1. Introduction
The growing global demand for Additive Manufacturing indicates a transformative trend across various industries. Additive manufacturing, characterized by the layer-by-layer deposition of material, is a recent and widely studied production method [
1,
2]. It includes terminologies such as 3D printing (3DP), rapid prototyping (RP), direct digital manufacturing (DDM), rapid manufacturing (RM), and solid freeform fabrication (SFF). As an advancing technology, 3D printing, or additive manufacturing (AM), has applications in diverse sectors such as aerospace, automotive, medical and healthcare, construction and architecture, and food and fashion industries [
1]. The aerospace sector has started utilizing the AM technology due to its ability to create lighter structures, resulting in lighter airplanes and spacecraft. Similarly, the automotive industry has recognized the potential of additive manufacturing to produce complex and high-quality parts that were previously unachievable and to replicate difficult-to-find parts. In the healthcare sector, AM has made it possible to perform complex transplants and produce precise anatomical models for surgical planning. Moreover, studies evaluating the strength of products manufactured through additive processes, including both non-metallic and metallic materials, have been conducted, highlighting the viability and limitations of the technique.
The decentralization of 3D printing represents a significant change in the manufacturing sector, making it accessible not only for large-scale industrial applications but also for general domestic use and small-scale manufacturing enterprises. The number of people using 3D printers for small-scale businesses and personal use has increased as they become more widely available, cheap, user-friendly, and portable. One of the advantages of decentralized 3D printing is that it allows users to express their ideas by creating complex, personalized objects on demand without requiring massive production facilities.
A notable use case for 3D printing lies in rapid prototyping, where the technology has emerged as an indispensable tool across various industries. The ability to quickly transform digital designs into physical prototypes enables an iterative design process, allowing engineers, designers, and researchers to test and refine their concepts rapidly. This accelerates the product development cycle and significantly reduces lead times, providing a competitive edge to industries such as aerospace, automotive, and consumer electronics. The efficiency and precision of 3D printing in rapid prototyping contribute to cost savings and enhanced innovation, highlighting its role in shaping the future of product design and development [
1].
Although there is no doubt that 3D printing has transformed several industries by providing unprecedented levels of flexibility in design and production, there are drawbacks as well, especially concerning sustainability and the impact it has on the environment given the rapid speed of decentralization. However, by using recycled elements in the 3D printing process, we may overcome these difficulties. For example, turning plastic waste into printed filaments reduces environmental impact while providing a range of material choices with different levels of rigidity, flexibility, and transparency. This greater flexibility opens up new possibilities for design innovation, making it possible to manufacture unique products depending on various requirements and preferences.
This comprehensive review analyzes the evolving landscape of material waste recyclability in additive manufacturing, starting its role in decentralized manufacturing. It then evaluates the usability and characteristics of various recycled materials in the AM sector, followed by an in-depth analysis of current recycling methodologies such as mechanical, chemical, and thermal processes. It then discusses the economic and societal impacts of additive manufacturing. The review highlights the necessity of sustainable practices in AM and stresses the significance of improving waste management by highlighting research gaps and future trends.
1.1. Evolution of Additive Manufacturing
The invention of additive manufacturing can be related back to the 1980s, when stereolithography (SLA) was invented by Charles "Chuck" Hull. SLA uses ultraviolet (UV) light focused into a UV photo-curable liquid polymer solution to build patterns layer by layer in order to create a three-dimensional object. This invention set the way for the establishment of 3D Systems in 1986, which led to the creation and production of 3D printers. After that, the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) patent grant in 1986 marked the development of Rapid Prototyping systems and pushed AM to the forefront of manufacturing technology [
3].
Despite its initial challenges, additive manufacturing is a major technological advancement that combines materials using a variety of processes like fusion, binding, and solidification. The parts are assembled layer by layer with the help of 3D CAD modeling which stores complicated object geometry using 3D computer data or Standard Tessellation Language (STL) files. The process of AM consists of three key stages: design, processing, and testing. Today's industries use a wide range of methods, such as Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS), Laminated Object Manufacturing (LOM), Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), Stereolithography (SLA), and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) [
4,
5]. While there are many advantages to additive manufacturing, there are also disadvantages, such as slower build times and lesser precision than CNC machines. The orientation of various parts plays a major role in improving accuracy, build times, the number of supports required, and eventually manufacturing costs.
1.2. Decentralized Manufacturing - 3D Printing
Decentralized manufacturing which is also called distributed manufacturing can be characterized by its ability to personalize product manufacturing across various scales and locations, be it at the point of consumption, sale, or within production sites that exploit local resources, which enhances user participation across product design, fabrication, and supply. This decentralization is typically enabled by digitalization and new production technologies, such as additive manufacturing. This manufacturing process has a lot of potential, especially when it comes to enabling manufacturing near the point where demand is greatest while meeting customized requirements. Large-scale customization using inventory-light production methods and improved accessibility to new markets and customers are all possible with decentralized manufacturing, particularly in industries like healthcare [
6].
Despite its widespread attention, many people are still unaware of additive manufacturing’s ability to decentralize production processes. It is anticipated that the resulting localization movement will replace globalization and dramatically reduce air, land, and sea travel. It is expected to significantly change global commerce, with a decline in goods trade and related macroeconomic changes in nations [
7]. Due to simplified logistics, supply chains will undergo significant changes as fewer businesses participate. Distribution will be made easier and the problems with international supply chains will be lessened by production that is closer to the consumer and driven by consumer demand. It is also anticipated that the skill and occupational demands of the new economy will change, with more logical, integrative, creative, and self-sufficient roles like designers, consultants, engineers, and product developers replacing jobs in installation, retail, packaging, transport, delivery, and construction. To manage socio-cultural difficulties, this shift needs careful attention via education and training [
8]. AM can enhance technical progress, providing underdeveloped nations with an alternate path to economic prosperity. The revolutionary potential of AM, which enables small companies to launch new goods without depending on international supply chains, is being recognized by both big and small businesses [
8].
Highly complex or even hybrid parts can be designed with the help of additive manufacturing, which allows for customized mass production using less material to minimize weight. Thus, the development of specialized materials has greatly benefited from the development of AM technologies. Because printable materials can now be precisely deposited in three dimensions with tiny accuracy, fewer production processes and resources can be used to build a desired framework. Presently, the main material for fused deposition modeling (FDM) 3D printing is thermoplastics, which subsequently increases the overall use of plastic. Plastic’s prominent problem is its adverse impact on both the environment and people. As a result, increasing sustainable production is becoming more and more crucial, particularly given the modern world's dense population and rising living standards caused by global industrialization [
9].
2. Materials and Methods
Recycling has become more and more significant these days with the growing amount of waste accumulation. Therefore, we turn to more and more innovative ways to recycle plastics. One such example is using recovered and recycled materials as inputs for the AM process. The process of converting plastic waste into printable filaments offers a variety of material options, improving design creativity and enabling customized goods.
In the upcoming sections, various materials used in AM will be identified, followed by a comprehensive review of the usability and properties of recycled materials and current recycling methodologies related to additive manufacturing.
2.1. Materials Landscape in Additive Manufacturing
Identifying various materials used in AM is vital for producing high-quality products through this technology, as the proper material selection is paramount for quality outcomes [
10]. The raw material used for various AM types has to be prepared in a way that is compatible with the specific process (e.g., powder, sheet, wire, liquid). For instance, a liquid thermoset plastic monomer that will crosslink when exposed to the right electromagnetic radiation is required as feedstock for vat polymerization and photopolymer-based material jetting. Material extrusion and powder bed fusion processes utilize thermoplastic polymers, both relying on thermal layer adhesion mechanisms while employing distinct techniques. Amorphous thermoplastics work best for material extrusion, whereas powder bed fusion usually uses semicrystalline polymers. Typical photopolymer materials used in AM are composed of monomers, oligomers, photoinitiators, and a variety of other additives including inhibitors, dyes, antifoaming agents, antioxidants, toughening agents, etc. that help fine-tune the photopolymer’s behaviors and properties [
11].
Table 1 outlines the general categories of polymers utilized in AM with their respective properties and symbols [
11].
2.2. Usability and Properties of Recycled Materials
Some emerging polymeric materials such as polyesters, polyamides, and acrylic compounds are characterized by their chemical composition, which influences their recyclability. Of these, PP and PET accounted for 46% of the world's polymer output in 2015; the packaging sector used 63.4% of these polymers. The most recycled polymer is PET, which is frequently used to make water bottles, followed by HDPE, which is frequently used to make shampoo bottles [
16]. Common commercial polymers including LDPE, HPDE, PP, PS, and PVC exhibit high mechanical strength up to 100°C. Conversely, polymers such as nylon, PET, and ABS can withstand temperatures beyond 100°C without losing their mechanical qualities.
Most commodity polymers are olefin-based making up more than 50% of plastic trash, whereas PET makes up just 10% of all plastic garbage. The strong CeC covalent link between the polymer chains in olefin-based polymers makes them difficult to recycle, resulting in the need for high temperatures and effective catalysts. However, the recycling cost does not add value to a recycled material resulting in a recycling rate of <10% for these polymers [
16].
Because of the low molecular diffusion rate, polymers frequently contain additives like colors, plasticizing agents, antioxidants, and reinforcing material, which makes it challenging to recover the basic polymer. When combined with organic coatings and additives, the polymers create strong van der Waals pressures that increase the energy and expense of recycling. For recycling purposes, for example, a thermoset polymer coating on a thermoplastic polymer has to be removed and separated. Second, the commercial value of recovered polymers is decreased by the use of dyes to create colored polymers. Therefore, to address this major difficulty in polymer recycling, innovative and inexpensive methods for removing coatings and additives are needed [
17].
The compositional hurdles experienced during the mechanical and thermochemical recycling of a few plastic packaging waste products were investigated by Martijn Roosen et.al (2020) [
17]. A summary of their findings is given in
Table 2.
A wide variety of materials are utilized during additive manufacturing which contain various combinations of polymers, additives, reinforcing content, plasticizing agents, pigments, and antioxidants to improve mechanical and chemical properties.
Table 3 provides a summary of a few specialized material compositions that can be utilized as a part of sustainable additive manufacturing processes that are identified through various studies.
HDPE mixed with RF demonstrates varying weight loss percentages, notably with HDPE 70% exhibiting a weight loss of 82.59%. Reinforcement 3D printed mortar with steel cables showcases improved flexural strength and bond strength, alongside specific flow ranges for fresh mortar and reinforced steel cable fluidity. Recycled ABS (RABS)/virgin ABS (VABS) blends exhibit enhancements in various mechanical attributes, with superior properties observed in samples printed with a 50% RABS/50% VABS composition. Incorporating recycled plastic waste, such as Resin8, into 3D printed concrete (3DPC) impacts compressive and flexural strengths inversely proportional to the amount of Resin8 utilized. Additionally, materials derived from PET, both in filament form and from water and soft drink bottles, display distinct mechanical properties including elasticity, mechanical strength, and hardness. Young's modulus increases when PET and HDPE are combined as feedstock materials for large-scale 3-D printing.
Using physical, chemical, and thermal characterization, one experiment utilized various percentage compositions of recycled flexible plastic with virgin PP and HDPE to determine the reinforcement effects of the polymer blends toward the virgin polymer [
18]. It has been shown in another investigation that the mechanical performance of 3D-printed samples was restored by the addition of virgin pellets. Reinforcement from virgin pellets can help recycled polymers regain their lost mechanical characteristics. Adding the right number of fibers and particles to polymers is another way to enhance their mechanical qualities [
16].
It is easy to create complex, personalized items with 3D printing. By using recycled materials in 3D printing, we may explore a diverse array of material qualities and features. Waste plastic, for instance, can be made into printable filaments that can be used to create a variety of rigid, flexible, and even transparent objects. This adaptability creates new opportunities for design innovation and makes it possible to create unique items that can be provided to requirements and preferences [
28].
2.3. Current Recycling Methodologies
The market for 3D printing is a rapidly expanding industry. A wide range of thermoplastic compounds, including recyclable ones, may be used to create printable filaments [
29]. Such polymeric material recycling usually involves several steps, including material separation, purification and decontamination, grinding, remelting, and extrusion. The logistical and financial components of this procedure are the key roadblocks.
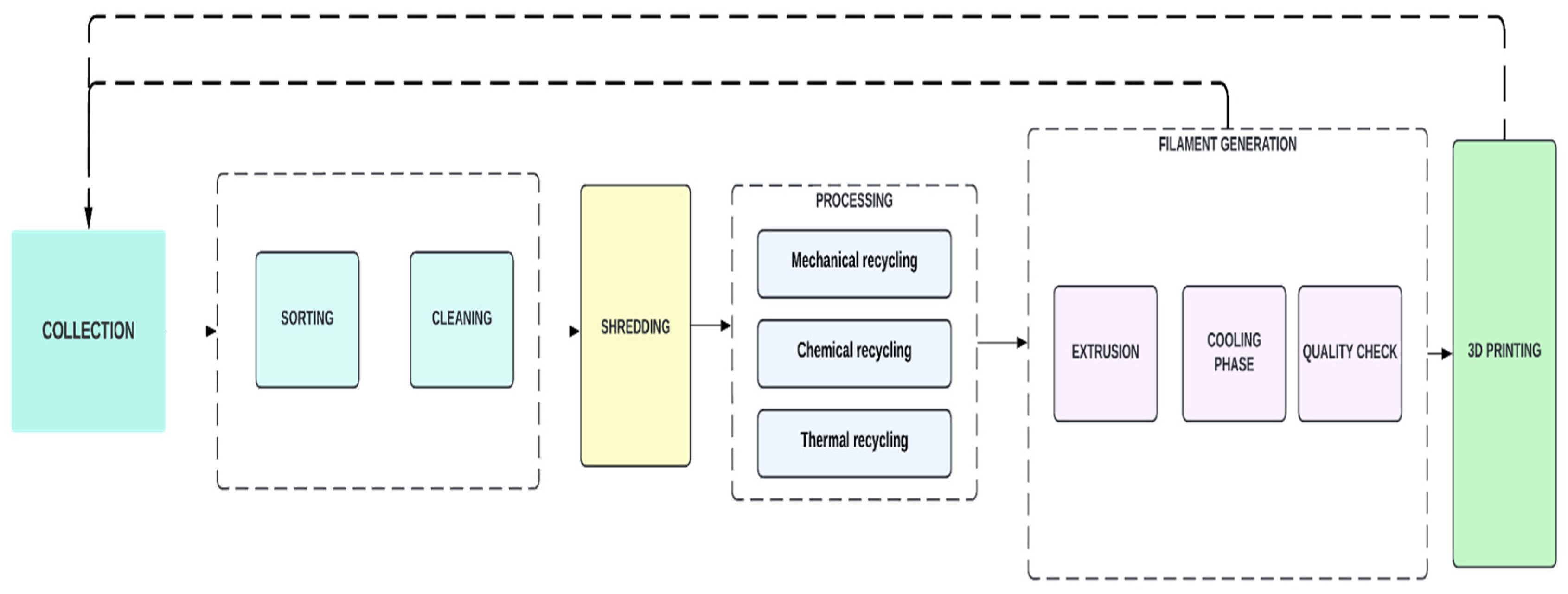
Figure 1 depicts the predominant methodology for recycling in AM. Several processes in the recycling procedure for 3D printing filaments are described in this section.
The first step is Collection, where suitable plastic materials for recycling are collected by different means depending on the classification. Solid waste can be classified into different types according to sources such as Municipal Solid Waste (MSW), Industrial Waste, Agricultural Waste, Municipal Sludge, and Other Wastes [
30]. As previously mentioned, AM operates as a decentralized method, as a result, the effectiveness of waste management becomes crucial in universities or colleges where continuous waste generation is common. The collection of these wastes from the location of waste generation and then locally recycling them will be more effective and much easier. On the other hand, a different kind of waste collection strategy is required in centralized areas like industries and municipalities. This strategy utilizes existing waste management techniques, such as those used by municipalities globally, including curbside collection, vehicle collection, drop-off waste disposal, buy-back centers, and deposit/refund programs [
31].
The second step which almost completes around 25% of the recycling process is Sorting. During this process, all the plastic waste collected is separated into different types for its characteristics. The majority of plastics are classified as HDPE, PP, or PET; however, if other polymers are found that cannot be recycled, they are separated from the other plastics and used for other purposes. Sorted plastic is then further divided into categories based on hues and kinds [
31]. The recycling process is not uniform and varies significantly depending on the type of polymer. Interestingly, even polymers with similar chemical structures, such as the CeC bond found in both LDPE and PP, cannot be melted together. Once mixed, these polymers pose a considerable challenge in terms of separation [
16]. Commercial products often compound this issue as they typically contain multiple types of polymers within a single product. This makes the task of polymer sorting a significant challenge. Automating the sorting procedure guarantees that the recovered polymer is of constant quality and can be handled efficiently, which is essential to the success of mechanical recycling [
24]. This is typically achieved using near-infrared spectroscopy (NIR). However, for larger volumes, X-ray fluorescence (XRF) is one of the preferred methods. The subsequent size of the shredded polymer pieces depends upon their intended use. As such, there is a growing demand for high-efficiency sorting techniques in the recycling industry. This highlights the need for innovative solutions to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of polymer recycling processes.
The third step involves processes such as removing contaminants such as labels and adhesive from the waste, known as Cleaning. The cleaning process incurs additional costs related to drying and wastewater treatment. Moreover, effectively removing food-derived pollutants presents a considerable challenge. Caustic cleaning methods, for instance, are ineffective in eradicating odor components. For example, plastic bottles (PET) are washed in hot water to remove label residues or general dirt. Furthermore, they go through various procedures to get rid of additional undesirable materials like paper or metal, but detergent bottles typically require a mechanical cleaning to get rid of all contamination.
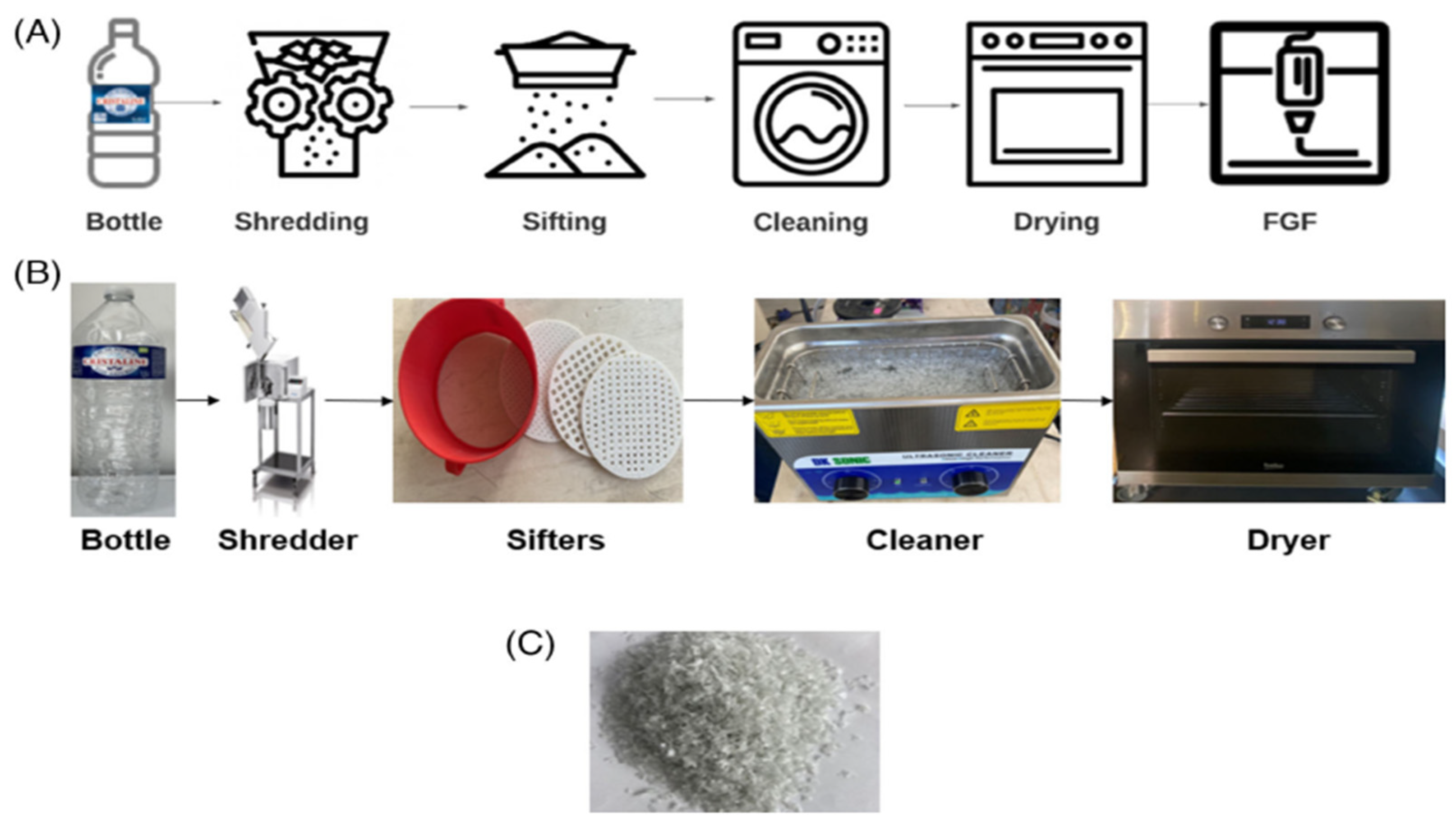
We tend to define Shredding as a process where it involves breaking down of, used or failed prints and other plastic wastes into smaller pieces to facilitate further processing. Shredding significantly increases the surface area which helps with melting, facilitating effective heat transfer and ensuring a complete and consistent melting process. Overall, shredding contributes to improved processing efficiency and homogeneity in material melting. For example, in one of the studies, a FriendTM plastic mill was used to shred the 3D-printed specimens, except for a few samples that were extracted for characterization. Since the goal of the study was to simulate closed-loop recycling of 3D printed products, washing, and sorting were not included in the experiment; instead, the PLA's source and end use were analyzed [
32].
Figure 2 gives the process stages for the preparation of the collected material, which comprises (A) a schematic representation outlining the process of material preparation, (B) the materials utilized in the process, and (C) the resultant material [
26].
The next step involved is the processing of the shredded plastics into the desired form such as pellets. The processing of these plastics can be then broadly divided into the following subsections.
2.3.1. Mechanical recycling
Polymers are recovered and recycled into new products through the process of mechanical recycling by utilizing specialized mechanisms capable of deforming the waste without altering its chemical structure. Technologies for size reduction, remelting, decontamination, sorting/separation, and production are all included in mechanical recycling. Many studies highlight the energy and environmental benefits of mechanical recycling, particularly for waste streams consisting solely of plastic or bioplastic. It is essential for completing the circle on polymer wastes and enabling a circular economy [
31,
33].
It’s important to note that not all types of plastic are suitable for mechanical recycling and the quality of the recycled plastic can degrade after multiple recycling [
34]. However, in addition to technical concerns about plastic degradation, mechanical recycling faces difficulties with intricate management and collection procedures [
33]. In one of the studies, the reference-grade printing wastes were ground up and placed through a severe 85°C washing process. The detergent used was Triton X-100, 0.3% wt., and the water-based solution of NaOH (1.5% wt.) similar to the ones used by the mechanical recycling companies [
35]. The purified components were dried in a vacuum oven for two hours at 85°C prior to processing in a vacuum oven [
35,
36].
2.3.2. Chemical recycling
Chemical recycling, also known as feedstock recycling, uses procedures like hydrolysis, pyrolysis, gasification, condensation, glycolysis, hydrocracking, dissolution, etc. to break down synthetic fibers for repolymerization and produce the monomers of the polymers (or partially depolymerized to oligomers) [
37]. Polymerization, purification, and depolymerization are some of the phases in this process. Chemical recycling technologies provide supplementary solutions to mechanical recycling for the recycling of polymeric waste.
In research, depolymerization is a chemical recovery technique that is used to produce initial carboxylic acids, diols, or diamines from polymers that undergo condensation (polyamides, polyesters, polyethers, and PET). Acidolysis, glycolysis, alcoholysis, and hydrolysis are examples of depolymerization processes. These reactions hold significance in the deconstruction of polymer structures, playing a pivotal role in the regeneration of constituent monomers [
34].
Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) was used to determine the chemical composition of the filaments by measuring reflectance using the non-destructive attenuated total reflectance (ATR) sampling technique [
38]. A Perkin Elmer Frontier Spectrometer (FTNIR/MIR, Waltham, USA) fitted with an FR-DTGS detector and a KBr beam splitter was used in another study to record the infrared spectrum (4000–550 cm-1) [
38]. The data from the study is then used to choose the proper chemical recycling method.
2.3.3. Thermal recycling
Thermal degradation, also known as thermal recycling, is the process of using heat to break down polymers into their component monomers or other compounds. In order to break the polymer down into smaller molecules, this technique usually entails heating the polymer to high temperatures without the presence of oxygen. New polymer goods and other compounds, such as fuels and waxes, can be made from the resultant products [
24].
The process of pyrolysis- which takes place in the absence of oxygen and usually at temperatures ranging from 400 to 980°C- was used to thermally breakdown polyethylene terephthalate, polystyrene, polymethylmethacrylate, and certain polyamides into its monomers. The resultant products include a fuel gas consisting of CO, CO2, H2, and CnHm, liquid components in the form of oils, and a solid residue known as char or black carbon [
34].
The mechanical approach uses a small amount of energy, the thermal recycling approach uses a moderate amount, and the chemical recycling approach uses the greatest amount of energy. All these modern recycling methods still use less energy than conventional methods like incineration and landfilling. In addition, the number of cycles that the polymer composite materials can be recycled depends on the individual components of these materials [
39].
Extrusion comes into play as the last step where the processed-shredded plastic is then fed into an extruder. In this process, the polymer is subjected to heat and pressure, which causes it to melt. This is usually done in an extruder head, a special device that pushes the polymer through a heated barrel using a screw mechanism. The polymer is pushed through a die once it has melted. This procedure makes it possible to produce pellets with particular dimensions and forms. This procedure produces a finished solid or flexible film product that has been carefully designed for additional applications [
40]. These pellets are then used as the raw material for the manufacture of a variety of new products, ranging from plastic containers and toys to automotive parts. This shows the adaptability and potential of recycled polymers across a range of sectors [
16].
An essential part of the extrusion devices, the cooling phase affects the change from the molten viscous fluid to the final solid or flexible film product. To achieve the correct dimensional and structural qualities of the extruded material, effective cooling is necessary. It plays a critical role in determining the final product's overall quality. Controlling the rate and uniformity of cooling is given great importance as the extruded material moves through the stages of solidification and cooling. This accuracy is essential to preventing errors and ensuring the final product's structural integrity. For the manufacturing of high-quality plastic goods that fulfill the required standards, the cooling and solidification processes must be part of the entire extrusion framework [
40].
Throughout the process, quality control procedures are crucial for ensuring that the produced plastic feedstock fulfills the specifications that are required. The cooling assembly, die assembly, plasticizing extruder, and winding apparatus all work together, giving the extrusion system its level of complexity. Specific quality control measures are put in place at each stage to keep an eye on and maintain the final product's desired qualities.
It was also noticed that in a study evaluating previous waste plastic extruder designs, commonly referred to as ‘RecycleBots’, a weighted evaluation matrix was employed. In light of that study, an updated design was developed and analyzed. This included an extensive component summary, testing procedures, a basic life cycle analysis, and extrusion results. The focus was on measuring power consumption and evaluating filament characteristics like density and diameter consistency. This approach allowed for a thorough examination of the performance and sustainability aspects of the newly developed extruder system [
41].
A study suggests that PET shreds could be dried under a vacuum at 120°C overnight to prevent melt hydrolysis. This study utilizes equal weights of each polymer and 5% of either SEBS or SEBS-MA to fix compatible blend ratios [
42].
3. Economic and Societal Impacts
Additive Manufacturing, as an emerging manufacturing process, not only impacts a product's life cycle but also offers sustainability benefits at various stages. While serving as a direct substitute for traditional manufacturing processes, its economic advantages lie in the production of customized single or small batches of goods. The technology's potential sustainability improvements are evident in its ability to provide design freedoms, enabling the redesign of components, products, and processes. However, realizing these benefits requires developing additive manufacturing skills, emphasizing the need for national policies promoting educational programs to equip designers and engineers with the necessary skills [
16].
These advanced additive manufacturing technologies present an unprecedented opportunity to reshape the organization of manufacturing activities. Beyond innovations in processes, these technologies can influence the distribution of manufacturing and the flow of materials and goods, offering numerous sustainability benefits [
44]. A key avenue for realizing these benefits is the potential transition towards a Circular Economy, an economic method aiming to enhance society's resource efficiency by eliminating the concept of waste and breaking away from the linear take-make-waste model. The core of a circular economy revolves around transforming end-of-life goods into resources for others, fostering closed loops in industrial ecosystems, and minimizing waste. This shift challenges traditional economic models by emphasizing sufficiency over excessive production- encouraging reuse, recycling, repair, and remanufacturing. The idea of replacing energy with labor was initially put up forty years ago in a paper submitted to the European Commission. During a period of rising energy prices and high unemployment in the early 1970s, the idea gained traction, particularly in the architectural realm, where refurbishing existing structures proved more labor-efficient than constructing new ones [
45].
Circular-economy business models generally fall into two categories: those promoting reuse and extended service life through repair, remanufacture, upgrades, and retrofits, and those converting old goods into new resources through material recycling. Central to this model is a shift from ownership to stewardship, where consumers transform into users and creators. The emphasis on remanufacturing and repair not only contributes to sustainability but also generates skilled job opportunities in local workshops, involving people of various ages and skill sets [
46].
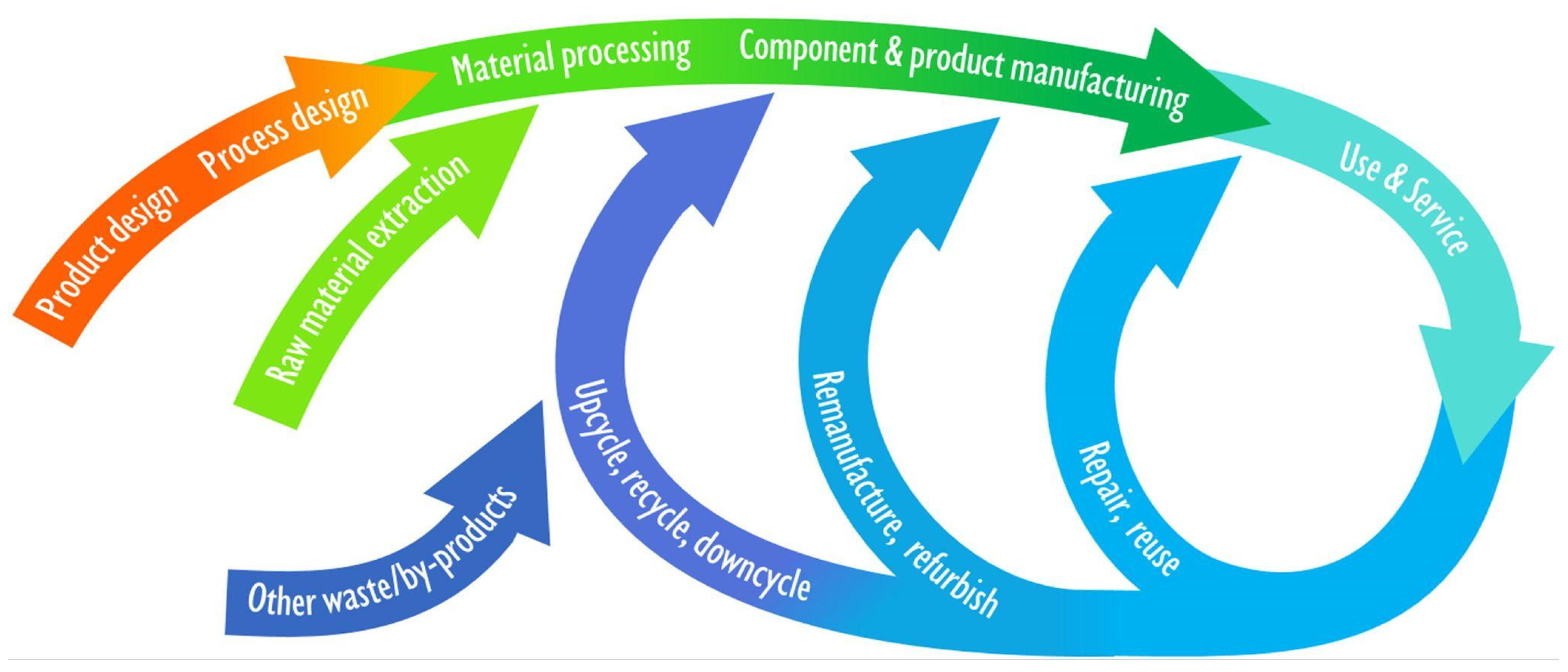
Current industrial applications of additive manufacturing are already contributing to more circular production systems by incorporating recycled and reclaimed materials as inputs for additive manufacturing processes. In metal AM, for example, over 95% of the unused powder can be locally filtered and reused directly, with the remaining 5% sent to a centralized recycling facility to produce virgin powder [
43]. The additive nature of 3D printing, where material is added only where needed, reduces material consumption compared to subtractive processes, minimizing material waste. Moreover, the entire system surrounding the 3D printing process can be designed to facilitate a closed-loop circulation of materials, enhancing sustainability. Implementing material-reuse methods in the context of a circular economy can yield cost reductions per part, such as a 10% reduction for Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) and a substantial 70–80% reduction for Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM). With breakaway support, FDM is indicated to be a more economical and less wasteful solution than SLS. FDM parts are about 20% more expensive than SLS parts when materials are used until they degrade, but they produce only 15% more waste material per part than SLS [
47]. Despeisse et al. (2017), elucidated the diversity and span of the entire product and material life cycles which is clearly illustrated in
Figure 3 [
43].
4. Environmental Impact
Managing plastic waste has emerged as one of the most important environmental issues confronting humanity today. The continuous environmental threat posed by non-biodegradable plastics is a grave concern due to their widespread presence in the waste stream. The accumulation of these waste plastics has led to significant challenges, including environmental litter, drain blockages, and critical health-related issues. Without efficient waste management, numerous countries choose careless dumping without following scientific waste disposal methods. This causes waste plastic pyramids to build up in landfills, taking up a lot of space and worsening general environmental problems. Further challenges to the recycling process are the low profitability and high technological difficulty involved in breaking down plastics into their constituent chemicals. Due to the growing demand for plastic-related products, their non-biodegradable nature, and the social risks they bring about, handling plastics recovered from MSW is becoming more and more difficult.
The study of environmentally friendly plastic recycling methods has been pushed by these environmental problems. Despite its effectiveness, mechanical recycling presents some drawbacks, such as a limited number of recyclable polymers and the potential for molecular weight reduction. Chemical recycling is a particular method that can convert plastic waste into valuable feedstock materials for the production of fuel and monomers. Although chemical recycling shows promise and it is more costly, labor- and energy-intensive than mechanical recycling and may produce additional pollutants. However, employing modern recycling methods, such as chemical recycling, can significantly decrease energy consumption, save costs, and contribute to the creation of a more sustainable future. In the context of plastic waste, AM or 3D Printing stands out as a distributed and inexpensive method to reuse polymer waste. Its adoption, especially through innovative techniques, can lead to the widespread reuse of polymer waste, providing an accessible solution for both companies and individuals and promoting circular economy principles [
47].
The application of additive manufacturing technology is growing, but there hasn't been a thorough analysis of how it affects the environment. Conventional manufacturing techniques frequently combine steps like casting, molding, bending, and welding, each of which has a different impact on the environment. In contrast, AM typically eliminates the need for such a combination in part production. Additive manufacturing stands out for its ability to produce intricately shaped products layer by layer, with high precision and significantly reduced material wastage. Compared to traditional manufacturing methods, AM technologies offer several positive environmental advantages. Notably, a considerable reduction in raw material waste, and the incorporation of new and intelligent materials further enhances sustainability. Additive Manufacturing emphasizes component output efficiency, minimizing material waste, energy consumption, and machine emissions [
49].
When considering AM procedures, three environmental aspects can be considered: energy consumption, waste disposal, and air pollution. The particular set of parameters for each process influences the energy consumption in AM operations. For example, more printing resolution leads to higher energy consumption and longer production periods. Reuse and recycling methods can be applied to waste material management in additive manufacturing procedures. Reusing waste polymer materials to create filaments is an effective technique to reduce the impact on the environment. Reducing waste materials can also increase the energy efficiency of AM operations.
Additive manufacturing technologies have both direct and indirect impacts on air pollution. Air pollution can be reduced directly by using non-toxic materials and biopolymer filaments. The decentralization due to additive manufacturing reduces shipping costs and produces goods closer to customers creating an indirect effect on improving air quality. Practical factors, such as the use of 3D printing to make replacement parts, help products that do not have support from their original manufacturers to extend their lifespan.
However, despite additive manufacturing's natural sustainability, there still exist problems because 3D printing techniques are simple to use, and production processes are decentralized, which results in a large volume of unmanaged plastic material. The advent of rapid prototyping, while advancing the field, has resulted in an increased generation of small-scale solid plastic waste. This surge necessitates the development of recycling solutions at the point of manufacturing. Managing such waste at its origin becomes important, given the decentralized nature of Additive Manufacturing and the advancement of 3D printing methodologies. Despite the challenges, 3D printing has the potential to play a pivotal role in the sustainable manufacturing industry, contributing to the goal of creating an environmentally friendly manufacturing landscape.
5. Research Gap and Future Trends
The potential of additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, appears promising in several fields, including research, construction, architecture, automotive, aerospace, medical, and healthcare, as well as the food and fashion industries [
1]. It allows various industries to reduce the weight and create complex designs that were previously thought to be impractical. Over the recent years, an array of studies has explored the structural integrity of products manufactured through additive processes, spanning both non-metal and metal materials, shedding light on additive manufacturing’s feasibility and its limitations. Nevertheless, a more in-depth investigation is essential for completely utilizing this technology, particularly in the field of enhancing material properties.
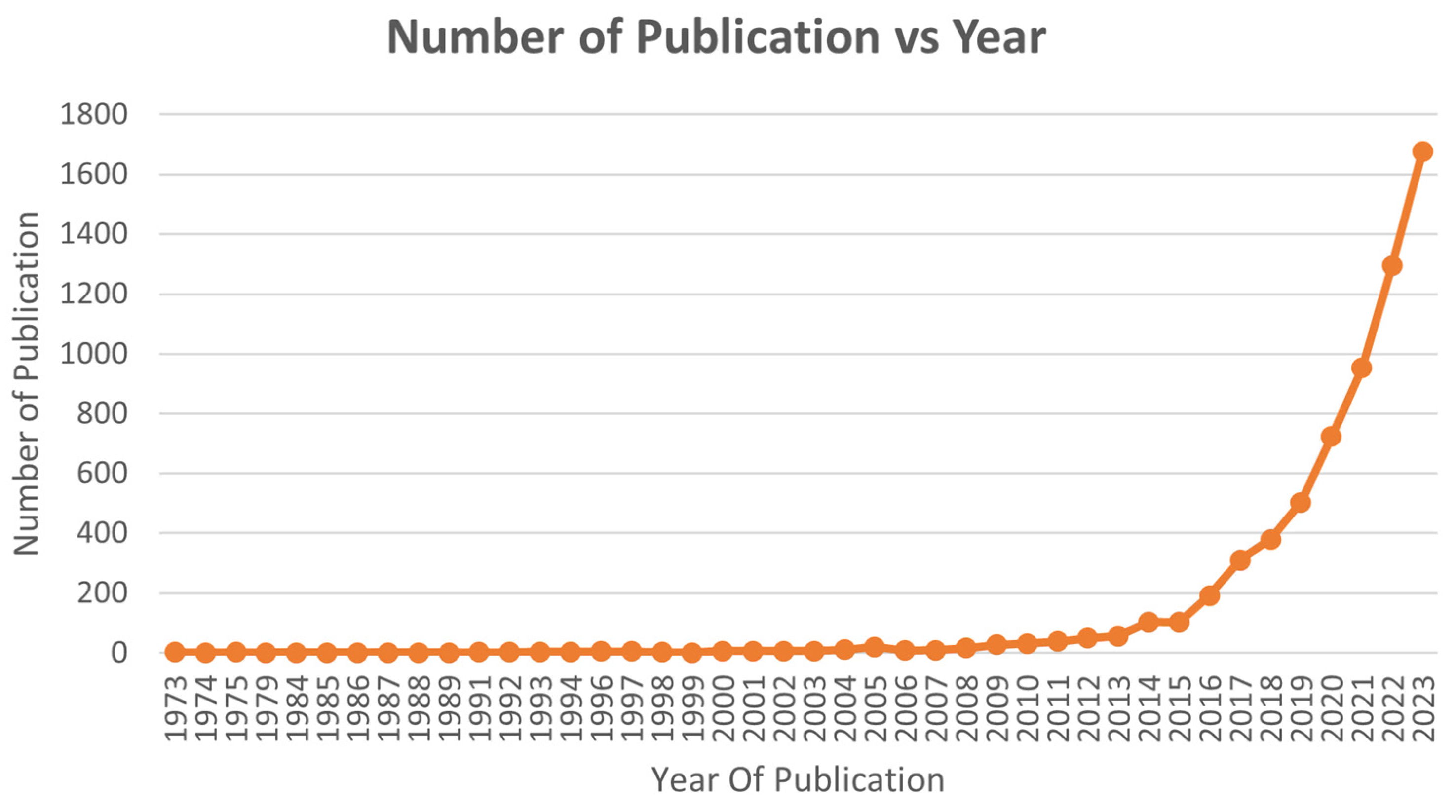
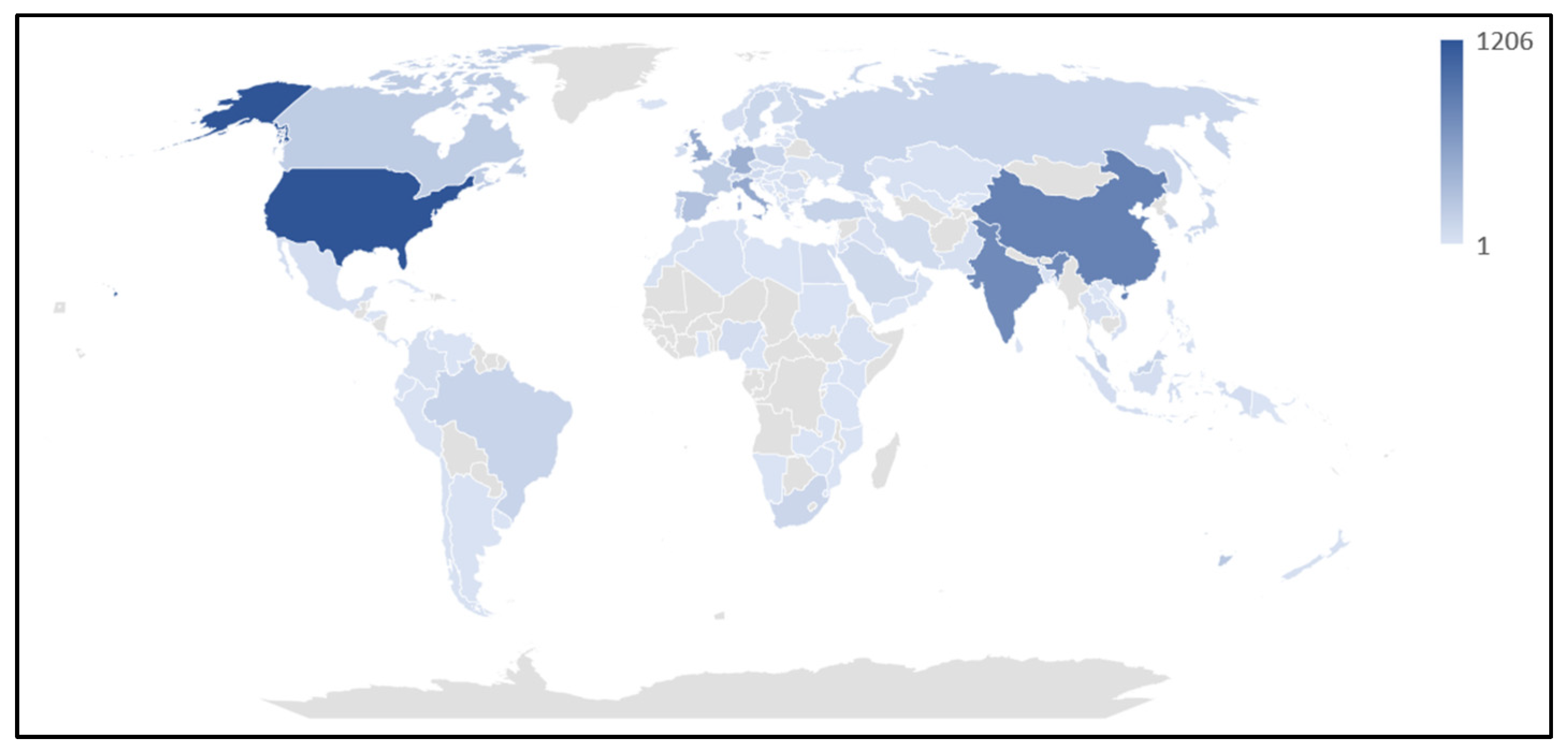
Over the past few years, the research community has seen a peculiar interest in additive manufacturing, focusing on sustainable practices such as material waste recycling aligning with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals. This trend can be noticed by comparing the number of publications per year, which indicate a significant rise in number of publications in the last decade. Research communities in the United States, China, India, and Italy have played a major role in the surge of interest in this area (
Figure 4 &
Figure 5).
The additive manufacturing industry provides several unique problems that demand specialized approaches and solutions such as increasing the efficiency of polymer recycling procedures. Future research is needed to better understand how the number of reuse cycles affects the material's characteristics to ensure proper quality standards during recycling. In addition, specific optimization conditions such as the effects of shifting the refresh rate for ABS are an important issue that needs more investigation because they may have an important effect on the overall effectiveness of 3D printing methods [
48,
49]. The lack of research on the degradation of mechanical qualities in PLA and ABS materials after many reuses in 3D printed structures is crucial as it highlights the lack of prior studies in this particular issue and shows the need for further research in this area.
Establishing a circular economy in 3D printing requires exploring alternative materials to reduce virgin feedstock demand for reused materials. The ideal material should be biodegradable to minimize environmental impact when degraded. Further investigation into 3D printing technologies is crucial to identify methods that reduce fabrication time and thermal degradation [
50].
This review emphasizes the importance of thorough research to validate the potential of upcoming trends in 3D printing. It also highlights the necessity for comprehensive investigations to provide a solid foundation for the promises these future trends hold. Through further investigation of these aspects, we can guide the development of additive manufacturing technology towards a sustainable path.
6. Conclusion
This review examines the critical issue of recycling material waste in the field of additive manufacturing. The environmental concerns connected to waste creation during 3D printing methods are growing due to the rapid growth of additive manufacturing. The review evaluates different methods for recycling, such as mechanical and chemical procedures, and examines the characteristics and use of recycled materials, with a focus on polymers like PLA, ABS, and PETG. The social and economic effects of using recycled materials in 3D printing are examined, showing the advantages and disadvantages of additive manufacturing. By minimizing transportation-related emissions and material waste, decentralized 3D printing improves sustainability and remains in terms of larger trends in distributed production. It additionally promotes public creativity. Reusing waste materials not only overcomes environmental problems but also promotes innovative thinking, showing how additive printing can be an environmentally friendly approach. This comprehensive review contributes to a deeper understanding of the evolving landscape of material waste recyclability in additive manufacturing, emphasizing the importance of sustainable practices and continued innovation in achieving environmental sustainability and economic viability.
Author Contributions
“Conceptualization, G.P., A.H., D.S., M.B.G.; methodology, A.H., D.S., M.B.G.; validation, A.H., D.S., M.B.G.; formal analysis, G.P., A.H., D.S., M.B.G.; investigation, G.P., A.H., D.S., M.B.G., A.J.; resources, G.P., A.H., D.S., M.B.G., A.J.; data curation, A.H., D.S., M.B.G.; writing—original draft preparation, G.P., A.H., D.S., M.B.G.; writing—review and editing, G.P., A.H., D.S., M.B.G., A.J, D.I.N.; visualization, G.P., A.H., D.S., M.B.G.; supervision, G.P., A.J, D.I.N.; project administration, G.P., A.J,. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.”
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No additional data and material other than the manuscript is to be produced. Data sharing does not apply to this article.
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our deep gratitude to the Chancellor of Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham, a world-renowned humanitarian, Dr. Mata Amritanandamayi Devi, popularly known as Amma. Her inspired mentorship facilitates unique opportunities for a seamless blend of personal integrity, and spiritual development.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Declaration of competing interest
The authors declare that we have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper. We hereby declare that certain sections of our paper utilize artificial intelligence tools for language generation and content optimization.
References
- Wong, K.V.; Hernandez, A. A Review of Additive Manufacturing. ISRN Mech. Eng. 2012, 2012, 208760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoj, A.; Panda, R.C. ; Amrita; Ch, R.; P, R. Biodegradable Filament for Three-Dimensional Printing Process: A Review. Eng. Sci. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- S. Bose, N. S. Bose, N. Sarkar, S. Vahabzadeh, D. Ke, and A. Bandyopadhyay, Additive manufacturing of ceramics, Additive Manufacturing, Second Edition. 2019. Accessed: Apr. 08, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.taylorfrancis.com/chapters/edit/10.1201/9780429466236-6/additive-manufacturing-ceramics-susmita-bose-naboneeta-sarkar-sahar-vahabzadeh-dongxu-ke-amit-bandyopadhyay.
- Singh, S.; Ramakrishna, S.; Singh, R. Material issues in additive manufacturing: A review. J. Manuf. Process. 2017, 25, 185–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, T.D.; Kashani, A.; Imbalzano, G.; Nguyen, K.T.Q.; Hui, D. Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing): A Review of Materials, Methods, Applications and Challenges. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 143, 172–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srai, J.S.; Kumar, M.; Graham, G.; Phillips, W.; Tooze, J.; Ford, S.; Beecher, P.; Raj, B.; Gregory, M.; Tiwari, M.K.; et al. Distributed manufacturing: scope, challenges and opportunities. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2016, 54, 6917–6935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- S. Zuboff, “Creating value in the age of distributed capitalism Artwork by Celia Johnson.
- Ben-Ner, A.; Siemsen, E. Decentralization and Localization of Production: The Organizational and Economic Consequences of Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing). Calif. Manag. Rev. 2017, 59, 5–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneevogt, H.; Stelzner, K.; Yilmaz, B.; Abali, B.E.; Klunker, A.; Völlmecke, C. Sustainability in additive manufacturing: Exploring the mechanical potential of recycled PET filaments. Compos. Adv. Mater. 2021, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.; Srivastav, A.; Singh, A.; Mushtaque; Khan, S. ; Kumar, H.; Arora, P. Investigation on the materials used in additive manufacturing: A study. Mater. Today: Proc. 2021, 43, 154–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourell, D.; Kruth, J.P.; Leu, M.; Levy, G.; Rosen, D.; Beese, A.M.; Clare, A. Materials for additive manufacturing. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 66, 659–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atakok, G.; Kam, M.; Koc, H.B. Tensile, three-point bending and impact strength of 3D printed parts using PLA and recycled PLA filaments: A statistical investigation. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 18, 1542–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raney, K.; Lani, E.; Kalla, D.K. Experimental characterization of the tensile strength of ABS parts manufactured by fused deposition modeling process. Mater. Today: Proc. 2017, 4, 7956–7961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. Z. Gebremedhen and H. S. Mengistie, “Developing Filament Extruder and Characterization of Recycled High-Density Polyethylene for 3D Printing Filament Material,” 2023.
- Ror, C.K.; Negi, S.; Mishra, V. Development and characterization of sustainable 3D printing filaments using post-consumer recycled PET: processing and characterization. J. Polym. Res. 2023, 30, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Rashid, A.; Koç, M. Additive manufacturing for sustainability and circular economy: needs, challenges, and opportunities for 3D printing of recycled polymeric waste. Mater. Today Sustain. 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roosen, M.; Mys, N.; Kusenberg, M.; Billen, P.; Dumoulin, A.; Dewulf, J.; Van Geem, K.M.; Ragaert, K.; De Meester, S. Detailed Analysis of the Composition of Selected Plastic Packaging Waste Products and Its Implications for Mechanical and Thermochemical Recycling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 13282–13293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alias, N.N.; Fatah, I.Y.A.; Seok, Y.B.; Abdullah, S.H.Y.S.; Bhat, A.H.; Diah, S.B.M. Material Characterizations of the Polymers Reinforced with Recycled Flexible Plastic Blends as Filament for 3D Printing. J. Adv. Res. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2024, 37, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Cheng, S.; Peng, B.; Chen, K.; Sun, C.; Tang, H. The buildability and flexural properties of 3D printed recycled mortar reinforced with synchronized steel cable under different reinforcement ratios. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Wang, J.; Hang, M.; Qu, S. Research on printing parameters and salt frost resistance of 3D printing concrete with ferrochrome slag and aeolian sand. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, V.; Negi, S.; Kar, S. Three-dimensional printing with waste acrylonitrile butadiene styrene: Processing and characterization. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oosthuizen, J.D.; Babafemi, A.J.; Walls, R.S. 3D-printed recycled plastic eco-aggregate (Resin8) concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-Y.; Kim, K.-W.; Yun, Y.-M.; Le, T.H.M. Evaluation of eco-friendly asphalt mixtures incorporating waste plastic aggregates and additives: Magnesium, fly ash, and steel slag. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlaváčiková, S.; Omaníková, L.; Horváth, V.; Alexy, P.; Jančovičová, V.; Baco, A.; Mikolajová, M.; Fogašová, M.; Tomanová, K.; Feranc, J.; et al. The possibility of using the regranulate of a biodegradable polymer blend based on polylactic acid and polyhydroxybutyrate in FDM 3D printing technology. Results Mater. 2024, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Małek, M.; Kluczyński, J.; Jasik, K.; Kardaszuk, E.; Szachogłuchowicz, I.; Łuszczek, J.; Torzewski, J.; Grzelak, K.; Ewiak, I. An Eco-Friendly and Innovative Approach in Building Engineering: The Production of Cement–Glass Composite Bricks with Recycled Polymeric Reinforcements. Materials 2024, 17, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, C.S.; Sanchez, F.A.C.; Boudaoud, H.; Nouvel, C.; Pearce, J.M. Multi-material distributed recycling via material extrusion: recycled high density polyethylene and poly (ethylene terephthalate) mixture. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2024, 64, 1555–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- C. Ben Aissa, A. E. H. C. Ben Aissa, A. E. H. Gabsi, S. Mathlouthi, and A. Ghanem, “Easy Conversion of PET Bottles to Eco-Filament for 3D Printing and Process Characterization,” 2024, pp. 170–178. [CrossRef]
- Olawumi, M.A.; Oladapo, B.I.; Ikumapayi, O.M.; Akinyoola, J.O. Waste to wonder to explore possibilities with recycled materials in 3D printing. Sci. Total. Environ. 2023, 905, 167109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, G.; Ramesh, M.V.; A, M.S.; T, R.; Thomas, G.M. Changing profile of natural organic matter in groundwater of a ramsar site in Kerala implications for sustainability. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2023, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. A. Ahmed and S. M. Moniruzzaman, “A study on plastic waste recycling process in Khulna City,” 4th International Conference on Civil Engineering for Sustainable Development (ICCESD 2018), 2018.
- Balwada, J.; Samaiya, S.; Mishra, R.P. Packaging Plastic Waste Management for a Circular Economy and Identifying a better Waste Collection System using Analytical Hierarchy Process (AHP). Procedia CIRP 2021, 98, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Rao, C.; Gu, F.; Sharmin, N.; Fu, J. Close-looped recycling of polylactic acid used in 3D printing: An experimental investigation and life cycle assessment. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 197, 1046–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, F.A.C.; Boudaoud, H.; Camargo, M.; Pearce, J.M. Plastic recycling in additive manufacturing: A systematic literature review and opportunities for the circular economy. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 264, 121602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kijo-Kleczkowska, A.; Gnatowski, A. Recycling of Plastic Waste, with Particular Emphasis on Thermal Methods—Review. Energies 2022, 15, 2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, A. M. , Yesodharan, G., Arun, K., & Prasad, G. Unveiling the factors influencing groundwater resources in a coastal environment–a review. Agronomy Research. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Beltrán, F.R.; Arrieta, M.P.; Moreno, E.; Gaspar, G.; Muneta, L.M.; Carrasco-Gallego, R.; Yáñez, S.; Hidalgo-Carvajal, D.; de la Orden, M.U.; Urreaga, J.M. Evaluation of the Technical Viability of Distributed Mechanical Recycling of PLA 3D Printing Wastes. Polymers 2021, 13, 1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aki, Sedef Uncu, Cevza Candan, Banu Nergis, and Neslihan Sebla Önder. "An Evaluation of Recycled Polymeric Materials Usage in Denim with Lifecycle Assesment Methodology." In Waste Material Recycling in the Circular Economy-Challenges and Developments. IntechOpen, 2021. [Online]. Available: www.intechopen.com.
- Pinho, A.C.; Amaro, A.M.; Piedade, A.P. 3D printing goes greener: Study of the properties of post-consumer recycled polymers for the manufacturing of engineering components. Waste Manag. 2020, 118, 426–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, M.Y.; Arif, Z.U.; Ahmed, W.; Arshad, H. Recent trends in recycling and reusing techniques of different plastic polymers and their composite materials. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2021, 31, e00382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- J. G. Kha N and S. Ga De K A R, “Defects in extrusion process and their impact on product quality,” 2014. [Online]. Available: www.ijmerr.com.
- Baechler, C.; DeVuono, M.; Pearce, J.M. Distributed recycling of waste polymer into RepRap feedstock. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2013, 19, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zander, N.E.; Gillan, M.; Burckhard, Z.; Gardea, F. Recycled polypropylene blends as novel 3D printing materials. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 25, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Despeisse, M.; Baumers, M.; Brown, P.; Charnley, F.; Ford, S.; Garmulewicz, A.; Knowles, S.; Minshall, T.; Mortara, L.; Reed-Tsochas, F.; et al. Unlocking value for a circular economy through 3D printing: A research agenda. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2017, 115, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebler, M.; Schoot Uiterkamp, A.J.M. , Visser, C. A global sustainability perspective on 3D printing technologies. Energy Policy 2014, 74, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- W. R. Stahel and G. Reday-Mulvey, “Jobs for tomorrow: the potential for substituting manpower for energy,” Vantage Press., 1981.
- Stahel, W.R. The circular economy. Nature 2016, 531, 435–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idumah, C.I.; Nwuzor, I.C. Novel trends in plastic waste management. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayathri, N.; Prasad, G.; Prabhakaran, V.; Priya, V. Understanding the impact of microplastic contamination on soil quality and eco-toxicological risks in horticulture: A comprehensive review. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2024, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaid, M.; Haleem, A.; Singh, R.P.; Suman, R.; Rab, S. Role of additive manufacturing applications towards environmental sustainability. Adv. Ind. Eng. Polym. Res. 2021, 4, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DePalma, K.; Walluk, M.; Murtaugh, A.; Hilton, J.; McConky, S.; Hilton, B. Assessment of 3D printing using fused deposition modeling and selective laser sintering for a circular economy. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 264, 121567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).