Submitted:
02 September 2024
Posted:
02 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
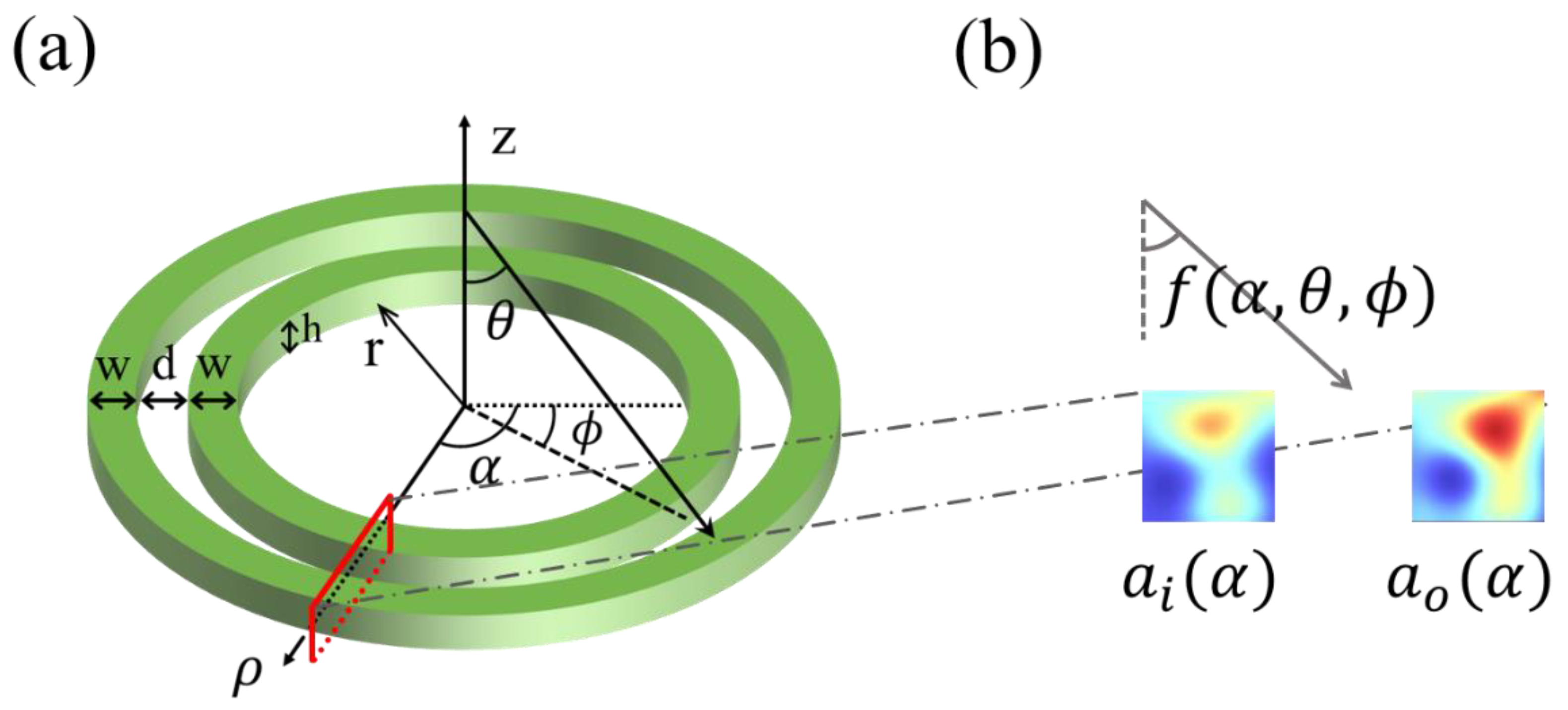
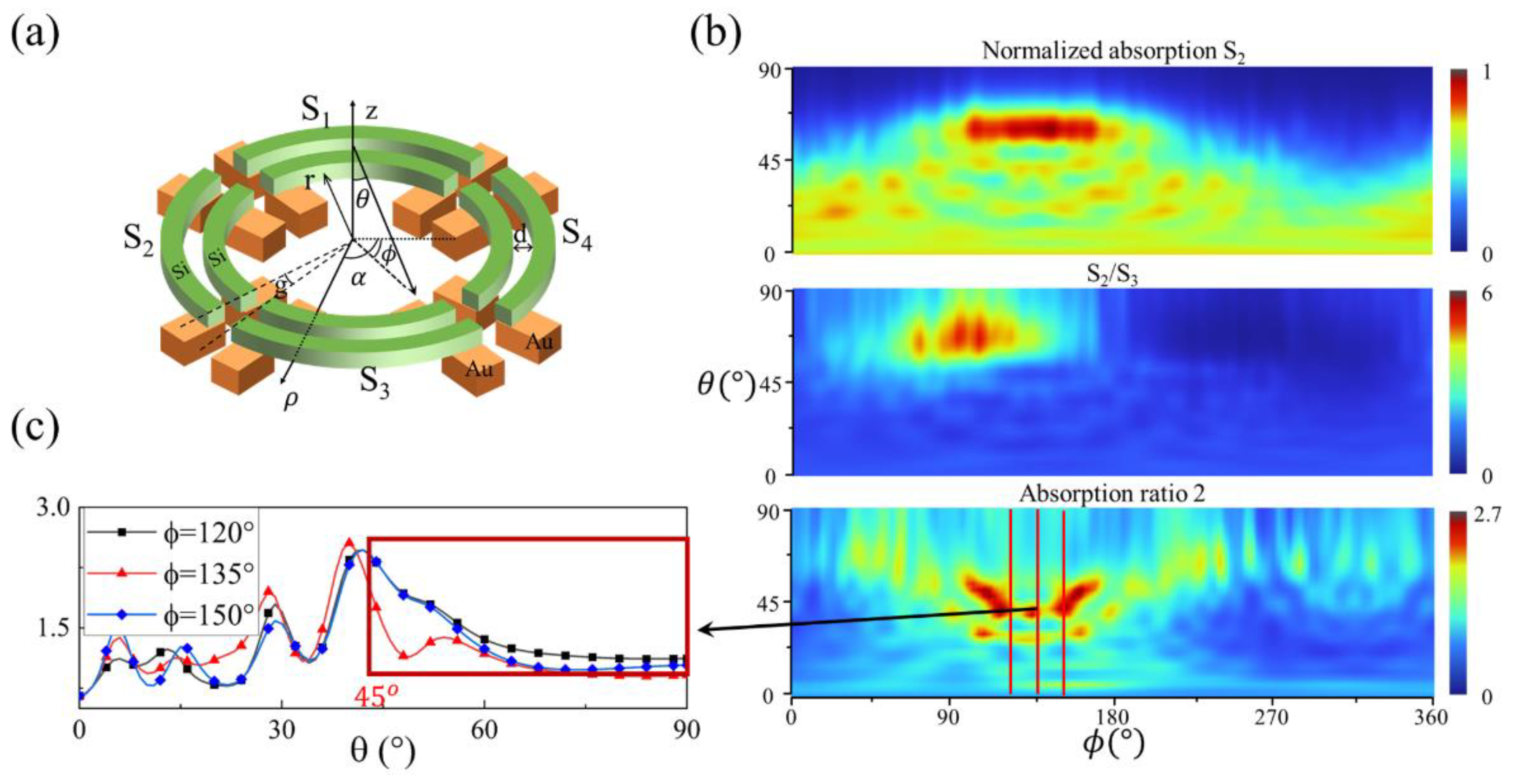
2.1. Nanorings Resonance for Angle Sensing
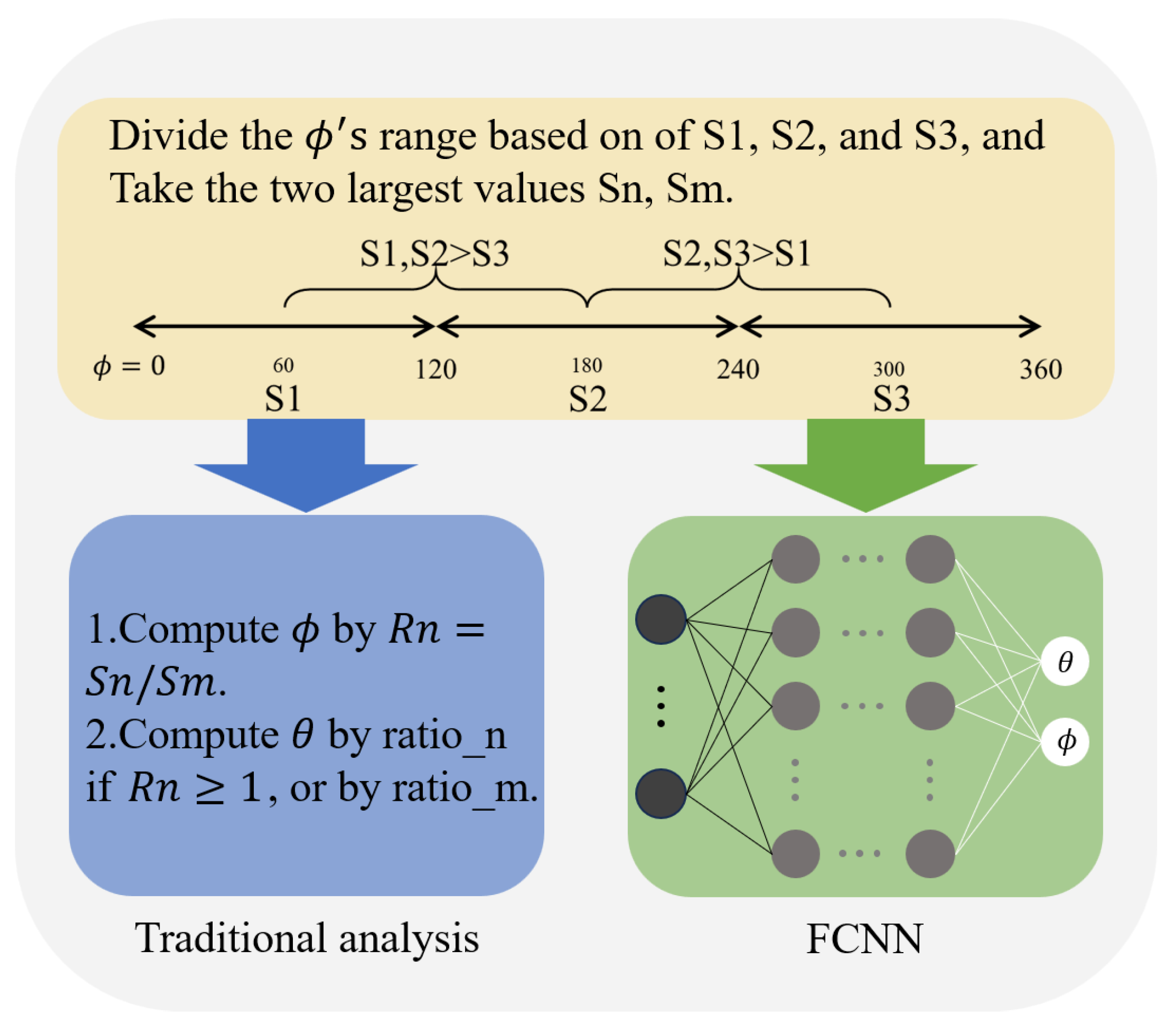
2.3. Deep Learning for Data Fitting
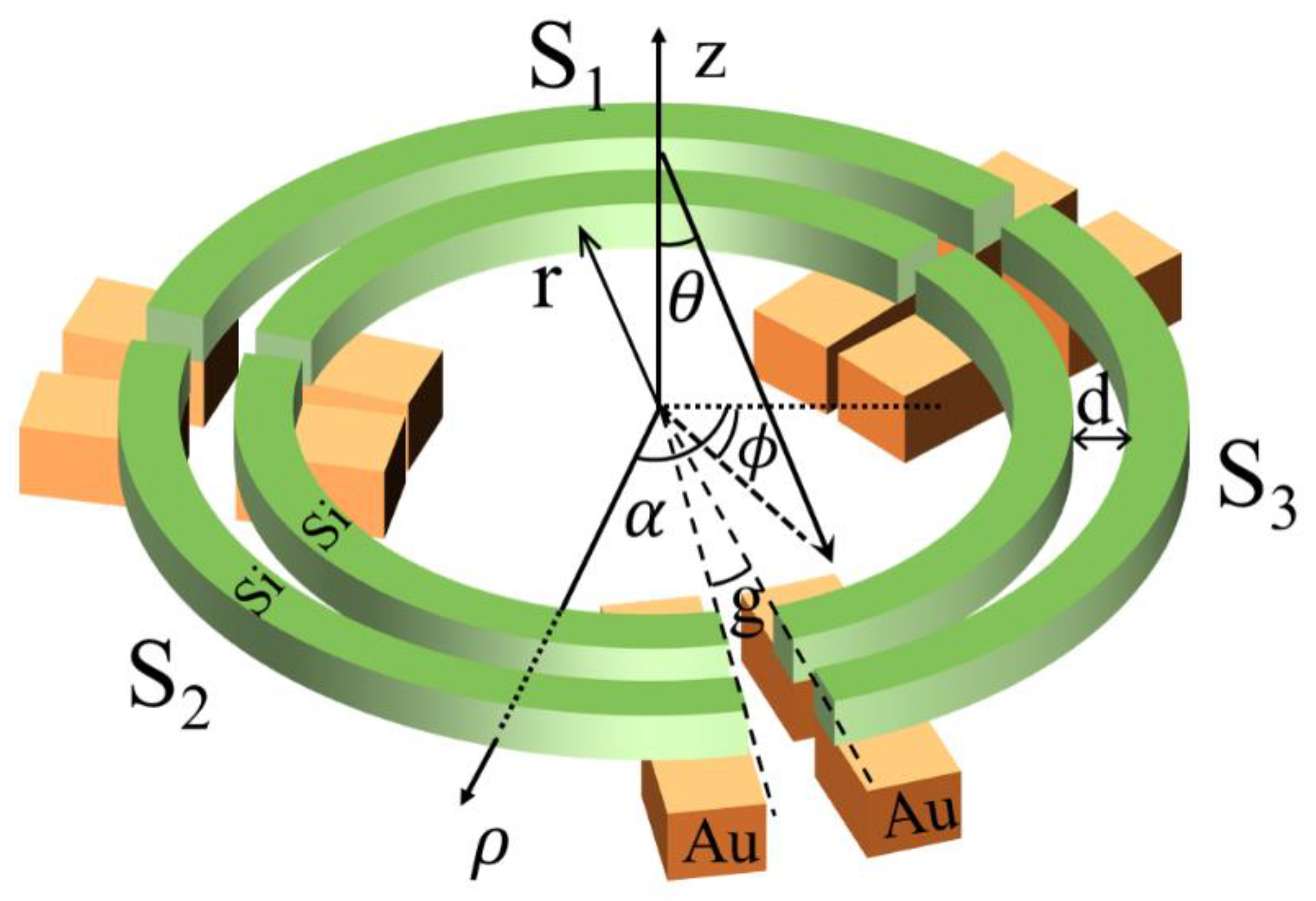
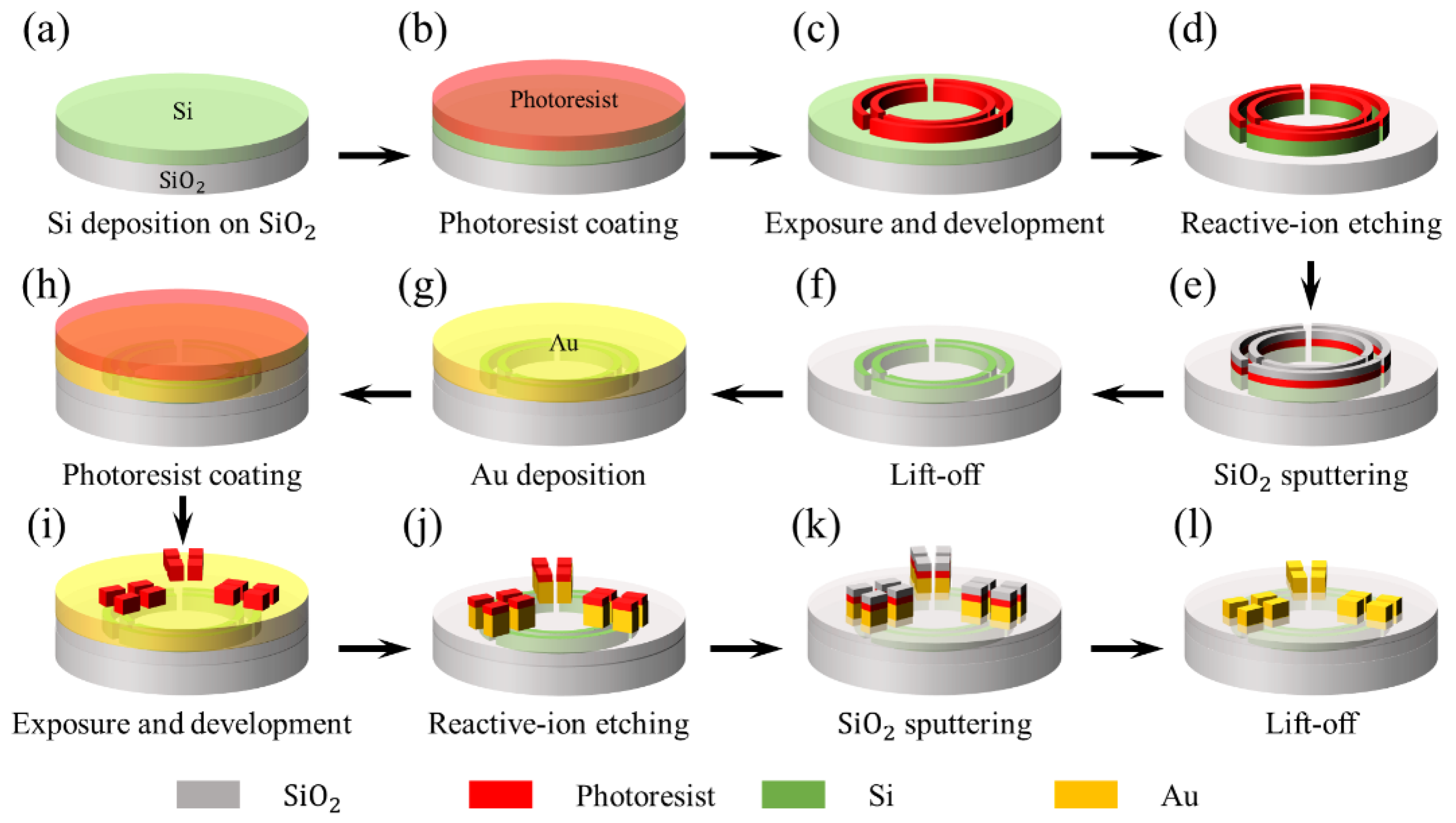
2.4. Fabrication Process
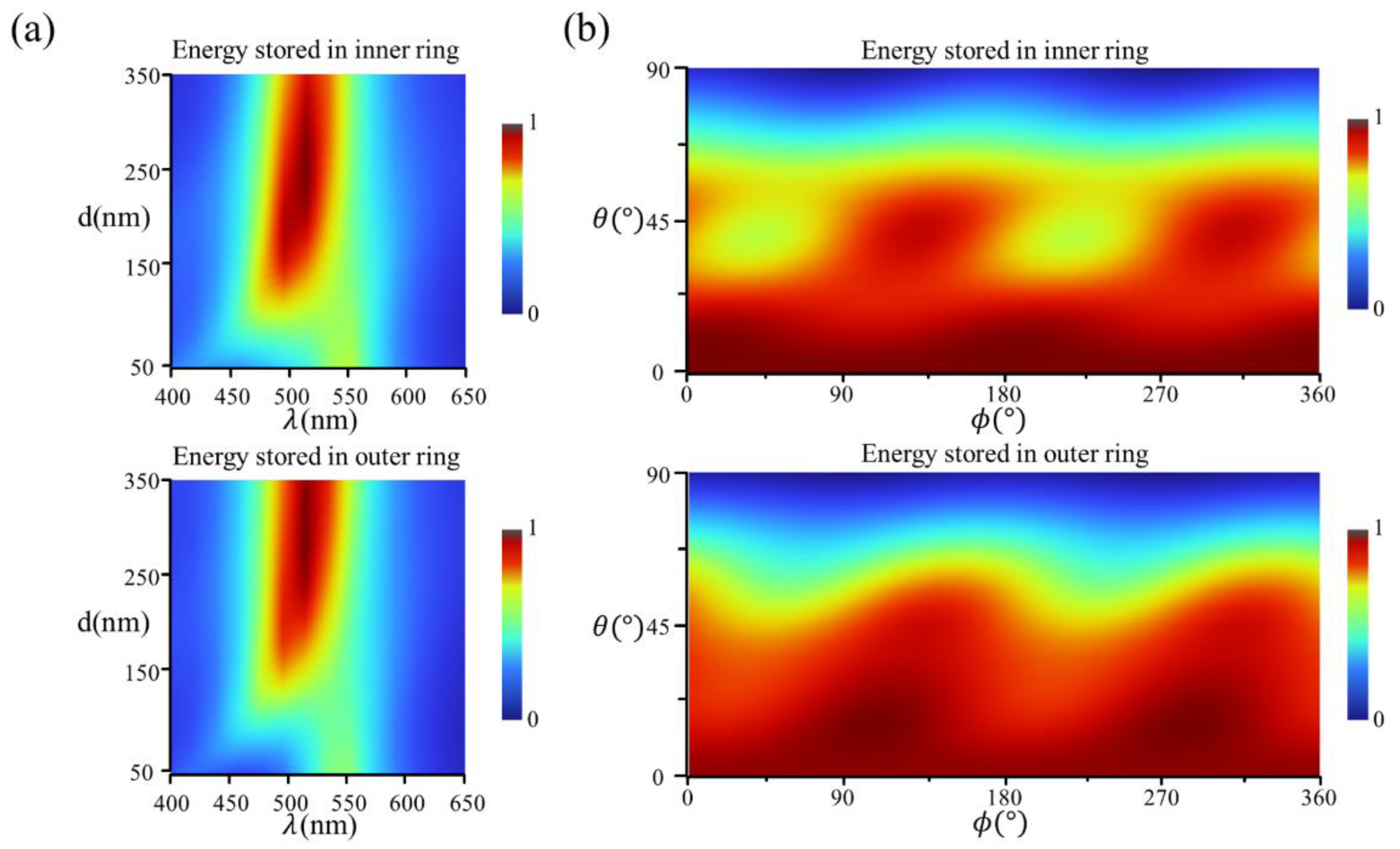
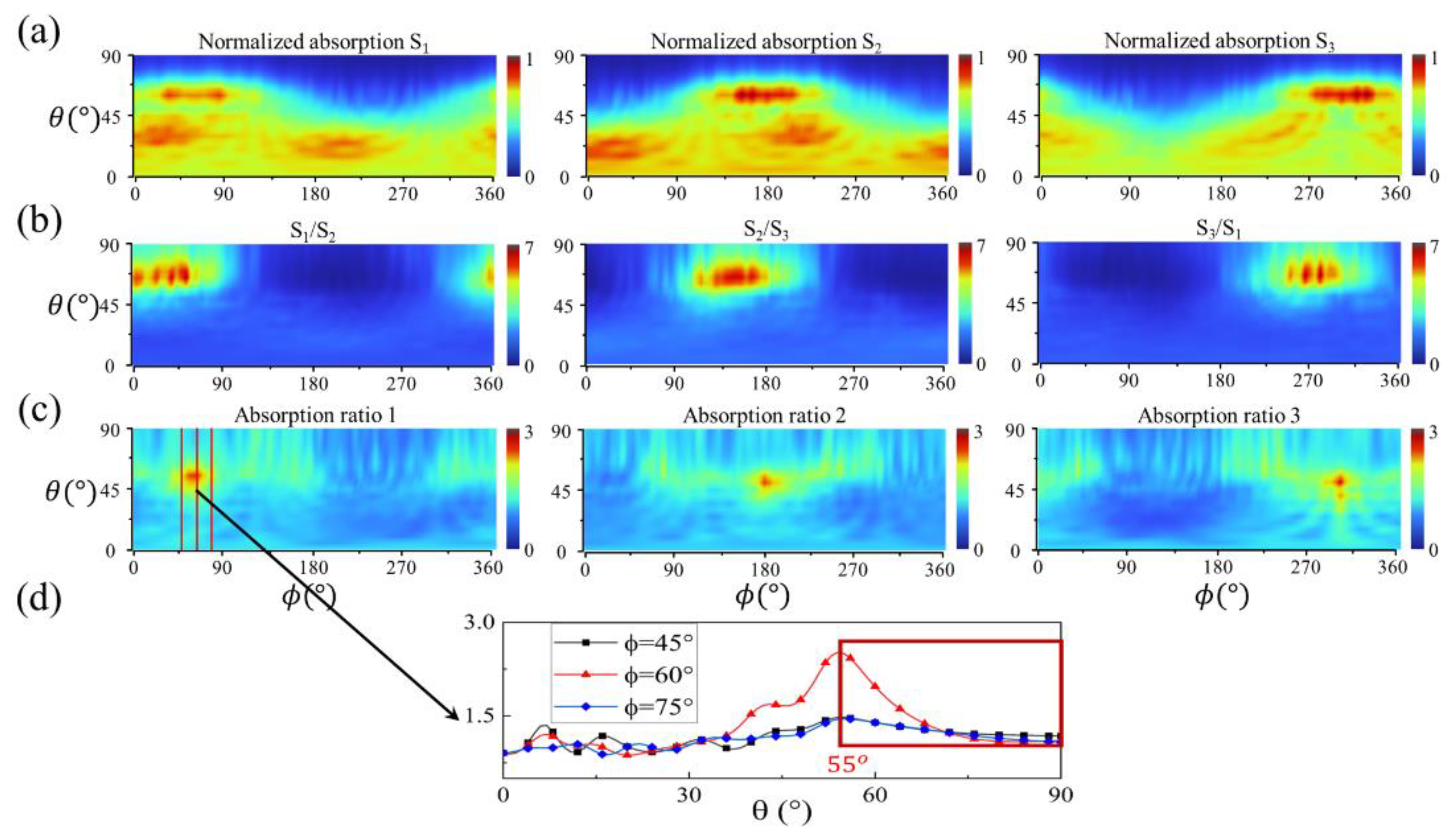
3. Results
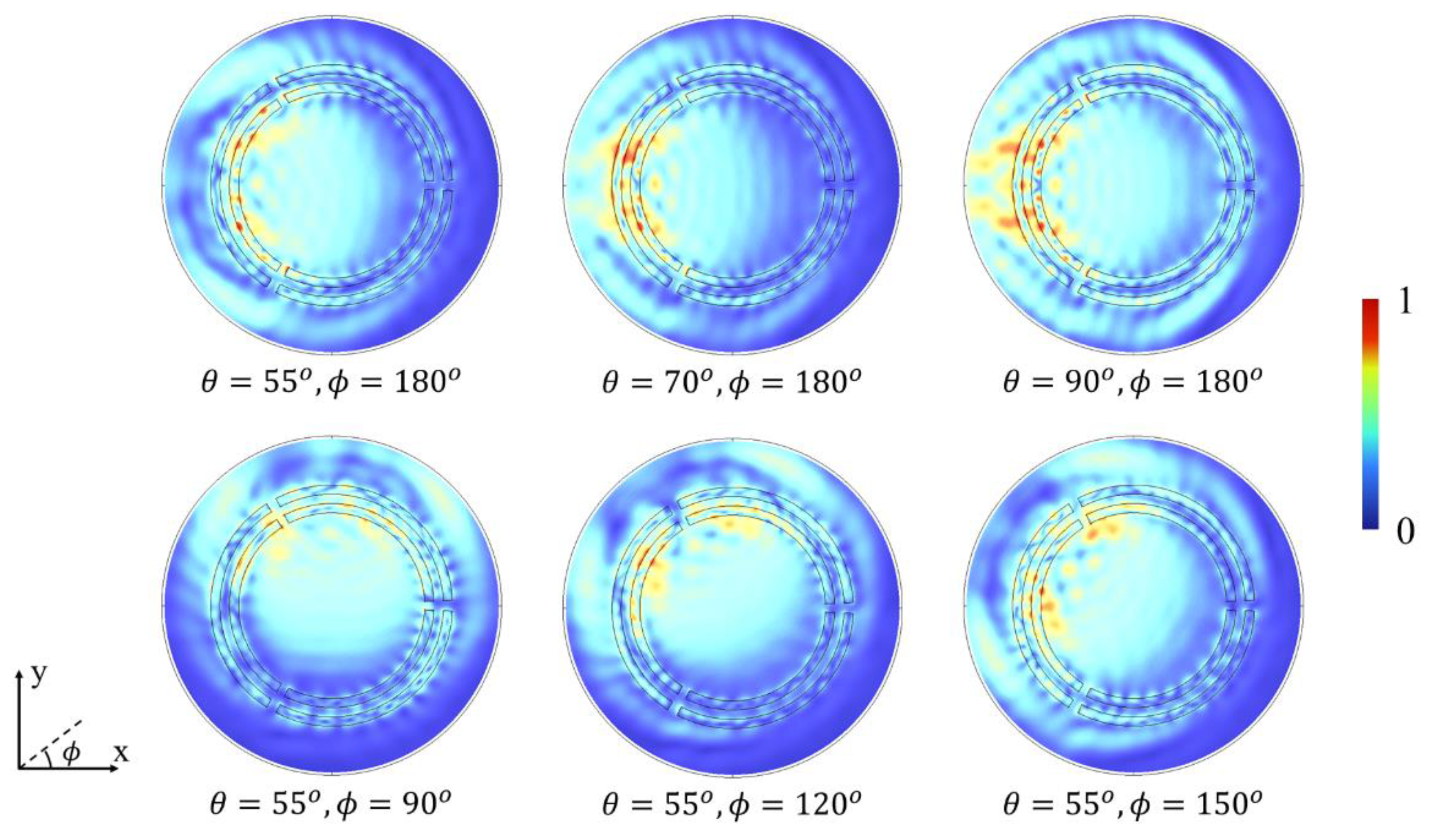
4. Discussion
4.1. 3D Light-Direction Angles Calculation
4.2. More Segments to Improve Detection
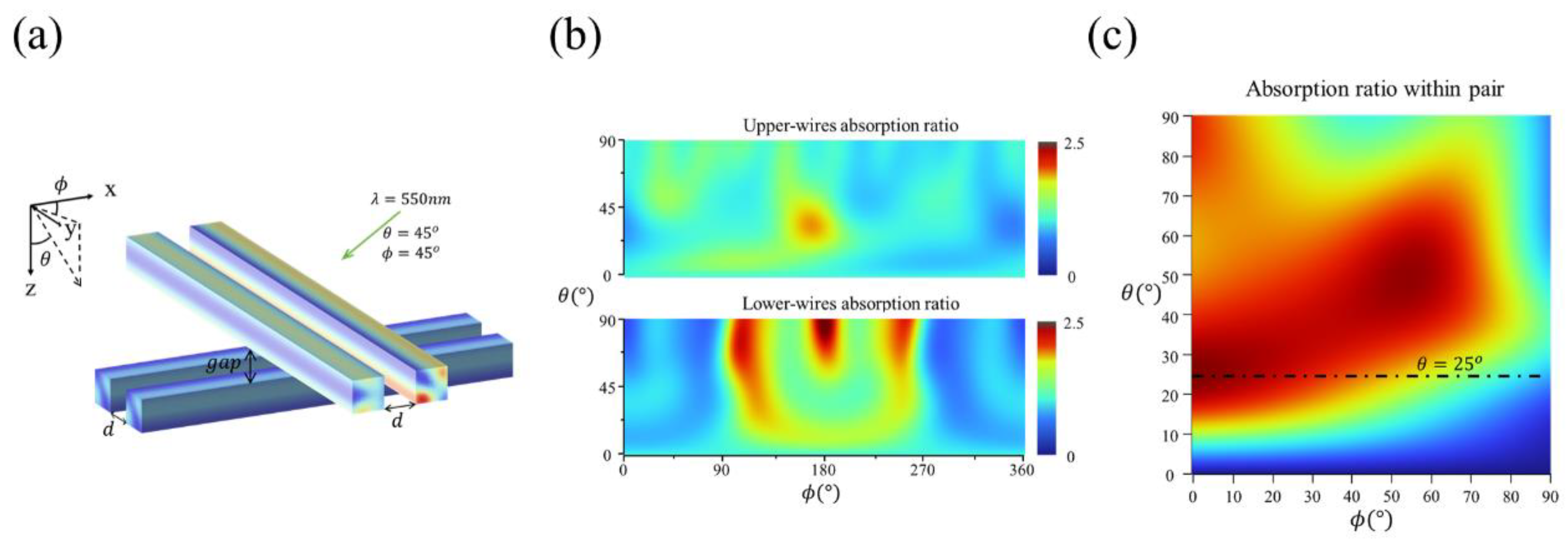
4.3. Cross-Arranged Nanowire-Pairs for 3D Light-Direction Sensing
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adelson, E.H.; Bergen, J.R. The plenoptic function and the elements of early vision; Vision and Modeling Group, Media Laboratory, Massachusetts Institute of …: 1991; Volume 2.
- Ng, R.; Levoy, M.; Brédif, M.; Duval, G.; Horowitz, M.; Hanrahan, P. Light field photography with a hand-held plenoptic camera. Stanford university, 2005.
- Wang, A.; Gill, P.; Molnar, A. Light field image sensors based on the Talbot effect. Applied optics 2009, 48, 5897–5905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Molnar, A. A light-field image sensor in 180 nm CMOS. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits 2011, 47, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; van de Groep, J.; Wang, Y.; Kik, P.G.; Brongersma, M.L. Transparent multispectral photodetectors mimicking the human visual system. Nature Communications 2019, 10, 4982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Feng, X.; Hu, P.; Lin, X.; Jing, T. Development of a 3-DOF Angle Sensor Based on a Single Laser Interference Probe. Micromachines 2023, 14, 2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, C.; Oehm, J.; Emde, J.; Budde, W. Light source position measurement technique applicable in SOI technology. IEEE journal of solid-state circuits 2008, 43, 1588–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.; Xiang, J.; Zhou, M.; Wu, Z.; Yang, L.; Yu, Z. Angle-based wavefront sensing enabled by the near fields of flat optics. Nature communications 2021, 12, 6002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Liu, S. Research on four-quadrant detector and its precise detection. Int. J. Digital Content Technol. Appl. 2011, 5, 138–143. [Google Scholar]
- Azaña, J.; Guillet de Chatellus, H. Angular talbot effect. Physical Review Letters 2014, 112, 213902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Hou, B.; Zhao, H.; Liu, X. X-ray-to-visible light-field detection through pixelated colour conversion. Nature 2023, 618, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanophotonics, R.T. Resonant thermoelectric nanophotonics. 2017.
- Yi, S.; Zhou, M.; Yu, Z.; Fan, P.; Behdad, N.; Lin, D.; Wang, K.X.; Fan, S.; Brongersma, M. Subwavelength angle-sensing photodetectors inspired by directional hearing in small animals. Nature nanotechnology 2018, 13, 1143–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, A.; Hara, S.; Satoh, H.; Panchanathan, A.P.; Inokawa, H. Angle-sensitive detector based on silicon-on-insulator photodiode stacked with surface plasmon antenna. Sensors 2020, 20, 5543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Born, M. Principles of optics - electromagnetic theory of propagation, interference and diffraction of light (7. ed.); Principles of optics - electromagnetic theory of propagation, interference and diffraction of light (7. ed.): 1999.
- Barlow, H.B. The size of ommatidia in apposition eyes. Journal of experimental Biology 1952, 29, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Liang, B.; Kan, W.; Peng, Y.; Cheng, J. Deep-subwavelength-scale directional sensing based on highly localized dipolar mie resonances. Physical Review Applied 2016, 5, 054015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.; Nomura, T.; Su, X.; Iizuka, H. Fano-Like Acoustic Resonance for Subwavelength Directional Sensing: 0–360 Degree Measurement. Advanced Science 2020, 7, 1903101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Y.; Hu, X.; Yang, C.; Shen, X.; Cao, X.; Lin, L.; Yan, F.; Yue, T. Angle-sensitive Pixels Based on Subwavelength Compound Gratings. Current Optics and Photonics 2022, 6, 359–366. [Google Scholar]
- Bakirova, L.I.; Voronkov, G.S.; Lyubopytov, V.S.; Butt, M.A.; Khonina, S.N.; Stepanov, I.V.; Grakhova, E.P.; Kutluyarov, R.V. Micro-Ring Resonator-Based Tunable Vortex Beam Emitter. Micromachines 2023, 15, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, W.; Wang, Z.; Fan, S. Temporal coupled-mode theory and the presence of non-orthogonal modes in lossless multimode cavities. IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics 2004, 40, 1511–1518. [Google Scholar]
- Torres, J.; Baptista, A.; Machado, V.M. Coupling analysis in concentric ring waveguides. Journal of lightwave technology 2013, 31, 2140–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verslegers, L.; Yu, Z.; Ruan, Z.; Catrysse, P.B.; Fan, S. From Electromagnetically Induced Transparency to Superscattering with a Single Structure: A Coupled-Mode Theory for Doubly Resonant Structures. Physical review letters 2012, 108, 083902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verslegers, L.; Yu, Z.; Catrysse, P.B.; Fan, S. Temporal coupled-mode theory for resonant apertures. JOSA B 2010, 27, 1947–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Ye, Z.; Wang, Y.; Park, Y.; Bartal, G.; Mrejen, M.; Yin, X.; Zhang, X. Anti-Hermitian Plasmon Coupling of an Array of Gold Thin-Film Antennas for Controlling Light at the Nanoscale. Physical review letters 2012, 109, 193902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Shi, L.; Zi, J.; Yu, Z. Extraordinarily large optical cross section for localized single nanoresonator. Physical review letters 2015, 115, 023903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; White, J.S.; Park, J.-S.; Schuller, J.A.; Clemens, B.M.; Brongersma, M.L. Engineering light absorption in semiconductor nanowire devices. Nature materials 2009, 8, 643–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cybenko, G. Approximation by superpositions of a sigmoidal function. Mathematics of control, signals and systems 1989, 2, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornik, K.; Stinchcombe, M.; White, H. Multilayer feedforward networks are universal approximators. Neural networks 1989, 2, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leshno, M.; Lin, V.Y.; Pinkus, A.; Schocken, S. Multilayer feedforward networks with a nonpolynomial activation function can approximate any function. Neural networks 1993, 6, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Chen, H. Universal approximation to nonlinear operators by neural networks with arbitrary activation functions and its application to dynamical systems. IEEE transactions on neural networks 1995, 6, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
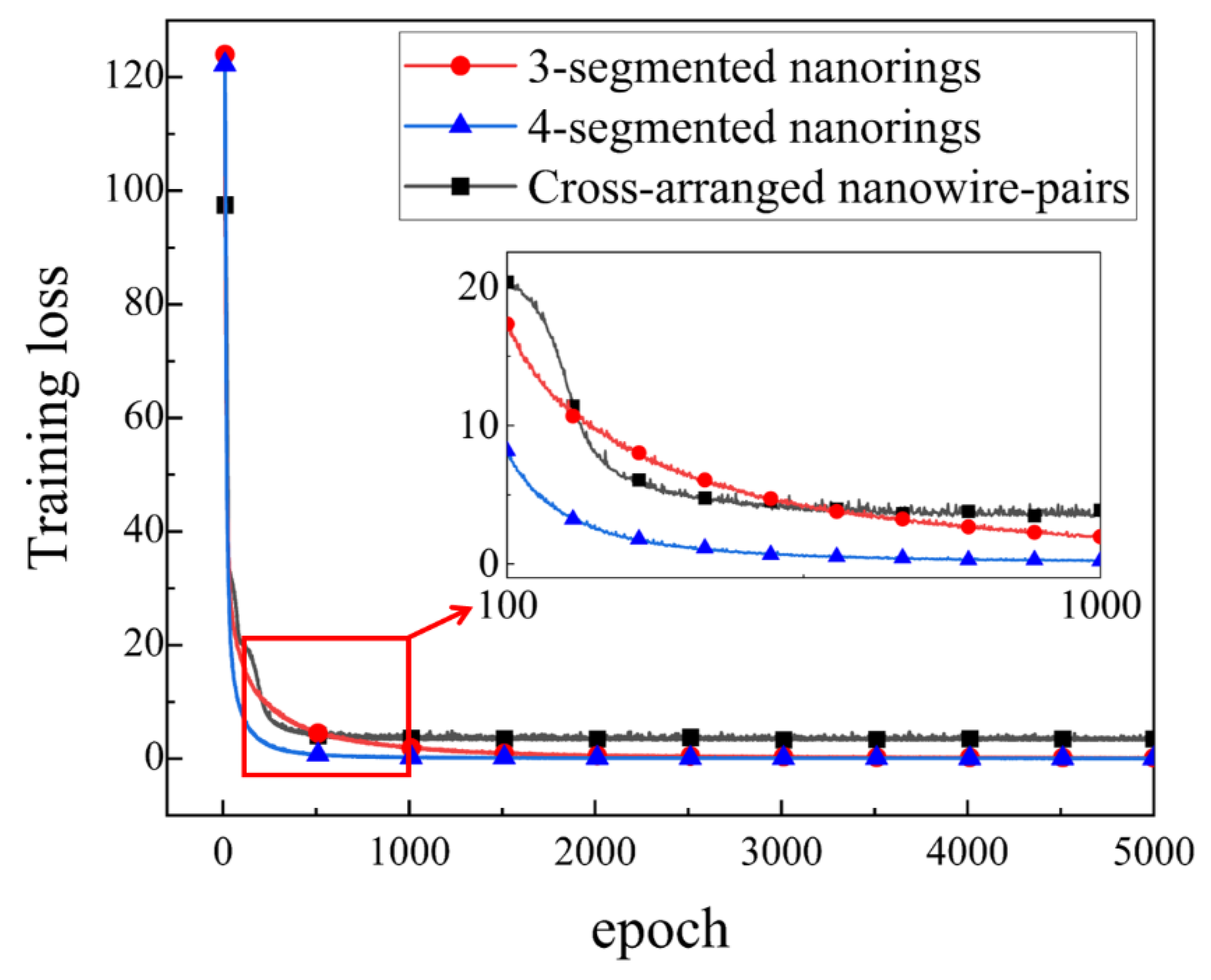
| Structure | ) | ) | ) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average | Maximum | Variance | Average | Maximum | Variance | ||
| 3-segmented nanorings |
55-90 | 0.372 | 2.077 | 0.121 | 0.350 | 2.550 | 0.102 |
| 4-segmented nanorings |
45-90 | 0.187 | 2.252 | 0.041 | 0.174 | 1.704 | 0.030 |
| Cross-arranged nanowire-pairs | 0-25 | 0.198 | 0.578 | 0.009 | 0.948 | 16.387 | 7.291 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





