1. Introduction
Autoimmune polyglandular syndromes (APS) includes 4 main categories of complex associations of autoimmune diseases [
1,
2], reviewed in [
3]. As regard autoimmune polyglandular syndrome Type 1 (APS1), namely Autoimmune–Polyendocrinopathy-Candidiasis-Ectodermal dystrophy syndrome (APECED, OMIM #240300, ORPHA 3453), is determined by loss of function mutations in the AutoImmune Regulator (AIRE) gene; the presence of at least two of the following disorders i.e. chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis (CMC), chronic hypoparathyroidism (HP) and primary adrenal insufficiency (Addison’s disease, AD) confirms the clinical diagnosis [
4]. The incidence of APS2 to 4 in published cohorts is estimated between 1.4 and 4.5 per 100000 inhabitants [
5].
More in detail, APS2 (Schmidt’s syndrome, OMIM #269200, ORPHA 3143) includes the combination of autoimmune thyroid disease (AITD), Type 1 diabetes mellitus, (T1D) and AD. APS3 refers to the association between AITD and one or more autoimmune diseases (AIDs) excluding AD. Since AITD is one of the most frequent autoimmune diseases APS3 is the most prevalent APS worldwide. APS3 (ORPHA 227982) includes subgroups APS3A-APS3D based on the associated AIDs: APS3A (AITD and endocrinopathies excluding AD), APS3B (AITD with gastrointestinal, hepatic, or pancreatic autoimmunity), APS3C (referring to the coexistence of AITD with skin, neurological and hematological diseases), APS3D (AITD presenting with autoimmune rheumatological, cardiac, and vascular diseases) [
1,
2,
6,
7]. APS4 (ORPHA 227990) includes any other AID combination that cannot be diagnosed as APS1, APS2 or APS3 [
1,
2].
APS2, APS3 and APS4 are strictly associated with peculiar HLA alleles of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) located on chromosome 6 [
5]. Further, their pathogenesis is contributed by SNPs of several susceptibility non-HLA genes [
3,
5], including the PTPN22 (protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor type 22) C1858T variant encoding for the R620W (rs2476601) Lyp frequently discovered in patients with T1D, AITD, AD and the APS2 syndrome [
8,
9]. Other gene polymorphisms associated with APS are detected in the CTLA4 (cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen 4) gene [
10], the IL2ra gene encoding for the IL2Ra (interleukin 2 receptor alpha) (CD25) [
11], the TNFα (tumor necrosis factor alpha) gene [
12,
13], the FOXP3 (forkhead box P3) gene which controls T regulatory cells (Treg) development and function [
14] and the MHC class I chain-related gene A (MICA) [
15,
16]. Further, T1D susceptibility is influenced by variable number of tandem repeats (VNTR) of the insulin gene [
17,
18]. It is generally recognized that AIRE locus variability and the presence of heterozygous loss of function AIRE mutations can affect the presentation of self-antigens at the thymus level [
19]. AIRE variants were detected in organ-specific autoimmune conditions [
20,
21,
22].
In future studies, whole exome sequencing (WES) may be useful in improving our understanding of the genetic causes of APS in different cohorts of patients leading to the identification of undiscovered SNPs in non-HLA genes [
23]. This could also contribute to the classification of APS and prediction strategies of the evolution of their clinical autoimmune characteristics within each category.
In the light of the foregoing, in this manuscript, WES investigation was conducted on the DNA of a female patient affected by APS3A/3B in order to explore the underlying genetic pathogenetic mechanism responsible for the complex phenotype. The study led to the identification of two compound heterozygous missense variants of the hepatitis A virus cell receptor 2 gene (HAVCR2) [OMIM #606652] encoding for the transmembrane protein TIM-3 (T cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain 3) [
24]. The putative pathogenetic significance in autoimmunity of the identified variants was unraveled in functional studies by confocal microscopy analysis, RT-qPCR, and screening of a cohort of polyendocrine patients.
2. Results
2.1. Identification and Structural Characterization of TIM-3 Variants
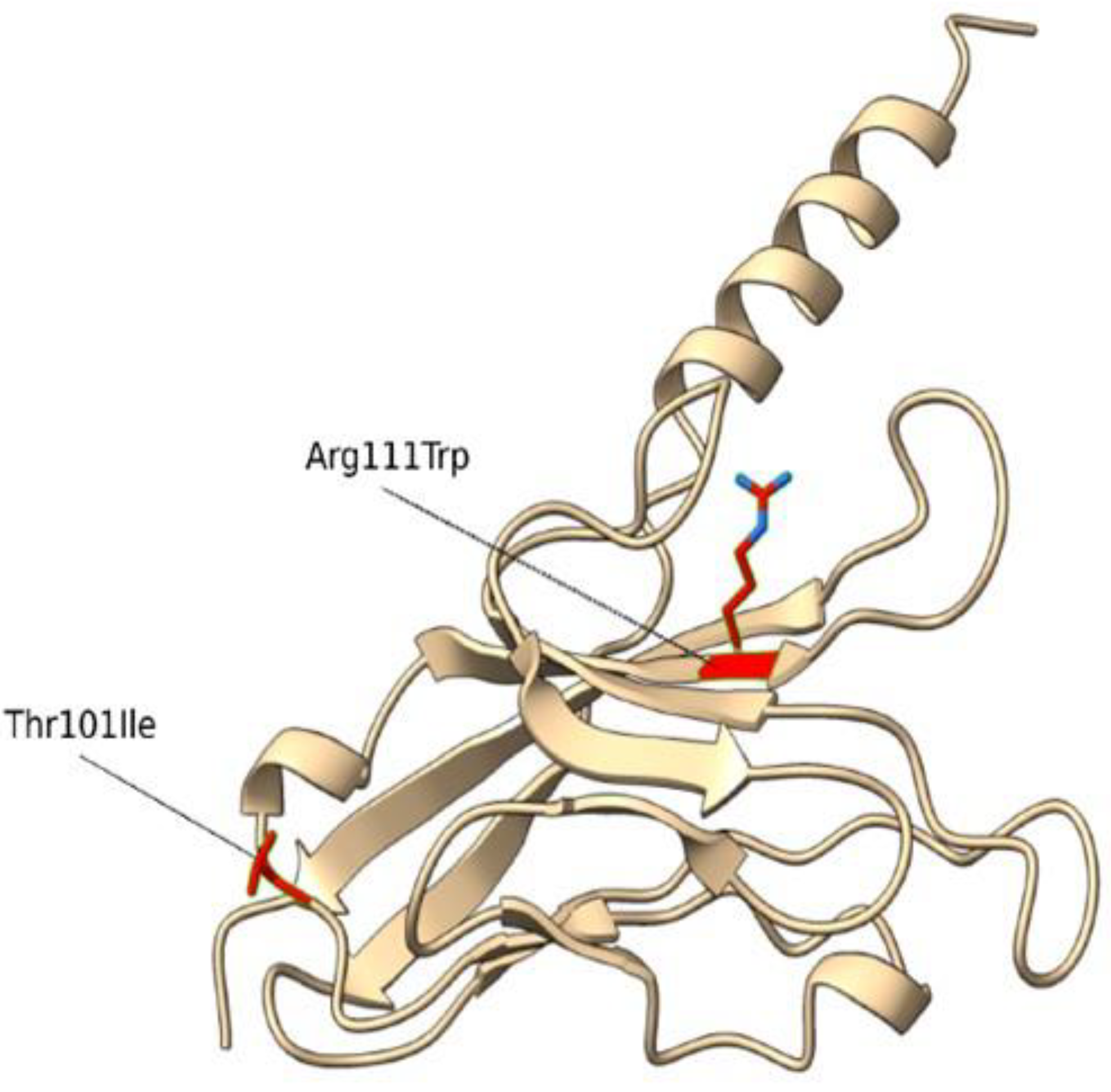
WES analysis identified 2 compound heterozygous missense variants in the TIM-3 (HAVCR2) gene, the c.331C>T (p.Arg111Trp) and the c.302C>T (p.Thr101Ile) (
Figure 1,
Table 1).
Phase has been determined directly using data from sequencing reads. The variant p.Arg111Trp (rs145478313) was shown to have an effect in the sporadic subcutaneous panniculitis-like T cell lymphoma [
25] and theoretically affecting membrane phosphatidylserine [
26]. The variant p.Thr101Ile (rs147827860) was reported by Tromp, Gillissen [
27] and they showed it abrogates TIM-3 expression.
Then, we conducted a structural characterization of the two variants to estimate their impact on the protein structure, stability, and dynamics. According to Missense3D, the p.Arg111Trp substitution determines the breakage of fundamental interactions in a buried region of the TIM-3 protein while no structural impact was detected for the p.Thr101Ile variant. Similarly, the difference in free energy ΔΔG results in a destabilizing effect on the p.Arg111Trp (ΔΔG(p.Arg111Trp) = 6.38599 Kcal/mol) structure while no impact on the protein stability was found for the p.Thr101Ile variant (ΔΔG(p.Thr101Ile) = -0.52554 Kcal/mol). Finally, molecular dynamics simulation-based evaluation was employed to determine the impact of the variants on the protein motions. In detail, RMSF profiles (
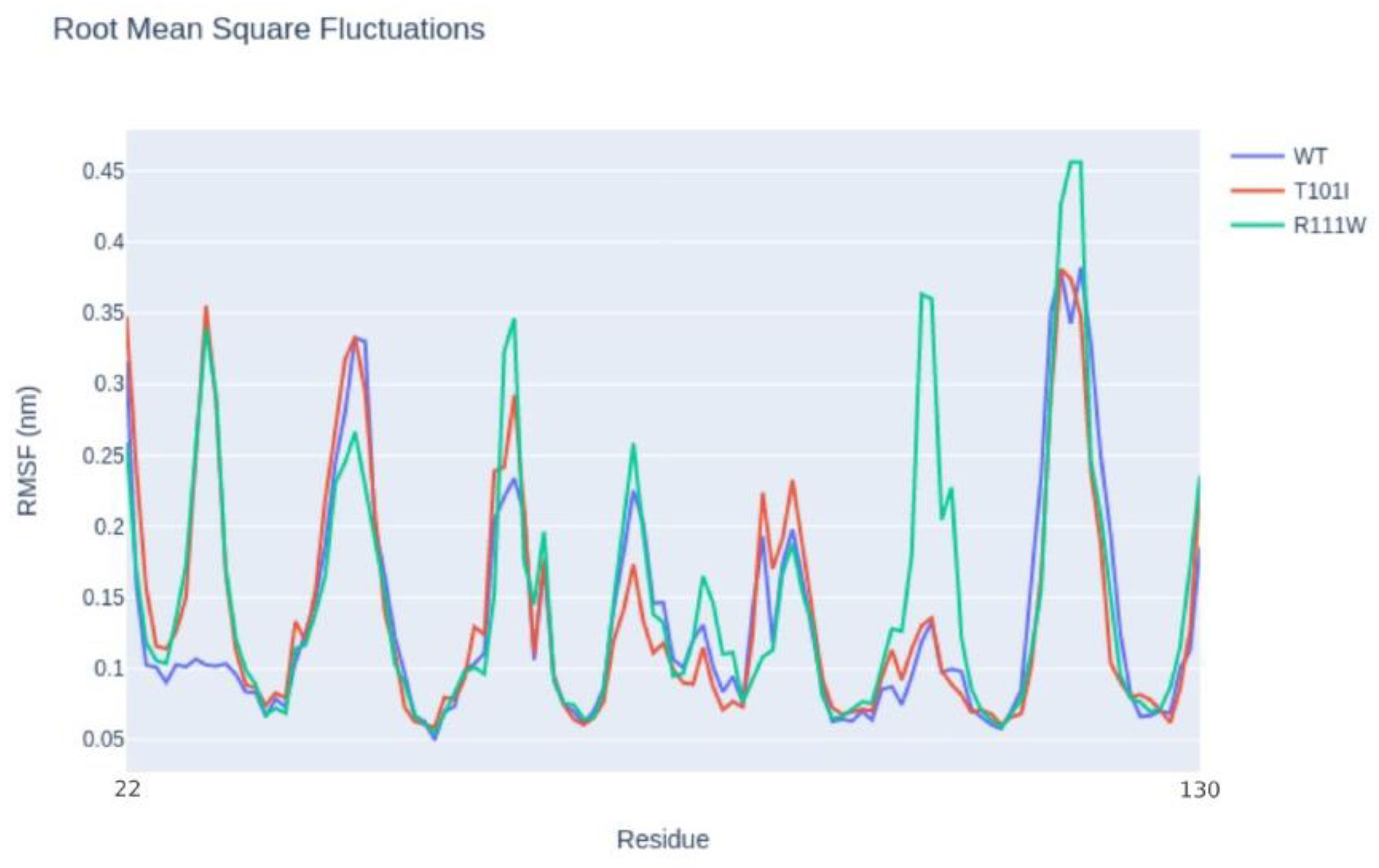
Figure 2), which provide a quantitative measure of residue fluctuation during simulation, show different fluctuation patterns, suggesting that the variants may affect the dynamic behavior of the molecule.
In particular, p.Arg111Trp shows multiple distinct peaks compared to the wild type, especially around residues 100 to 130, where the variant introduces additional flexibility or disorder in that specific region of the molecule. On the other hand, p.Thr101Ile shows a very similar fluctuation pattern to the wild type, with a distinct peak only at the region made by residues 22 to 30. Finally, comparing the molecular interactions such as hydrogen bonds and van der Waals interactions, the high flexibility observed with the p.Arg111Trp mutant is caused by the loss of a fundamental hydrogen bond between the mutant residue and the asparagine 120, with a clear impact on the stability of the entire protein. On the contrary, the p.Thr101Ile contact network resembles the wild-type profile except for the increased interaction frequencies between the mutant residue and the arginine 81 that could result in the increased flexibility observed in the RMSF profile.
2.2. Evaluation of TIM-3 Expression on PBMC
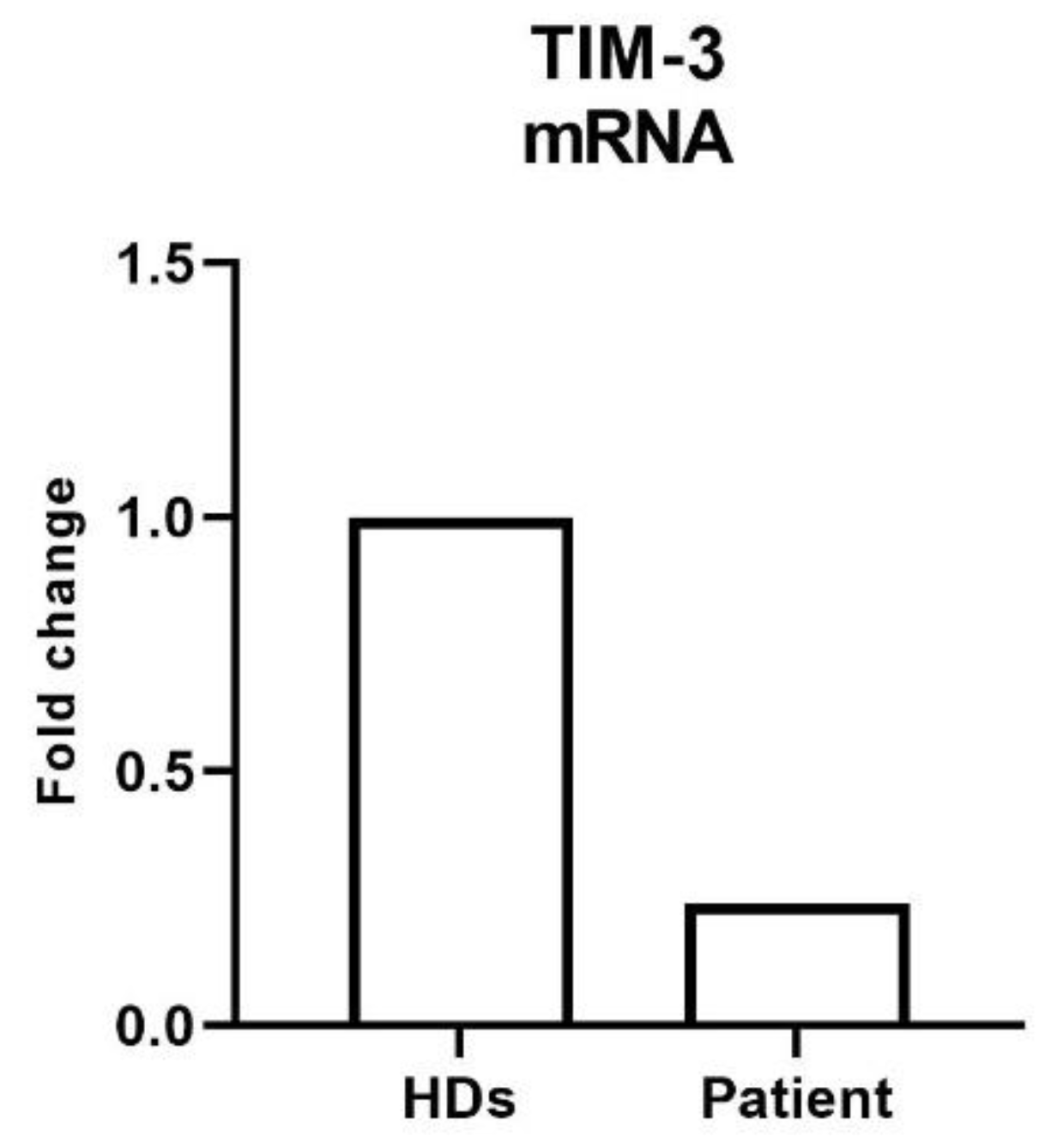
LSCM analysis of PBMC preparations from the patient and two healthy controls did not show differences in the TIM-3 localization and intensity (
Supplementary Figure S1). However, RT-qPCR analysis revealed lower TIM-3 mRNA levels in the patient cells compared to healthy donor-derived PBMC (
Figure 3).
2.3. Exon 2 TIM-3 Sequencing in APS Patients’ DNA
In a cohort of 30 polyendocrine patients no patient harbored the exon 2 TIM-3 c.331C>T (p.Arg111Trp) and the c.302C>T (p.Thr101Ile) variants reported in the proband were the disease association could be influenced by the eventual presence of AIRE SNPs (5 patients presenting heterozygous intronic IVS9+6G>A polymorphism and 3 patients harboring the S278R (c.834C>G variant) [
28], AIRE promoter SNPs (present in 12 patients) [
3] and C1858T PTPN22 variant (present in 8 patients) [
8] (
Supplementary Table S1).
3. Discussion
With the aim to identify the molecular etiology in polyendocrine autoimmune syndrome WES studies were conducted on the DNA of an APS3 patient leading to the identification of the compound heterozygous c.331C>T (p.Arg111Trp)/ c.302C>T (p.Thr101Ile) variants of TIM-3. Molecular dynamic profiling and functional studies lead to the hypothesis that mutations could affect the patient’s autoimmune phenotype by reducing the protein stability. In particular, evidence is provided that p.Arg111Trp affect TIM-3 structure and stability and both mutants influence protein dynamics.
TIM-3 is a type I transmembrane protein located on chromosome 5q33.2 (protein length 302 amino acids) and composed of four parts: variable immunoglobulin domains (IgV), mucin domain, transmembrane region and intracellular stem [
29]. Four TIM-3 related proteins have so far been identified as ligands for TIM-3 interacting with its IgV domain to mediate signal transduction: these include Gal-9 important for maintaining cell homeostasis and inflammation, phosphatidylserine (PtdSer) whose interaction with TIM-3 promotes phagocytosis of apoptotic bodies and enhances cross antigen presentation of dendritic cells [
30,
31]. Other ligands are the DNA binding protein HMGB1 [
32] and the carcinoembryonic antigen cell adhesion molecule 1 (Ceacam 1) [
33].
TIM-3 was initially reported to be expressed on the surface of Th1, Th17, innate immune cells such as monocytes and macrophages, NK and dendritic cells and cancer stem cells [
24,
29,
34,
35,
36,
37]. TIM-3 protein and its ligands can cause peripheral immune tolerance and blocking TIM-3 can eliminate the development of tolerance in Th1 lymphocytes [
38].
In recent years, although mechanisms of its complex regulatory functions are not fully elucidated, the putative immune checkpoint TIM-3 has received increasing attention in reference to chronic infection diseases, to mediate an anti-tumor immune response and in affecting the adaptive immune response in autoimmune diseases [
29]. These evidences have envisaged that TIM-3 could serve as a potential target for breakthrough immunotherapy [
29]. Several single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) were identified in the TIM-3 gene underlying rheumatoid arthritis (RA) susceptibility [
39]. Furthermore, SNPs of TIM-3 promoter region were postulated to affect susceptibility to multiple sclerosis [
40]. The expression of TIM-3 was correlated with disease activities in patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) [
41]. Further TIM-3 is an important negative regulator of T cell function in patients affected by multiple sclerosis (MS) that may cause autoreactive T cells and pathogenic T cells to escape negative regulation [
42]. TIM-3 dysregulation on Th1 cells was also found in patients with Crohn’s disease [
43] and correlated with imbalanced CD4 helper T cell function in ulcerative colitis [
44]. Reduced expression of TIM-3 was reported in T1D patients that may affect the Th1/Th2 balance thus putatively participating in the disease progression [
45]. TIM-3 mainly inhibits Th1 cells thus acting as an anti-inflammatory molecule, while TIM-1 regulates the T cell activation being mainly expressed on Th2 cells. The ratio of TIM-3 to TIM-1 was decreased in T1D patients most notably in the defective islet function group. Further the TIM-3/TIM-1 ratio in different T cell subsets was increased in the remission phase of the disease indicating an imbalance between pro- and anti-inflammatory activities. Evidence also indicates that the molecular mechanism of TIM-3 is also involved in human allergic reactions [
29] and induction of respiratory tolerance in experimental asthma [
46].
In further unravelling the putative effect of the compound heterozygous c.331C>T/ c.302C>T genotype of TIM-3 in the patient analyzed in the present investigation, we could not evidence qualitative or quantitative (data not shown) differences at confocal microscopy examination between healthy control and patient derived PBMC. Nevertheless, an in dept evaluation by RT-qPCR evidenced a reduced expression of TIM-3 in the patient PBMC than in three healthy controls further supporting the hypothesis of the putative functional effect on the protein stability and immunological function. The apparent discrepancy is explained by the upmost efficiency of detection when evaluation is carried out at the mRNA level by RT-qPCR.
The identified TIM-3 exon 2 genetic variants were not present in the DNA of 30 additional polyendocrine patients. Nevertheless, the result of the present investigation opens the pathway to discover novel TIM-3 variants that could underlie the pathogenesis of a complex autoimmune phenotype in APS patients and identify a specific clustering of association with peculiar clinical manifestations thus contributing to APS classification and diagnosis.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients
4.1.1. Case History
A 16.4-years old girl from the central region of Italy affected by patent (Botallo) ductus arteriosus [
47] was admitted to Children’s Hospital Bambino Gesù at the age of 1.8 years with symptoms of polyuria, polydipsia, hyperglycemia and severe ketoacidosis. The diagnosis of T1D was ascertained, and the patient started insulin substitutive treatment. The patient also presented IgA deficit. At the age of 3.5 years the patient was diagnosed to be affected by celiac disease. At the age of 5 years the patient underwent surgery to percutaneously close patent ductus arteriosus through Amplatzer device. At the age of 12 years metformin treatment was added to insulin administration. At the age of 13 years the patient had an epileptic crisis and preclinical autoimmune thyroiditis was diagnosed and at 13.3 years old hypertransaminasemia was detected with increased markers of hepatic cytolysis, elevated levels of IgG, anti-LKM (liver-kidney-microsomal) autoantibodies (Ab) and ASMA (
Table 2).
At histopathological examination chronic autoimmune hepatitis was confirmed with partially disturbed architecture due to the presence of portoportal arched septa. In the portal spaces, found expanded due to fibrosis and irregular profile, a dense lymphomonocytic CD3+ CD20+ inflammatory infiltrate was observed with an advancing MUM1 (multiple myeloma oncogene-1) positive front rich in plasma cells exceeding the limiting lamina (interface hepatitis). A similar but smaller infiltrate was also described in the lobular site with particle necrosis. The patient underwent cyclosporine and azathioprine treatment leading to macrocytosis.
At the age of 16.2 years D hypovitaminosis, leukopenia and neutropenia were found. For the cohort of autoimmune clinical manifestations, according to the updated APS classification [
2] the patient could be diagnosed as APS3A/B (
Table 2).
4.1.2. Study Population
Thirty patients affected by APS i.e. variable association of organ and non-organ specific autoimmune disorders (12 males, 18 females with age ranges at presentation between 0.9 and 19.6 years old) were recruited at Bambino Gesù Children’s Hospital (OPBG) in Rome for the screening of the exon 2 TIM-3 mutations identified in the proband (vide infra) (
Supplementary Table S1).
According to the current criteria for classification of APS [
1,
2,
48,
49], one patient was affected by APS2 (patient n° 22), 17 patients were affected by APS3A (patients n° 1, 2, 7-9, 11-13, 15, 19, 21, 24-29), 8 patients were affected by APS3B (patients n° 1, 8, 11, 13, 19, 22, 23, 30), 5 patients were affected by APS3C (patient n° 2, 6, 18, 21, 30), one patient was affected by APS3D (patient n° 6) and 10 patients by APS4 (patients n° 3-5, 7, 10, 14, 16, 17, 20, 27).
Informed consent was obtained from all those who took part in the present study, including the proband, in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. The investigation was approved by the local Institutional Review Board (IRB) of OPBG, which regulates human samples usage for experimental studies (Study protocol no. 1385_OPBG_2017).
4.2. Autoantibodies Screening
The patients' sera were assayed for T1D-related autoantibodies (Ab), i.e., glutamic acid decarboxylase isoform 65 (GADAb), tyrosine phosphatase-related islet antigen 2 (IA2Ab), insulin Ab (IAA) and zinc transporter 8 Ab (ZnT8Ab) by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA); for AD i.e., adrenal cortex (ACA) and 21-hydroxylase Ab (21-OHAb) by ELISA; for AITD -related Ab, i.e., thyrotropin (TSH)-receptor Ab (TRAb) by immunoassay (Immulite TSI, Siemens Healthcare, Tarrytown, NY, USA), thyroglobulin (TgAb), and thyroperoxidase Ab (TPOAb) via electrochemiluminescence immunoassay (ECLIA) (Siemens, Erlangen, Germany); celiac-disease-related Ab were screened by chemiluminescence (ADVIA Centaur analyzer, Siemens Healthcare, Germany), i.e., anti-transglutaminase-IgA Ab (TRGAb) and deaminated gliadin-IgG Ab (DGP-IgGAb) by EliA; for autoimmune hepatic diseases, i.e., anti-liver kidney microsomal Ab (LKMAb), smooth muscle Ab (SMA), liver cytosol type 1 Ab (LC1Ab) and soluble liver antigen/liver pancreas Ab (SLA/LPIgG), for stomach-related Ab i.e parietal cells Ab (APCA) were measured by IFL and intrinsic factor Ab (IFIAb) were tested by ELISA. Anti-SP100 Ab and anti-glycoprotein GP210 were tested by immuno-dot and anti-Saccharomyces cerevisiae Ab by ELISA. Non-organ specific Ab, i.e., nuclear Ab (ANA), extractable nuclear antigen (ENA) (ELiA, Thermo Fisher, Waltham, MA, USA), neutrophil cytoplasmic Ab (ANCA), double stranded DNA Ab (dsDNAAb), SCL-70 antigen Ab (SCL-70Ab), reticulin Ab (ARA), mitochondrial Ab (AMA), ribosomal Ab (RAb), phospholipid Ab or anti-cardiolipin Ab (CAb), beta2glycoprotein I-IgG or IgM Ab (β2GP-1IgGAb), anti-beta2glycoprotein I-IgM (β2GP-1IgMAb), dense fine speckled 70 Ab (DSF70Ab) (ELiA) and cyclic citrullinated peptide Ab (CAb) (EliA) were also tested.
4.3. Molecular Studies
Genomic leukocyte DNA was extracted from patient whole blood by the QIAmp DNA Blood Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s guidelines.
4.3.1. AIRE Gene Screening
All 14 exons and intronic regions of the AIRE gene were sequenced according to already described protocols in the DNA of recruited patients [
50]. AIRE promoter SNPs were also identified as previously reported [
3].
4.3.2. Screening for the Presence of C1858T PTPN22
Detection of the C1858T variant in the PTPN22 gene was carried out by PCR with specific primers for exon 14 of the PTPN22 gene (GenBank ID: 26191): forward 5’-GATAATGTTGCTTCAACGGAATTT-3’ and reverse 5’-CCTCAAACTCAAGGCTCACAC-3’. The amplification lasted thirty-five cycles, generating PCR products of 318bp that were purified using NucleoSpin Gel and PCR Clean-up kit (Bioanalysis). PCR sequencing was carried out with the BigDye Terminator v.3.1 Cycle sequencing protocol (Life Technologies, Applied Biosystems, Paisley, Scotland, UK) on 3500 Genetic Analyzer (Applied Biosystems) as reported [
8,
51].
4.3.3. Whole Exome Sequencing
After obtaining informed consent of the patient for the genetic testing, patient genomic DNA was extracted as above described. Library preparation was carried out by using the Twist Human Comprehensive Exome enrichment kit, according to the manufacturer’s protocol (Twist Bioscience, South San Francisco, CA, USA), and sequenced on a NovaSeq 6000 (Illumina, Inc., San Diego, CA, USA) platform. The BaseSpace pipeline (Illumina,
https://basespace.illumina.com/, accessed on 21 December 2023) and the Geneyx Analysis (AI-driven NGS Analysis platform) formerly known as TGx Gene Cards were used for the variant calling and annotating variants, respectively. Sequencing data were aligned to the hg19 human reference genome. The variants were analyzed in silico by using Combined Annotation Dependent Depletion (CADD) V.1.3 (Rentzsch 2019), Sorting Intolerant from Tolerant (SIFT) [
52], Polymorphism Phenotyping v2 (PolyPhen-2) [
53], and Mutation Taster [
54] for the prediction of deleterious non-synonymous variants for human diseases. In summary, the pathogenicity of each variant was evaluated by gathering evidence from the above sources, including population data, computational and predictive data, and segregation data, in accordance with the guidelines of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG) [
55]. Variants were examined for coverage and Qscore (minimum threshold of 30) and visualized by the Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV).
4.3.4. Structural Modeling and Simulation
A high-resolution crystal structure of the IgV-like domain (from residue 22 to residue 130) of the TIM-3 protein was retrieved from the RCSB Protein Data Bank (PBD ID: 7M3Z). Then, a comprehensive structural evaluation was performed to characterize the impact of the two missense variants, p.Arg111Trp and p.Thr101Ile, on the TIM-3 protein structure. In detail, Missense 3D web-tool [
56] was employed to predict the structural changes introduced by the mutations. Then, the stability of both mutant structures was assessed through the BuildModel function implemented in the FoldX v.5.0 [
57], run using standard parameters.
Finally, we employed advanced molecular dynamics (MD) simulation techniques [
58] to further describe the eventual variant perturbations on the protein dynamics, following the protocol described in Cocciadiferro, Mazza [
59] and resorting to gaming enabled GPU graphic cards [
60]. In brief, the wild-type structure was mutated in silico to introduce the two missense variants and each system was embedded into a simulation box, extending up to 12 Å, filled with TIP3P water molecules and Na+ and Cl- counter ions, using the web-based tool CHARMM-GUI Enhanced Sampler [
61]. Then, each system was firstly subjected to energy minimization to refine potential clashes, gradually heated to 300 K and equilibrated for 500 ps, and finally simulated using a standard “dual-boost” Gaussian accelerated MD (GaMD) simulation protocol, which includes a preparatory 2 ns run to collect potential statistic, an 8 ns “equilibration run” and a final production run of 200 ns. Each MD simulation was then analyzed using GROMACS v.2018, measuring the Root-Mean-Square Deviation (RMSD) and the Root-Mean-Square Fluctuation (RMSF), respectively to assess the average distance and deviation over time between the positions of the Cα atomic coordinates of each residue and those of the starting structure, while all fundamental interactions and their residence time during each trajectory were computed using the GetContacts (
https://getcontacts.github.io) tool.
4.3.5. Screening for the Presence of Exon 2 TIM-3 Variants
The presence of identified SNPs of the T cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain-containing protein 3 (TIM-3, GenBank ID: 84868) gene was analyzed in the DNA of a cohort of 30 polyendocrine patients by PCR amplification with specific primers (Sigma-Genosys Ltd, St Louis, MO) for exon 2: forward 5’-GAATCATCCTCCAAACAG-3’, reverse 5’AGATGAGAACAATCAGTACC-3’. The amplification was carried out with Power SYBR Green PCR Master Mix (Thermo Fisher), generating PCR products of 545 bp that were purified using NucleoSpin Gel and PCR Clean-up kit (Bioanalysis). Sequencing was carried out as reported above.
4.4. Functional Studies
4.4.1. Confocal Microscopy Analysis
To compare the expression and distribution of TIM-3, peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells (PBMC) isolated from the patient carrying the c.331C>T (p.Arg111Trp) and the c.302C>T (p.Thr101Ile) TIM-3 variants and two healthy donors were quickly thawed in a 37°C water bath, transferred to pre-warmed culture medium, and centrifuged at 1200 rpm for 5 minutes. Cells were then counted and washed two times with Phosphate Buffer Saline (PBS). 1.5 x106 cells per condition were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA) at 4°C for 10 minutes. 100 μL of each cell suspension were placed on microscopy slides inside a PAP Pen delimited spot and dried at room temperature (RT) for 30 minutes. Samples were permeabilized with 0.1% Triton X-100 in PBS for 20 minutes at RT and blocked with 1% bovine serum albumin (BSA), 5% normal goat serum (NGS) in PBS for 30 minutes at RT. Samples were transferred to a humidity chamber; incubation with mouse α-TIM-3 monoclonal antibody (Invitrogen, MA5-32840) was performed for 1 hour at RT (1:25 in blocking solution); then, samples were washed three times with PBS for 5 minutes each and treated with F(ab')2-Goat anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) Cross-Adsorbed Secondary Antibody (Invitrogen, A21425) for 1 hour at RT (1:500 in 1% BSA/PBS blocking solution). Samples were washed again three times with PBS, and cover slips were mounted on microscopy slides using 60% glycerol in PBS.
Confocal microscopy was performed with a Leica TCS-SP8X laser-scanning confocal microscope (Leica Microsystems, Mannheim, Germany) equipped with tunable white light laser (WLL) source, 405 nm diode laser, 3 Internal Spectral Detector Channels (PMT) and 2 Internal Spectral Detector Channels (HyD) GaAsP. Sequential confocal images were acquired using an HC PL APO 63x oil-immersion objective (1.40 numerical aperture, NA, Leica Microsystems) with a 1024 × 1024 format and scan speed 400 Hz.
4.4.2. RT-qPCR
In order to quantitatively compare the TIM-3 SNPs mRNA, PBMC isolated from the patient carrying the c.331C>T (p.Arg111Trp) and the c.302C>T (p.Thr101Ile) variants (vide infra) and three healthy donors as control were quickly thawed in a 37°C water bath, transferred to pre-warmed culture medium, and centrifuged at 1200 rpm for 5 minutes. Total RNA was extracted using RNeasy Plus Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The quality and concentration of the extracted RNA were assessed using a NanoDrop ND-1000 spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). For reverse transcription, RNA was converted to cDNA using SuperScript II reverse transcriptase (Thermo Fisher Scientific) and Random Primers (Thermo Fisher Scientific) according to manufacturer’s instructions in a total reaction volume of 20 µL. Quantitative PCR was performed using the the QuantStudio 7 Real-Time PCR System (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA) and Power SYBR Green Master Mix (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Each 20 µL reaction contained 10 µL of SYBR Green Master Mix, 0.15 µM of forward and reverse primers (GAPDH Fw: 5’ – CGACCACTTTGTCAAGCTCA - 3’, GAPDH Rev: 5’ – AGGGGTCTACATGGCAACTG - 3’; TIM-3 Fw: 5’ - CCTGTCCTGTGTTTGAATG - 3’, TIM-3 Rev: 5’ – GTTTGATGACCAACTTCAGG - 3’), and 9 µL of cDNA template.
The qPCR cycling conditions were as follows: initial activation at 50°C for 2 minutes and then 95°C for 2 minutes, followed by 40 cycles of denaturation at 95°C for 15 seconds, annealing at 60°C for 1 minute, and extension at 72°C for 30 seconds. A melt curve analysis was performed to ensure the specificity of the amplification products. All reactions were run in triplicate, and no-template controls (NTCs) were included to check for contamination.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Alessandra Fierabracci, Emanuele Agolini and Tommaso Mazza; Data curation, Alessandra Fierabracci, Andrea Ariolli, Emanuele Agolini, Tommaso Mazza and Francesco Petrizzelli; Formal analysis, Alessandra Fierabracci, Andrea Ariolli, Tommaso Mazza and Stefania Petrini; Funding acquisition, Alessandra Fierabracci; Investigation, Alessandra Fierabracci, Andrea Ariolli, Emanuele Agolini, Francesco Petrizzelli and Annamaria Cudini; Methodology, Alessandra Fierabracci, Andrea Ariolli, Emanuele Agolini, Tommaso Mazza, Francesco Petrizzelli, Stefania Petrini, Valentina D’Oria and Caterina Nardella; Project administration, Alessandra Fierabracci; Resources, Donatella Comparcola and Marco Cappa; Software, Emanuele Agolini, Tommaso Mazza, Francesco Petrizzelli and Stefania Petrini; Supervision, Alessandra Fierabracci; Validation, Alessandra Fierabracci, Tommaso Mazza and Stefania Petrini; Writing – original draft, Alessandra Fierabracci, Andrea Ariolli, Emanuele Agolini, Tommaso Mazza and Stefania Petrini; Writing – review & editing, Alessandra Fierabracci and Andrea Ariolli.
Funding
This work was supported by the Italian Ministry of Health with “current research funds”.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the local Institutional Review Board of OPBG (Study protocol no. 1385_OPBG_2017).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets presented in this article are not readily available because of ethical consent for patients. All reported variants of the AIRE, PTPN22 and TIM-3 gene are already described in the literature. Requests to access the datasets should be directed to corresponding author and clinicians Marco Cappa and Donatella Comparcola.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge Anna Lorusso and Alessia Palma for technical support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Nomenclature
21-OHAb, 21-hydroxylase autoantibodies; ACA, Adrenal cortex autoantibodies; AIDs, Autoimmune diseases; AIRE, AutoImmune Regulator; AITD, Autoimmune thyroid disease; ALP, alkaline phosphatase; ALT, alanine transaminase; AMA, Mitochondrial autoantibodies; ANA, Nuclear autoantibodies; ANCA, Neutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibodies; APCA, Parietal cells autoantibodies; APECED, Autoimmune–Polyendocrinopathy-Candidiasis-Ectodermal dystrophy syndrome; APS, Autoimmune polyglandular syndromes; APS1, Autoimmune polyglandular syndrome Type 1; APS2, Autoimmune polyglandular syndrome Type 2; APS3, Autoimmune polyglandular syndrome Type 3; APS3A, AITD and endocrinopathies excluding AD; APS3B, AITD with gastrointestinal, hepatic, or pancreatic autoimmunity; APS3C: AITD with skin, neurological, and hematological diseases; APS3D, AITD with autoimmune rheumatological, cardiac, and vascular diseases; APS4, Autoimmune polyglandular syndrome Type 4; AR, Autosomal Recessive; ARA, Reticulin autoantibodies; AST, aspartate transferase; β2GP-1IgGAb, Beta2glycoprotein I-IgG autoantibodies; β2GP-1IgMAb: Anti-beta2glycoprotein I-IgM autoantibodies; CAb, Anti-cardiolipin autoantibodies / Cyclic citrullinated peptide autoantibodies; Ceacam 1, Carcinoembryonic antigen cell adhesion molecule 1; CMC, Chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis; CTLA4, Cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen 4; DGP-IgGAb: Deaminated gliadin-IgG autoantibodies; dsDNAAb, Double stranded DNA autoantibodies; DSF70Ab, Dense fine speckled 70 autoantibodies; ECLIA, Electrochemiluminescence immunoassay; ELISA, Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; ENA, Extractable nuclear antigen autoantibodies; FOXP3, Forkhead box P3; GADAb, Glutamic acid decarboxylase isoform 65 autoantibody; Gal-9, Galectin-9; GGT: gamma-glutamyl transferase; GP210, Anti-glycoprotein GP210 autoantibodies; HAVCR2, Hepatitis A virus cell receptor 2; HGVSC, Human Genome Variation Society coding sequence name; HGVSP, Human Genome Variation Society protein sequence name; HLA, Human leukocyte antigen; HMGB1, High-mobility group box 1; IA2Ab, Tyrosine phosphatase-related islet antigen 2 autoantibody; IAA, Insulin autoantibodies; IFIAb, Intrinsic factor autoantibodies; IgV, Immunoglobulin Variable; IL2Ra, Interleukin 2 receptor alpha; LC1Ab, Liver cytosol type 1 autoantibodies; LKMAb, Anti-liver kidney microsomal autoantibodies; MHC, Major histocompatibility complex; MICA, MHC class I chain-related gene A; NK: Natural killer; OMIM: Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man; ORPHA, Orphanet (a reference portal for information on rare diseases); PT, prothrombin time; PtdSer, Phosphatidylserine;
PTPN22, Protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor type 22; RA, Rheumatoid arthritis; RAb, Ribosomal autoantibodies; RMSD, Root mean square deviation; RMSF, Root mean square fluctuation; SCL-70Ab, SCL-70 antigen autoantibodies; SLA/LPIgG, Soluble liver antigen/liver pancreas autoantibodies; SLE, Systemic lupus erythematosus; SMA, Smooth muscle autoantibodies; SNPs, Single nucleotide polymorphisms; SP100Ab, Anti-SP100 autoantibodies; T1D, Type 1 diabetes mellitus; TIM-3, T cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain 3; TgAb, Thyroglobulin autoantibodies; TNFα, Tumor necrosis factor alpha; TPOAb, Thyroperoxidase autoantibodies; TRAb, Thyrotropin receptor autoantibodies; TRGAb, Anti-transglutaminase-IgA autoantibodies; TSH, Thyrotropin; VNTR, Variable number of tandem repeats; WES, Whole exome sequencing; ZnT8Ab, Zinc transporter 8 autoantibodies.
References
- Betterle, C.; Sabbadin, C.; Scaroni, C.; Presotto, F. Autoimmune Polyendocrine Syndromes (APS) or Multiple Autoimmune Syndromes (MAS). In Polyendocrine Disorders and Endocrine Neoplastic Syndromes, Colao, A., Jaffrain-Rea, M.-L., Beckers, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2019; pp. 1–50. [Google Scholar]
- Betterle, C.; Furmaniak, J.; Sabbadin, C.; Scaroni, C.; Presotto, F. Type 3 autoimmune polyglandular syndrome (APS-3) or type 3 multiple autoimmune syndrome (MAS-3): an expanding galaxy. J Endocrinol Invest 2023, 46, 643–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cudini, A.; Nardella, C.; Bellacchio, E.; Palma, A.; Delfino, D.V.; Betterle, C.; Cappa, M.; Fierabracci, A. Analysis of the AIRE Gene Promoter in Patients Affected by Autoimmune Polyendocrine Syndromes. Int J Mol Sci 2024, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fierabracci, A. Type 1 Diabetes in Autoimmune Polyendocrinopathy-Candidiasis-Ectodermal Dystrophy Syndrome (APECED): A "Rare" Manifestation in a "Rare" Disease. Int J Mol Sci 2016, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frommer, L.; Kahaly, G.J. Autoimmune Polyendocrinopathy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2019, 104, 4769–4782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, T.J.; Hegedüs, L. Graves' Disease. N Engl J Med 2016, 375, 1552–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralli, M.; Angeletti, D.; Fiore, M.; D'Aguanno, V.; Lambiase, A.; Artico, M.; de Vincentiis, M.; Greco, A. Hashimoto's thyroiditis: An update on pathogenic mechanisms, diagnostic protocols, therapeutic strategies, and potential malignant transformation. Autoimmun Rev 2020, 19, 102649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianchecchi, E.; Palombi, M.; Fierabracci, A. The putative role of the C1858T polymorphism of protein tyrosine phosphatase PTPN22 gene in autoimmunity. Autoimmun Rev 2013, 12, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vang, T.; Congia, M.; Macis, M.D.; Musumeci, L.; Orrú, V.; Zavattari, P.; Nika, K.; Tautz, L.; Taskén, K.; Cucca, F.; et al. Autoimmune-associated lymphoid tyrosine phosphatase is a gain-of-function variant. Nature Genetics 2005, 37, 1317–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houcken, J.; Degenhart, C.; Bender, K.; König, J.; Frommer, L.; Kahaly, G.J. PTPN22 and CTLA-4 Polymorphisms Are Associated With Polyglandular Autoimmunity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2018, 103, 1977–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downes, K.; Marcovecchio, M.L.; Clarke, P.; Cooper, J.D.; Ferreira, R.C.; Howson, J.M.; Jolley, J.; Nutland, S.; Stevens, H.E.; Walker, N.M.; et al. Plasma concentrations of soluble IL-2 receptor α (CD25) are increased in type 1 diabetes and associated with reduced C-peptide levels in young patients. Diabetologia 2014, 57, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Mandal, R.K.; Jawed, A.; Dar, S.A.; Wahid, M.; Panda, A.K.; Areeshi, M.Y.; Ahmed Khan, M.E.; Haque, S. TNF-α -308 G > A (rs1800629) Polymorphism is Associated with Celiac Disease: A Meta-analysis of 11 Case-Control Studies. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 32677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dittmar, M.; Kaczmarczyk, A.; Bischofs, C.; Kahaly, G.J. The Proinflammatory Cytokine TNF-α -308 AA Genotype is Associated with Polyglandular Autoimmunity. Immunological Investigations 2009, 38, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grover, P.; Goel, P.N.; Greene, M.I. Regulatory T Cells: Regulation of Identity and Function. Front Immunol 2021, 12, 750542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, S.; Groh, V.; Wu, J.; Steinle, A.; Phillips, J.H.; Lanier, L.L.; Spies, T. Activation of NK cells and T cells by NKG2D, a receptor for stress-inducible MICA. Science 1999, 285, 727–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ide, M.; Dittmar, M.; Wurm, M.; Kanitz, M.; Kahaly, G.J. [Polymorphisms of MICA microsatellites in thyroidal autoimmunity]. Med Klin (Munich) 2007, 102, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomer, Y.; Menconi, F. Type 1 diabetes and autoimmune thyroiditis: the genetic connection. Thyroid 2009, 19, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittmar, M.; Kahaly, G.J. Immunoregulatory and susceptibility genes in thyroid and polyglandular autoimmunity. Thyroid 2005, 15, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruserud, Ø.; Oftedal, B.E.; Wolff, A.B.; Husebye, E.S. AIRE-mutations and autoimmune disease. Curr Opin Immunol 2016, 43, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, D.; Røyrvik, E.C.; Aranda-Guillén, M.; Berger, A.H.; Landegren, N.; Artaza, H.; Hallgren, Å.; Grytaas, M.A.; Ström, S.; Bratland, E.; et al. GWAS for autoimmune Addison's disease identifies multiple risk loci and highlights AIRE in disease susceptibility. Nat Commun 2021, 12, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oftedal, B.E.; Assing, K.; Baris, S.; Safgren, S.L.; Johansen, I.S.; Jakobsen, M.A.; Babovic-Vuksanovic, D.; Agre, K.; Klee, E.W.; Majcic, E.; et al. Dominant-negative heterozygous mutations in AIRE confer diverse autoimmune phenotypes. iScience 2023, 26, 106818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oftedal, B.E.; Hellesen, A.; Erichsen, M.M.; Bratland, E.; Vardi, A.; Perheentupa, J.; Kemp, E.H.; Fiskerstrand, T.; Viken, M.K.; Weetman, A.P.; et al. Dominant Mutations in the Autoimmune Regulator AIRE Are Associated with Common Organ-Specific Autoimmune Diseases. Immunity 2015, 42, 1185–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Retterer, K.; Juusola, J.; Cho, M.T.; Vitazka, P.; Millan, F.; Gibellini, F.; Vertino-Bell, A.; Smaoui, N.; Neidich, J.; Monaghan, K.G.; et al. Clinical application of whole-exome sequencing across clinical indications. Genet Med 2016, 18, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monney, L.; Sabatos, C.A.; Gaglia, J.L.; Ryu, A.; Waldner, H.; Chernova, T.; Manning, S.; Greenfield, E.A.; Coyle, A.J.; Sobel, R.A.; et al. Th1-specific cell surface protein Tim-3 regulates macrophage activation and severity of an autoimmune disease. Nature 2002, 415, 536–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moonla, C.; Polprasert, C.; Komvilaisak, P.; Rattanathammethee, T.; Kongkiatkamon, S.; Wudhikarn, K.; Kobbuaklee, S.; Boonyabaramee, P.; Tangcheewinsirikul, N.; Pakakasama, S.; et al. Germline HAVCR2 mutations and their relation to the clinical spectrum of subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma and hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: results from a multicenter study and meta-analysis. Haematologica 2023, 108, 2743–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeKruyff, R.H.; Bu, X.; Ballesteros, A.; Santiago, C.; Chim, Y.L.; Lee, H.H.; Karisola, P.; Pichavant, M.; Kaplan, G.G.; Umetsu, D.T.; et al. T cell/transmembrane, Ig, and mucin-3 allelic variants differentially recognize phosphatidylserine and mediate phagocytosis of apoptotic cells. J Immunol 2010, 184, 1918–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tromp, S.A.M.; Gillissen, M.A.; Bernelot Moens, S.J.; van Leeuwen, E.M.M.; Jansen, M.H.; Koens, L.; Rutten, C.E.; Kuijpers, T.W. Treatment of an HLH-mimic disease based on HAVCR2 variants with absent TIM-3 expression. Blood Adv 2022, 6, 4501–4505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierabracci, A.; Belcastro, E.; Carbone, E.; Pagliarosi, O.; Palma, A.; Pacillo, L.; Giancotta, C.; Zangari, P.; Finocchi, A.; Cancrini, C.; et al. In Search for the Missing Link in APECED-like Conditions: Analysis of the AIRE Gene in a Series of 48 Patients. J Clin Med 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Cheng, S.; Fan, L.; Zhang, B.; Xu, S. TIM-3: An update on immunotherapy. Int Immunopharmacol 2021, 99, 107933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, G.J.; Casasnovas, J.M.; Umetsu, D.T.; DeKruyff, R.H. TIM genes: a family of cell surface phosphatidylserine receptors that regulate innate and adaptive immunity. Immunol Rev 2010, 235, 172–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, M.; Akiba, H.; Takeda, K.; Kojima, Y.; Hashiguchi, M.; Azuma, M.; Yagita, H.; Okumura, K. Tim-3 mediates phagocytosis of apoptotic cells and cross-presentation. Blood 2009, 113, 3821–3830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Lotze, M.T. Tumor immunity times out: TIM-3 and HMGB1. Nat Immunol 2012, 13, 808–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.H.; Zhu, C.; Kondo, Y.; Anderson, A.C.; Gandhi, A.; Russell, A.; Dougan, S.K.; Petersen, B.S.; Melum, E.; Pertel, T.; et al. Corrigendum: CEACAM1 regulates TIM-3-mediated tolerance and exhaustion. Nature 2016, 536, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, A.C.; Anderson, D.E.; Bregoli, L.; Hastings, W.D.; Kassam, N.; Lei, C.; Chandwaskar, R.; Karman, J.; Su, E.W.; Hirashima, M.; et al. Promotion of tissue inflammation by the immune receptor Tim-3 expressed on innate immune cells. Science 2007, 318, 1141–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastings, W.D.; Anderson, D.E.; Kassam, N.; Koguchi, K.; Greenfield, E.A.; Kent, S.C.; Zheng, X.X.; Strom, T.B.; Hafler, D.A.; Kuchroo, V.K. TIM-3 is expressed on activated human CD4+ T cells and regulates Th1 and Th17 cytokines. Eur J Immunol 2009, 39, 2492–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, A.C.; Joller, N.; Kuchroo, V.K. Lag-3, Tim-3, and TIGIT: Co-inhibitory Receptors with Specialized Functions in Immune Regulation. Immunity 2016, 44, 989–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakova, J.; Truxova, I.; Holicek, P.; Salek, C.; Hensler, M.; Kasikova, L.; Pasulka, J.; Holubova, M.; Kovar, M.; Lysak, D.; et al. TIM-3 levels correlate with enhanced NK cell cytotoxicity and improved clinical outcome in AML patients. Oncoimmunology 2021, 10, 1889822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Fueyo, A.; Tian, J.; Picarella, D.; Domenig, C.; Zheng, X.X.; Sabatos, C.A.; Manlongat, N.; Bender, O.; Kamradt, T.; Kuchroo, V.K.; et al. Tim-3 inhibits T helper type 1-mediated auto- and alloimmune responses and promotes immunological tolerance. Nat Immunol 2003, 4, 1093–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y. The -1541 C>T and +4259 G>T of TIM-3 polymorphisms are associated with rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility in a Chinese Hui population. Int J Immunogenet 2011, 38, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaghoobi, E.; Abedian, S.; Babani, O.; Izad, M. TIM-3 Rs10515746 (A/C) and Rs10053538 (C/A) Gene Polymorphisms and Risk of Multiple Sclerosis. Iran J Public Health 2016, 45, 644–649. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, L.; Yang, X.; Xia, Q.; Zhen, J.; Zhuang, X.; Peng, T. Expression of human T cell immunoglobulin domain and mucin-3 (TIM-3) on kidney tissue from systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients. Clin Exp Med 2014, 14, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koguchi, K.; Anderson, D.E.; Yang, L.; O'Connor, K.C.; Kuchroo, V.K.; Hafler, D.A. Dysregulated T cell expression of TIM3 in multiple sclerosis. J Exp Med 2006, 203, 1413–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morimoto, K.; Hosomi, S.; Yamagami, H.; Watanabe, K.; Kamata, N.; Sogawa, M.; Machida, H.; Okazaki, H.; Tanigawa, T.; Nagahara, H.; et al. Dysregulated upregulation of T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain-3 on mucosal T helper 1 cells in patients with Crohn's disease. Scand J Gastroenterol 2011, 46, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, F.; Guo, X.; Jiang, X.; Zhou, P.; Xiao, Y.; Zhou, T.; Chen, G.; Zhao, Z.; Xiao, H.; Hou, C.; et al. Dysregulated Tim-3 expression and its correlation with imbalanced CD4 helper T cell function in ulcerative colitis. Clin Immunol 2012, 145, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhou, Z. Altered expression of Tim family molecules and an imbalanced ratio of Tim-3 to Tim-1 expression in patients with type 1 diabetes. Frontiers in Endocrinology 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehne, C.; Behrendt, A.K.; Meyer-Bahlburg, A.; Boettcher, M.; Drube, S.; Kamradt, T.; Hansen, G. Tim-3 is dispensable for allergic inflammation and respiratory tolerance in experimental asthma. PLoS One 2021, 16, e0249605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eilers, L.F.; Kyle, W.B.; Allen, H.D.; Qureshi, A.M. Patent Ductus Arteriosus. Pediatrics In Review 2021, 42, 632–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neufeld, M.; Maclaren, N.; Blizzard, R. Autoimmune polyglandular syndromes. Pediatr Ann 1980, 9, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husebye, E.S.; Anderson, M.S.; Kämpe, O. Autoimmune Polyendocrine Syndromes. N Engl J Med 2018, 378, 1132–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, A.; Gianchecchi, E.; Palombi, M.; Luciano, R.; Di Carlo, P.; Crinò, A.; Cappa, M.; Fierabracci, A. Analysis of the autoimmune regulator gene in patients with autoimmune non-APECED polyendocrinopathies. Genomics 2013, 102, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arena, A.; Belcastro, E.; Ceccacci, F.; Petrini, S.; Conti, L.A.; Pagliarosi, O.; Giorda, E.; Sennato, S.; Schiaffini, R.; Wang, P.; et al. Improvement of Lipoplexes With a Sialic Acid Mimetic to Target the C1858T PTPN22 Variant for Immunotherapy in Endocrine Autoimmunity. Front Immunol 2022, 13, 838331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Henikoff, S.; Ng, P.C. Predicting the effects of coding non-synonymous variants on protein function using the SIFT algorithm. Nature Protocols 2009, 4, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adzhubei, I.; Jordan, D.M.; Sunyaev, S.R. Predicting functional effect of human missense mutations using PolyPhen-2. Curr Protoc Hum Genet, 7. [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, J.M.; Cooper, D.N.; Schuelke, M.; Seelow, D. MutationTaster2: mutation prediction for the deep-sequencing age. Nat Methods 2014, 11, 361–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: a joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genetics in Medicine 2015, 17, 405–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ittisoponpisan, S.; Islam, S.A.; Khanna, T.; Alhuzimi, E.; David, A.; Sternberg, M.J.E. Can Predicted Protein 3D Structures Provide Reliable Insights into whether Missense Variants Are Disease Associated? J Mol Biol 2019, 431, 2197–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schymkowitz, J.; Borg, J.; Stricher, F.; Nys, R.; Rousseau, F.; Serrano, L. The FoldX web server: an online force field. Nucleic Acids Res 2005, 33, W382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biagini, T.; Chillemi, G.; Mazzoccoli, G.; Grottesi, A.; Fusilli, C.; Capocefalo, D.; Castellana, S.; Vescovi, A.L.; Mazza, T. Molecular dynamics recipes for genome research. Briefings in Bioinformatics 2017, 19, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cocciadiferro, D.; Mazza, T.; Vecchio, D.; Biagini, T.; Petrizzelli, F.; Agolini, E.; Villani, A.; Minervino, D.; Martinelli, D.; Rizzo, C.; et al. Exploiting in silico structural analysis to introduce emerging genotype-phenotype correlations in DHCR24-related sterol biosynthesis disorder: a case study. Front Genet 2023, 14, 1307934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biagini, T.; Petrizzelli, F.; Truglio, M.; Cespa, R.; Barbieri, A.; Capocefalo, D.; Castellana, S.; Tevy, M.F.; Carella, M.; Mazza, T. Are Gaming-Enabled Graphic Processing Unit Cards Convenient for Molecular Dynamics Simulation? Evol Bioinform Online 2019, 15, 1176934319850144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, D.; Feng, S.; Lee, H.; Zhang, H.; Park, S.J.; Kim, S.; Lee, J.; Choi, S.; Im, W. CHARMM-GUI Enhanced Sampler for various collective variables and enhanced sampling methods. Protein Sci 2022, 31, e4446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).