1. Introduction
With the increasing emphasis on Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) technology in fields such as low-altitude economies [
1,
2,
3,
4] and offensive & defensive confrontations [
5,
6], the threat posed by high-dynamic electromagnetic targets is on the rise. Consequently, efficient electromagnetic awareness of high-maneuverability targets in complex environments has become an urgent requirement for remote-sensing practices. The identification of electromagnetic targets is fundamentally based on the recognition of the attributes of the Radio Frequency (RF) signals they emit. This encompasses the recognition of both signal and device attributes. Signal attributes include modulation type [
7,
8], signal bandwidth [
9], center frequency [
10,
11], etc, whereas device attribute is primarily defined by RF fingerprints [
12,
13,
14].
With the advancement of machine learning, methods for RF signal attribute recognition based on deep learning have made significant progress in recent years, injecting new vitality into the identification of electromagnetic emitter. Despite these strides, the propagation of RF signals is frequently confronted with challenges posed by dynamic, time-varying, and intricate wireless channel conditions across various spatio-temporal contexts, such as Air-to-Ground (A2G) channels in low-altitude economic zones [
15,
16,
17]. Air-to-ground channel scenarios, in contrast to the Ground-to-Ground (G2G) channel scenario, are subject to a multitude of influences, including transceiver mobility, fluctuating atmospheric conditions, and diverse terrains and topographies. These factors exert distinct impacts on RF signal propagation, introducing variability and uncertainty in the data distribution. Consequently, traditional deep learning models, trained on data from a single scenario, struggle to adapt and accurately discern the characteristics of RF signals across various scenarios. Moreover, the diversity and complexity of communication environments significantly complicate the task of effectively capturing RF signals and assigning them accurate labels. Collectively, these factors amplify the difficulties associated with cross-scenario deep learning-based RF signal attribute recognition.
Facing the challenges of the distribution discrepancy of signal data across scenarios and the scarcity of data & label, traditional deep learning methods struggle to effectively cope. Transfer Learning (TL) offers an effective solution by allowing the migration of prior knowledge learned in one scenario to another, thereby enhancing the performance of RF signal attribute recognition in new environments [
18,
19,
20]. Specifically, domain adaptation within the realm of transfer learning facilitates the acquisition of knowledge in the target domain by leveraging insights from the source domain [
21,
22]. This strategy addresses the challenges stemming from distribution discrepancy and label paucity in the target domain [
23,
24,
25,
26]. Therefore, domain adaptation methods not only optimize the utilization of existing data resources but also adapt to changes in the feature distribution of signal attributes across different scenarios, bringing new development opportunities and challenges to the field of RF signal attribute recognition.
In the realm of RF signal attribute recognition, domain adaptation-based methods have demonstrated considerable promise and benefits. Bu et al. [
27] introduced an innovative adversarial TL framework to address the challenge of Automatic Modulation Recognition (AMR) amidst shifting data distributions and limited signal data availability. This method leverages a synergy of adversarial training and knowledge transfer, aiming to minimize disparities in data distributions through adversarial training, while simultaneously exploiting knowledge transfer to extract prior knowledge from the source domain. To tackle the issue of divergent data distributions between test and training sets, Liu et al. [
28] presented a Radio Frequency Fingerprint Identification (RFFI) technique for long-term specific transmitter identification. This method achieves domain alignment between source and target domain samples through unsupervised domain adaptation, thereby diminishing the intra-class variability of deep features and alleviating the misclassification of edge samples in the target domain. Nonetheless, current TL-based methods for RF signal attribute recognition often employ a random selection of training samples from the target domain. This practice can result in decreased correlation between samples cross source and target domains, as well as a reduction in distribution similarity of batch domains , which hinders the alignment and extraction of domain-invariant features.
To address the aforementioned challenges in the cross-scenarios, this paper focuses on the study of cross-scenario RF signal attribute recognition. We propose a Progressive Maximum Similarity-based Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (PMS-UDA) method for RF signal attribute recognition cross G2G and A2G channel scenarios. Initially, to enhance the model’s robustness in diverse noisy environments, a noise perturbation consistency optimization method is introduced. This method leverages the subtle feature differences induced by random noise in the signals of target domain to learn feature representations under various Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) conditions. Subsequently, addressing the challenge of effectively learning feature similarities at both the sample and distribution levels in high-dimensional spaces, we introduce a Progressive Label Alignment Training (PLAT) method. This method optimizes the learning of maximum sample-level correlation and distribution-level similarity. Finally, to mitigate the impact of channel differences on feature learning, a domain adversarial optimization method is incorporated. This method employs adversarial learning to extract domain-invariant RF signal attribute features, enhancing the generalizability and accuracy of the model across diverse operational scenarios.
The main contributions of this paper are as follows:
- (1)
A noise perturbation consistency optimization learning method is introduced to utilize slight noise perturbations during training, enhancing the model’s robustness to various SNR conditions and improving the performance at low SNRs.
- (2)
We propose a progressive label alignment training method, which combined with optimization for maximizing sample-level correlation and distribution-level similarity, effectively enhances the similarity between the feature distributions of the source and target domains, thus increasing the cross-scenarios adaptability of RF signal attribute features.
- (3)
Utilization of domain adversarial optimization learning methods to extract domain-invariant features, significantly reducing the impact of channel scenario differences on recognition outcomes.
- (4)
Compared to baseline methods, the proposed method demonstrates superior performance in AMR and RFFI tasks cross G2G and A2G channel scenarios.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows.
Section 2 presents the problem formulation and the corresponding solutions developed for addressing the challenges in wireless communication systems.
Section 3 explores the network architectures of backbone employed for feature extraction.
Section 4 delves into the proposed UDA method.
Section 5 presents the experimental setup and analyzes the outcomes of the proposed UDA method. Finally,
Section 6 concludes the paper with a summary of our findings.
2. Problem Formulation and Solution
2.1. Problem Formulation
In the wireless communication systems, the interaction between transmitted signals and the channel through which they propagate is of paramount importance. The received signal,
, is formulated as the convolution of the transmitted signal
with the channel impulse response
, in addition to additive white Gaussian noise (AWGN),
), represented as:
This model captures the essence of signal propagation in wireless channels, including the effects of multipath fading and noise. Eq. (
1) is also described in the form of multiple taps:
where
,
,
and
denote the amplitude, path delay, frequency and phase offset of the
kth tap, respectively.
The spatial scope of the G2G channel under urban topography and geomorphology discussed is relatively small, with the relative movement speed and height difference between the transceivers being negligible. In contrast, the A2G channel in an urban environment comprises a direct path and a ground-reflected path, with a probabilistic existence of 3-9 multipath components. Additionally, due to the high flight speed of drones, the A2G channel exhibits significant Doppler effects compared to the new G2G scenarios. Generally, the A2G channel scenario covers a wider spatial range, leading to relatively severe path loss.
Therefore, the constructed G2G and A2G channel models exhibit significant differences within their channel parameters, specifically in , , , and . Furthermore, the distribution of may also vary. These variations lead to different distributions of the radio frequency (RF) signal data across channel models. To better describe the problem of domain adaptation, we denote the signal input to the deep model as X, which represents the radio frequency signal that has undergone wireless channel effects. Meanwhile, Y is used to denote the label of the signal X. Suppose the sample datas of RF signal in the G2G scenario follows the distribution , denoted as , similarly, the sample data of RF signal in the A2G scenario adheres to the distribution , represented as . Due to these distributional differences in sample data of RF signal across scenarios, deep learning-based methods for RF signal attribute recognition experience a significant performance degradation in cross-scenario applications.
2.2. Problem Solution
In practical wireless communication scenarios, we can obtain samples of RF signals along with their corresponding labels in familiar environments. However, the task often extends to performing similar tasks in new communication scenarios. Based on the previous analysis of two communication channel conditions, a distribution discrepancy exits between the sample spaces of RF signals in these two scenarios. Moreover, in the new communication scenarios, only a few of RF signal samples are known, with no access to the corresponding labels.
2.2.1. Traditional Deep Learning Paradigm
In the traditional deep learning, the empirical risk within the source domain is represented as:
where
denotes the loss function, and
symbolizes the joint probability distribution within the source domain. The summation
represents the aggregation across discrete categorical labels, signifying that the risk is assessed over all possible outcomes within the label space
. Concurrently, the integral
is performed over the continuous input space
, capturing the expected loss across the entire data distribution within the source domain. This dual operation of summation and integration is pivotal in computing the comprehensive expected risk, ensuring the model’s performance is evaluated over both the entire input domain and the categorical outcomes.
For the unfamiliar target domain, the empirical risk is represented as:
However, the labels of target domain, , is unavailable. Therefore, the traditional deep learning paradigm is incapable of effectively addressing the task with unlabeled sample in the target domain.
2.2.2. Deep Domain Adaptation Paradigm
The solution to domain adaptation involves learning a model that performs well on a target domain T, characterized by a low risk , using labeled data from a source domain S and unlabeled data from a target domain T. To enhance the model’s generalizability across different distributions, both domains are leveraged simultaneously.
The fundamental expression for the risk on the source domain is given in Eq. (
3). The risk in the target domain,
, can be conceptually derived as the expectation of the loss function with respect to the target distribution:
where
is a domain adaptation factor in the transformation, which serves to reconcile the distributions discrepancy of two domains.
For the practical implementation of training a model under this paradigm, the empirical risk on the target domain is minimized by evaluating:
where
are samples drawn from the target domain distribution
, and
n represents the number of samples. Crucial to this process is estimating the ratio, commonly referred to as the domain adaptation factor.
To address the issue of unlabeled data in the target domain, it is necessary to minimize the loss function while maximizing the similarity between the source and target domains.
3. Network Architectures for Task of Feature Extraction
To more effectively extract features relevant to two types of RF signal attributes, we introduce two distinct deep learning-based network architectures from our previous works, namely the Multi-Scale Correlation Networks (MSCNs) [
29] and Multi-Periodicity Dependency Transformer (MPDFormer) [
30].
3.1. Multi-Scale Correlation Networks for AMR Task
In the task of AMR, we incorporate our previous work [
29] with the MSCNs network architecture for extracting the features from modulated signals in the cross-scenarios. The MSCNs can effectively suppress noise and enhance the features of the modulated signals, thereby achieving AMR task under low SNRs. The network architecture of MSCNs for AMR task is shown in
Table 1.
3.2. Multi-Periodicity Dependency Transformer for RFFI Task
In the task of RF signal attribute recognition, we have introduced a Transformer network architecture based on a periodicity-dependency attention mechanism, termed MDPFormer. The MPDFormer utilizes a spectrum offset-based periodic embedding representation to enhance the differentiation of intrinsic features. We explore the complexities of the periodicity-dependency attention mechanism, which incorporates both inter-period and intra-period attention frameworks. This mechanism enables the effective extraction of both long-range and short-range periodicity-dependent features, thereby emphasizing feature distinctions while simultaneously reducing the disturbances introduced by background noise and features with weak periodicity.
The network architecture of MPDFormer is shown in
Table 2.
4. Method
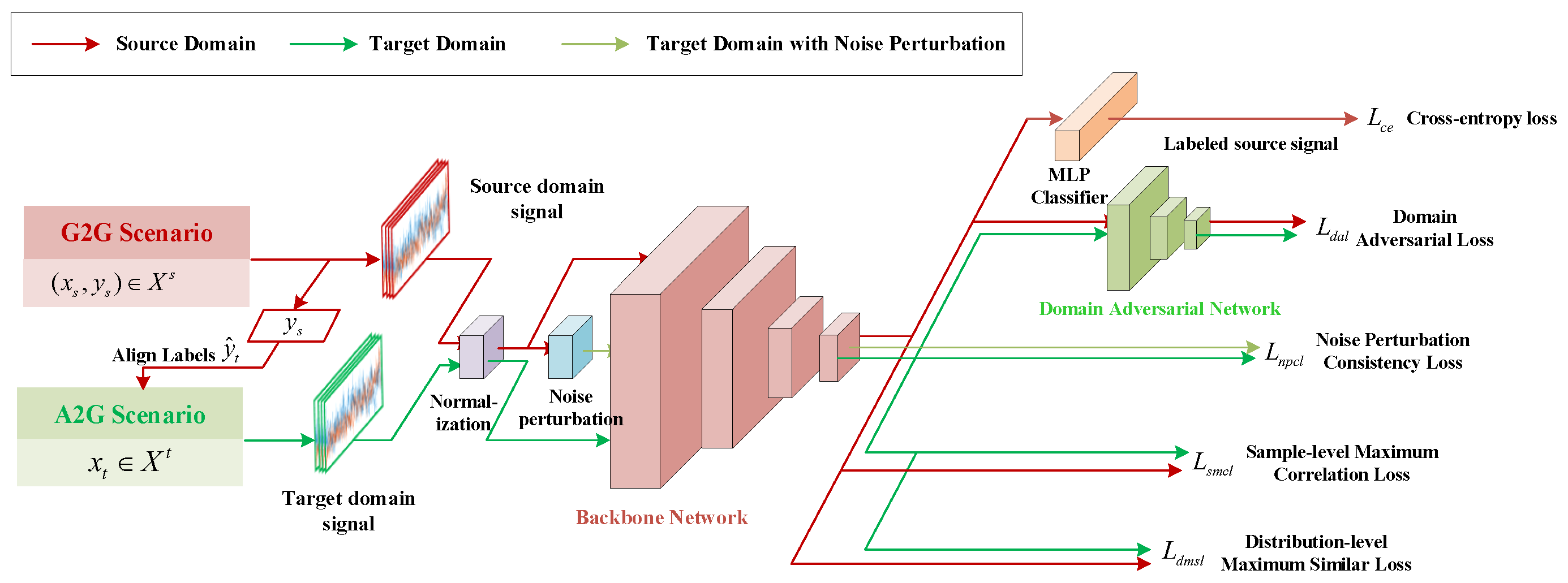
The unsupervised domain adaptation method described is depicted in
Figure 1. Initially, the method utilizes the MSCNs and MPDFormer networks to process the input signal samples from both the source and target domains, thereby deriving feature representations. Subsequently, the extracted features are leveraged to achieve cross-scenario domain adaptation and RF signal attribute recognition. This is accomplished through a series of learning strategies, including noise perturbation consistency learning, sample-level maximum correlation learning, distribution-level maximum similarity learning, domain adversarial learning, and source-domain cross-entropy optimization learning. Additionally, a balancing factor is introduced to adjust the gradient weight of these learning strategies during the backpropagation optimization process. The formulation of the learning strategies with loss function proposed is as follows:
where
represents the set of trainable parameters of backbone model. The variables
,
, and
correspond to the normalized signals of source domain, target domain, and target domain with noise perturbation, respectively. Additionally,
,
,
, and
are the balancing factors for their respective loss functions.
We proceed to detail the following learning strategies: noise perturbation consistency comparison learning, sample-level maximum correlation learning, distribution-level maximum similarity learning, domain adversarial learning, and source-domain cross-entropy optimization learning.
4.1. Noise Perturbation Consistency Learning
Labeling a vast array of signal samples in a novel environment is challenging, yet even a modest collection of signal samples can be an invaluable source of data. Consequently, to make the most of the numerous unlabeled signal samples present in a new setting and, concurrently, to discern the intrinsic features of RF signal attributes amidst the interference of noise perturbation while mitigating the adverse effects of noise on RF signals, this section introduces the Noise Perturbation Constancy Loss (NPCL). This loss function is predicated on the principle of noise perturbation consistency and employs comparative learning to facilitate the effective extraction of features.
Noise perturbation consistency learning serves as an unsupervised learning technique designed to enhance a model’s resilience to noise and fluctuations in input data. It operates by incorporating minor noise perturbation into the training process and demanding that the model yield consistent predictions for both the pristine and the noise-perturbed data. This method compels the model to learn the genuine distribution and properties of the data rather than merely internalizing the noise and anomalies present in the training set. Incorporating such losses aids in reducing model overfitting and enhances its capacity to generalize to new, unseen data. The formulation for incorporating noise perturbation into the signal is outlined as follows:
where
denotes additive Gaussian white noise.
The noise perturbation consistency loss is quantified through the metric of cosine similarity. Let the model parameters be denoted by
, with the original source and target domain signal data represented by
and
respectively. The corresponding signal data perturbed by noise are
and
, respectively. The model’s feature extraction outputs for both the original and perturbed data are given by
and
respectively. Consequently, the cosine similarity loss can be formulated as the discrepancy between the cosine distances of the pairs of feature vectors:
where
and
denote the feature map of original and perturbed signal, · denote the inner product of vectors, and
denote their L2 norms, respectively.
Minimizing the cosine similarity loss compels the model to generate similar feature extraction outcomes for both pristine and perturbed data, thereby enhancing the model’s robustness and capacity for generalization. This process effectively curbs the model’s tendency to overfit on the noise and fluctuations within the training dataset, guiding the model to more accurately capture the intrinsic feature distribution of the data. In contrast to traditional supervised learning paradigms, this method places a greater emphasis on the model’s generalization capabilities, equipping the model to exhibit enhanced resilience when confronted with unfamiliar data or varied environmental contexts. Moreover, the incorporation of noise perturbation consistency loss is cost-effective, as it leverages data transformation and perturbation techniques during training, eliminating the need for additional labeling efforts.
4.2. Sample-Level Maximum Correlation Learning
To effectively diminish the divergence among samples sharing identical labels, this section introduces the Sample-level Maximum Correlation Loss (SMCL). The sample-level maximum correlation loss is designed to refine the distinctiveness of the feature representation by amplifying the correlation among samples that belong to the same class. This strategy is instrumental in enhancing the model’s proficiency in the domain of RF signal attribute recognition. The incorporation of a sample-level correlation constraint within the loss function enables SMCL to efficiently mitigate intra-class variance, thereby improving the model’s proficiency in discerning the intra-class distribution. Consequently, during the training phase, the model is compelled to integrate samples with the same label into a closely-knit feature space.
The sample-level maximum correlation loss is crafted to cultivate a feature representation that is more generalizable by emphasizing the correlation between analogous samples cross both the source and target domains. The formulation of this loss function is expressed as follows:
where
and
denote the feature means of the samples in the source and target domains, respectively,
and
denote the feature representations of the samples
and
, respectively,
and
denote the mean of
and
, respectively,
represents the trace of a matrix, and
n is the total number of signal samples,
is a weighting parameter used to control the influence of the squared correlation coefficient, and we set
. The sample-level maximum correlation loss is distinguished by its efficacy in narrowing the distributional disparities between the source and target domains, thereby enhancing the model’s generalization capabilities on the target domain.
4.3. Distribution-Level Maximum Similarity Learning
The Distribution-level Maximum Similarity Loss (DMSL) reduces the distributional difference between the source and target domains by maximizing the similarity of the signal feature distributions of the source and target domains taken within each batch to improve the generalization performance of the model on the target domain. DMSL improves the generalization performance of the model on the target domain by using the Jensen-Shannon (JS) divergence [
31] to optimize the feature distributions of the two domains and improve their similarity. In contrast to the Kullback-Leibler (KL) divergence [
32], JS divergence is symmetric and smooth, which addresses the problem that KL divergence is asymmetric and may produce infinite values if the probability distributions do not support the same events. It is used to measure the similarity between two probability distributions, providing a score ranging between 0 and 1, where 0 means the distributions are identical and 1 means the distributions are completely different.
Assuming that the distributions of the source and target domain data features in the probability space are
and
, respectively, the JS divergence of these two distributions is defined through the KL divergence of their mean distribution M. The expression for the mean distribution M is:
Therefore, JS divergence is defined as:
where
is the KL divergence of Q to P and it can be expressed as:
where
denotes the set of all possible events in distributions P and Q. This leads to the mathematical expression of DMSL as follows:
4.4. Domain Adversarial Learning
The Domain Adversarial Loss (DAL) serves as an optimization metric aimed at mitigating discrepancies in data distributions between the source and target domains. Its objective is to facilitate the seamless transfer of knowledge acquired from the source domain during model training to the target domain. DAL fosters the extraction of domain-invariant features by incorporating an adversarial mechanism, thereby diminishing the model’s susceptibility to performance degradation due to domain variations.
Employing this strategy, the model transcends its proficiency in the source domain, extending its high-accuracy performance to the unlabeled target domain. The conceptual foundation of DAL is rooted in adversarial training, which aims to align the feature distributions of the source and target domains through iterative optimization. This alignment bolsters the model’s capability to accurately recognize RF signal attributes across various scenarios.
The Domain adversarial loss operates through a binary domain discriminator, which is a domain classification network designed to discern the origin of input feature maps—whether from the source or target domain. The network architecture of this domain discriminator is illustrated in
Table 3. The domain adversarial loss is expressed as follows:
where
is the domain adversarial network, and
is the parameters of the adversarial network,
x denotes the signal samples from source and target domain,
is the feature maps extracted by the backbone network.
Throughout the training process, the objective of the domain domain classifier is to maximally confuse the adversarial network regarding the provenance of the features, thereby fostering convergence in the feature representations cross the two domains. In this process, the domain classifier with the adversarial network engage in a competitive game. The domain classifier continually refines its parameters to produce features that are unidentifiable by domain, while the adversarial network strives to precisely ascertain the origins of these features. Consequently, the domain classifier is compelled to acquire more generalized, domain-independent feature representations, while still maintaining its performance on its primary task.
The domain adversarial loss markedly diminishes the model’s susceptibility to distributional disparities between the source and target domains, thereby enhancing the model’s adaptability and precision in the target domain. When compared with conventional domain adaptation methods, adversarial loss offers a dynamic mechanism for aligning feature distributions, ensuring greater consistency between domains. Moreover, as adversarial training operates directly at the feature level, it does not require label information from the target domain. This trait renders the domain adversarial loss particularly advantageous for scenarios where labeling is either prohibitively expensive or impractical. The incorporation of this loss notably amplifies the model’s robustness and generalization capacity across diverse tasks and environments, highlighting its substantial utility in practical applications.
4.5. Source-Domain Cross-Entropy Optimization Learning
In the field of unsupervised domain adaptation, all signal data in the target domain is unlabeled, making it difficult to perform supervised learning effectively. However, the labeled sample data of RF signal in the source domain carries important prior knowledge of the source domain scenario and is the source of knowledge transfer. These labeled source domain sample data of RF signal provide critical supervised information that effectively guides the model to better distinguish different categories during target domain learning. Therefore, the model is effectively trained to minimize the difference between the predicted outputs and the true labels by calculating the cross-entropy loss function of the source domain data. The cross-entropy loss function allows the model to have better RF signal attribute recognition ability in the source domain by comparing the probability distribution predicted by the model with the true label distribution. At this point, with the co-optimization of the loss functions in sub
Section 4.1 to
Section 4.4, the feature distributions of the target domain and the source domain become highly similar in the high-dimensional space. These two cases jointly contribute to enhancing the RF signal attribute recognition accuracy in the target domain scenario. The categorical cross-entropy loss function expression for the experiments is:
where,
where
and
denote the trainable parameters of the feature extraction and Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP) classification network, respectively,
and
denote the truth and predicted category labels, respectively,
denotes the classifier for the task of the RF signal attribute recognition, and
denotes the number of samples in the source domain.
4.6. Progressive Label Alignment Training Method
The PLAT method represents a sophisticated machine learning strategy tailored to address the challenge of different data distributions between the source and target domains, as outlined in Algorithm 1. The essence of this method lies in its iterative training process, in which the model identifies a batch of data from the source domain, complete with its accurate labels. These authentic labels subsequently guide the selection of corresponding pseudo-labeled data from the target domain’s dataset, which are based on the model’s predictions from the preceding training iteration. This method harnesses progressive label alignment, along with sample-level correlation learning and distribution-level similarity learning, to amplify the learning efficacy. The rationale is that when signals from the same class are selected, the data from both domains within the same batch exhibit the highest correlation and the closest similarity in distribution. Consequently, the model undergoes incremental optimization, with the quality of pseudo-labels in the target domain progressively enhanced, thereby facilitating a more effective transfer of knowledge from the source domain to the target domain. The training regimen emphasizes the foundational role of the source domain data and the dynamic refinement of the target domain labels, focusing intensively on minimizing the distributional divergence between the two domains.
|
Algorithm 1 Progressive label alignment training method |
- 1:
Input: Source domain signal data and labels ; - 2:
Target domain unlabeled signal data ; - 3:
Initialization of backbone, domain adversarial and MLP classifier networks; - 4:
Set key training parameters. - 5:
Output: Predicted labels for target domain signal sample . - 6:
begin - 7:
for epoch = 1 to 300 do - 8:
if convergence condition not met then - 9:
Randomly sample a set of source domain signal data and corresponding labels ; - 10:
Based on the batch of source domain labels, select pseudo-labeled signal data from the target domain that matches the source domain labels ; - 11:
Use the backbone network to extract features and from the source and target domain signals; - 12:
Use the task classification network to predict the labels and for the features of the source and target domains ; - 13:
Use the domain confusion classification network to predict the domain labels and for the features of the source and target domains ; - 14:
Compute the loss for the batch according to Eq. ( 7); - 15:
Update the parameters of backbone network: ; - 16:
Update the parameters of task classification network: ; - 17:
Update the parameters of domain confusion classification network: ; - 18:
end if - 19:
end for - 20:
end |
5. Experimental Results and Analysis
5.1. Experimental Setup
5.1.1. RF Signal Dataset
To assemble the RF signal dataset for both wireless channel scenarios, this section initially employs Software-Defined Radio (SDR) technology [
33] within a G2G setting to authentically capture RF signals associated with AMR and RFFI tasks, thereby establishing the G2G channel RF signal dataset. Subsequently, the RF signal dataset construction methodology constructs the A2G channel scenario model using real-world measured and calibrated channel parameters [
34]. The RF signals for the A2G channel scenario are then produced by integrating the RF signals gathered from the G2G channel scenario with simulated sample data of RF signal.
The A2G channel scenario features an urban and suburban terrain. An unmanned aerial vehicle functions as the transmitter, operating at an approximate altitude of 600 meters above ground level, traversing distances ranging from 1.64 km to 41.49 km from the receiver, and maintaining speeds between 74.2 m/s and 92 m/s. A consistent LOS transmission exists between the receiver and the transmitter. The A2G channel fading model is divided into two components: large-scale fading and small-scale fading. Large-scale fading encompasses path loss and shadowing, with a closed-form expression provided as follows:
where
is the path loss defined with a value of
=98.2 at an initial distance
, the path loss exponent is denoted by
n=1.7, and the initial distance is set at
=1.3 km,
assumes the values of ±1, where
and
correspond to the UAV moving away from and towards the receiver, respectively. Additionally,
represents a heading adjustment factor, and
X is a Gaussian random variable with a mean of zero and a standard deviation
, which is utilized to model shadow fading.
For small-scale fading, the A2G channel is characterized by LOS propagation. The complex baseband impulse response for multipath fading is given by the following expression:
where
,
and
denote amplitude, phase and delay, respectively,
denotes the probability of occurrence of the kth intermittent multipath component (MPC); the subscripts LOS, 2 and k denote the LOS component, the ground reflectance component, and the kth intermittent MPC, respectively, where
;
and
are calculated jointly with the curved-earth two-ray model; the relative power of the intermittent taps
follows a Gaussian distribution with a mean of -23.3 dB and a standard deviation of 5.1 dB; and
follows a uniform distribution from 0 to
.
Table 5.
Fitting coefficients for the occurrence probability of Tap 3-9 in the multipath decay model.
Table 5.
Fitting coefficients for the occurrence probability of Tap 3-9 in the multipath decay model.
|
Tap |
|
|
|
| 3 |
0.65 |
-0.09 |
0.39 |
| 4 |
-0.61 |
-0.08 |
0.32 |
| 5 |
-0.87 |
-0.10 |
0.46 |
| 6 |
-1.42 |
-0.10 |
0.57 |
| 7 |
-2.60 |
-0.02 |
0.48 |
| 8 |
-3.63 |
0.03 |
0.47 |
| 9 |
-4.53 |
0.048 |
0.67 |
Based on the above channel modeling method, this section will simultaneously validate the AMR and RFFI tasks across scenarios. In the AMR task, based on the RadioML 2018.01A datasets of multiple modulation types in the G2G channel scenario collected using the SDR-based USRP B210 [
35], the modulated RF signal datasets under the A2G channel scenario are generated using the above channel modeling method. Similarly, in the RFFI task, the ZigBee RF signal dataset under the A2G channel scenario is simulated based on the ZigBee signal dataset of the same type of the ground channel scenario constructed in previous work [
30]. As a result, the RF signal datasets of the G2G and A2G channel scenarios for the two tasks can be obtained to provide data support for the validation of the cross-scenario domain adaptation method.
In addition, in order to better solve the problem of the difficulty to collect and label sample data of RF signal present in the target domain under cross-scenario, the sample size of the target domain dataset is only half of that of the source domain, and all RF signal samples in the target domain are unlabeled. The RF signal dataset constructed in this way under cross-scenario can be used to verify the feasibility of the UDA-based RF signal attribute recognition method.
Table 6 and
Table 7 show the basic attributes of the RF signal dataset under the two tasks of AMR and RFFI, respectively.
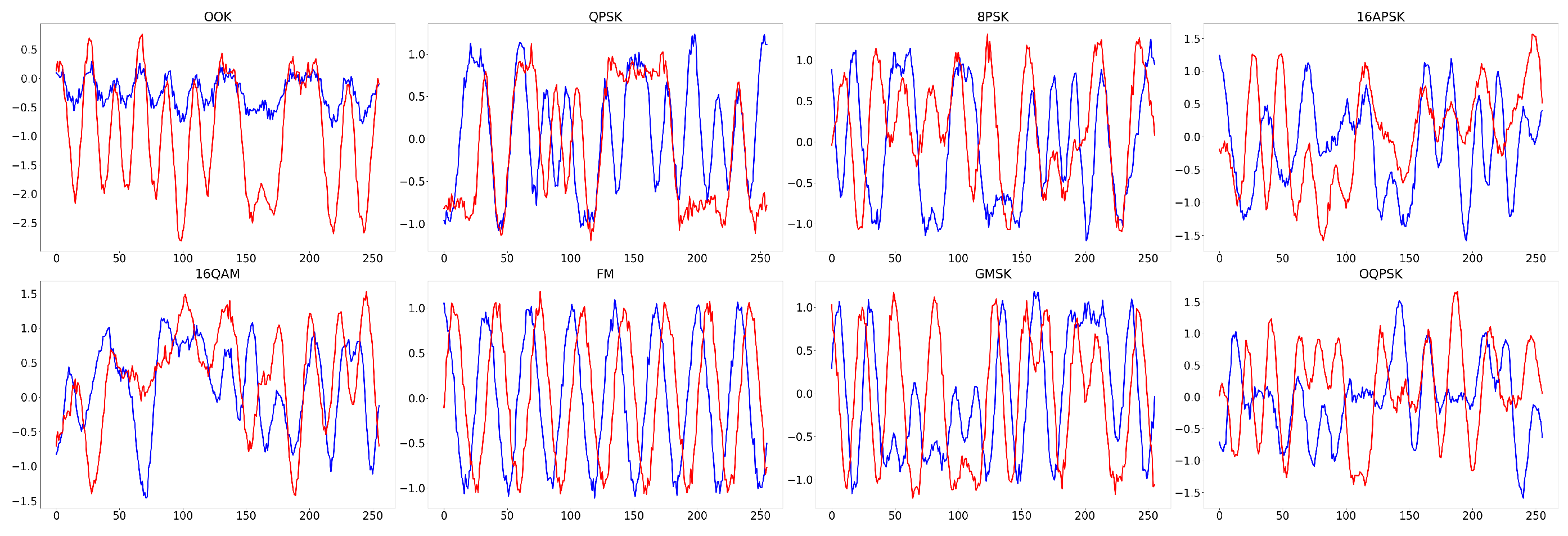
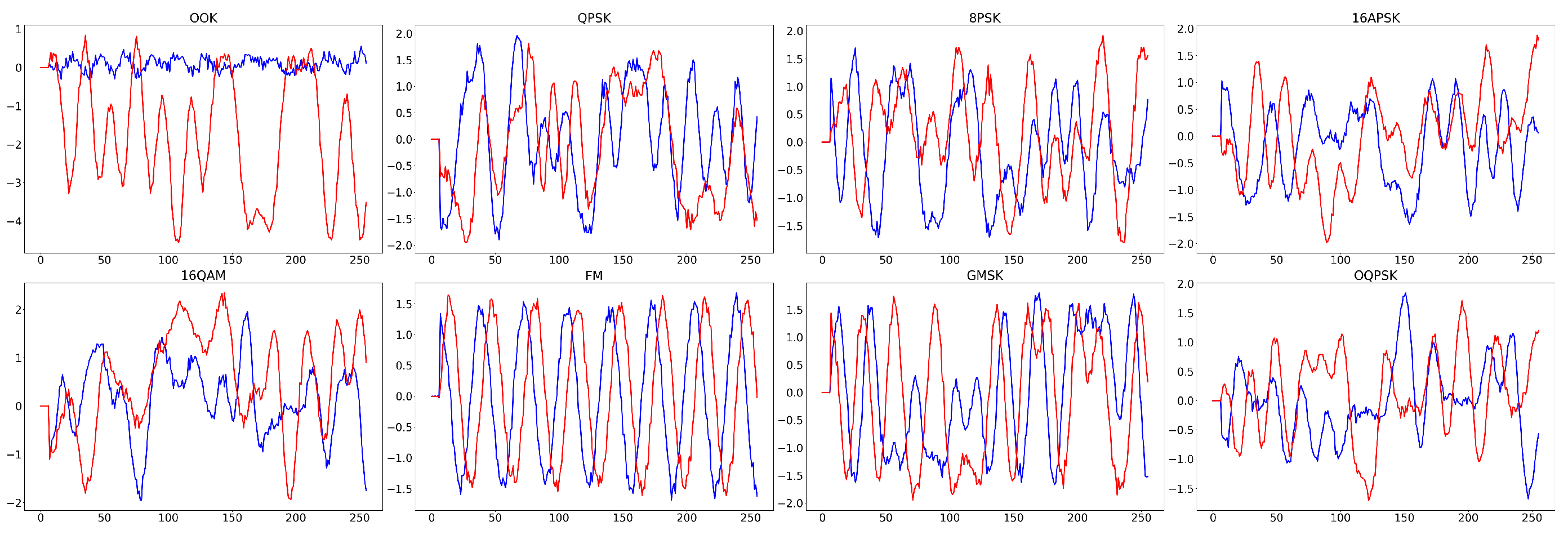
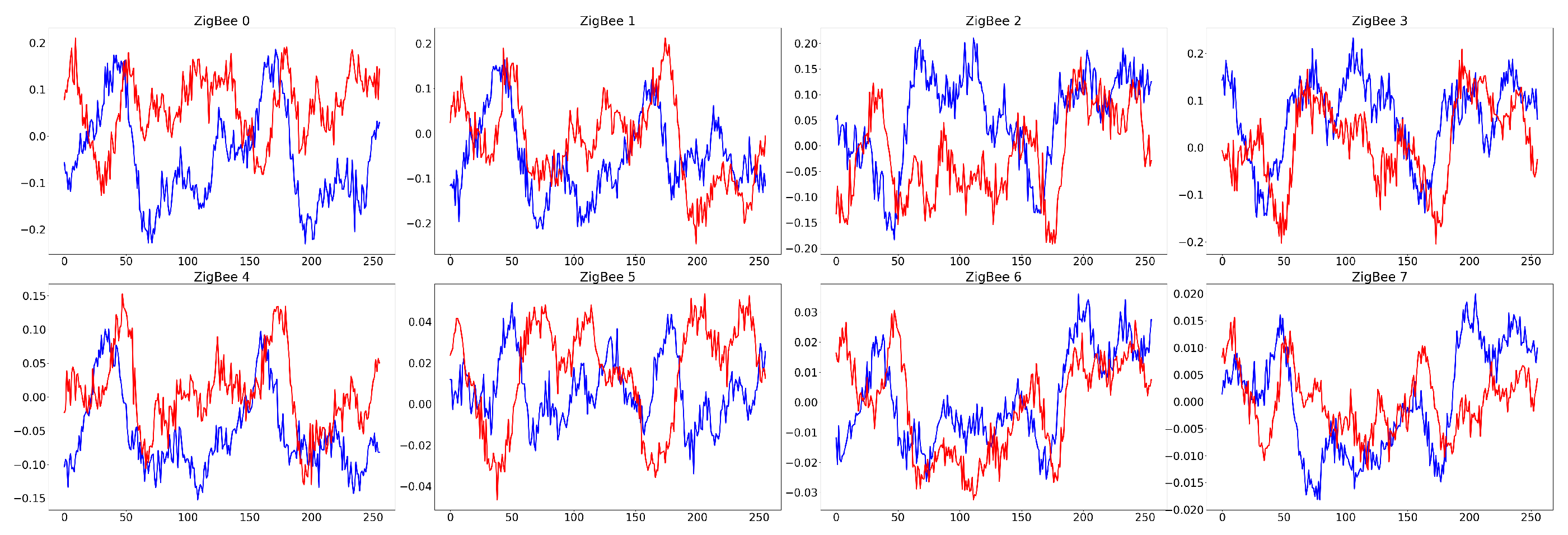
Figure 2,
Figure 3,
Figure 4 and
Figure 5 present the time-domain waveform of G2G and A2G scenarios in these two tasks.
5.1.2. Experimental Setup
The experimental setup is presented across two dimensions: software and hardware. On the software front, the Ubuntu 18.04 operating system is selected, with Python 3.8 serving as the primary programming language for the experiments conducted herein. The deep learning framework of choice is PyTorch, which is integrated with CUDA acceleration libraries to utilize the full computational capabilities of GPUs.
Regarding the hardware configuration, an NVIDIA TITAN XP graphics card with 12 GB of memory and an architecture optimized for parallel computing is used, thereby expediting the model training process. Supplementing this is an Intel Xeon E5-2650 V4 processor and 64 GB RAM, endowing the computing platform with ample computational resources and memory to handle data processing and model training efficiently.
5.1.3. Experimental Performance Evaluation
In experimental performance evaluation, accuracy serves as the primary metric in this study. In multi-class scenarios, accuracy represents the proportion of samples correctly classified across the entire test set. The formula for calculating the accuracy of radio frequency signal attribute recognition is as follows:
where
denotes the number of correctly recognized samples for the
i-th attribute,
C is the total number of attribute categories, and
N is the total number of samples in the test set. This metric provides an intuitive assessment of the model’s overall performance in recognizing different modulation schemes.
Moreover, we also introduce the t-distributed Stochastic Neighbor Embedding (t-SNE) for visual representation and analysis of results. t-SNE is a nonlinear dimensionality reduction technique that maps high-dimensional data to two or three-dimensional spaces while preserving local relationships between data points. Through t-SNE, one can observe the distribution of outputs from different methods, gaining insight into the cohesion within different emitter categories and the separation between them. This visual analysis aids in understanding the model’s performance in multi-class classification tasks and comparing the merits and demerits of different feature extraction.
5.1.4. Experimental Comparison of Baseline Methods
To compare and highlight the effectiveness of the proposed UDA method, we have set up an experimental framework where the performance of baseline methods is systematically analyzed. In this experimental setup, the results obtained by supervised training on labeled data from the target domain and testing directly within the same domain serve as the lower limit of the baseline comparison. Conversely, the results achieved by training and testing on all available signal data in the target domain, with true labels, represent the upper limit of the baseline comparison. Additionally, this study employs two methods designed to address distribution discrepancies in cross-domain data: LTS-SEI and DANN. The LTS-SEI method is used for unsupervised domain adaptation in RFFI, enhancing cross-scenario performance in RF signal attribute recognition. DANN, a pivotal method in domain adaptation, employs adversarial training to adjust the model to the data feature distribution in new scenarios, effectively overcoming the limitations traditional methods face when dealing with inconsistencies in data distribution between source and target domains. Thus, these four baseline methods provide a comprehensive assessment of the effectiveness and robustness of the UDA method proposed herein, thereby better understanding its potential and limitations in practical applications.
5.1.5. Experimental Settings
Experimental model training configurations are pivotal in the realm of UDA. The choice of parameter settings during model training significantly influences the learning outcomes. Initially, the balancing factors are crucial for modulating the influence of various loss functions, ensuring seamless model transfer across domains. Specifically, the parameters
,
,
, and
govern the noise perturbation consistency loss, the sample-level maximum correlation loss, the distribution-level maximum similarity loss, the domain adversarial loss, and the classification loss, respectively. Proper tuning of these parameters aids in maintaining the model’s performance stability during different datasets, such as from G2G to A2G and vice versa. Furthermore, the learning rate
impacts the model’s optimization velocity and convergence quality. An inappropriate learning rate, whether too high or too low, may result in learning process instability or delayed convergence. A comprehensive consideration of these parameters enhances the model’s generalization and adaptability.
Table 8 provides a comprehensive overview of the specific values for these five critical parameter configurations across the four transfer scenarios examined in the experiments.
5.2. Results and Analysis
5.2.1. Performance Degradation Cross Various Communication Scenarios
Table 9 presents the test results for modulation recognition and radio frequency fingerprint identification tasks within the G2G and A2G channel scenarios, without domain adaptation, where the number of training signal samples is consistent across all scenarios.
In the AMR task, the accuracy for training and testing within the same channel scenario, G2G and A2G, were 72.9% and 69.3%, respectively. However, the model trained in the G2G scenario and tested in the A2G scenario yielded an accuracy of 34.7%, representing a substantial decrease from 69.3% to 34.7%, a relative drop of 49.6%. Similarly, the model trained in the A2G scenario and tested in the G2G scenario achieved an accuracy of 53.5%, indicating a decline from 72.9% to 53.5%, or a 26.6% reduction relative to the original accuracy.
In the RFFI task, training and testing within the A2G scenario achieved an accuracy of 94.9%. When the model trained in the G2G scenario was tested in the A2G scenario, the accuracy dropped to 79.3%, a relative decrease of 16.4% from the initial 94.9%. Conversely, training and testing within the G2G scenario resulted in an accuracy of 95.9%. When the model trained in the A2G scenario was tested in the G2G scenario, the accuracy plummeted to 55.5%, indicating a significant performance decline from 95.9% to 55.5%, or a 42.1% decrease.
These experimental findings indicate that models trained and tested in different scenarios exhibit varying degrees of performance degradation when tested across scenarios. This decline in performance prevents the practical deployment and application of trained models across different channel scenarios.
5.2.2. Comparison of Unsupervised Domain Adaptation Methods
Table 10 showcases the recognition performance of the proposed PMS-UDA and baseline methods in cross-scenario tasks of RF signal attribute recognition for G2G→A2G and A2G→G2G scenarios. The accuracy of lower limit, representing the results of supervised training on source domain signal data followed by direct testing in the target domain without any knowledge transfer, is used to measure the performance enhancement facilitated by the UDA method. This lower limit corresponds to the results of supervised training on target domain RF signal samples, which are half in number compared to the source domain. As shown in
Table 9, compared to not implementing domain adaptation, the PMS-UDA method improved recognition accuracy by 29.1%, 16.4%, 9.8%, and 18.3%, respectively.
Moreover, the accuracy of upper limit in
Table 10 indicates the results obtained by directly using target domain signal data for supervised training and testing. This upper limit serves as a benchmark to compare against the performance of the UDA method approximating supervised training results. According to
Table 10, the accuracy of the PMS-UDA method in RF signal attribute recognition compared to the upper limit are 95.1%, 99.1%, 94.8%, and 77.8%. Except for the A2G→G2G scenario, the PMS-UDA method achieves recognition accuracies greater than 90.0% in other cross-scenario tasks, closely approaching supervised training performance. This indicates that the PMS-UDA method effectively facilitates the transfer of essential prior knowledge from the source to the target domain.
Table 10 reveals that LTS-SEI outperforms DANN, primarily due to the inclusion of domain classification and cross-entropy loss functions within LTS-SEI. Across the four cross-scenario cases, the PMS-UDA method shows an average improvement of 0.9%, 0.1%, 3.9%, and 9.8% over baseline methods. Thus, the PMS-UDA method exhibits the highest average recognition accuracy among the three UDA methods examined.
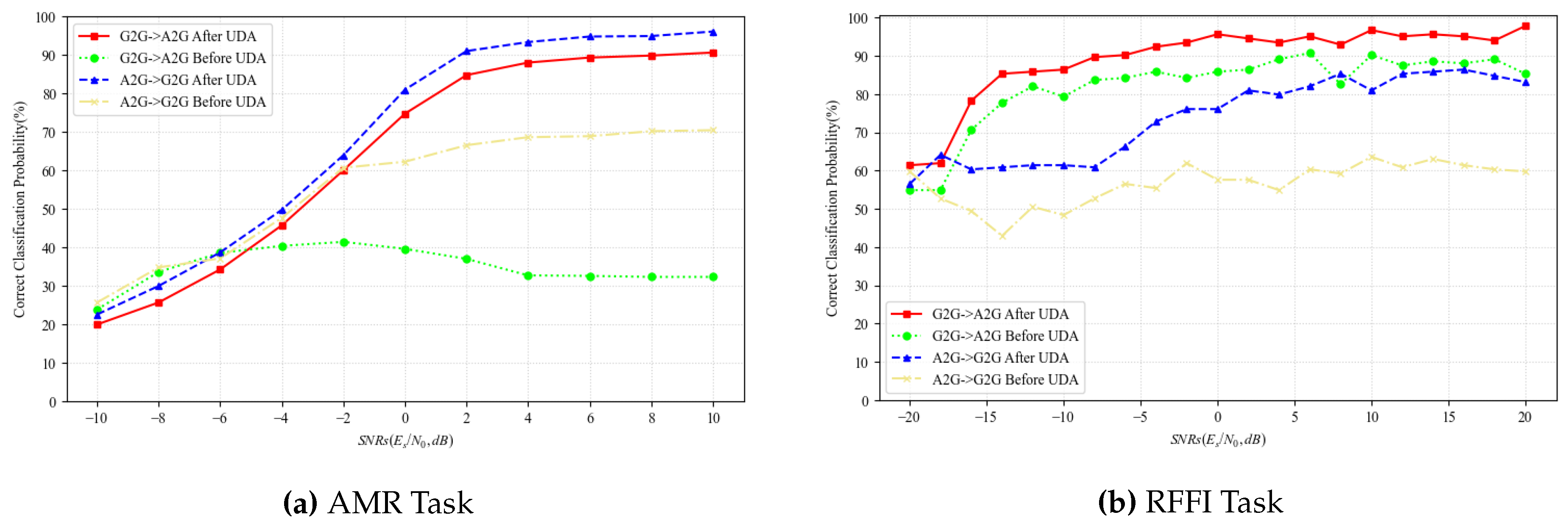
Furthermore,
Figure 6 demonstrates that, compared to the performance prior to the application of the PMS-UDA method, the model exhibits enhanced recognition accuracy under both tasks across various SNRs after applying the PMS-UDA method. This indicates that the PMS-UDA method effectively facilitates the transfer of prior knowledge across scenarios under both high and low SNR conditions.
Consequently, this experiment concludes that the PMS-UDA method effectively achieves prior knowledge transfer across scenarios and closely approximates the performance of supervised training; additionally, it demonstrates superior cross-scenario knowledge transfer capability relative to baseline methods.
5.2.3. Ablation Study of the Optimization of Loss Functions
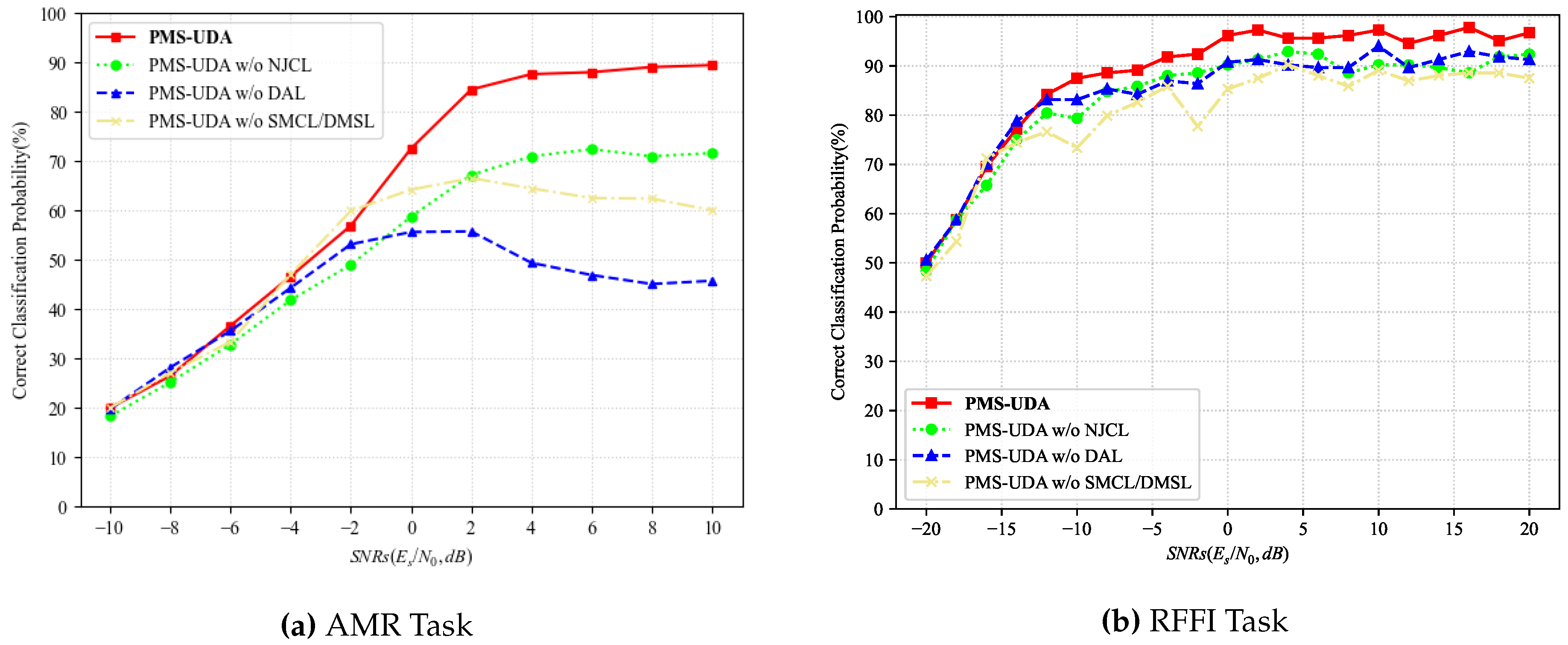
Table 11 illustrates the experimental results of an ablation study designed to assess the contribution of each loss function within the proposed PMS-UDA method. When the noise perturbation consistency loss, the sample-level maximum correlation loss, and the distribution-level maximum similarity loss are omitted from the proposed UDA method, the accuracies for AMR are 52.7%, 51.5%, and 43.6%, respectively, representing decreases of 11.3%, 12.5%, and 20.4% from the complete model. The RFFI task exhibits a similar trend; without these loss functions, the accuracies are 83.4%, 80.4%, and 84.4%, with reductions of 5.7%, 8.7%, and 4.7%, respectively. This experiment confirms that these three types of losses functions are pivotal in enabling effective knowledge transfer in the UDA methods.
As depicted in
Figure 7, the version of the proposed UDA method without NPCL exhibits reduced accuracy at low SNRs, indicating that incorporating noise perturbation consistency learning enhances the method’s robustness against noise in low SNR conditions. This is achieved by introducing random noise perturbation. Conversely, the variant of the PMS-UDA method without DAL shows a more pronounced decline in performance at high SNRs. This suggests that domain adversarial learning is instrumental in fostering the acquisition of domain-invariant features across different scenarios at high SNRs, thereby enhancing the representation learning capacity of cross-scenario UDA methods.
In comparison to the complete PMS-UDA method, the performance of the method lacking SMCL and DMSL drops significantly at high SNRs. This underscores the necessity of addressing data distribution discrepancies through optimization at both the sample and distribution levels. Such optimization is essential for minimizing differences in cross-domain data distributions between the source and target domains.
5.2.4. Ablation Study with Progressive Label Alignment Training Methods
Table 12 presents the accuracies of the proposed PLAT method with or without the employment of the progressive label alignment method, across two tasks in the cross-scenario: G2G to A2G and A2G to G2G. In the absence of the PLAT method, the accuracies of AMR task for two cross-scenarios are 61.3% and 64.6%, respectively. When the PLAT method is employed, the accuracies improve to 64.0% and 69.9%, reflecting gains of 2.7% and 5.3%, respectively.
In the RFFI task, the method’s performance without PLAT yields accuracies of 83.1% for the G2G→A2G scenario and 53.4% for the A2G to G2G scenario. Upon incorporating the progressive label alignment method, these figures rise to 89.1% and 73.8%, demonstrating significant improvements of 6.0% and 18.8%, respectively. These results underscore the effectiveness of the progressive label alignment method in facilitating domain knowledge transfer for both RF signal attribute recognition tasks in the unsupervised domain adaptation.
5.2.5. Similarity of Feature Distribution via T-SNE Visualization
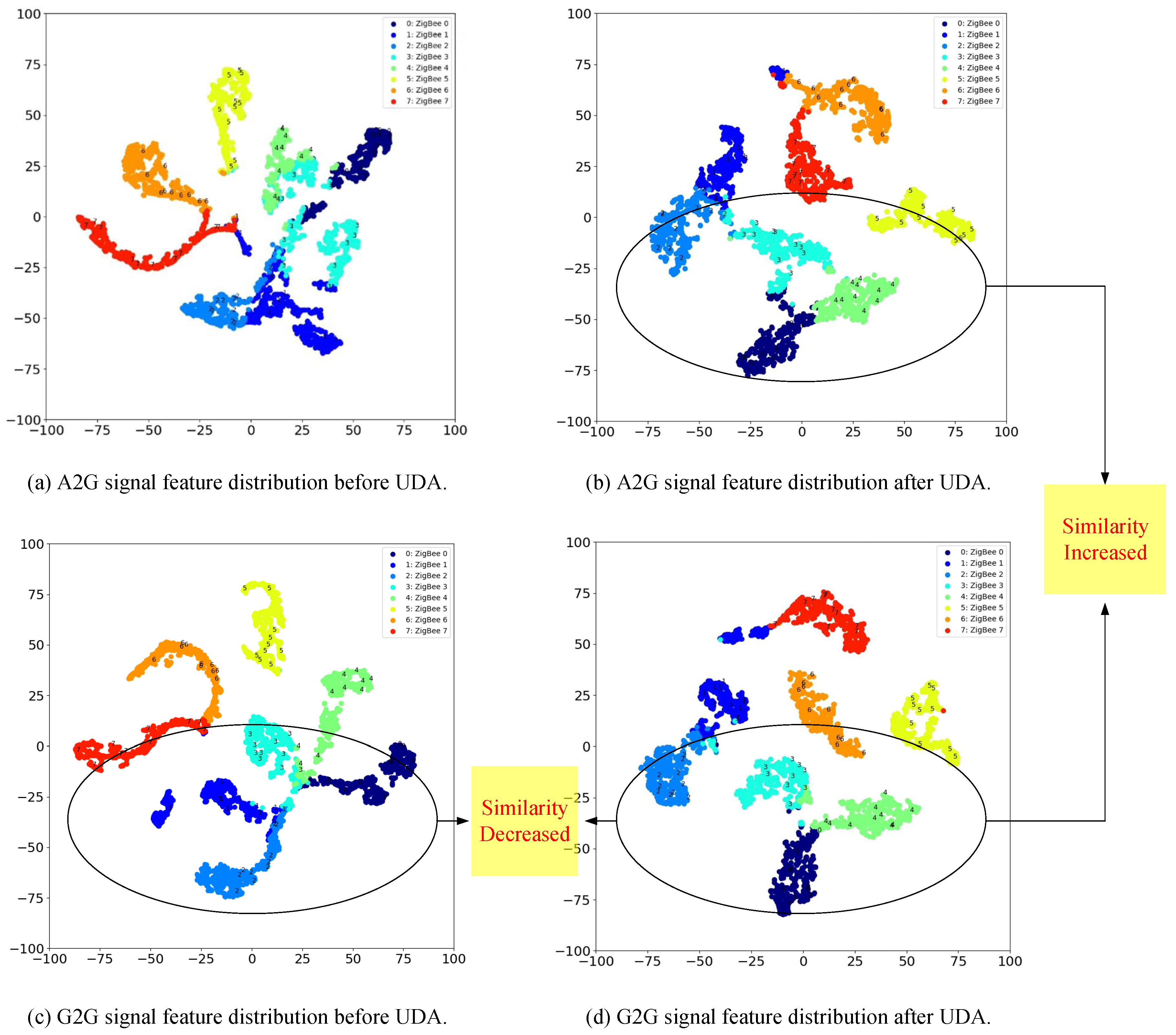
Figure 8 illustrates the experiment designed to showcase the evolution of feature distributions through domain adaptation for the G2G→A2G scenario. Initially, as depicted in
Figure 8(a) and (c), there is a noticeable divergence in the feature distribution between the source domain G2G and the target domain A2G. However, following domain adaptation, the scenario changes, as indicated in
Figure 8(b) and (d), with a increase in the similarity of the feature distributions between the two domains.
Furthermore, the accuracies for the source domain G2G scenario are observed to be 95.2% before and 95.6% after domain adaptation, as shown in
Figure 8(c) and (d). This minor yet significant improvement of 0.4% post-adaptation not only enhances the recognition accuracy but also aligns the feature similarities more closely with those in the target domain. A comparison between
Figure 8(a) and (b) reveals that the domain adaptation for A2G scenario exhibit greater inter-class dispersion and tighter intra-class distribution compared to their pre-adaptation state.
The conclusions drawn from this experiment suggest that the proposed UDA method is effective in achieving analogous feature distributions across the source and target domains. Additionally, it fosters greater dispersion among classes and tighter cohesion within classes for RFFI in the target domain.
6. Conclusion
In this paper, we propose a PMS-UDA method for RF signal attribute recognition, which demonstrated remarkable robustness against noise and the maximum similarity of signal distribution across communication scenarios. This method effectively enables the model to handle signals across various SNRs by recognizing that samples perturbed by slight noise sharing the same label. Additionally, our method incorporate a sample-level maximum correlation and distribution-level maximum similarity optimization, enhancing the alignment and similarity of feature distribution between the source and target domains. Through domain adversarial learning, the model extracts domain-invariant features, minimizing the impact of channel scenario differences. A progressive label alignment training method further refines this process by utilizing pseudo-labels from unlabeled samples in prior phases to achieve maximum sample-level correlation and distribution-level similarity in subsequent phases. Experimental results confirmed that our PMS-UDA method approached the upper limit of the target domain supervised training. It also proved particularly effective under low SNR conditions, affirming its utility in achieving feature distribution similarity between the source and target domains.
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant numbers U20B2042).
References
- Labib, N.S.; Danoy, G.; Musial, J.; Brust, M.R.; Bouvry, P. A Multilayer Low-Altitude Airspace Model for UAV Traffic Management. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 9th ACM Symposium on Design and Analysis of Intelligent Vehicular Networks and Applications, New York, NY, USA, 2019; DIVANet ’19, pp. 57–63. [CrossRef]
- Watson, T. Maximizing the Value of America’s Newest Resource, Low-Altitude Airspace: An Economic Analysis of Aerial Trespass and Drones. Indiana Law Journal 2020, 95, 1399–1435. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Tian, T.; Yin, J. A Review of Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Low-Altitude Remote Sensing (UAV-LARS) Use in Agricultural Monitoring in China. Remote Sensing 2021, 13, 1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, F.; Ning, C.; Liu, H.; Zhong, G. An Operational Capacity Assessment Method for an Urban Low-Altitude Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Logistics Route Network. Drones 2023, 7, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Jiang, N.; Li, B.; Zhu, X.; Wang, Y.; Du, W. UAV Navigation in High Dynamic Environments: A Deep Reinforcement Learning Approach. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics 2021, 34, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, C.; Zhan, R. Global Analysis of Active Defense Technologies for Unmanned Aerial Vehicle. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine 2022, 37, 6–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Gan, F.; Cao, X.; Liu, W.; Li, P. Radar Intra–Pulse Signal Modulation Classification with Contrastive Learning. Remote Sensing 2022, 14, 5728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, T.; Feng, Z.; Yang, S. Towards the Automatic Modulation Classification with Adaptive Wavelet Network. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking 2023, pp. 1–1. [CrossRef]
- Paul, A.K.; Tachibana, A.; Hasegawa, T. An Enhanced Available Bandwidth Estimation Technique for an End-to-End Network Path. IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management 2016, 13, 768–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdoush, Y.; Pojani, G.; Corazza, G.E. Adaptive Instantaneous Frequency Estimation of Multicomponent Signals Based on Linear Time–Frequency Transforms. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 2019, 67, 3100–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Lin, C.L.; Chen, W.; Juang, C.F.; Wu, X. Signal Frequency Estimation Based on RNN. In Proceedings of the 2020 Chinese Control And Decision Conference (CCDC); 2020; pp. 2030–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Ke, D.; Wang, X.; Huang, Z.; Huang, K. Robustness of Deep Learning-Based Specific Emitter Identification under Adversarial Attacks. Remote Sensing 2022, 14, 4996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Gong, Y.; Liu, J.; Lin, S.; Han, Z.; Cao, R.; Huang, K.; Letaief, K.B. Multi-Channel Attentive Feature Fusion for Radio Frequency Fingerprinting. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications 2023, pp. 1–1. [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Hu, A.; Zhang, Z. Data-and-Channel-Independent Radio Frequency Fingerprint Extraction for LTE-V2X. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking 2024, 10, 905–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Chu, X.; Calvo-Ramirez, C.; Briso, C.; Yin, X. Low Altitude UAV Air-to-Ground Channel Measurement and Modeling in Semiurban Environments. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing 2017, 2017, 1587412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, K.; Rodríguez-Piñeiro, J.; Yin, X.; Tian, L. Low Altitude Air-to-Ground Channel Modelling Based on Measurements in a Suburban Environment. In Proceedings of the 2019 11th International Conference on Wireless Communications and Signal Processing (WCSP); 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Prakash, J. Internet of Low-Altitude UAVs (IoLoUA): A Methodical Modeling on Integration of Internet of “Things” with “UAV” Possibilities and Tests. Artificial Intelligence Review 2023, 56, 2279–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Lin, Y.; Tian, Q.; Si, G. Transfer Learning Promotes 6G Wireless Communications: Recent Advances and Future Challenges. IEEE Transactions on Reliability 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wei, Z.; Ng, D.W.K.; Yuan, J.; Liang, Y.C. Deep Transfer Learning for Signal Detection in Ambient Backscatter Communications. IEEE 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, L.J.; Michaels, A.J. Transfer Learning for Radio Frequency Machine Learning: A Taxonomy and Survey. sensors 2022, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Xu, Q.; Li, S.; Wang, X.; Huang, Z. Cross-Domain Automatic Modulation Classification Using Multimodal Information and Transfer Learning. Remote Sensing 2023, 15, 3886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Z.; Li, P.; Wu, B.; Yuan, S.; Chen, Y. An Adaptive Focal Loss Function Based on Transfer Learning for Few-Shot Radar Signal Intra-Pulse Modulation Classification. Remote Sensing 2022, 14, 1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, V.M.; Gopalan, R.; Li, R.; Chellappa, R. Visual Domain Adaptation: A survey of recent advances. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine 2015, 32, 53–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Deng, W. Deep Visual Domain Adaptation: A Survey. Neurocomputing 2018, 312, 135–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, G.; Cook, D. A Survey of Unsupervised Deep Domain Adaptation. ACM transactions on intelligent systems and technology 2020, 11, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farahani, A.; Voghoei, S.; Rasheed, K.; Arabnia, H.R. A Brief Review of Domain Adaptation 2021.
- Bu, K.; He, Y.; Jing, X.; Han, J. Adversarial transfer learning for deep learning based automatic modulation classification. IEEE Signal Processing Letters 2020, 27, 880–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Guo, L.; Zhao, H.; Shang, P.; Chu, Z.; Lu, X. A Long Time Span-Specific Emitter Identification Method Based on Unsupervised Domain Adaptation. Remote Sensing 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Ma, Q.; Ding, W. Multiscale Correlation Networks Based On Deep Learning for Automatic Modulation Classification. IEEE Signal Processing Letters 2023, pp. 1–5. [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Ding, W.; Shao, Z.; Zhang, D.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J. Multi-Periodicity Dependency Transformer Based on Spectrum Offset for Radio Frequency Fingerprint Identification, 2024, [2408.07592]. [CrossRef]
- Endres, D.M.; Schindelin, J.E. A new metric for probability distributions. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory 2003, 49, 1858–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kullback, S.; Leibler, R.A. On Information and Sufficiency. Annals of Mathematical Statistics 1951, 22, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.; Lin, Y.; Zha, H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Gui, G.; Mao, S. Large-Scale Real-World Radio Signal Recognition with Deep Learning. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics 2022, 35, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matolak, D.W.; Sun, R. Air–ground channel characterization for unmanned aircraft systems—Part III: The suburban and near-urban environments. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 2017, 66, 6607–6618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shea, T.J.; Roy, T.; Clancy, T.C. Over-the-Air Deep Learning Based Radio Signal Classification. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing 2018, 12, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Optimization method for cross-scenario RF signal attribute recognition.
Figure 1.
Optimization method for cross-scenario RF signal attribute recognition.
Figure 2.
Time-domain waveforms of various modulated signals for G2G channel scenarios at SNR=10dB.
Figure 2.
Time-domain waveforms of various modulated signals for G2G channel scenarios at SNR=10dB.
Figure 3.
Time-domain waveforms of various modulated signals for A2G channel scenario at SNR=10dB.
Figure 3.
Time-domain waveforms of various modulated signals for A2G channel scenario at SNR=10dB.
Figure 4.
Time-domain waveform of ZigBee signals for G2G channel scenario at SNR=10dB.
Figure 4.
Time-domain waveform of ZigBee signals for G2G channel scenario at SNR=10dB.
Figure 5.
Time-domain waveform of ZigBee signals for A2G channel scenario at SNR=10dB.
Figure 5.
Time-domain waveform of ZigBee signals for A2G channel scenario at SNR=10dB.
Figure 6.
Comparison of the performance before and after using PMS-UDA method.
Figure 6.
Comparison of the performance before and after using PMS-UDA method.
Figure 7.
Ablation study of the optimization of loss function.
Figure 7.
Ablation study of the optimization of loss function.
Figure 8.
Feature distribution of ZigBee signal before and after UDA in G2G→A2G cross-scenario.
Figure 8.
Feature distribution of ZigBee signal before and after UDA in G2G→A2G cross-scenario.
Table 1.
Layout of MSCNs network architecture for AMR task. LSWT denotes learnable stationary wavelet transform, MSC denotes multi-scale correlation, SAFS denotes subband-adaptive frequency selection, FS-ResNet denotes frequency selection ResNet, GAP is global average pooling, and FC is full connection.
Table 1.
Layout of MSCNs network architecture for AMR task. LSWT denotes learnable stationary wavelet transform, MSC denotes multi-scale correlation, SAFS denotes subband-adaptive frequency selection, FS-ResNet denotes frequency selection ResNet, GAP is global average pooling, and FC is full connection.
| Layer |
Output Dimension |
Number of Parameters |
kFLOPs |
| Input |
|
- |
0 |
| LSWT |
|
120 |
245.8 |
| MSC |
|
- |
143.4 |
| SAFS |
|
426 |
130.5 |
| FS-ResNet |
|
2256 |
3313.3 |
| FS-ResNet |
|
6544 |
5426.9 |
| FS-ResNet |
|
23312 |
10675.1 |
| GAP |
64 |
- |
8.2 |
Table 2.
Layout of MPDFormer network architecture for RFFI task.
Table 2.
Layout of MPDFormer network architecture for RFFI task.
| Layers |
Output Dimension |
Parameters |
kFLOPs |
| Input |
1024 × 2 |
– |
– |
| Periodic Embedding Representation |
16 × 128 |
– |
13799.4 |
| Projection |
16 × 128 |
16,512 |
|
| Scaling |
16 × 128 |
– |
|
| Positional Encoding |
16 × 128 |
– |
|
| Encoding Layers |
16 × 128 |
1,193,472 |
|
| Transpose |
128 × 16 |
– |
|
| GAP |
128 × 1 |
– |
|
| Squeeze |
128 |
– |
|
| Periodic Embedding Representation |
25 × 84 |
– |
9626.4 |
| Projection |
25 × 84 |
7,140 |
|
| Scaling |
25 × 84 |
– |
|
| Positional Encoding |
25 × 84 |
– |
|
| Encoding Layers |
25 × 84 |
517,104 |
|
| Transpose |
84 × 25 |
– |
|
| GAP |
84 × 1 |
– |
|
| Squeeze |
84 |
– |
|
| Periodic Embedding Representation |
8 × 256 |
– |
27004.9 |
| Projection |
8 × 256 |
65,792 |
|
| Scaling |
8 × 256 |
– |
|
| Positional Encoding |
8 × 256 |
– |
|
| Encoding Layers |
8 × 256 |
4,746,240 |
|
| Transpose |
256 × 8 |
– |
|
| GAP |
256 × 1 |
– |
|
| Squeeze |
256 |
– |
|
| Concatenation |
468 |
– |
0.1 |
| Adaptive Fusion |
468 |
144 |
|
Table 3.
Layout of domain adversarial network architecture.
Table 3.
Layout of domain adversarial network architecture.
| Layer |
Output dimension |
| |
AMR |
RFFI |
| Input |
64 |
468 |
| Linear |
128 |
128 |
| SELU |
128 |
128 |
| Dropout |
128 |
128 |
| Linear |
128 |
128 |
| SELU |
128 |
128 |
| Dropout |
128 |
128 |
| Linear |
2 |
2 |
Table 4.
Layout of MLP classification network architecture for AMR and RFFI tasks.
Table 4.
Layout of MLP classification network architecture for AMR and RFFI tasks.
| Layer |
Output dimension |
| |
AMR |
RFFI |
| Input |
64 |
468 |
| Linear |
128 |
128 |
| SELU |
128 |
128 |
| Dropout |
128 |
128 |
| Linear |
64 |
64 |
| SELU |
64 |
64 |
| Dropout |
64 |
64 |
| Linear |
8 |
8 |
Table 6.
RF signal dataset for the AMR task across G2G→A2G and A2G→G2G scenarios.
Table 6.
RF signal dataset for the AMR task across G2G→A2G and A2G→G2G scenarios.
| Dataset settings |
Ground-to-ground→Air-to-ground |
Air-to-ground→Ground-to-ground |
| (G2G→A2G) |
(A2G→G2G) |
| Source |
Target |
Source |
Target |
| Sample size |
84480 |
42240 |
84480 |
42240 |
| Percentage with label |
100% |
0% |
100% |
0% |
| Signal dimension |
1024×2 |
| SNR |
-10dB to 10dB, with a interval of 2dB |
| Training: testing |
9:1 |
| Type of modulation |
8 modulation types: |
| OOK, QPSK, 8PSK, 16APSK, 16QAM, FM, GMSK, OQPSK |
Table 7.
RF signal dataset for the RFFI task across G2G→A2G and A2G→G2G scenarios.
Table 7.
RF signal dataset for the RFFI task across G2G→A2G and A2G→G2G scenarios.
| Dataset settings |
Ground-to-ground→Air-to-ground |
Air-to-ground→Ground-to-ground |
| (G2G→A2G) |
(A2G→G2G) |
| Source |
Target |
Source |
Target |
| Sample size |
38640 |
19320 |
38640 |
19320 |
| Percentage with label |
100% |
0% |
100% |
0% |
| Signal dimension |
1024×2 |
| SNR |
-20dB to 20dB, intervals 2dB |
| Training: testing |
9:1 |
| Type of ZigBee devices |
8 ZigBee devices: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 |
Table 8.
Experimental configuration for two tasks.
Table 8.
Experimental configuration for two tasks.
| Tasks |
Hyperparameters |
|
|
|
|
lr |
| AMR |
1.0 |
0.1 |
1.0 |
2.0 |
1e-3 |
| RFFI |
7e-4 |
Table 9.
Performance degradation of AMR and RFFI tasks cross various communication scenarios.
Table 9.
Performance degradation of AMR and RFFI tasks cross various communication scenarios.
| Task |
Accuracy (%) |
| AMR |
RFFI |
|
Test Scenario |
G2G |
A2G |
G2G |
A2G |
| Train Scenario |
|
| G2G |
72.9 |
34.9 |
95.9 |
79.3 |
| A2G |
53.5 |
69.3 |
55.5 |
94.9 |
Table 10.
Comparison of UDA methods for cross-scenario RF signal attribute recognition in two tasks.
Table 10.
Comparison of UDA methods for cross-scenario RF signal attribute recognition in two tasks.
| Method |
Accuracy(%) |
| AMR |
RFFI |
| G2G→A2G |
A2G→G2G |
G2G→A2G |
A2G→G2G |
| Lower limit |
34.9 |
53.5 |
79.3 |
55.5 |
| DANN |
62.6 |
68.3 |
83.8 |
58.3 |
| LTS-SEI |
63.7 |
70.2 |
86.7 |
69.7 |
| PMS-UDA (ours) |
64.0 |
69.9 |
89.1 |
73.8 |
| Upper limit |
67.3 |
70.5 |
94.0 |
94.8 |
Table 11.
Ablation study of optimization loss function in G2G→A2G scenario.
Table 11.
Ablation study of optimization loss function in G2G→A2G scenario.
| Tasks |
Accuracy(%) |
| PMS-UDA |
w/o NPCL |
w/o SMCL/DMSL |
w/o DAL |
| AMR |
64.0 |
52.7 |
51.5 |
43.6 |
| RFFI |
89.1 |
83.4 |
80.4 |
84.4 |
Table 12.
Ablation study of progressive label alignment method across scenarios.
Table 12.
Ablation study of progressive label alignment method across scenarios.
Progressive label
alignment method |
Accuracy(%) |
| AMR |
RFFI |
| G2G→A2G |
A2G→G2G |
G2G→A2G |
A2G→G2G |
| ✗ |
61.3 |
64.6 |
83.1 |
55.0 |
| ✓ |
64.0 |
69.9 |
89.1 |
73.8 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).