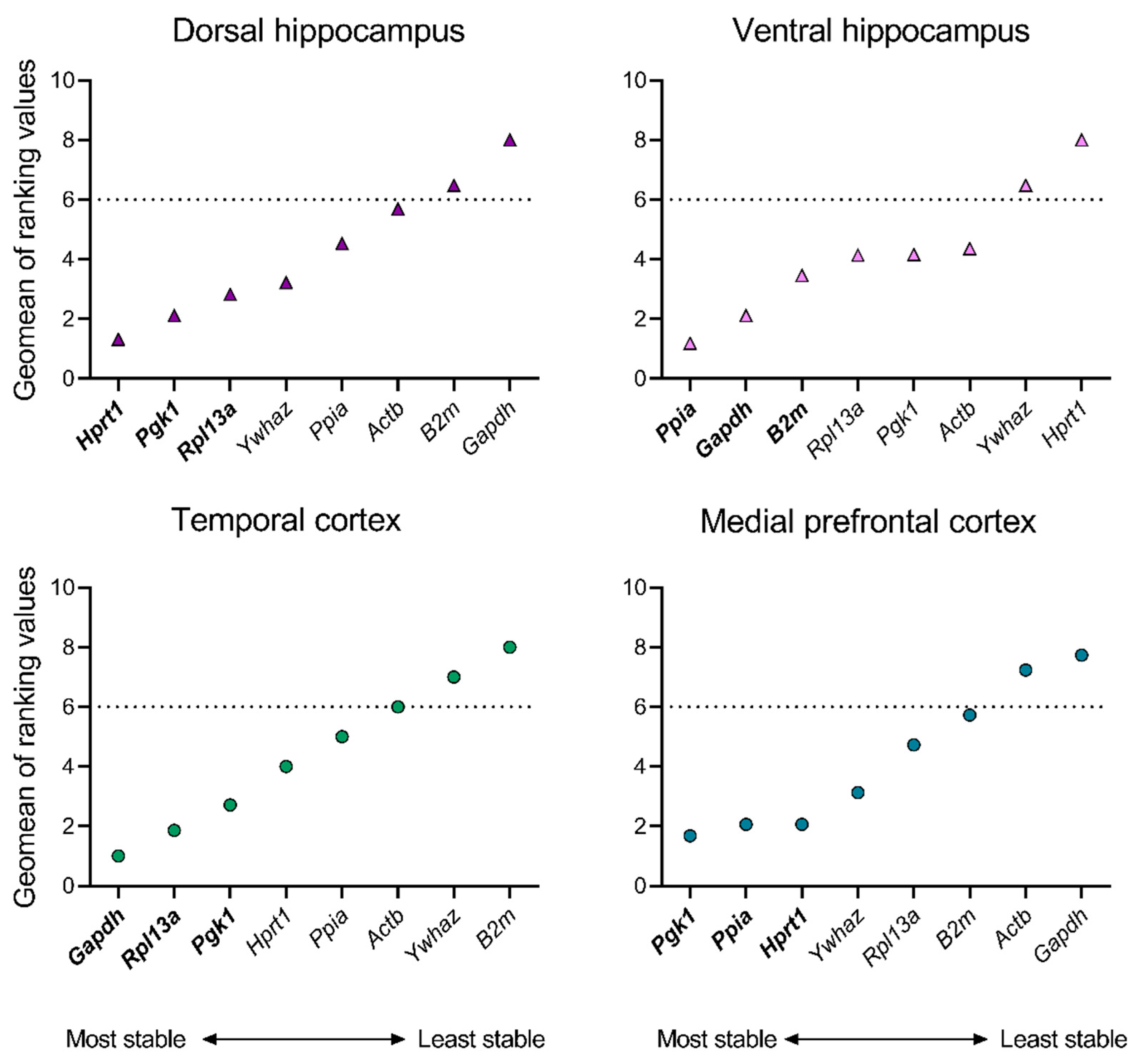
Figure 1.
Geometric means of ranking values of reference genes in dorsal and ventral hippocampus, temporal and medial prefrontal cortex of rats. The stability of mRNA production in all samples of intact animals at P14, P21, and P50 was evaluated using the online tool RefFinder (
https://blooge.cn/RefFinder/ (accessed on 27 May 2024)). The dashed line corresponds to a sufficient stability index.
Figure 1.
Geometric means of ranking values of reference genes in dorsal and ventral hippocampus, temporal and medial prefrontal cortex of rats. The stability of mRNA production in all samples of intact animals at P14, P21, and P50 was evaluated using the online tool RefFinder (
https://blooge.cn/RefFinder/ (accessed on 27 May 2024)). The dashed line corresponds to a sufficient stability index.
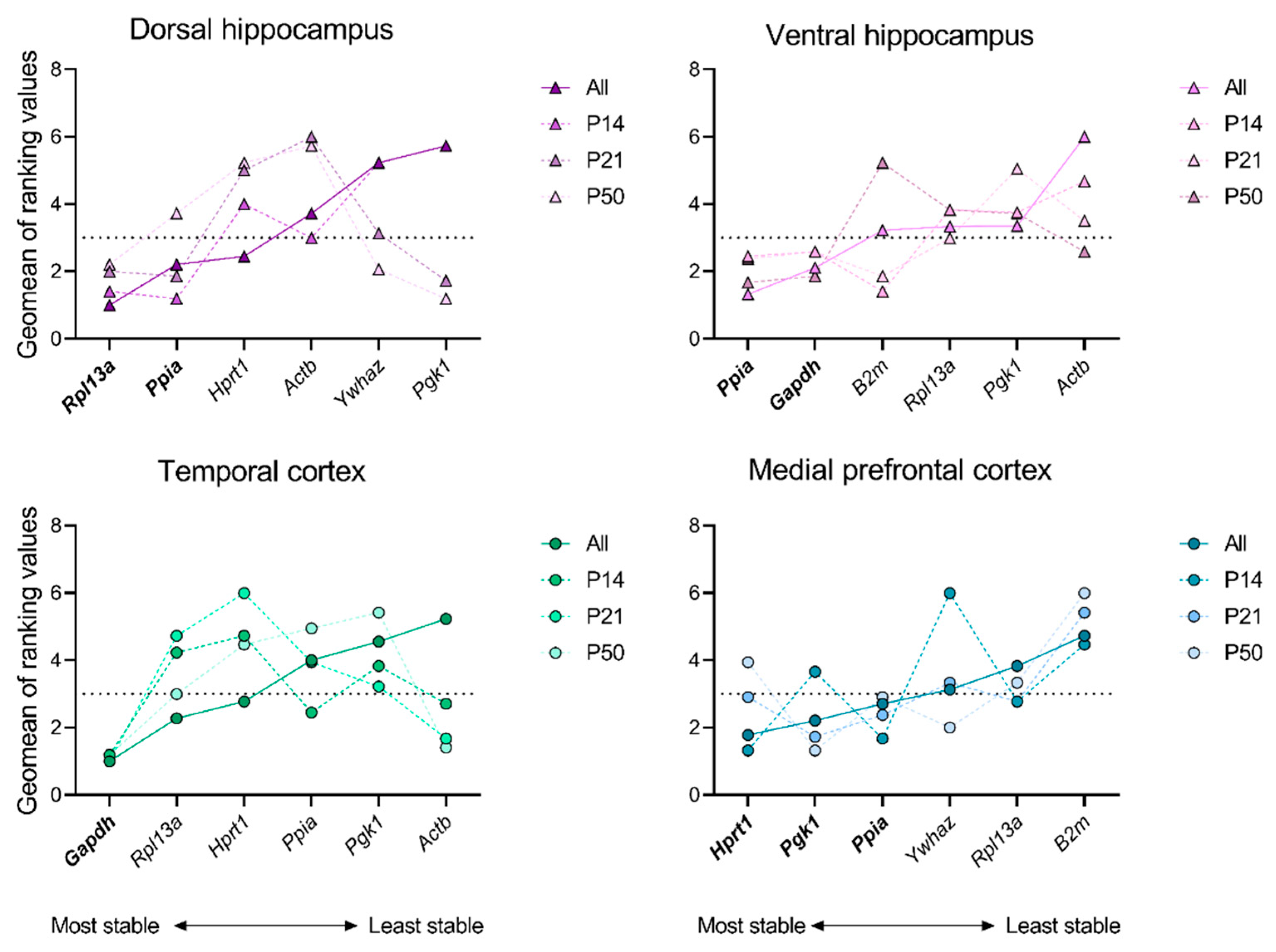
Figure 2.
Ranking values of reference genes in dorsal and ventral hippocampus, temporal and medial prefrontal cortex of rats after febrile seizures. The stability of mRNA production in all intact, control and experimental samples at P14, P21, P50 and at all ages was evaluated using the online tool RefFinder (
https://blooge.cn/RefFinder/ (accessed on 27 May 2024)). The dashed line corresponds to a sufficient stability index.
Figure 2.
Ranking values of reference genes in dorsal and ventral hippocampus, temporal and medial prefrontal cortex of rats after febrile seizures. The stability of mRNA production in all intact, control and experimental samples at P14, P21, P50 and at all ages was evaluated using the online tool RefFinder (
https://blooge.cn/RefFinder/ (accessed on 27 May 2024)). The dashed line corresponds to a sufficient stability index.
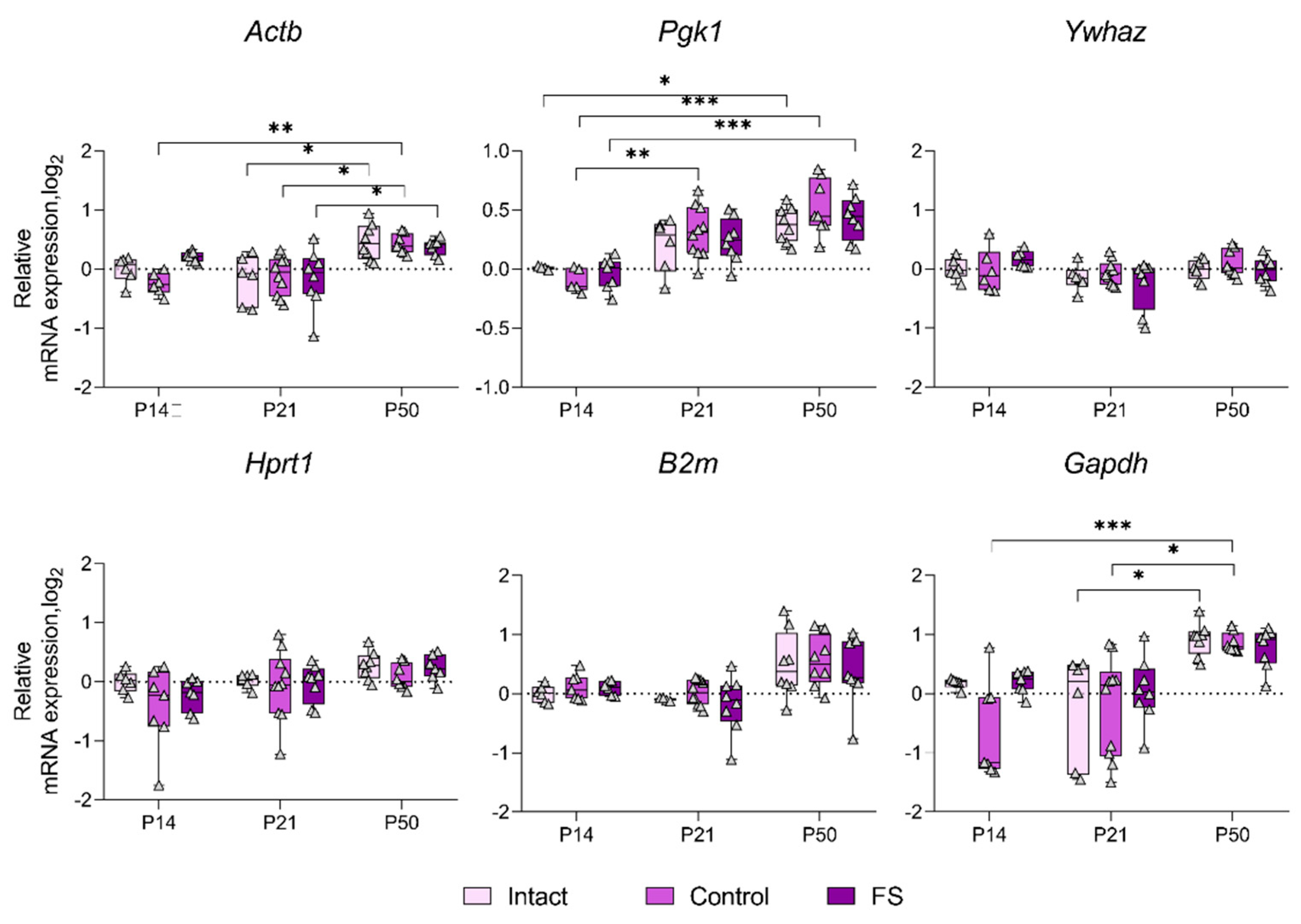
Figure 3.
Expression dynamics of unstable genes in the rat dorsal hippocampus in a febrile seizure model at P14, P21, and P50. The Rpl13a and Ppia genes were used to data normalization. Intact: intact group; Control: control group; FS: experimental group. *, **, *** – p < 0.05, p < 0.01 or p < 0.001, respectively (two-way ANOVA followed by Sidak post hoc test). The results are presented in the form of boxes, which include the median, the first and third quartiles, and individual values (triangles) with minimum and maximum values.
Figure 3.
Expression dynamics of unstable genes in the rat dorsal hippocampus in a febrile seizure model at P14, P21, and P50. The Rpl13a and Ppia genes were used to data normalization. Intact: intact group; Control: control group; FS: experimental group. *, **, *** – p < 0.05, p < 0.01 or p < 0.001, respectively (two-way ANOVA followed by Sidak post hoc test). The results are presented in the form of boxes, which include the median, the first and third quartiles, and individual values (triangles) with minimum and maximum values.
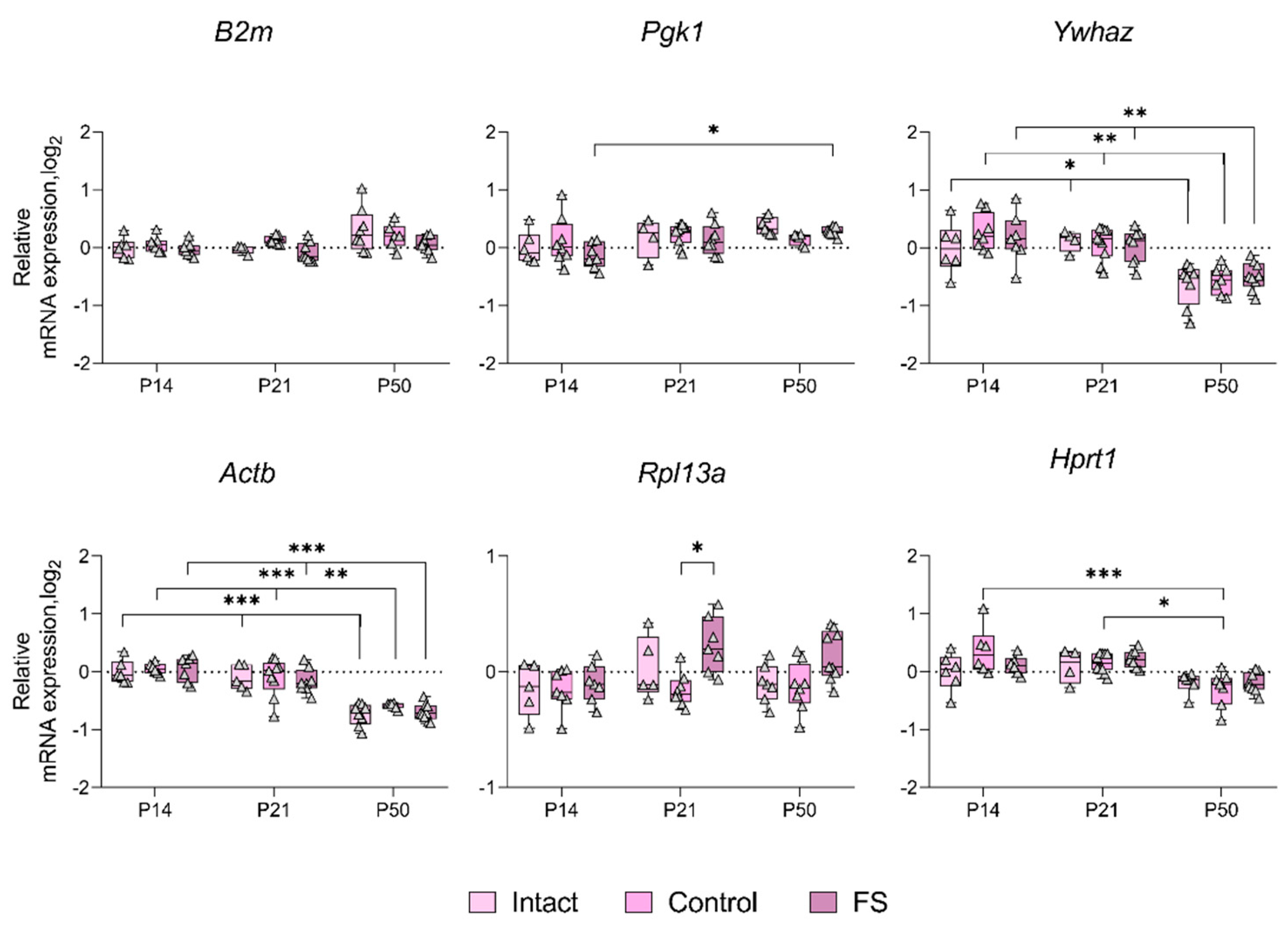
Figure 4.
Expression dynamics of unstable genes in the rat ventral hippocampus in a febrile seizure model at P14, P21, and P50. The Ppia and Gapdh genes were used to data normalization. Intact: intact group; Control: control group; FS: experimental group. *, **, *** – p < 0.05, p < 0.01 or p < 0.001, respectively (two-way ANOVA followed by Sidak post hoc test). The results are presented in the form of boxes, which include the median, the first and third quartiles, and individual values (triangles) with minimum and maximum values.
Figure 4.
Expression dynamics of unstable genes in the rat ventral hippocampus in a febrile seizure model at P14, P21, and P50. The Ppia and Gapdh genes were used to data normalization. Intact: intact group; Control: control group; FS: experimental group. *, **, *** – p < 0.05, p < 0.01 or p < 0.001, respectively (two-way ANOVA followed by Sidak post hoc test). The results are presented in the form of boxes, which include the median, the first and third quartiles, and individual values (triangles) with minimum and maximum values.
Figure 5.
Expression dynamics of unstable genes in the rat temporal cortex in a febrile seizure model at P14, P21, and P50. The Gapdh gene was used to data normalization. Intact: intact group; Control: control group; FS: experimental group. *, **, *** – p < 0.05, p < 0.01 or p < 0.001, respectively (two-way ANOVA followed by Sidak post hoc test). The results are presented in the form of boxes, which include the median, the first and third quartiles, and individual values (circles) with minimum and maximum values.
Figure 5.
Expression dynamics of unstable genes in the rat temporal cortex in a febrile seizure model at P14, P21, and P50. The Gapdh gene was used to data normalization. Intact: intact group; Control: control group; FS: experimental group. *, **, *** – p < 0.05, p < 0.01 or p < 0.001, respectively (two-way ANOVA followed by Sidak post hoc test). The results are presented in the form of boxes, which include the median, the first and third quartiles, and individual values (circles) with minimum and maximum values.
Figure 6.
Expression dynamics of unstable genes in the rat medial prefrontal cortex in a febrile seizure model at P14, P21, and P50. The Hprt1, Pgk1, and Ppia gene were used to data normalization. Intact: intact group; Control: control group; FS: experimental group. *, **, *** – p < 0.05, p < 0.01 or p < 0.001, respectively (two-way ANOVA followed by Sidak post hoc test). The results are presented in the form of boxes, which include the median, the first and third quartiles, and individual values (circles) with minimum and maximum values.
Figure 6.
Expression dynamics of unstable genes in the rat medial prefrontal cortex in a febrile seizure model at P14, P21, and P50. The Hprt1, Pgk1, and Ppia gene were used to data normalization. Intact: intact group; Control: control group; FS: experimental group. *, **, *** – p < 0.05, p < 0.01 or p < 0.001, respectively (two-way ANOVA followed by Sidak post hoc test). The results are presented in the form of boxes, which include the median, the first and third quartiles, and individual values (circles) with minimum and maximum values.
Figure 7.
Dynamics of S100b mRNA production in the dorsal and ventral hippocampus of rats in a febrile seizure model at P14, P21, and P50. Intact: intact group; Control: control group; FS: experimental group. *, **, *** – p < 0.05, p < 0.01 or p < 0.001, respectively (two-way ANOVA followed by Sidak post hoc test). The results are presented in the form of boxes, which include the median, the first and third quartiles, and individual values (triangles) with minimum and maximum values.
Figure 7.
Dynamics of S100b mRNA production in the dorsal and ventral hippocampus of rats in a febrile seizure model at P14, P21, and P50. Intact: intact group; Control: control group; FS: experimental group. *, **, *** – p < 0.05, p < 0.01 or p < 0.001, respectively (two-way ANOVA followed by Sidak post hoc test). The results are presented in the form of boxes, which include the median, the first and third quartiles, and individual values (triangles) with minimum and maximum values.
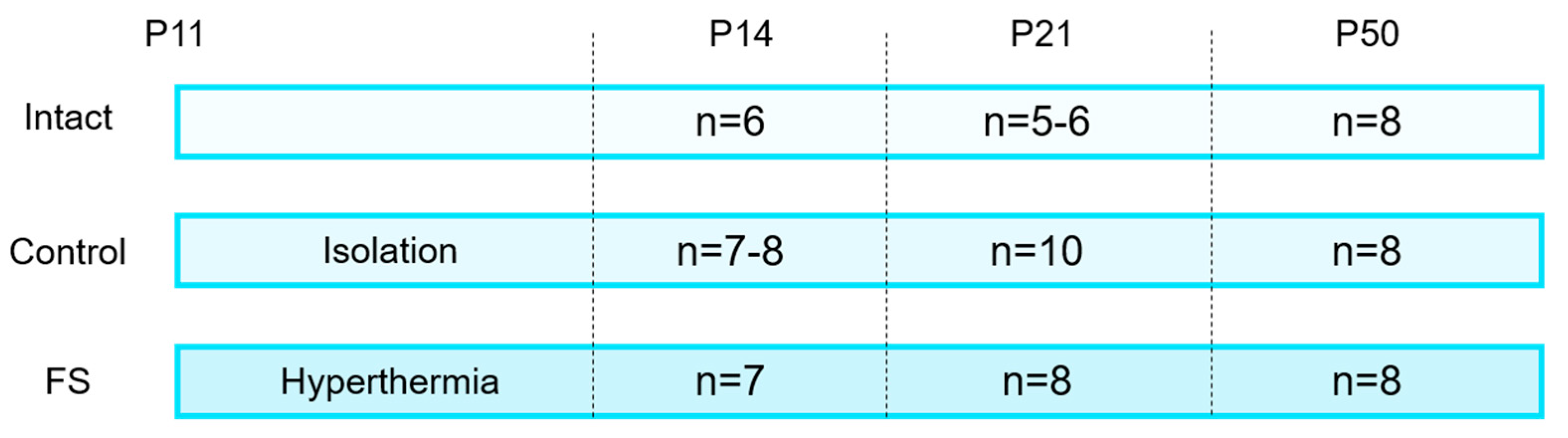
Figure 8.
The number of animals in different groups. Intact: completely intact rats; Control: littermate animals that were weaned from the female at P11 but were not subjected to hyperthermia; FS: littermate animals that were induced with prolonged febrile seizures (>15 minutes) at P11.
Figure 8.
The number of animals in different groups. Intact: completely intact rats; Control: littermate animals that were weaned from the female at P11 but were not subjected to hyperthermia; FS: littermate animals that were induced with prolonged febrile seizures (>15 minutes) at P11.