Submitted:
28 August 2024
Posted:
29 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
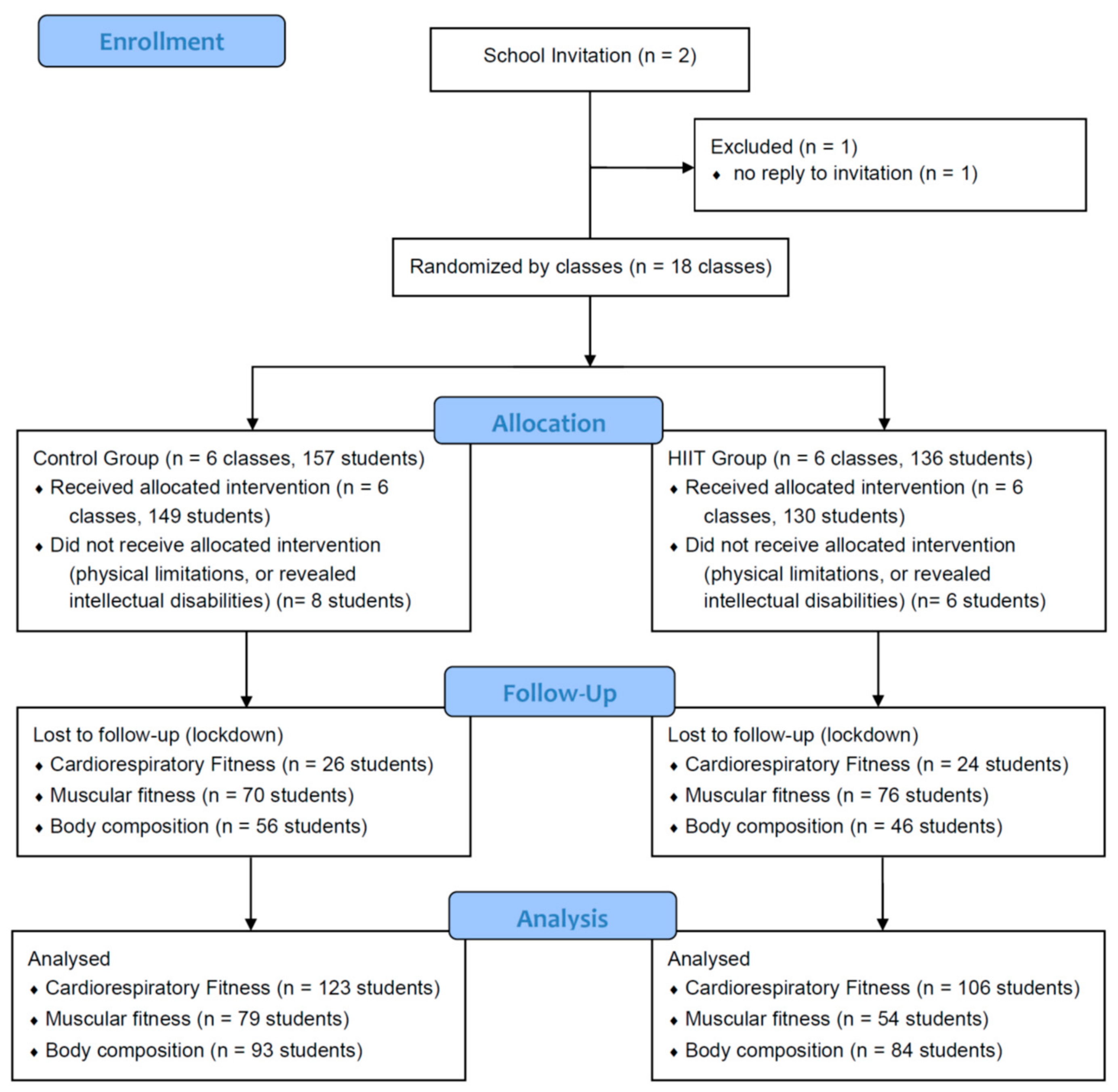
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Randomization
2.4. Sample Size
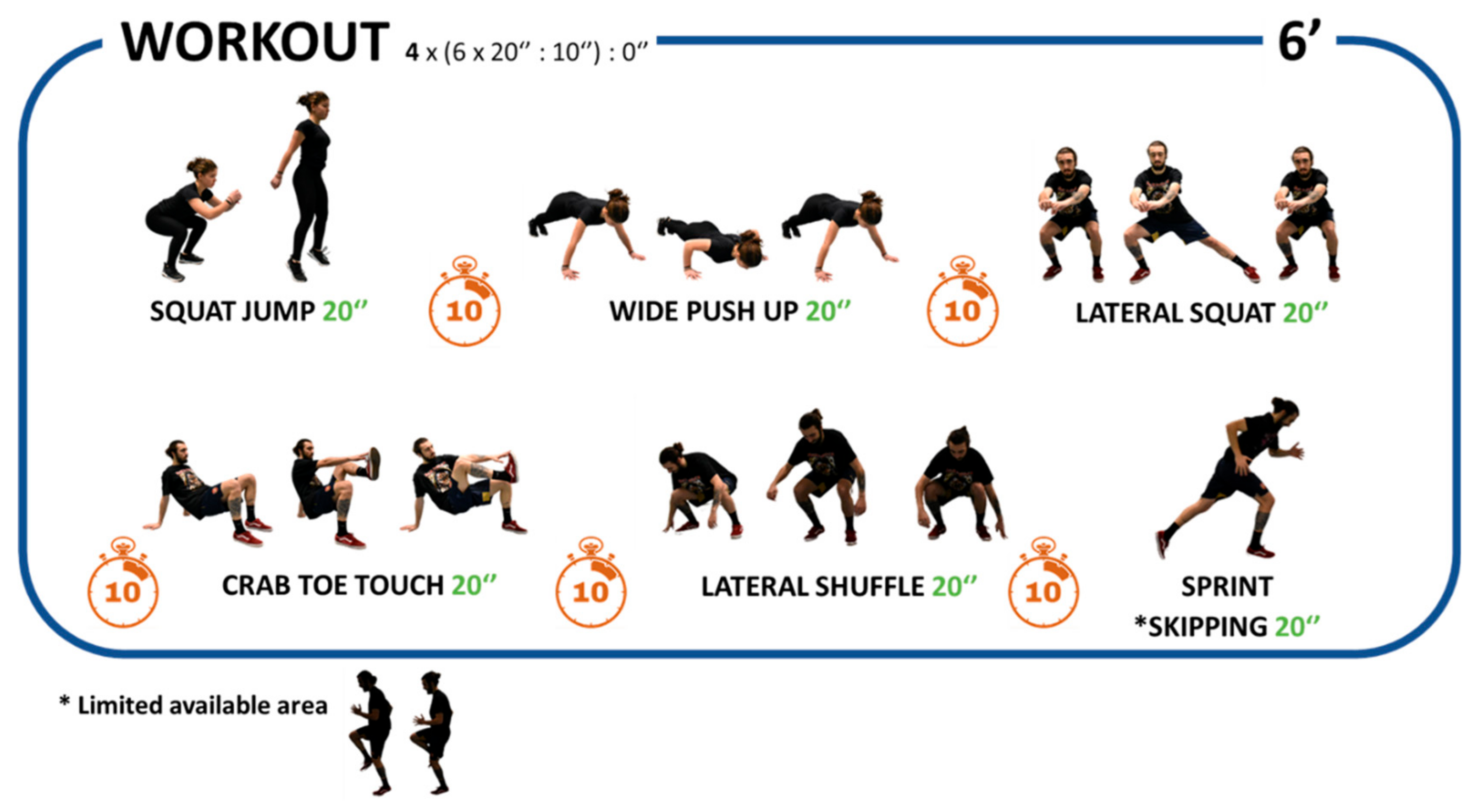
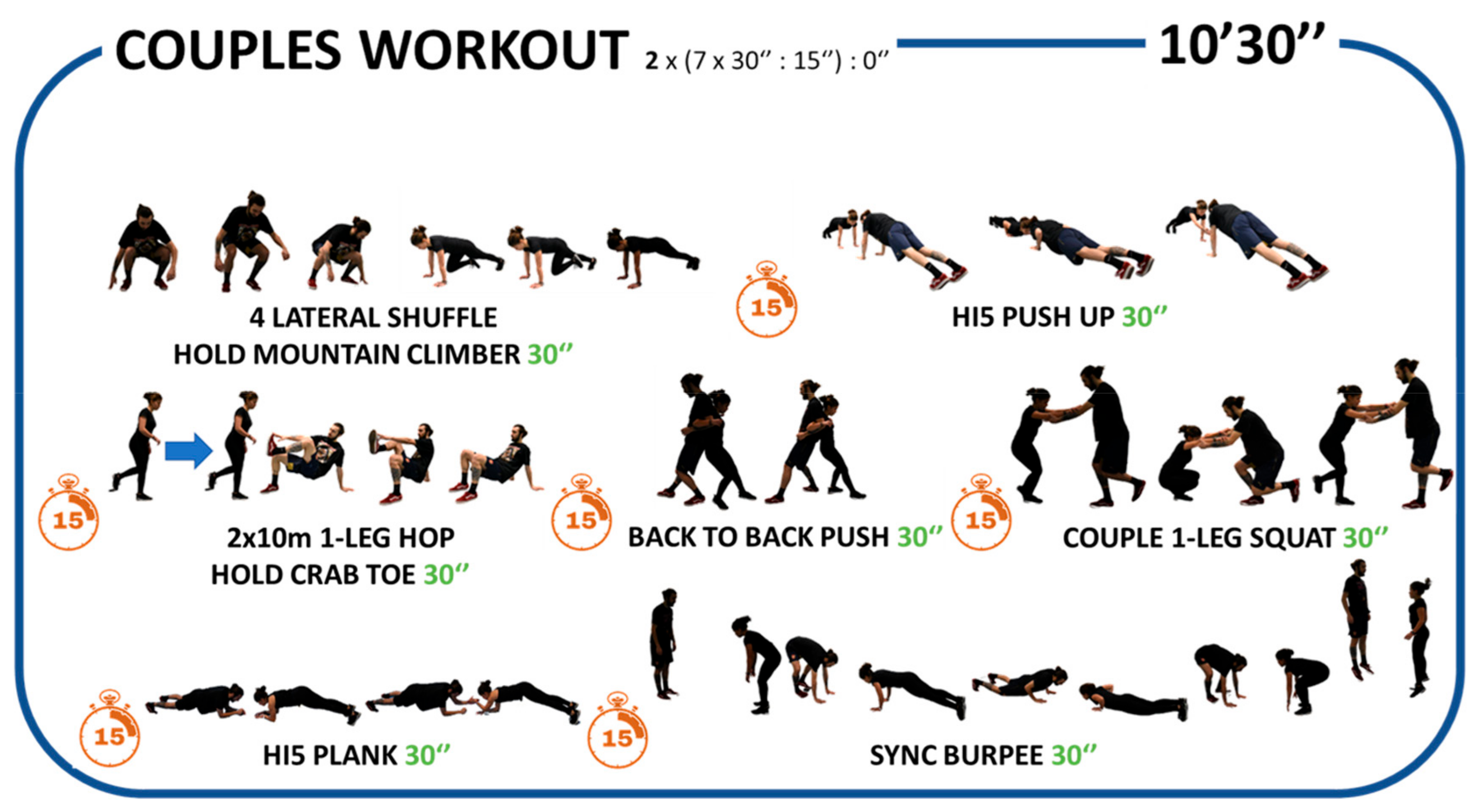
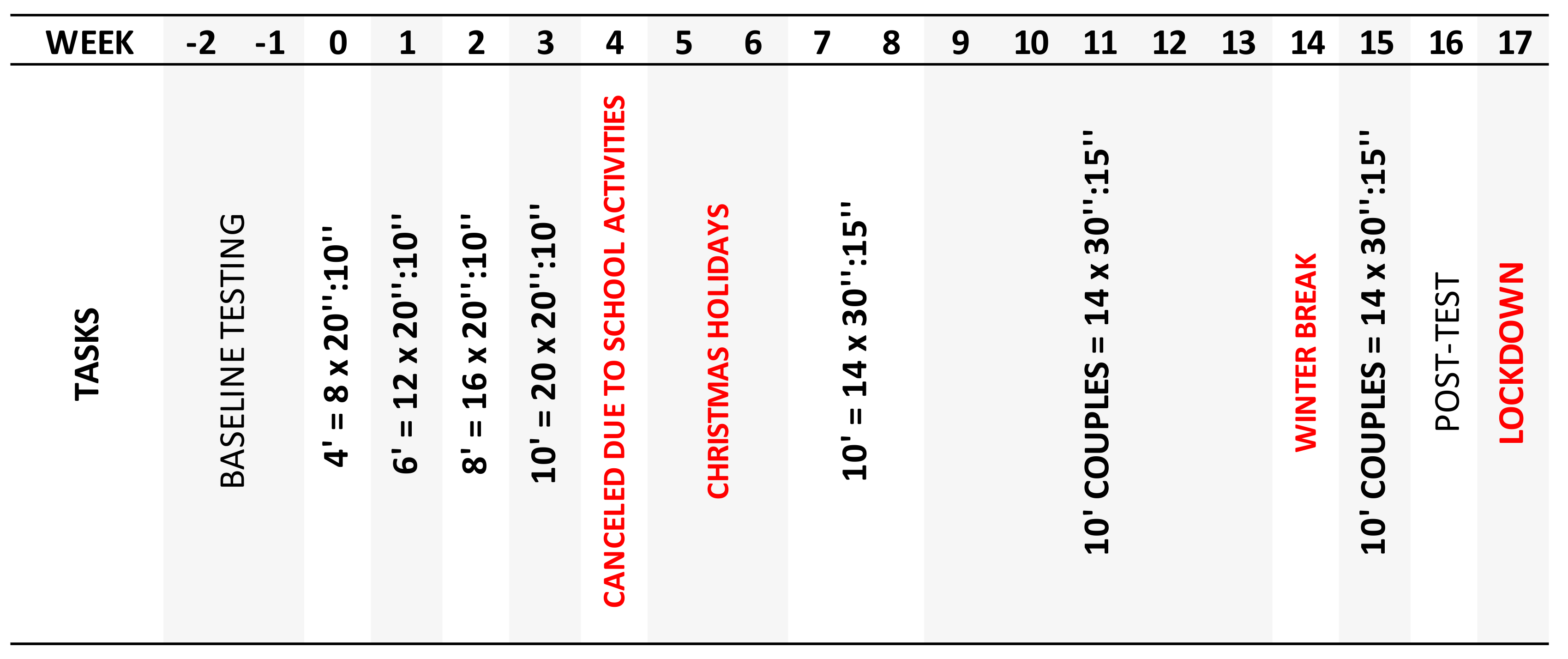
2.5. Intervention Program
2.6. Measures
2.7. Physical Fitness Assessment
2.8. Body Composition Assessment
2.9. Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carnethon, M.R.; Gidding, S.S.; Nehgme, R.; Sidney, S.; Jacobs, J., David R.; Liu, K. Cardiorespiratory Fitness in Young Adulthood and the Development of Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors. JAMA 2003, 290, 3092–3100. [CrossRef]
- Logan, G.R.; Harris, N.; Duncan, S.; Schofield, G. A review of adolescent high-intensity interval training. Sports Med 2014, 44, 1071–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, K.A.; Coombes, J.S.; Green, D.J.; Gomersall, S.R.; Keating, S.E.; Tjonna, A.E.; Hollekim-Strand, S.M.; Hosseini, M.S.; Ro, T.B.; Haram, M.; et al. Effects of exercise intensity and nutrition advice on myocardial function in obese children and adolescents: a multicentre randomised controlled trial study protocol. BMJ Open 2016, 6, e010929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herget, S.; Reichardt, S.; Grimm, A.; Petroff, D.; Kapplinger, J.; Haase, M.; Markert, J.; Bluher, S. High-Intensity Interval Training for Overweight Adolescents: Program Acceptance of a Media Supported Intervention and Changes in Body Composition. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2016, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, G.R.; Harris, N.; Duncan, S.; Plank, L.D.; Merien, F.; Schofield, G. Low-Active Male Adolescents: A Dose Response to High-Intensity Interval Training. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2016, 48, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, A.; Calmeiro, L.; Loureiro, N.; Frasquilho, D.; de Matos, M.G. Health complaints among adolescents: Associations with more screen-based behaviours and less physical activity. J Adolesc 2015, 44, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bluher, S.; Kapplinger, J.; Herget, S.; Reichardt, S.; Bottcher, Y.; Grimm, A.; Kratzsch, J.; Petroff, D. Cardiometabolic risk markers, adipocyte fatty acid binding protein (aFABP) and the impact of high-intensity interval training (HIIT) in obese adolescents. Metabolism 2017, 68, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, P.W.C.; Wong, D.P.; Ngo, J.K.; Liang, Y.; Kim, C.G.; Kim, H.S. Effects of high-intensity intermittent running exercise in overweight children. European Journal of Sport Science 2015, 15, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin-Smith, R.; Buchan, D.S.; Baker, J.S.; Macdonald, M.J.; Sculthorpe, N.F.; Easton, C.; Knox, A.; Grace, F.M. Sprint Interval Training and the School Curriculum: Benefits Upon Cardiorespiratory Fitness, Physical Activity Profiles, and Cardiometabolic Risk Profiles of Healthy Adolescents. Pediatric exercise science 2019, 31, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvetkovic, N.; Stojanovic, E.; Stojiljkovic, N.; Nikolic, D.; Scanlan, A.T.; Milanovic, Z. Exercise training in overweight and obese children: Recreational football and high-intensity interval training provide similar benefits to physical fitness. Scand J Med Sci Sports 2018, 28 Suppl 1, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bull, F.C.; Al-Ansari, S.S.; Biddle, S.; Borodulin, K.; Buman, M.P.; Cardon, G.; Carty, C.; Chaput, J.P.; Chastin, S.; Chou, R.; et al. World Health Organization 2020 guidelines on physical activity and sedentary behaviour. Br J Sports Med 2020, 54, 1451–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courneya, K.S. Efficacy, effectiveness, and behavior change trials in exercise research. International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity 2010, 7, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.P.; Wai, J.P.; Tsai, M.K.; Yang, Y.C.; Cheng, T.Y.; Lee, M.C.; Chan, H.T.; Tsao, C.K.; Tsai, S.P.; Wu, X. Minimum amount of physical activity for reduced mortality and extended life expectancy: a prospective cohort study. Lancet 2011, 378, 1244–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Z.; Sun, S.; Liu, M.; Shi, Q. Short-Term High-Intensity Interval Training on Body Composition and Blood Glucose in Overweight and Obese Young Women. Journal of diabetes research 2016, 2016, 4073618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Tong, T.K.; Qiu, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, S.; Liu, Y.; He, Y. Comparable Effects of High-Intensity Interval Training and Prolonged Continuous Exercise Training on Abdominal Visceral Fat Reduction in Obese Young Women. Journal of diabetes research 2017, 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilian, Y.; Engel, F.; Wahl, P.; Achtzehn, S.; Sperlich, B.; Mester, J. Markers of biological stress in response to a single session of high-intensity interval training and high-volume training in young athletes. Eur J Appl Physiol 2016, 116, 2177–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Hermoso, A.; Cerrillo-Urbina, A.J.; Herrera-Valenzuela, T.; Cristi-Montero, C.; Saavedra, J.M.; Martinez-Vizcaino, V. Is high-intensity interval training more effective on improving cardiometabolic risk and aerobic capacity than other forms of exercise in overweight and obese youth? A meta-analysis. Obes Rev 2016, 17, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, N.K.; Dulson, D.K.; Logan, G.R.M.; Warbrick, I.B.; Merien, F.L.R.; Lubans, D.R. Acute Responses to Resistance and High-Intensity Interval Training in Early Adolescents. J Strength Cond Res 2017, 31, 1177–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzer, S.; Tringali, G.; Caccavale, M.; De Micheli, R.; Abbruzzese, L.; Sartorio, A. Effects of high-intensity interval training on physical capacities and substrate oxidation rate in obese adolescents. J Endocrinol Invest 2017, 40, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, G.; Schwartz, D.D.; Quindry, J.; Barberio, M.D.; Foster, E.B.; Jones, K.W.; Pascoe, D.D. Lymphocyte enzymatic antioxidant responses to oxidative stress following high-intensity interval exercise. J Appl Physiol (1985) 2011, 110, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibala, M.J.; Jones, A.M. Physiological and performance adaptations to high-intensity interval training. Nestle Nutrition Institute workshop series 2013, 76, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuckey, M.I.; Tordi, N.; Mourot, L.; Gurr, L.J.; Rakobowchuk, M.; Millar, P.J.; Toth, R.; MacDonald, M.J.; Kamath, M.V. Autonomic recovery following sprint interval exercise. Scand J Med Sci Sports 2012, 22, 756–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, A.Y.; Wallman, K.E.; Fairchild, T.J.; Guelfi, K.J. Effects of High-Intensity Intermittent Exercise Training on Appetite Regulation. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2015, 47, 2441–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costigan, S.A.; Eather, N.; Plotnikoff, R.C.; Taaffe, D.R.; Lubans, D.R. High-intensity interval training for improving health-related fitness in adolescents: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Sports Med 2015, 49, 1253–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eddolls, W.T.B.; McNarry, M.A.; Stratton, G.; Winn, C.O.N.; Mackintosh, K.A. High-Intensity Interval Training Interventions in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review. Sports medicine (Auckland, N.Z.) 2017, 47, 2363–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, B.; Cockcroft, E.J.; Williams, C.A.; Harris, S.; Gates, P.E.; Jackman, S.R.; Armstrong, N.; Barker, A.R. Two weeks of high-intensity interval training improves novel but not traditional cardiovascular disease risk factors in adolescents. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2015, 309, H1039–H1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costigan, S.A.; Eather, N.; Plotnikoff, R.C.; Taaffe, D.R.; Pollock, E.; Kennedy, S.G.; Lubans, D.R. Preliminary efficacy and feasibility of embedding high intensity interval training into the school day: A pilot randomized controlled trial. Preventive medicine reports 2015, 2, 973–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leahy, A.A.; Eather, N.; Smith, J.J.; Hillman, C.H.; Morgan, P.J.; Plotnikoff, R.C.; Nilsson, M.; Costigan, S.A.; Noetel, M.; Lubans, D.R. Feasibility and Preliminary Efficacy of a Teacher-Facilitated High-Intensity Interval Training Intervention for Older Adolescents. Pediatric exercise science 2019, 31, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Bacha, F.; Hannon, T.; Kuk, J.L.; Boesch, C.; Arslanian, S. Effects of aerobic versus resistance exercise without caloric restriction on abdominal fat, intrahepatic lipid, and insulin sensitivity in obese adolescent boys: a randomized, controlled trial. Diabetes 2012, 61, 2787–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weston, K.L.; Azevedo, L.B.; Bock, S.; Weston, M.; George, K.P.; Batterham, A.M. Effect of Novel, School-Based High-Intensity Interval Training (HIT) on Cardiometabolic Health in Adolescents: Project FFAB (Fun Fast Activity Blasts) - An Exploratory Controlled Before-And-After Trial. PLoS One 2016, 11, e0159116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonsdale, C.; Rosenkranz, R.R.; Peralta, L.R.; Bennie, A.; Fahey, P.; Lubans, D.R. A systematic review and meta-analysis of interventions designed to increase moderate-to-vigorous physical activity in school physical education lessons. Preventive Medicine 2013, 56, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mura, G.; Rocha, N.B.F.; Helmich, I.; Budde, H.; Machado, S.; Wegner, M.; Nardi, A.E.; Arias-Carrión, O.; Vellante, M.; Baum, A.; et al. Physical activity interventions in schools for improving lifestyle in European countries. Clin Pract Epidemiol Ment Health 2015, 11, 77–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharp, C.A.; McNarry, M.A.; Eddolls, W.T.B.; Koorts, H.; Winn, C.O.N.; Mackintosh, K.A. Identifying facilitators and barriers for adolescents participating in a school-based HIIT intervention: the eXercise for asthma with commando Joe's® (X4ACJ) programme. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tottori, N.; Morita, N.; Ueta, K.; Fujita, S. Effects of High Intensity Interval Training on Executive Function in Children Aged 8-12 Years. International journal of environmental research and public health 2019, 16, 4127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogataj, Š.; Trajković, N.; Cadenas-Sanchez, C.; Sember, V. Effects of School-Based Exercise and Nutrition Intervention on Body Composition and Physical Fitness in Overweight Adolescent Girls. Nutrients 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketelhut, S.; Kircher, E.; Ketelhut, S.R.; Wehlan, E.; Ketelhut, K. Effectiveness of Multi-activity, High-intensity Interval Training in School-aged Children. Int J Sports Med 2020, 41, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchan, D.S.; Young, J.D.; Simpson, A.D.; Thomas, N.E.; Cooper, S.M.; Baker, J.S. The effects of a novel high intensity exercise intervention on established markers of cardiovascular disease and health in Scottish adolescent youth. J Public Health Res 2012, 1, 155–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Fernández, D.; Fernández-Rodríguez, R.; Taboada-Iglesias, Y.; Gutiérrez-Sánchez, Á. Impact of a HIIT protocol on body composition and VO2max in adolescents. Science & Sports 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costigan, S.A.; Ridgers, N.D.; Eather, N.; Plotnikoff, R.C.; Harris, N.; Lubans, D.R. Exploring the impact of high intensity interval training on adolescents' objectively measured physical activity: Findings from a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Sports Sciences 2018, 36, 1087–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.; Buchan, D.S.; Baker, J.S.; Young, J.; Sculthorpe, N.; Grace, F.M. Sprint interval training (SIT) is an effective method to maintain cardiorespiratory fitness (CRF) and glucose homeostasis in Scottish adolescents. Biology of sport 2015, 32, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, F.A.; Wagner, M.O.; Schelhorn, F.; Deubert, F.; Leutzsch, S.; Stolz, A.; Sperlich, B. Classroom-Based Micro-Sessions of Functional High-Intensity Circuit Training Enhances Functional Strength but Not Cardiorespiratory Fitness in School Children-A Feasibility Study. Front. Public Health 2019, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, C.M.; Vervaecke, L.S.; Kutz, M.R.; Green, J.M. Sex-specific responses to self-paced, high-intensity interval training with variable recovery periods. J Strength Cond Res 2014, 28, 920–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriques-Neto, D.; Minderico, C.; Peralta, M.; Marques, A.; Sardinha, L.B. Test–retest reliability of physical fitness tests among young athletes: The FITescola® battery. Clinical Physiology and Functional Imaging 2020, 40, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabata, I.; Nishimura, K.; Kouzaki, M.; Hirai, Y.; Ogita, F.; Miyachi, M.; Yamamoto, K. Effects of moderate-intensity endurance and high-intensity intermittent training on anaerobic capacity and VO2max. Med Sci Sports Exerc 1996, 28, 1327–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanssen, H.; Nussbaumer, M.; Moor, C.; Cordes, M.; Schindler, C.; Schmidt-Trucksass, A. Acute effects of interval versus continuous endurance training on pulse wave reflection in healthy young men. Atherosclerosis 2015, 238, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helgerud, J.; Hoydal, K.; Wang, E.; Karlsen, T.; Berg, P.; Bjerkaas, M.; Simonsen, T.; Helgesen, C.; Hjorth, N.; Bach, R.; et al. Aerobic high-intensity intervals improve VO2max more than moderate training. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2007, 39, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonsu, B.; Terblanche, E. The training and detraining effect of high-intensity interval training on post-exercise hypotension in young overweight/obese women. Eur J Appl Physiol 2016, 116, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchheit, M.; Laursen, P.B. High-intensity interval training, solutions to the programming puzzle: Part I: cardiopulmonary emphasis. Sports Med 2013, 43, 313–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borg, G. Perceived exertion as an indicator of somatic stress. Scandinavian journal of rehabilitation medicine 1970, 2, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, J.G.; Eston, R.G.; Stretch, C. Use of the Rating of Perceived Exertion to Control Exercise Intensity in Children. 1991, 3, 21. [CrossRef]
- Krustrup, P.; Mohr, M.; Amstrup, T.; Rysgaard, T.; Johansen, J.; Steensberg, A.; Pedersen, P.K.; Bangsbo, J. The yo-yo intermittent recovery test: physiological response, reliability, and validity. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2003, 35, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, A.S.; Pollock, M.L.; Graves, J.E.; Mahar, M.T. Reliability and validity of bioelectrical impedance in determining body composition. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1988, 64, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fritz, C.O.; Morris, P.E.; Richler, J.J. Effect size estimates: current use, calculations, and interpretation. Journal of experimental psychology. General 2012, 141, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacInnis, M.J.; Zacharewicz, E.; Martin, B.J.; Haikalis, M.E.; Skelly, L.E.; Tarnopolsky, M.A.; Murphy, R.M.; Gibala, M.J. Superior mitochondrial adaptations in human skeletal muscle after interval compared to continuous single-leg cycling matched for total work. The Journal of physiology 2017, 595, 2955–2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, D.E.; Albers, P.H.; Prats, C.; Baba, O.; Birk, J.B.; Wojtaszewski, J.F. Human muscle fibre type-specific regulation of AMPK and downstream targets by exercise. The Journal of physiology 2015, 593, 2053–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaccari, F.; Giovanelli, N.; Lazzer, S. High-intensity decreasing interval training (HIDIT) increases time above 90%VO2peak. Eur J Appl Physiol 2020, 120, 2397–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchan, D.S.; Ollis, S.; Young, J.D.; Cooper, S.M.; Shield, J.P.; Baker, J.S. High intensity interval running enhances measures of physical fitness but not metabolic measures of cardiovascular disease risk in healthy adolescents. BMC Public Health 2013, 13, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racil, G.; Ben Ounis, O.; Hammouda, O.; Kallel, A.; Zouhal, H.; Chamari, K.; Amri, M. Effects of high vs. moderate exercise intensity during interval training on lipids and adiponectin levels in obese young females. Eur J Appl Physiol 2013, 113, 2531–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biddle, S.J.H.; Batterham, A.M. High-intensity interval exercise training for public health: a big HIT or shall we HIT it on the head? International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity 2015, 12, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| HIIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Total (n =106) |
Girls (n =55) |
Boys (n =51) |
|
| Planned Sessions (n) | 26 | ||
| Sessions, mean (sd) | 12.2 (3.5) | 12.2 (3.6) | 12.2 (3.4) |
| Time in seconds >90%HRmáx/session, mean (sd) | 179.9 (128.2)§ | 221.6 (127.8) | 132.9 (112.4) |
| RPE/session, mean (sd) | 17.4 (0.7) | 17.6 (1.5) | 17.4 (0.7) |
 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





