1. Introduction
Laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) is becoming increasingly prominent in the aerospace and automotive industries, with a rising demand for materials specifically designed for this process. In the first two decades of metal additive manufacturing (AM) development, the focus on materials primarily involved using conventional grades [
1]. Most of the literature has focused on the investigation of existing alloys that show promising results when fabricated using AM techniques. Examples include 304L and 316L in the stainless steel category, AlSi10Mg and AlSi12 in aluminum-based alloys, Ti-6Al-4V in titanium-based alloys, In718 in nickel-based alloys, among others [
2]. Despite the promising results obtained with these alloys in AM, their production requires optimizing a wide range of processing parameters. Indeed, the additive nature of these processes and the associated complex thermal histories introduce many difficulties, making it challenging to produce components that are both dense and structurally robust. Porosity, cracks, residual stresses and microstructure in the as-solidified state can significantly degrade the mechanical properties of AM-produced parts compared to conventionally manufactured pieces [
3]. Many alloys are associated to a specific or preferred processing route; for instance, there are nickel base superalloys specifically optimized to be produced by forging (e.g., 718 grade), casting (e.g., 738), directional solidification (e.g., CMSX-4) or powder metallurgy (e.g., N18), so similar efforts should be undertaken towards the design of AM-specific alloys. Nevertheless, few studies have focused on optimizing alloy composition to improve the overall properties of AM products and most alloy design efforts have been devoted primarily to aluminum and its alloys [
4,
5]. Improving process robustness, minimizing defects and achieving superior mechanical properties can be obtained by designing new alloys tailored for AM. This, in turn, has the potential to significantly improve the performance of 3D printed parts. In recent years, several authors have presented successful approaches to design novel compositions using a combination of different computational tools [
6,
7,
8,
9]. This approach includes the use of computational thermodynamics to predict phases [
10] and other physical models to predict material properties [
11,
12]. However, depending on the specific property of interest, physical models may not always be readily available. In such cases, the use of machine learning (ML) algorithms to build and train models using existing data has been widely adopted [
13,
14].
Previous studies have often used a general approach to alloy selection and sorting [
15,
16]. However, these studies usually do not rely on a comprehensive multi-criteria exploration. In a recent development, Ackers
et al designed titanium alloys using thermodynamic calculations [
17], considering constraints to prevent solidification cracking. They specifically tested compositions suitable for LPBF while maintaining associated process conditions, and while considering surface defects, phase structure and cracking susceptibility. The printability of stainless steel has been studied by Sabzi
et al [
18,
19], who proposed a defect prevention method that integrates material-dependent properties. Their approach, validated on 316L stainless steel, improved printability compared to other alloys, but was limited to compositions close to the nominal composition of 316L. Despite promising results in existing studies, a method is needed that focuses on material composition while addressing various material-dependent phenomena that are related to defects in current AM parts, including porosity formation, cracking, surface roughness and elements loss by selective evaporation.
This work aims to contribute to the current progresses in alloy design approaches for the discovery of new austenitic alloys optimized for additive manufacturing processes. In the first section, we establish optimization criteria to guide the alloy design process. These criteria fall into two categories. The first group consists in criteria specific to the LPBF process, aimed at minimizing the risk of defects. A second group of criteria is related to the microstructure and the desired mechanical properties, with a focus on maintaining properties suitable for mechanical engineering applications. These criteria can be determined through the combined use of computational thermodynamics, physical models and machine learning algorithms for predicting relevant alloy properties. In the second part, we integrate these criteria into a multi-objective genetic algorithm (GA) to automate the optimization process. This algorithm ultimately proposes a set of optimized alloy compositions. Finally, we validate the models through experimental evaluation. An alloy composition selected from the optimized set is produced in powder form, processed using an AM technique (LPBF) and evaluated experimentally for defects, microstructure, as well as physical and mechanical properties. The resulting microstructure and properties are compared to those of 316L, selected as a reference alloy, to determine the potential improvements in printability and performance resulting from the design process.
2. Materials and Methods
The powder of the selected alloy was manufactured externally by LERMPS UTBM using gas atomization under argon atmosphere. Particle size was assessed using a laser granulometer Malvern Mastersizer 3000, with a gas pressure of 3.5 bars. The particle size ranges from d10= 11 µm to d90= 40 µm, with a median value of d50= 22 µm. Using a ProX200 LPBF machine from 3D Systems, cubes (10x10x10 mm) and rectangular specimens (42x14x4 mm) for tensile tests were fabricated on a 316L stainless steel substrate. A near-infrared laser source (λ=1064 nm) was used, with scan speeds (v) of 1000 and 1200 mm/s. Gradual laser power (P) increments from 120 to 250W in +6W (+2%) steps were tested. The hatching distance was set to 60 µm and the powder layer thickness was 30 µm. The scanning strategy was 45°/225° relative to the orthogonal axis of the substrate. The focal distance was -6.0 mm. Specimens were arranged in staggered rows on the building platform, with a building sequence oriented in the opposite direction of the Ar gas flow to prevent spatter deposition. All processing conditions were based on ranges optimized for 316L, without specific adjustment, to test the desired robustness of the new alloy. Among these ranges, based on visual inspection via optical microscopy, the best result in terms of surface roughness was obtained for P=144W and v=1200 mm/s.
The chemical composition of the powder and samples produced by LPBF was measured by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy ICP-OES. The carbon content was measured by combustion infrared absorption (CIR). The values are listed in
Table 1, showing some difference in the powder composition from the nominal values, especially with slightly lower amounts of some alloying elements, like Co and Al. The Co content further decreases slightly after LPBF processing
Microstructure observations were conducted on a scanning electron microscope (SEM) Zeiss SUPRA55VP operated at 20 kV in backscattered electrons (BSE) mode and for Electron Back-Scattered Diffraction (EBSD) mapping. Variations in chemical composition were assessed using Energy Dispersive X-Ray Spectrometry (EDX) mapping, with an Oxford SDD detector XmaxN 80. Phase identification was accomplished using an X-ray Diffractometer (XRD) X’Pert Pro MPD Panalytical with Cu Kα radiation operated at 40 mA and 45 kV. Divergence slits at 0.5° were set for the incident beam and a graphite monochromator with a Miniprop point detector were used for the diffracted beam. The analyzed angle was between 20° and 120° with a step size of 0.03° and a counting time of 25 s/step.
Thermal expansion tests were performed using a DIL 402 Expedis Select Netzsch dilatometer in a horizontal configuration. Specimens of size 3x3x12 mm were placed in the alumina sample holder and tested in a temperature range from 25° to 850°C, under a protective argon gas atmosphere (flow rate of 40 ml/min). Measurements were performed at a heating rate of 3°C/min. For each material, three measurements were performed; they demonstrated a high repeatability, with a variation of approximately 1% across experiments. An alumina reference sample was used for calibration. The measurements were performed according to the recommendations of the DIN EN ISO 17562 standard.
Tensile tests were performed on flat specimens at room temperature using an Instron 1186 machine, at a strain rate of 10-3 s-1. Specimens were cut from 42x4x15 mm³ plates in two orientations: one along the scanning direction (SD) and the other along the building direction (BD). Specimens had a reduced cross-sectional area of 16 mm² and a length of 12 mm. They were tested in the as-machined condition and strain was measured using a clip-on extensometer with an initial gauge length of 10 mm.
3. Results
3.1. Criteria for Alloy Design
The design criteria must be solely dependent on the material itself. In other words, the calculated criteria should, whenever possible, accurately represent the behavior of the material or trends in specific characteristics, regardless of processing conditions, or at the very least, they should be applicable within a broad range of processing conditions. Then, it is desirable to gain a physical understanding of the impact of each feature on the overall outcome. The design criteria can be categorized into four groups. First, a criterion is set to manage the microstructure and ensure the stability of the desired phases. Secondly, a set of criteria is established to prevent the occurrence of solidification cracking. The third group focuses on maintaining meltpool stability, aiming to minimize melt instabilities that can lead to gas entrapment and subsequent pore formation. Lastly, several thermomechanical properties must be controlled, including yield stress and the coefficient of thermal expansion, to ensure a good strength of the material as well as to control the level of distortions and residual stresses.
3.1.1. Phase Stability: Targeting an Austenitic Structure
To illustrate and demonstrate the method to design alloys that are specific to AM, we chose to propose austenitic stainless alloys, with the primary objective being the predominant presence of austenite (γ, i.e., a face-centered cubic (FCC) solid solution) in the microstructure. Computational thermodynamics, with the calculation of phase diagrams (CALPHAD) method, can be employed to predict phase formation under equilibrium conditions. However, additive manufacturing generates out-of-equilibrium microstructures and CALPHAD may become inaccurate for such processes, somehow similar to welding. One possible solution is to use the Scheil model [
23,
24] to predict the solidification sequence. This model, based on the CALPHAD method, assumes non-equilibrium conditions in which the solid phase forms instantaneously without diffusion, while the liquid phase stays fully homogeneous and in equilibrium with the last solid formed. It provides predictions of the composition and amount of each phase as the material cools and solidifies. However, this model is not well-suited for predicting the phase fractions after complete cooling. For instance, the Scheil model could predict the formation of δ ferrite at very high temperature whereas that phase could transform into austenite in solid state during subsequent cooling; similarly, austenite formed at high temperature may transform into α ferrite or martensite upon cooling. In the present work, an empirical approach was preferred.
Therefore, the prediction of phases resulting from AM was approached using an empirical diagram usually applied to welding [
20]. It relies on the quantification of γ-stabilizing elements and of elements promoting body-centered cubic (BCC) ferritic phases (α, δ), through quantities respectively named the “nickel equivalent” (Ni
eq) and the “chromium equivalent” (Cr
eq). One of the most frequently employed graphic representations for this purpose is the Schaeffler-Delong diagram [
20,
21]. Yet, in our specific case, in order to account for the influence of as many alloying elements as possible, we consider the Hull equations and diagram which are an extension of the former [
22], where contents are expressed in wt.%:
This approach can serve as a straightforward tool for estimating the phases that will be present after solidification and cooling down to room temperature. It aids in a quick preliminary classification of compositions into two categories: potentially acceptable alloys (referred to as “feasible”) and unacceptable ones (“unfeasible”). This step helps avoid unnecessary and computationally intensive thermodynamic calculations, which may not always accurately predict all final phases (such as austenite, ferrite and martensite) in a reliable manner.
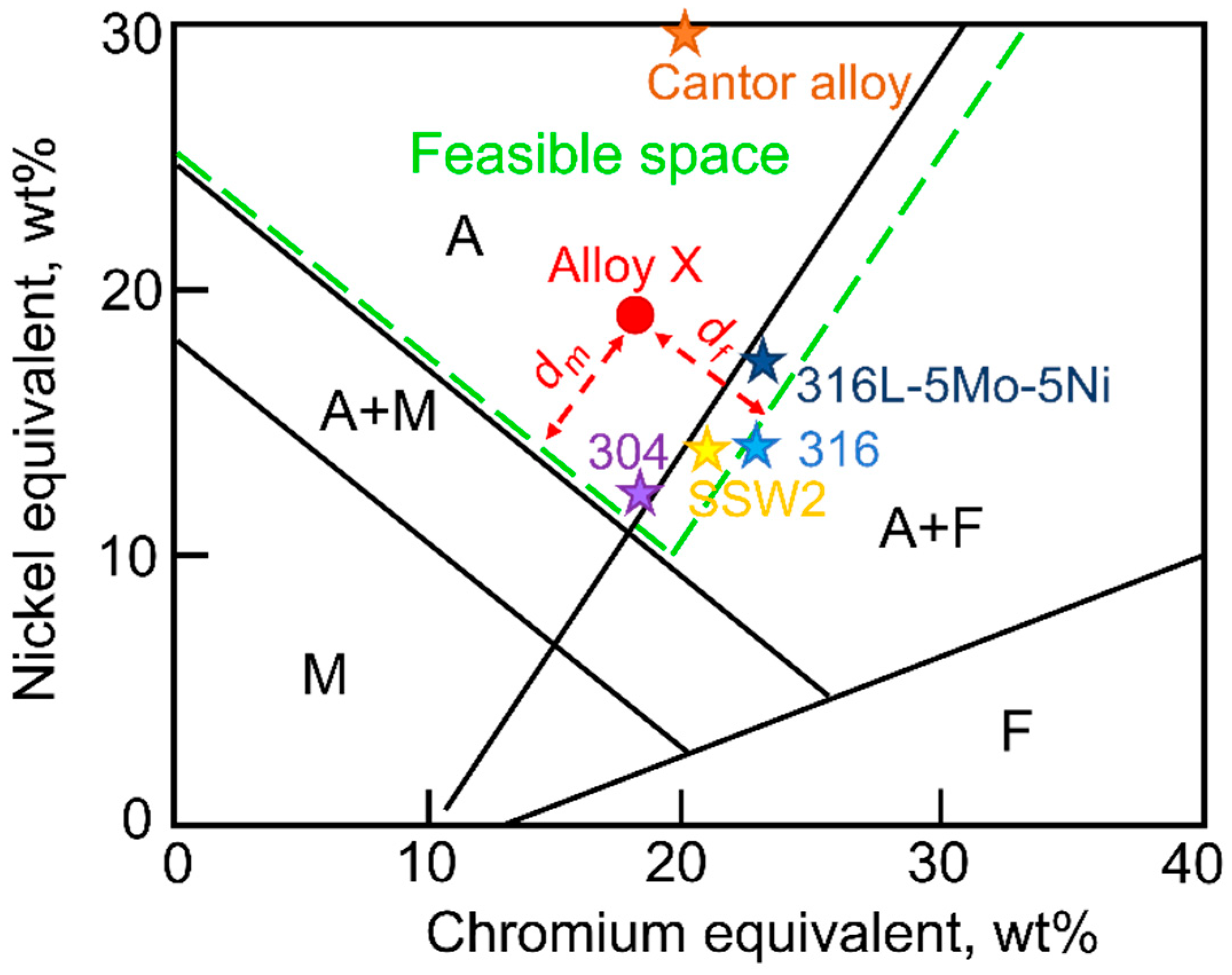
In
Figure 1, the diagram illustrates the feasible space, defined with green dashed lines. The objective is to narrow down the search space to alloys that are characterized by a fully austenitic microstructure after solidification and cooling down to room temperature. The feasible space is defined by two boundaries: one setting a limit on ferrite content and another on martensite content. Unlike martensite, which is to be completely avoided due to its brittleness, there is a small margin of around 5% allowed for the boundary with ferrite. Indeed, it is generally admitted that alloys containing less than 5% ferrite exhibit properties that are undistinguishable from those of fully austenitic ones.
Figure 1 displays the distribution of several existing alloys on the Hull diagram, with ferrite content ranging from 0% to 5%. These alloys include 304, 316, SSW2 [
25], 316L-5Mo-5Ni [
26] and the so-called Cantor alloy, an equimolar CoCrFeMnNi “high entropy alloy” (HEA) [
27]. Furthermore, to encourage the search for alloys that preferably reside within the austenitic region, the distances of the alloy composition from both the ferrite and martensite boundaries (illustrated as d
m and d
f from a random alloy X in
Figure 1) is defined. An objective for alloy design is then set to maximize the smallest of the two distances. In conclusion, this criterion regarding phase stability combines a constraint on composition to ensure the presence of austenite and an objective to maximize its stability.
To further validate the austenitic nature of the alloy, the output prediction of the Scheil model is also considered. The simulation is conducted using Thermo-Calc 2021b with the TCFE10 database and TC-Python API. Although this model is primarily used to predict hot cracking, as discussed in the following section, it also provides insight into the phase fractions after solidification. To address the risk of excessive formation of undesirable brittle phases and intermetallics, which could potentially affect mechanical properties, a second constraint has been implemented. This constraint ensures that δ-ferrite and austenite together constitute at least 99% of the phases after solidification, effectively rejecting alloy compositions containing more than 1% of other phases.
3.1.2. Solidification Cracking
The issue of solidification cracking has been extensively investigated in conventional manufacturing techniques such as casting and welding, but it also occurs in the specific case of LPBF process [
28]. One of the key factors influencing the susceptibility of an alloy to cracking is its solidification temperature range. Therefore, calculating this value serves as a means to quantify the cracking susceptibility of an alloy [
15]. More specifically, it is crucial to consider the Critical Temperature Range (CTR) [
29,
30]. Lowering this range in the mushy zone during solidification minimizes shrinkage, reduces liquid suction in the interdendritic spacing and ultimately lowers the risk of void and crack formation. Definitions vary across sources, but generally, the CTR is defined as the difference between temperatures at which certain fractions of solids have formed. This study adopts the definition corresponding to fractions of solids between 95% (T
1) and 99% (T
2), as these values are commonly reported [
12,
18,
19]. To predict the solidification range and associated phases, including their order and the evolution of their fractions, the classical Scheil model from Thermo-Calc is employed. This computational tool enables the calculation of the complete solidification range. This model is only applied to alloys predicted by the Hull diagram to be austenitic, whereas alloys judged unsatisfactory by the Hull criterion are excluded from the Scheil calculation to limit computation time.
When considering processes with high solidification rates, various studies have demonstrated that the primary formation of ferrite from the liquid can significantly reduce the susceptibility to solidification cracking compared to the primary formation of austenite. Such a beneficial effect is observed when solidification produces ferrite only (F mode) or ferrite then austenite (FA mode) compared to the production of austenite only (A mode) or austenite then ferrite (AF mode) [
31,
32,
33,
34]. An important factor contributing to this effect is the higher solubility of harmful impurities (S, P...) in ferrite compared to that in austenite. This results in less segregation during the primary ferrite solidification. The cracking behavior of several austenitic stainless steels is influenced by the impurity content of S and P, as well as the Cr
eq/Ni
eq ratio [
35]. Bollinghaus
et al. [
36] noted that as the Cr
eq/Ni
eq ratio approaches 1.48, the impurity content of S and P, which leads to cracking, becomes significantly higher. Beyond this value (~1.48), cracking becomes rare, even with somewhat elevated impurity contents (> 0.2 wt.%). This value of Cr
eq/Ni
eq corresponds to the range where the solidification mode changes from A or AF to FA. To ensure that the solidification mode is FA or F, it would be possible to use a minimum value of the Cr
eq/Ni
eq ratio as a design constraint. Instead, our choice was to impose the first phase formed during solidification as predicted by Thermo-Calc, which is set to δ-ferrite. Moreover, using Thermo-Calc with the Scheil model makes it possible to estimate the fraction of ferrite formed, unlike the Cr
eq/Ni
eq ratio alone. As a precaution, a minimum of 10% δ-ferrite formation is specified to reduce the risk of cracking [
37]. However, the ultimate desired microstructure being austenitic, it is also useful to establish an upper limit on the fraction of δ-ferrite formed during solidification, in addition to the Hull diagram criterion, to avoid an incomplete transformation of ferrite into austenite during cooling. The assessment of several existing alloys indicates that, beyond 50% of ferrite predicted in a Scheil simulation, a risk exists that the microstructure is not fully austenitic after welding or AM.
3.1.3. Meltpool Composition and Stability
AM processes involve the use of liquid metal, making it imperative to examine various properties of materials in this state. Among these properties, surface tension (ST) plays a critical role and significantly impacts the wetting conditions of the previously deposited solid phase by the liquid phase. The value of ST influences the ability of the melt pool to form a continuous and stable seam. At high scanning speeds and with low deposited energy, the length of the melt pool increases relative to its diameter, leading to the phenomenon known as the “balling effect” [
2]. This happens when the melt zone, which can be roughly seen as a “cylinder”, becomes unstable and splits into beads for a given ratio of its diameter over its length. The melt cylinder is attached to the solid substrate by a contact band; however the physical phenomenon can be compared to some extent to a free-falling liquid jet and the resulting stability criterion differs only of a constant geometric factor [
38,
39]. A material-dependent criterion can be determined by considering the stability of a free-falling jet over time. Equation 1 [
40] provides the expression of the characteristic time
τ for the breakup of a fluid jet into drops:
where R denotes the jet radius,
ρ signifies fluid density and
γ stands for the surface tension value. It can be inferred that reducing the ST value would result in an extended breakup time, potentially longer than the solidification time, thus mitigating the balling effect. This decrease in ST would, overall, enhance the geometric stability of the seam. Due to the absence of a reliable physical model to predict the surface tension of metallic alloys as a function of composition, a general machine learning (ML) approach was employed. The model relies on a Bayesian algorithm, specifically Gaussian process regression (GPR); the method and the assessment of the model are detailed elsewhere [
41].
Another phenomenon contributing to melt pool instability is vaporization. As reported by King
et al. [
42], the vaporization of the melt can lead to the occurrence of keyholing. This may result in the formation of pores if gas bubbles become trapped [
43]. Reducing the risks associated with such instabilities can be achieved by lowering the vaporization flux of the elements. Additionally, selective vaporization may induce significant composition changes as shown by Mukherjee
et al. [
44]. To assess the risks related to instabilities arising from vaporization and composition changes, the vaporization flux of each element is estimated. Equation 2 shows the Langmuir expression for the vaporization flux (J
i) of element i [
45] :
where P
i and M
i are the equilibrium vapor pressure and molecular weight of element i, respectively, T is the temperature and λ
c is a positive constant that accounts for the condensation, typically assigned a value of 1 under vacuum conditions. Estimating J
i for individual elements requires to determine their respective vapor pressure values. One approach to achieve this is by estimating it at a specific temperature using Alcock equations [
46] in the form of a polynomial:
where A
i, B
i, C
i and D
i are coefficients specific to i-th element, with commonly used values sourced from [
46]. The Equation 3 is applicable within the indicated temperature range and the fitted coefficients depend on the state of the material (solid or liquid). Yet, coefficients are often available over only a limited temperature range, and sometimes for the solid or liquid state only, the latter being the one needed. To overcome this problem, we will assume that the equations can be extended beyond the specified temperature ranges, and hold for both solid and liquid states. To verify these hypotheses, the vapor pressure calculated from Alcock equation at temperatures above the provided temperature range were compared in some cases for which the necessary data exists. For instance, for aluminum, its vapor pressure is of 2 atm at 2610 ⁰C [
47], compared to 1.97 atm calculated using the Alcock equation. Additionally, the equations for the liquid state are available for several metals, but for other ones (W, Mo, Cr, Nb and Mn), only equations for the solid can be found. However, when equations are found for both the liquid and solid metal, they seem to give similar values over the range of temperatures of interest. Consequently, it is here estimated that the use of equations established for solid state, when equations for the liquid are not found for the concerned metal, will still give a good estimation. In our study, we set both the average vaporization flux of the elements and the standard deviation of their corresponding values as objectives to be minimized at the boiling temperature of the alloy (estimated by a rule of mixtures), respectively to avoid porosity through keyholing and to avoid compositional changes due to differential vaporization.
3.1.4. Physical and Mechanical Properties
For crystalline materials, yield stress can be increased by mechanisms such as the grain size effect (Hall-Petch), precipitation hardening, strain hardening or solid solution hardening. In this particular study, we have ignored the effect of precipitation since we focus on the design of single-phase alloys. The influence of grain size was also omitted from the optimization criteria, as it is assumed to be mostly process-dependent. Strain hardening is also ignored as we primarily focus on AM – i.e., non deformed– alloys. A remaining possible level of action to increase alloy strength is to maximize solid solution hardening. Labusch suggested that the solid solution hardening can be represented as [
48]:
where X
i is the atomic fraction of component i and B
i is a constant defined by [
11,
49]:
Bi = 3µεi(4/3)Z, with µ the shear modulus, εi the mismatch parameter and Z a fitting constant;
εi = (ηi2 +α2.δi2)0.5, with ηi the term of the elastic misfit.
Using Vegard’s law [
50], for Fe-based alloys, one can estimate the atomic size misfit δ
i by:
with
the atomic radius of the solute and
the atomic radius of the iron solvent. As for the term of the elastic misfit, in general, the variation of shear modulus with composition is assumed to be linear [
51] and so, the parameter η
i can be estimated as:
where
and
are the shear moduli of solvent Fe and solute i, respectively. Finally, by considering a value of α=16 which is typically used for FCC alloys to account for the interaction of solute atoms with edge dislocations [
52], is it possible to calculate a solid solution strengthening index according to Equations 4-6. For alloy design, the solid solution index
is an objective to be maximized.
The addition and melting of layers in LPBF directly affect residual stresses and distortions in the built component. These issues in AM components result from the spatial temperature gradient due to localized heating and cooling, leading to uneven strain distribution [
53,
54]. Assessing the risk of distortion and residual stresses is a very complex task but, for a given thermal history (as in thermal shock [
55]), the extent of thermal strains scales, overall, with the coefficient of thermal expansion, α
CTE, stresses then being proportional to a product of strains and elastic constants. For different alloy elements
i, with
,
can be estimated using a simple rule of mixtures [
56], where
represents the coefficient of thermal expansion for pure element
i:
Elastic coefficients usually exhibit a limited variation, especially for austenitic stainless alloys (e.g., steels). Therefore, for alloy design it is here proposed to minimize and to ignore any possible variation in elastic properties.
3.2. Optimization of Alloys with a Genetic Algorithm
3.2.1. Compositional Space Explored
Austenitic steels contain iron and primarily rely on Ni, Mn and Co as key alloying elements to stabilize the FCC solid solution, along with Cr to ensure corrosion resistance. In this study, we focus on iron-rich alloys, requiring a minimum of 30 wt.% Fe. To ensure good corrosion resistance and intergranular corrosion resistance, we set a minimum Cr content at 15 wt.% and a C content of 200 wt. ppm, similar to low carbon stainless steels. Indeed, increasing chromium and limiting carbon content prevents intergranular precipitation of Cr carbides. Nickel plays a crucial role in stabilizing the austenitic phase, therefore the upper limit for this element is set to a high value of 35% wt. Manganese and cobalt, both serving as austenite stabilizers, have an upper limit of 25%. Adjustments to the maximum concentrations of the remaining elements were made based on data from commercial alloy compositions [
57]. The compositional search space is indicated in
Table 2.
3.2.2. Genetic Algorithm for the Global Optimization
The multi-objective optimization was conducted using the NSGA-II algorithm [
58], which was implemented using the pymoo Python package [
59]. The optimization was performed on a population of 100 alloys, with the same number of offsprings, to ensure a constant population size while keeping computation times reasonable. At each optimization step, new individuals were generated through simulated binary crossover with a distribution index set to η = 20. The algorithm also used polynomial mutation with a distribution index set to η = 20.
The objective functions - i.e., quantities that must be either maximized or minimized- and constraints –i.e., binary conditions that must be fulfilled - are summed up in
Table 3 and were employed to evaluate and sort the various alloys within the population. The optimization algorithm followed a three-step process. In the first step, the Hull diagram was used to rapidly assess the potential of an alloy for being austenitic (constraint
a in
Table 3). If this criterion was not met, the alloy was penalized by setting low fitness scores for all the other criteria and non-feasible constraints, thereby saving computational time. In the second step, the Scheil model was applied using Thermo-Calc, and its outputs were used to estimate constraints
b to
e and objective
g in
Table 3. In the third step, additional objectives were calculated using GPR-ML for objective
h and analytical formulas were used for objectives
f and
i to
l. The convergence of the algorithm is measured by the replacement rate: beyond 40 generations it drops to a rather low value of 1% of the population per step, indicating a good convergence. The optimization loop was terminated after 50 generations, for a replacement rate of 0.5% per step.
3.2.3. Selection of a Specific Alloy
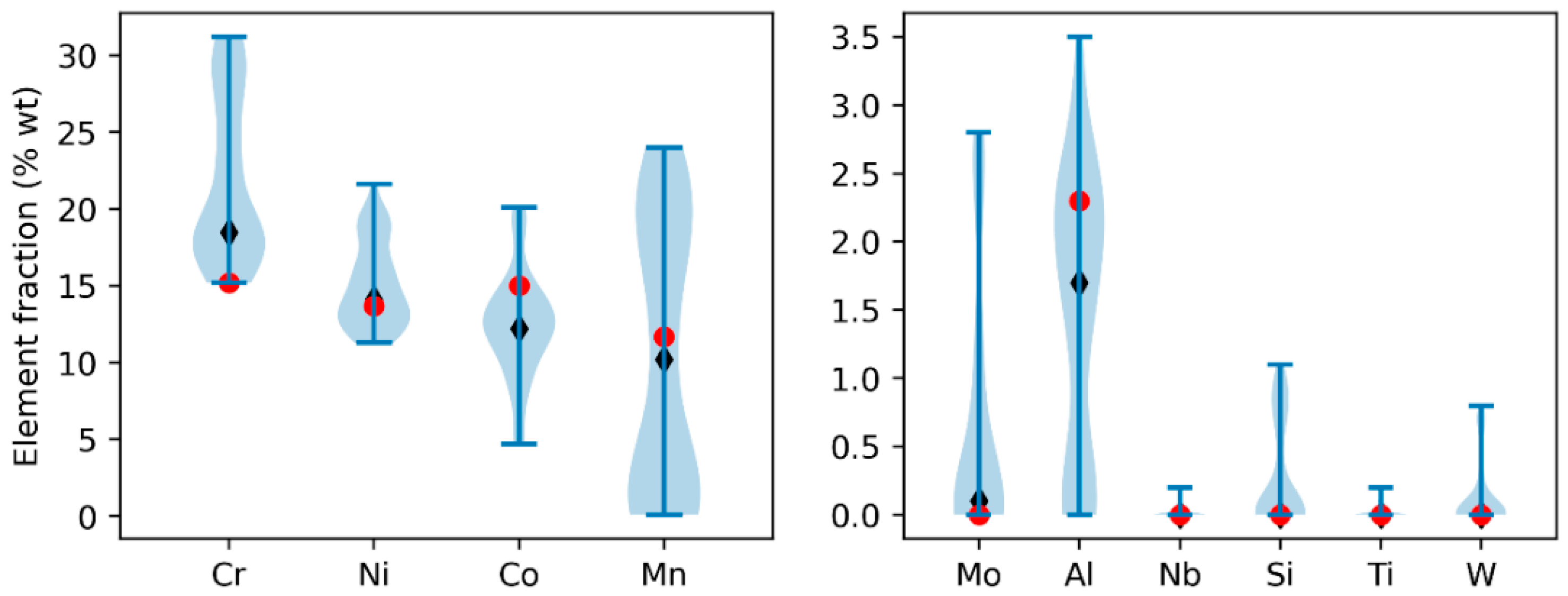
The distribution of compositions for the optimized population of alloys is illustrated in
Figure 2 using a violin plot. Cr content ranges between 15% and 31 wt.%, while Ni falls within the range of 11% to 22 wt.%. Mn exhibits a broader range, spanning from 0% to 24wt.%. Notably, a significant amount of Co, ranging from 5% to 20wt.%, is prevalent in most of the alloys. This elevated cobalt content is likely a result of the criterion for enhancing solid solution hardening and stabilizing the austenitic structure. The content of other elements is generally limited to a few percent: Mo and Al do not exceed 3% and 4wt.%, respectively. On the other hand, elements like Nb, Ti and W have average values well below a fraction of a percent and are considered negligible, despite their potentially high solid solution hardening capability. It seems possible that the strong tendency of these three elements towards primary segregation conflicts with the objective of minimizing the CTR value. Besides, these three elements also act as ferrite stabilizers, ultimately raising the Cr
eq value and rendering their inclusion unfavorable.
After optimization, all the alloys in the population belong to a Pareto front. Selecting a single optimal alloy is challenging as each performs better in some specific criteria. To determine the best overall option, we ranked the alloys by their average performance across all objectives. To aid in selection, we introduced an additional criterion: the temperature range for austenite stability at equilibrium, predicted by Thermo-Calc. Although not initially included in the multi-objective optimization due to computational costs, it is essential for avoiding unwanted phase transformations during post-AM heat treatments. This criterion helped differentiate between otherwise equivalent alloys based on other factors. From optimized alloys, one composition was chosen based on the previously discussed criteria and it is indicated in
Table 1 and by red dots on
Figure 2.
Table 4 presents a comparison of the values of our defined objective functions for the selected material, calculated based on the effective powder composition specified in
Table 1, and for 316L. Overall, the optimized alloy outperforms 316L, except for the thermal expansion coefficient, which is slightly higher than that of this reference alloy.
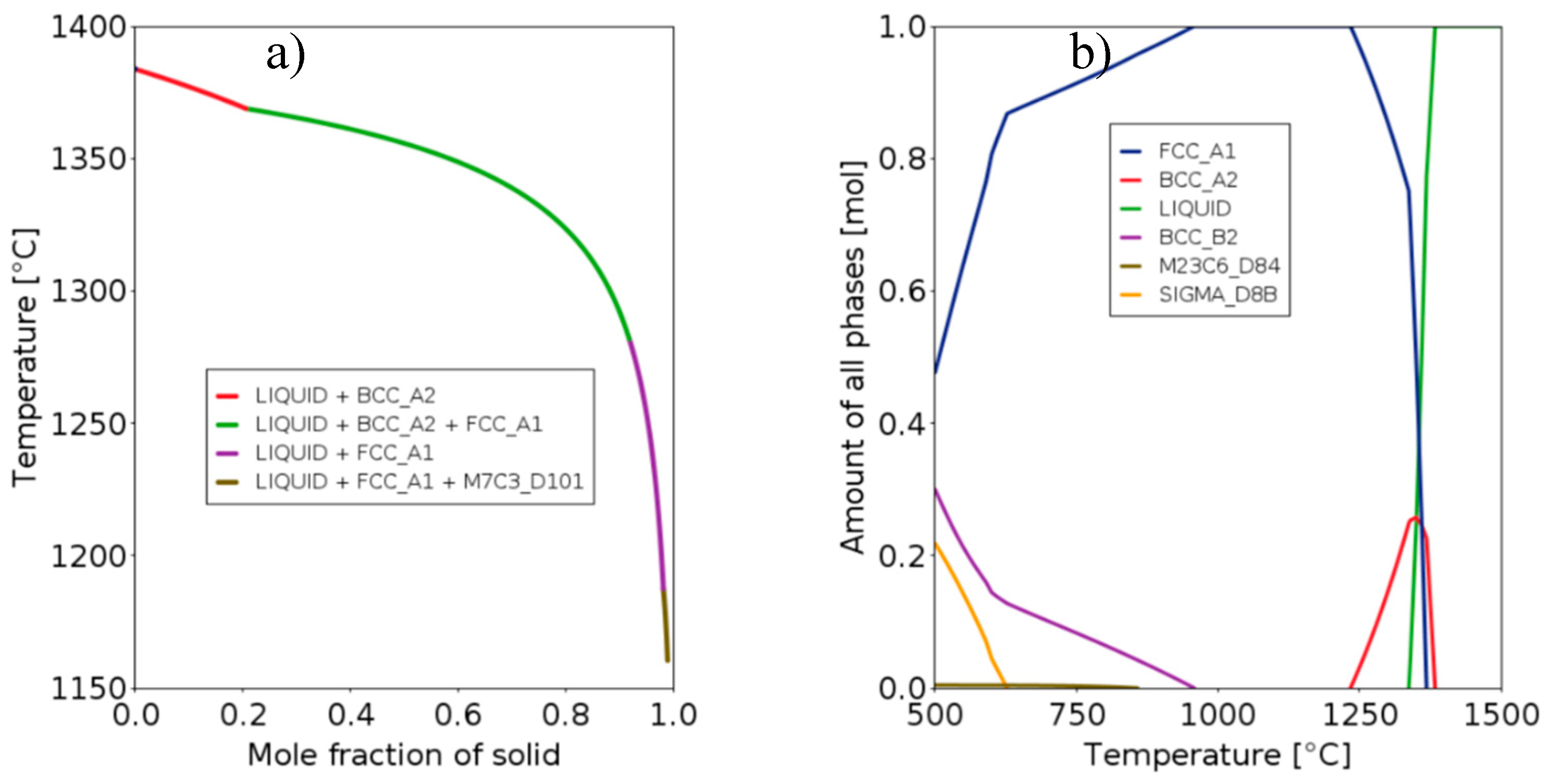
The Scheil simulation of solidification and phases fraction with temperature for the selected alloy are depicted in
Figure 3. The Scheil diagram on
Figure 3a reveals that the alloy initially solidifies into δ-ferrite (BCC_A2) for a solid fraction up to 20%, then austenite is formed (FCC_A1). By the end of the solidification, these two phases collectively make up 99% of the material. The predicted CTR is relatively low, with a value of 77 K, compared to the value of 92 K for the 316L alloy. Consequently, the risk of solidification cracking is minimal. According to the equilibrium calculation of
Figure 3b, the alloy is expected to maintain a single FCC structure within the temperature range of 950 to 1230°C. Below 950°C, an ordered BCC phase of the B2 type is predicted to form at equilibrium. Nevertheless, the Cr
eq and Ni
eq values, in accordance with the Hull diagram, suggest the alloy is anticipated to remain fully austenitic after solidification and cooling in a welding-type process. A negligible amount of chromium-rich M
23C
6 carbides (< 0.005%) is predicted below approximately 800°C.
3.3. Experimental Validation
3.3.1. Evaluation of the Coefficient of Linear Thermal Expansion
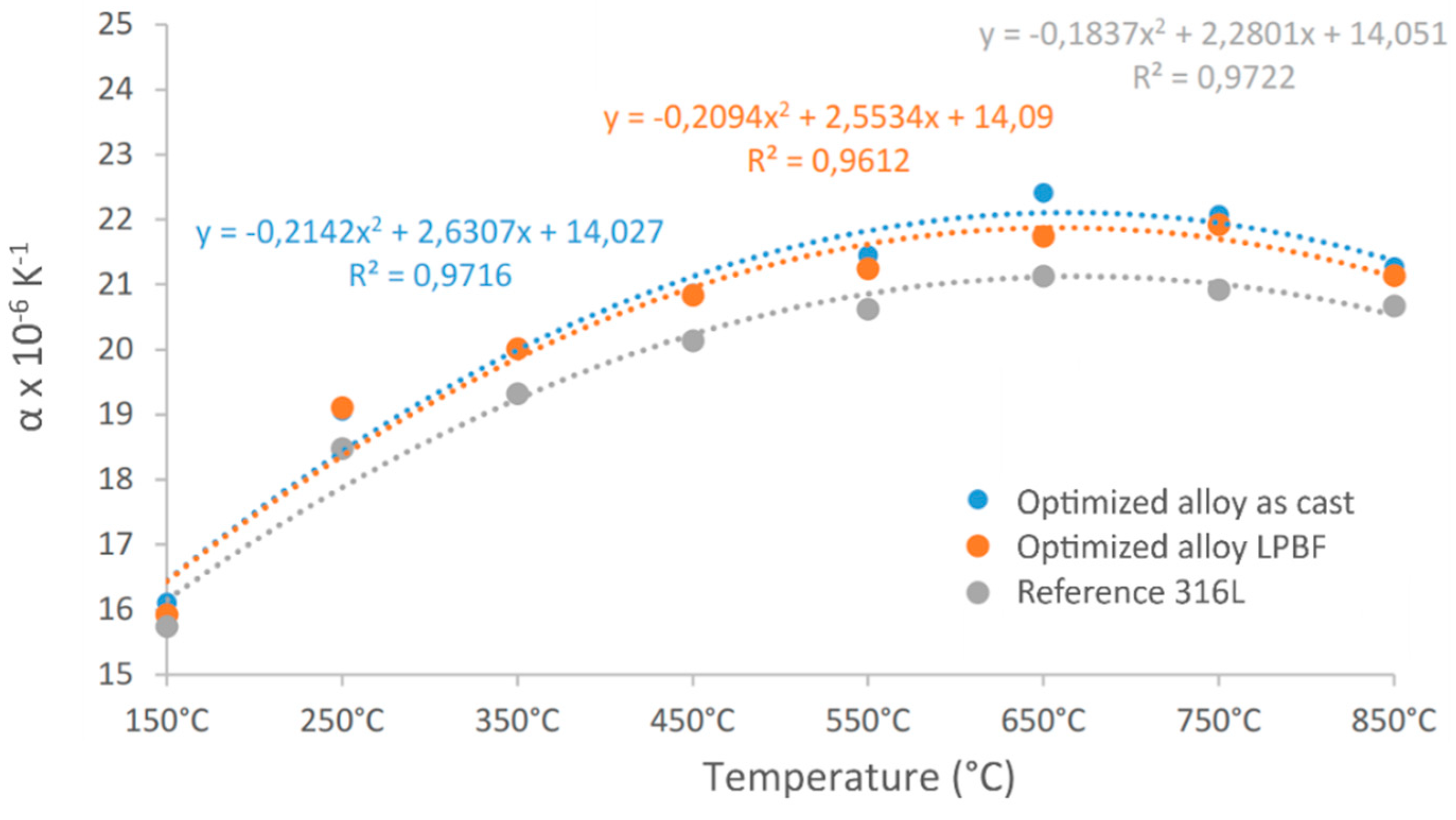
Dilatometry measurements were performed for three materials: 316L stainless steel, the optimized alloy after casting and the same optimized alloy produced by LPBF. The
Figure 4 shows the variation of the expansion coefficient for the different alloys as a function of temperature. Each point was determined by averaging the values within a range of -50°C to +50°C around the experimental point. The coefficient α systematically increases by about 30% with temperature and then stabilizes above 500°C.
The average coefficient of expansion over the three measurements was found to be nearly identical for both the cast material (
) and the LPBF material (
). The average value for 316L was slightly lower
, which is consistent with the predictions (
Table 4). However, for all the alloys, the experimental values were significantly higher than the predicted ones. This discrepancy highlights the limitations of a linear mixture model for predicting α
CTE: while it can quickly estimate the relative variation in α
CTE between different alloys, the accuracy of the predicted absolute values remains poor and they should not be used directly. Nevertheless, since trends seem correctly captured, such a simple tool can be used for alloy design if the property is to be optimized (e.g., minimized), which is the case here.
3.3.2. Microstructure after AM Processing
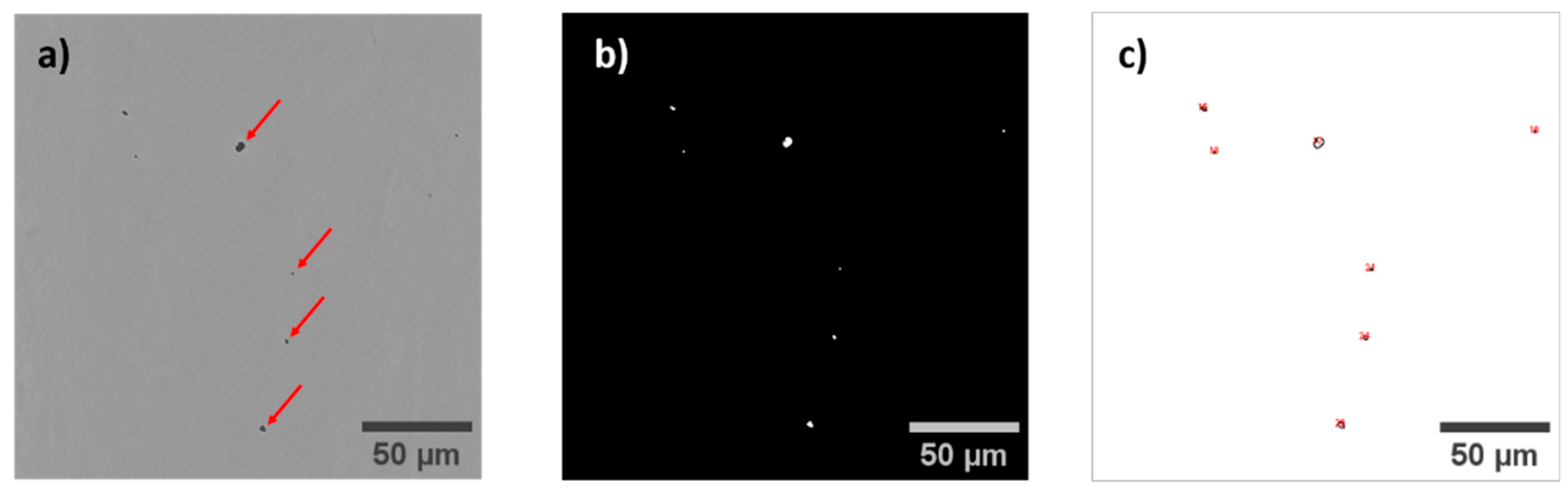
To determine the porosity, the alloy produced through LPBF is characterized by SEM observations: a set of images is taken over a total surface of 4 mm². The images are then thresholded to capture the pore fraction and size distribution using ImageJ software. An example is shown for the material built at P=144W and v=1200 mm/s: it displays an average porosity of 0.05%, with a standard deviation of 0.02%. This rate is notably low compared to those observed in similar alloys, especially considering that standard processing parameters were used without any specific adjustment. Typically, the porosity rate reaches values around 0.8-1% for common alloys like 316L [
60,
61].
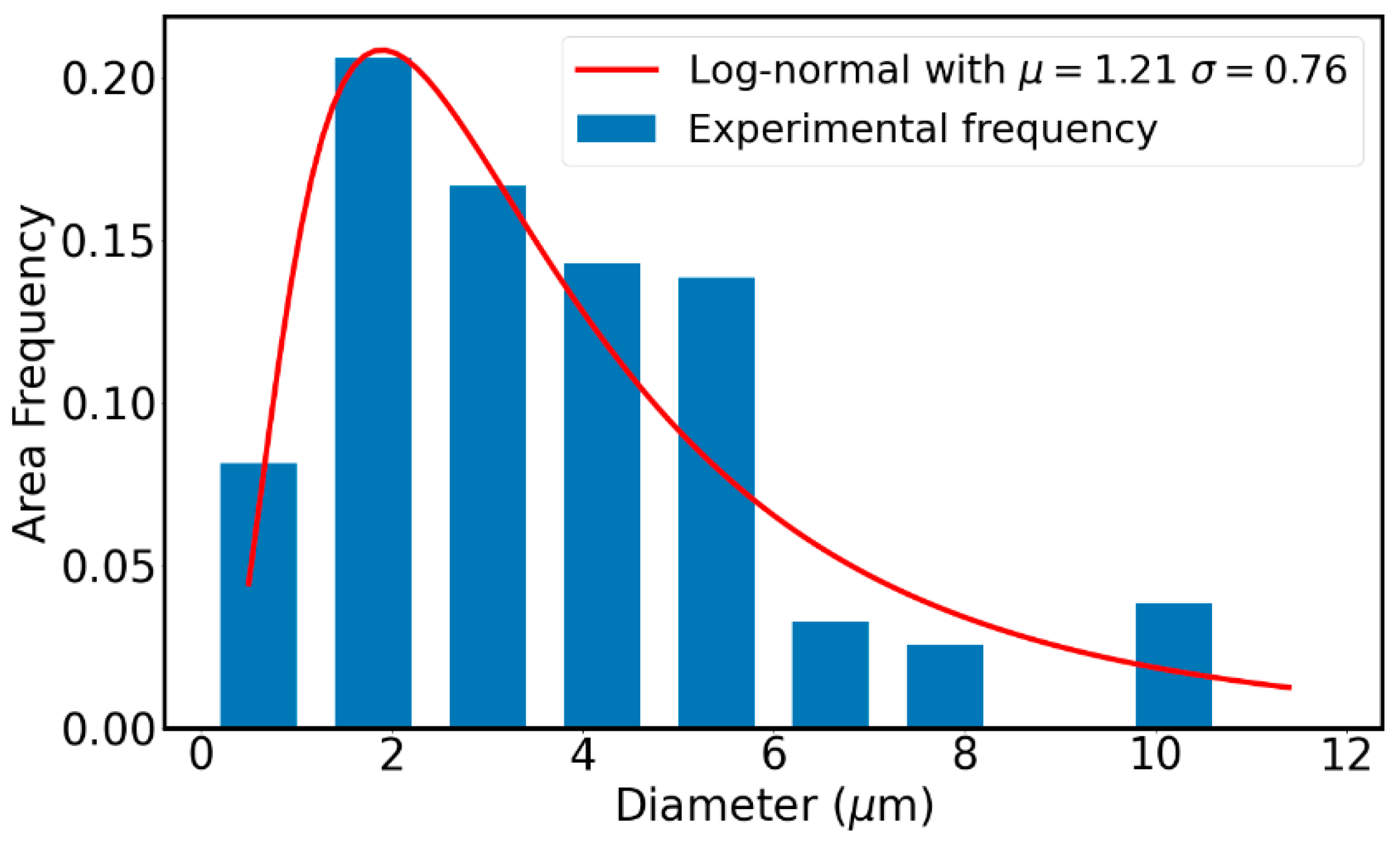
Figure 6 illustrates the pore size distribution, which is roughly a lognormal distribution with an average size of 4.5 µm and a median value of 3.4 µm. The pore size remains less than or equal to 10 µm. This is below the critical defect size that can initiate crack propagation, even under fatigue conditions. Indeed, assuming a very low crack propagation threshold of 2 MPa.m
1/2 to be conservative and a penny-shaped crack of radius 5 µm associated to a conventional geometrical factor of
, cracking would be likely to occur only for a stress amplitude superior to 560 MPa, which is higher than the yield stress (see section 4.3). Given that a pore is normally less critical than a crack and that the actual crack propagation threshold more likely lies between 5 and 10 MPa.m
1/2 for this category of alloys, it is almost certain that the observed pores cannot become critical defects and initiate any damage.
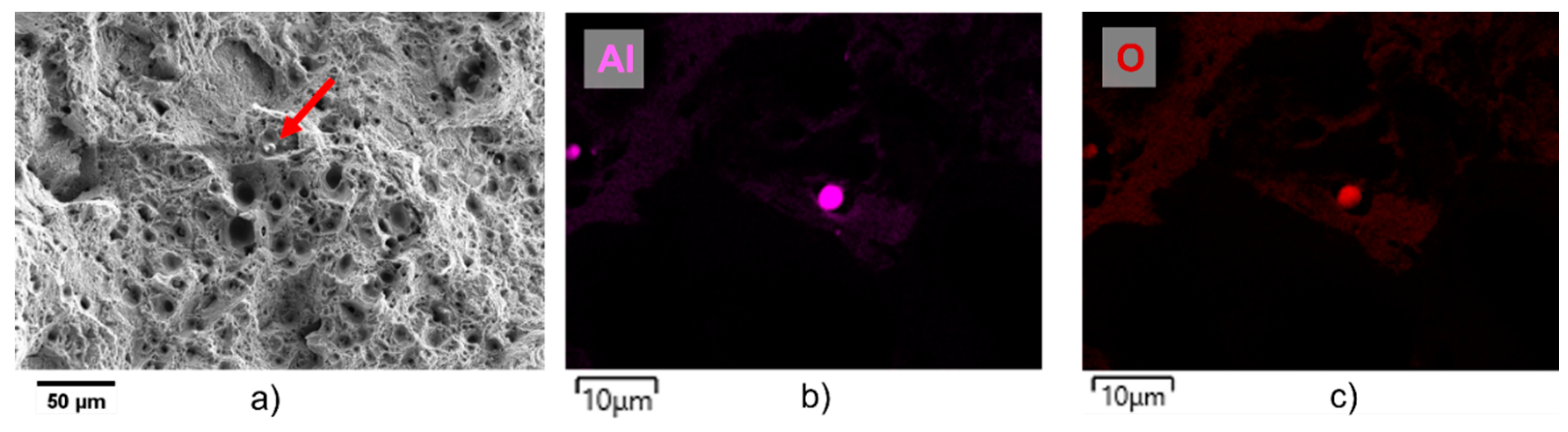
Figure 5.
a) Observation of the pores by SEM (red arrows), b) Thresholding of the image to detect pores, c) Detection using ImageJ software.
Figure 5.
a) Observation of the pores by SEM (red arrows), b) Thresholding of the image to detect pores, c) Detection using ImageJ software.
Figure 6.
Pore size distribution obtained by SEM image analysis for a material built at P=144W v=1200mm/s.
Figure 6.
Pore size distribution obtained by SEM image analysis for a material built at P=144W v=1200mm/s.
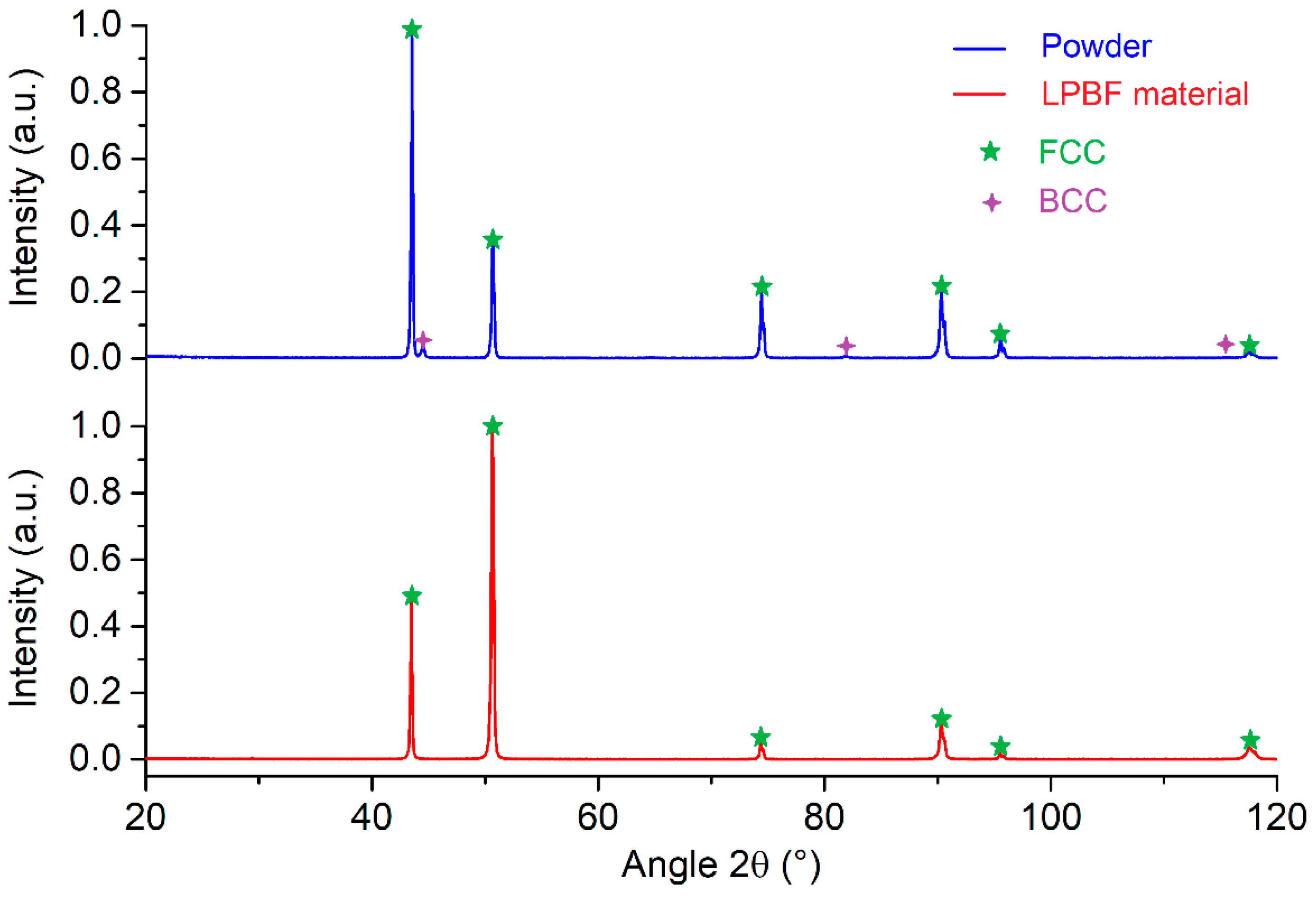
X-ray diffraction analysis was performed to identify the phases present in the powder and in the LPBF built material (
Figure 7). The observed peaks indicate the presence of two phases in the powder. The primary FCC phase corresponds to the austenite phase (γ), with a theoretical lattice parameter a=3.606 Å, according to JCPDS card n°01-081-8775. Additionally, a minor BCC phase, estimated to constitute 3% of the material, corresponds to the ferrite phase, characterized by a theoretical lattice parameter a=2.882 Å (JCPDS card n°04-003-2920). The LPBF built material characterized in the same conditions shows the presence of only the austenite phase. The ferrite phase observed in the powder is therefore not detected in the LPBF built samples. It is possible that the ferrite phase was first formed during solidification, as predicted, and then transformed into austenite.
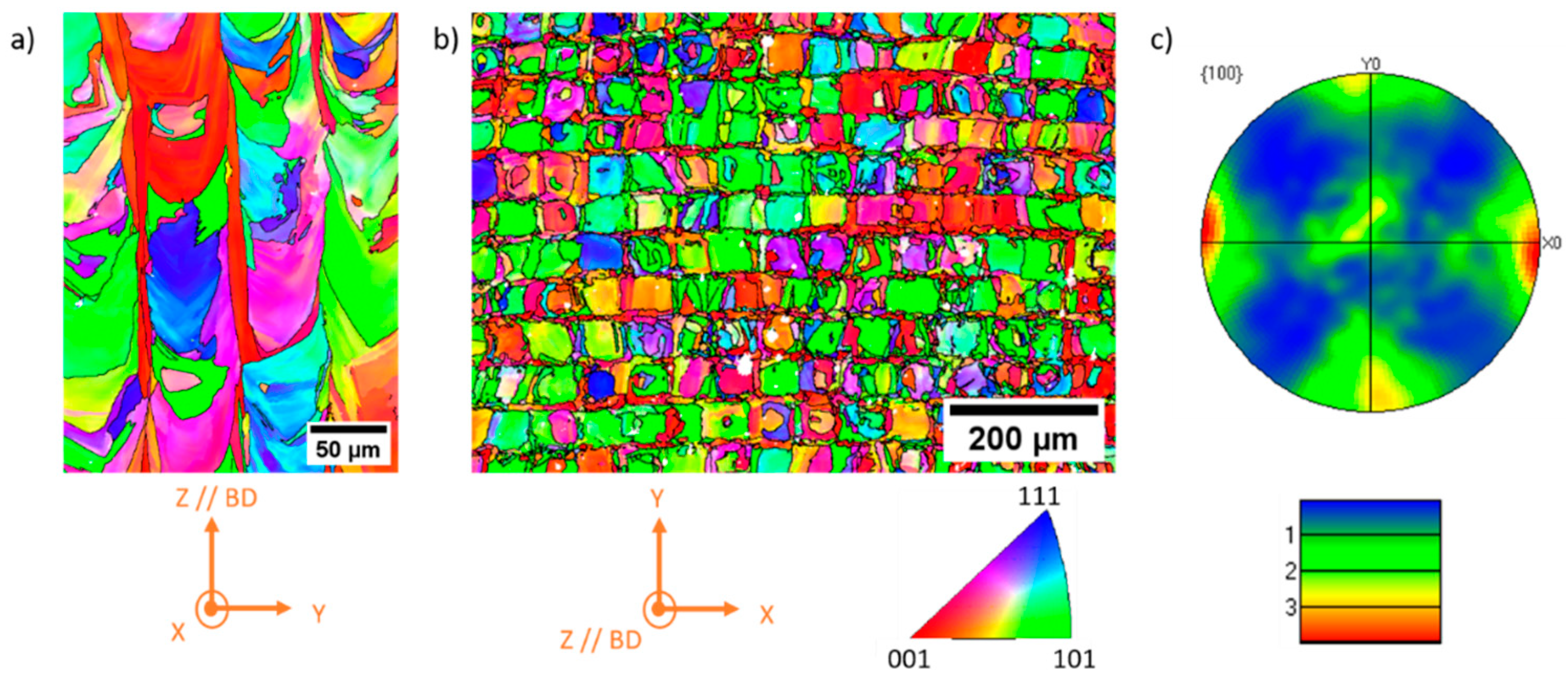
The crystalline orientation in the melt pools is characterized using EBSD. The Inverse Pole Figure (IPF) map is shown in
Figure 8a, illustrating the crystalline orientation along the building direction (BD) with the laser scanning direction (SD) along the X and Y axes. Large grains with melt pool geometry are observed and high angle boundaries (>15°) are represented by black lines. Small variations in the IPF color code within grains suggest the presence of a post-solidification substructure, indicating that a significant portion of the FCC phase formed directly during the solidification step. This observation is consistent with predictions from the Scheil model (
Figure 3a), suggesting a likely liquid →
γ solidification for much of the observed austenite. It is noteworthy that the microstructure does not consist of long columnar grains, as is commonly observed in the 316L alloy [
62]. The crystalline orientation of each successive layer is different from the previous one, indicating that solidification does not occur by epitaxial growth between successive layers.
Figure 8b shows an IPF map along BD, with BD normal to the figure and SD along the X and Y axes. This map confirms the presence of large grains in the melt pool, resulting in a microstructure that follows a lattice pattern. The pole figure corresponding to
Figure 8b is shown in
Figure 8c for {100} planes, showing that this crystalline orientation is preferentially aligned along the BD and SD axes and is close to a cube texture.
3.3.3. Mechanical Properties
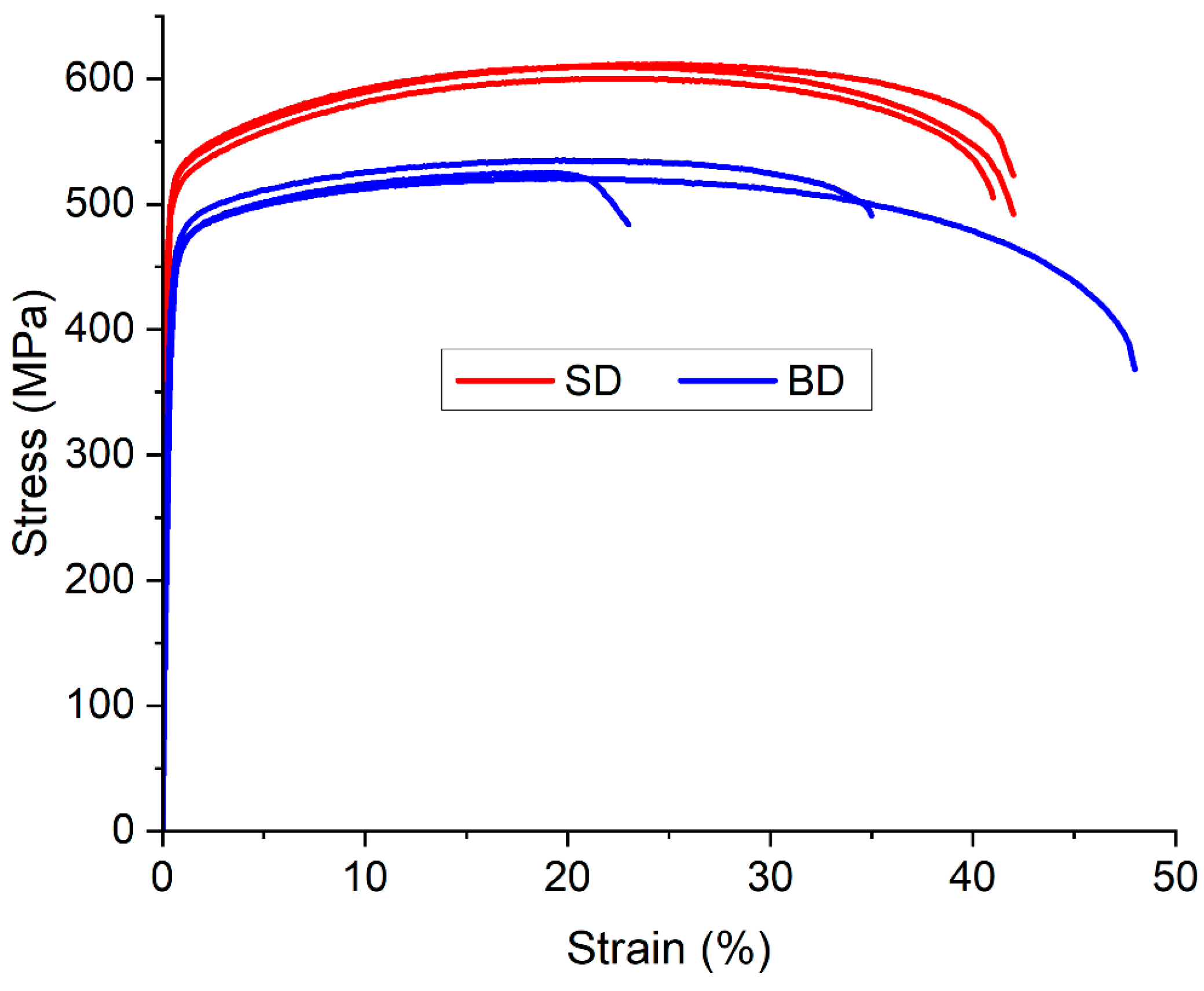
Tensile tests were conducted at room temperature along two distinct orientations, with the tensile axis aligned either parallel to the building direction (BD) or to the scanning direction (SD) to evaluate a potential anisotropic behavior. Three tests were performed for each orientation. The test results (
Figure 9) exhibit good reproducibility, showing yield stress differences below 5 MPa between specimens for both SD and BD orientations. The material tested along SD exhibits the highest strength, with an average yield stress of 520 MPa, an ultimate tensile stress (UTS) of 600 MPa and an elongation to fracture of 40%. In contrast, the material tested along BD displays a yield stress 6% lower (490 MPa) and a UTS 14% lower (525 MPa). These differences may be due to the slight anisotropy of the cellular dendrite microstructure of the samples as observed in [
63], along with the fact that metallurgical defects are more easily introduced into the bonding area between two consecutive layers [
64]. While stress-strain curves in horizontally cut samples are quite reproducible, vertically cut ones exhibit notable discrepancies in elongation to fracture, suggesting potential microstructure variations.
The fracture surfaces of the tensile specimens were observed by SEM (
Figure 10a). In all samples, ductile fracture is observed, with microvoids and dimples characteristic of ductile fracture. However, occasional small spherical inclusions were noted, as illustrated in
Figure 10 with a red arrow. The EDX analysis of these inclusions (
Figure 10b,c) show the presence of Al and O, indicating they are probably alumina. Interestingly, these inclusions were not initially detected through SEM imaging of the powder. As aluminum exhibits a significantly higher affinity for oxygen compared to other alloying elements, the presence of aluminum oxides may result from a small oxygen fraction within the powder or the atmosphere of the laser chamber. Consequently, these inclusions are likely due to contamination during the process. To mitigate their occurrence, a better control over powder processing and storage conditions, coupled with monitoring and regulating the oxygen content within the LPBF chamber, may prove effective in reducing the incidence of such inclusions. However, the latter are always a few µm in diameter, as for pores so that, for the reasons already invoked, they cannot be at the origin of cracking under static or even cyclic loading.
The challenge of powder oxidation could nevertheless be addressed in future alloy design research. The introduction of additional criteria may help to penalize elements that are particularly prone to oxidation. For example, one possible method could be to develop a penalty function based on the standard free enthalpies of formation of their respective oxides. This strategy would aim to minimize the risk of oxidation during laser melting and powder storage, thereby avoiding the formation of potentially embrittling (i.e. larger) oxide inclusions.
5. Conclusions
In this study, a genetic algorithm was used to optimize a single-phased, iron-rich austenitic alloy for additive manufacturing. The Hull diagram provided feasibility constraints and the Scheil model addressed solidification conditions. The Labusch model was used to evaluate and to increase solid solution strengthening, to promote improved mechanical resistance. Minimizing the coefficient of thermal expansion (αCTE), vaporization fluxes and reducing surface tension were key objectives to reduce porosity or distortions. The risk of cracking was also minimized via several criteria. These objectives and constraints were integrated into a multi-objective genetic algorithm, resulting in the identification and selection of a new optimized composition with improved printability. The optimized alloy powder was produced by gas atomization and then used in the LPBF process to produce specimens for microstructural and mechanical characterization. The LPBF samples were crack free with a low porosity fraction, even though printing was performed with standard processing parameters. This confirms the effectiveness of the design process in preventing the occurrence of critical defects and maintaining high ductility. As expected, the LPBF material consists of a single FCC phase. The coefficient of thermal expansion is, as predicted, just slightly higher than that of 316L stainless steel. Tensile tests showed good ductility with strength values close to those of other LPBF-printed austenitic steels such as 316L. Future steps could consider additional criteria such as material cost, density, spatter formation or reduced sensitivity to oxidation. While the study demonstrates feasibility, targeting specific applications has promising industrial potential.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.T., A.F. and J.F.; methodology, M.A., J.F., F.T. and A.F.; formal analysis, M.A., J.F., A.F. and F.T.; investigation, M.A., M.B.; resources, A.F. and F.T.; writing—original draft preparation, M.A., J.F.; writing—review and editing, J.F., F.T. and A.F.; supervision, J.F., F.T. and A.F.; funding acquisition: J.F. and A.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Clare, A.T.; Mishra, R.S.; Merklein, M.; Tan, H.; Todd, I.; Chechik, L.; Li, J.; Bambach, M. Alloy Design and Adaptation for Additive Manufacture. Journal of Materials Processing Technology 2022, 299, 117358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DebRoy, T.; Wei, H.L.; Zuback, J.S.; Mukherjee, T.; Elmer, J.W.; Milewski, J.O.; Beese, A.M.; Wilson-Heid, A.; De, A.; Zhang, W. Additive Manufacturing of Metallic Components – Process, Structure and Properties. Progress in Materials Science 2018, 92, 112–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanaei, N.; Fatemi, A. Defects in Additive Manufactured Metals and Their Effect on Fatigue Performance: A State-of-the-Art Review. Progress in Materials Science 2021, 117, 100724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauzon, C.; Buttard, M.; Després, A.; Charlot, F.; Fivel, M.; Chehab, B.; Blandin, J.-J.; Martin, G. Direct Ageing of LPBF Al-1Fe-1Zr for High Conductivity and Mechanical Performance. Acta Materialia 2023, 258, 119199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buttard, M.; Freixes, M.L.; Josserond, C.; Donnadieu, P.; Chéhab, B.; Blandin, J.-J.; Gault, B.; De Geuser, F.; Martin, G. Ageing Response and Strengthening Mechanisms in a New Al-Mn-Ni-Cu-Zr Alloy Designed for Laser Powder Bed Fusion. Acta Materialia 2023, 259, 119271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tancret, F. Computational Thermodynamics, Gaussian Processes and Genetic Algorithms: Combined Tools to Design New Alloys. Modelling Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2013, 21, 045013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tancret, F.; Toda-Caraballo, I.; Menou, E.; Rivera Díaz-Del-Castillo, P.E.J. Designing High Entropy Alloys Employing Thermodynamics and Gaussian Process Statistical Analysis. Materials & Design 2017, 115, 486–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deschamps, A.; Tancret, F.; Benrabah, I.-E.; De Geuser, F.; Van Landeghem, H.P. Combinatorial Approaches for the Design of Metallic Alloys. Comptes Rendus Physique 2018, 19, 737–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menou, E.; Toda-Caraballo, I.; Rivera-Díaz-del-Castillo, P.E.J.; Pineau, C.; Bertrand, E.; Ramstein, G.; Tancret, F. Evolutionary Design of Strong and Stable High Entropy Alloys Using Multi-Objective Optimisation Based on Physical Models, Statistics and Thermodynamics. Materials & Design 2018, 143, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tancret, F. Computational Thermodynamics and Genetic Algorithms to Design Affordable Γ′-Strengthened Nickel–Iron Based Superalloys. Modelling Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2012, 20, 045012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieurin, H.; Zander, J.; Sandström, R. Modelling Solid Solution Hardening in Stainless Steels. Materials Science and Engineering: A 2006, 415, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menou, E.; Ramstein, G.; Bertrand, E.; Tancret, F. Multi-Objective Constrained Design of Nickel-Base Superalloys Using Data Mining- and Thermodynamics-Driven Genetic Algorithms. Modelling Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 24, 055001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Sha, W. Modelling the Correlation between Processing Parameters and Properties of Maraging Steels Using Artificial Neural Network. Computational Materials Science 2004, 29, 12–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, K.; Vecchio, K.S. Searching for High Entropy Alloys: A Machine Learning Approach. Acta Materialia 2020, 198, 178–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.S.; Thapliyal, S. Design Approaches for Printability-Performance Synergy in Al Alloys for Laser-Powder Bed Additive Manufacturing. Materials & Design 2021, 204, 109640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, J.; Derguti, F.; Todd, I. Selection of Steels Suitable for Additive Layer Manufacturing. Ironmaking & Steelmaking 2014, 41, 254–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackers, M.A.; Messé, O.M.D.M.; Hecht, U. Novel Approach of Alloy Design and Selection for Additive Manufacturing towards Targeted Applications. Journal of Alloys and Compounds 2021, 866, 158965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabzi, H.E.; Rivera-Díaz-del-Castillo, P.E.J. Defect Prevention in Selective Laser Melting Components: Compositional and Process Effects. Materials 2019, 12, 3791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabzi, H.E.; Maeng, S.; Liang, X.; Simonelli, M.; Aboulkhair, N.T.; Rivera-Díaz-del-Castillo, P.E.J. Controlling Crack Formation and Porosity in Laser Powder Bed Fusion: Alloy Design and Process Optimisation. Additive Manufacturing 2020, 34, 101360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaeffler, A.L. Constitution Diagram for Stainless Steel Weld Metal. Metal Progress 1949, 56, 680. [Google Scholar]
- Delong, W.T. Ferrite in Austenitic Stainless Steel Weld Metal. Welding Journal 1974, 53, 273. [Google Scholar]
- Hull, F.C. Delta Ferrite and Martensite Formation in Stainless Steels. Welding Journal 1973, 52, 193. [Google Scholar]
- Scheil, E. Bemerkungen Zur Schichtkristallbildung. International Journal of Materials Research 1942, 34, 70–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, T.; Lindwall, G.; Ghosh, S.; Ma, L.; Lane, B.M.; Zhang, F.; Kattner, U.R.; Lass, E.A.; Heigel, J.C.; Idell, Y.; et al. Application of Finite Element, Phase-Field, and CALPHAD-Based Methods to Additive Manufacturing of Ni-Based Superalloys. Acta Materialia 2017, 139, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, E.; Eissa, M.M.; Tageldin, A.S. Distinct Properties of Tungsten Austenitic Stainless Alloy as a Potential Nuclear Engineering Material. Nuclear Engineering and Technology 2019, 51, 784–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indacochea, J.E.; Gattu, V.K.; Chen, X.; Rahman, T. Performance of a Steel/Oxide Composite Waste Form for Combined Waste Steams from Advanced Electrochemical Processes; 2017; p. DOE/NEUP--13-5059, 1364135.
- Cantor B., Chang I.T.H., Knight P., Vincent A.J.B., Microstructural development in equiatomic multicomponent alloys, MSE-A, 2004 375-377, 213-218. [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Tan, X.P.; Descoins, M.; Mangelinck, D.; Tor, S.B.; Lim, C.S. Revealing Hot Tearing Mechanism for an Additively Manufactured High-Entropy Alloy via Selective Laser Melting. Scripta Materialia 2019, 168, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rappaz, M.; Drezet, J.-M.; Gremaud, M. A New Hot-Tearing Criterion. Metall Mater Trans A 1999, 30, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galy, C.; Le Guen, E.; Lacoste, E.; Arvieu, C. Main Defects Observed in Aluminum Alloy Parts Produced by SLM: From Causes to Consequences. Additive Manufacturing 2018, 22, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suutala, N. Effect of Manganese and Nitrogen on the Solidification Mode in Austenitic Stainless Steel Welds. Metall Trans A 1982, 13, 2121–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suutala, N. Effect of Solidification Conditions on the Solidification Mode in Austenitic Stainless Steels. Metall Trans A 1983, 14, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishnan, V.M. Hot Cracking in Austenitic Stainless Steel Weld Metals. Science and Technology of Welding and Joining 2000, 5, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimoto, K.; Mori, H. Hot Cracking Susceptibility in Laser Weld Metal of High Nitrogen Stainless Steels. Science and Technology of Advanced Materials 2004, 5, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, V.; Gill, T.P.S.; Mannan, S.L.; Sundaresan, S. Solidification Cracking in Austenitic Stainless Steel Welds. Sadhana 2003, 28, 359–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
-
Hot Cracking Phenomena in Welds II; Böllinghaus, T., Herold, H., Cross, C.E., Lippold, J.C., Eds.; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2008; ISBN 978-3-540-78627-6.
- Saluja, R.; Moeed, K. Experimental Investigation Of Solidification-Mode And Response Surface Modeling Of Ferrite-Content In Grade 304L Pulse GMA Welded Plates. Materials Today: Proceedings 2019, 18, 3876–3890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusarov, A.V.; Smurov, I. Modeling the Interaction of Laser Radiation with Powder Bed at Selective Laser Melting. Physics Procedia 2010, 5, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekhar, S. Hydrodynamic and Hydromagnetic Stability; Dover ed.; Dover Publications: New York, 1981; ISBN 978-0-486-64071-6.
- De Gennes, P.-G.; Brochard-Wyart, F.; Quéré, D. Capillarity and Wetting Phenomena; Springer New York: New York, NY, 2004; ISBN 978-1-4419-1833-8. [Google Scholar]
- Assi, M.; Favre, J.; Fraczkiewicz, A.; Tancret, F. Machine Learning-Based Model of Surface Tension of Liquid Metals: A Step in Designing Multicomponent Alloys for Additive Manufacturing. J Mater Sci 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, W.E.; Anderson, A.T.; Ferencz, R.M.; Hodge, N.E.; Kamath, C.; Khairallah, S.A.; Rubenchik, A.M. Laser Powder Bed Fusion Additive Manufacturing of Metals; Physics, Computational, and Materials Challenges. Applied Physics Reviews 2015, 2, 041304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.A.; Calta, N.P.; Hammons, J.A.; Khairallah, S.A.; Nielsen, M.H.; Shuttlesworth, R.M.; Sinclair, N.; Matthews, M.J.; Jeffries, J.R.; Willey, T.M.; et al. Ultrafast Dynamics of Laser-Metal Interactions in Additive Manufacturing Alloys Captured by in Situ X-Ray Imaging. Materials Today Advances 2019, 1, 100002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, T.; Zuback, J.S.; De, A.; DebRoy, T. Printability of Alloys for Additive Manufacturing. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 19717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; DebRoy, T.; Fuerschbach, P.W. Alloying Element Vaporization during Laser Spot Welding of Stainless Steel. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 2003, 36, 3079–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcock, C.B.; Itkin, V.P.; Horrigan, M.K. Vapour Pressure Equations for the Metallic Elements: 298–2500K. Canadian Metallurgical Quarterly 1984, 23, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
-
CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics; Haynes, W.M., Ed.; 0 ed.; CRC Press, 2014; ISBN 978-0-429-17019-5.
- Labusch, R. A Statistical Theory of Solid Solution Hardening. Physica Status Solidi (b) 1970, 41, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischer, R.L. Substitutional Solution Hardening. Acta Metallurgica 1963, 11, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denton, A.R.; Ashcroft, N.W. Vegard’s Law. Phys. Rev. A 1991, 43, 3161–3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledbetter, H.M.; Reed, R.P. Elastic Properties of Metals and Alloys, I. Iron, Nickel, and Iron-Nickel Alloys. Journal of Physical and Chemical Reference Data 1973, 2, 531–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zander, J.; Sandström, R.; Vitos, L. Modelling Mechanical Properties for Non-Hardenable Aluminium Alloys. Computational Materials Science 2007, 41, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruth, J.-P.; Deckers, J.; Yasa, E.; Wauthlé, R. Assessing and Comparing Influencing Factors of Residual Stresses in Selective Laser Melting Using a Novel Analysis Method. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part B: Journal of Engineering Manufacture 2012, 226, 980–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levkulich, N.C.; Semiatin, S.L.; Gockel, J.E.; Middendorf, J.R.; DeWald, A.T.; Klingbeil, N.W. The Effect of Process Parameters on Residual Stress Evolution and Distortion in the Laser Powder Bed Fusion of Ti-6Al-4V. Additive Manufacturing 2019, 28, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.J.; Fleck, N.A. The Thermal Shock Resistance of Solids. Acta Materialia 1998, 46, 4755–4768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toda-Caraballo, I.; Galindo-Nava, E.I.; Rivera-Díaz-del-Castillo, P.E.J. Unravelling the Materials Genome: Symmetry Relationships in Alloy Properties. Journal of Alloys and Compounds 2013, 566, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granta Design Limited CES EduPack Software 2019.
- Deb, K.; Pratap, A.; Agarwal, S.; Meyarivan, T. A Fast and Elitist Multiobjective Genetic Algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE Trans. Evol. Computat. 2002, 6, 182–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blank, J.; Deb, K. Pymoo: Multi-Objective Optimization in Python. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 89497–89509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadroitsev, I.; Smurov, I. Selective Laser Melting Technology: From the Single Laser Melted Track Stability to 3D Parts of Complex Shape. Physics Procedia 2010, 5, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, S.; Chen, Y.; Boardman, R.; Yang, S.; Gao, N. Investigation on Porosity and Microhardness of 316L Stainless Steel Fabricated by Selective Laser Melting. Metals 2017, 7, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Tan, X.; Tor, S.B.; Chua, C.K. Simultaneously Enhanced Strength and Ductility for 3D-Printed Stainless Steel 316L by Selective Laser Melting. NPG Asia Mater 2018, 10, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, K.N.; Gaytan, S.M.; Murr, L.E.; Martinez, E.; Shindo, P.W.; Hernandez, J.; Collins, S.; Medina, F. Microstructures and Mechanical Behavior of Inconel 718 Fabricated by Selective Laser Melting. Acta Materialia 2012, 60, 2229–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Wang, Z.; Gao, M.; Zeng, X. Layer Thickness Dependence of Performance in High-Power Selective Laser Melting of 1Cr18Ni9Ti Stainless Steel. Journal of Materials Processing Technology 2015, 215, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).