Submitted:
03 September 2024
Posted:
04 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Material
2.2. Esterification Reaction
2.3. Product Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
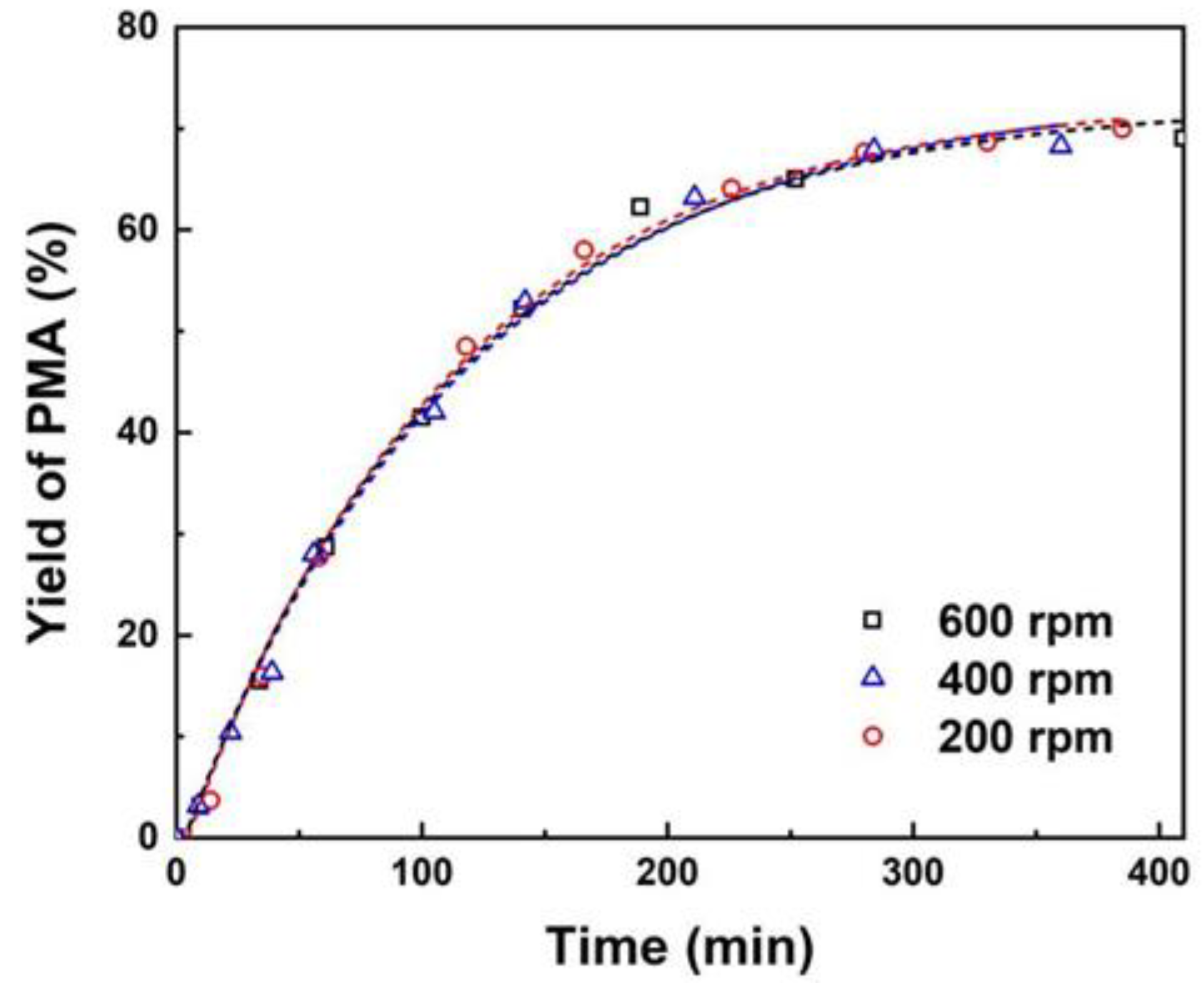
3.1. Effect of Mass Transfer
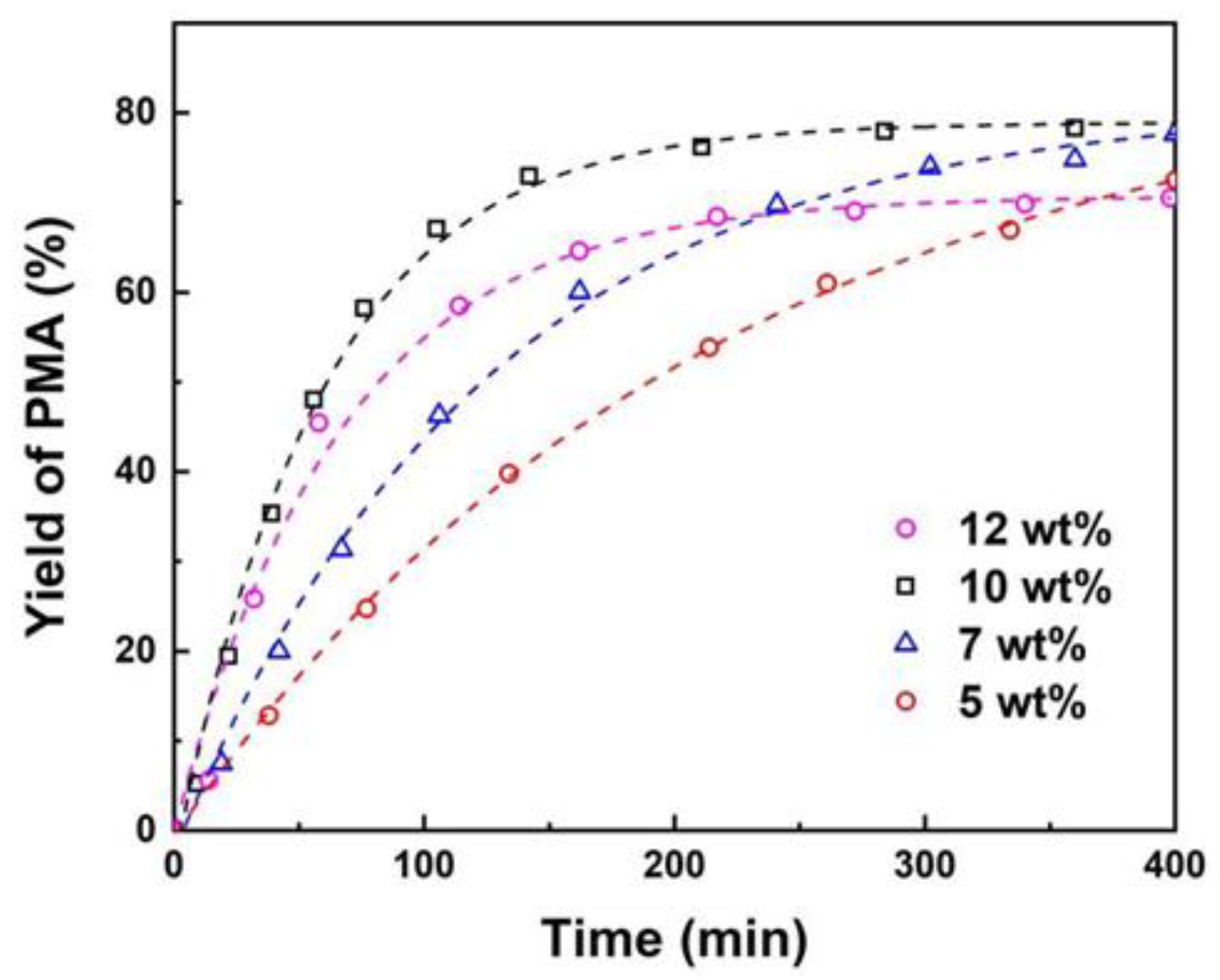
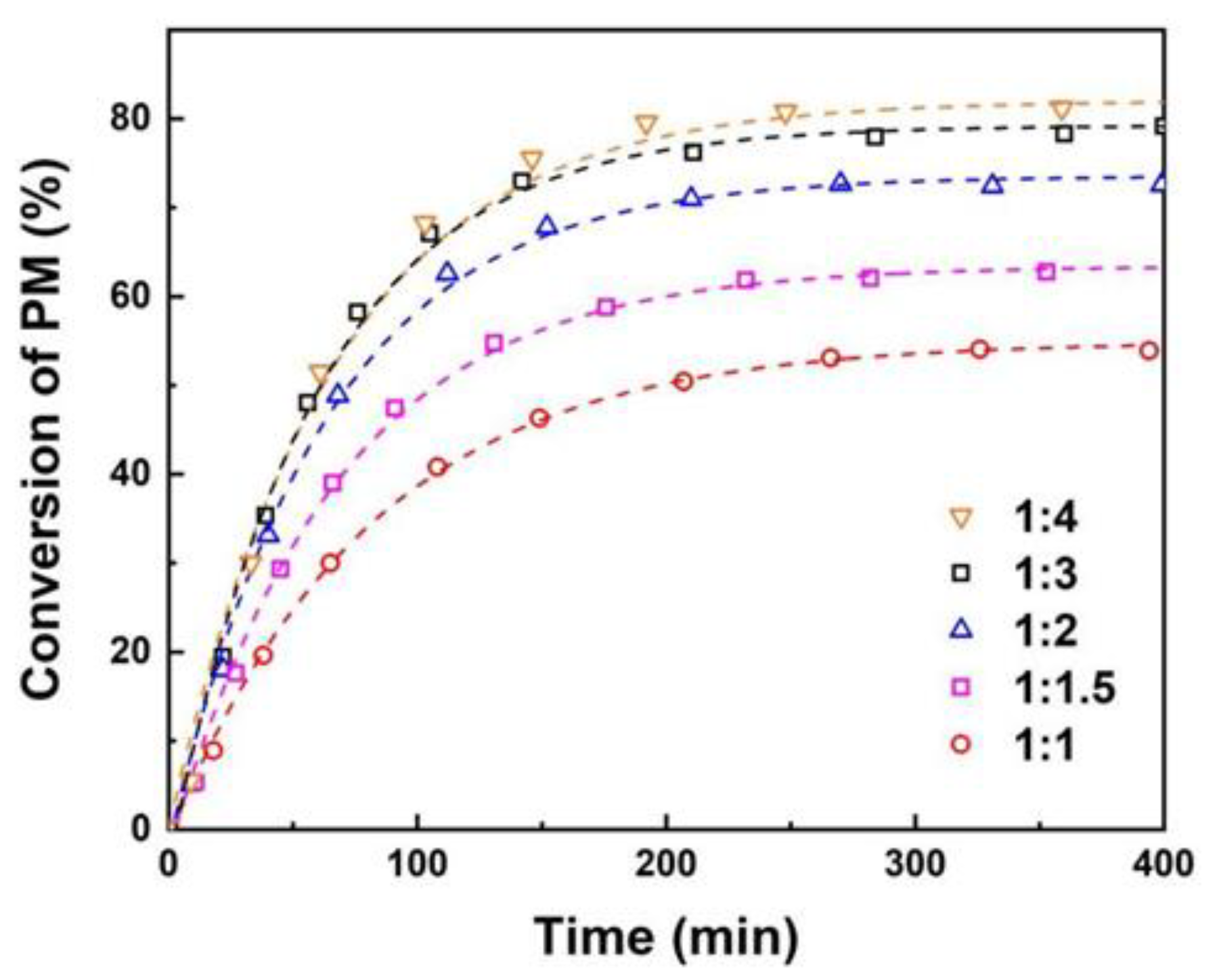
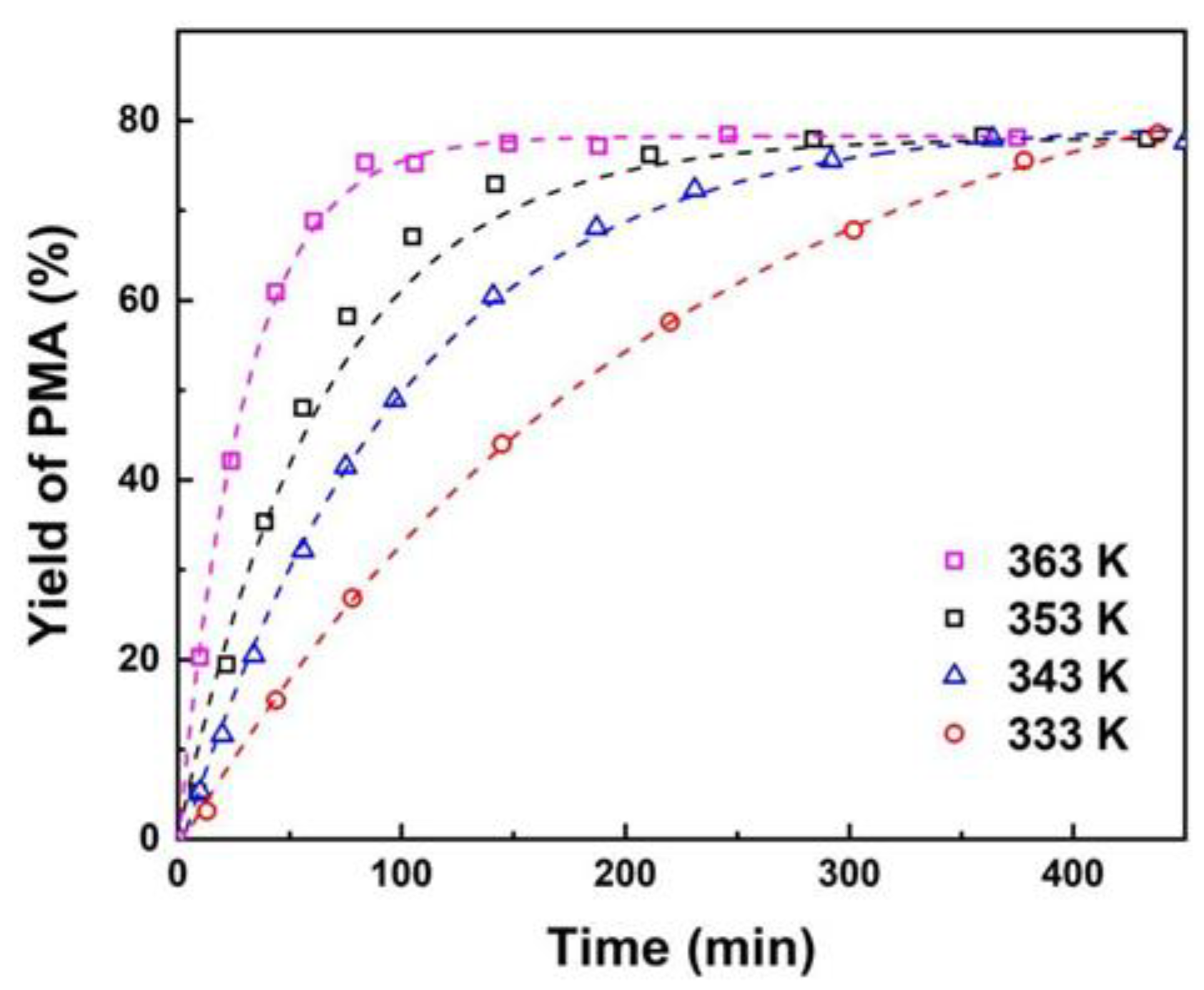
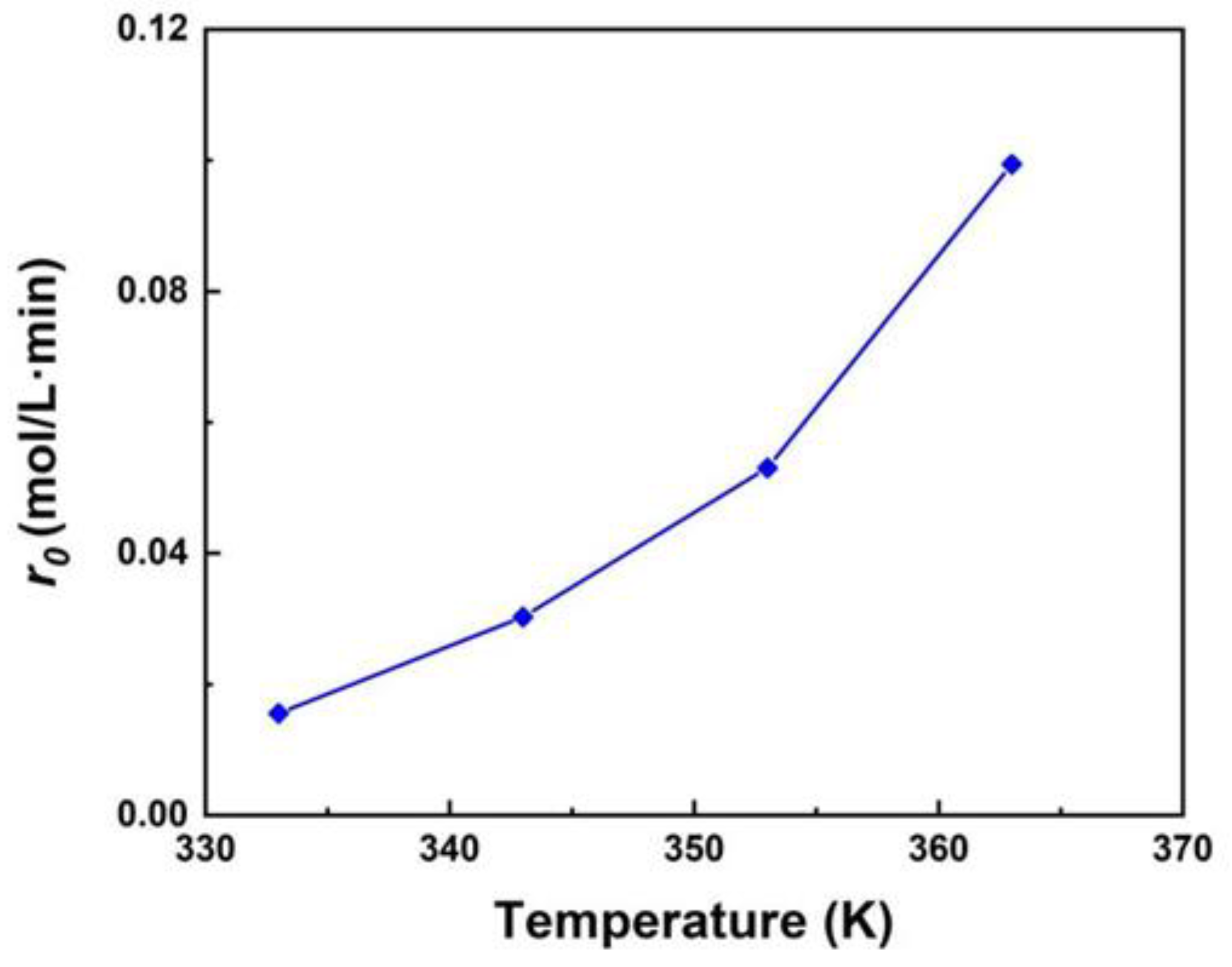
3.2. The Effect of Reaction Conditions
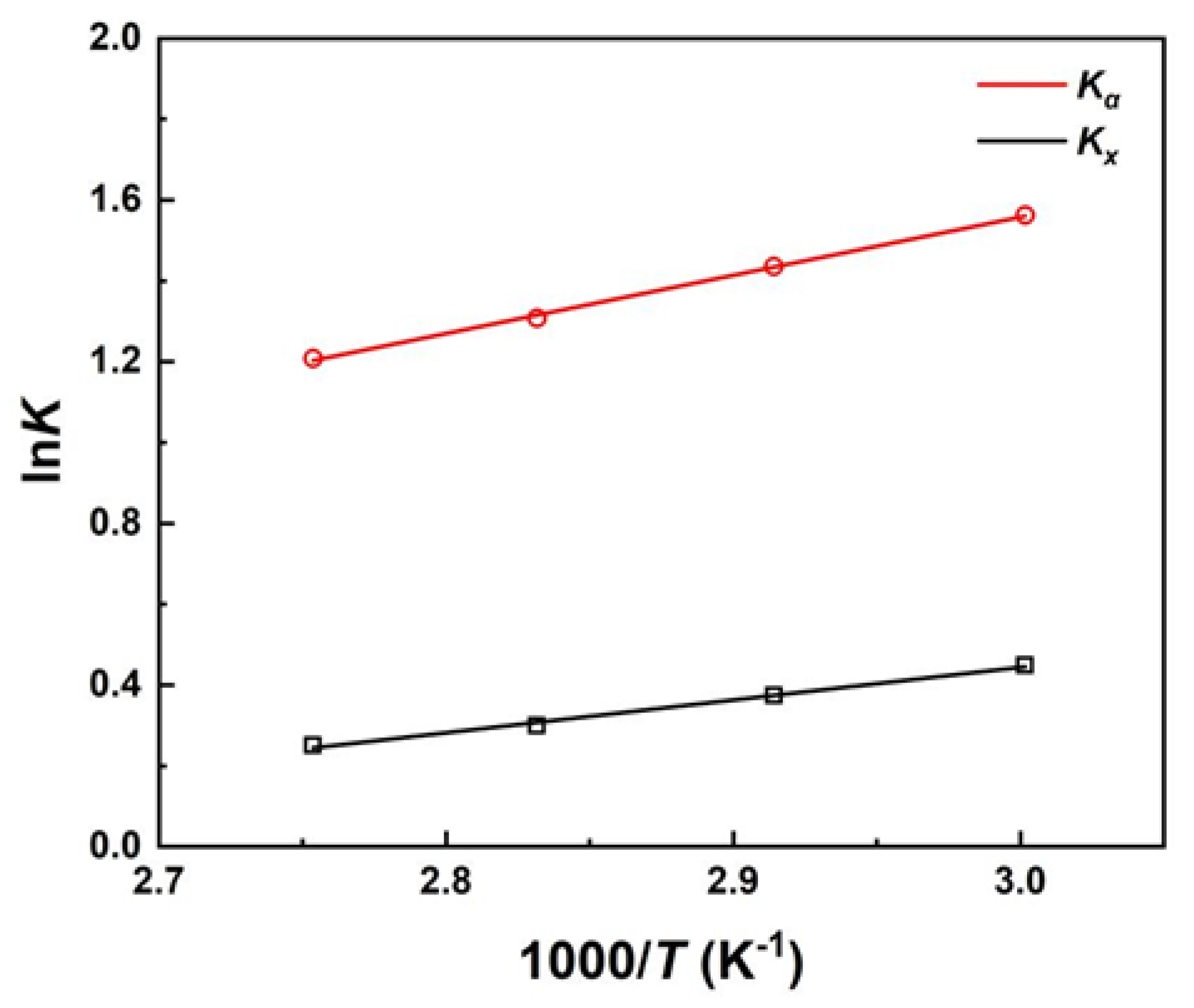
3.3. Chemical Reaction Thermodynamic Equilibrium
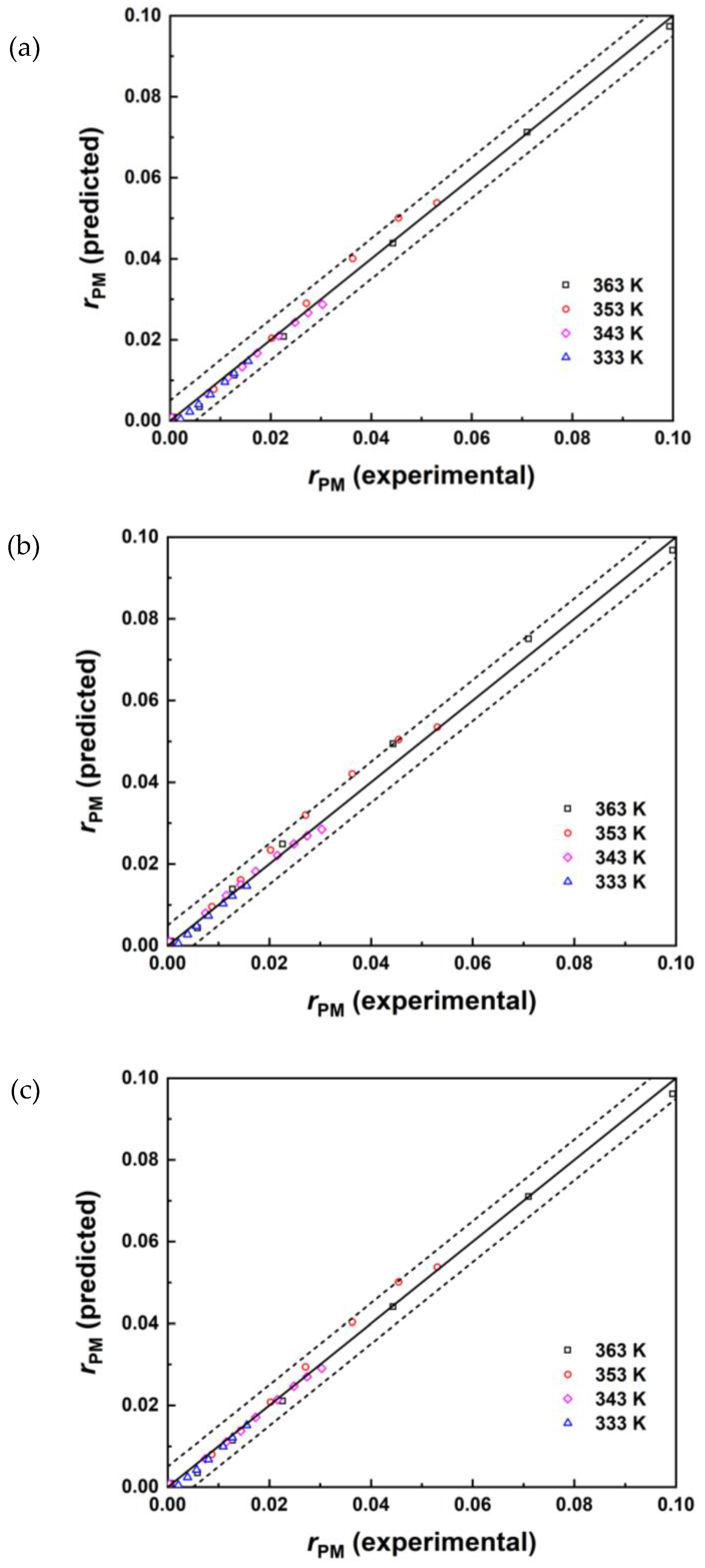
3.4. Reaction Kinetic Modelling
4. Conclusions
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hussain, A.; Chaniago, Y. D.; Riaz, A.; Lee, M. Process design alternatives for producing ultra-high-purity electronic-grade propylene glycol monomethyl ether acetate. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaniago, Y. D.; Hussain, A.; Andika, R.; Lee, M. Reactive pressure-swing distillation toward sustainable process of novel continuous ultra-high-purity electronic-grade propylene glycol monomethyl ether acetate manufacture. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 18677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Lin, Y.; Li, L.; Ye, C.; Qiu, T. Preparation and shaping of solid acid SO42−/TiO2 and its application for esterification of propylene glycol monomethyl ether and acetic acid. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2017, 25, 1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C. S.; Dong, X. L.; Zhu, W. J.; Cai, D. R.; Qiu, T. Isobaric vapor-liquid equilibria of the binary mixtures propylene glycol methyl ether plus propylene glycol methyl ether acetate, methyl acetate plus propylene glycol methyl ether and methanol plus propylene glycol methyl ether acetate at 101.3 kPa. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2014, 367, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaniago, Y. D.; Lee, M. Distillation design and optimization of quaternary azeotropic mixtures for waste solvent recovery. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 67, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jyothi, M. S.; Nagarajan, V.; Chandiramouli, R. Adsorption properties of glycol ethers on cubic germanane nanosheets: A first-principles study. J. Phys. Chem. Solids. 2024, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelsey, J. R. Ethylene oxide derived glycol ethers: A review of the alkyl glycol ethers potential to cause endocrine disruption. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2022, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelsey, J. R.; Cnubben, N. H. P.; Bogaards, J. J. P.; Braakman, R. B. H.; van Stee, L. L. P.; Smet, K. The urinary metabolic profile of diethylene glycol methyl ether and triethylene glycol methyl ether in Sprague-Dawley rats and the role of the metabolite methoxyacetic acid in their toxicity. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-W.; Li, X.-X.; Zhang, Z.-L.; Liu, Q.; Li, D.; Wang, X. Volumetric, viscosimetric and spectroscopic studies for aqueous solution of ethylene glycol monoethyl ether. J. Mol. Liq. 2014, 196, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.; Sreedhar, B.; Donaldson, M. E.; Frank, T. C.; Schultz, A. K.; Bommarius, A. S.; Kawajiri, Y. Transesterification of propylene glycol methyl ether in chromatographic reactors using anion exchange resin as a catalyst. J. Chromatogr. A. 2016, 1466, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.; Sreedhar, B.; Donaldson, M. E.; Frank, T. C.; Schultz, A. K.; Bommarius, A. S.; Kawajiri, Y. Transesterification of propylene glycol methyl ether by reactive simulated moving bed chromatography using homogeneous catalyst. Adsorpt.-J. Int. Adsorpt. Soc. 2018, 24, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadekar-Shinde, S.; Reddy, B.; Khan, M.; Chavan, S.; Saini, D.; Mahajani, S. Reactive distillation for the production of methoxy propyl acetate: experiments and simulation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.; Agrawal, G.; Sreedhar, B.; Donaldson, M. E.; Schultz, A. K.; Frank, T. C.; Bommarius, A. S.; Kawajiri, Y. Conversion improvement for catalytic synthesis of propylene glycol methyl ether acetate by reactive chromatography: Experiments and parameter estimation. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 259, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Cai, X.; Lu, L.; Ma, J. A combination of low-temperature reactive and extractive distillation for methoxy-2-propyl acetate synthesis and separation process: simulations and experiments. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2019, 94, 3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.; Han, M. Dynamics and control of entrainer enhanced reactive distillation using an extraneous entrainer for the production of butyl acetate. J. Process Control. 2018, 61, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, A. A. Novel catalytic reactive distillation processes for a sustainable chemical industry. Top. Catal. 2019, 62, 1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, M.; Li, P. Z.; Diaz, I. A control strategy for extractive and reactive dividing wall columns. Chem. Eng. Process. 2017, 113, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simasatitkul, L.; Kaewwisetkul, P.; Wiyaratn, W.; Assabumrungrat, S.; Arpornwichanop, A. Optimal design and performance analyses of the glycerol ether production process using a reactive distillation column. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 43, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R. Z.; Chen, G. Z.; Qin, H.; Cheng, H. Y.; Chen, L. F.; Qi, Z. W. Systematic screening of bifunctional ionic liquid for intensifying esterification of methyl heptanoate in the reactive extraction process. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2021, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Hu, B.; Cheng, H. Y.; Chen, L. F.; Huang, J. M.; Qi, Z. W. Liquid-liquid equilibrium for the system of ionic liquid [BMIm][HSO4] catalysed isobutyl isobutyrate formation. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2018, 122, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Song, Z.; Qin, H.; Cheng, H. Y.; Chen, L. F.; Pan, M.; Heng, Y.; Qi, Z. W. Ionic liquid [BMIm][HSO4] as dual catalyst-solvent for the esterification of hexanoic acid with n-butanol. Catal. Today. 2020, 339, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, T.; Wang, H.-J.; Wang, F.; Pan, X.-Y. Synthesis of acetyl salicylic acid over WO3/ZrO2 solid superacid catalyst. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 174, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, A.; Chen, H.; Tang, J.; Xie, K.; Hou, A. Efficient extraction of cellulose nanocrystals from waste Calotropis gigantea fiber by SO42-/TiO2 nano-solid superacid catalyst combined with ball milling exfoliation. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M. A.; Wang, W.; Chang, Z.; Li, M.; Dong, B.; Ndonfack, K. I. A.; Li, W.; Sun, C. TiO2/SO42- solid superacid catalyst prepared by recovered TiO2 from waste SCR and its application in transesterification of ethyl acetate with n-butanol. Waste Biomass Valorization. 2023, 14, 4035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwahara, Y.; Kaburagi, W.; Nemoto, K.; Fujitani, T. Esterification of levulinic acid with ethanol over sulfated Si-doped ZrO2 solid acid catalyst: Study of the structure-activity relationships. Appl. Catal., A 2014, 476, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokman, I. M.; Goto, M.; Rashid, U.; Taufiq-Yap, Y. H. Sub- and supercritical esterification of palm fatty acid distillate with carbohydrate-derived solid acid catalyst. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 284, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, R.; Choi, M.-S.; Im, J.-S.; Park, Y.-H. Study on the solid acid catalysts in biodiesel production from high acid value oil. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2013, 19, 1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firouzjaee, M. H.; Taghizadeh, M. n-Butane isomerization over 0.5 Pt/HPA/MCM-41 catalyst: Optimization study using central composite design. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2024, 47, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, Y.; Wu, K.; Liu, C.; Tang, S.; Yue, H.; Lu, H.; Liang, B. Catalytic solvent regeneration of a CO2-loaded MEA solution using an acidic catalyst from industrial rough metatitanic acid. Greenh. Gases. 2020, 10, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yati, I.; Yeom, M.; Choi, J.-W.; Choo, H.; Suh, D. J.; Ha, J.-M. Water-promoted selective heterogeneous catalytic trimerization of xylose-derived 2-methylfuran to diesel precursors. Appl. Catal., A 2015, 495, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Ollevier, T.; Kleitz, F. Iron-modified mesoporous silica as an efficient solid lewis acid catalyst for the mukaiyama aldol reaction. Acs Catalysis. 2018, 8, 1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orabona, F.; Capasso, S.; Perez-Sena, W. Y.; Taddeo, F.; Eränen, K.; Verdolotti, L.; Tesser, R.; Di Serio, M.; Murzin, D.; Russo, V.; Salmi, T. Solvent-free condensation of ethyl levulinate with phenol promoted by Amberlyst-15: Kinetics and modeling. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badia, J. H.; Soto, R.; Ramírez, E.; Bringué, R.; Fité, C.; Iborra, M.; Tejero, J. Role of ion-exchange resins in hydrogenation reactions. Catalysts. 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Zhao, Q.; Li, M.; Yin, H. Preparation of mesoporous titania solid superacid and its catalytic property. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 159, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Mu, J.; Liang, M.; Qi, R.; Wu, M.; Xu, L.; Xu, H.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, J.; Miao, Z. One-pot synthesis of MoO3-ZrO2 solid acid catalyst for solvent-free solketal production from glycerol. Mol. Catal. 2024, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldron, C.; Pankajakshan, A.; Quaglio, M.; Cao, E.; Galvanin, F.; Gavriilidis, A. Closed-Loop Model-Based Design of Experiments for Kinetic Model Discrimination and Parameter Estimation: Benzoic Acid Esterification on a Heterogeneous Catalyst. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 22165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echaroj, S.; Asavatesanupap, C.; Chavadej, S.; Santikunaporn, M. Kinetic study on microwave-assisted oligomerization of 1-decene over a HY catalyst. Catalysts. 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertero, N. M.; Apesteguia, C. R.; Marchi, A. J. Selective synthesis of 1-indanol by 1-indanone liquid-phase hydrogenation over metal-based catalysts: A LHHW kinetic approach. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2022, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, P.; Sanz, M. T.; Beltran, S. Kinetic study for esterification of lactic acid with ethanol and hydrolysis of ethyl lactate using an ion-exchange resin catalyst. Chem. Eng. J. 2007, 126, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, W.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Chang, H.; Zhang, X.; Han, J. Thermodynamic and kinetic study of tert-amyl methyl ether (TAME) synthesis. Chem. Eng. Process. 2008, 47, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuusisto, J.; Mikkola, J.-P.; Sparv, M.; Waerna, J.; Karhu, H.; Salmi, T. Kinetics of the catalytic hydrogenation of D-lactose on a carbon supported ruthenium catalyst. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 139, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, X.; Cheng, Z.; Yuan, P. Reaction kinetics and mechanism for hydration of cyclohexene over ion-exchange resin and H-ZSM-5. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 175, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sert, E.; Atalay, F. S. Kinetic study of the esterification of acetic acid with butanol catalyzed by sulfated zirconia. React. Kinet., Mech. Catal. 2010, 99, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casas, C.; Bringué, R.; Fité, C.; Iborra, M.; Tejero, J. Kinetics of the Liquid Phase Dehydration of 1-Octanol to Di-n-Octyl Ether on Amberlyst 70. AIChE J. 2017, 63, 3966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, A. C. K.; Hu, X. Catalytic Activity of Clay-Based Titanium Silicalite-1 Composite in Cyclohexanone Ammoximation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 8441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akyalcin, S.; Altiokka, M. R. Kinetics of esterification of acetic acid with 1-octanol in the presence of Amberlyst 36. Appl. Catal., A 2012, 429, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S. H.; Merchant, S. Q. Kinetic study of Dowex 50 Wx8-catalyzed esterification and hydrolysis of benzyl acetate. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, D.; Saha, B. Esterification of Acetic Acid with n-Hexanol in Batch and Continuous Chromatographic Reactors Using a Gelular Ion-Exchange Resin as a Catalyst. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 11965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, A. F.; Sanchez, C. A.; Orjuela, A.; Gil, I. D.; Rodriguez, G. Isobutyl acetate by reactive distillation. Part II. Kinetic study. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2020, 160, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, Y. R.; Park, J. K.; Shin, E. W.; Moon, S. P.; Park, H. E. Synthesis of propylene glycol methyl ether acetate: Reaction kinetics and process simulation using heterogeneous catalyst. Processes. 2024, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Zhao, X.; Guo, N.; Lyu, Z.; Du, Y.; Xi, S.; Guo, R.; Chen, C.; Chen, Z.; Liu, W.; Yao, C.; Li, J.; Pennycook, S. J.; Chen, W.; Su, C.; Zhang, C.; Lu, J. Atomic engineering of high-density isolated Co atoms on graphene with proximal-atom controlled reaction selectivity. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, S. Y.; Ahmad, M. A. A.; Kamaruzaman, M. R.; Cheng, C. K. Kinetic studies of the esterification of pure and dilute acrylic acid with 2-ethyl hexanol catalysed by Amberlyst 15. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2015, 129, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S. H. Kinetics of catalytic esterification of propionic acid with different alcohols over Amberlyst 15. Int. J. Chem. Kinet. 2009, 41, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Xue, W.; Zeng, Z.; Shi, X. Kinetics of the reaction of ethanol and lauric acid catalyzed by deep eutectic solvent based on benzyltrimethylammonium chloride. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 97, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Hu, X.; Wang, J.; Cheng, H.; Chen, L.; Qi, Z. Overview of acidic deep eutectic solvents on synthesis, properties and applications. Green Energy Environ. 2020, 5, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Qin, H.; Wang, J.; Cheng, H.; Chen, L.; Qi, Z. Reactive extraction for intensifying 2-ethylhexyl acrylate synthesis using deep eutectic solvent Im:2PTSA. Green Energy Environ. 2021, 6, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhou, L.; Guo, X.; Li, L.; Zhang, P.; Hong, R.; Qiu, T. Study on the esterification for ethylene glycol diacetate using supported ionic liquids as catalyst: Catalysts preparation, characterization, and reaction kinetics, process. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 280, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Cui, X.; Jie, H.; Yu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, T.; Liu, H.; Song, K. Kinetic study and process simulation of transesterification of methyl acetate and isoamyl alcohol catalyzed by ionic liquid. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| T (K) | DA (cm2/s) | De (cm2/s) | Cwp |
|---|---|---|---|
| 333.15 | 2.31×10-5 | 2.42×10-6 | 0.06 |
| 343.15 | 2.58×10-5 | 2.71×10-6 | 0.11 |
| 353.15 | 2.84×10-5 | 2.98×10-6 | 0.18 |
| 363.15 | 3.10×10-5 | 3.25×10-6 | 0.30 |
| T (K) | PM | AA | PMA | H2O | ||||
| xPM | αPM | xAA | αAA | xPMA | αPMA | xH2O | αH2O | |
| 333.15 | 0.0547 | 0.8870 | 0.5516 | 0.9333 | 0.1969 | 1.1870 | 0.1969 | 1.8158 |
| 343.15 | 0.0530 | 0.8433 | 0.5504 | 0.9239 | 0.1983 | 1.1794 | 0.1983 | 1.8119 |
| 353.15 | 0.0502 | 0.7963 | 0.5493 | 0.9135 | 0.2002 | 1.1685 | 0.2002 | 1.8000 |
| 363.15 | 0.0470 | 0.7447 | 0.5504 | 0.9033 | 0.2013 | 1.1521 | 0.2013 | 1.7772 |
| Equilibrium constant | ΔrHθ (kJ·mol-1) | ΔrSθ (J·mol-1·K-1) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kx | -6.734 | -16.51 | 0.9942 |
| Kα | -11.97 | -22.97 | 0.9988 |
| Component | qm (g/g) | Ki | R2 |
| PM | 0.4768 | 0.0271 | 0.995 |
| AA | 0.3582 | 0.0250 | 0.833 |
| PMA | 2.1921 | 0.0001 | 0.926 |
| H2O | 0.7357 | 0.0071 | 0.953 |
| Model | k0+ | Ea+(kJ/mol) | KPM | KAA | KPMA | KH2O | MAE | RMSE | R2 |
| PH | 2.88×106 | 63.2 | / | / | / | / | 1.26×10-3 | 1.59×10-3 | 0.9964 |
| ER | 4.25×106 | 63.3 | 0.12 | / | / | 0.01 | 1.22×10-3 | 1.57×10-3 | 0.9947 |
| LHHW | 6.84×106 | 62.0 | 0.13 | 0.04 | 8.2×10-4 | 0.15 | 1.13×10-3 | 1.59×10-3 | 0.9946 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





