1. Introduction
The BRICS nations, namely Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa, have become prominent participants in the global economy, Representing a significant proportion of the global populace, economic production, and utilization of natural resources (Padhan 2023; Jahanger 2023). However, the rapid economic growth and industrialization in these countries has prompted worries about their environmental footprints and the long-term viability of their development strategies. The BRICS group of nations welcomed additional members in 2024. On January 1st, Egypt, Ethiopia, Iran, and the United Arab Emirates officially joined into the BRICS (Antony 2023).
The BRICS+ nations are richly endowed with a diverse array of natural resources that fuel their economic powerhouses. This economic juggernaut, with a combined GDP of $56.1 trillion (WDI 2022) , thrives on an abundant bounty of resources. Brazil's vast iron ore reserves, the second-largest globally, are the lifeblood of global steel production (USGS 2023). South Africa's mineral wealth includes diamonds, gold, and platinum group metals, making it a significant contributor to the global mining industry (Minerals Council South Africa 2023). Russia stands as a veritable storehouse of energy resources, being the world's prime exporter of natural gas and the second-largest exporter of unpolished oil (IEA 2023). Saudi Arabia has one of the greatest proven oil reserves globally, estimated at over 260 billion barrels, representing over 14% of global reserves and 33% of OPEC member nations' reserves (EIA, 2021). India's fertile plains, nourished by the mighty Ganges and Indus rivers, sustain a vast population and vibrant agricultural activities (World Population Review 2023). China, the manufacturing powerhouse of the world, harnesses its dominance in rare earth elements, accounting for over 60% of global production, to produce cutting-edge technology . Even the sun-drenched deserts of the UAE, once known primarily for their vast oil reserves, have embraced a brighter future by becoming a leader in solar power generation and deployment (Fuinhas 2023). These countries are significant contributors to global natural resource consumption and economic output, with a combined GDP of $56.1 trillion in 2022.
While the BRICS+ economies consider natural resource exploration an important part of economic activity, they have also acknowledged its substantial contribution to environmental deterioration (Padhan 2023). The mining and use of fossil fuels, minerals, and other non-renewable resources has resulted in higher glasshouse gas emissions, deforestation, and ecological imbalances. Recognizing the gravity of the situation, the BRICS+ countries have underlined the need of transitioning to renewable energy and promoting sustainable development methods. Renewable energy consumption has been identified as a potential mitigation strategy to reduce ecological footprints and promote organic sustainability (Ojekemi 2023).
In conducting an in-depth review of the existing literature, this study has identified several significant gaps that require further exploration. Firstly, current studies focus on individual BRICS nations Padhan et al. (2023), but there is a need for research covering all member countries, including recent additions. Each country's unique economic, political, and environmental factors affect how natural resource use, renewable energy, GDP, biocapacity, and ICT impact ecological footprints. Closing this gap is crucial for developing effective, country-specific policies. Additionally, Existing studies often overlook how factors like ecological footprint, natural resources, renewable energy, GDP, biodiversity, and ICT interact across BRICS+ nations. By studying these factors together, researchers can better understand their combined effects and shape sustainable policies that address environmental challenges comprehensively.
Furthermore, The expanded BRICS+ group, including countries like UAE and Ethiopia, brings diverse contexts such as UAE's advancements in solar energy and Ethiopia's rapid growth, affecting ecological footprints (Al-mulali et al. 2015). This study aims to develop tailored policies focusing on biocapacity, renewable energy, and ICT integration to promote environmental sustainability. Finally, Previous research by Udeagha & Muchapondwa (2023) and Samour et al. (2023) emphasizes the importance of integrating ICT and enhancing biocapacity to reduce ecological footprints. This study explores how natural resource use, renewable energy adoption, GDP growth, biocapacity, and ICT influence ecological footprints in BRICS+ nations, advocating for customized strategies to address these challenges.
The significance of this study is multifaceted. Firstly, by examining the ecological footprints of BRICS+ nations, it addresses key research gaps. The study explores the complex interplay between natural resource exploration, renewable energy usage, economic progress, biocapacity, and ICT in these diverse countries, which collectively represent a significant share of global GDP and population. Secondly, the study's value lies in its comprehensive analysis of how economic progress, renewable energy adoption, and natural resource exploitation influence ecological footprints. By investigating these factors within the BRICS+ context, this research sheds light on the environmental sustainability dynamics unique to these emerging economies, offering clarity on conflicting findings in existing literature. Moreover, the study provides critical insights for policymakers in BRICS+ nations, illustrating how natural resource extraction and renewable energy adoption impact ecological footprints. These findings can guide the development of targeted policies aimed at sustainable development, greenhouse gas reduction, and the transition to greener economies. Finally, in alignment with global environmental goals and sustainable development agendas, such as the Paris Climate Agreement and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), this study contributes empirical evidence on the benefits of renewable energy use and the potential risks associated with unchecked natural resource exploitation.
The study aims to understand the complex relationships between natural resource exploitation, renewable energy adoption, and economic progress in these rapidly industrializing and urbanizing economies, where ecological footprints are a growing concern. The distinct findings in the literature addressing the effects of natural resource utilization (Zafar 2019; S. T. Hassan 2019), renewable energy use (Al-mulali 2015 and Charfeddine & Mrabet 2017), and economic growth (Danish 2019; Acar 2023) underscore the need for a focused analysis within the BRICS+ framework. Additionally, this study explores the role of biocapacity in ecological sustainability, addressing conflicting views on its impact (Sarkodie 2021 ; Pandey 2020). By analyzing these patterns, the study seeks to provide useful insights for designing long-term strategies that balance economic advancement and environmental preservation in BRICS+ countries. Furthermore, it emphasises the importance of implementing sustainable energy regulations, eco-innovations, and green financing efforts to achieve a harmonious equilibrium between economic progress and environmental preservation.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Natural Resources with Ecological Footprint
Several studies used economic models to examine the relationship between the utilis Several studies used economic models to examine the relationship between the utilization of natural resources and the ecological footprint across different areas. For example, S. T. Hassan et al., (2019) To study this link in Pakistan, we used the Granger causality techniques (ARDL) and (VECM). Their findings unequivocally showed that the utilization of resources of nature has a persistent positive influence over ecological footprints. In inverse, Zafar et al. (2019) ARDL was utilized as an alternative analytical framework to evaluate the United States. Their studies revealed a significant and enduring inverse relationship between the ecological footprint and natural resource consumption. Furthermore, Neifar et al. (2024) examined data from Morocco using the ARDL model, dynamic ARDL (DYNARDL), (KRLS), and (FDC) techniques. The findings of their study showed a statistically significant and opposite correlation between the availability of natural resources and the ecological footprints in the immediate term. Similarly, Zia (2021) adopted the innovative dynamically simulated ARDL technique to analyze data from China spanning the years 1985 to 2018. Based on their research, economic growth and biodiversity had significant beneficial effects on the environmental impact, both in both the immediate and future.
Moreover, Jie (2023) discovered a favorable connection to natural wealth and ecological impact. Their findings Their research contributes to our understanding of how resource use and environmental sustainability interact. Additionally, A. Hassan et al. (2023) suggest the use of the Cross-Sectional ARDL (CS-ARDL) method to differentiate the impacts of natural resources on the ecological footprint in developed as well as emerging nations. Their study found that energy resources have a tendency to augment the ecological footprint in developing economies as time progresses, while concurrently diminishing the ecological footprint in developed economies. Lastly, He et al. (2024) He (2024) examined how a lack of natural resources and mineral rentals affected the environmental impact of states with high emissions. The findings of their study showed an important negative connection between mineral rents and foreign trade with ecological footprints, whereas government spending and natural resource depletion have a positive relationship.
H1: Natural resources with ecological footprint.
2.2. Renewable Energy Use with Ecological Footprint
Multiple studies provide evidence that energy consumption exerts a beneficial influence on the environment. For instance, Al-mulali et al. (2015) the fixed effects (FE) and generalized method of moments (GMM) techniques. Their findings show a statistically significant and positive correlation regarding energy consumption and the ecological footprint of countries, regardless of their socioeconomic status. Similarly, Charfeddine et al. (2017) discovered a clear link among consumption of energy and ecological consequences into Qatar. Charfeddine & Mrabet (2017) conducted a survey in 2017 across 15 nations in the MENA region and noticed persistent sustainable connection with utilization of energy and ecological consequences. Likewise, Sarkodie (2018) employed FE and RE models to demonstrate that higher energy use is associated with a higher ecological impact. Moreover, Imamoglu et al. (2018) employed the FMOLS, DOLS, and ARDL methodologies analyzing Turkey, uncovering a significant and positive influence of usage of energy and environmental impact. Similarly, Zafar et al. (2019) utilized ARDL method to investigate the United States and found evidence supporting the positive and sustained correlation between energy usage and ecological impact. Conversely, studies indicate that utilizing energy has a negative effect on the Environmental footprints (Kongbuamai et al., 2020).
Ozturk et al. (2016) employed Gaussian Mixture Model and System Panel GMM techniques to study over 140 nations. Their research showed that there were both favorable and unfavorable correlations between consumption of energy and ecological footprint throughout various income levels. Additionally, Alola et al. (2019) deployed Panel Mean Group Autoregressive Distributed Lag (PMG-ARDL) method for analyzing the nations within the European Union. Their research showed a consistent and positive association between the ecological print and the amount of energy consumed, whether recyclable and non-recyclable. Applying instrumental variable regression, Kongkuah et al. (2023) examined data from the GFN and WDI from 2021. The results showed a noteworthy negative correlation between the utilisation of renewable energy and its impact on the environment. A study conducted in Iran unveiled a unidirectional causal connection between usage of energy and environmental impact (Wang 2019). Similarly, Mishra & Jena (2019) conducted an analysis of eight Asian economies and found a significant and beneficial linkage between consumption of energy and its impact on the environment.
Arouri et al. (2012) employed bootstrap a panel root-level testing and cointegration methods to analyze the countries in the (MENA) region. The findings demonstrate substantial and sustained impact of energy usage on the environmental footprint. Another study employed advanced econometric methods. The long-term cointegration research discovered that renewable energy usage favorably influences environmental quality, whereas using non-renewable energy has an adverse effect (Ivan A. Duran et al. 2023). Lastly, Padhan et al. (2023) deployed parametric and non-parametric techniques to evaluate data from BRICS-T countries in 2017. This research revealed that renewable energy and eco-innovations considerably minimize environmental effect.
H2: Renewable energy use with ecological footprint.
2.3. Economic Growth with Ecological Footprint
Several studies have employed various econometric methods to examine the effects of growth in the economy on environmental footprint. For instance, Danish (2019) employed the autoregressive distributed lag (ARDL) approach to analyze data from the years 1971 to 2014. The findings of their study show that there is a positive correlation between economic growth and bio-capacity, both of which contribute to the expansion of ecological footprints, subsequently leading to environmental degradation. Similarly, Ahmed et al. (2022) employed advanced statistical methods to examine the correlation among democracy, environmental regulations, economic growth, and the ecological footprint (EF) in the G7 nations from 1985 to 2017. The findings showed that economic progress has a beneficial effect on the ecological footprint (EF), while democracy and environmental regulation contribute to ecological sustainability by reducing the EF.
Moreover, Alola et al. (2022) discovered a favorable relationship between (EG) and (EF) in their analysis of EF patterns from 1971 to 2016. This observation is consistent with the conclusions drawn by Balsalobre-Lorente et al. (2018). The empirical findings reported by (Magazzino, 2024) demonstrated a relationship between economic growth and CO2 emissions that follows an N-shaped pattern. Furthermore, Neifer (2024) used advanced econometric approaches, including DYNARDL, KRLS, and FDC tests, to analyses the correlation regarding Morocco's growth in an economy with its EF from 1980 to 2021. Their findings point to a robust, lasting positive correlation between economic growth and ecological sustainability. Additionally, Vu . (2023) conducted a comprehensive analysis in the MENA region spanning about 1990 to 2017, employing the CS-ARDL methods. The results suggest that an increased EF is a significant indicator of how economic growth and globalization are aggravating environmental problems. Similarly, Shahbaz. (2023) showed that the expansion of financial growth and economic progress increases the EF.
Likewise, Acar et al. (2023), employed the autoregressive distributed lag (ARDL) bound test method, incorporating structural breakdowns, to examine the association between economic freedom (EF), financial development, and economic progress in Azerbaijan during the period of 1996 to 2017. Their findings reveal that the relationship between economic growth and EF deteriorated at first, but then improved. Furthermore, Yasmeen et al. (2023) found that the early phases of economic progress have a minimal effect on diminishing energy poverty and EF. Finally, Gabbi (2021) Gabbi (2021) emphasized the critical significance of aligning economic expansion with ecological constraints. They emphasized the necessity for growth models that adhere to natural limitations to guarantee long-term sustainability.
H3: Economic growth with ecological footprint.
2.4. Biocapacity with an Ecological Footprint
Biocapacity, perceived as a type of ecological wealth, significantly impacts geopolitical competitiveness, international relations, and community quality of life Nic Colucci et al. (2012). For instance, Sarkodie, (2021) employed novel cross-country time series approaches to examine the correlation between biocapacity, ecological efficiency, and carbon footprint from a socio-economic standpoint. The results show that improved bio-capacity has a beneficial impact on ecological performance. Furthermore, there is an increasing quantity of research that evaluates this connection between biocapacity and ecological sustainability in response to the diminishing Bio-capacity of nations as a major environmental concern. However, Danish et al. (2019) discovered that, in Pakistan, bio capacity played a role in causing an expansion of the ecological footprint. Similarly, Pandey et al. (2020) discovered interesting evidence in Asia showing that biocapacity plays a significant role in causing environmental contamination.
Additionally, Marti & Puertas (2020) identified a similar pattern in Africa, whereas Nathaniel, (2021) established this correlation among G7 nations. These studies collectively emphasize that Bio-capacity speeds up environmental degradation in many geographical and economic situations. Further, Ünal & Aktuğ (2022) separated their study into two categories: developing economies and G20 developed nations. According to their findings, Bio-capacity significantly affects emerging countries' both in the short and long terms ecological footprints (EF). Based on the findings, developed economies that are part of the G20 experienced a short-term positive impact on EF because of bio-capacity. Finally, Yang & Khan (2022) conducted a study that included 30 nations associated with the International Energy Agency. The findings of their study revealed, in both the short and long term, biological capacity has a positive and enduring impact on the augmentation of ecological footprint (EF).
H4: Biocapacity with ecological footprint.
2.5. ICT with Ecological Footprint
Research on the environmental effects of ICT generated inconsistent results. Certain studies provide evidence of ICT's capacity to mitigate the carbon footprint, while others contend that it could have detrimental effects on nature Al-Mulali. (2015); Añón Higón. (2017). Such as, A. Hassan et al. (2023) demonstrates that ICT assists decreasing the environmental impact in developing nations over time, while the CS-ARDL technique consistently reduces the EF in developed countries. Similarly, Asongu (2018) conducted a panel data analysis to evaluate the association between ICT and EF in EU-5 nations from 1961 to 2016, discovering that ICT improvement reduce EF. Furthermore, Huang (2022) examined the relationship among ICT, renewable energy, economic complexity, human assets, financial growth, and ecological effects within the E-7 and G-7 countries, revealing that ICT and human capital transfers in G-7 countries significantly decrease ecological footprints.
Additionally, Kahouli et al. (2022) identified a long-term adverse correlation among renewable energy, usage of electricity, trade of technology, total factor productivity, ecological footprint, with ICT having a negative short-term effect on the environmental footprint. Similarly, Opoku-Mensah et al., (2024) examined the ecological footprint of (SCO) nations in the combined impact of ICT and green institutional quality. Their findings reveal that integrating green institutional governance with ICT lowers the EF by 0.0748%, emphasizing the importance of ICT and strong environmental governance in minimizing ecological consequences. Moreover, Recent literature has emphasized the significance of renewable energy and ICT in reducing EF. For instance, Kahouli (2022) revealed a substantial adverse link between the long-term environmental effects of ICT utilization and the short-term ecological footprints.
Conversely, Kongbuamai et al. (2023) found that in N-11 countries, increased ICT use speeds up environmental degradation in the long run, demonstrating ICT's major effect on ecological viability. Furthermore, Kazemzadeh (2023) employed the STIRPAT method and quantile panel regression to investigate the effects of economical difficulty, growth level, and ICT on rising nations' ecological footprints, revealing a significantly adverse effect of ICT among all scales. Additionally, Onwe (2024) applied second-generation econometric methodologies, the study examined ICT, economic complexity, technical invention, renewable energy utilization, and the EF in G7 nations, revealing that ICT factors had a considerable impact on ecological footprints. Lastly, Raza et al. (2022) Raza, et al. (2022). QARDL was used to assess the short and long-term effects of Pakistan's ecological footprint and factors such as fossil fuels, energy, financial depth, commerce, GDP, and information and communication technologies. They discovered that ICT has a considerable influence on ecological well-being throughout different phases of Pakistan's ecological footprint.
H5: ICT with ecological footprint.
3. Methodology
3.1. Conceptual Framework
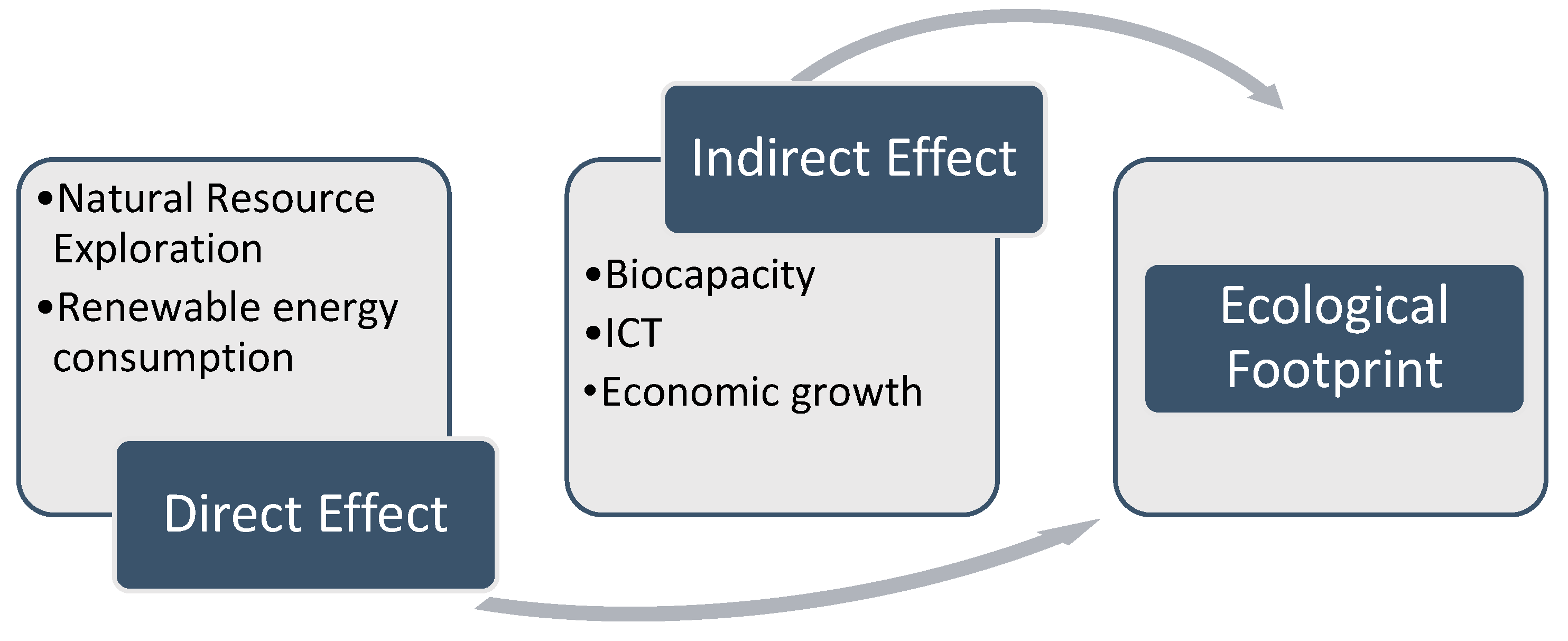
The theoretical framework of this study investigates the direct and indirect effects of natural resource extraction, renewable energy consumption, economic growth, and ICT on the ecological footprint in BRICS+ nations. This framework is illustrated in
Figure 1. Firstly, the impact of natural resource exploration on the ecological footprint is mixed, with some studies indicating a long-term positive impact (S. T. Hassan et al., 2019); (Zia et al., 2021) and others showing a negative short-term impact (Neifer et al. 2024). Further, renewable sources of energy use, which refers to the proportion of renewable energy in the overall consumption of energy, contributes much to reducing the impact of the environment. Renewable sources, such as hydroelectric power, wind, and solar, can alleviate climate change and reduce the environmental impact ( Al-mulali et al. 2015); (Charfeddine 2017); (Kongkuah, 2023). Moreover, economic growth elevates the ecological footprint due to increased resource consumption and waste generation (Danish et al., 2019); Ahmed et al. (2022); Alola et al. (2022).
However, ICT has a mixed effect on the ecological footprint. Some studies emphasize the potential of ICT to decrease environmental impact by improving efficiency and fostering innovation (A. Hassan et al. 2023); Asongu et al. (2018) while others suggest it may exacerbate Ecological deterioration Kongbuamai et al. (2023). Lastly, bio-capacity, measure of ecological wealth, significantly affects environmental sustainability. Increasing bio-capacity enhances ecological performance, reducing the ecological footprint Sarkodie, (2021); Ünal & Aktuğ (2022) whereas diminishing bio-capacity often leads to increased ecological degradation Danish. (2019); Pandey (2020) ; Nathaniel, (2021).
3.2. Data Sources and Variables Description
This study employed panel data from 1991 to 2019 in order to examine the link between natural resource extraction, renewable energy consumption, economic growth, biocapacity, information, communication and technology, and ecological footprint in BRICS+ countries. The data was gathered from a pair of databases: the World Bank's online database called World Development Indicators (WDI, 2022) and the Global Footprint Network (GFN, 2023).
Table 1 presents the examined variables together with their respective sources.
3.3. Econometric Analysis
3.3.1. Model Development
This study examines the association with natural resource exploitation (NRE), renewable energy consumption (REC), economic growth (GDP), biocapacity (BIO), information communication and technology (ICT), and ecological footprint (EFP). The function model has the following general form:
where, EFE indicates ecological footprint, NRE denotes natural resource exploration, REC stands for renewable energy consumption, GDP represents economic growth, BIO shows biocapacity, while ICT represents information, communication and technology.
The equation that establishes the associations between the variables under examination is established afterward (Shakib et al., 2022). Equation 1 serves as a foundational model, chosen for its suitability in capturing the nuances of the relationships. To enhance clarity and statistical robustness, the model is reformulated using natural logarithms:
where, the superscript ‘i’ denotes the country index within the panel, and ‘t’ represents the time dimension. The notation ‘ln’ signifies the natural logarithm, ‘
’ indicates the intercept, ‘
’ represents the coefficients of the explanatory variables, and ‘
’ denotes the error term in Equation 2.
In the initial phase of analysis, a comprehensive tabulation of descriptive statistics was conducted for each variable to assess central tendencies and dispersions. This step provided insights into the basic characteristics of the data set, laying a foundation for subsequent analytical procedures. Following this, a correlation analysis examined linear relationships among the variables and detected potential multicollinearity. The severity of multicollinearity was further investigated using the Variance Inflation Factor (VIF) analysis, quantifying its impact on the econometric model's robustness and reliability. Additionally, tests for heterogeneity within the panel data were performed to ensure the validity of subsequent analyses, accounting for potential variations across cross-sectional units and supporting the study's findings' accuracy and generalizability. Pesaran's CD test (Pesaran, 2004), Friedman's test (Friedman, 1937), and Frees' test (Frees, 1995) were employed to examine cross-sectional dependency within the panel data, providing insights into the strength of dependencies across panel units.
Detection of cross-sectional dependencies necessitates advanced unit root tests due to potential biases in conventional tests. Therefore, second-generation unit root tests, specifically the Cross-sectional Im, Pesaran, and Shin (CIPS) test (Pesaran, 2007) and the Cross-sectional Augmented Dickey-Fuller (CADF) test (Pedroni, 1999)(Pesaran, 2007) were utilized. These tests adjust for cross-sectional dependencies by incorporating cross-sectional averages, offering more reliable insights into the data's stationarity properties. The CIPS test extends the traditional Im, Pesaran, and Shin (IPS) test by accommodating cross-sectional dependence, while the CADF test enhances the robustness of the Augmented Dickey-Fuller (ADF) check when cross-sectional dependencies are present.
The study used the Pedroni (1999) and Kao Residual Cointegration tests Kao (1999) to investigate long-term cointegration among the selected variables, building on the results of these unit root tests. The Pedroni test allows for heterogeneity across cross-sectional units in short-term dynamics and long-term cointegrating vectors, whereas the Kao Residual Cointegration test assumes homogeneity in long-term cointegrating relationships. These tests validated the theoretical framework by confirming how variables move together over time and verifying the presence of long-term cointegration, crucial for understanding sustainable relationships among economic variables.
3.4. The Regression Analysis
This study explores the correlation between economic growth, information and communication technologies, biocapacity, renewable consumption, and natural resource exploration. In the present investigation, annual numerical data were analysed using Dynamic Ordinary Least Squares (DOLS), Canonical Cointegrating Regression (CCR), and Fully Modified Ordinary Least Squares (FMOLS). The FMOLS analysis, which was devised by Hansen and Phillips (1995), modifies the least squares approach to account for the consequences of cointegration on autocorrelation and endogeneity in the variables that are explained. The problems associated with high-power regression of linear parts, unit root issues, and integrated processes are addressed by this method. The FMOLS test is useful for determining causal linkages between variables across a wide range of values and for addressing concerns such as autocorrelation and variance shifts. In this case, the constant term compensates for any potential link between error term differences and explanatory factors.
Similarly, Park (1992) developed the Canonical Cointegrating Regression (CCR) system, It converts numerical data utilizing the stationary component of a linked system. This transformation guarantees that the cointegrating link created by the cointegration model is preserved. The CCR fix separates error terms in cointegrating methods coming from zero-regularity explanatory variables, resulting in significantly stronger tests of chi-square and more efficient estimations. By investigating the impact of correlation, both the FMOLS and CCR methodologies achieve asymptotic cohesiveness. The long-term elasticity of the coefficients is evaluated using these methods, as illustrated in Equation (13), which leads to a comprehensive and reliable analysis of the cointegration relationships between the variables.
The study employed Dynamic Ordinary Least Squares (DOLS), an enhanced version of Ordinary Least Squares (OLS), in addition to FMOLS and CCR, as suggested by Kao and Chiang (2000) and Stock and Watson (1993). To address endogeneity, the DOLS technique comprises independent variables, as well as leads and lags of their initial differences, and standard errors are computed using a robust autocorrelation covariance matrix of errors. DOLS estimators give trustworthy statistical significance measurements. The evaluation of the endogenous variable on the exogenous variables in levels, leads, and lags has become an advantageous approach for addressing varying integration orders, enabling the inclusion of distinctive elements in the cointegrated framework. One of the primary benefits of the DOLS approach is its capacity to incorporate various factors in varying orders of integration within the cointegrated structure. It is capable of addressing issues such as shortened sample bias, endogeneity, and autocorrelation by integrating information regarding the timing of every variable of explanation observation.
The subsequent equation is employed to quantify the outcomes of FMOLS and DOLS:
where
and
. In this context, ‘
’ denotes the long-run stationarity matrix, accompanied by ‘
’, which indicates the rejection of covariance presence among error terms pertinent to stationarity. Furthermore, ‘
’ signifies the adjusted covariance terms among the independent variables within the panel data.
In order to confirm the robustness of the findings, a panel data robustness test was conducted using the two-step Generalised Method of Moments (GMM) approach. Lagged variables were implemented as tools to mitigate endogeneity and errors (Arellano & Bond 1991). Lastly, diagnostic techniques were used to validate results after determining the long-term effects of variables. These consisted of the Wooldridge examination for autocorrelation, the Ramsey RESET examination for model stability, and the Breusch-Pagan / Cook-Weisberg examine for heteroskedasticity. Figure 2 illustrates the comprehensive methodological framework implemented in this investigation, which incorporates a variety of tests and methodologies to facilitate meticulous analysis and interpretation of findings.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Descriptive Statistic
The summary statistics for the variables are presented in
Table 2, which includes the results of normality tests such as skewness and kurtosis. The descriptive analysis reveals that the variables exhibit positive skewness, indicating that future data points for all variables are expected to be higher than one. However, the kurtosis statistics reveal that all variables, except for lnGDP, are leptokurtic, with values less than 3. Additionally, the pairwise correlation analysis presented in
Table 3 shows that lnEFP is positively correlated with lnGDP, lnBIO, and lnICT, while lnNRE and lnREU are negatively correlated with lnEFP. This suggests a modest association of all series with lnEFP. Furthermore, a higher Variance Inflation Factor (VIF) value, presented in
Table 4, indicates a greater likelihood of multicollinearity, which requires further investigation. A VIF value exceeding 10 suggests significant multicollinearity that needs to be addressed. The findings suggest that multicollinearity doesn't constitute a substantial concern when the VIF value is less than 10.
4.2. Heterogeneity of Slope Test
Neglecting the heterogeneity of slope coefficients can result in inaccurate estimations and biased conclusions. Consequently, the
Table 5 demonstrates that the alternative hypothesis of slope coefficient heterogeneity is supported, as evidenced by the Pesaran and Yamagata (2008) test. To address heterogeneous scenarios and account for cross-sectional dependency, robust estimators were employed.
4.3. Cross Sectional Dependence Test
The results of the a total of four cross-sectional dependency experiments are presented in
Table 6. The cross-sectional test results indicate that the null hypothesis of cross-sectional independence experienced refuted, as evidenced by statistically significant P-values. The refusal implies that the variables under investigation exhibit cross-sectional dependency at the 1% and 5% significance levels. Consequently, the econometric estimations were adjusted to account for cross-sectional dependency, which corroborated the conclusion that there was an adequate amount of data to substantiate a cross-sectional correlation between the variables in each of the groups in the error terms.
4.4. Unit Root Test
The panel root test findings support the existence of a consistent order of integration, as illustrated in
Table 7. The null hypothesis of a unit root is confirmed independent of temporal trends or levels by the use of second-generation panel unit root tests (CIPS and CADF) to resolve the issue of cross-sectional dependence (CSD). The six variables remained significant at the 1%, 5%, and 10% levels after the initial difference. In econometric terminology, the variables are subsequently determined to be of order 0, I(0), followed by of order 1, I(1). This conclusion enables additional investigation of the long-term equilibrium relationships between each factor.
4.5. Pedroni and Kao Residual Cointegration Test
Each of the variables were determined to be stationary at the first difference. It is imperative to establish the stationarity of variables in order to proceed to the subsequent phase of panel cointegration testing.
Table 8 indicates that the null hypothesis of no cointegration is rejected by four out of seven statistics, as determined by the Pedroni tests conducted within and between the dimensions respectively. This conclusion substantiates the long-term cointegration of the ecological footprint, ICT, economic growth, biocapacity, renewable energy consumption, and natural resource exploitation. The Kao ADF cointegration test also verifies the existence of this long-term cointegration relationship.
4.6. FMOLS, DOLS, and CCR
The Ecological Footprint and determined explanatory variables, including Natural Resource Exploration, Renewable Energy Consumption, Economic Growth, Biocapacity, and Information and Communication Technology (ICT), were analysed using Canonical Cointegrating Regression (CCR), Dynamic Ordinary Least Squares (DOLS), and Fully Modified Ordinary Least Squares (FMOLS). The results of these robust econometric approaches are presented in
Table 9, which offers substantial insights into the dynamics of these variables in the context of BRICS states.
The FMOLS findings show that Natural Resource Exploration has a considerable positive influence on the ecological footprint, with a coefficient of 0.342, which is statistically significant at the 1% level. This research demonstrates that increased exploration and extraction of natural resources greatly contribute to environmental degradation, which is consistent with the decisions of Hasan et al (2023), Jie et al (2023), and Zia et al (2021). In BRICS+ countries, rapid industrialization and the pursuit of economic growth often drive extensive natural resource exploitation, thereby exacerbating environmental impacts.
On the contrary, renewable energy utilisation significantly minimises the ecological footprint, as indicated by a negative coefficient of 0.467, which also proves statistically noteworthy at the 1% level. This report highlights the paramount importance of renewable energy in mitigating environmental issues, corroborating the findings of previous research conducted by Ivan A. Duran et al (2023), Kongbuamai et al (2020), Kongkuah, (2023), and Padhan et al (2023). The use of renewable energy sources in BRICS nations diminishes reliance on fossil fuels, thereby mitigating carbon emissions and environmental deterioration.
Moreover, there is an important and beneficial connection between Economic Growth and the ecological footprint, as evidenced by a correlation coefficient of 0.743. This highlights the ecological expenses associated with economic expansion, confirming the conclusions of recent research conducted by Ahmed et al (2022), Alola et al (2022), Danish et al (2019), and Neifar et al (2024). The BRICS+ countries often experience a rise in economic growth, which is typically accompanied by an increase in industrial activity, development, and consumption levels. These factors contribute to a higher level of environmental stress and larger ecological footprints.
Similarly, there is an upward correlation between biocapacity and the ecological footprint, with a coefficient of 0.196. This means that increased biocapacity is associated with more resource utilisation and environmental effect. The results align with the research conducted by Pandey et al (2020), Sarkodie (2021), Ünal & Aktuğ (2022), and Yang & Khan (2022). BRICS+ countries possess. BRICS+ countries have abundant natural resources, but their excessive use typically results in a larger ecological impact, emphasising the importance of sustainable resource management.
However, Information and Communication Technology (ICT) does not exhibit a significant effect Regarding the ecological imprint in the FMOLS model, validating the findings of recent studies by Al-Mulali et al (2015), Añón Higón et al (2017), Onwe et al (2024), and Opoku-Mensah et al (2024). This may be due to the varied stages of ICT development across BRICS+ nations, where the potential environmental benefits of ICT, such as improved energy efficiency and reduced resource consumption, are not yet fully realized or widespread.
The DOLS technique offers comparable insights, as it incorporates leads and delays of explanatory variable initial differences to account for potential endogeneity and autocorrelation. Exploring natural resources has a positive impact on the ecological footprint (coefficient of 0.312), which is statistically significant at the 5% level. The negative impact of renewable energy use remains substantial (coefficient of -0.378). The ecological footprint continues to be significantly positively influenced by economic growth, with a value of 0.712. The ecological footprint is positively affected by biocapacity, as evidenced by its value of 0.251. Information and communication technology (ICT) does not have a significant impact on the ecological footprint, as demonstrated by the DOLS model.
The findings of FMOLS and DOLS are substantiated by the CCR approach, which transforms data by utilising the stationary component of an interconnected system to provide efficient estimations. Exploration of natural resources has an advantageous effect on the ecological footprint (coefficient of 0.321, statistically significant at the 1% level). The consumption of renewable energy has a significant negative influence (coefficient of -0.450). The ecological legacy remains significantly positively correlated with economic growth, with a correlation coefficient of 0.733. The ecological footprint is also significantly influenced by biocapacity, with a coefficient of 0.201. Information and communication technology (ICT) does not have a substantial impact on the ecological footprint in the CCR model, as it does in other models.
4.7. Robustness Test
To validate the robustness of these conclusions, as presented in
Table 10, a two-step system Generalized Method of Moments (GMM) was employed. The results of the robustness test closely align with those of FMOLS, DOLS, and CCR, affirming their reliability. Natural Resource Exploration exhibits a positive association with the Ecological Footprint, while Renewable Energy Consumption consistently shows a negative impact. Economic Growth continues to demonstrate a significant positive relationship with the Ecological Footprint. Biocapacity maintains a positive influence, albeit slightly weaker, and Information and Communication Technology remains statistically insignificant. Diagnostic checks confirm the validity and appropriateness of the model specifications and instruments used.
4.8. Diagnostic Estimations
Using the FMOLS, DOLS, and CCR estimators, the long-term effects of the independent variables on carbon emissions were thoroughly investigated. The model's accuracy was verified through a variety of diagnostic tests, such as the Wooldridge measure for serial correlation, the Breusch-Pagan/Cook-Weisberg test for heteroskedasticity, and the Ramsey RESET assess for the specification of the model. The model's robustness was confirmed by the presence of heteroskedasticity and serial correlation, as indicated by the results in
Table 11.
4.9. Dumitrescu Hurlin Panel Causality Test
This study utilises the Dumitrescu Hurlin panel causality assessment to ascertain the presence of short-term causation between the dependent and independent variables. The causality test developed by Dumitrescu and Hurlin (2012), designed specifically to tackle issues related to heterogeneity, is employed.
Table 12 displays extensive data illustrating the unidirectional correlation between extraction of natural resources and renewable energy usage with environmental contamination. Conversely, there exists a reciprocal connection between economic growth, biocapacity, and ICT.
5. Conclusions and Policy Implications
5.1. Conclusions
This study examines the ecological footprint of BRICS+ nations by utilising panel data from 1991 to 2019 to examine the impact of economic growth, biocapacity, renewable energy consumption, natural resource extraction, and ICT. Advanced econometric techniques, including FMOLS, DOLS, and CCR, were employed to assess these relationships. The results indicate that economic growth and natural resource exploitation significantly worsen ecological footprints, highlighting their detrimental impact on environmental sustainability. These findings underscore the urgent need for BRICS+ nations to decouple economic growth from environmental degradation and transition to cleaner, more sustainable energy sources. Conversely, the study finds that renewable energy consumption, globalization, technological advancements, and biocapacity have a positive impact on reducing ecological footprints. These factors contribute to environmental sustainability, suggesting that greater integration of renewable energy, sustainable trade practices, green technology innovations, and enhanced biocapacity can help mitigate environmental impacts in these emerging economies.
5.2. Policy Implications
The main findings of the econometric research indicated substantial correlations, providing useful insights for policymakers seeking to achieve sustainable development. Firstly, natural resource exploration is consistently shown to increase the ecological footprint, emphasizing the need for sustainable resource management practices. Policymakers in BRICS+ countries should implement stricter regulations on resource extraction, encourage the application of ecologically friendly technologies in mining and drilling activities., and encourage the adoption of circular economy principles to minimize waste and resource depletion.
Secondly, the consumption of renewable energy greatly minimizes the ecological footprint, emphasizing the importance of clean energy in minimizing environmental repercussions. Despite progress, the BRICS+ countries must speed up the shift to greener energy by means of rewards to renewable energy investments, financing the research and deployment of renewable energy technology, and establishing aggressive renewable energy targets. Additionally, integrating renewable energy sources into national grids and improving energy storage solutions can enhance the reliability and efficiency of renewable energy systems.
Thirdly, economic development has a positive relationship with the ecological footprint, implying that current growth rates in BRICS+ countries are unsustainable. Policymakers should work to decouple economic growth from environmental degradation by supporting green technologies, encouraging sustainable production and consumption patterns, and enforcing strict environmental rules. Investing in research and development for sustainable technologies and fostering innovation in green industries can drive sustainable economic growth.
Fourthly, biocapacity positively impacts the ecological footprint, suggesting that higher biocapacity leads to greater environmental exploitation. To address this, BRICS+ countries should invest in restoring degraded ecosystems, enhancing biodiversity conservation efforts, and implementing sustainable land management practices. Policies aimed at boosting resource efficiency and avoiding ecological overshoot are critical for ensuring ecological balance.
Lastly, information and communication technology (ICT) has no substantial impact on the ecological footprint in this study. However, the potential of ICT to contribute to sustainability should not be overlooked. Policymakers should advance the acceptance and growth of ICT solutions that enhance energy efficiency, reduce resource consumption, and support environmental monitoring and management. Encouraging the use of smart technologies in industries, cities, and households can help optimize resource use and minimize environmental impacts.
5.3. Limitations and Future Research
This study has various limitations that must be recognized. Firstly, reliance on data from various sources introduces potential inconsistencies and gaps, affecting the accuracy of the findings. Secondly, the study does not extensively analyze other relevant factors such as technological advancements, government policies, and social factors, which could influence ecological footprints. Thirdly, the specific econometric models used have inherent limitations, and alternative methodologies could provide different insights. Fourthly, the study's focus on a specific timeframe restricts the generalizability of the findings over different periods. Moreover, for future research, firstly, incorporating additional variables like technological innovations and detailed policy impacts is crucial. Secondly, conducting longitudinal studies over extended periods can provide deeper insights into long-term effects. Thirdly, expanding the analysis to include more countries beyond the BRICS+ framework can identify global patterns and regional differences. Fourthly, utilizing advanced econometric techniques and machine learning models can improve the robustness of the analysis. Lastly, assessing the success of specific policy measures can provide policymakers with practical data for designing focused interventions aimed at lowering ecological footprint.