Submitted:
29 August 2024
Posted:
29 August 2024
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
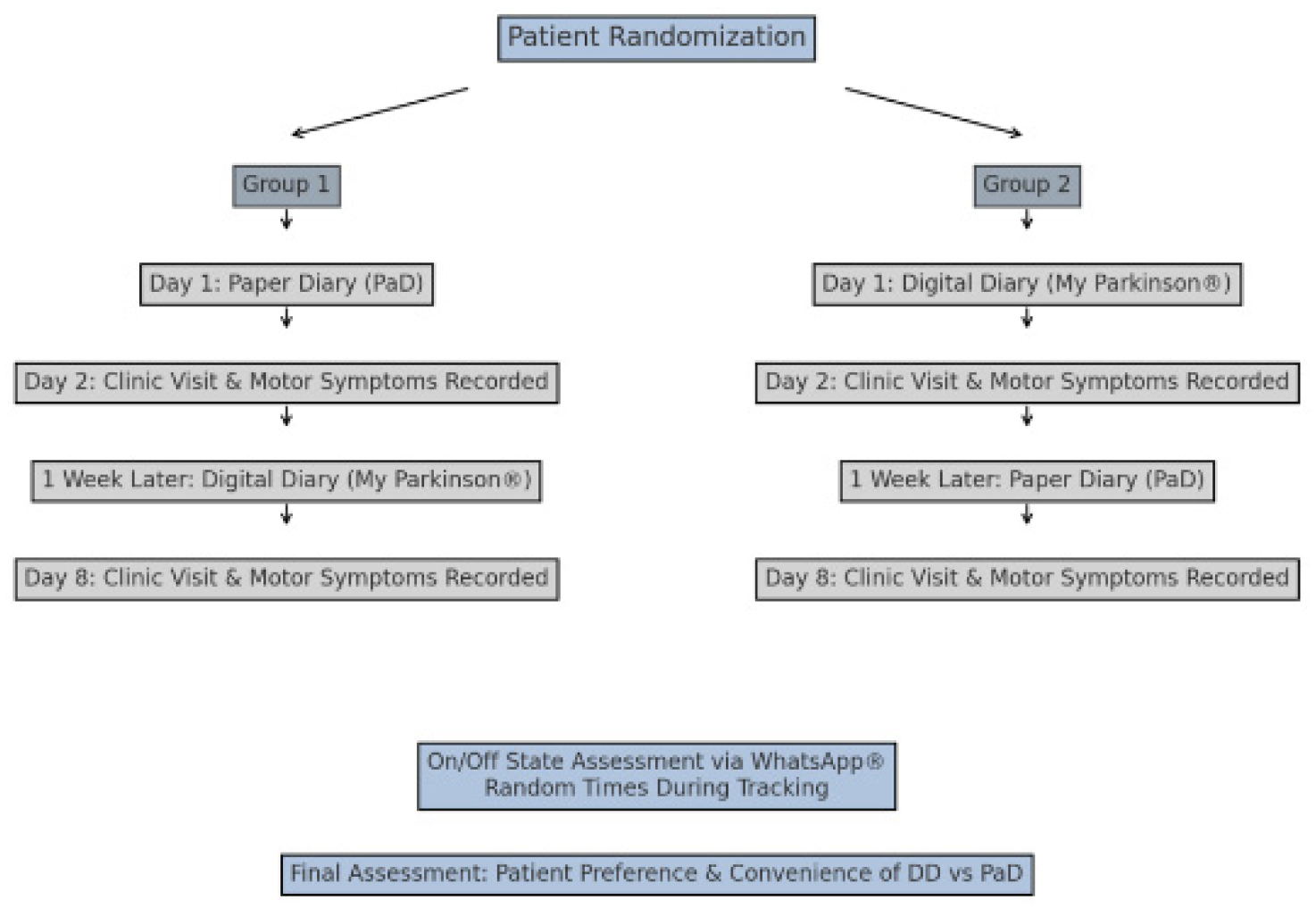
2.1. Study Design and Participants
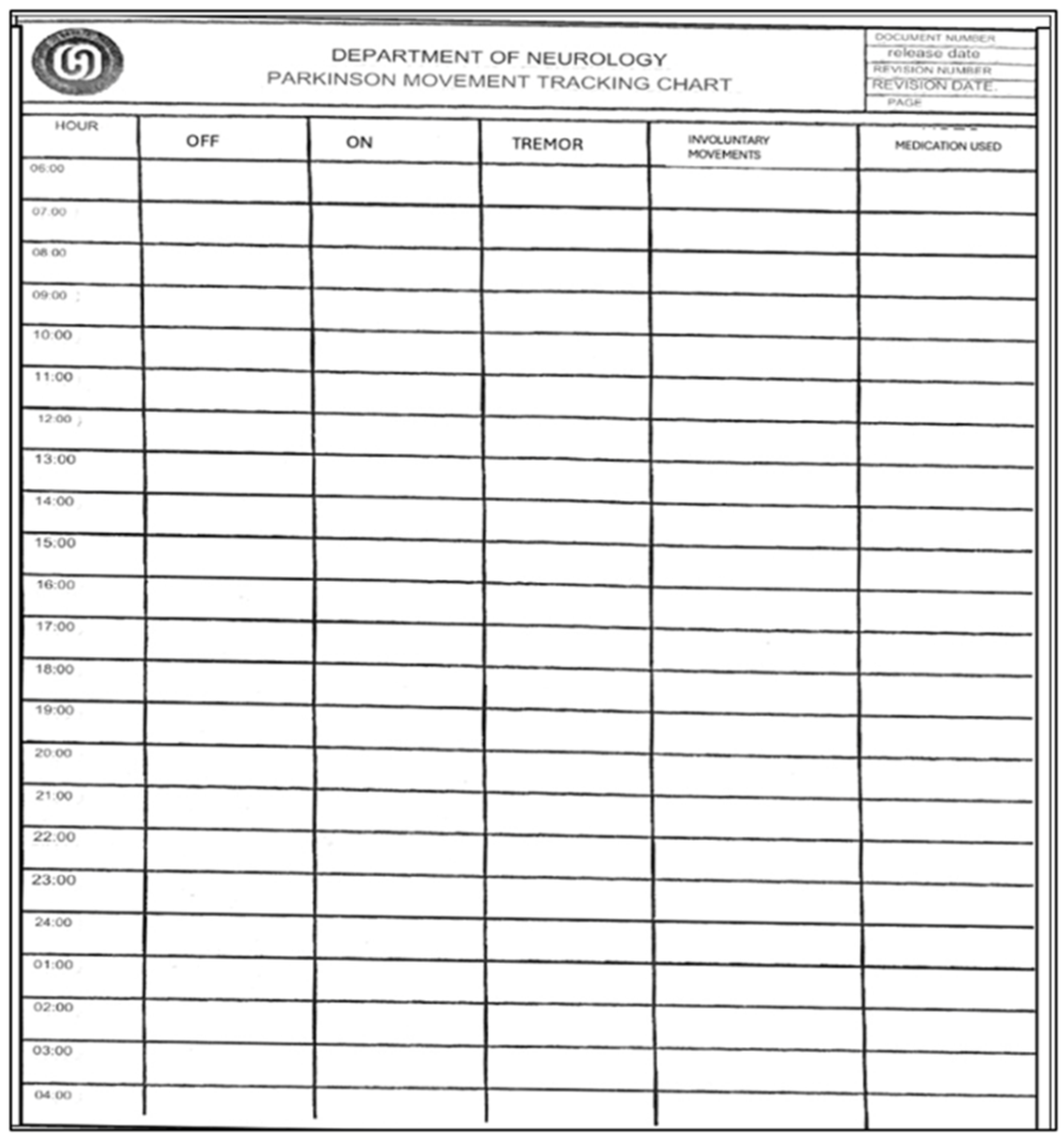
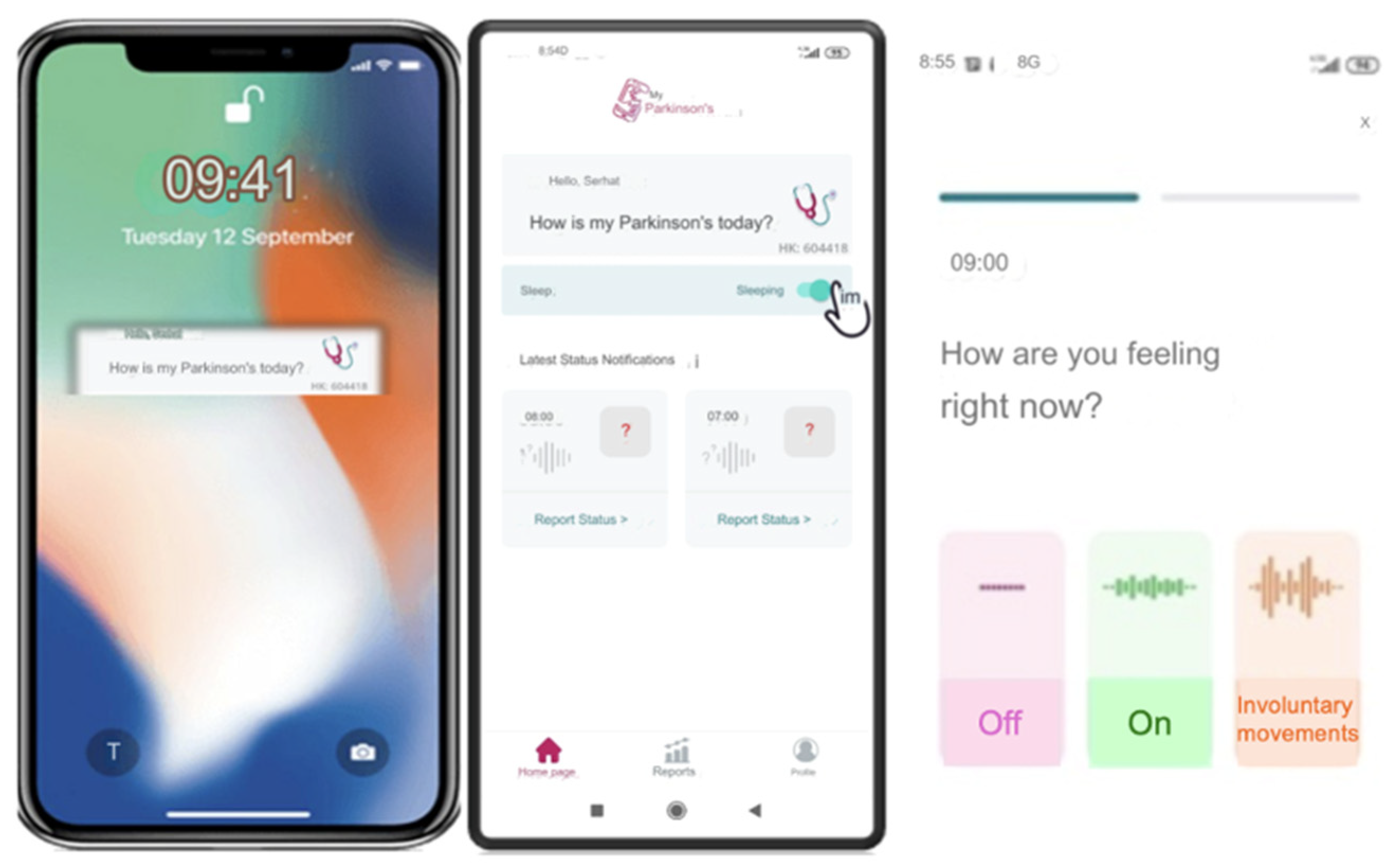
2.2. Procedures
2.3. Randomization and Group Assignment
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Clinical Characteristics of the Study Cohort
3.2. Comparative Analysis of Paper and Digital Diaries in Parkinson’s Disease Management
3.2.1. Patient Enrollment and Baseline Characteristics
3.2.2. Compliance and Agreement Analysis
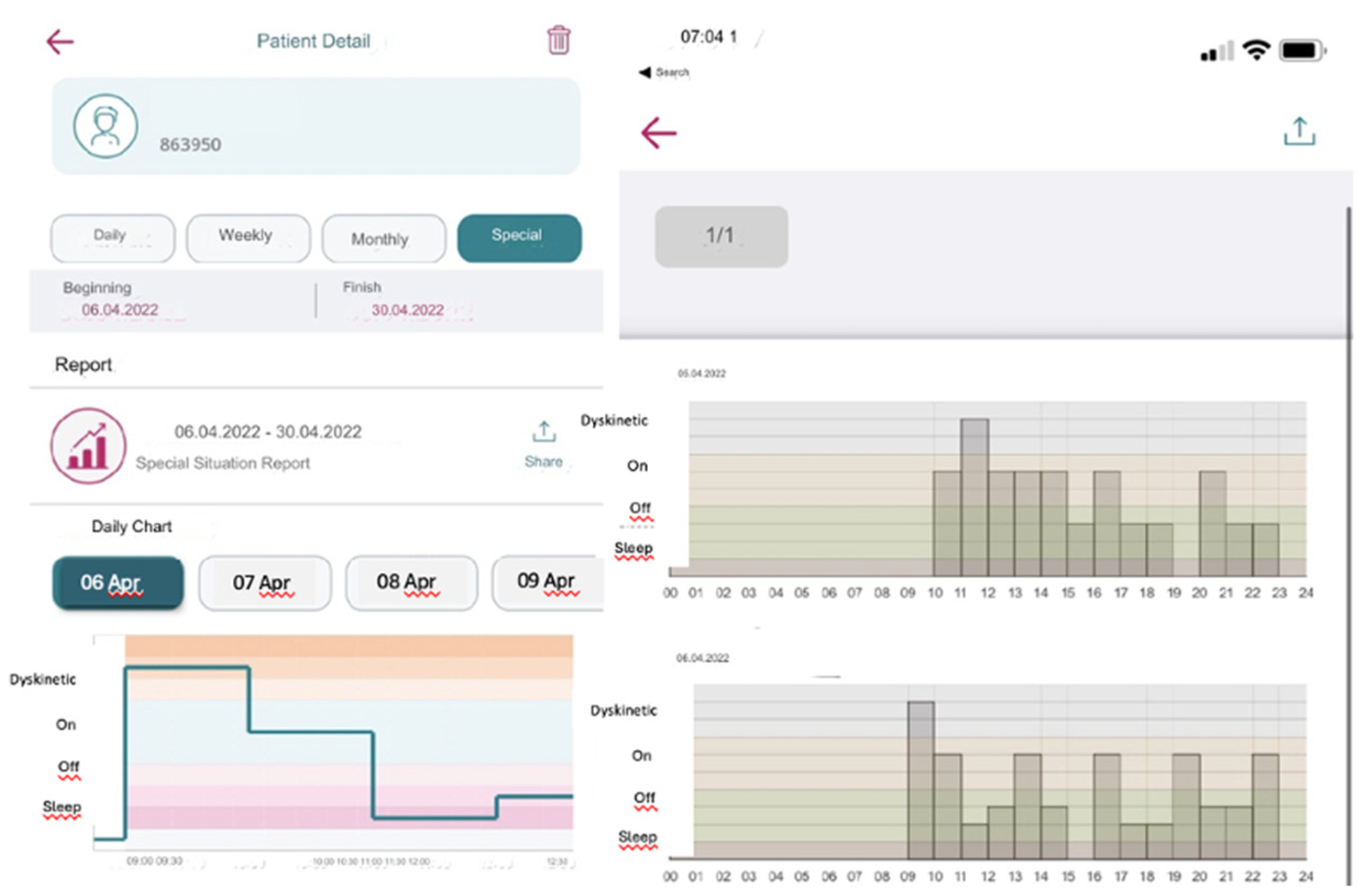
3.2.3. Detailed Evaluation of Compliance across Diary Formats
3.2.4. User Preferences and Diary Usability
3.2. Figures, Tables, and Schemes
4. Discussion
Limitations:
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dorsey ER, Sherer T, Okun MS, Bloem BR. The Emerging Evidence of the Parkinson’s Pandemic. J Parkinsons Dis. 2018;8(s1):S3-S8. [CrossRef]
- Raza C, Anjum R, Shakeel NUA. Parkinson’s disease: Mechanisms, translational models and management strategies. Life Sci. 2019;226:77-90. [CrossRef]
- Poewe W, Antonini A, Zijlmans JC, Burkhard PR, Vingerhoets F. Levodopa in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease: an old drug still going strong. Clin Interv Aging. 2010;5:229-38. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isaacson SH. Effective Treatment Strategies for Motor and Nonmotor Symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease. J Clin Psychiatry. 2020;81(1). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanellos FS, Tsamis KI, Rigas G, Simos YV, Katsenos AP, Kartsakalis G, et al. Clinical Evaluation in Parkinson’s Disease: Is the Golden Standard Shiny Enough? Sensors (Basel). 2023;23(8). [CrossRef]
- Peasgood T, Caruana JM, Mukuria C. Systematic Review of the Effect of a One-Day Versus Seven-Day Recall Duration on Patient Reported Outcome Measures (PROMs). Patient. 2023;16(3):201-21. [CrossRef]
- Vizcarra JA, Sánchez-Ferro Á, Maetzler W, Marsili L, Zavala L, Lang AE, et al. The Parkinson’s disease e-diary: Developing a clinical and research tool for the digital age. Mov Disord. 2019;34(5):676-81. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauser RA, Friedlander J, Zesiewicz TA, Adler CH, Seeberger LC, O’Brien CF, et al. A home diary to assess functional status in patients with Parkinson’s disease with motor fluctuations and dyskinesia. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2000;23(2):75-81. [CrossRef]
- Marinus J, Visser M, Stiggelbout AM, Rabey JM, Bonuccelli U, Kraus PH, et al. Activity-based diary for Parkinson’s disease. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2002;25(1):43-50. [CrossRef]
- Reimer J, Grabowski M, Lindvall O, Hagell P. Use and interpretation of on/off diaries in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2004;75(3):396-400. [CrossRef]
- Ossig C, Sippel D, Fauser M, Gandor F, Jost WH, Ebersbach G, et al. Assessment of Nonmotor Fluctuations Using a Diary in Advanced Parkinson’s disease. J Parkinsons Dis. 2016;6(3):597-607. [CrossRef]
- Papapetropoulos SS. Patient diaries as a clinical endpoint in Parkinson’s disease clinical trials. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2012;18(5):380-7. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deb R, An S, Bhat G, Shill H, Ogras UY. A Systematic Survey of Research Trends in Technology Usage for Parkinson’s Disease. Sensors (Basel). 2022;22(15). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes AJ, Daniel SE, Kilford L, Lees AJ. Accuracy of clinical diagnosis of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease: a clinicopathological study of 100 cases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1992;55(3):181-4. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arevalo-Rodriguez I, Smailagic N, Roqué I Figuls M, Ciapponi A, Sanchez-Perez E, Giannakou A, et al. Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) for the detection of Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias in people with mild cognitive impairment (MCI). Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015;2015(3):CD010783.
- Tomlinson CL, Stowe R, Patel S, Rick C, Gray R, Clarke CE. Systematic review of levodopa dose equivalency reporting in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord. 2010;25(15):2649-53. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbostanci MC, Bayram E, Yilmaz V, Rzayev S, Özkan S, Tokcaer AB, et al. Turkish Standardization of Movement Disorders Society Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale and Unified Dyskinesia Rating Scale. Mov Disord Clin Pract. 2018;5(1):54-9. [CrossRef]
- Hoehn MM, Yahr MD. Parkinsonism: onset, progression and mortality. Neurology. 1967;17(5):427-42.
- RANDOM.ORG: True Random Number Service [ONLINE] [Internet]. 2023. Available from: https://www.random.org.
- Landis JR, Koch GG. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics. 1977;33(1):159-74.
- Löhle M, Bremer A, Gandor F, Timpka J, Odin P, Ebersbach G, et al. Validation of the PD home diary for assessment of motor fluctuations in advanced Parkinson’s disease. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2022;8(1):69. [CrossRef]
- Cubo E, Delgado-López PD. Telemedicine in the Management of Parkinson’s Disease: Achievements, Challenges, and Future Perspectives. Brain Sci. 2022;12(12).
- Marxreiter F, Buttler U, Gassner H, Gandor F, Gladow T, Eskofier B, et al. The Use of Digital Technology and Media in German Parkinson’s Disease Patients. J Parkinsons Dis. 2020;10(2):717-27. [CrossRef]
- Habets J, Heijmans M, Herff C, Simons C, Leentjens AF, Temel Y, et al. Mobile Health Daily Life Monitoring for Parkinson’s Disease: Development and Validation of Ecological Momentary Assessments. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2020;8(5):e15628. [CrossRef]
- Lakshminarayana R, Wang D, Burn D, Chaudhuri KR, Galtrey C, Guzman NV, et al. Using a smartphone-based self-management platform to support medication adherence and clinical consultation in Parkinson’s disease. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2017;3:2. [CrossRef]
- Stone AA, Shiffman S, Schwartz JE, Broderick JE, Hufford MR. Patient compliance with paper and electronic diaries. Control Clin Trials. 2003;24(2):182-99. [CrossRef]
- Broderick JE, Stone AA. Paper and electronic diaries: Too early for conclusions on compliance rates and their effects--Comment on Green, Rafaeli, Bolger, Shrout, and Reis (2006). Psychol Methods. 2006;11(1):106-11; discussion 23-5. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palermo TM, Valenzuela D, Stork PP. A randomized trial of electronic versus paper pain diaries in children: impact on compliance, accuracy, and acceptability. Pain. 2004;107(3):213-9. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyons KE, Pahwa R. Electronic motor function diary for patients with Parkinson’s disease: a feasibility study. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2007;13(5):304-7. [CrossRef]
- 30. Chuapakdee O, Punyakaew P, Ratanasirisawad V, Kongdachalert S, Winyooviji C, Bhidayasiri R. Feasibility of a simplified, symptom-based electronic diary to improve evaluation of motor and non-motor complications in Parkinson’s disease [abstract]. Mov Disord. 2020;35.
- Nyholm D, Kowalski J, Aquilonius SM. Wireless real-time electronic data capture for self-assessment of motor function and quality of life in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord. 2004;19(4):446-51. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terroba-Chambi C, Bruno V, Medina-Escobar A, Nanni F, Cerquetti D, Rossi M, et al. Open-Access Electronic Diary for Motor Fluctuation and Dyskinesia Evaluation in Parkinson Disease: Comparison With Paper Diary. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2018;41(1):20-2. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riggare S, Stamford J, Hägglund M. A Long Way to Go: Patient Perspectives on Digital Health for Parkinson’s Disease. J Parkinsons Dis. 2021;11(s1):S5-S10. [CrossRef]
- Espay AJ, Bonato P, Nahab FB, Maetzler W, Dean JM, Klucken J, et al. Technology in Parkinson’s disease: Challenges and opportunities. Mov Disord. 2016;31(9):1272-82. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora S, Venkataraman V, Zhan A, Donohue S, Biglan KM, Dorsey ER, et al. Detecting and monitoring the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease using smartphones: A pilot study. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2015;21(6):650-3. [CrossRef]
- Tsukita K, Sakamaki-Tsukita H, Takahashi R. Long-term Effect of Regular Physical Activity and Exercise Habits in Patients With Early Parkinson Disease. Neurology. 2022;98(8):e859-e71. [CrossRef]
- Viwattanakulvanid P, Somrongthong R, Vankwani M, Kavita FN, Kumar R. Predictors and Level of Knowledge Regarding Parkinson’s Disease among Patients: A Cross-sectional Study from Thailand. Int J Prev Med. 2020;11:25. [CrossRef]
- Tennigkeit J, Feige T, Haak M, Hellqvist C, Seven Ü, Kalbe E, et al. Structured Care and Self-Management Education for Persons with Parkinson’s Disease: Why the First Does Not Go without the Second-Systematic Review, Experiences and Implementation Concepts from Sweden and Germany. J Clin Med. 2020;9(9).
- Dorsey ER, Topol EJ. State of Telehealth. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(2):154-61.
- Luis-Martínez R, Monje MHG, Antonini A, Sánchez-Ferro Á, Mestre TA. Technology-Enabled Care: Integrating Multidisciplinary Care in Parkinson’s Disease Through Digital Technology. Front Neurol. 2020;11:575975. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
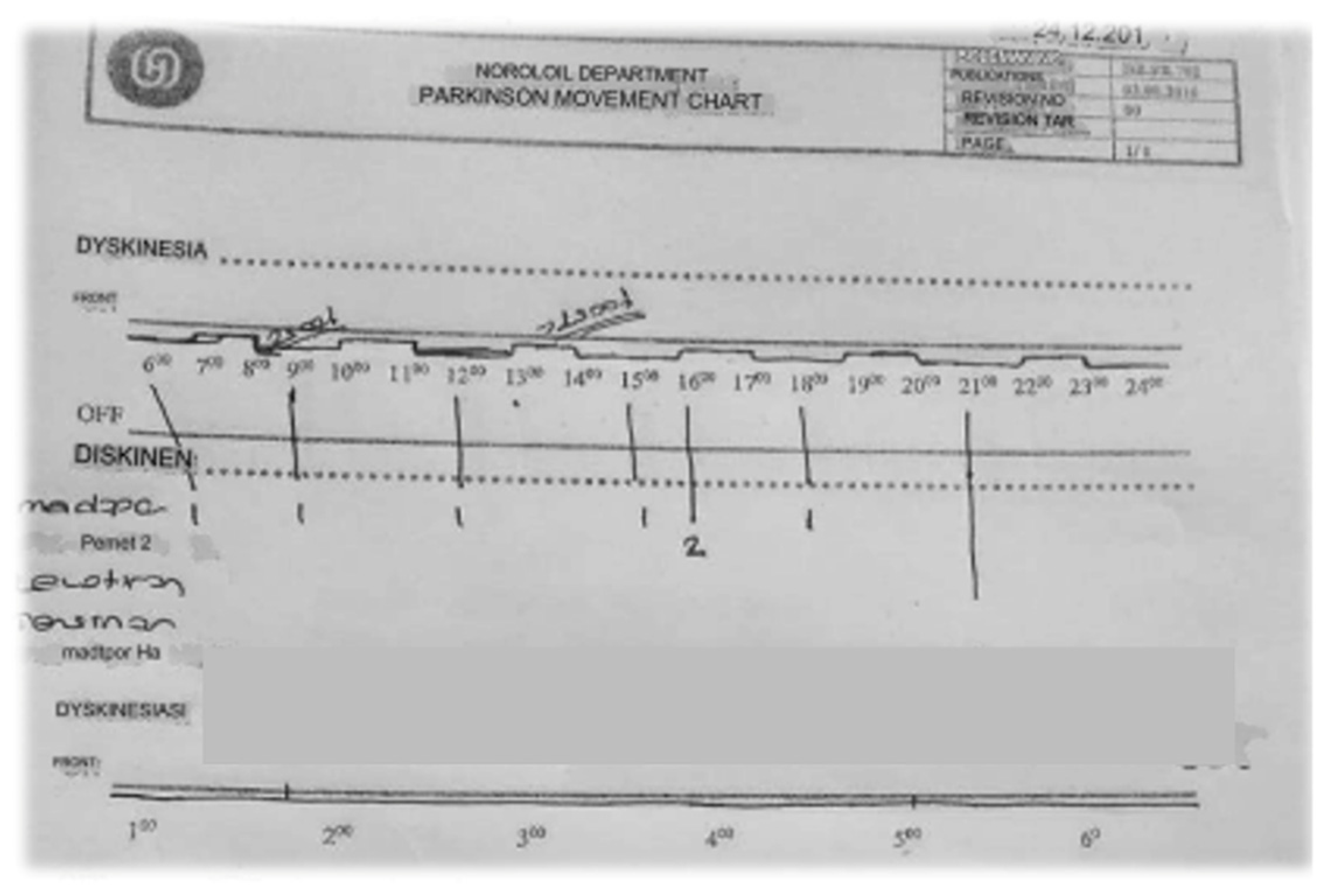
| n | % | |
|---|---|---|
| Paper | ||
| No agreement | 6 | 37,5 |
| Slight | 2 | 12,5 |
| Fair | 4 | 25 |
| Moderate | 3 | 18,75 |
| Substantial | 1 | 6,25 |
| Almost Perfect | 0 | 0 |
| Application | ||
| No agreement | 1 | 6,25 |
| Slight | 4 | 25 |
| Fair | 4 | 25 |
| Moderate | 2 | 12,5 |
| Substantial | 3 | 18,75 |
| Almost Perfect | 2 | 12,5 |
| Paper diary*( )κ | Digital diary*( )κ | Paper diary | Digital diary | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measurement 1 | 0,574 | 0,483 | Moderate | Moderate |
| Measurement 2 | 0,000 | 0,615 | Slight | Substantial |
| Measurement 3 | -0,071 | 0,818 | No agreement | Almost Perfect |
| Measurement 4 | 0,524 | 0,259 | Moderate | Fair |
| Measurement 5 | -0,042 | -0,143 | No agreement | No agreement |
| Measurement 6 | 0,661 | 0,556 | Substantial | Moderate |
| Measurement 7 | 0,500 | 0,623 | Moderate | Substantial |
| Measurement 8 | 0,091 | 0,091 | Slight | Slight |
| Measurement 9 | 0,000 | 0,388 | Slight | Fair |
| Measurement 10 | 0,388 | 0,423 | Fair | Moderate |
| Measurement 11 | -0,111 | 0,783 | No agreement | Substantial |
| Measurement 12 | -0,111 | 0,123 | No agreement | Slight |
| Measurement 13 | -0,071 | 0,545 | No agreement | Moderate |
| Measurement 14 | 0,583 | 0,388 | Moderate | Fair |
| Measurement 15 | -0,111 | 0,231 | No agreement | Fair |
| Measurement 16 | 0,286 | 0,815 | Fair | Almost Perfect |
| n | % | |
|---|---|---|
| Paper | ||
| No agreement | 2 | 12,5 |
| Slight | 3 | 18,75 |
| Fair | 6 | 37,5 |
| Moderate | 5 | 31,25 |
| Substantial | 0 | 0 |
| Almost Perfect | 0 | 0 |
| Application | ||
| No agreement | 4 | 25 |
| Slight | 8 | 50 |
| Fair | 3 | 18,75 |
| Moderate | 1 | 6,25 |
| Substantial | 0 | 0 |
| Almost Perfect | 0 | 0 |
| Paper diary*( κ) | Digital diary* ( κ) | Paper diary | Digital diary | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measurement 1 | 0,265 | 0,136 | Fair | Slight |
| Measurement 2 | 0,524 | 0,000 | Middle | Slight |
| Measurement 3 | 0,107 | 0,206 | Slight | Fair |
| Measurement 4 | 0,524 | -0,212 | Middle | No agreement |
| Measurement 5 | 0,123 | 0,000 | Slight | Slight |
| Measurement 6 | 0,219 | 0,000 | Fair | Slight |
| Measurement 7 | -0,111 | 0,184 | No agreement | Slight |
| Measurement 8 | 0,206 | -0,029 | Fair | No agreement |
| Measurement 9 | 0,268 | 0,153 | Fair | Slight |
| Measurement 10 | 0,474 | 0,231 | Middle | Fair |
| Measurement 11 | 0,545 | 0,492 | Middle | Middle |
| Measurement 12 | -0,029 | 0,032 | No agreement | Slight |
| Measurement 13 | 0,231 | 0,038 | Fair | Slight |
| Measurement 14 | 0,000 | -0,296 | Slight | No agreement |
| Measurement 15 | 0,250 | -0,167 | Fair | No agreement |
| Measurement 16 | 0,464 | 0,231 | Middle | Fair |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





