Submitted:
31 August 2024
Posted:
02 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Machine Learning and AI Applications in Protein Design
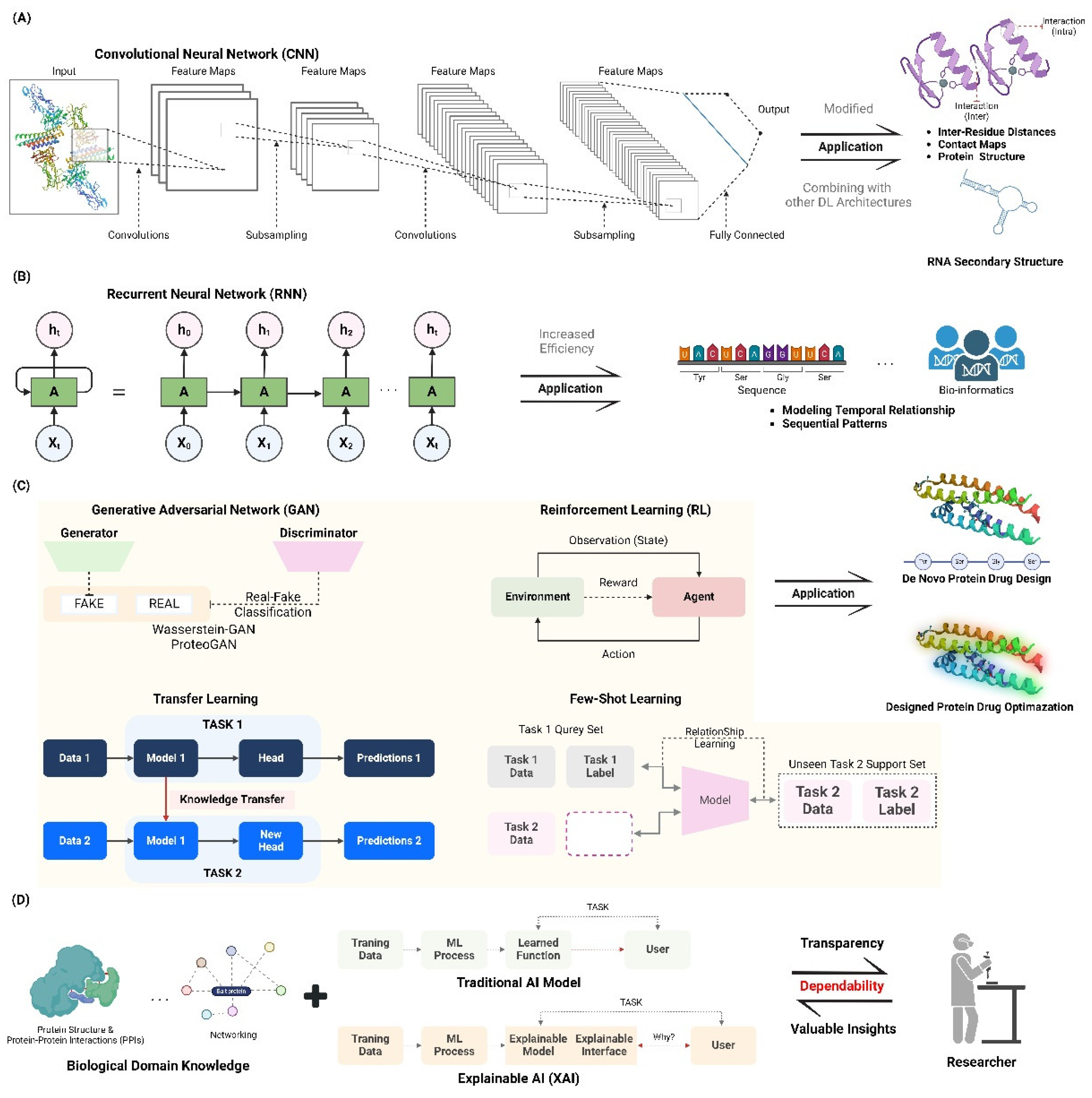
2.1. Deep Learning Approaches
2.1.1. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) for Structure Prediction
2.1.2. Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) for Sequence Optimization
2.1.3. Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) In De Novo Protein Design
2.2. Reinforcement Learning in Protein Engineering
2.2.1. Optimization of Protein Properties
2.2.2. Design of Protein-Protein Interactions
2.3. Transfer Learning and Few-Shot Learning
2.3.1. Leveraging Pre-Trained Models for Protein Design
2.3.2. Addressing the Challenge of Limited Data in Protein Engineering
2.4. Interpretable AI for Protein Design
2.4.1. Explainable AI Models for Rational Protein Engineering
2.4.2. Integration of Domain Knowledge with AI-Driven Approaches
3. Computational Methods in Enzyme Engineering
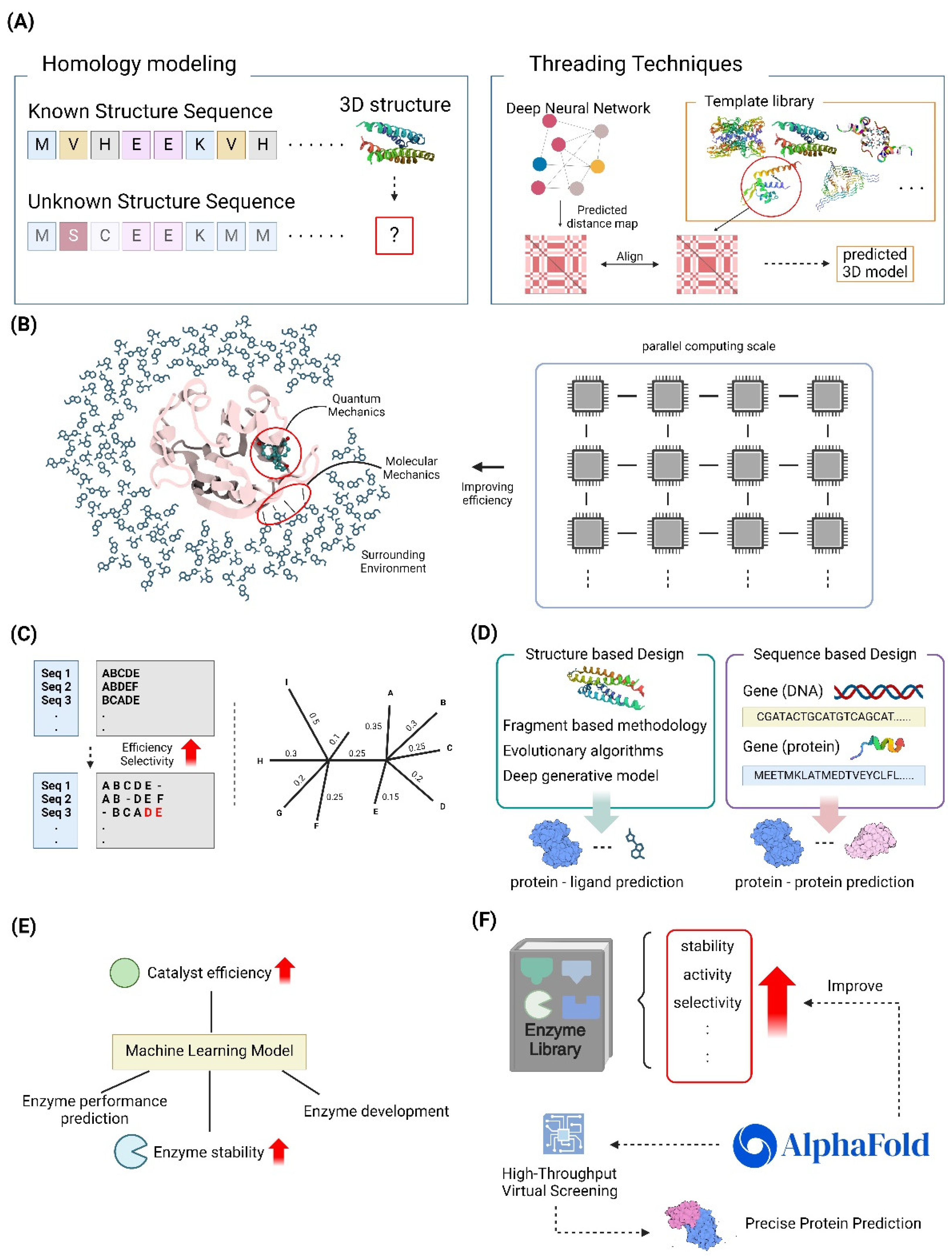
3.1. Structure-Based Design Strategies
3.1.1. Homology Modeling and Threading Techniques
3.1.2. Quantum Mechanics/Molecular Mechanics (QM/MM) Approaches
3.2. Sequence-Based Design Methods
3.2.1. Multiple Sequence Alignments and Phylogenetic Analysis
3.2.2. Coevolution-Based Approaches for Enzyme Design
3.3. Hybrid Methods
3.3.1. Integration of Structure and Sequence Information
3.3.2. Machine Learning-Assisted Enzyme Engineering
3.4. High-Throughput Virtual Screening
3.4.1. In-Silico Directed Evolution
3.4.2. Computational Library Design for Enzyme Engineering
4. Molecular Dynamics Simulation Studies of Biomolecular Systems
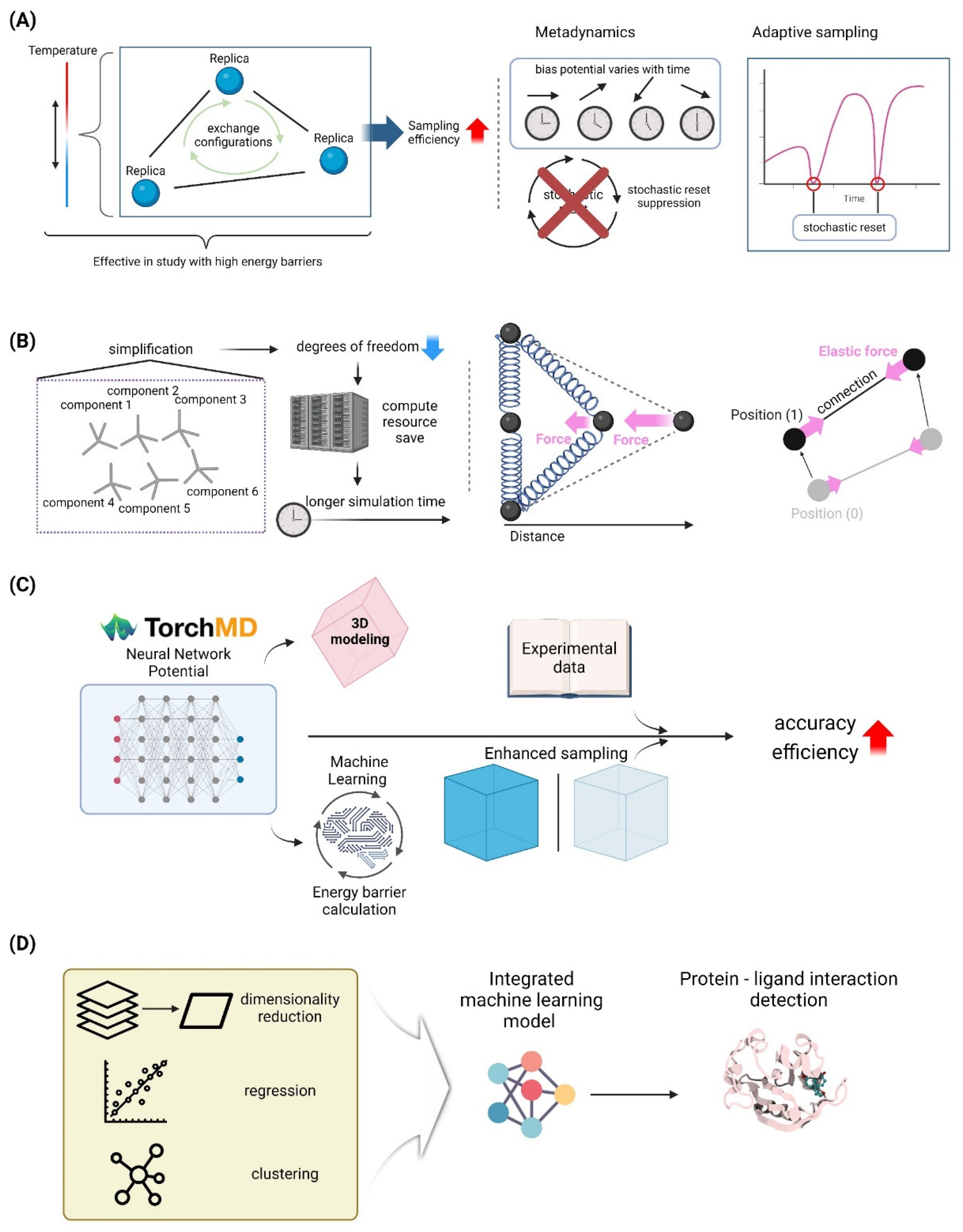
4.1. Advanced Sampling Techniques
4.1.1. Replica Exchange Molecular Dynamics
4.1.2. Metadynamics and Adaptive Sampling Methods
4.2. Coarse-Grained Models
4.2.1. MARTINI force Field and Its Applications
4.2.2. Elastic Network Models for Large-Scale Simulations
4.3. Long-Timescale Simulations
4.3.1. Specialized Hardware for MD Simulations
4.3.2. Enhanced Sampling Techniques for Accessing Biologically Relevant Timescales
4.4. Machine Learning-Enhanced MD Simulations
4.4.1. Neural Network Potentials for Accurate and Efficient Simulations
4.4.2. AI-Driven Analysis of MD Trajectories
5. Advances in Computational Docking and Drug Design
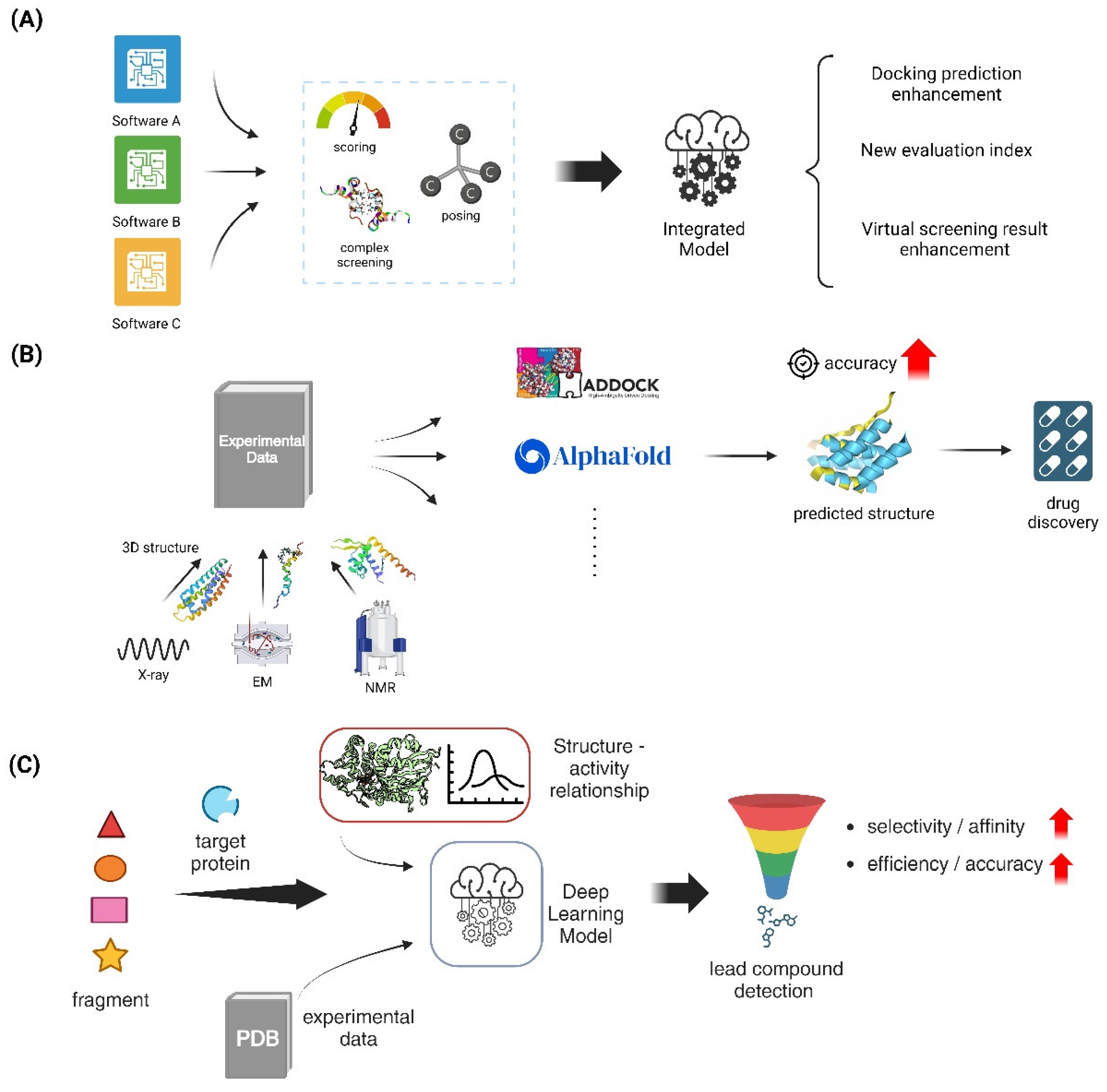
5.1. Protein-Ligand Docking
5.1.1. Flexible Docking Algorithms
5.1.2. Consensus Docking Approaches
5.2. Protein-Protein Docking
5.2.1. Template-Based Docking Methods
5.2.2. Integration of Experimental Data in Docking Protocols
5.3. Fragment-Based Drug Design
5.3.1. In Silico Fragment Growing and Linking Strategies
5.3.2. Machine Learning in Fragment-Based Approaches
5.4. Structure-Based Virtual Screening
5.4.1. Pharmacophore Modeling and Shape-Based Screening
5.4.2. AI-Driven Virtual Screening Pipelines
6. Design and Development of Novel Proteins with Enhanced Functionalities
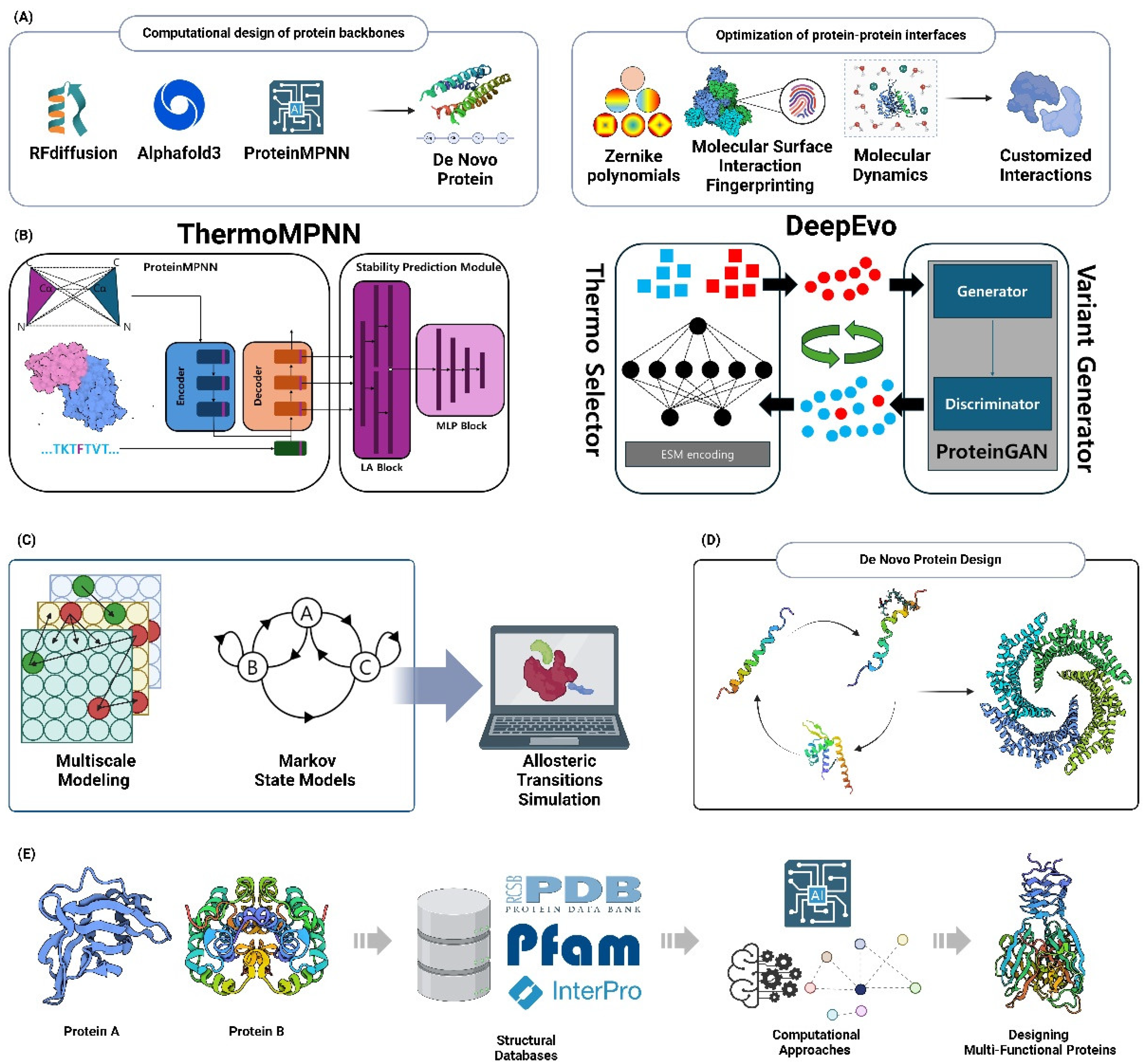
6.1. De Novo Protein Design
6.1.1. Computational Design of Protein Backbones
6.1.2. Optimization of Protein-Protein Interfaces
6.2. Protein Stability Engineering
6.2.1. Computational Prediction of Stabilizing Mutations
6.2.2. Design of Thermostable Proteins
6.3. Protein Functionalization
6.3.1. Computational Design of Allosteric Regulation
6.3.2. Engineering Proteins with Novel Binding Properties
6.4. Designing Multi-Functional Proteins
6.4.1. Computational Approaches for Domain Fusion
6.4.2. Rational Design of Chimeric Proteins
7. Case Studies and Applications in Biotechnology and Pharmaceuticals
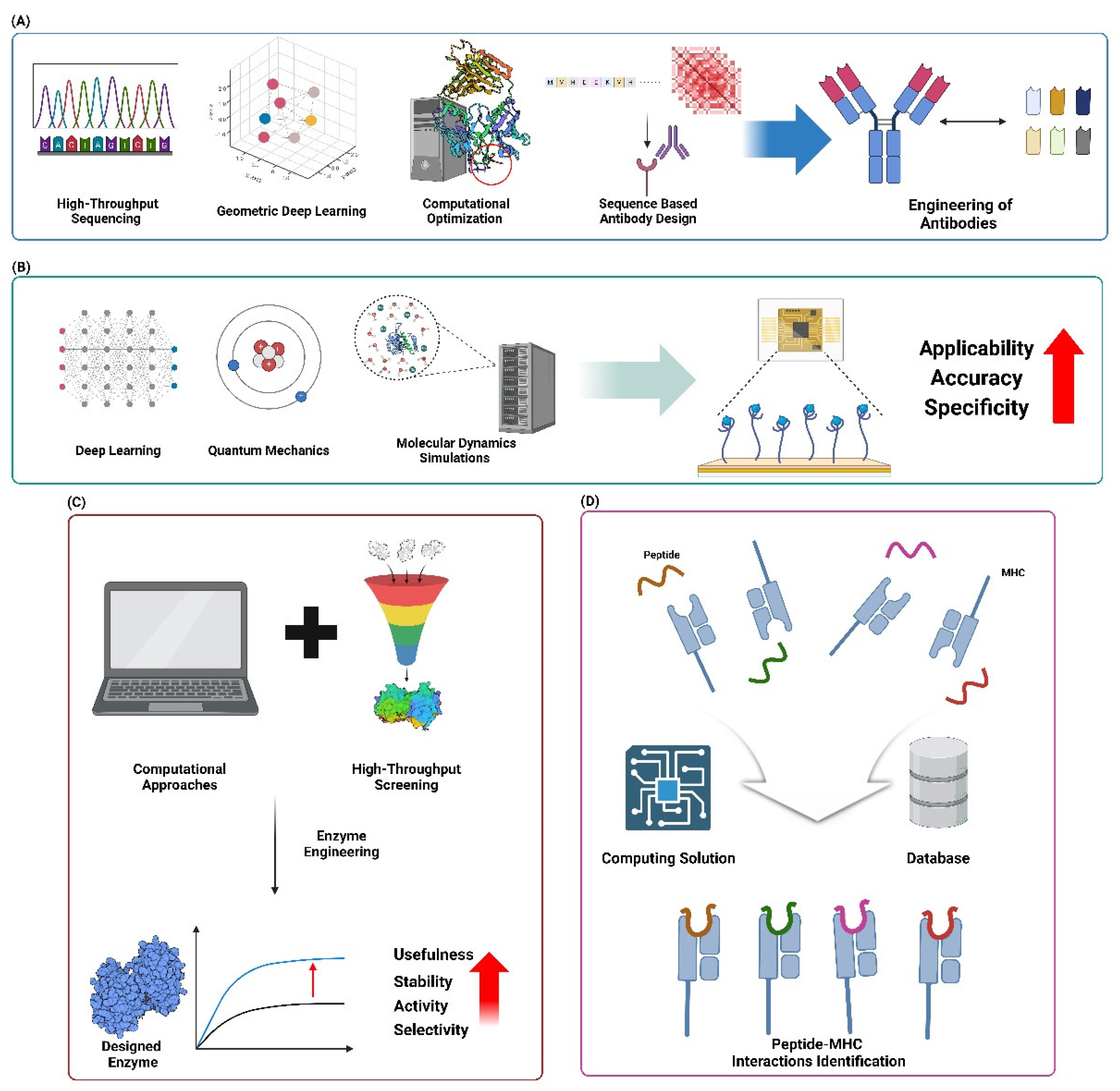
7.1. Engineered Antibodies and Immunotherapeutics
7.1.1. Computational Design of Antibody-Antigen Interfaces
7.1.2. In Silico Optimization of Antibody Stability and Specificity
7.2. Biosensors and Diagnostics
7.2.1. Rational Design of Protein-Based Biosensors
7.2.2. Computational Approaches for Enhancing Sensor Sensitivity and Specificity
7.3. Industrial Enzymes
7.3.1. Computational Engineering of Enzymes for Biocatalysis
7.3.2. Design of enzymes for Biodegradation and Environmental Applications
7.4. Therapeutic Protein Design
7.4.1. Computational Approaches for Improving Protein Drug Properties
7.4.2. In Silico Prediction of Immunogenicity and Optimization of Protein Therapeutics
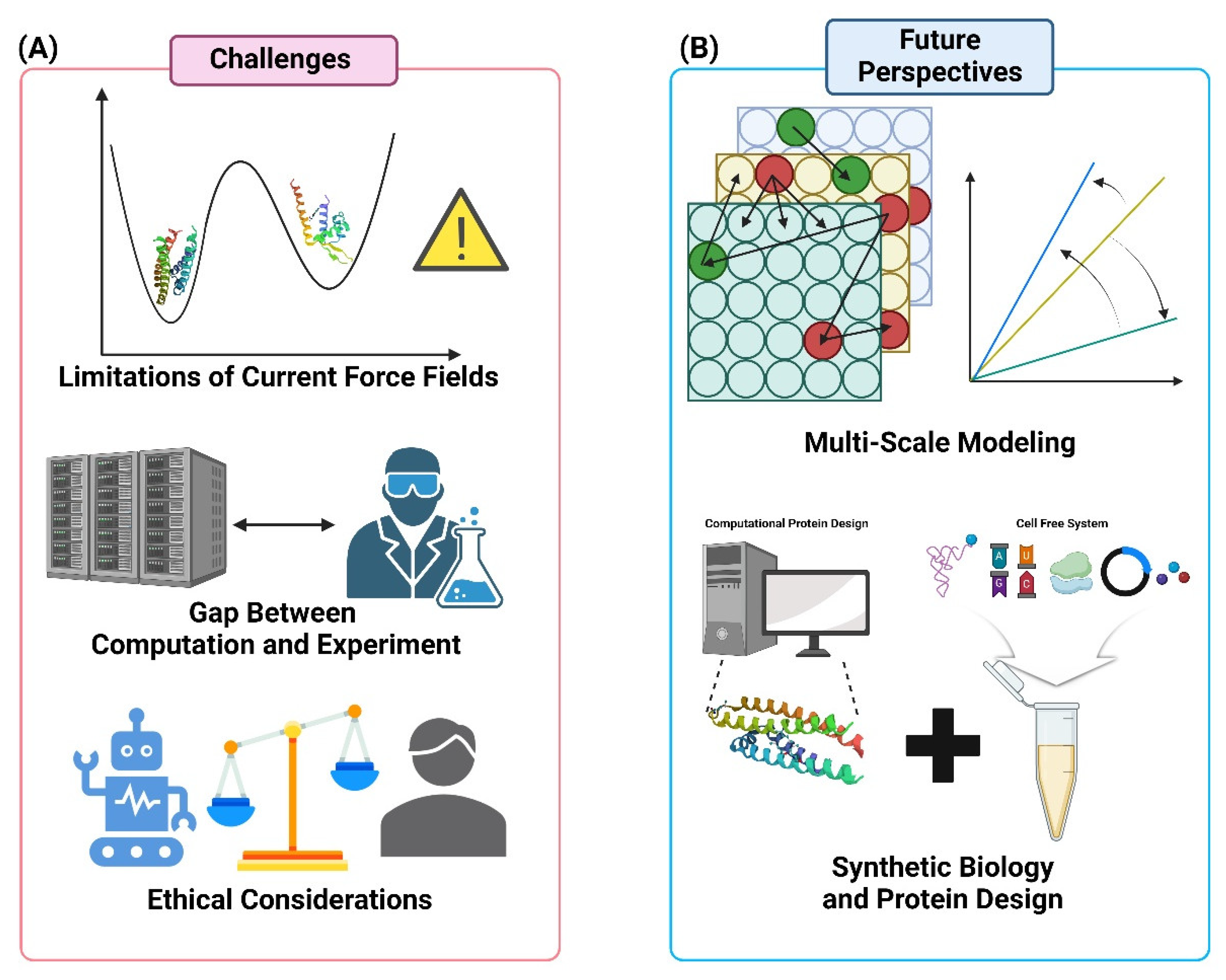
8. Challenges and Future Perspectives
8.1. Integration of Multi-Scale Modeling Approaches
8.2. Addressing the Limitations of Current Force Fields
8.3. Bridging the Gap Between Computation and Experiment
8.4. Ethical Considerations in AI-Driven Protein Engineering
8.5. Emerging Opportunities in Synthetic Biology and Protein Design
9. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sequeiros-Borja, C.E.; Surpeta, B.; Brezovsky, J. Recent advances in user-friendly computational tools to engineer protein function. Brief Bioinform 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Chen, Y.; Xue, W. Computational Protein Design - Where it goes? Curr Med Chem 2024, 31, 2841–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derat, E.; Kamerlin, S.C.L. Computational Advances in Protein Engineering and Enzyme Design. J Phys Chem B 2022, 126, 2449–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.J.; Shao, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Jurich, C.; Ran, X.; Juarez, R.J.; Yan, B.; Stull, S.L.; Gollu, A.; Ding, N. Mutexa: A Computational Ecosystem for Intelligent Protein Engineering. J Chem Theory Comput 2023, 19, 7459–7477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ben-Sasson, A.J. Precision materials: Computational design methods of accurate protein materials. Curr Opin Struct Biol 2022, 74, 102367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadybekov, A.V.; Katritch, V. Computational approaches streamlining drug discovery. Nature 2023, 616, 673–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gligorijevic, V.; Renfrew, P.D.; Kosciolek, T.; Leman, J.K.; Berenberg, D.; Vatanen, T.; Chandler, C.; Taylor, B.C.; Fisk, I.M.; Vlamakis, H.; et al. Structure-based protein function prediction using graph convolutional networks. Nat Commun 2021, 12, 3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Mahajan, S.P.; Sulam, J.; Gray, J.J. Deep Learning in Protein Structural Modeling and Design. Patterns (N Y) 2020, 1, 100142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saman Booy, M.; Ilin, A.; Orponen, P. RNA secondary structure prediction with convolutional neural networks. BMC Bioinformatics 2022, 23, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Zhang, D.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Li, S.; Guo, Y.; Webb, G.I.; Nguyen, A.T.N.; et al. GraphormerDTI: A graph transformer-based approach for drug-target interaction prediction. Comput Biol Med 2024, 173, 108339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulikova, A.V.; Diaz, D.J.; Loy, J.M.; Ellington, A.D.; Wilke, C.O. Learning the local landscape of protein structures with convolutional neural networks. J Biol Phys 2021, 47, 435–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, N.; Srivastava, R. Deep learning in structural bioinformatics: current applications and future perspectives. Brief Bioinform 2024, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asabuki, T.; Kokate, P.; Fukai, T. Neural circuit mechanisms of hierarchical sequence learning tested on large-scale recording data. PLoS Comput Biol 2022, 18, e1010214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.; Jain, A.; Mauro, E.; LeShane, K.; Densmore, D. ICOR: improving codon optimization with recurrent neural networks. BMC Bioinformatics 2023, 24, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, F.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Fan, L.; Yang, Y.; Guo, X.; Wang, Y.; Yan, S.; Qiao, Z.; Li, Y.; et al. Recurrent neural network for predicting absence of heterozygosity from low pass WGS with ultra-low depth. BMC Genomics 2024, 25, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Tariq, A.; Santos, T.; Kantareddy, S.S.; Banerjee, I. Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs): Architectures, Training Tricks, and Introduction to Influential Research. In Machine Learning for Brain Disorders, Colliot, O., Ed.; New York, NY, 2023; pp. 117-138.
- Lin, E.; Lin, C.H.; Lane, H.Y. De Novo Peptide and Protein Design Using Generative Adversarial Networks: An Update. J Chem Inf Model 2022, 62, 761–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucera, T.; Togninalli, M.; Meng-Papaxanthos, L. Conditional generative modeling for de novo protein design with hierarchical functions. Bioinformatics 2022, 38, 3454–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strokach, A.; Kim, P.M. Deep generative modeling for protein design. Curr Opin Struct Biol 2022, 72, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atz, K.; Cotos, L.; Isert, C.; Hakansson, M.; Focht, D.; Hilleke, M.; Nippa, D.F.; Iff, M.; Ledergerber, J.; Schiebroek, C.C.G.; et al. Prospective de novo drug design with deep interactome learning. Nat Commun 2024, 15, 3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Choi, H.; Kang, D.; Lee, W.B.; Na, J. Materials discovery with extreme properties via reinforcement learning-guided combinatorial chemistry. Chem Sci 2024, 15, 7908–7925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Huang, M. Navigating the landscape of enzyme design: from molecular simulations to machine learning. Chem Soc Rev 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Xing, M.; Yuan, Q.; He, H.; Sun, S. Universal Approach to De Novo Drug Design for Target Proteins Using Deep Reinforcement Learning. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 5464–5474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palukuri, M.V.; Patil, R.S.; Marcotte, E.M. Molecular complex detection in protein interaction networks through reinforcement learning. BMC Bioinformatics 2023, 24, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietrich, L.; Rathmer, B.; Ewan, K.; Bange, T.; Heinrichs, S.; Dale, T.C.; Schade, D.; Grossmann, T.N. Cell Permeable Stapled Peptide Inhibitor of Wnt Signaling that Targets beta-Catenin Protein-Protein Interactions. Cell Chem Biol 2017, 24, 958–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Liu, X.; Wang, K.; Gao, Y.; Li, G.; Baptista-Hon, D.T.; Yang, X.H.; Xue, K.; Tai, W.H.; Jiang, Z.; et al. Deep-learning-enabled protein-protein interaction analysis for prediction of SARS-CoV-2 infectivity and variant evolution. Nat Med 2023, 29, 2007–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhang, L.; Yu, Y.; Wu, B.; Li, M.; Hong, L.; Tan, P. Enhancing efficiency of protein language models with minimal wet-lab data through few-shot learning. Nat Commun 2024, 15, 5566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, R.; Bouatta, N.; Biswas, S.; Floristean, C.; Kharkar, A.; Roy, K.; Rochereau, C.; Ahdritz, G.; Zhang, J.; Church, G.M.; et al. Single-sequence protein structure prediction using a language model and deep learning. Nat Biotechnol 2022, 40, 1617–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khakzad, H.; Igashov, I.; Schneuing, A.; Goverde, C.; Bronstein, M.; Correia, B. A new age in protein design empowered by deep learning. Cell Syst 2023, 14, 925–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Listov, D.; Goverde, C.A.; Correia, B.E.; Fleishman, S.J. Opportunities and challenges in design and optimization of protein function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2024, 25, 639–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafri, M.; Metzl-Raz, E.; Jona, G.; Barkai, N. The Cost of Protein Production. Cell Rep 2016, 14, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, Y.F.; Dorr, M.; Menke, M.J.; Born, S.; Heuson, E.; Bornscheuer, U.T. Data-Driven Protein Engineering for Improving Catalytic Activity and Selectivity. Chembiochem 2024, 25, e202300754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derry, A.; Carpenter, K.A.; Altman, R.B. Training data composition affects performance of protein structure analysis algorithms. Pac Symp Biocomput 2022, 27, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Illig, A.M.; Siedhoff, N.E.; Davari, M.D.; Schwaneberg, U. Evolutionary Probability and Stacked Regressions Enable Data-Driven Protein Engineering with Minimized Experimental Effort. J Chem Inf Model 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medl, M.; Leisch, F.; Durauer, A.; Scharl, T. Explainable deep learning enhances robust and reliable real-time monitoring of a chromatographic protein A capture step. Biotechnol J 2024, 19, e2300554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M. Recent Advances in Deep Learning for Protein-Protein Interaction Analysis: A Comprehensive Review. Molecules 2023, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Kang, D.; Kim, M.S.; Choe, J.C.; Lee, S.H.; Ahn, J.H.; Oh, J.H.; Choi, J.H.; Lee, H.C.; Cha, K.S.; et al. Acute myocardial infarction prognosis prediction with reliable and interpretable artificial intelligence system. J Am Med Inform Assoc 2024, 31, 1540–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinverno, L.; Barros, V.; Ghisoni, F.; Visona, G.; Kern, R.; Nickel, P.J.; Ventura, B.E.; Simic, I.; Stryeck, S.; Manni, F.; et al. A historical perspective of biomedical explainable AI research. Patterns (N Y) 2023, 4, 100830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, T.; Chitlangia, S.; Ahuja, A.; Srinivasan, A. A review of some techniques for inclusion of domain-knowledge into deep neural networks. Sci Rep 2022, 12, 1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirocchi, C.; Bogliolo, A.; Montagna, S. Medical-informed machine learning: integrating prior knowledge into medical decision systems. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak 2024, 24, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laxmi, B.; Devi, P.U.M.; Thanjavur, N.; Buddolla, V. The Applications of Artificial Intelligence (AI)-Driven Tools in Virus-Like Particles (VLPs) Research. Curr Microbiol 2024, 81, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khlaif, Z.N.; Mousa, A.; Hattab, M.K.; Itmazi, J.; Hassan, A.A.; Sanmugam, M.; Ayyoub, A. The Potential and Concerns of Using AI in Scientific Research: ChatGPT Performance Evaluation. JMIR Med Educ 2023, 9, e47049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musa, N.; Gital, A.Y.; Aljojo, N.; Chiroma, H.; Adewole, K.S.; Mojeed, H.A.; Faruk, N.; Abdulkarim, A.; Emmanuel, I.; Folawiyo, Y.Y.; et al. A systematic review and Meta-data analysis on the applications of Deep Learning in Electrocardiogram. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput 2023, 14, 9677–9750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dikmen, M.; Burns, C. The effects of domain knowledge on trust in explainable AI and task performance: A case of peer-to-peer lending. International Journal of Human-Computer Studies 2022, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wodak, S.J.; Vajda, S.; Lensink, M.F.; Kozakov, D.; Bates, P.A. Critical Assessment of Methods for Predicting the 3D Structure of Proteins and Protein Complexes. Annu Rev Biophys 2023, 52, 183–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuyun, Q.; Chen, Y.; Shen, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, G.; Cui, W.; Gao, J.; Zheng, W. Recent Progress of Protein Tertiary Structure Prediction. Molecules 2024, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoline, L.M.F.; Lima, A.N.; Krieger, J.E.; Teixeira, S.K. Before and after AlphaFold2: An overview of protein structure prediction. Front Bioinform 2023, 3, 1120370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Roche, R.; Shuvo, M.H.; Bhattacharya, D. Recent Advances in Protein Homology Detection Propelled by Inter-Residue Interaction Map Threading. Front Mol Biosci 2021, 8, 643752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramson, J.; Adler, J.; Dunger, J.; Evans, R.; Green, T.; Pritzel, A.; Ronneberger, O.; Willmore, L.; Ballard, A.J.; Bambrick, J.; et al. Accurate structure prediction of biomolecular interactions with AlphaFold 3. Nature 2024, 630, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavan, B.; Paulikat, M.; Ahmad, K.; Callea, L.; Rizzi, A.; Ippoliti, E.; Mandelli, D.; Bonati, L.; De Vivo, M.; Carloni, P. Drug Design in the Exascale Era: A Perspective from Massively Parallel QM/MM Simulations. J Chem Inf Model 2023, 63, 3647–3658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossetti, G.; Mandelli, D. How exascale computing can shape drug design: A perspective from multiscale QM/MM molecular dynamics simulations and machine learning-aided enhanced sampling algorithms. Curr Opin Struct Biol 2024, 86, 102814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginex, T.; Vazquez, J.; Estarellas, C.; Luque, F.J. Quantum mechanical-based strategies in drug discovery: Finding the pace to new challenges in drug design. Curr Opin Struct Biol 2024, 87, 102870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubar, T.; Elstner, M.; Cui, Q. Hybrid Quantum Mechanical/Molecular Mechanical Methods For Studying Energy Transduction in Biomolecular Machines. Annu Rev Biophys 2023, 52, 525–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giese, T.J.; Zeng, J.; Lerew, L.; McCarthy, E.; Tao, Y.; Ekesan, S.; York, D.M. Software Infrastructure for Next-Generation QM/MM-DeltaMLP Force Fields. J Phys Chem B 2024, 128, 6257–6271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, C.; Liu, B.; Williams, K.P.; Warnow, T. EMMA: a new method for computing multiple sequence alignments given a constraint subset alignment. Algorithms Mol Biol 2023, 18, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, M.K.; Yusof, U.K.; Eisa, T.A.E.; Nasser, M. Bioinspired Algorithms for Multiple Sequence Alignment: A Systematic Review and Roadmap. Applied Sciences 2024, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Hu, H.; Hao, Y.; Huang, S.; Li, B. Common Methods for Phylogenetic Tree Construction and Their Implementation in R. Bioengineering (Basel) 2024, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapli, P.; Kotari, I.; Telford, M.J.; Goldman, N.; Yang, Z. DNA Sequences Are as Useful as Protein Sequences for Inferring Deep Phylogenies. Syst Biol 2023, 72, 1119–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, W.; Wu, L.Y.; Xia, X.Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z.X.; Pan, X.M. A sequence-based evolutionary distance method for Phylogenetic analysis of highly divergent proteins. Sci Rep 2023, 13, 20304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, J.; Tang, F.; Xu, L. Developments in Algorithms for Sequence Alignment: A Review. Biomolecules 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Noh, M.H.; Park, M.; Kim, I.; Ahn, H.; Ye, D.Y.; Jung, G.Y.; Kim, S. Enzyme activity engineering based on sequence co-evolution analysis. Metab Eng 2022, 74, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, X.; Deng, M.; Lai, L. Coevolution-based prediction of key allosteric residues for protein function regulation. Elife 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossack, E.J.; Hardy, F.J.; Green, A.P. Building Enzymes through Design and Evolution. ACS Catalysis 2023, 13, 12436–12444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, G.P.; Corbella, M.; Demkiv, A.O.; Kamerlin, S.C.L. Exploiting enzyme evolution for computational protein design. Trends Biochem Sci 2022, 47, 375–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Moretti, R.; Meiler, J. Recent Advances in Automated Structure-Based De Novo Drug Design. J Chem Inf Model 2024, 64, 1794–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isert, C.; Atz, K.; Schneider, G. Structure-based drug design with geometric deep learning. Curr Opin Struct Biol 2023, 79, 102548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, A.; Saha, S.; Tvedt, N.C.; Yang, L.W.; Bahar, I. Mutually beneficial confluence of structure-based modeling of protein dynamics and machine learning methods. Curr Opin Struct Biol 2023, 78, 102517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinshuk, S.; Li, L.; Meckes, B.; Chan, C.T.Y. Sequence-Based Protein Design: A Review of Using Statistical Models to Characterize Coevolutionary Traits for Developing Hybrid Proteins as Genetic Sensors. Int J Mol Sci 2024, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Basu, S.; Kurgan, L. HybridDBRpred: improved sequence-based prediction of DNA-binding amino acids using annotations from structured complexes and disordered proteins. Nucleic Acids Res 2024, 52, e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummer, A.M.; Abanades, B.; Deane, C.M. Advances in computational structure-based antibody design. Curr Opin Struct Biol 2022, 74, 102379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siedhoff, N.E.; Schwaneberg, U.; Davari, M.D. Machine learning-assisted enzyme engineering. Methods Enzymol 2020, 643, 281–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gantz, M.; Neun, S.; Medcalf, E.J.; van Vliet, L.D.; Hollfelder, F. Ultrahigh-Throughput Enzyme Engineering and Discovery in In Vitro Compartments. Chem Rev 2023, 123, 5571–5611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, K.; Chin, M.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, W.; Mai, B.K.; Wang, H.; Liu, P.; Yang, Y.; Luo, Y. Machine learning-guided co-optimization of fitness and diversity facilitates combinatorial library design in enzyme engineering. Nat Commun 2024, 15, 6392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atomwise, A.P. AI is a viable alternative to high throughput screening: a 318-target study. Sci Rep 2024, 14, 7526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlsson, J.; Luttens, A. Structure-based virtual screening of vast chemical space as a starting point for drug discovery. Curr Opin Struct Biol 2024, 87, 102829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudy, O.J.; Nallathambi, A.; Kinjo, T.; Randolph, N.Z.; Kuhlman, B. In silico evolution of autoinhibitory domains for a PD-L1 antagonist using deep learning models. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2023, 120, e2307371120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLure, R.J.; Radford, S.E.; Brockwell, D.J. High-throughput directed evolution: a golden era for protein science. Trends in Chemistry 2022, 4, 378–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, Z.J. EnzyHTP Computational Directed Evolution with Adaptive Resource Allocation. J Chem Inf Model 2023, 63, 5650–5659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orsi, E.; Schada von Borzyskowski, L.; Noack, S.; Nikel, P.I.; Lindner, S.N. Automated in vivo enzyme engineering accelerates biocatalyst optimization. Nat Commun 2024, 15, 3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, M.; Fleishman, S.J.; Jones, P.R.; Dandekar, T.; Bencurova, E. Computational Enzyme Engineering Pipelines for Optimized Production of Renewable Chemicals. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 2021, 9, 673005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanella, R.; Kovacevic, G.; Doffini, V.; Fernandez de Santaella, J.; Nash, M.A. High-throughput screening, next generation sequencing and machine learning: advanced methods in enzyme engineering. Chem Commun (Camb) 2022, 58, 2455–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Tao, C.; Shen, X.; Sun, X.; Wang, J.; Yuan, Q. Unlocking the potential of enzyme engineering via rational computational design strategies. Biotechnol Adv 2024, 73, 108376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardi, R.C.; Melo, M.C.R.; Schulten, K. Enhanced sampling techniques in molecular dynamics simulations of biological systems. Biochim Biophys Acta 2015, 1850, 872–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J. Advanced Sampling Methods for Multiscale Simulation of Disordered Proteins and Dynamic Interactions. Biomolecules 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, R.; Wei, G.; Ma, B.; Nussinov, R. Replica Exchange Molecular Dynamics: A Practical Application Protocol with Solutions to Common Problems and a Peptide Aggregation and Self-Assembly Example. Methods Mol Biol 2018, 1777, 101–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blumer, O.; Reuveni, S.; Hirshberg, B. Combining stochastic resetting with Metadynamics to speed-up molecular dynamics simulations. Nat Commun 2024, 15, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiman, D.E.; Nadeem, H.; Shukla, D. Adaptive Sampling Methods for Molecular Dynamics in the Era of Machine Learning. J Phys Chem B 2023, 127, 10669–10681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, C.L., 3rd; MacKerell, A.D., Jr.; Post, C.B.; Nilsson, L. Biomolecular dynamics in the 21st century. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj 2024, 1868, 130534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrink, S.J.; Monticelli, L.; Melo, M.N.; Alessandri, R.; Tieleman, D.P.; Souza, P.C.T. Two decades of Martini: Better beads, broader scope. WIREs Computational Molecular Science 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjolbye, L.R.; Pereira, G.P.; Bartocci, A.; Pannuzzo, M.; Albani, S.; Marchetto, A.; Jimenez-Garcia, B.; Martin, J.; Rossetti, G.; Cecchini, M.; et al. Towards design of drugs and delivery systems with the Martini coarse-grained model. QRB Discov 2022, 3, e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periole, X.; Marrink, S.J. The Martini coarse-grained force field. Methods Mol Biol 2013, 924, 533–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacCallum, J.L.; Hu, S.; Lenz, S.; Souza, P.C.T.; Corradi, V.; Tieleman, D.P. An implementation of the Martini coarse-grained force field in OpenMM. Biophys J 2023, 122, 2864–2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Togashi, Y.; Flechsig, H. Coarse-Grained Protein Dynamics Studies Using Elastic Network Models. Int J Mol Sci 2018, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Abdelmoneim, A.A.; Liang, Z.; Wang, L.; Jin, J.; Dai, Q.; Ye, F. Elastic network models and molecular dynamic simulations reveal the molecular basis of allosteric regulation in ubiquitin-specific protease 7 (USP7). Comput Biol Med 2023, 162, 107068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leioatts, N.; Romo, T.D.; Grossfield, A. Elastic Network Models are Robust to Variations in Formalism. J Chem Theory Comput 2012, 8, 2424–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, J.E.; Hynninen, A.P.; Phillips, J.C.; Schulten, K. Early Experiences Porting the NAMD and VMD Molecular Simulation and Analysis Software to GPU-Accelerated OpenPOWER Platforms. High Perform Comput (2016) 2016, 9945, 188–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, M.; Maldonado, A.M.; Durrant, J.D. From byte to bench to bedside: molecular dynamics simulations and drug discovery. BMC Biol 2023, 21, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, M.; Herbordt, M.C. Molecular Dynamics Simulations on High-Performance Reconfigurable Computing Systems. ACM Trans Reconfigurable Technol Syst 2010, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.; Allen, J.E.; Yang, Y.; Drew Bennett, W.F.; Gokhale, M.; Moshiri, N.; Rosing, T.S. Accelerators for Classical Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Biomolecules. J Chem Theory Comput 2022, 18, 4047–4069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollingsworth, S.A.; Dror, R.O. Molecular Dynamics Simulation for All. Neuron 2018, 99, 1129–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzi, V.; Aureli, S.; Ansari, N.; Gervasio, F.L. OneOPES, a Combined Enhanced Sampling Method to Rule Them All. J Chem Theory Comput 2023, 19, 5731–5742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doerr, S.; Majewski, M.; Perez, A.; Kramer, A.; Clementi, C.; Noe, F.; Giorgino, T.; De Fabritiis, G. TorchMD: A Deep Learning Framework for Molecular Simulations. J Chem Theory Comput 2021, 17, 2355–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelaez, R.P.; Simeon, G.; Galvelis, R.; Mirarchi, A.; Eastman, P.; Doerr, S.; Tholke, P.; Markland, T.E.; De Fabritiis, G. TorchMD-Net 2.0: Fast Neural Network Potentials for Molecular Simulations. J Chem Theory Comput 2024, 20, 4076–4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thaler, S.; Zavadlav, J. Learning neural network potentials from experimental data via Differentiable Trajectory Reweighting. Nat Commun 2021, 12, 6884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, G.S.; Choi, J.Y.; Lee, S.M. Active learning of neural network potentials for rare events. Digital Discovery 2024, 3, 514–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duignan, T.T. The Potential of Neural Network Potentials. ACS Phys Chem Au 2024, 4, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaptan, S.; Vattulainen, I. Machine learning in the analysis of biomolecular simulations. Advances in Physics: X 2022, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustali, J.; Yasuda, I.; Hirano, Y.; Yasuoka, K.; Gautieri, A.; Arai, N. Unsupervised deep learning for molecular dynamics simulations: a novel analysis of protein-ligand interactions in SARS-CoV-2 M(pro). RSC Adv 2023, 13, 34249–34261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.; Luber, S. Trajectory-based machine learning method and its application to molecular dynamics. Molecular Physics 2020, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prašnikar, E.; Ljubič, M.; Perdih, A.; Borišek, J. Machine learning heralding a new development phase in molecular dynamics simulations. Artificial Intelligence Review 2024, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.Y. Comprehensive assessment of flexible-ligand docking algorithms: current effectiveness and challenges. Brief Bioinform 2018, 19, 982–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Chen, E.A.; Zhang, Y. Protein-Ligand Docking in the Machine-Learning Era. Molecules 2022, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.Y.; Zou, X. Advances and challenges in protein-ligand docking. Int J Mol Sci 2010, 11, 3016–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, P.H.M.; Sodero, A.C.R.; Jofily, P.; Silva-Jr, F.P. Key Topics in Molecular Docking for Drug Design. Int J Mol Sci 2019, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palacio-Rodriguez, K.; Lans, I.; Cavasotto, C.N.; Cossio, P. Exponential consensus ranking improves the outcome in docking and receptor ensemble docking. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanes-Mira, C.; Fernandez-Aguado, P.; de Andres-Lopez, J.; Fernandez-Carvajal, A.; Ferrer-Montiel, A.; Fernandez-Ballester, G. Comprehensive Survey of Consensus Docking for High-Throughput Virtual Screening. Molecules 2022, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, I.M.; Chakrabarti, S. MetaDOCK: A Combinatorial Molecular Docking Approach. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 5850–5860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, L.C.; Rodrigues, J.; Dobbs, D.; Honavar, V.; Bonvin, A. Template-based protein-protein docking exploiting pairwise interfacial residue restraints. Brief Bioinform 2017, 18, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Guo, F.; Wang, E.; Tang, J. ComDock: A novel approach for protein-protein docking with an efficient fusing strategy. Comput Biol Med 2023, 167, 107660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, P.; Pozzati, G.; Elofsson, A. Improved prediction of protein-protein interactions using AlphaFold2. Nat Commun 2022, 13, 1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneidman-Duhovny, D.; Rossi, A.; Avila-Sakar, A.; Kim, S.J.; Velazquez-Muriel, J.; Strop, P.; Liang, H.; Krukenberg, K.A.; Liao, M.; Kim, H.M.; et al. A method for integrative structure determination of protein-protein complexes. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 3282–3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchiya, Y.; Yamamori, Y.; Tomii, K. Protein-protein interaction prediction methods: from docking-based to AI-based approaches. Biophys Rev 2022, 14, 1341–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Souza Neto, L.R.; Moreira-Filho, J.T.; Neves, B.J.; Maidana, R.; Guimaraes, A.C.R.; Furnham, N.; Andrade, C.H.; Silva, F.P., Jr. In silico Strategies to Support Fragment-to-Lead Optimization in Drug Discovery. Front Chem 2020, 8, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.X.; Wang, Z.Z.; Wang, F.; Hao, G.F.; Yang, G.F. ACFIS 2.0: an improved web-server for fragment-based drug discovery via a dynamic screening strategy. Nucleic Acids Res 2023, 51, W25–W32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouchlis, V.D.; Afantitis, A.; Serra, A.; Fratello, M.; Papadiamantis, A.G.; Aidinis, V.; Lynch, I.; Greco, D.; Melagraki, G. Advances in de Novo Drug Design: From Conventional to Machine Learning Methods. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powers, A.S.; Yu, H.H.; Suriana, P.; Koodli, R.V.; Lu, T.; Paggi, J.M.; Dror, R.O. Geometric Deep Learning for Structure-Based Ligand Design. ACS Cent Sci 2023, 9, 2257–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukaidaisi, M.; Vu, A.; Grantham, K.; Tchagang, A.; Li, Y. Multi-Objective Drug Design Based on Graph-Fragment Molecular Representation and Deep Evolutionary Learning. Front Pharmacol 2022, 13, 920747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opo, F.; Rahman, M.M.; Ahammad, F.; Ahmed, I.; Bhuiyan, M.A.; Asiri, A.M. Structure based pharmacophore modeling, virtual screening, molecular docking and ADMET approaches for identification of natural anti-cancer agents targeting XIAP protein. Sci Rep 2021, 11, 4049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, D.; Biancaniello, C.; Argenio, M.A.; Facchiano, A. Drug Design by Pharmacophore and Virtual Screening Approach. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 2022, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyano-Gomez, P.; Lehtonen, J.V.; Pentikainen, O.T.; Postila, P.A. Building shape-focused pharmacophore models for effective docking screening. J Cheminform 2024, 16, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieslak, M.; Danel, T.; Krzysztynska-Kuleta, O.; Kalinowska-Tluscik, J. Machine learning accelerates pharmacophore-based virtual screening of MAO inhibitors. Sci Rep 2024, 14, 8228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visan, A.I.; Negut, I. Integrating Artificial Intelligence for Drug Discovery in the Context of Revolutionizing Drug Delivery. Life (Basel) 2024, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turon, G.; Hlozek, J.; Woodland, J.G.; Kumar, A.; Chibale, K.; Duran-Frigola, M. First fully-automated AI/ML virtual screening cascade implemented at a drug discovery centre in Africa. Nat Commun 2023, 14, 5736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qureshi, R.; Irfan, M.; Gondal, T.M.; Khan, S.; Wu, J.; Hadi, M.U.; Heymach, J.; Le, X.; Yan, H.; Alam, T. AI in drug discovery and its clinical relevance. Heliyon 2023, 9, e17575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, J.T.; Freemont, P.S. Computational protein design with backbone plasticity. Biochem Soc Trans 2016, 44, 1523–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.; Kortemme, T. Recent advances in de novo protein design: Principles, methods, and applications. J Biol Chem 2021, 296, 100558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, J.L.; Juergens, D.; Bennett, N.R.; Trippe, B.L.; Yim, J.; Eisenach, H.E.; Ahern, W.; Borst, A.J.; Ragotte, R.J.; Milles, L.F.; et al. De novo design of protein structure and function with RFdiffusion. Nature 2023, 620, 1089–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, N.R.; Coventry, B.; Goreshnik, I.; Huang, B.; Allen, A.; Vafeados, D.; Peng, Y.P.; Dauparas, J.; Baek, M.; Stewart, L.; et al. Improving de novo protein binder design with deep learning. Nat Commun 2023, 14, 2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kortemme, T. De novo protein design-From new structures to programmable functions. Cell 2024, 187, 526–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Rienzo, L.; Milanetti, E.; Testi, C.; Montemiglio, L.C.; Baiocco, P.; Boffi, A.; Ruocco, G. A novel strategy for molecular interfaces optimization: The case of Ferritin-Transferrin receptor interaction. Comput Struct Biotechnol J 2020, 18, 2678–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gainza, P.; Wehrle, S.; Van Hall-Beauvais, A.; Marchand, A.; Scheck, A.; Harteveld, Z.; Buckley, S.; Ni, D.; Tan, S.; Sverrisson, F.; et al. De novo design of protein interactions with learned surface fingerprints. Nature 2023, 617, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, S.; Mittal, N.; Bhat, A.; Adiga, R.S.; Ganesan, A.; Nagarajan, D.; Varadarajan, R. Improved Prediction of Stabilizing Mutations in Proteins by Incorporation of Mutational Effects on Ligand Binding. Proteins 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, F.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wen, Y.; Li, M. Assessing computational tools for predicting protein stability changes upon missense mutations using a new dataset. Protein Sci 2024, 33, e4861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaabjerg, L.M.; Kassem, M.M.; Good, L.L.; Jonsson, N.; Cagiada, M.; Johansson, K.E.; Boomsma, W.; Stein, A.; Lindorff-Larsen, K. Rapid protein stability prediction using deep learning representations. Elife 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musil, M.; Stourac, J.; Bendl, J.; Brezovsky, J.; Prokop, Z.; Zendulka, J.; Martinek, T.; Bednar, D.; Damborsky, J. FireProt: web server for automated design of thermostable proteins. Nucleic Acids Res 2017, 45, W393–W399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musil, M.; Jezik, A.; Horackova, J.; Borko, S.; Kabourek, P.; Damborsky, J.; Bednar, D. FireProt 2.0: web-based platform for the fully automated design of thermostable proteins. Brief Bioinform 2023, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, N.A.; Li, B.A.; McCully, M.E. The stability and dynamics of computationally designed proteins. Protein Eng Des Sel 2022, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomson, R.E.S.; Carrera-Pacheco, S.E.; Gillam, E.M.J. Engineering functional thermostable proteins using ancestral sequence reconstruction. J Biol Chem 2022, 298, 102435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumida, K.H.; Nunez-Franco, R.; Kalvet, I.; Pellock, S.J.; Wicky, B.I.M.; Milles, L.F.; Dauparas, J.; Wang, J.; Kipnis, Y.; Jameson, N.; et al. Improving Protein Expression, Stability, and Function with ProteinMPNN. J Am Chem Soc 2024, 146, 2054–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, D.; Liu, Y.; Kong, R.; Yu, Z.; Lu, S.; Zhang, J. Computational elucidation of allosteric communication in proteins for allosteric drug design. Drug Discov Today 2022, 27, 2226–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verkhivker, G.M.; Agajanian, S.; Hu, G.; Tao, P. Allosteric Regulation at the Crossroads of New Technologies: Multiscale Modeling, Networks, and Machine Learning. Front Mol Biosci 2020, 7, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheik Amamuddy, O.; Veldman, W.; Manyumwa, C.; Khairallah, A.; Agajanian, S.; Oluyemi, O.; Verkhivker, G.; Tastan Bishop, O. Integrated Computational Approaches and Tools forAllosteric Drug Discovery. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Vishweshwaraiah, Y.L.; Dokholyan, N.V. Design and engineering of allosteric communications in proteins. Curr Opin Struct Biol 2022, 73, 102334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, S.B.; Samanta, D. Engineering protein-based therapeutics through structural and chemical design. Nat Commun 2023, 14, 2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvisi, N.; de Vries, R. Biomedical applications of solid-binding peptides and proteins. Mater Today Bio 2023, 19, 100580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vymetal, J.; Mertova, K.; Bousova, K.; Sulc, J.; Tripsianes, K.; Vondrasek, J. Fusion of two unrelated protein domains in a chimera protein and its 3D prediction: Justification of the x-ray reference structures as a prediction benchmark. Proteins 2022, 90, 2067–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, K.; Ikura, M. Domain fusion analysis by applying relational algebra to protein sequence and domain databases. BMC Bioinformatics 2003, 4, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zaro, J.L.; Shen, W.C. Fusion protein linkers: property, design and functionality. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 2013, 65, 1357–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Zhao, K.; Liu, D.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, G. Multi-domain and complex protein structure prediction using inter-domain interactions from deep learning. Commun Biol 2023, 6, 1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferruz, N.; Noske, J.; Hocker, B. Protlego: a Python package for the analysis and design of chimeric proteins. Bioinformatics 2021, 37, 3182–3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Paz, F.M.; Del Moral, S.; Morales-Arrieta, S.; Ayala, M.; Trevino-Quintanilla, L.G.; Olvera-Carranza, C. Multidomain chimeric enzymes as a promising alternative for biocatalysts improvement: a minireview. Mol Biol Rep 2024, 51, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, R.A.; Ambrosetti, F.; Bonvin, A.; Colwell, L.J.; Kelm, S.; Kumar, S.; Krawczyk, K. Computational approaches to therapeutic antibody design: established methods and emerging trends. Brief Bioinform 2020, 21, 1549–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; McFee, M.; Fang, Q.; Abdin, O.; Kim, P.M. Computational and artificial intelligence-based methods for antibody development. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2023, 44, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madsen, A.V.; Mejias-Gomez, O.; Pedersen, L.E.; Preben Morth, J.; Kristensen, P.; Jenkins, T.P.; Goletz, S. Structural trends in antibody-antigen binding interfaces: a computational analysis of 1833 experimentally determined 3D structures. Comput Struct Biotechnol J 2024, 23, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutchinson, M.; Ruffolo, J.A.; Haskins, N.; Iannotti, M.; Vozza, G.; Pham, T.; Mehzabeen, N.; Shandilya, H.; Rickert, K.; Croasdale-Wood, R.; et al. Toward enhancement of antibody thermostability and affinity by computational design in the absence of antigen. MAbs 2024, 16, 2362775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaczmarski, J.A.; Mitchell, J.A.; Spence, M.A.; Vongsouthi, V.; Jackson, C.J. Structural and evolutionary approaches to the design and optimization of fluorescence-based small molecule biosensors. Curr Opin Struct Biol 2019, 57, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quijano-Rubio, A.; Yeh, H.W.; Park, J.; Lee, H.; Langan, R.A.; Boyken, S.E.; Lajoie, M.J.; Cao, L.; Chow, C.M.; Miranda, M.C.; et al. De novo design of modular and tunable protein biosensors. Nature 2021, 591, 482–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, M. Design, Optimization and Application of Small Molecule Biosensor in Metabolic Engineering. Front Microbiol 2017, 8, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Sharma, A.; Ahmed, A.; Sundramoorthy, A.K.; Furukawa, H.; Arya, S.; Khosla, A. Recent Advances in Electrochemical Biosensors: Applications, Challenges, and Future Scope. Biosensors (Basel) 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naresh, V.; Lee, N. A Review on Biosensors and Recent Development of Nanostructured Materials-Enabled Biosensors. Sensors (Basel) 2021, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, C.; Stogios, P.J.; Savchenko, A.; Mahadevan, R. Computation-guided transcription factor biosensor specificity engineering for adipic acid detection. Comput Struct Biotechnol J 2024, 23, 2211–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markus, B.; C, G.C.; Andreas, K.; Arkadij, K.; Stefan, L.; Gustav, O.; Elina, S.; Radka, S. Accelerating Biocatalysis Discovery with Machine Learning: A Paradigm Shift in Enzyme Engineering, Discovery, and Design. ACS Catal 2023, 13, 14454–14469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, E.L.; Finnigan, W.; France, S.P.; Green, A.P.; Hayes, M.A.; Hepworth, L.J.; Lovelock, S.L.; Niikura, H.; Osuna, S.; Romero, E.; et al. Biocatalysis. Nature Reviews Methods Primers 2021, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radley, E.; Davidson, J.; Foster, J.; Obexer, R.; Bell, E.L.; Green, A.P. Engineering Enzymes for Environmental Sustainability. Angew Chem Weinheim Bergstr Ger 2023, 135, e202309305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wu, J.; Zeng, X.; Shi, X.; Liu, L.; Chen, J. A comprehensive review on enzymatic biodegradation of polyethylene terephthalate. Environ Res 2024, 240, 117427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesbah, N.M. Industrial Biotechnology Based on Enzymes From Extreme Environments. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 2022, 10, 870083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Huang, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z. Accelerating therapeutic protein design with computational approaches toward the clinical stage. Comput Struct Biotechnol J 2023, 21, 2909–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewaisha, R.; Anderson, K.S. Immunogenicity of CRISPR therapeutics-Critical considerations for clinical translation. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 2023, 11, 1138596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, C.T.; Cohen, S. Reducing Immunogenicity by Design: Approaches to Minimize Immunogenicity of Monoclonal Antibodies. BioDrugs 2024, 38, 205–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingolfsson, H.I.; Bhatia, H.; Aydin, F.; Oppelstrup, T.; Lopez, C.A.; Stanton, L.G.; Carpenter, T.S.; Wong, S.; Di Natale, F.; Zhang, X.; et al. Machine Learning-Driven Multiscale Modeling: Bridging the Scales with a Next-Generation Simulation Infrastructure. J Chem Theory Comput 2023, 19, 2658–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Wei, G.W. Artificial intelligence-aided protein engineering: from topological data analysis to deep protein language models. Brief Bioinform 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poleto, M.D.; Lemkul, J.A. Integration of Experimental Data and Use of Automated Fitting Methods in Developing Protein Force Fields. Commun Chem 2022, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamenik, A.S.; Handle, P.H.; Hofer, F.; Kahler, U.; Kraml, J.; Liedl, K.R. Polarizable and non-polarizable force fields: Protein folding, unfolding, and misfolding. J Chem Phys 2020, 153, 185102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, P.E.; Guvench, O.; MacKerell, A.D., Jr. Current status of protein force fields for molecular dynamics simulations. Methods Mol Biol 2015, 1215, 47–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamezai, S.; Maresca di Serracapriola, G.; Morris, F.; Hildebrandt, R.; Amil, M.A.S.; Sporadicate i, G.E.M.T.; Ledesma-Amaro, R. Protein engineering in the computational age: An open source framework for exploring mutational landscapes in silico. Eng Biol 2023, 7, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrozo, A.; Borstnar, R.; Marloie, G.; Kamerlin, S.C. Computational protein engineering: bridging the gap between rational design and laboratory evolution. Int J Mol Sci 2012, 13, 12428–12460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, R.; Schwaneberg, U.; Roccatano, D. Computer-Aided Protein Directed Evolution: a Review of Web Servers, Databases and other Computational Tools for Protein Engineering. Comput Struct Biotechnol J 2012, 2, e201209008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carobene, A.; Padoan, A.; Cabitza, F.; Banfi, G.; Plebani, M. Rising adoption of artificial intelligence in scientific publishing: evaluating the role, risks, and ethical implications in paper drafting and review process. Clin Chem Lab Med 2024, 62, 835–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kargl, M.; Plass, M.; Muller, H. A Literature Review on Ethics for AI in Biomedical Research and Biobanking. Yearb Med Inform 2022, 31, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzinger, A.; Keiblinger, K.; Holub, P.; Zatloukal, K.; Muller, H. AI for life: Trends in artificial intelligence for biotechnology. N Biotechnol 2023, 74, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resnik, D.B.; Hosseini, M. The ethics of using artificial intelligence in scientific research: new guidance needed for a new tool. AI and Ethics 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maccaro, A.; Stokes, K.; Statham, L.; He, L.; Williams, A.; Pecchia, L.; Piaggio, D. Clearing the Fog: A Scoping Literature Review on the Ethical Issues Surrounding Artificial Intelligence-Based Medical Devices. J Pers Med 2024, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohyama, S.; Frohn, B.P.; Babl, L.; Schwille, P. Machine learning-aided design and screening of an emergent protein function in synthetic cells. Nat Commun 2024, 15, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, K.; Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Kai, L. Advancing synthetic biology through cell-free protein synthesis. Comput Struct Biotechnol J 2023, 21, 2899–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, D.B.; Budisa, N. Synthetic biology encompasses metagenomics, ecosystems, and biodiversity sustainability within its scope. Frontiers in Synthetic Biology 2023, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagata, M. SynBio: A Journal for Advancing Solutions to Global Challenges. SynBio 2023, 1, 190–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




