1. Introduction
Chinese strong-aroma liquor is renowned for its distinctive cellar aroma (Qiao et al., 2023; Ren et al., 2024c), which is primarily derived from the fermentation, distillation, and aging processes (Wei et al., 2020). This aroma results from the decomposition of raw materials by cellar microorganisms and enzymes (Ren et al., 2024b), microbial metabolites, and the transformation of these metabolites during fermentation (Liu et al., 2023; Tang et al., 2014; Wang et al., 2019). Pit mud serves as the primary environment for the growth and proliferation of functional bacteria that contribute to the strong aroma of the liquor (Li et al., 2024). Microbial metabolites such as organic acids and esters formed during fermentation are fundamental to this characteristic aroma (Hirst & Richter, 2016; Ren et al., 2024d; Xu et al., 2022).
Pit mud is a unique fermentation vessel for strong-aroma liquor and also functions as a habitat and breeding ground for essential brewing microorganisms (Gong et al., 2022; Zhang et al., 2020; Zhou et al., 2024b). Over time, and through repeated selection and adaptation in high-alcohol, high-acidity, and closed fermentation environments, pit mud becomes enriched with anaerobic bacteria that produce aromatic compounds (Ren et al., 2024a). Studies on the distribution of anaerobic bacteria in old pit mud reveal that these bacteria are more abundant than in new cellars (Sun et al., 2017), correlating with the superior quality of old cellar wine compared to that from new cellars (Hu et al., 2021). Thus, the production of strong-aroma liquor relies heavily on pit mud microorganisms, particularly anaerobic ones (Hu et al., 2015).
Research has identified and studied hundreds of anaerobic bacteria in pit mud, with significant groups including Clostridium, Lactobacillus, Bacillus (Liu et al., 2022a), and Actinomycetes (Liu et al., 2022b). Acid-producing bacteria, such as those producing caproic and butyric acids, are particularly crucial as they directly influence the formation of characteristic flavor compounds in strong-aroma liquor (Yuan et al., 2022).
For instance, Zhao Hui et al. isolated three facultative anaerobic bacteria from strong-aroma liquor pit mud, measuring caproic acid production by gas chromatography at 2.13 mg/mL, 1.70 mg/mL, and 1.03 mg/mL, respectively. Wan Zhen et al. isolated a butyric acid-producing bacterium from old pit mud at Daohuaxiang Winery, achieving butyric acid production of up to 300 mg/100 mL. When butyric acid and caproic acid bacteria were co-inoculated at a 1:1 ratio, caproic acid production increased by approximately 50%. Additionally, Hu Cheng et al. demonstrated that adding a carbon source for methanogens to the growth medium of caproic acid bacteria resulted in an 8.69% increase in caproic acid production compared to controls. These findings suggest that while individual acid-producing strains may exhibit limited acid production, synergistic fermentation can significantly enhance yields (Luo et al., 2018).
Optimized acid-producing bacterial mixtures can be utilized for cellar maintenance and artificial pit mud cultivation, effectively improving the microecological environment of pit mud and thereby enhancing the quality of strong-aroma liquor (Li et al., 2023b; Zhou et al., 2024a). Techniques for optimizing culture media, such as partial factorial experimental design and response surface experimental design (Luo et al., 2022), as well as the addition of butanol (Xue et al., 2013) or butyric acid (Regestein et al., 2015), have been applied in the production of biofuels and biomaterials.
This study aims to optimize compound fermentation using anaerobic functional bacteria isolated from pit mud. By employing Design Expert software, ramp tests, response surface analysis, Box-Behnken Design (BBD), and variance analysis, we seek to identify the optimal conditions for synergistic production of caproic and butyric acids. The findings of this study will provide valuable insights for expanding dominant bacterial populations in artificial pit mud and improving the quality of strong-aroma liquor.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains and Culture Media
Strains SJ-1 (Bacillus tequilensis), SJ-3 (Bacillus aerius), and SJ-8 (Clostridium butyricum subsp.), along with pit mud enrichment, were prepared at the Liquor Making Biotechnology and Application Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province. The fermentation medium composition (g/L) was as follows: MES 0.50, KH2PO4 0.50, Na2SO4 0.50, NaCl 1.00, MgCl2·6H2O 0.40, NaHCO3 0.30, CaCl2·2H2O 0.15, yeast extract 1.00, peptone 1.50, glucose 0.50, sodium acetate 3.00, soluble starch 5.00, sodium caproate 3.00, and cysteine hydrochloride 0.25. All chemicals were purchased from Chengdu Kelong Chemical Reagent Factory (Chengdu, China). The medium was adjusted to pH 6.8 and sterilized at 121 °C for 15 minutes (Liu et al., 2014).
2.2. Seed Culture
Activated strains were transferred to seed culture at a concentration of 105/mL. The cells were subjected to a water bath at 80 °C for 10 minutes. Each strain’s seed culture was then inoculated into sterile tubes to prepare a mixed seed culture. These strains were added to 80 mL of deoxygenated, sterilized fermentation medium at a 3% inoculation rate and cultured at 28 °C for 12 days.
2.3. Gas Chromatography (GC) and Mass Spectrometry (MS) Procedures
GC conditions: A DB-WAX column (60 m × 250 μm × 0.25 μm; Agilent, USA) was used. Helium (high purity) was the carrier gas, with a flow rate of 1 mL/min and an inlet temperature of 230 °C. The temperature program was as follows: initial temperature at 60 °C for 1 minute, ramped to 180 °C at 8 °C/min, then to 230 °C at 15 °C/min for 5 minutes.
MS conditions (Agilent, USA) : The electron ion source operated at 70 eV in full scanning mode, with a mass range of 20-550 u. The ion source temperature was 230 °C, the quadrupole rod temperature was 150 °C, and the interface temperature was 230 °C (Amaral et al., 2018).
A group of mixed strains with optimal fermentative effects were selected and inoculated with equal amounts of the enriched culture. The fermentation products were analyzed by GC-MS. Characteristic ions were used for qualitative analysis, with a matching degree greater than 80%. Identification was confirmed by comparing mass spectra with the standard database (NIST05a.L) provided by Agilent, USA (Wang et al., 2011).
2.4. Experimental Design
Design-Expert software (Version 8.0.6) was used to optimize the culture medium. The study investigated five factors: pH, ethanol, peptone, sodium acetate, and sodium butyrate (Li et al., 2023a). Each factor was tested at three levels: +1 (high), 0 (intermediate), and -1 (low). The experimental design levels and coding are shown in
Table 1.
Significant factors were optimized using hill-climbing and response surface analysis (Yıldız, 2009). The optimal levels for each significant factor were determined using Box-Behnken Design and ANOVA. The optimal fermentation medium for hexanoic and butyric acid production was identified. Each trial was performed in triplicate, and the average values were normalized to a scale of 0 to 1 (Jensen et al., 2008).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Pure Culture and Mixed Culture Fermentation
To evaluate the impact of synergistic fermentation on target product formation, we tested three strains of anaerobic bacteria in both pure culture and mixed culture conditions. In the pure culture fermentations, the yields of butyric acid, n-butanol, and hexanoic acid were lower compared to those achieved in synergistic (co-culture) fermentations involving SJ-1 and SJ-3. Notably, ethyl hexanoate and ethyl butyrate were not detected in the pure culture fermentations, indicating that the two strains can enhance each other’s primary metabolite production when co-cultured. The synergistic fermentation of SJ-1 and SJ-8 led to increased production of butyric acid and ethanol but reduced the production of 2,3-butanediol. In contrast, co-culturing SJ-8 with SJ-3 did not produce n-butanol, but the yields of acetic acid and 2,3-butanediol increased. This suggests that SJ-3 inhibits n-butanol production by SJ-8, while SJ-8 promotes the production of acetic acid and 2,3-butanediol from SJ-3.
The mixed culture fermentation involving SJ-1, SJ-3, SJ-8, and the enriched pit mud culture achieved a yield of 27.70 g/L, significantly higher than the yield of 9.86 g/L obtained from the pit mud enriched culture alone. Additionally, the concentrations of butyric acid and hexanoic acid increased to 11.67 g/L and 8.02 g/L, respectively, compared to 4.84 g/L and 2.22 g/L in the pit mud enriched culture fermentation. These results demonstrate that the combined use of SJ-1, SJ-3, and SJ-8 with the enriched pit mud culture enhances synergistic effects, making it a promising approach for optimizing the pit mud environment.
3.2. Fractional Factorial Design to Determine the Main Influencing Factors of the Culture Medium
In this study, a fractional factorial design was employed to optimize the fermentation conditions, using N=5 factors as detailed in
Table 1. A total of 16 experiments were conducted based on this design. The weights for caproic acid and butyric acid contents were both set at 0.5. The comprehensive value (Y) for each sample was calculated by normalizing each index, multiplying by its weight, and then summing the results. The formula used is: Comprehensive value (Y) = caproic acid normalized value × 0.5 + butyric acid normalized value × 0.5. The results of the fractional factorial design are summarized in
Table 3.
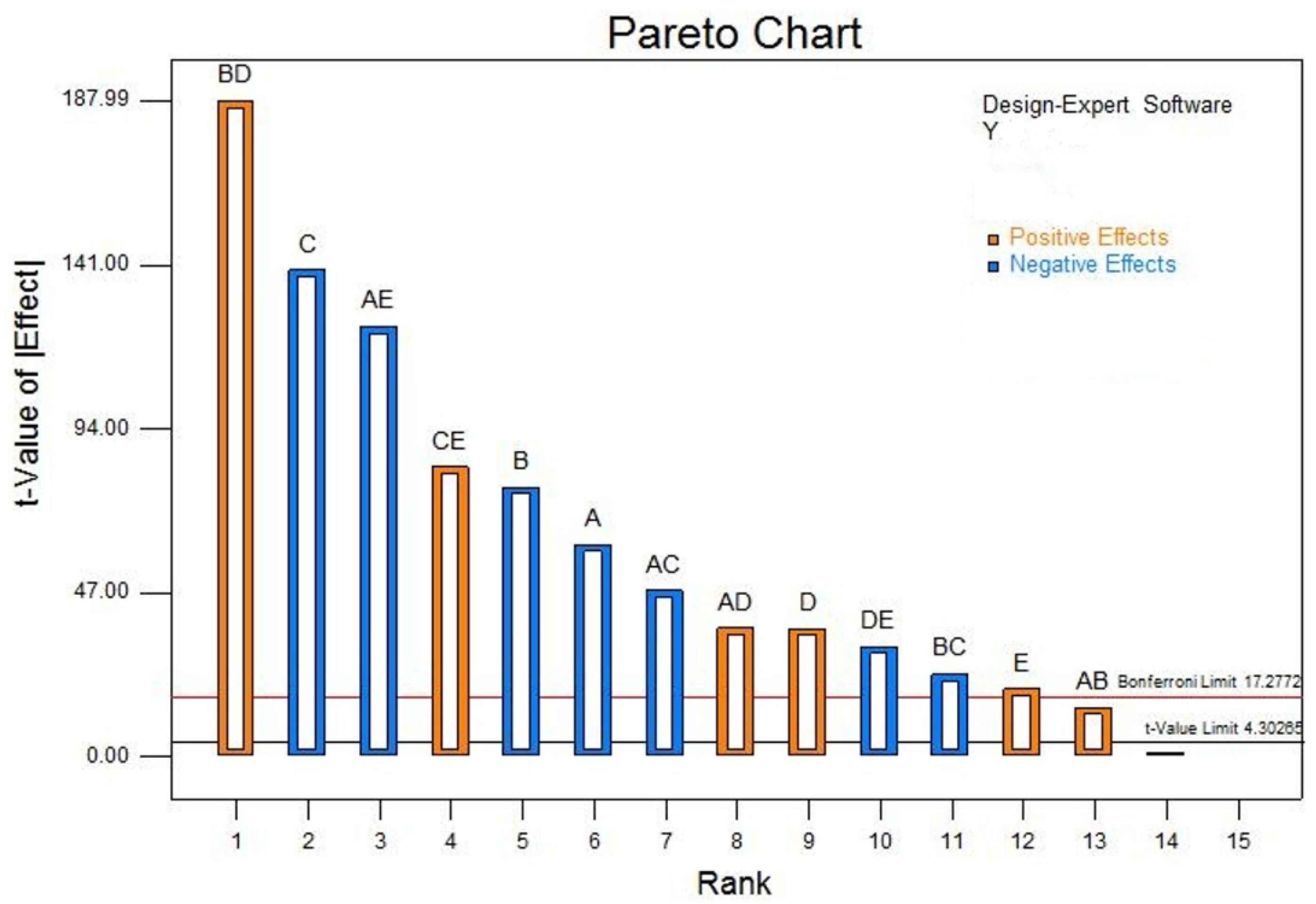
Variance analysis was performed using Design-Expert software to evaluate the effect coefficients of each factor and determine their significance. This analysis identified pH, ethanol, peptone, sodium acetate, and sodium butyrate as major influencing factors on the production of hexanoic acid and butyric acid (P < 0.01). The order of significance for the production of caproic acid and butyric acid was determined to be: peptone > ethanol > pH > sodium acetate > sodium butyrate (
Figure 1).
The effect coefficients for sodium acetate and sodium butyrate were positive, indicating a significant positive impact on the production of both caproic acid and butyric acid. Conversely, the effect coefficients for pH, ethanol, and peptone were negative, reflecting a significant negative impact on the production of these acids. The regression equation derived from the coefficients is: Y=0.52-0.052A-0.066B-0.12C+0.031D+0.017E+0.012AB-0.041AC+0.031AD-0.10AE-0.02BC+0.16BD+0.071CE-0.027DE. The signal-to-noise ratio of the model is 314.077, and the coefficient of determination (R²) is 0.988. These metrics indicate a high level of model reliability and fit, suggesting minimal experimental error. This regression model is thus effective for predicting and analyzing the production of hexanoic acid and butyric acid during fermentation.
3.3. The Steepest Climb Test Determines the Center Point of Significant Influencing Factor Levels
Based on the analysis of the factor tests, it was determined that pH, ethanol, peptone, sodium acetate, and sodium butyrate all significantly affect the production of caproic acid and butyric acid. To maximize the production of these acids, pH, sodium acetate, sodium butyrate, and peptone were selected as variables for further optimization, while ethanol was excluded from the tests. The steepest climb test was used to identify the optimal levels for these variables, adjusting the step size and climbing direction based on the coefficients from the fractional factorial design.
In these experiments, peptone was reduced, sodium acetate and sodium butyrate were increased, and the pH was lowered. The specific conditions and results of the steepest climb test are detailed in
Table 5. The production of caproic acid and butyric acid initially increased with changes in the culture medium components, but eventually began to decrease after reaching a peak. The comprehensive value (Y) for caproic and butyric acids peaked at 0.960 in the fourth experimental group, indicating that the concentrations of the components in this group approached the optimal range for maximizing acid production.
Given that the difference in initial pH values between Group 4 and the neighboring Groups 3 and 5 was minimal, the initial pH value (pH = 6.4) was not varied in the subsequent Box-Behnken experimental design. Consequently, the center point of the component concentrations from Group 4 was chosen for further testing and data analysis.
3.4. Box-Behnken Experimental Design
The center points for values of the three factors of peptone, sodium acetate, and sodium butyrate were determined through the steepest climb test. The Design Expert software was used for Box-Behnken experimental design and data analysis. The coding level obtained by taking the three significant influencing factors of peptone, sodium acetate, and sodium butyrate as independent variables is shown in
Table 6. Taking the Y comprehensive value as the response value, the Design Expert software was used to conduct the Box-Behnken experimental design, in which the factorial part was carried out 17 times, and the center point repeated experiments were 5 times. The experimental design and results are shown in
Table 7.
Use Design Expert software to perform multiple quadratic regression fitting on the test result data of the BBD experimental design and establish a quadratic regression equation for the full variable coding level with Y comprehensive value as the response value. The transformation formula between independent variables and coding variables is xi= (Xi-X0) /Δ, in the formula: Δ is Independent variable step size, xi is the encoded value of the independent variable, Xi is the actual value of the independent variable, and X0 is the actual value of the independent variable at the center.
Using the transformation formula of independent variables and coding variables, the quadratic regression equation of the coding level of all variables is converted into the quadratic regression equation of the non-coding level of all variables as follows: Y comprehensive value=-52.90106+3.55969A+7.21500B+11.95750C-0.078125AB-0.25365AC-0.23125BC-0.19965A2-0.57431B2-1.06719C2.
From the variance analysis Table 8, it can be seen that the model P<0.01, the lack of fit item P=0.0654>0.05, indicating that the model is significant. The coefficient of determination of the regression equation R2=0.8992 shows that the second-order regression equation fits the experiment well and has a small experimental error. It shows that the reliability of the experimental method is relatively high and can be used to theoretically predict the comprehensive score value of the test produced by fermentation of caproic acid and butyric acid. In the regression equation, C and A2 are significant on the comprehensive score (P<0.01), B and B2 have a significant impact on the comprehensive score (P<0.05), while A, AB, AC, BC, and C2 are not significant (P> 0.05). The order of priority of the influence for these three factors is C>B>A, that is, sodium butyrate>sodium acetate>peptone.
3.5. Optimization of Significant Factor Levels
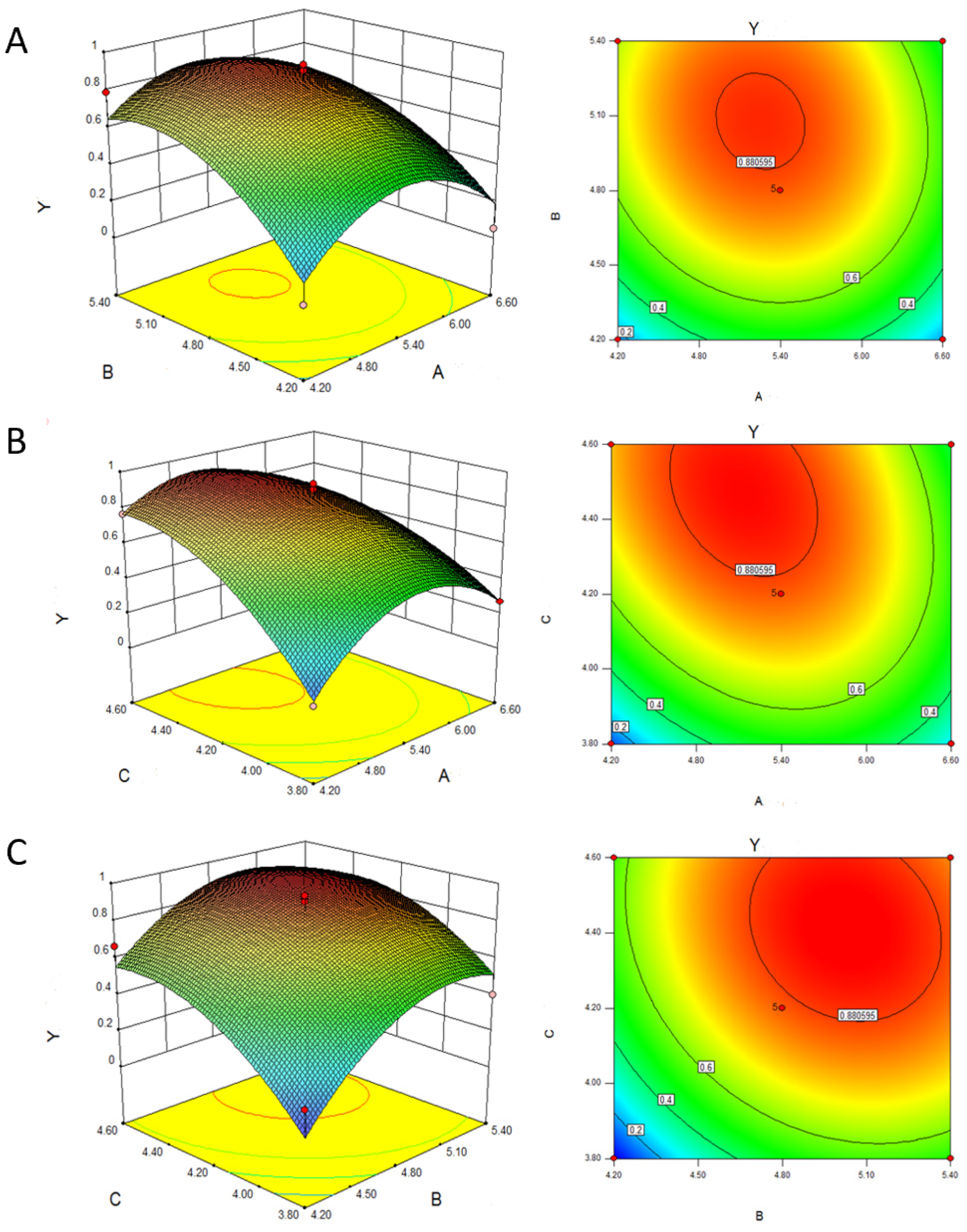
To illustrate the impact of peptone, sodium acetate, and sodium butyrate on the comprehensive score, a response surface was generated using Design Expert software (
Figure 2). The optimal levels of the factors, as determined from the regression model, are peptone (A) at 5.1 g/L, sodium acetate (B) at 5.04 g/L, and sodium butyrate (C) at 4.45 g/L. At these levels, the model predicts a maximum comprehensive score (Y) of 0.962. Additionally, the maximum estimated concentrations for caproic acid and butyric acid under these conditions are 1184.21 mg/100 mL and 2387.84 mg/100 mL, respectively (
Figure 2).
3.6. Verification Test of the Optimization Results
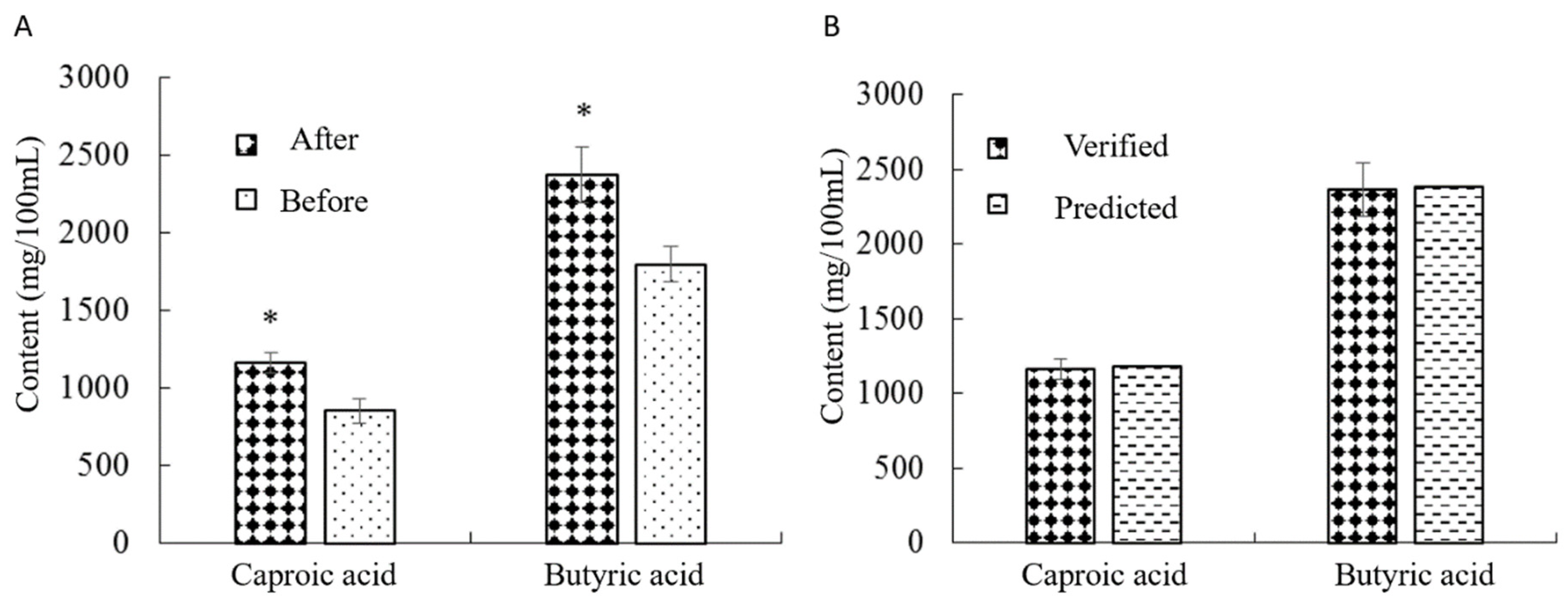
To assess the impact of the optimized culture medium formula on the production of caproic acid and butyric acid, a verification test was performed with the original culture medium formula as a control. Using the optimized fermentation medium, the contents of caproic acid and butyric acid were 1172.73 mg/100 mL and 2382.45 mg/100 mL, respectively. The results indicated a significant increase in caproic acid and butyric acid levels compared to those obtained with the original medium (P<0.05) (
Figure 3A). Furthermore, these values did not differ significantly from the model’s predicted values (P>0.05), confirming the effectiveness of the model (
Figure 3B).
4. Conclusions
This study optimized the production of caproic acid and butyric acid using both pure and mixed cultures through response surface methodology. The results revealed significant differences in the flavor compounds produced by pure culture fermentation compared to mixed culture fermentation. The best results were achieved by adding a mixed culture of Bacillus tequilensis, Bacillus aerius, and Clostridium butyricum to the enriched pit mud culture for collaborative fermentation. This approach resulted in notably higher levels of total volatile compounds, butyric acid, and caproic acid compared to other groups. Specifically, the production of caproic acid and butyric acid reached 801.936 mg/100 mL and 1167.33 mg/100 mL, respectively, showing significant improvements over other collaborative fermentation conditions (P<0.05). The optimal medium formulation was found to be: peptone 5.1 g/L, sodium acetate 5.04 g/L, and sodium butyrate 4.45 g/L, with a pH of 6.4. The concentrations of hexanoic acid and butyric acid after optimization were significantly higher than those before optimization (P<0.05). The yields of caproic acid and butyric acid obtained from the verification test were consistent with the model’s predicted values, demonstrating the model’s high accuracy and effectiveness. This study utilized anaerobic Clostridium and Bacillus strains as functional bacteria in the fermentation process and optimized the acid-producing culture medium. The findings provide a theoretical foundation for the application of functional bacteria in cellar maintenance, cellar protection, the cultivation of artificial cellar mud, and the production of esterification liquid for strong-aroma Daqu.
Author Contributions
Chunhui Wei, Conceptualization, Methodology, Supervision, Funding acquisition, Writing-review and editing; Yilian Tu: Data curation, Data visualization, Writing-original draft preparation; Jun Xie, Writing-original draft preparation, Formal analysis, Data visualization, Writing-review and editing; Zhiguo Huang, Supervision, Resources, Funding acquisition. All authors have read and approved the final version of this manuscript.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Scientific Research Project of the Science and Technology Department of Sichuan Province (project no. 2016SZ0074 and 2016CC0032), Opening fund of Sichuan Provincial Academician Experts Workstation of Sichuan University of Science & Engineering (project no. 2017YSGZZ01), Scientific Research Project of Sichuan Education Department (project no. 17ZB0306), and Opening fund of Liquor Making Biotechnology and Application Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province (project no. NJ2017-09).
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
References
- Amaral, M.S., Marriott, P.J., Bizzo, H.R., Rezende, C.M.J.A. 2018. Ionic liquid capillary columns for analysis of multi-component volatiles by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry: performance, selectivity, activity and retention indices. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 410, 4615-4632. [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y., Ma, N., Tang, H. 2022. Analysis of microbial community diversity and physicochemical factors in pit mud of different ages based on high-throughput sequencing. Can J Microbiol. 68 (11), 674-686. [CrossRef]
- Hirst, M.B., Richter, C.L. 2016. Review of aroma formation through metabolic pathways of Saccharomyces cerevisiae in beverage fermentations. Am. J. Enol. Vitic.67 (4), 361-370. [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.-l., Du, H., Xu, Y. 2015. Identification and quantification of the caproic acid-producing bacterium Clostridium kluyveri in the fermentation of pit mud used for Chinese strong-aroma type liquor production. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 214, 116-122. [CrossRef]
- Hu, X., Feng, D., Yu, M., Wang, S., Zhang, Y., Chi, L., Zhang, Z., He, P., Wang, Y., Zhu, W. 2021. The Effect of Spatial Location of Fermentation Pit on Prokaryotic Community Diversity in Pit Mud for Chinese Strong-Flavor Baijiu Production. Can J Microbiol. [CrossRef]
- Jensen, G.S., Wu, X., Patterson, K.M., Barnes, J., Carter, S.G., Scherwitz, L., Beaman, R., Endres, J.R., Schauss, A.G. 2008. In vitro and in vivo antioxidant and anti-inflammatory capacities of an antioxidant-rich fruit and berry juice blend. Results of a pilot and randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled, crossover study. J. Agric. Food Chem. 56 (18), 8326-8333. [CrossRef]
- Li, H., Gao, F., Wang, Z., Gao, Z. 2023a. The optimization of sequential fermentation in the dealcoholized apple juice for reducing lipids. J Food Sci Technol. 60 (7), 2063-2077. [CrossRef]
- Li, J., Ding, Z., Dong, W., Li, W., Wu, Y., Zhu, L., Ma, H., Sun, B., Li, X. 2024. Analysis of differences in microorganisms and aroma profiles between normal and off-flavor pit mud in Chinese strong-flavor Baijiu. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 137 (5), 360-371. [CrossRef]
- Li, M., Li, T., Zheng, J., Qiao, Z., Zhang, K., Luo, H., Zou, W. 2023b. Genome Analysis and Optimization of Caproic Acid Production of Clostridium butyricum GD1-1 Isolated from the Pit Mud of Nongxiangxing Baijiu. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 33 (10), 1337. [CrossRef]
- Liu, C., Du, Y., Zheng, J., Qiao, Z., Luo, H., Zou, W. 2022a. Production of caproic acid by Rummeliibacillus suwonensis 3B-1 isolated from the pit mud of strong-flavor baijiu. J. Biotechnol. 358, 33-40. [CrossRef]
- Liu, S., Lou, Y., Li, Y., Zhao, Y., Laaksonen, O., Li, P., Zhang, J., Battino, M., Yang, B., Gu, Q. 2023. Aroma characteristics of volatile compounds brought by variations in microbes in winemaking. Food Chem. 420, 136075. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y., Tang, T.-X., Pei, X.-Q., Zhang, C., Wu, Z.-L. 2014. Identification of ketone reductase ChKRED20 from the genome of Chryseobacterium sp. CA49 for highly efficient anti-Prelog reduction of 3,5-bis (trifluoromethyl) acetophenone. J. Mol. Catal. B: Enzym. 102, 1-8. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y., Xu, M., Zhao, Z., Wu, J., Wang, X., Sun, X., Han, S., Pan, C. 2022b. Analysis on bacterial community structure of new and old fermented pit mud of Shedian Liquor. Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip. 36 (1), 653-661. [CrossRef]
- Luo, H., Li, T., Zheng, J., Zhang, K., Qiao, Z., Luo, H., Zou, W. 2022. Isolation, Identification, and Fermentation Medium Optimization of a Caproic AcidProducing Enterococcus casseliflavus Strain from Pit Mud of Chinese Strong Flavor Baijiu Ecosystem. Polish J. Microbiol. 71 (4), 563. [CrossRef]
- Luo, H., Yang, R., Zhao, Y., Wang, Z., Liu, Z., Huang, M., Zeng, Q. 2018. Recent advances and strategies in process and strain engineering for the production of butyric acid by microbial fermentation. Bioresour. Technol.253, 343-354. [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L., Wang, J., Wang, R., Zhang, N., Zheng, F. 2023. A review on flavor of Baijiu and other world-renowned distilled liquors. Food Chem: X, 100870. [CrossRef]
- Regestein, L., Doerr, E.W., Staaden, A., Rehmann, L. 2015. Impact of butyric acid on butanol formation by Clostridium pasteurianum. Bioresour. Technol. 196, 153-159. [CrossRef]
- Ren, D., Liu, S., Qin, H., Huang, M., Han, X., Zhang, S., Mao, J. 2024a. Heterogenetic mechanism in multidimensional pit mud with different fermentation years: From microbial structure dynamic succession to metabolism phenotypes. Food Res. Int. 192, 114770. [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z., Chen, Q., Tang, T., Huang, Z. 2024b. Unraveling the water source and formation process of Huangshui in solid-state fermentation. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 1-11. [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z., Liu, L., Tang, T., Huang, K., Huang, Z. 2024c. Effectively Increase the L (+) -Isomer Proportion of Ethyl Lactate in Baijiu by Isolating and Applying L (+) -Lactic Acid-Producing Bacteria. in: Preprints. [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z., Xie, J., Tang, T., Huang, Z. 2024d. Short-chain carboxylates facilitate the counting of yeasts in Sub-high temperature Daqu. Polish J. Microbiol. [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z., Chen, C., Hou, X., Zhang, J., Tian, F., Li, C. 2017. Prokaryotic diversity and biochemical properties in aging artificial pit mud used for the production of Chinese strong flavor liquor. 3 Biotech, 7, 1-9. [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.-X., Liu, Y., Wu, Z.-L. 2014. Characterization of a robust anti-Prelog short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase ChKRED20 from Chryseobacterium sp. CA49. J. Mol. Catal. B: Enzym. 105, 82-88. [CrossRef]
- Wang, S., Wu, Q., Nie, Y., Wu, J., Xu, Y. 2019. Construction of synthetic microbiota for reproducible flavor compound metabolism in Chinese light-aroma-type liquor produced by solid-state fermentation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 85 (10), e03090-18. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y., Kang, W., Xu, Y., Li, J. 2011. Effect of different indigenous yeast β-glucosidases on the liberation of bound aroma compounds. J. Inst. Brew. 117 (2), 230-237. [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y., Zou, W., Shen, C.H., Yang, J.G. 2020. Basic flavor types and component characteristics of Chinese traditional liquors: A review. J. Food Sci. 85 (12), 4096-4107. [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y., Zhao, J., Liu, X., Zhang, C., Zhao, Z., Li, X., Sun, B. 2022. Flavor mystery of Chinese traditional fermented baijiu: The great contribution of ester compounds. Food Chem.369, 130920. [CrossRef]
- Xue, C., Zhao, X.-Q., Liu, C.-G., Chen, L.-J., Bai, F.-W.J.B.a. 2013. Prospective and development of butanol as an advanced biofuel. Biotechnol. Adv. 31 (8), 1575-1584. [CrossRef]
- Yıldız, A.R. 2009. An effective hybrid immune-hill climbing optimization approach for solving design and manufacturing optimization problems in industry. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 209 (6), 2773-2780. [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S., Jin, Z., Ali, A., Wang, C., Liu, J. 2022. Caproic acid-producing bacteria in Chinese Baijiu brewing. Front Microbiol, 13, 883142. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M., Wu, X., Mu, D., Yang, W., Jiang, S., Sun, W., Shen, Y., Cai, J., Zheng, Z., Jiang, S. 2020. Profiling the effects of physicochemical indexes on the microbial diversity and its aroma substances in pit mud. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 71 (6), 667-678. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H., Xu, S., Xu, B., Jiang, C., Zhao, E., Xu, Q., Hong, J., Li, X. 2024a. Effect of Caproicibacterium lactatifermentans inoculation on the microbial succession and flavor formation of pit mud used in Chinese Baijiu fermentation. Food Res. Int. 175, 113730. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L., Tang, T., Deng, D., Wang, Y., Pei, D. 2024b. Isolation and Electrochemical Analysis of a Facultative Anaerobic Electrogenic Strain sp. SQ-1. Polish J. Microbiol. 73 (2), 143-153. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).