Submitted:
30 August 2024
Posted:
03 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Methodology
- Ethical statement:
- Type of the study:
- Place and date of the study:
- Collection of the samples:
- Detection of resistant patterns to the test antibiotics:
- Detection of impact of antibiotic resistance:
- In Silico analysis of the test antibiotics:
- Statistical Analysis
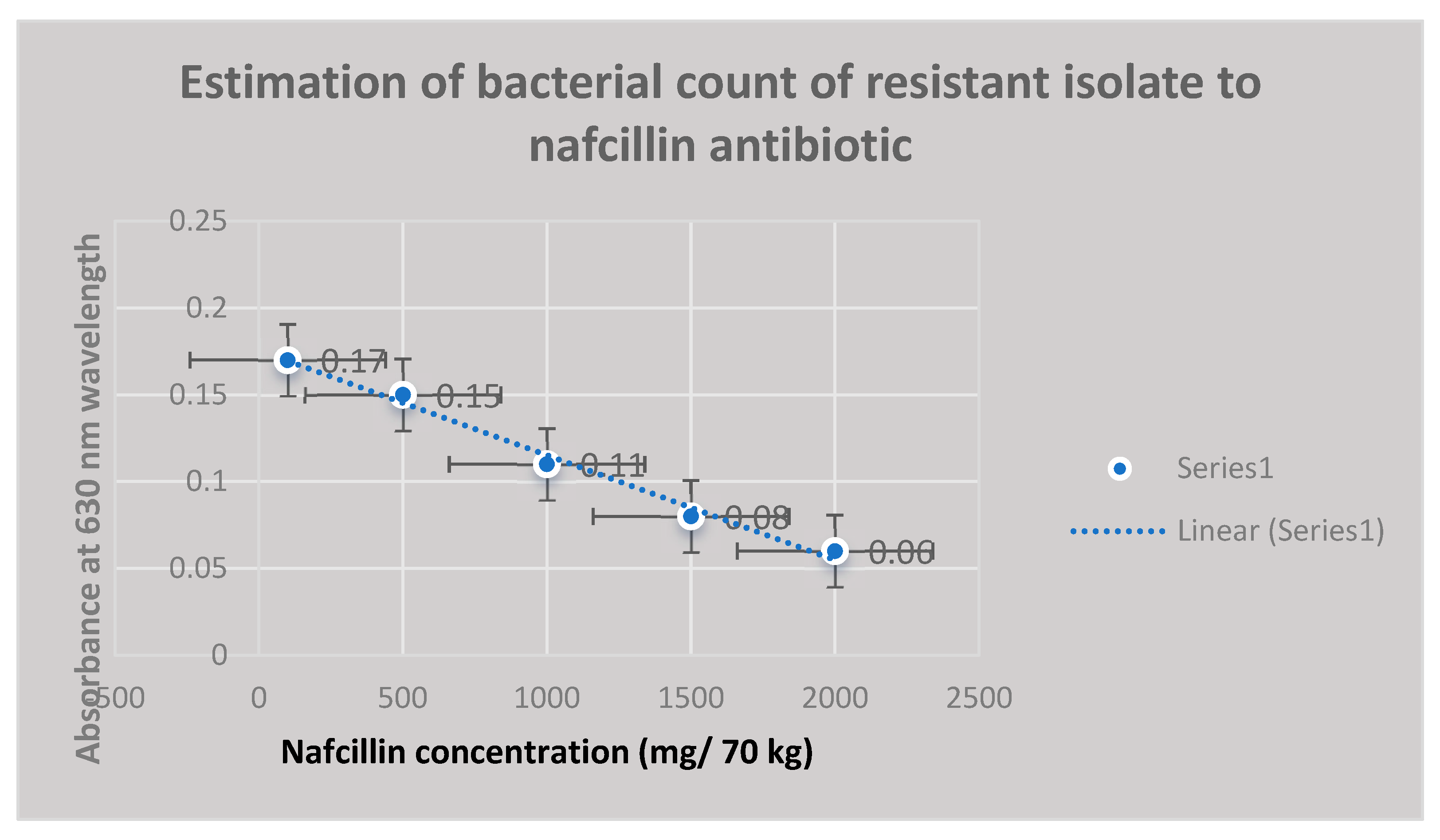
Results
Discussion
Conclusion
Funding
Conflict of interest/Competing of interests
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Consent for publication
Authors’ contributions
Data availability and material
Acknowledgement
References
- Lim JM, Singh SR, Duong MC, Legido-Quigley H, Hsu LY, Tam CC. Impact of national interventions to promote responsible antibiotic use: a systematic review. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2020 Jan 1;75(1):14-29. PMID: 31834401; PMCID: PMC6910191. [CrossRef]
- Baquero F, Martínez JL, F Lanza V, Rodríguez-Beltrán J, Galán JC, San Millán A, Cantón R, Coque TM. Evolutionary Pathways and Trajectories in Antibiotic Resistance. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2021 Dec 15;34(4):e0005019. Epub 2021 Jun 30. PMID: 34190572; PMCID: PMC8404696. [CrossRef]
- Iwu CD, Korsten L, Okoh AI. The incidence of antibiotic resistance within and beyond the agricultural ecosystem: A concern for public health. Microbiologyopen. 2020 Sep;9(9):e1035. Epub 2020 Jul 25. PMID: 32710495; PMCID: PMC7520999. [CrossRef]
- Larsson DGJ, Flach CF. Antibiotic resistance in the environment. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2022 May;20(5):257-269. Epub 2021 Nov 4. PMID: 34737424; PMCID: PMC8567979. [CrossRef]
- Muteeb G, Rehman MT, Shahwan M, Aatif M. Origin of Antibiotics and Antibiotic Resistance, and Their Impacts on Drug Development: A Narrative Review. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Nov 15;16(11):1615. PMID: 38004480; PMCID: PMC10675245. [CrossRef]
- Bengtsson-Palme J, Kristiansson E, Larsson DGJ. Environmental factors influencing the development and spread of antibiotic resistance. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2018 Jan 1;42(1):fux053. PMID: 29069382; PMCID: PMC5812547. [CrossRef]
- Jaén-Luchoro D, Busquets A, Karlsson R, Salvà-Serra F, Åhrén C, Karami N, Moore ERB. Genomic and Proteomic Characterization of the Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase (ESBL)-Producing Escherichia coli Strain CCUG 73778: A Virulent, Nosocomial Outbreak Strain. Microorganisms. 2020 Jun 13;8(6):893. PMID: 32545759; PMCID: PMC7355845. [CrossRef]
- Karkman A, Pärnänen K, Larsson DGJ. Fecal pollution can explain antibiotic resistance gene abundances in anthropogenically impacted environments. Nat Commun. 2019 Jan 8;10(1):80. PMID: 30622259; PMCID: PMC6325112. [CrossRef]
- Yu D, Ryu K, Zhi S, Otto SJG, Neumann NF. Naturalized Escherichia coli in Wastewater and the Co-evolution of Bacterial Resistance to Water Treatment and Antibiotics. Front Microbiol. 2022 May 30;13:810312. PMID: 35707173; PMCID: PMC9189398. [CrossRef]
- Martínez JL, Baquero F. What are the missing pieces needed to stop antibiotic resistance? Microb Biotechnol. 2023 Oct;16(10):1900-1923. Epub 2023 Jul 7. PMID: 37417823; PMCID: PMC10527211. [CrossRef]
- Emgård M, Mwangi R, Mayo C, Mshana E, Nkini G, Andersson R, Msuya SE, Lepp M, Muro F, Skovbjerg S. Tanzanian primary healthcare workers’ experiences of antibiotic prescription and understanding of antibiotic resistance in common childhood infections: a qualitative phenomenographic study. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2021 Jun 27;10(1):94. PMID: 34176486; PMCID: PMC8237496. [CrossRef]
- Selvarajan R, Obize C, Sibanda T, Abia ALK, Long H. Evolution and Emergence of Antibiotic Resistance in Given Ecosystems: Possible Strategies for Addressing the Challenge of Antibiotic Resistance. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Dec 24;12(1):28. PMID: 36671228; PMCID: PMC9855083. [CrossRef]
- Smith DR, Temime L, Opatowski L. Microbiome-pathogen interactions drive epidemiological dynamics of antibiotic resistance: A modeling study applied to nosocomial pathogen control. Elife. 2021 Sep 14;10:e68764. PMID: 34517942; PMCID: PMC8560094. [CrossRef]
- Gwenzi W. The ‘thanato-resistome’ - The funeral industry as a potential reservoir of antibiotic resistance: Early insights and perspectives. Sci Total Environ. 2020 Dec 20;749:141120. Epub 2020 Jul 25. PMID: 32836113; PMCID: PMC7381411. [CrossRef]
- Noel HR, Petrey JR, Palmer LD. Mobile genetic elements in Acinetobacter antibiotic-resistance acquisition and dissemination. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2022 Dec;1518(1):166-182. Epub 2022 Oct 31. PMID: 36316792; PMCID: PMC9771954. [CrossRef]
- Alves G, Ogurtsov A, Karlsson R, Jaén-Luchoro D, Piñeiro-Iglesias B, Salvà-Serra F, Andersson B, Moore ERB, Yu YK. Identification of Antibiotic Resistance Proteins via MiCId’s Augmented Workflow. A Mass Spectrometry-Based Proteomics Approach. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2022 Jun 1;33(6):917-931. Epub 2022 May 2. PMID: 35500907; PMCID: PMC9164240. [CrossRef]
- Smart JI, Corey GR, Stryjewski ME, Wang W, Barriere SL. Assessment of Minimum Inhibitory Concentrations of Telavancin by Revised Broth Microdilution Method in Phase 3 Hospital-Acquired Pneumonia/Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia Clinical Isolates. Infect Dis Ther. 2016 Dec;5(4):535-544. Epub 2016 Oct 7. PMID: 27718118; PMCID: PMC5125136. [CrossRef]
- Mira P, Yeh P, Hall BG. Estimating microbial population data from optical density. PLoS One. 2022 Oct 13;17(10):e0276040. PMID: 36228033; PMCID: PMC9562214. [CrossRef]
- Ciorba V.; Odone A.; Veronesi L.; Pasquarella C.; Signorelli C. Antibiotic resistance as a major public health concern: epidemiology and economic impact. Ann. Ig 2015, 27 (3), 562–579.
- Darwish RM, Matar SG, Snaineh AAA, Alsharif MR, Yahia AB, Mustafa HN, Hasabo EA. Impact of antimicrobial stewardship on antibiogram, consumption and incidence of multi drug resistance. BMC Infect Dis. 2022 Dec 7;22(1):916. PMID: 36476448; PMCID: PMC9730561. [CrossRef]
- Cabellos C, Guillem L, Pelegrin I, Tubau F, Ardanuy C, Gudiol F, Ariza J, Viladrich PF. Penicillin- and Cephalosporin-Resistant Pneumococcal Meningitis: Treatment in the Real World and in Guidelines. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2022 Dec 20;66(12):e0082022. Epub 2022 Nov 3. PMID: 36326246; PMCID: PMC9764967. [CrossRef]


| Description | Scientific Name | Max Score | Per. Ident |
|---|---|---|---|
| Staphylococcus aureus DNA, complete genome, strain: GN3 | Staphylococcus aureus | 1188 | 99.69 |
| Staphylococcus aureus DNA, complete genome, strain: GN1 | Staphylococcus aureus | 1188 | 99.69 |
| Staphylococcus aureus strain SR434 chromosome, complete genome | Staphylococcus aureus | 1188 | 99.69 |
| Staphylococcus aureus strain Sau37 chromosome, complete genome | Staphylococcus aureus | 1188 | 99.69 |
| Staphylococcus aureus strain Sau59 chromosome, complete genome | Staphylococcus aureus | 1188 | 99.69 |
| Staphylococcus aureus strain Sau92 chromosome, complete genome | Staphylococcus aureus | 1188 | 99.69 |
| Staphylococcus aureus strain UNC_SA56 chromosome, complete genome | Staphylococcus aureus | 1188 | 99.69 |
| Staphylococcus aureus subsp. aureus Tager 104 chromosome, complete genome | Staphylococcus aureus subsp. aureus Tager 104 | 1188 | 99.69 |
| Staphylococcus aureus strain 16CS0209 chromosome, complete genome | Staphylococcus aureus | 1188 | 99.69 |
| Staphylococcus aureus strain SCAID OTT1-2022 (150) chromosome, complete genome | Staphylococcus aureus | 1188 | 99.69 |
| Staphylococcus aureus strain TCD14 chromosome | Staphylococcus aureus | 1188 | 99.69 |
| Staphylococcus aureus strain TCD9 chromosome | Staphylococcus aureus | 1188 | 99.69 |
| Staphylococcus aureus strain TCD17 chromosome | Staphylococcus aureus | 1188 | 99.69 |
| Staphylococcus aureus strain TCD15 chromosome | Staphylococcus aureus | 1188 | 99.69 |
| Description | Scientific Name | Total Score | Per. Ident |
|---|---|---|---|
| Enterococcus faecium strain JE1 | Enterococcus faecium | 2116 | 98.66 |
| Enterococcus lactis strain J-1-A | Enterococcus lactis | 2116 | 98.66 |
| Enterococcus lactis strain J-3-A | Enterococcus lactis | 2116 | 98.66 |
| Enterococcus lactis strain J-4-A | Enterococcus lactis | 2116 | 98.66 |
| Enterococcus lactis strain IDCC 2105 | Enterococcus lactis | 2919 | 98.66 |
| Enterococcus faecium T110 | Enterococcus faecium T110 | 2116 | 98.66 |
| Enterococcus lactis strain KCTC 21015 | Enterococcus lactis | 3218 | 98.66 |
| Enterococcus faecium strain TK-P5D | Enterococcus faecium | 2116 | 98.66 |
| Enterococcus faecium strain 642 | Enterococcus faecium | 1584 | 98.64 |
| Enterococcus lactis strain DH9003 | Enterococcus lactis | 3522 | 98.64 |
| Enterococcus lactis strain HJS001 | Enterococcus lactis | 1913 | 98.39 |
| Enterococcus faecium strain FB-1 | Enterococcus faecium | 1998 | 96.47 |
| Enterococcus faecium strain DB-1 | Enterococcus faecium | 1998 | 96.47 |
| Enterococcus faecium strain ww_sludge_ent_V1_zoecandies_230529 | Enterococcus faecium | 1639 | 95.3 |
| Enterococcus faecium isolate E4239 | Enterococcus faecium | 1162 | 95.02 |
| Enterococcus faecium isolate E4227 | Enterococcus faecium | 1162 | 95.02 |
| Enterococcus faecium strain T17-1 | Enterococcus faecium | 1754 | 97.07 |
| Enterococcus faecium strain AD21B | Enterococcus faecium | 1053 | 92.34 |
| Bacterial Count (CFU/ml) | Antibiotic Concentration (mg/70 kg) | UV Absorbance at 630 nm Wavelength | P Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4*105 | 500 | 0.21 | 0.05 |
| 3*104 | 750 | 0.18 | 0.01 |
| 2*104 | 900 | 0.12 | 0.05 |
| 2*103 | 1000 | 0.09 | 0.02 |
| 102 | 1500 | 0.05 | 0.01 |
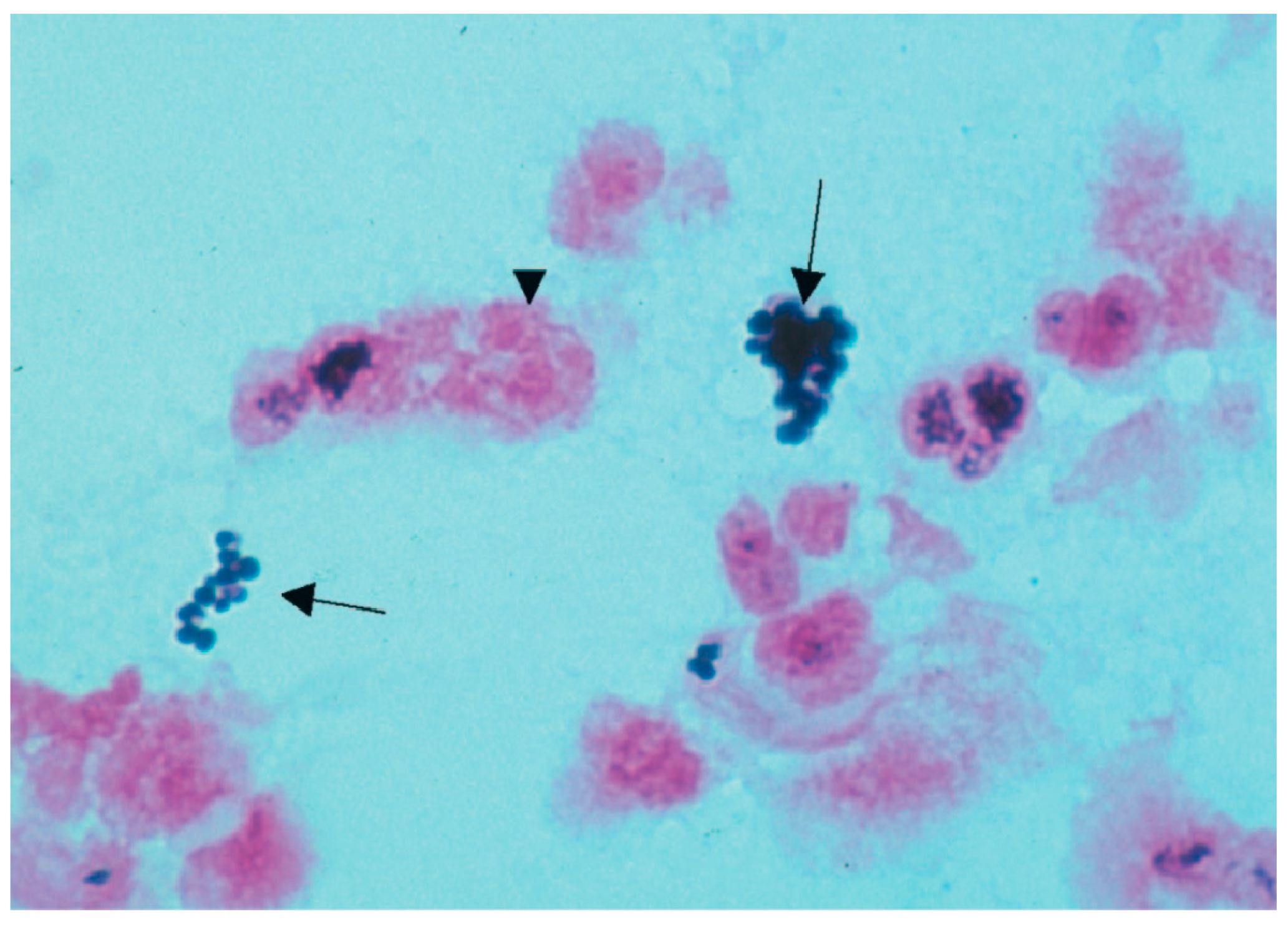
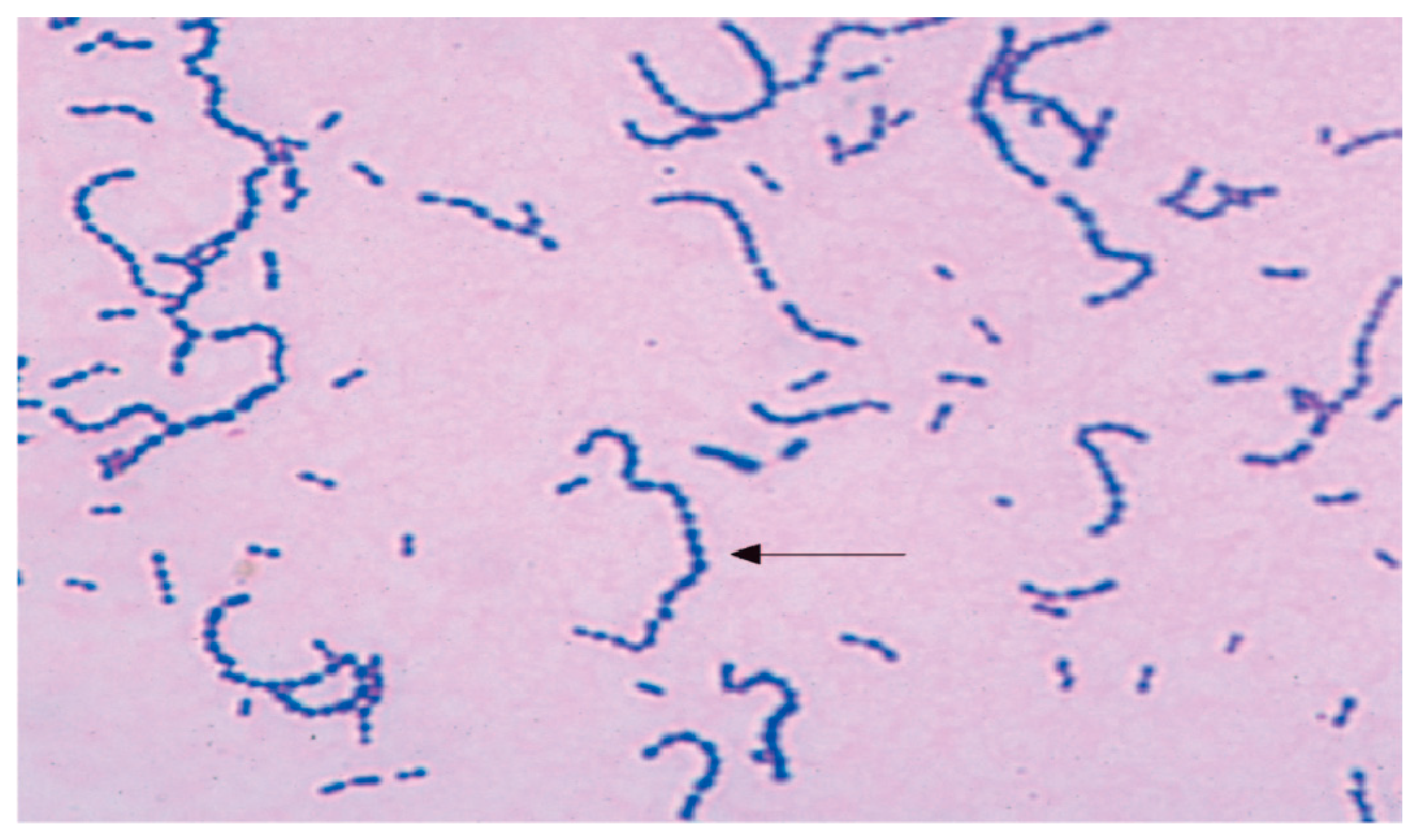
| Characteristic Biochemical Reactions of Resistant Staphyllococcus aureus Isolates | Characteristic Biochemical Reactions of Resistant Enterococcus faecium Isolates |
|---|---|
| Grape-like clusters of Gram-positive cocci were shown by staphylococcal isolates that were resistant. Golden-yellow colonies with remarkable β-hemolysis were proven to be produced by S. aureus cultures. A coagulase positive strain of Staphylococcus aureus was found. The fermentation of mannitol was detected in Staphylococcus aureus isolates on mannitol-salt agar. Agar became yellow as a result of this action, which decreased pH. | Gram-positive streptococci were found in smears from isolates of resistant enterococci. When bile was present, these bacterial isolates were shown to hydrolyze esculin. On bile-esculin agar, they generated a black pigment. Furthermore, in a hypertonic 6.5% NaCl saline solution, it was shown that bacterial isolates of Enterococcus faecium were growing. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





