1. Introduction
Rice plays an important role in supporting over three billion people worldwide, with more than 6.7 billion bowls of rice consumed every day [
1]. According to data from [
2], the cultivation area was 0.71 million hectares and the production rate was 3.60 million metric tons in South Korea. Sustainable agriculture is a crucial global issue [
3]. Several strategies have been proposed, among which organic products called biostimulants are the most investigated and promising products to make agriculture more sustainable [
4,
5,
6,
7,
8,
9]. Plant extracts have recently been extensively researched as a practical strategy for improving the sustainability of crop production, particularly for the generation of biostimulants. Plant extracts have recently been extensively researched as a practical strategy for improving the sustainability of crop production, particularly for the generation of biostimulants [
3].
The 45 plant extracts are among the 1,642 eco-friendly agricultural materials recognized in Korea for soil improvement, growth promotion, and controlling diseases and insects [
10]. Korean agriculture books dating back to the 1920s describe farming systems that emphasize the need to use readily available natural resources to promote growth [
11]. These traditional organic methods can contribute to the advancement of the current organic farming technologies. However, several agricultural organic materials utilized in traditional farming have not been adequately studied for their impact on growth promotion [
12].
The number of studies attempting to determine the efficacy and potential of plant extracts has increased, but the current knowledge is still very limited to biological systems under learning, leaving aside the production systems and all potential applications, resulting in gaps that require further research. In addition to the application of plant extracts, it is necessary to understand how and where research in this area has been conducted and disseminated to provide useful information for planning, conducting, and publishing future research on the use of plant extracts in agriculture, with a focus on seedlings. The research hypothesis confirmed that less knowledge of plant extracts promotes growth physiology and chemical characteristics in rice plants.
The main objectives of the present study were to determine the effect of various extracts on the growth of rice; to investigate the effect of planting and spraying methods on the growth of rice treated with various plant extracts from water, ethanol, and boiling water extracts; to determine the effect of extract efficacy persistence, and to study the effect of selected water extracts on the growth of rice sprayed once on different sowing days.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Effect of Diverse Agricultural Materials on the Growth of Rice
In this study, the growth promotion rates of rice were assessed using 17 water extracts from 15 different plant materials at concentrations of 0.05, 0.1, 0.5, and 1% in Petri dish bioassays (
Table 1). All tested extracts boosted shoot length by 10-50%, root length by 10-70%, and seedling length by 10-50%. Shoot length was found to be 40-50% in three (
P. guajava, A. vera, G. max stem) of the 17 water extracts. Root length was significantly increased by 50-70% in two (
P. guajava and
A. sativum) of the 17 water extracts. Seedling length increased by 40-50% in four (
P. guajava, A. sativum, G. max stems and leaves) of the 17 water extracts tested. The bioassay results indicated that
P. guajava,
A. vera,
A. sativum,
M. sativa,
A. tuberosum, and
G. max (leaves and stems) extracts must studied further, as these seven extracts had the highest rate of rice growth. Furthermore, in vitro bioassays showed that 0.05, 0.1, and 0.5% doses improved rice growth at all concentrations. Regardless of the two metrics, the rice root length had a higher growth rate percentage than the rice shoot length in this study. A stimulated photosynthesis system reflects an enhanced food factory, which may have influenced the height and root length in all tested plants [
13,
14]. Previous studies have shown that enhanced root activity can be influenced by root growth promotion in
Arabidopsis [
15]. Promoted root growth further facilitates the uptake of nutrients from the rhizosphere, thus enabling plants to accumulate incremented doses of water and soluble nutrients, subsequently improving plant growth [
16].
2.2. Effect of Selected Extracts by Different Extraction and Planting Methods on Rice Growth
In the Petri dish assay, the extracts (
P. guajava, A. vera, A. sativum, M. sativa, A. tuberosum, and G. max (stems and leaves)) from the three extraction methods had a positive effect on rice growth at low concentrations compared to the control (data not shown). The reason for this was that the excluded extracts inhibited the growth of rice seedlings by 1% compared with the control. These results indicate the allelopathy of garlic, where low concentrations were growth-promoting, while higher concentrations inhibited the growth of the plants in question [
17]. Aqueous garlic extract consists of organosulfur compounds, in particular, “allicin,” which is a strong antioxidant [
18] and can inhibit the growth of recipient plants at higher concentrations [
19]. Of all the treatments, the extracts of
P. guajava and
M. sativa had the greatest effect on rice growth for all extraction techniques and concentrations.
In the direct seeding and transplanting methods (data not shown), the results showed a significant difference in plant height and shoot fresh weight of rice seedlings when using the water extract method compared to the other methods used in this experiment. Water extracts offer numerous advantages: they are environmentally friendly, easily degradable, non-persistent in soil, and non-toxic to animals and humans [
20]. This study showed that soil application was more effective in promoting rice growth than foliar treatment for all extracts in the transplantation method. When rice seedlings were treated with the lowest concentrations (0.05, 0.1, and 0.5%) of these extracts, plant height and shoot fresh weight increased. However, there were no significant differences in the shoot fresh weight of rice seedlings between treatments at 7 and 14 DAT. In another study, the effect of biostimulants was found to vary depending on species and variety. Environmental factors, dosage amount, and timing of application were also found to influence the effectiveness of extract applications [
21].
2.3. Effect of Persistence of Four Selected Extracts on Rice Growth
In this study, P. guajava, A. vera, A. sativum, and M. sativa were selected based on the results of a previous study (data not shown). For the water extracts, the results of shoot fresh weight stimulation showed that the Hopyeong variety had a significant difference in shoot fresh weight of direct seeding methods, ranging from 30 to 48%, whereas the Saenuri variety had a significant difference ranging from 35 to 48%. The fresh weight of the shoot was stimulated by the ethanol extracts by 28-38% for the Hopyeong variety and 30-35% for the Saenuri variety. In the transplanting trials, the water extracts with soil application increased the fresh weight of the shoots by 60-67% for the Hopyeong varieties and 60-65% for the Saenuri variety. Soil-applied ethanol extracts increased shoot fresh weight by 58-68% for Hopyeong and 55-63% for Saenuri. Foliar application of water extracts increased shoot fresh weight by 55-56% for Hopyeong and 55-60% for Saenuri. The ethanol extracts with foliar application increased shoot fresh weight by 55-65% in Hopyeong cultivars and almost 60% in Saenuri cultivars.
In both planting and extraction methods, the extracts of
P. guajava and
A. sativum showed the highest increase in shoot fresh weight in both cultivars compared with the control. The tested extracts had almost the same effect on the fresh weight of the shoots of both cultivars. The four extracts used in this study showed higher growth promotion rates than urea at 0.6% in transplanting tests; however, urea treatment had almost the same benefits as the tested plant extracts in direct seeding trials four weeks after treatment. The results showed that the fresh weight of shoots increased by up to 48% with direct sowing and by up to 68% with transplanting. Therefore, the transplantation method was more suitable for determining the influence of plant extracts on rice growth. A total yield of 46-50% was obtained with the transplanting method compared with 13-38% with direct seeding [
22]. Transplanted rice had a higher leaf chlorophyll content index, N concentration, total root length, and total root tip number than direct-seeded plants [
23]. Planting methods can also influence early root development, allometric distribution of root and shoot biomass, fruit development, and marketable yields [
24,
25].
The results of this study indicated that soil application influenced rice growth more effectively than foliar treatment for all extracts and planting methods. The soil application of
S. araboricola plant by garlic extract resulted in a significant increase in the number of leaves, leaf area, chlorophyll content of leaves, dry weight of total vegetation, and percentage of carbohydrates in leaves compared with foliar application of the plant [
26]. In addition, the highest shoot fresh weight of these rice varieties was obtained at 7 DAT in both water and ethanol treatments. Shoot fresh weight decreased slightly between 14 and 28 DAT. Similarly, [
12] showed that extracts of Chinese chives, soybean leaves, and stems had a greater effect on the fresh weight of lettuce shoots when applied 7 days after sowing (DAS) than when applied at 14 and 21 DAS. Biostimulants can act directly on plant physiology and metabolism or by improving soil conditions [
27].
2.4. Effect of Selected Water Extracts on Application Times in Various Growth Stages of Rice
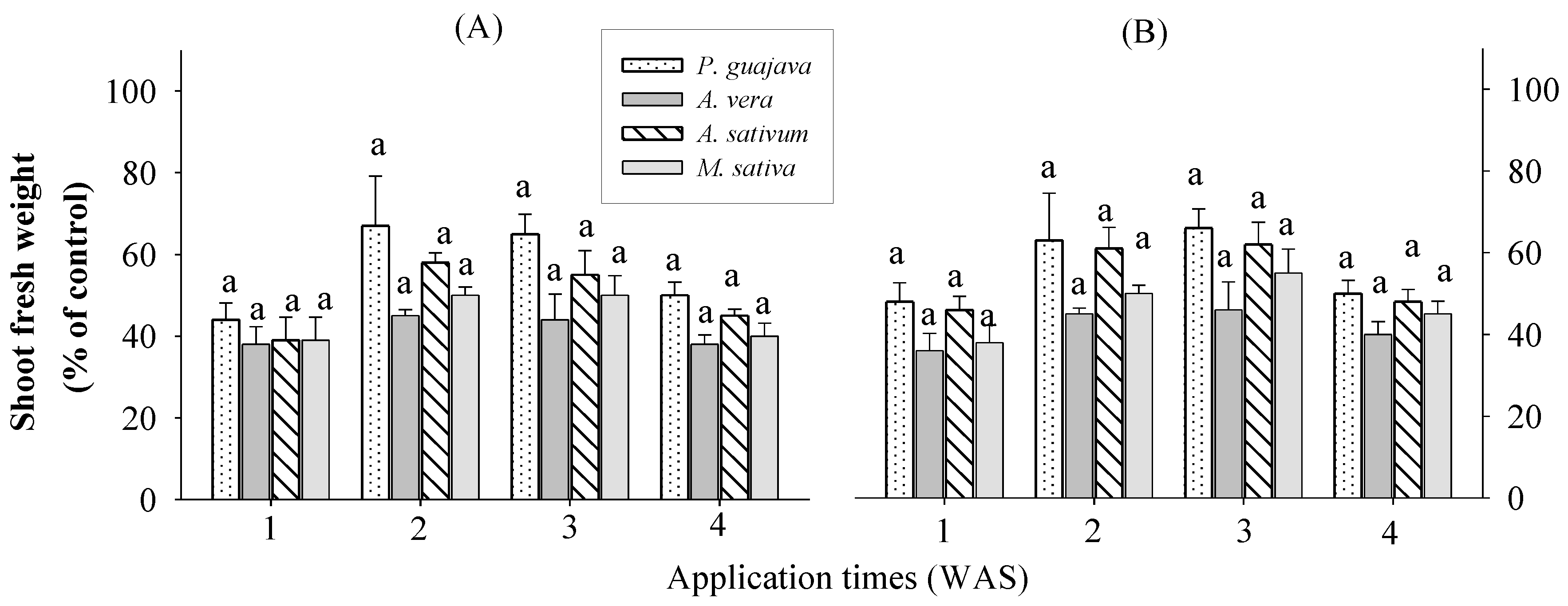
There were no significant differences between the crops and extracts at all application times (
Figure 1). Shoot fresh weight increased by 28-48% when sprayed one week after sowing (WAS); 35-67% when sprayed 2 WAS; 36-66% when sprayed 3 WAS; and 26-50% when sprayed 4 WAS in rice. This means that all these extracts can increase the fresh weight of rice shoots at any growth stage and application time. The treated eggplants showed stimulatory responses in terms of growth and physiology depending on the repetition of the aqueous garlic bulb extract and the growth stage of the plants [
28]. The highest shoot fresh weight values were observed in response to 0.1 and 0.5%
P. guajava extract, followed by
A. sativum extract in the rice plant. Garlic contains at least 33 sulfur compounds, enzymes, vitamins B and C, minerals (such as Na, K, Zn, P, Mn, Mg, Ca, and Fe), carbohydrates, saponins, alkaloids, flavonoids, and free sugars (such as sucrose, fructose, and glucose) [
29,
30]. Guava leaves are rich in nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium, depending on the month of growth [
31], which supports the finding that guava leaf compost results in the best growth of the Temulawak plant (
Curcuma xanthorrhiza Roxb). Therefore, it provides a balanced source of nutrients for plant growth.
2.5. Effect of Selected Water Extracts on Secondary Metabolites in Rice at Different Application Times
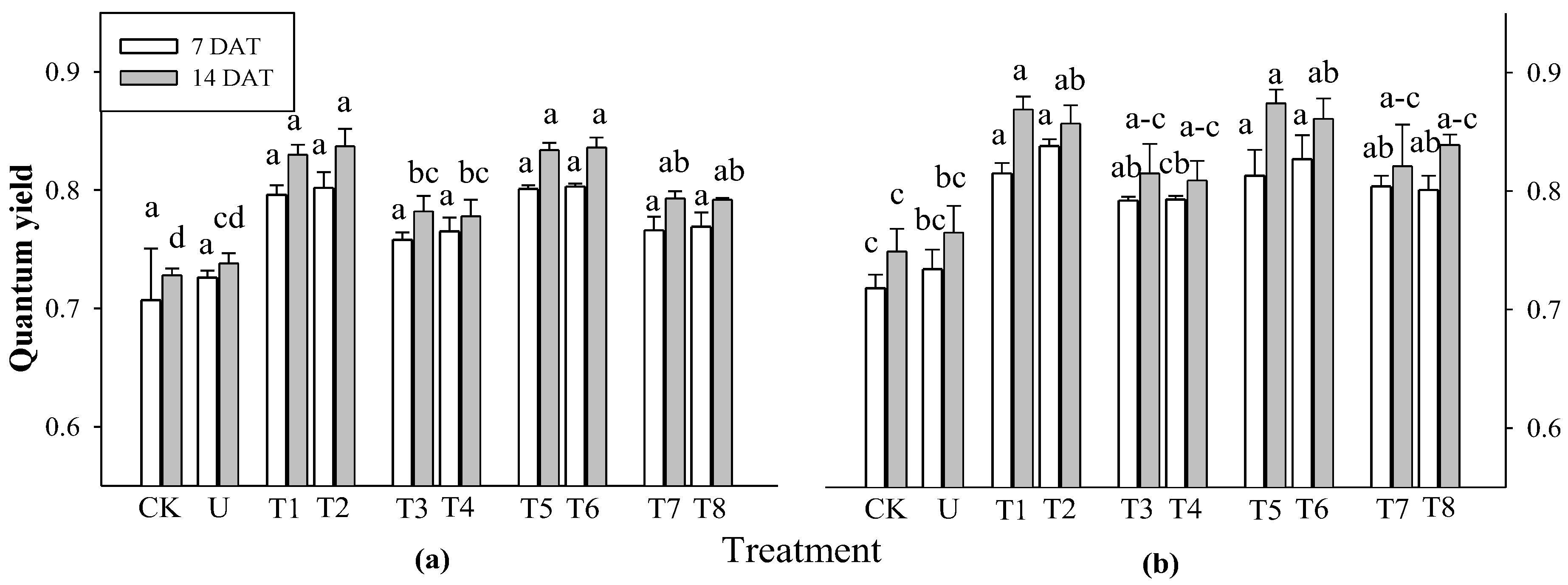
Based on the results of the previous experiment, rice plants were selected to evaluate photosynthetic efficiency at 7 and 14 DAT. At 7 DAT, there was a significant difference in rice at 3 WAS for all treatments, but no significant difference was observed in rice at 2 WAS (
Figure 2). At 14 DAT, there was a significant difference in the photosynthetic performance of the rice plants at 2 and 3 WAS. Photosynthetic performance increased in all extract treatments compared to that in the control and urea treatments. Among the extract treatments, the extracts of
P. guajava and
A. sativum resulted in a greater increase in photosynthesis in rice plants than the extracts of
A. vera and
M. sativa. These results strongly confirm that garlic root exudates increase chlorophyll content to enhance the absorption of light energy by tomatoes, and peppers, resulting in improved photosynthetic rates [
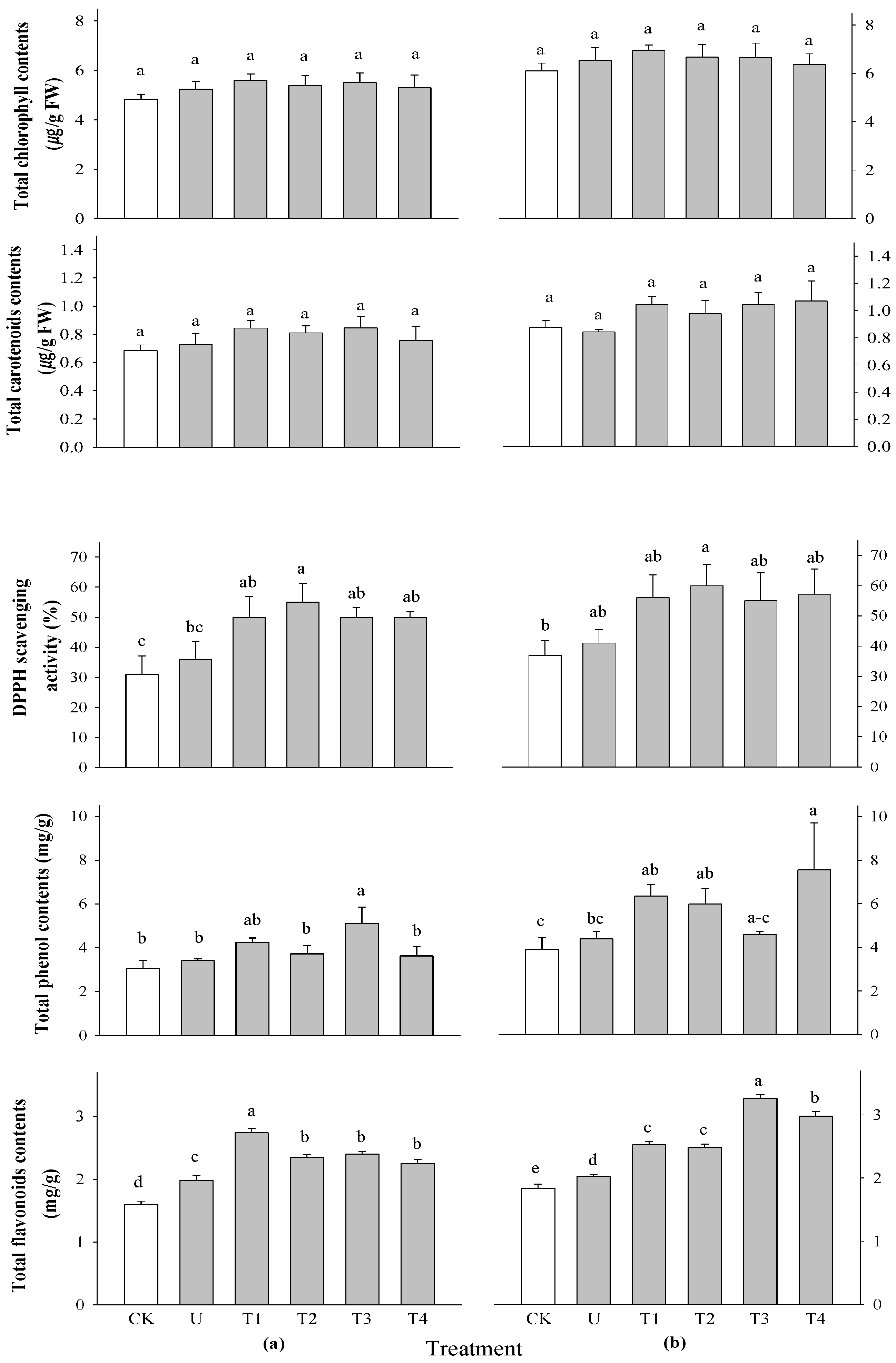
32]. None of the treatments did not differ significantly affected the total chlorophyll and carotenoid content of rice plants at any of the application times (
Figure 3).
There was a significant difference in the DPPH radical scavenging activity of rice at 2 WAS; however, no significant difference was observed at 3 WAS (
Figure 3). Moreover, the highest activity was found in rice treated with 0.5%
P. guajava extract. The significant DPPH radical scavenging activity of
F. religiose could be related to the presence of flavonoids and other polyphenols during extraction as shown in the current study [
33]. The antioxidant activity of the extracts evaluated by the DPPH assay was strongly correlated with the total phenolic and flavonoid content [
34]. There was no significant difference in the total phenolic content of the rice plants (
Figure 3), but there was a significant difference in the total flavonoid content of the rice plants at 2 and 3 WAS (
Figure 3). The highest flavonoid content was found in the 0.1%
P. guajava treatment at 2 WAS and the 0.1%
A. sativum treatment at 3WAS in the rice plant. The phenolic and flavonoid groups may be largely responsible for the antioxidant activities of the selected plant extracts [
35].
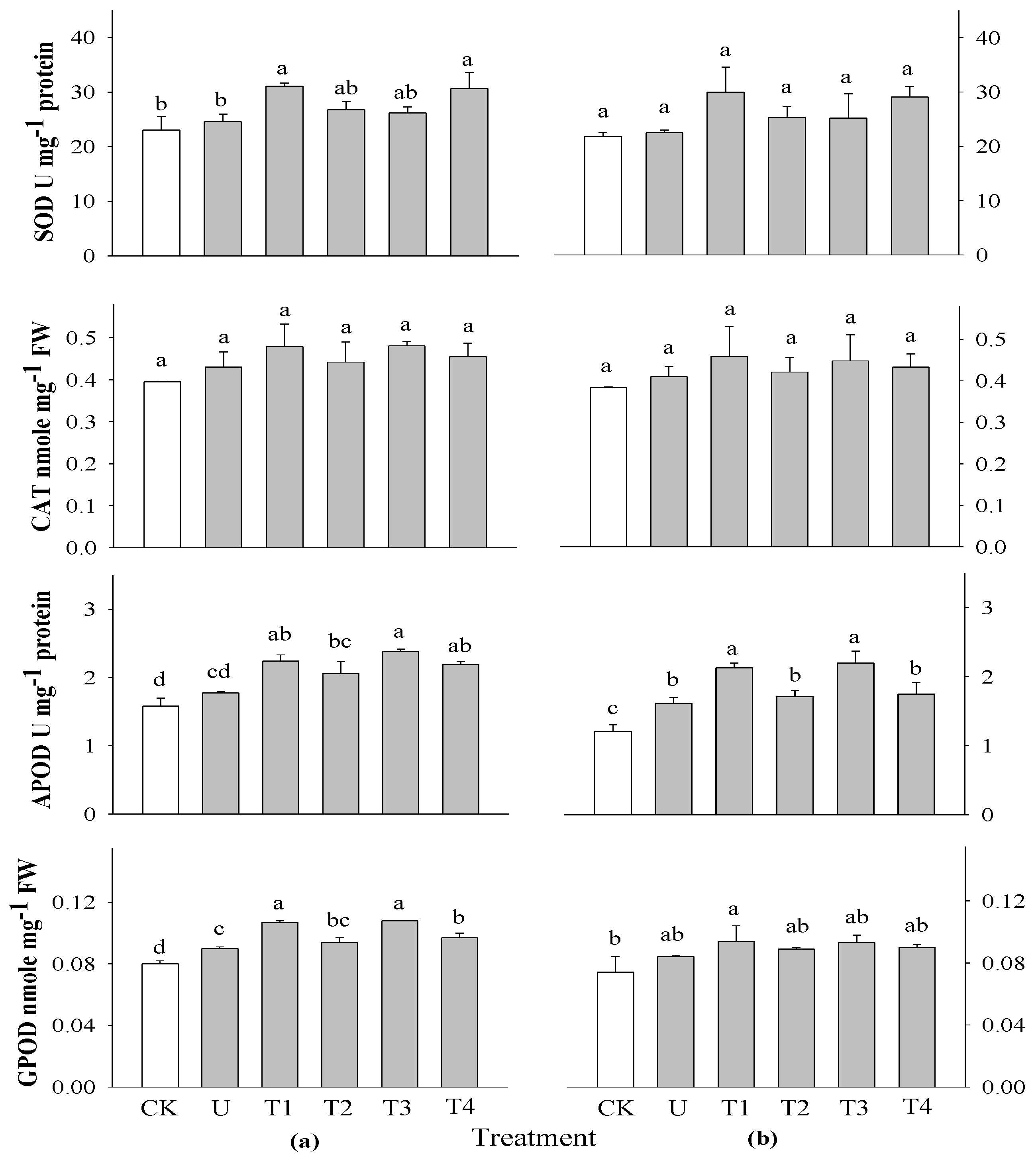
The activities of SOD, CAT, GPOD, and APOD were investigated 2 and 3 WAS in rice plants using extracts of
P. guajava and
A. sativum at concentrations of 0.1 and 0.5% (
Figure 4). There were no significant differences in SOD and CAT activities at all application times in rice plants compared with the control. This could not be related to SOD and CAT activities during the growth of rice. However, there were highly significant differences in APOD activity at different application times in rice plants compared with the control. The highest APOD activity was observed in rice treated with 0.1%
A. sativum at both 2 and 3 WAS. There was no significant difference in the GPOD activity of rice at 3 WAS, but there was a significant difference in rice at 2 WAS when compared to the control. The highest GPOD was observed in the 0.1%
P. guajava and
A. sativum extract treatments at all application times. Spraying aqueous garlic extract stimulated the activity of antioxidant enzymes. Moderate application activated antioxidants and possibly reactive oxygen species (ROS), which led to enhanced plant growth; this was inhibited by a higher frequency of application [
28]. An increase in SOD and POD activities during the early stages of plant growth suggests an increase in oxidative stress [
36].
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Preparation of Plant Materials and Extraction Methods
Rice seeds (cv. Hopyeong) were provided by Jeollanamdo Agricultural Research and Extension Service. Seventeen plant materials were collected from the fields and purchased through the Chonnam Hanyaknonghyup Cooperation (
Table 2). The 17 plant extracts were prepared from plant species such as leaves of
Mentha arvense,
Centella asiatica,
Moringa oleifera,
Vigna radiata,
Vigna unguiculate,
Psidium guajava,
Aloe vera,
Allium tuberosum, aboveground plant parts of
Cyperus rotundus,
Medicago sativa, and
Perilla frutescens, roots of
Rheum undulatum, tubers of
Allium sativum, leaves and stems of
Glycine max (cv. Taegwang) as well as rice straw and hull (cv. Hopyeong).
Different plant species, including leaves, roots, tubers, and above-ground components were dried, crushed, and extracted using ethanol, boiling water, and water [
12]. For the water extract, 50 g of each agricultural material was homogenized in 1,000 mL of distilled water for 24 h. For the ethanol extract, 1,000 mL of ethanol was used for 24 h instead of distilled water. For the boiling water extract, 50 g of each agricultural material was dissolved in 1,000 mL of distilled water and the mixture was boiled at 100 °C for 30 min before being homogenized for 24 h. The extracts were filtered using a Whatman No. 1 polypropylene filter (45 × 50 cm) and then filtered through a double layer of Mira cloth (22-25 µm pore size). To ensure that the final concentration was 50%, each extract was evaporated using a rotary evaporator (N-1300, EYELA), and the concentrations were subsequently diluted with distilled water to obtain 0.05, 0.1, 0.5, and 1% concentrations. All extracts were stored in a refrigerator until further investigation.
3.2. Effect of Extracts from Diverse Agricultural Materials on the Growth of Rice
In the first phase of the experiment, rice (cv. Hopyeong) was used as a test crop, and different concentrations of 17 water extracts were evaluated (
Table 2). To begin the experiment, rice seeds were soaked in distilled water for 24 h. Ten milliliters of 0.05, 0.1, 0.5, and 1% concentrations of the extracts were placed in a double layer of Whatman No.1 filter paper in 90 mm diameter Petri dishes. Distilled water was used as the control. Ten rice seeds were added to each petri dish after the extractions. The Petri dishes were maintained at room temperature for a week. After seven days of treatment, shoot and root lengths were measured.
3.3. Effect of Selected Extracts by Different Extraction and Planting Methods on Rice Growth
Direct seeding and transplanting tests were performed under greenhouse conditions, and a Petri dish assay was also carried out in a growth chamber. The planting methods used included Petri dish bioassays, direct seedlings, and transplanting. P. guajava, A. vera, A. sativum, M. sativum, A. tuberosum, and G. max (stems and leaves) extracts were prepared using water, boiling water, and ethanol. The Petri dish assay was performed using the same procedure as the initial test.
The rice seeds were soaked in distilled water for 24 h. Commercial soil for rice nursery media (No.1 Sunghwa, South Korea) of approximately 130 g was filled into each pot (6 cm in height and 6 cm in diameter). For direct seeding, three rice seeds were placed in each pot after the soil had been filled. Three to five days later, selected 7 extracts were soil drenched with 10 mL per pot at concentrations of 0.05, 0.1, 0.5, and 1% into the soil. For transplanting, three rice seedlings were transplanted into each pot two weeks after sowing (three to four leaf stages). Seven selected extracts (10 mL per pot) with concentrations of 0.05, 0.1, 0.5, and 1% were applied either as a soil drench or via foliar application at three-five days after transplanting. Distilled water was used as the control. Urea at 0.6% was used for comparison to evaluate the growth effectiveness of the extracts. Plants were watered as required. The pots were kept in a greenhouse for two weeks after the extract treatments. The greenhouse conditions included 14 h of light and 10 h of darkness, with a day/night temperature of 30 ± 2 °C/20 ± 3 °C, 70% relative humidity, and photosynthetically active radiation (PAR) of 500 µmol m-2 s-1 PAR. Plant height was measured at 7 and 14 DAT, and shoot fresh weight was measured at 14 DAT.
3.4. Effect of Persistence of Four Selected Extracts on Rice Growth
Rice seeds (cv. Hopyeong, and Saenuri) were provided for research by the Jeollanamdo Agricultural Research and Extension Service. The two extraction methods used in these tests were water, and ethanol, whereas the planting methods included direct seeding, and transplanting.
P. guajava, A. vera, A. sativum, and
M. sativum were the four extracts chosen. Shoot fresh weight of rice was measured at weekly intervals on days 7, 14, 21, and 28 after treatment. All other procedures followed the same protocols described in
Section 3.3.
3.5. Effect of Selected Water Extracts on Application Times in Rice Crop
The growth-promoting effects of four water extracts at concentrations of 0.1 and 0.5% were investigated when applied at different growth stages of rice. The application times were different for each growth stage (1, 2, 3, and 4 weeks after sowing). Shoot fresh weight was measured at 14 DAT. The other producers remained consistent with those described in
Section 3.3.
3.6. Effect of Selected Water Extracts on Secondary Metabolites in Rice at Different Application Times
Three plants from each of the three replicates were sampled two weeks and three weeks after the application of the extracts. The leaf samples were immediately frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at -80 °C for subsequent biochemical analysis.
3.6.1. Determination of Quantum Yield, Total Chlorophyll and Carotenoid Contents
The chlorophyll α fluorescence of photosystem II (PSII), i.e., the quantum yield (Fv/Fm) of rice was measured at 7 and 14 DAT. At 2 and 3 weeks after sowing (WAS), each plant received 10 mL of water extracts at concentrations of 0.1 and 0.5% administered via a soil drench. At 7 and 14 DAT, the second leaves of the rice plants were selected for determination using a portable pulse modulation fluorometer (Fluorpen FP10, Photon Systems Instruments, Drásov, Czech Republic). Before the measurements, the fronts were darkened for 15 min and adjusted to open all antenna pigments.
Chlorophyll and carotenoid analyses were performed according to a previously described method [
12]. Seedling leaves (0.5 g) from each treatment group were ground in a 100% methanol solution. The extracts were centrifuged at 10,000 × g for 3 min, and the absorbance of the supernatant was measured spectrophotometrically at 665, 652, and 470 nm. The chlorophyll and carotenoid contents were calculated using the following equation:
3.6.2. Determination of DPPH Radical Scavenging Activity, Total Phenol, and Flavonoid Contents
DPPH radical scavenging activity and total phenol and flavonoid contents were determined according to a previously described method [
37]. These activities were analyzed after 0.5 g of the dried plant samples were mixed with 10 mL of 99.9% ethanol, shaken at 120 rpm for 24 h at 27 °C in a shaking bath and centrifuged at 13,000 rpm for 10 min (VS-24SMTI, high-speed refrigerated centrifuge, Vision Scientific Co. LTD).
To measure DPPH radical scavenging activity, 0.1 mL of the extract, 0.5 mL of a 0.1 M acetate buffer solution (pH 5.5), 0.25 mL of 0.5 mM DPPH (2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydarzyl) and 0.4 mL of ethanol were mixed at room temperature and allowed to react for 30 min. The mixed solution was analyzed using a UV spectrometer at 517 nm (SPECTROstar Nana, BMG LABTECH, GmbH). Ascorbic acid was used as a positive control and the DPPH radical scavenging activity of the extracts was calculated using the following formula:
Where Ac is the absorbance of the control, and As is the absorbance of the test sample [
38].
To determine the total phenol content, 0.2 mL of the extract was mixed with 0.6 mL distilled water and 0.2 mL Folin-Denis reagent and then shaken for 5 min. After 5 min, 0.2 mL of Na2CO3 was added and the mixed solution was allowed to stand for 1 h at room temperature and measured using a UV spectrophotometer at 640 nm (SPECTROstar Nana, BMG LABTECH, GmbH). The standard values were obtained with ferulic acid at 0-100 µg/mL and the values of total phenol were calculated as a standard curve. All values are expressed as the mean (mg of ferulic acid equivalents per g of extracted sample).
To measure total flavonoid content, 0.2 mL of the extract was mixed with 0.45 mL of ethanol (95%), 10% AlCl3 0.03 mL, 1 M potassium acetate 0.03 mL and 0.79 mL distilled water. The mixed solution was then allowed to stand for 40 min at room temperature and the absorbance was measured using a UV spectrophotometer at 640 nm (SPECTROstar Nana, BMG LABTECH, GmbH). The standard values were obtained with quercetic acid 0-5 µg/mL and the values of total flavonoids were calculated as a standard curve. All values are expressed as the mean (mg of quercetinic acid equivalents per g of extracted sample).
3.6.3. Determination of Antioxidant Activities
For enzyme extraction, frozen leaves (approximately 0.5 g) were homogenized with 3.75 mL of a 100 mM buffer solution (pH 7.5) containing 2 mM EDTA, 1% PVP and 1 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (PMSF, C7H7FO2S), crushed with a mortar and pestle and incubated at 14,000 g for 20 min in a refrigerated centrifuge (VS-24SMTI, high-speed refrigerated centrifuge, Vision Scientific Co. LTD).
Superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity was determined according to the method described in [
39] with some modifications [
40,
41]. A 230 µL reaction mixture contained 1.26 mM NBT (Nitroblue tetrazolium), 260 mM riboflavin, 260 µM methionine, 2 mM EDTA, 200 mM phosphate buffer (pH 7.0), and 20 µL of enzyme extract in a total volume of 300 µL. The test tubes containing the mixture were placed under light at 78 mmol photons s
-1 m
-2 for 10 min and the absorbance at 560 nm was recorded. A nonirradiated reaction mixture that did not develop color served as the control and its absorbance was subtracted from A560 of the reaction solution. One unit of SOD activity was defined as the amount of enzyme required to cause 50% inhibition of the NBT reduction rate at 560 nm (SPECTROstar Nano, BMG LABTECH, GmbH).
The activities of catalase (CAT) and guaiacol peroxidase (GPOD) were measured using a previously described method [
42,
43]. For CAT activity, the decomposition of H
2O
2 was measured by the decrease in absorbance at 240 nm for 1 min (SPECTROstar Nano, BMG LABTECH, GmbH). The reaction mixture contained 150 µL of 200 mM phosphate buffer (pH 7.0), 15 µL of 15 mM H
2O
2, 135 µL of distilled water, and 5 µL of enzyme extract in a total volume of 300 µL, which initiated the reaction. For GPOD activity, the oxidation of guaiacol was measured by the increase in absorbance at 470 nm for 1 min (SPECTROstar Nano, BMG LABTECH, GmbH). The reaction mixture contained 5 µL of 200 mM guaiacol, 280 µL of 200 mM phosphate buffer (pH 7.0), and 15 µL of enzyme extract. The reaction was initiated using 5 µL of 40 mM H
2O
2.
Ascorbate peroxidase (APOD) activity was assayed according to the method of [
44], using the initial rate of decrease in ascorbate concentration, as measured by its absorbance at 290 nm. The reaction mixture contained 150 µL of 200 mM phosphate buffer (pH 7.0), 30 µL of 5 mM ascorbate, 12 µL of 20 mM H
2O
2, 30 µL distilled water, and 15 µL enzyme extract in a total volume of 300 µL. The reaction was initiated by adding H
2O
2 and the change in absorbance was measured using a UV spectrophotometer (SPECTROstar Nano, BMG LABTECH, GmbH).
3.7. Experimental Design and Statistical Analysis
The experiment was designed with three replicates in a completely randomized design with a factorial layout. Multiple comparisons were conducted to evaluate the differences in the variables between the factors. Significant differences were evaluated using an analysis of variance (ANOVA) with a statistical computer program (Statistix version 8.0 software). When there was a significant difference, the means were separated using Tukey’s honestly significant difference (HSD) and Least significant difference (LSD) tests at α = 0.05.
4. Conclusions
This study found that plant extracts, especially water extracts, were more effective in promoting rice growth when applied as soil-applied than foliar-application. Transplanting methods were better suited for determining the influence of plant extracts on rice growth. All extracts increased the fresh weight of shoots in rice plants, with concentrations of 0.1 and 0.5% achieving the best growth promotion rates. The effectiveness of the extracts was maintained even after 14 days of treatment. Therefore, all extracts can be sprayed on rice plants at two- or three-week intervals. This study suggests that photosynthesis and antioxidant activity may play crucial roles in plant growth. This study showed that growth promotion rates are highly dependent on the types of materials and extraction methods used in the production of plant extracts, application methods, frequency of applications, concentration of extracts, and cultivation methods. This study suggests that the extracts can be used to promote plant growth in organic farming.
Author Contributions
Data curation, E.E.; writing-review and editing, Y.I.K. All authors read and agreed to the published version of the manuscripts.
Funding
“This research was supported by the Sunchon National University. This paper is part of the Ph.D. thesis by Ei Ei”.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article. The data presented in this study are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- IRRI (International Rice Research Institute). Annual Report 2010; Los Baños, Philippines, International Rice Research Institute, 2011; pp. 1–44. [Google Scholar]
- World Agricultural Production. Global Market Analysis. Foreign agricultural service, USDA, Circular Series WAP; 2023; pp. 8–23. [Google Scholar]
- Godlewska, K.; Ronga, D.; Michalak, I. Plant extracts – importance in sustainable agriculture. Italian Journal of Agronomy 2021, 16, 1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Pascale, S.; Rouphael, Y.; Colla, G. Plant biostimulants: Innovative tool for enhancing plant nutrition in organic farming. European Journal of Horticultural Science 2017, 82, 277–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dipak Kumar, H.; Aloke, P. Role of biostimulant formulations in crop production: an overview. International Journal of Agricultural Science and Veterinary Medicine 2020, 8, 8–46. [Google Scholar]
- Ertani, A.; Sambo, P.; Nicoletto, C.; Santagata, S.; Schiavon, M.; Nardi, S. The use of organic biostimulants in hot pepper plants to help low-input sustainable agriculture. Chemical and Biological Technologies in Agriculture 2015, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parađiković, N.; Teklić, T.; Zeljković, S.; Lisjak, M.; Špoljarević, M. Biostimulants research in some horticultural plant species - a review. Food and Energy Security 2018, 8, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouphael, Y.; Colla, G. Synergistic biostimulatory action: designing the next generation of plant biostimulants for sustainable agriculture. Frontiers Plant Science 2018, 871, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouphael, Y.; Colla, G. Toward a sustainable agriculture through plant biostimulants: from experimental data to practical applications. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RDA National Academy of Agricultural Science. 2016; p. 293.
- Guh, J.O.; Kim, M.H.; Kim, Y.J. “Ongoijisin” for modern application of technologies used in old agriculture books; RDA: Korea, 2011; p. 300. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Jang, S.J.; Kuk, Y.I. Growth promotion effects of plant extracts on various leafy vegetable crops. Horticultural Science and Technology 2019, 37, 322–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, P.; Nelson, L.; Klopper, J.W. Agricultural uses of plant biostimulants. Plant Soil 2014, 383, 3–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puga-Freitas, R.; Blouin, M. A review of the effects of soil organisms on plant hormone signaling pathways. Environmental and Experimental Botany 2015, 114, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lariguet, P.; Ranocha, P.; Meyer, M.D.; Barbier, O.; Penel, C.; Dunand, C. Identification of a hydrogen peroxide signaling pathway in the control of light-dependent germination in Arabidopsis. An International Journal of Plant Biology 2013, 238, 381–395. [Google Scholar]
- Candan, N.; Tarhan, L. Relationship among chlorophyll carotenoid content, antioxidant enzyme activities, and lipid peroxidation levels by Mg2+ deficiency in the Mentha pulegium leaves. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry 2003, 41, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Cheng, Z.; Meng, H.; Yang, X.; Ahmad, I. Allelopathic effect of decomposed garlic (Allium sativum L.) stalk on lettuce (L. Sativa var. crispa L.). Pakistan Journal of Botany 2013, 45, 225–233. [Google Scholar]
- Leelarungrayub, N.; Rattanapanone, V.; Chanarat, N.; Gebicki, J.M. Quantitative evaluation of the antioxidant properties of garlic and shallot preparations. Nutrition 2016, 22, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, F.; Cheng, Z.H.; Jin, R.; Zhou, L.Y. Allelopathy of methanol dissolved ingredient from garlic plant aqueous extracts. Journal of Northwest A&F University (Natural Science Edition) 2007, 35, 119–124. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Zhihui, C. Allium sativum extract as a biopesticide affecting pepper blight. International Journal of Vegetable Science 2009, 15, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunicki, E.; Grabowska, A.; Sekara, A.; Wojciechowska, R. The effect of cultivar type, time of cultivation, and biostimulant treatment on the yield of spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.). Folia Horticulturae Ann. 2010, 22, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leskovar, D.I.; Othman, Y.A. Direct seeding and transplanting influence root dynamics, morpho-physiology, yield, and heat quality of globe artichoke. Plants 2021, 10, 899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hongyan, L.; Weiqin, W.; Aibin, H.; Lixiao, N. Correlation of leaf and root senescence during ripening in dry seeded and transplanted rice. Rice Science 2018, 25, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanadzo, M.; Chiduza, C.; Mnkeni, P. Comparative response of direct seeded and transplanted maize (Zea mays L.) to nitrogen fertilization at Zanyokwe irrigation scheme, Eastern Cape, South Africa. African Journal of Agricultural Research 2009, 4, 689–694. [Google Scholar]
- Leskovar, D.; Cantliffe, D.; Stoffella, P. Root growth and root-shoot interaction in transplants and direct seeded pepper plants. Environmental and Experimental Botany 2019, 30, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumaa, R.M.A. The Effect of Some Natural Extracts on the Growth and Chemical Components of Schefflera araboricola Plant. MSc. Thesis, College of Agriculture, Cairo University, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Nardi, S.; Carletti, P.; Pizzeghello, D.; Muscolo, A. Biological activities of humic substances, in biophysico-chemical processes involving natural nonliving organic matter in environmental systems. In Part I. Fundamentals and impact of mineral-organic biota interactions on the formation, transformation, turnover, and storage of natural nonliving organic matter (NOM); Senesi, N., Xing, B., Huang, P.M., Eds.; John Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Muhammad, A.; Cheng, Z.; Sikandar, H.; Husain, A.; Muhammad, I.G.; Liu, T. Foliar spraying of aqueous garlic bulb extract stimulates growth and antioxidant enzyme activity in eggplant (Solanum melongena L.). Journal of Integrative Agriculture 2019, 18, 1001–1013. [Google Scholar]
- Bhandari, S.R.; Yoon, M.K.; Kwak, J.H. Contents of phytochemical constituents and antioxidant activity of 19 garlic (Allium sativum L.) parental lines and cultivars. Horticulture, Environment, and Biotechnology 2019, 55, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hamied, S.A.A.; El-Amary, E.I. Improving growth and productivity of “pear” trees using some natural plant extracts under North Sinai conditions. IOSR Journal of Agriculture and Veterinary Sciences 2015, 8, 01–09. [Google Scholar]
- Nautiyal, P.; Lal, S.; Singh, C.P. Effect of shoot pruning severity and plant spacing on leaf nutrient status and yield of guava cv. Pant Prabhat. International Journal of Basic and Applied Agricultural Research 2016, 14, 288–294. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.L.; Zhihui, C.; Wen, M.H.; Chun, G.H. Allelopathy of garlic root aqueous extracts and root exudates. Journal of Northwest A&F University (Natural Science Edition) 2007, 35, 87–92. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Baliyan, S.; Mukherjee, R.; Priyadarshini, A.; Vibhuti, A.; Gupta, A.; Pandey, R.P.; Chang, C.M. Determination of antioxidants by DPPH radical scavenging activity and quantitative phytochemical analysis of Ficus religiose. Journal of Molecules 2022, 27, 1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akullo, J.O.; Kiage-Mokua, B.N.; Nakimbugwe, D.; Ng’ang’a, J.; Kinyuru, J. Phytochemical profile and antioxidant activity of various solvent extracts of two varieties of ginger and garlic. Heliyon 2023, 9, e18806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryal, S.; Baniya, M.K.; Danekhu, K.; Kunwar, P.; Gurung, R.; Koirala, N. Total phenolic content, flavonoid content, and antioxidant potential of wild vegetables from Western Nepal. Journal of Plants 2019, 8, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, X.; Shen, D.; Oiu, Y.; Song, J. Diversity evaluation of morphological traits and allicin content in garlic (Allium sativum L.) from China. Euphytica 2014, 198, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.H. Increasement of Growth and Secondary Metabolites in Chicory (Cichorium intybus L.) Plants by Extraction and Application Methods of Agricultural By-products. MSc. Dissertation, Sunchon National University, South Korea, 2021; p. 56. (In Korean). [Google Scholar]
- Mahmood, S.K.; Abdulla, S.M.; Hassan, K.I.; Mahmood, A.B. Effect of some processing methods on the physiochemical properties of black mulberry. Euphrates Journal of Agricultural Science 2024, 16, 440–451. [Google Scholar]
- Giannopolitis, C.N.; Ries, S.K. Superoxide dismutase. 1. Occurrence in higher plants. Plant Physiology 1977, 59, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, S.R.; Choudhuri, M.A. Hydrogen peroxide metabolism as an index of water stress tolerance in jute. Physiologia Plantarum 1985, 65, 476–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Cui, S.; Li, J.; Kirkham, M.B. Protoplasmic factors, antioxidant responses, and chilling resistance in maize. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry 1995, 33, 567–575. [Google Scholar]
- Chance, B.; Maehly, A.C. Assay of catalases and peroxidases. Methods in Enzymology 1995, 2, 764–775. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J.; Huang, B. Involvement of antioxidants and lipid peroxidation in the adaptation of two cool-season grasses to localized drought stress. Environmental and Experimental Botany 2001, 45, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Asada, K. Ascorbate peroxidase in tea leaves: occurrence of two isozymes and the differences in their enzymatic and molecular properties. Plant and Cell Physiology 1989, 30, 987–998. [Google Scholar]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).