Submitted:
29 August 2024
Posted:
02 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
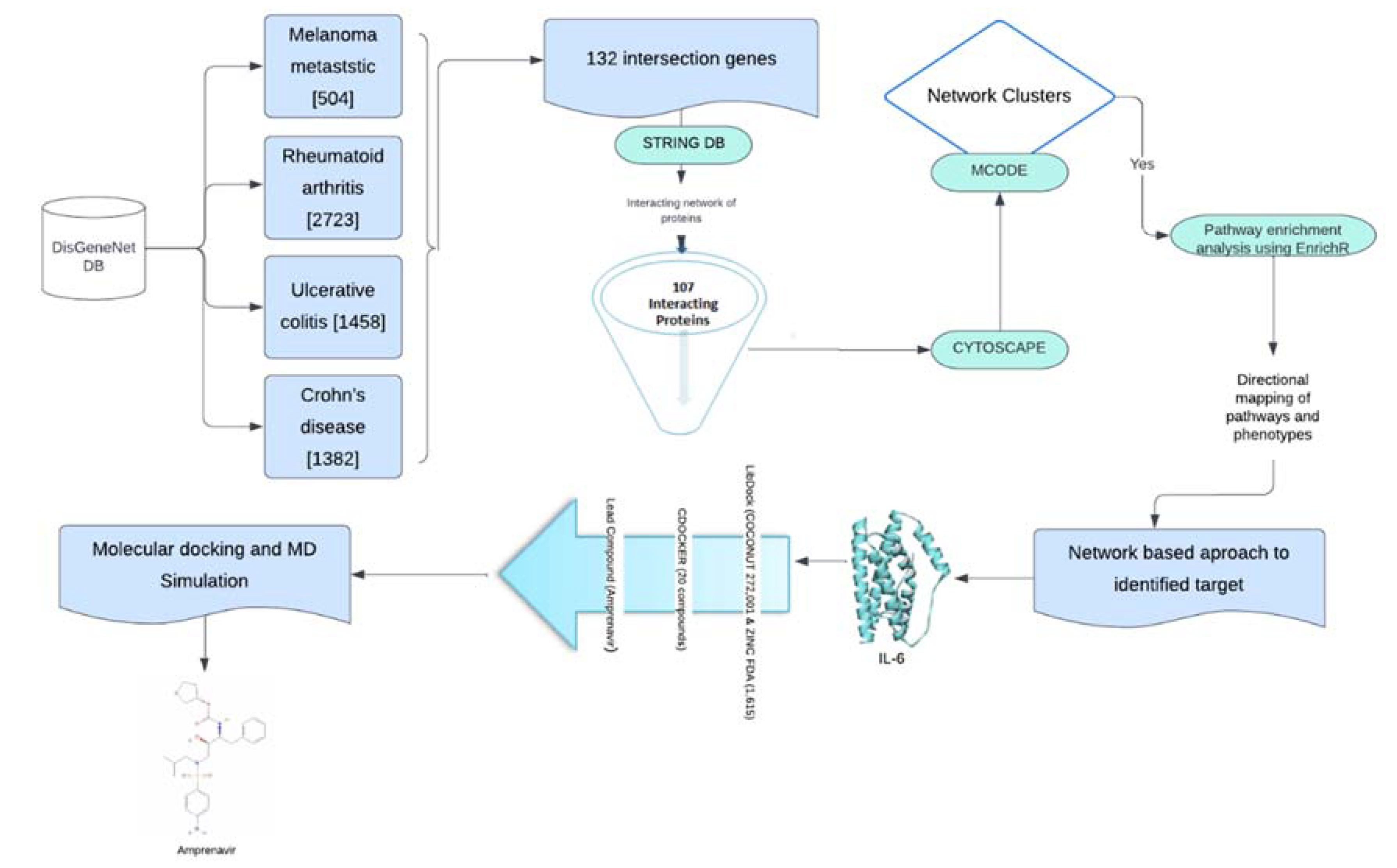
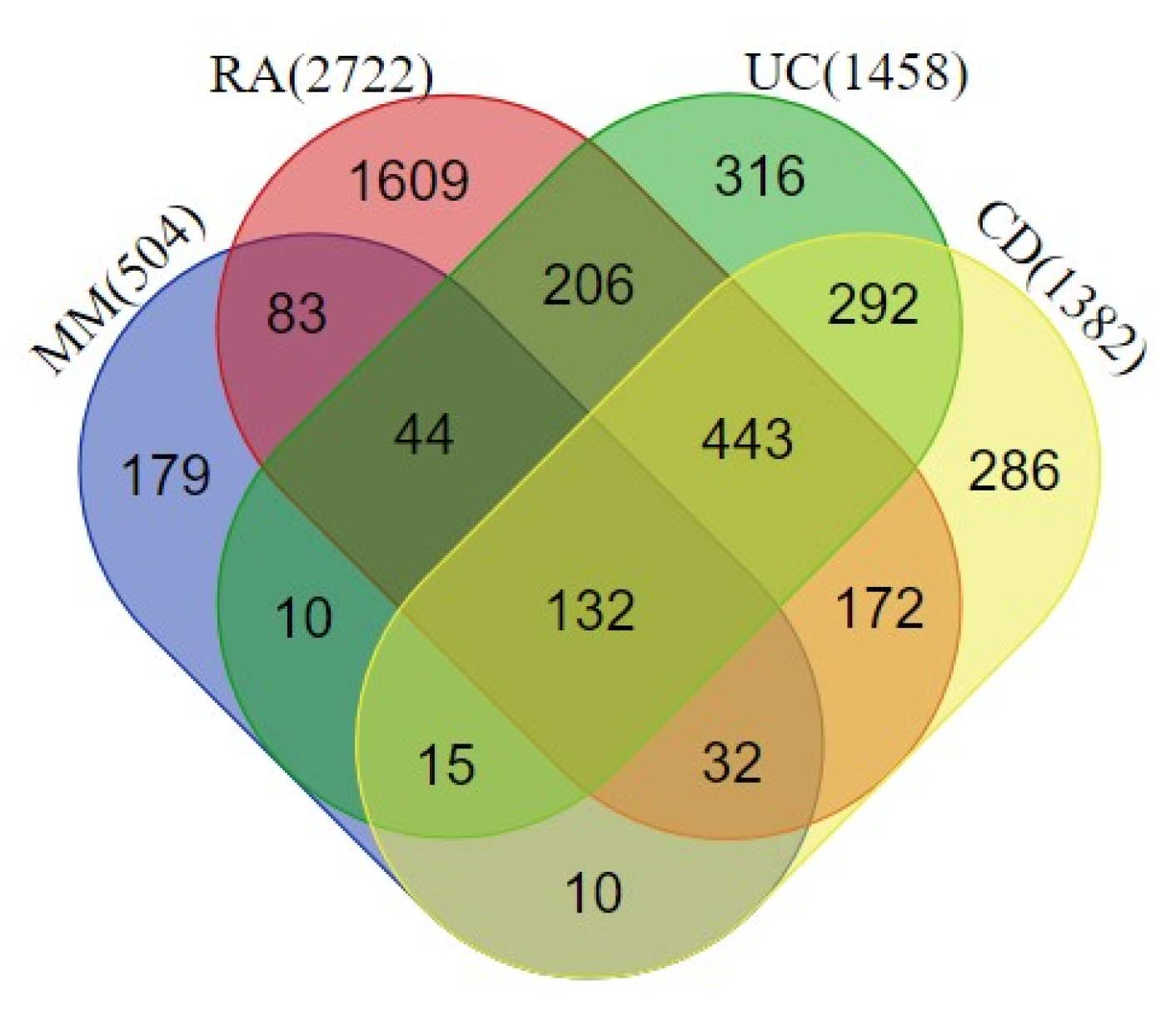
2.1. Protein-Protein Interaction Network at the Interface of Melanoma and Autoimmune Diseases
2.2. Identification of Hub Genes from the PPI Network Associated with the Crosstalk between Melanoma and Autoimmune Diseases
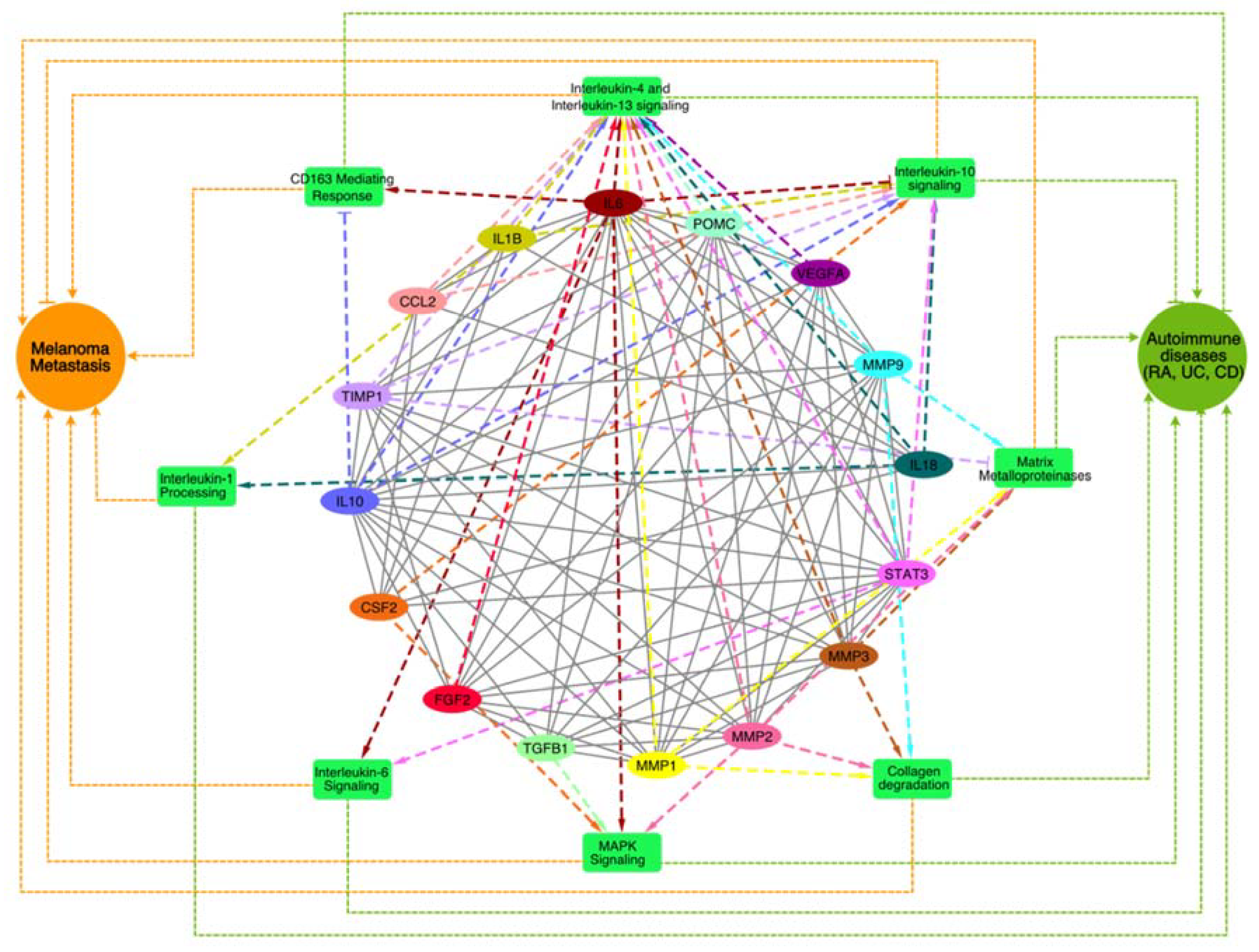
2.3. Pathway Enrichment Analysis of top MCODE Cluster
2.4. Identification of Lead Molecule and Molecular Docking
2.5. Molecular Dynamics Simulation
3. Methods and Methodology
3.1. Data Collection and Protein-Protein Interaction (PPI)
3.2. Identification of Highly Interconnected Clusters in the Tumor-Autoimmune PPI Network
3.3. Pathway Enrichment Analysis
3.4. 3D Structure Preparation and Screening of Lead Compounds
3.5. Molecular Dynamic Simulation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Authors’ Contributions
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lowe L 2023 Metastatic melanoma and rare melanoma variants: a review Pathology 55 236–44. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rausch M P and Hastings K T 2017 Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in the Treatment of Melanoma: From Basic Science to Clinical Application Cutaneous Melanoma: Etiology and Therapy 121–42.
- Shah V, Panchal V, Shah A, Vyas B, Agrawal S and Bharadwaj S 2024 Immune checkpoint inhibitors in metastatic melanoma therapy (Review) Medicine International 4.
- Rausch M P and Hastings K T 2017 Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in the Treatment of Melanoma: From Basic Science to Clinical Application Cutaneous Melanoma: Etiology and Therapy 121–42.
- Shiravand Y, Khodadadi F, Kashani S M A, Hosseini-Fard S R, Hosseini S, Sadeghirad H, Ladwa R, O’byrne K and Kulasinghe A 2022 Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Cancer Therapy Current Oncology 29 3044.
- Shiravand Y, Khodadadi F, Kashani S M A, Hosseini-Fard S R, Hosseini S, Sadeghirad H, Ladwa R, O’byrne K and Kulasinghe A 2022 Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Cancer Therapy Current Oncology 29 3044.
- Motofei I G 2019 Melanoma and autoimmunity: spontaneous regressions as a possible model for new therapeutic approaches Melanoma research 29 231–6. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibis B, Aliazis K, Cao C, Yenyuwadee S and Boussiotis V A 2023 Immune-related adverse effects of checkpoint immunotherapy and implications for the treatment of patients with cancer and autoimmune diseases Frontiers in Immunology 14.
- Darvin P, Toor S M, Sasidharan Nair V and Elkord E 2018 Immune checkpoint inhibitors: recent progress and potential biomarkers Experimental & Molecular Medicine 2018 50:12 50 1–11.
- Khan S and Gerber D E 2020 Autoimmunity, Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy and Immune-related Adverse Events: A Review Seminars in cancer biology 64 93.
- Hassel J C 2021 Checkpoint blocker induced autoimmunity as an indicator for tumour efficacy in melanoma British Journal of Cancer 2021 126:2 126 163–4. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portenkirchner C, Kienle P and Horisberger K 2021 Checkpoint inhibitor-induced colitis—a clinical overview of incidence, prognostic implications and extension of current treatment options Pharmaceuticals 14 367.
- Lo C H, Khalili H, Lochhead P, Song M, Lopes E W, Burke K E, Richter J M, Chan A T and Ananthakrishnan A N 2021 Immune-mediated disease and Risk of Crohn’s Disease or Ulcerative Colitis: A Prospective Cohort Study Alimentary pharmacology & therapeutics 53 598.
- Jeurling S and Cappelli L C 2020 Treatment of immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced inflammatory arthritis Current opinion in rheumatology 32 315. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bader G D and Hogue C W V 2003 An automated method for finding molecular complexes in large protein interaction networks BMC bioinformatics 4.
- Iwaszko M, Biały S and Bogunia-Kubik K 2021 Significance of Interleukin (IL)-4 and IL-13 in Inflammatory Arthritis Cells 10.
- Eddy K, Shah R and Chen S 2021 Decoding Melanoma Development and Progression: Identification of Therapeutic Vulnerabilities Frontiers in Oncology 10 626129.
- Napolitano M, di Vico F, Ruggiero A, Fabbrocini G and Patruno C 2023 The hidden sentinel of the skin: An overview on the role of interleukin-13 in atopic dermatitis Frontiers in Medicine 10.
- Hoejberg L, Bastholt L and Schmidt H 2012 Interleukin-6 and melanoma Melanoma research 22 327–33.
- Nemunaitis J, Fong T, Shabe P, Martineau D and Ando D 2001 Comparison of serum interleukin-10 (IL-10) levels between normal volunteers and patients with advanced melanoma Cancer investigation 19 239–47.
- Tanaka T, Narazaki M and Kishimoto T 2014 IL-6 in inflammation, immunity, and disease Cold Spring Harbor perspectives in biology 6.
- Voronov E, Carmi Y and Apte R N 2014 The role IL-1 in tumor-mediated angiogenesis Frontiers in physiology 5.
- Iwakura Y 2002 Roles of IL-1 in the development of rheumatoid arthritis: Consideration from mouse models Cytokine and Growth Factor Reviews 13 341–55.
- Silva F A R, Rodrigues B L, Ayrizono M D L S and Leal R F 2016 The Immunological Basis of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Gastroenterology research and practice 2016.
- Hofmann U B, Westphal J R, Van Muijen G N P and Ruiter D J 2000 Matrix metalloproteinases in human melanoma The Journal of investigative dermatology 115 337–44.
- Cabral-Pacheco G A, Garza-Veloz I, Rosa C C D La, Ramirez-Acuña J M, Perez-Romero B A, Guerrero-Rodriguez J F, Martinez-Avila N and Martinez-Fierro M L 2020 The Roles of Matrix Metalloproteinases and Their Inhibitors in Human Diseases International journal of molecular sciences 21 1–53.
- Lakatos G, Hritz I, Varga M Z, Juhász M, Miheller P, Cierny G, Tulassay Z and Herszényi L 2012 The impact of matrix metalloproteinases and their tissue inhibitors in inflammatory bowel diseases Digestive diseases (Basel, Switzerland) 30 289–95.
- Guo Y, Pan W, Liu S, Shen Z, Xu Y and Hu L 2020 ERK/MAPK signalling pathway and tumorigenesis Experimental and therapeutic medicine 19.
- Wei Z and Liu H T 2002 MAPK signal pathways in the regulation of cell proliferation in mammalian cells Cell research 12 9–18.
- Skytthe M K, Graversen J H and Moestrup S K 2020 Targeting of CD163+ Macrophages in Inflammatory and Malignant Diseases International journal of molecular sciences 21 1–31.
- Etzerodt A and Moestrup S K 2013 CD163 and inflammation: biological, diagnostic, and therapeutic aspects Antioxidants & redox signaling 18 2352–63.
- Miskolczi Z, Smith M P, Rowling E J, Ferguson J, Barriuso J and Wellbrock C 2018 Collagen abundance controls melanoma phenotypes through lineage-specific microenvironment sensing Oncogene 37 3166–82.
- Van Kempen L C L T, Rijntjes J, Mamor-Cornelissen I, Vincent-Naulleau S, Gerritsen M J P, Ruiter D J, Van Dijk M C R F, Geffrotin C and Van Muijen G N P 2008 Type I collagen expression contributes to angiogenesis and the development of deeply invasive cutaneous melanoma International journal of cancer 122 1019–29.
- Gencoglu H, Orhan C, Sahin E and Sahin K 2020 Undenatured Type II Collagen (UC-II) in Joint Health and Disease: A Review on the Current Knowledge of Companion Animals Animals : an open access journal from MDPI 10.
- Jarlborg M and Gabay C 2022 Systemic effects of IL-6 blockade in rheumatoid arthritis beyond the joints Cytokine 149 155742. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rašková M, Lacina L, Kejík Z, Venhauerová A, Skaličková M, Kolář M, Jakubek M, Rosel D, Smetana K and Brábek J 2022 The Role of IL-6 in Cancer Cell Invasiveness and Metastasis-Overview and Therapeutic Opportunities Cells 11.
- Shahini A and Shahini A 2023 Role of interleukin-6-mediated inflammation in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease: focus on the available therapeutic approaches and gut microbiome Journal of Cell Communication and Signaling 17 55. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorokina M, Merseburger P, Rajan K, Yirik M A and Steinbeck C 2021 COCONUT online: Collection of Open Natural Products database Journal of Cheminformatics 13 1–13.
- Lipinski C A 2004 Lead- and drug-like compounds: The rule-of-five revolution Drug Discovery Today: Technologies 1 337–41.
- Tran Q H, Nguyen Q T, Vo N Q H, Mai T T, Tran T T N, Tran T D, Le M T, Trinh D T T and Minh Thai K 2022 Structure-based 3D-Pharmacophore modeling to discover novel interleukin 6 inhibitors: An in silico screening, molecular dynamics simulations and binding free energy calculations PloS one 17.
- Balasubramaniyan S, Irfan N, Umamaheswari A and Puratchikody A 2018 Design and virtual screening of novel fluoroquinolone analogs as effective mutant DNA GyrA inhibitors against urinary tract infection-causing fluoroquinolone resistant Escherichia coli RSC Advances 8 23629–47.
- Pal S, Kumar V, Kundu B, Bhattacharya D, Preethy N, Reddy M P and Talukdar A 2019 Ligand-based Pharmacophore Modeling, Virtual Screening and Molecular Docking Studies for Discovery of Potential Topoisomerase I Inhibitors Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal 17 291–310.
- Love L A, Rader J I, Crofford L J, Raybourne R B, Principato M A, Page S W, Trucksess M W, Smith M J, Dugan E M, Turner M L, Zelazowski E, Zelazowski P and Sternberg E M 1993 Pathological and immunological effects of ingesting L-tryptophan and 1,1’-ethylidenebis (L-tryptophan) in Lewis rats The Journal of clinical investigation 91 804–11.
- Yamaoka K A, Miyasaka N, Inuo G, Saito I, Kolb J P, Fujita K and Kashiwazaki S 1994 1,1′-Ethylidenebis(tryptophan) (peak E) induces functional activation of human eosinophils and interleukin 5 production from T lymphocytes: Association of eosinophilia-myalgia syndrome with a l-tryptophan contaminant Journal of Clinical Immunology 14 50–60.
- Polli J W, Jarrett J L, Studenberg S D, Humphreys J E, Dennis S W, Brouwer K R and Woolley J L 1999 Role of P-glycoprotein on the CNS disposition of amprenavir (141W94), an HIV protease inhibitor Pharmaceutical research 16 1206–12.
- Yu Y X, Wang W, Sun H B, Zhang L L, Wu S L and Liu W T 2021 Insights into effect of the Asp25/Asp25’ protonation states on binding of inhibitors Amprenavir and MKP97 to HIV-1 protease using molecular dynamics simulations and MM-GBSA calculations SAR and QSAR in environmental research 32 615–41.
- Jiang W, Li X, Li T, Wang H, Shi W, Qi P, Li C, Chen J, Bao J, Huang G and Wang Y 2017 Repositioning of amprenavir as a novel extracellular signal-regulated kinase-2 inhibitor and apoptosis inducer in MCF-7 human breast cancer International journal of oncology 50 823–34.
- Yan Y, Tao H, He J and Huang S Y 2020 The HDOCK server for integrated protein–protein docking Nature Protocols 2020 15:5 15 1829–52.
- Boulanger M J, Chow D chone, Brevnova E E and Garcia K C 2003 Hexameric structure and assembly of the interieukin-6/IL-6 α-receptor/gp130 complex Science 300 2101–4.
- Piñero J, Bravo Á, Queralt-Rosinach N, Gutiérrez-Sacristán A, Deu-Pons J, Centeno E, García-García J, Sanz F and Furlong L I 2017 DisGeNET: a comprehensive platform integrating information on human disease-associated genes and variants Nucleic Acids Research 45 D833–9.
- Szklarczyk D, Gable A L, Lyon D, Junge A, Wyder S, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Doncheva N T, Morris J H, Bork P, Jensen L J and Von Mering C 2019 STRING v11: protein–protein association networks with increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide experimental datasets Nucleic Acids Research 47 D607.
- Kuleshov M V., Jones M R, Rouillard A D, Fernandez N F, Duan Q, Wang Z, Koplev S, Jenkins S L, Jagodnik K M, Lachmann A, McDermott M G, Monteiro C D, Gundersen G W and Maayan A 2016 Enrichr: a comprehensive gene set enrichment analysis web server 2016 update Nucleic Acids Research 44 W90.
- Chen E Y, Tan C M, Kou Y, Duan Q, Wang Z, Meirelles G V., Clark N R and Ma’ayan A 2013 Enrichr: interactive and collaborative HTML5 gene list enrichment analysis tool BMC bioinformatics 14.
- Somers W, Stahl M and Seehra J S 1997 1.9 A crystal structure of interleukin 6: implications for a novel mode of receptor dimerization and signaling The EMBO journal 16 989–97.
- Gogoi B, Chowdhury P, Goswami N, Gogoi N, Naiya T, Chetia P, Mahanta S, Chetia D, Tanti B, Borah P and Handique P J 2021 Identification of potential plant-based inhibitor against viral proteases of SARS-CoV-2 through molecular docking, MM-PBSA binding energy calculations and molecular dynamics simulation Molecular Diversity 25 1963.
- Vanommeslaeghe K, Hatcher E, Acharya C, Kundu S, Zhong S, Shim J, Darian E, Guvench O, Lopes P, Vorobyov I, Mackerell A D and Jr. 2010 CHARMM general force field: A force field for drug-like molecules compatible with the CHARMM all-atom additive biological force fields. Journal of computational chemistry 31 671–90.
- Sterling T and Irwin J J 2015 ZINC 15 - Ligand Discovery for Everyone Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling 55 2324–37. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang W, Wang S, Zhang X, Sun H, Zhang M, Chen H, Cui J, Li J, Peng F, Zhu M, Yu B, Li Y, Yang L, Min W, Xue M, Pan L, Zhu H, Wu B and Gu Y 2023 New natural compound inhibitors of PDGFRA (platelet-derived growth factor receptor α) based on computational study for high−grade glioma therapy Frontiers in Neuroscience 16 1060012.
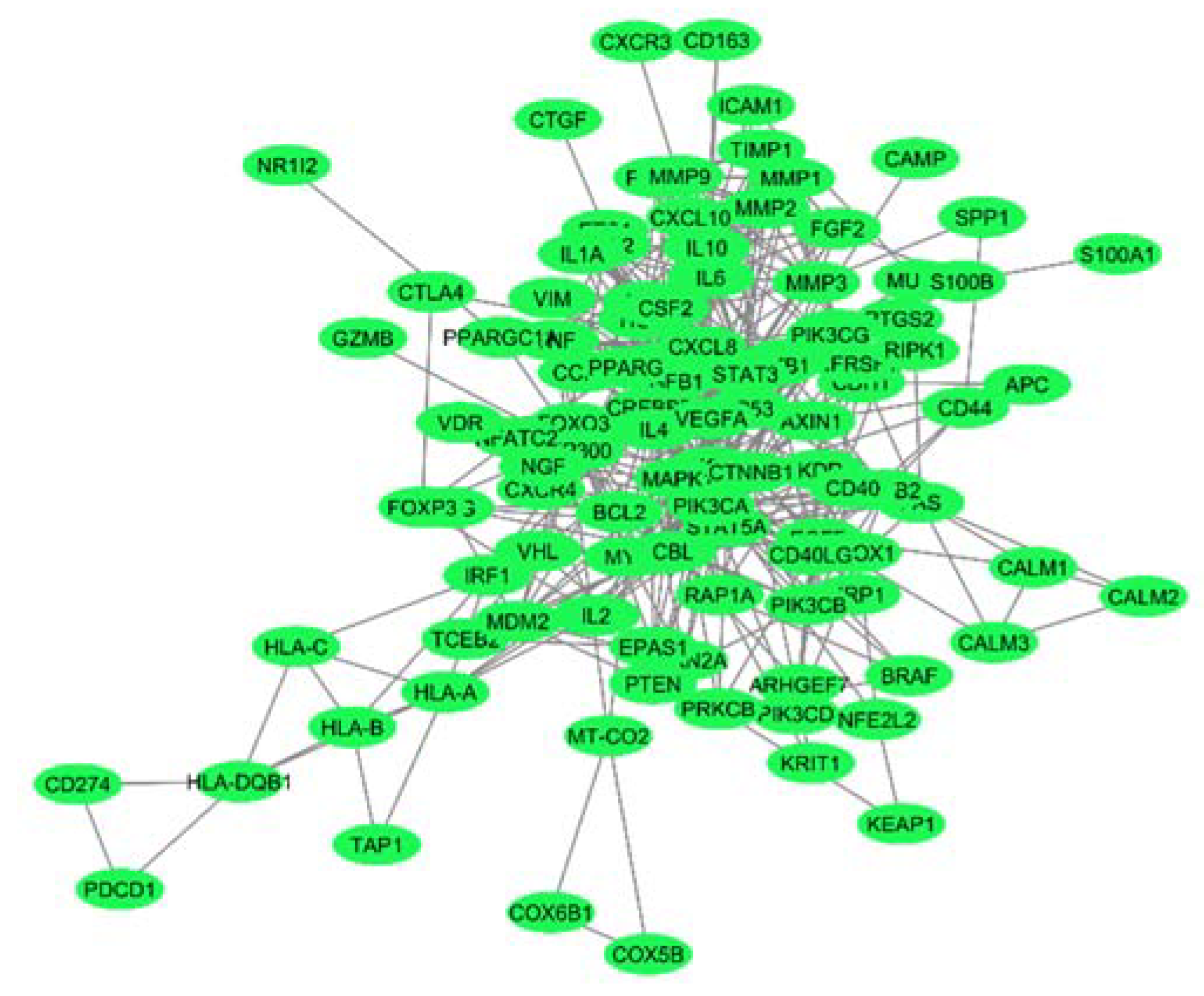
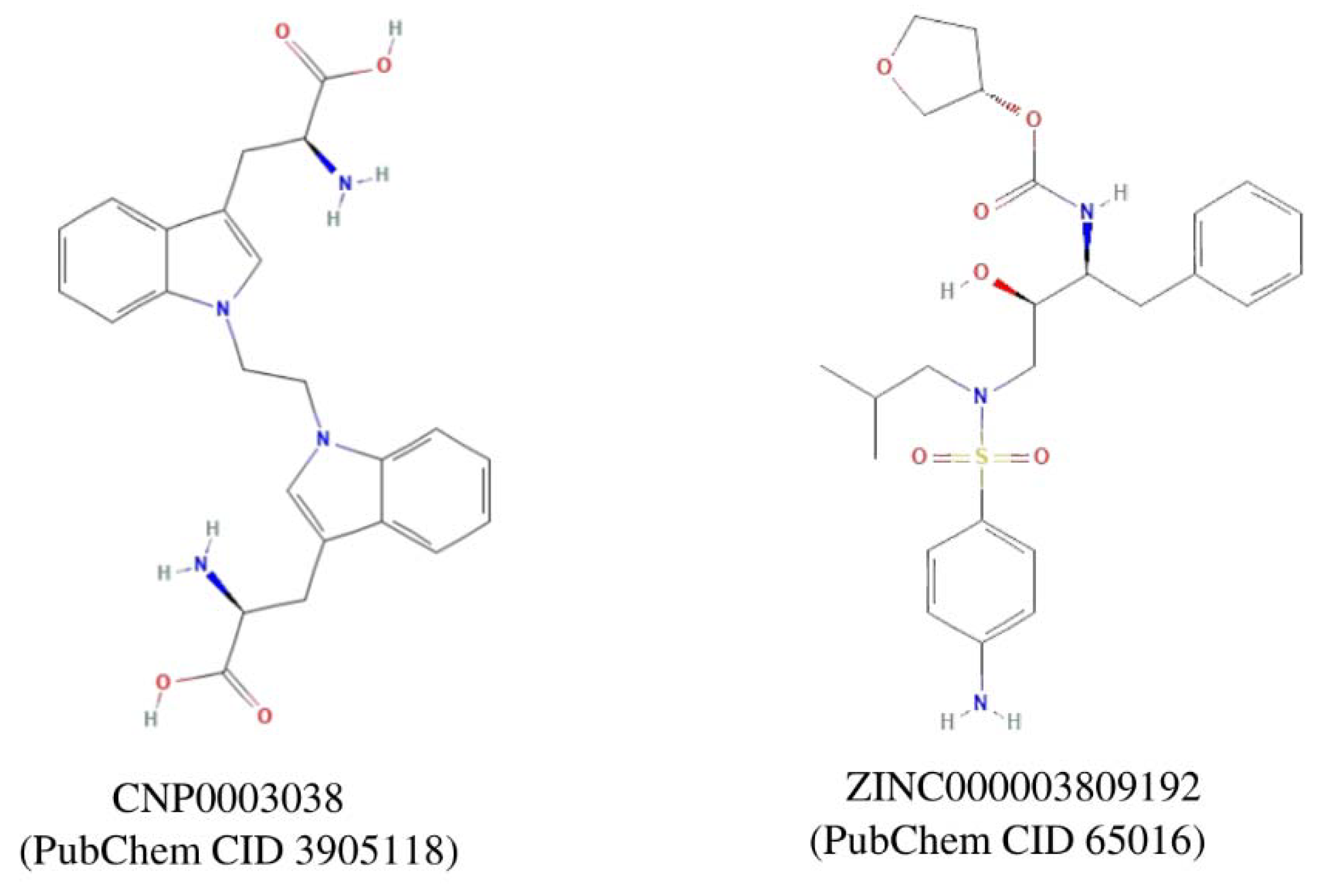
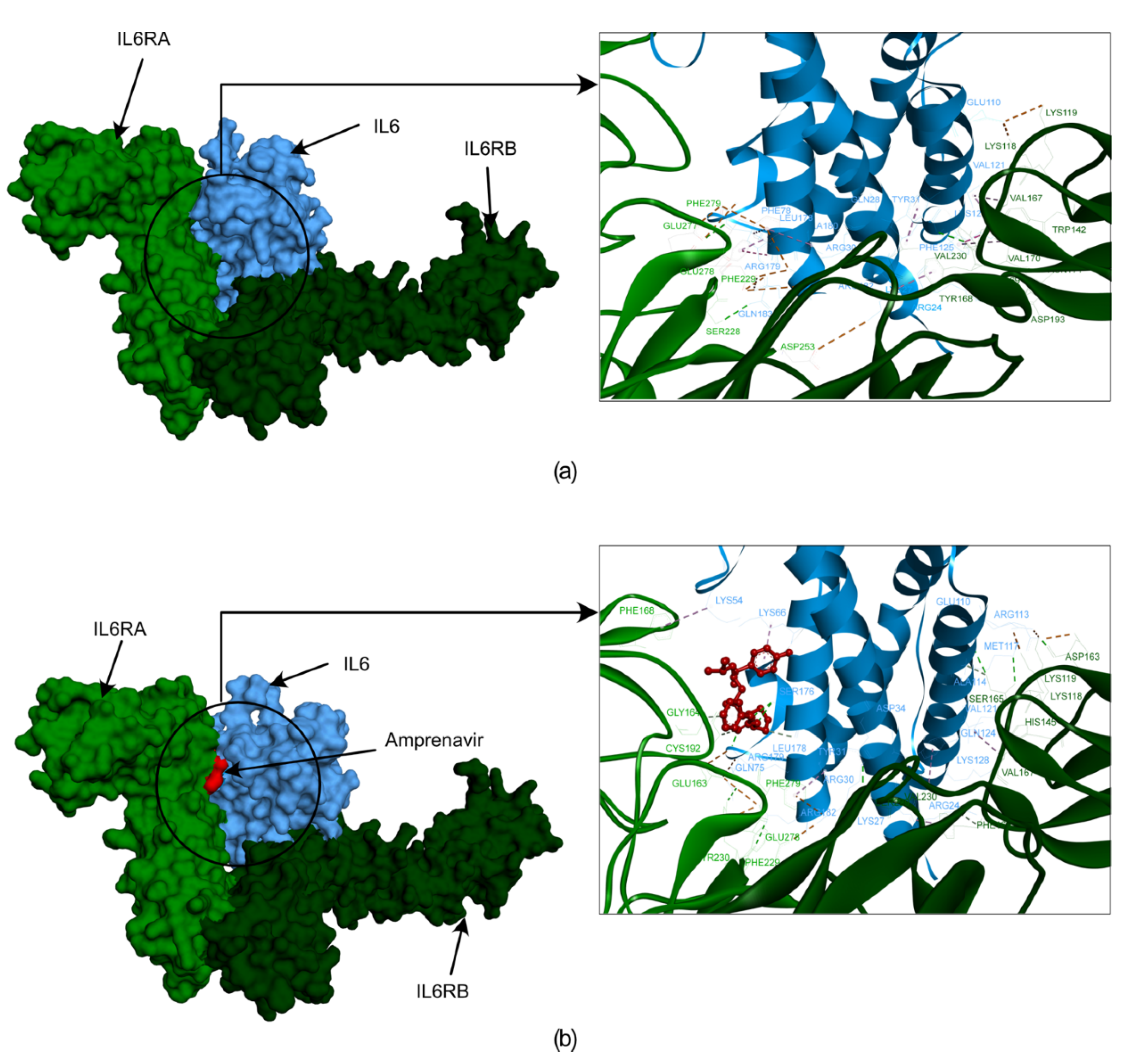
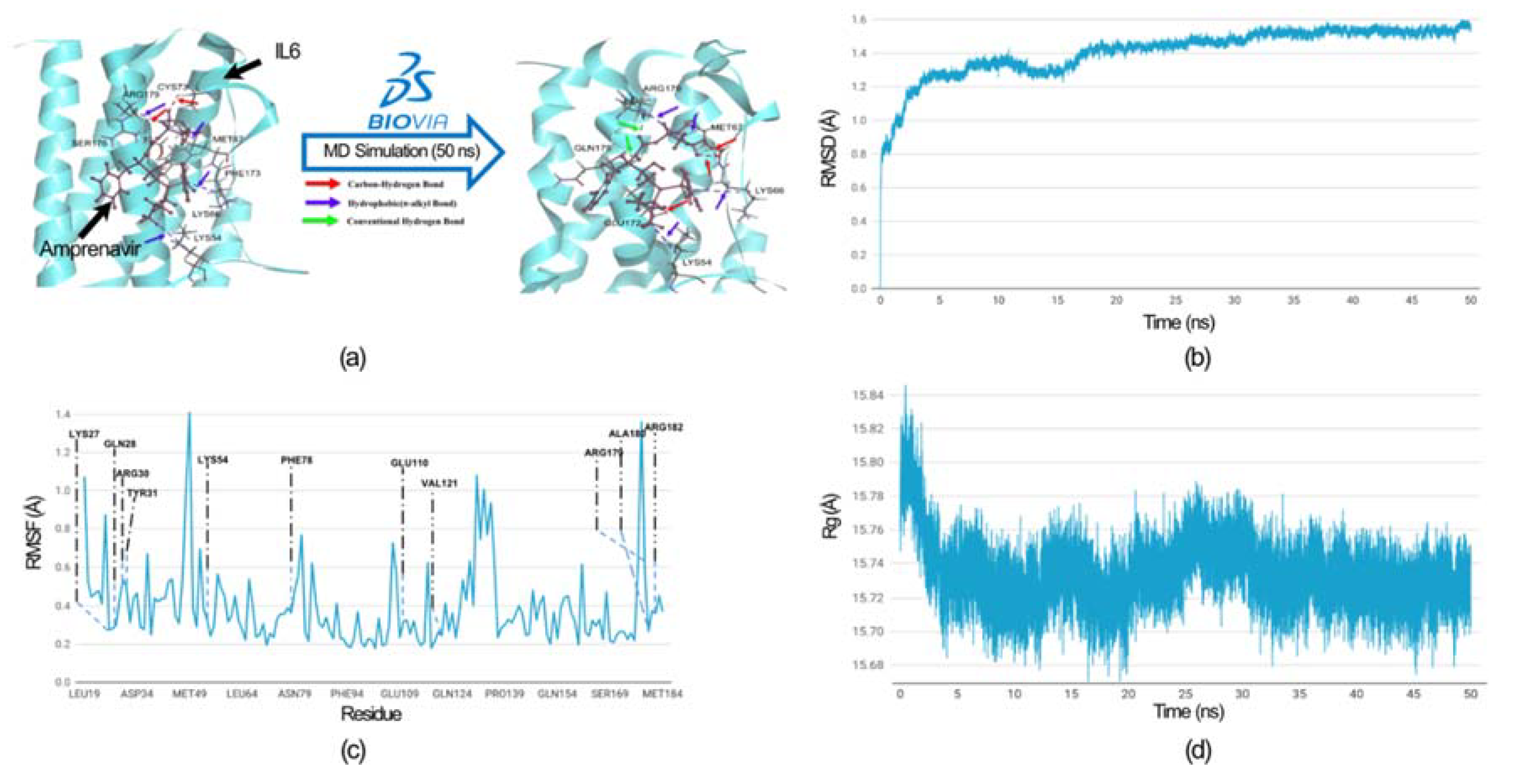
| Modules | Nodes | Interaction | MCODE Score | Genes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 16 | 76 | 10.133 | CCL2,CSF2,FGF2,IL10,IL18,IL1B,IL6,MMP1,MMP2,MMP3,MMP9,POMC,STAT3,TGFB1,TIMP1,VEGFA |
| 2 | 7 | 18 | 6 | CREBBP,EP300,FOXO3,HIF1A,MAPK1,MDM2,TP53 |
| 3 | 4 | 6 | 4 | AKT1,CD40,CD40LG,PIK3CG |
| 4 | 8 | 13 | 3.71 | CTNNB1,CXCL10,CXCL8,IL1A,IL4,MYC,NFKB1,TNF |
| 5 | 7 | 10 | 3.33 | CALM1,CALM2,CALM3,CXCR4,FAS,PIK3CB,STAT5A |
| 6 | 3 | 3 | 3 | HLA-B,HLA-C,HLA-DQB1 |
| S.No. | Compounds ID | Database | Compounds Name | Libdock score | -CDOCKER Energy (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CNP0003841 | Coconut | N-[(3-methoxyphenyl)methyl]-3-({5-[(4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)methyl]-1,2-oxazol-3-yl}methyl)oxetan-3-amine | 127.506 | NA |
| 2 | CNP0004058 | Coconut | 2-chloro-5-hydroxy-N-{[4-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-3-{4-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]piperazin-1-yl}oxolan-2-yl]methyl}benzamide | 126.919 | NA |
| 3 | CNP0004582 | Coconut | 2-{[({3-methyl-4-[(7-methyl-1H-1,3-benzodiazol-2-yl)methyl]-6-(propan-2-yl)cyclohex-2-en-1-yl}methyl)carbamoyl]methoxy}acetic acid | 122.508 | 18.4652 |
| 4 | CNP0004629 | Coconut | 2-{[({3-methyl-4-[(1-methyl-1H-1,3-benzodiazol-2-yl)methyl]-6-(propan-2-yl)cyclohex-2-en-1-yl}methyl)carbamoyl]methoxy}acetic acid | 121.359 | 13.0031 |
| 5 | CNP0000288 | Coconut | 7-methoxy-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4-[2-(4-methoxyphenyl)ethyl]-3,4-dihydro-2H-1-benzopyran | 120.936 | 25.4486 |
| 6 | ZINC03809192 | ZINC | [(3S)-oxolan-3-yl] N-[(2S,3R)-4-[(4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl-(2-methylpropyl)amino]-3-hydroxy-1-phenylbutan-2-yl]carbamate | 120.668 | 34.7136 |
| 7 | CNP0004224 | Coconut | 4-(dimethylamino)-N-[5-hydroxy-7a-(2-{[2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl]carbamoyl}ethyl)-3,3,5-trimethyl-octahydro-1H-inden-1-yl]benzamide | 118.314 | NA |
| 8 | CNP0004392 | Coconut | 4-[(2-{3-[2-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)pyridin-4-yl]-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl}pyrrolidin-1-yl)methyl]benzoic acid | 118.034 | NA |
| 9 | CNP0003909 | Coconut | 3-[4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-imidazol-2-yl]-4-[(4-methylphenyl)methyl]morpholine | 117.757 | 17.5344 |
| 10 | ZINC03955219 | ZINC | [(3aS,4R,6aR)-2,3,3a,4,5,6a-hexahydrofuro[2,3-b]furan-4-yl] N-[(2S,3R)-4-[(4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl-(2-methylpropyl)amino]-3-hydroxy-1-phenylbutan-2-yl]carbamate | 117.727 | 18.3056 |
| 11 | CNP0004686 | Coconut | 4-cyano-N-{2,3-dihydroxy-5-[6-(morpholin-4-yl)pyridin-3-yl]cyclopentyl}benzamide | 117.281 | NA |
| 12 | CNP0004257 | Coconut | N-[(2H-1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)methyl]-3-({5-[(dimethylamino)methyl]-1,2-oxazol-3-yl}methyl)oxetan-3-amine | 116.072 | NA |
| 13 | CNP0003888 | Coconut | 3-[4-(4-chlorophenyl)-1H-imidazol-2-yl]-4-[(1-methyl-1H-imidazol-2-yl)methyl]morpholine | 115.838 | 16.6375 |
| 14 | CNP0004329 | Coconut | N-[(2H-1,3-benzodioxol-4-yl)methyl]-3-({5-[(4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)methyl]-1,2-oxazol-3-yl}methyl)oxetan-3-amine | 115.688 | NA |
| 15 | CNP0004277 | Coconut | (5-{[(3-{[5-(pyridin-2-yl)-1,2-oxazol-3-yl]methyl}oxetan-3-yl)amino]methyl}furan-2-yl)methanol | 115.539 | NA |
| 16 | CNP0004720 | Coconut | 2-{[(3-{[5-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1,2-oxazol-3-yl]methyl}oxetan-3-yl)amino]methyl}phenol | 115.352 | NA |
| 17 | CNP0003796 | Coconut | N-[(4-methoxyphenyl)methyl]-3-{[5-(pyridin-2-yl)-1,2-oxazol-3-yl]methyl}oxetan-3-amine | 113.167 | NA |
| 18 | CNP0004058 | Coconut | 2-chloro-5-hydroxy-N-{[4-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-3-{4-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]piperazin-1-yl}oxolan-2-yl]methyl}benzamide | 112.619 | NA |
| 19 | CNP0003038 | Coconut | 2-amino-3-(1-{1-[3-(2-amino-2-carboxyethyl)-1H-indol-1-yl]ethyl}-1H-indol-3-yl)propanoic acid | 111.568 | 41.6684 |
| 20 | CNP0005022 | Coconut | 4-({3-[4-(pyridin-4-yl)-1H-imidazol-2-yl]morpholin-4-yl}methyl)benzoic acid | 111.381 | 22.286 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





