1. Introduction.
Mucormycosis is a serious disease caused by a group of fungi called Mucorales. There are more than two dozen species of these fungi that can cause this deadly disease. The most common culprits are species from the genera
Rhizopus and
Mucor, with
Rhizopus arrhizus being the most prevalent [
1]. People with diabetes, neutropenia, and those who have received hematopoietic or soldi organ transplants are more susceptible to mucormycosis. Unfortunately, the number of diabetic patients, especially in developing countries, is increasing, which puts them at a higher risk for this disease. In fact, diabetes is a major risk factor for mucormycosis in over 70% of cases in countries like India, compared to 36-40% globally [
2,
3,
4].
Mucormycosis is challenging because treatment with first-line therapy of lipid formulation amphotericin B formulations are often associated with severe toxicities that in many cases limit their use [
5,
6]. Importantly, Mucorales fungi exhibit higher MICs and in many cases, resistance to azoles (e.g. posaconazole [POSA] and isavuconazole [ISAV]) that are used as a stepdown therapy for mucormycosis [
7,
8]. The disease is intrinsically resistant to short tailed azoles like fluconazole (FLC) and voriconazole (VCZ) which otherwise are the most widely used antifungal drugs[
9].
Studies on azole resistance mechanisms in various pathogenic fungi have revealed similarities across different species. These mechanisms often involve the overexpression of efflux pumps, mutations in target gene
ERG11, or increased expression of target enzyme lanosterol 14α-demethylase (LDM) [
10,
11]. It is important to note that the prevalence of these resistance mechanisms can vary among different fungi. For example, in
Candida species, the most common mechanism is the overexpression of efflux pump genes, while in
Aspergillus fumigatus, mutations in the azole target enzyme lanosterol 14α-demethylase (LDM) are more prevalent [
12].
Cryptococcus species have been found to exhibit overexpression of various genes due to reversible chromosomal duplications, point mutations in
ERG11, and increased efflux pump activity [
13,
14]. In contrast, the molecular basis of drug resistance in Mucorales is not well understood and remains an area that requires further exploration. Studies have shown that the genome of
Mucor circinelloides contains eight potential PDR-type transporters, and the regulation of these genes appears to be interconnected. Both Pdr1 and Pdr2 have been found to contribute to the resistance of
M. circinelloides against certain azole drugs like PCZ, ICZ, and ravuconazole (RVZ). However, it is worth noting that azole resistance in general cannot be fully explained solely by the activity of these tested efflux pumps. The involvement of other PDR genes and novel mechanisms cannot be ruled out and may play a role in drug resistance [
7].
Azoles represent a crucial class of medications targeting lipids, specifically lanosterol 14α-demathylase (LDM), an enzyme encoded by the
ERG11 gene. By inhibiting LDM, azole drugs impede the production of ergosterol, a vital component of fungal cell membranes, resulting in the build-up of toxic sterols [
15]. While our comprehension of acquired resistance to triazole drugs in fungi like
Aspergillus and
Candida species is substantial, the inherent resistance of Mucorales to short-tailed triazoles such as VCZ and FLC warrants further exploration [
16]. In many fungal species, acquired azole resistance often arises from specific mutations in the LDM gene, reducing affinity for certain triazole drugs. However, the absence of
in vitro activity of FLC and VCZ against Mucorales suggests their resistance may be innate rather than acquired, possibly due to ancient amino acid substitutions. A 2017 study by Rita Caramalho
et al. aligned LDM sequences from six Mucorales species, identifying a conserved Y129F substitution likely responsible for innate resistance to short-tailed azoles like FLC and VCZ [
17]. Analysis, based on the known LDM structure, indicates a mechanism for this mutation involving the disruption of a water-mediated hydrogen bond [
17]. Significantly, introducing this mutation into the homologous protein of
Saccharomyces cerevisiae conferred resistance to short-tailed azoles [
18]. Other point mutations in genes involved in ergosterol biosynthesis have also been observed in Mucorales, raising concerns about the implications of emerging resistance to current antifungal drugs. Further research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms of innate resistance in Mucorales and to develop effective strategies for combating this resistance
Research has highlighted the significant role of lipids, the target of common antifungal drugs, in determining drug susceptibility and virulence in various pathogenic fungi [
19]. However, this aspect remains poorly understood in Mucorales. Considering the severity of Mucorales infections as secondary complications in Covid-19 and diabetes patients [
20], it becomes imperative to gain a comprehensive understanding of the lipid landscape and imbalances to facilitate the development of effective treatments. In this study, we selected the genome-sequenced
Rhizopus delemar 99-880 strain as a reference strain to investigate the lipidomic landscape of Mucorales [
21]. Utilizing high-throughput liquid chromatography electro spray ionisation mass spectrometry (LC-ESI/MSMS) and gas chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry (GCMS) approaches, we successfully conducted qualitative and quantitative analyses of a wide range of lipids including sphingolipids (SLs), glycerophospholipids (GPLs), and sterols. This dataset presents, for the first time, a comprehensive overview of the lipidomic profile in the well-defined
R. delemar 99-880 strain, which is anticipated to serve as a foundational platform for future investigations in this field.
2. Materials and Methods.
2.1. Strains, Media and Growth Conditions.
R. delemar 99-880 spores were revived from archived glycerol stocks stored at -80°C. Spores were inoculated on YPD plates and incubated for 3-4 days until spores were formed. Plates were flooded with 10 mL phosphate buffered saline with 0.01% tween (PBST) and spores were collected by aspiration. Spores were counted using hemocytometer and adjusted to a density of 106 spores mL-1 for further experimental use.
2.2. Drug Susceptibility.
Approximately 103 spores were spotted on YPD plates containing different concentrations of the drugs, Myriocin (MYR) (Sigma) or Aureobasidin A (AbA) (Takara). Plates were incubated at 30°C for 48 hours and then imaged (Bio-rad Molecular Imager®).
2.3. Sphingolipid Isolation.
Spores were inoculated in 100 mL YPD and grown at 30°C with constant shaking untill mycelia were formed (~24 hours). Mycelia were harvested and washed with 0.9% saline and dried. Approximately 100 mg of mycelia were used for SL isolation using methods as described earlier by Kumar
et al [
22]. C17 sphingosine and C17 ceramide (Avanti Polar Lipids Inc. AL, USA) were added as internal standards before isolation. Dried SL extracts were dissolved in 300 µL organic buffer (methanol with 1 mM ammonium formate and 0.2% formic acid). From this, 20 µL sample was transferred to glass insert and final volume adjusted to 200 µL in organic buffer for LC-MS/MS analysis.
2.4. Phospholipid Isolation.
PLs were extracted using the Folch method with slight modifications[
23]. Equisplash® (Avanti Polar Lipids Inc. AL, USA) containing an equal proportion of deuterated PLs of each class was added as internal standard before isolation. Briefly 100 mg mycelia were homogenized in 1 mL LC/MS grade water using glass beads in FastPrep(MP Biomedicals). To this lysate, 9 mL of 2:1 chloroform:methanol was added and incubated for 2 hours with periodic vortexing. The upper layer was discarded and 2 mL of 0.9% saline was added. Lower layer was then separated by centrifugation at 3000 rpm for 5 min and dried with N
2 gas. Dried extracts were dissolved in 1 mL organic buffer. From this 10 µL sample was transferred to glass insert and final volume adjusted to 200 uL in organic buffer for LC-MS/MS analysis.
2.5. Sterol Extraction.
Harvested mycelia were finely crushed in liquid N
2 and approx. 20 mg of it was weighed and used for sterol extraction. Sterols were extracted as described by Morio
et al [
24]. Mycelia was resuspended in 300 µL saponification solution containing 12.5g KOH dissolved in 18 mL MQ water and adjusted to 50 mL with 98% ethanol. The mixture was then heated at 80°C for 1h in a capped glass vial. After cooling at RT, 100 µL MQ water, 400 µL hexane and 1 µL cholestane (5 mg/ml) as internal standard was added. The mixture was vortexed and after phase separation, the top layer of ~350 µL (hexane) was separated and 600 µL hexane was again added to the remaining lysate. After vortexing and phase separation, 550 µL of the top layer was separated and both hexane fractions were combined and dried in vacuum centrifugation at room temperature. The dried sterol extracts were re-dissolved in 60 µL hexane and 10 µL Silylation mixture (Sigma, 85432) for derivatization, vortexed and incubated for 1 hour at room temperature. From this 50 µL of the debris-free extract was transferred into glass inserts for GCMS analysis.
2.6. Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry.
SLs were analyzed by employing Shot-gun and multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) approaches using LC-MS (QTRAP® 4500, AB SCIEX). For untargeted shotgun lipidomics, different confirmatory scans were used and the spectra obtained are given in Supplementary File S1. For the targetted MRM approach, SLs and PLs were separated on C8-Column and C18 columns maintained at 60°C and 50°C respectively (Waters, USA). Organic buffer (methanol with 1 mM ammonium formate and 0.2% formic acid) and aqueous buffer (water with 2 mM ammonium formate and 0.2% formic acid) were used as mobile phase. A combined flow rate of 300 µL per min was maintained in a gradient manner starting with 80% organic buffer, gradually increased to 88%, then 99%, decreased to 88% and finally restored to 80% before final run. Mass spectrometric parameters were standardized as follows: Source temperature was set at 600°C for SL, nebulizer and desolvation gases (GS1 and GS2 respectively) were set at 50 psi each , electrospray ionization voltage at 5500 V and curtain gas at 45 psi. For PL analysis the source temperature was set as 400°C, GS1 and GS2 at 45 psi, electrospray ionization voltage at 4500 V and curtain gas at 45 psi.
2.7. Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry
Derivatized sterol samples were analyzed by on Thermo Scientific GCMS system (Trace 1300 ISQ QD). Samples were injected in split mode at 250°C with a ratio of 1:10 and helium at a flow rate of 1.4 mL per min was used as carrier gas. Starting temperature was held at 50°C for 1 min, ramped at a rate of 50°C/min upto 260°C , then again ramped at 2°C/min upto 325°C and held for 3 min. Masses were detected within a range of 50 to 600 atomic mass units using electron impact ionization (70 eV). Transfer line and the detector were operated at 325°C and 250°C respectively.
Different sterol intermediates were identified by their retention times with respect to the internal standard, cholestane and fragmentation patterns using Chromeleon 7 (Thermo Scientific). The spectra obtained were matched to NIST library and those described by Muller
et al [
25]. The relative abundance was calculated from the peak area of each sterol molecule normalized to the internal standard signal.
2.8. Protein Estimation.
An aliquot of 25 µL was taken from lysate of each replicate for total protein estimation inorder to normalize the quantified data. Protein estimation was done using bicinchoninic acid (BCA) protein assay kit (G-Biosciences, MO, USA) as described previously [
26].
2.9. Data Analysis.
Mass spectrometric chromatograms of SL and PL molecules were analyzed by MultiQuant™ software (SCIEX). As mentioned earlier, separate internal standards for SLs and PLs were used to normalize the area of each lipid species. Three biological replicates were run for all analyses and data was presented as % of total SL, PL or sterol content. Data was plotted using GraphPad Prism 8. Structures of lipid molecules were drawn using structure drawing tools available on
https://www.lipidmaps.org/resources/tools/structure.
3. Results
3.1. R. delemar Harbours All Major SL Classes
The relevance of SLs in
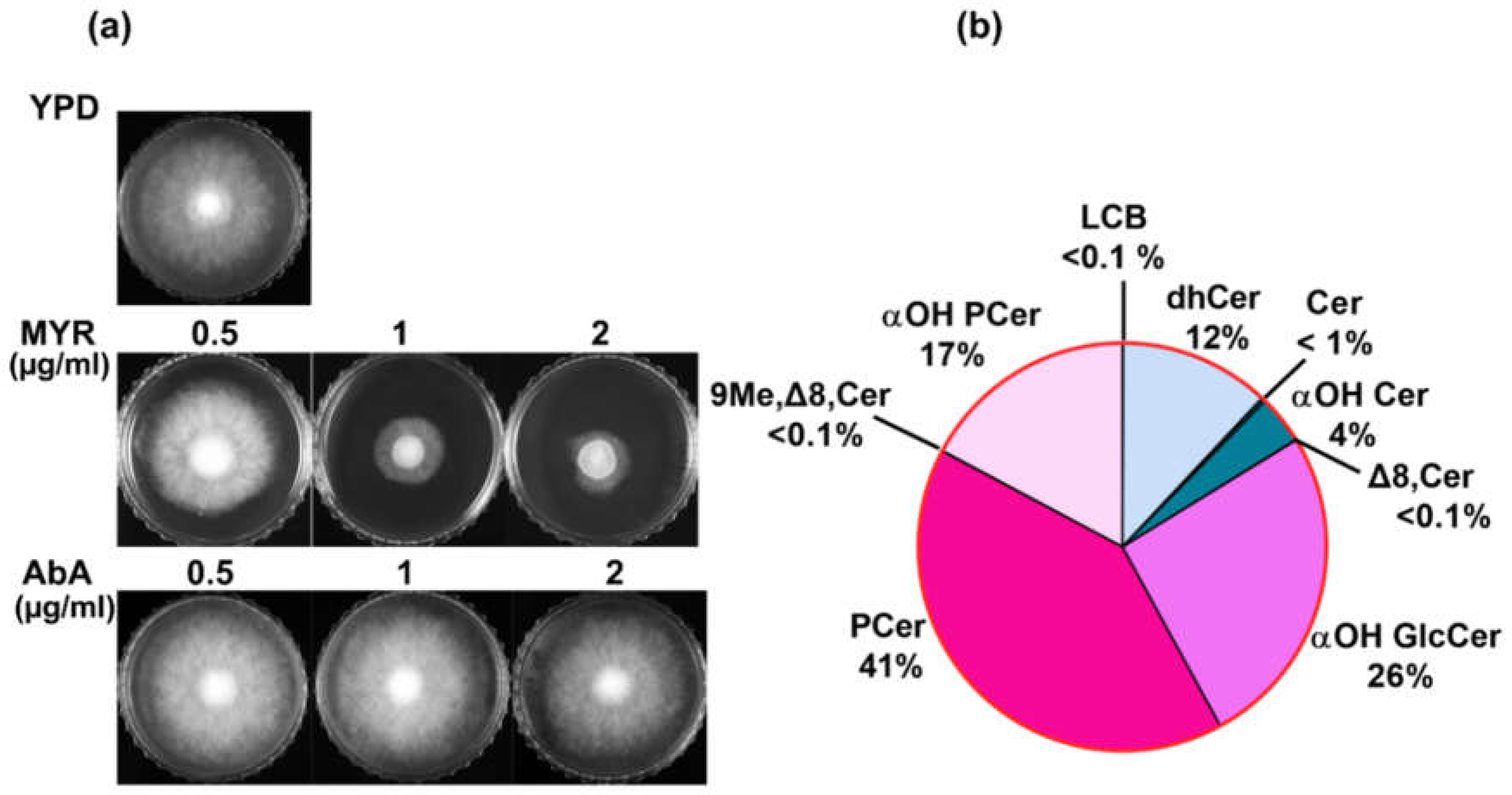
R. delemar became apparent when we checked its susceptibility towards specific inhibitors.
R. delemar cells were susceptible to myriocin, a potent inhibitor of serine palmitoyltransferase (SPT), which is the enzyme responsible for the first and rate-limiting step in SLs biosynthesis (
Figure 1a). By inhibiting SPT, myriocin disrupts SLs homeostasis in yeast cells, which can have various downstream effects on cell physiology and function [
27]. On the other hand,
R. delemar cells were resistant to
aureobasidin A (AbA), a cyclic depsipeptide antibiotic that inhibits inositol phosphorylceramide (IPC) synthase encoded by the
AUR1 gene (
Figure 1a). The resistance to AbA indicated a lack of acidic SL pathway in
R. delemar cells (discussed below). Our susceptibility profile of
R. delemar underscores the relevance of SLs in its various cellular processes which prompted us to analyse SL composition in detail. SLs were detected in base hydrolyzed lipid samples by Shotgun and MRM approaches described previously [
22,
28]. Multiple confirmatory scans specific for the detection of different SL intermediates were performed in positive mode ([M+H]
+). Since it was the first high throughput analysis of this fungal pathogen, we subjected the samples to unbiased scanning over mass range of
m/z 200 to 1000 dalton (Da) which included most of the commonly found SLs in fungi. Separate chromatograms were recorded for each type of scan, which included numerous masses. The mass signals obtained in each chromatogram corresponded to SL molecular species representing the different SL classes which are structurally unique from each other. The different confirmatory scans and the detected SL intermediates are given in Supplementary File S1.
Our analyses of the detected masses enabled us to identify all diverse classes of SLs that differed based on headgroup, presence of double bonds and number of hydroxyl groups on the sphingoid base (backbone). These included commonly found SL classes such as long chain bases (LCBs), dihydroceramides(dhCer), ceramides, alpha-hydroxy ceramides(α-OH Cer), alpha-hydroxy glucosylceramides (α-OH GlcCer), phytoceramides (PCer) and alpha-hydroxy phytoceramides (α-OH PCer) [
22,
26,
28]. In addition, fungal specific lipids such as Δ8-ceramide and 9-methyl, Δ8-ceramide were also detected (
Figure 1b). Additionally, all the molecular species detected had five types of backbones. Also the fatty acids acylated to sphingoid base were either saturated, or mono-unsaturated, hydroxylated (likely at C-2 position) or non-hydroxylated thus combinedly generating multiple pools of SL species. Selected masses from the shotgun approach were further detected via MRMs and the samples were subjected to LC-ESI/MSMS for separation and quantification of each lipid species. Peak identification and quantification of each species was done on the basis of retention time (RT) with respect to available natural SL standards. The complete list of identified SL species and their relative abundance is given in Supplementary File S2
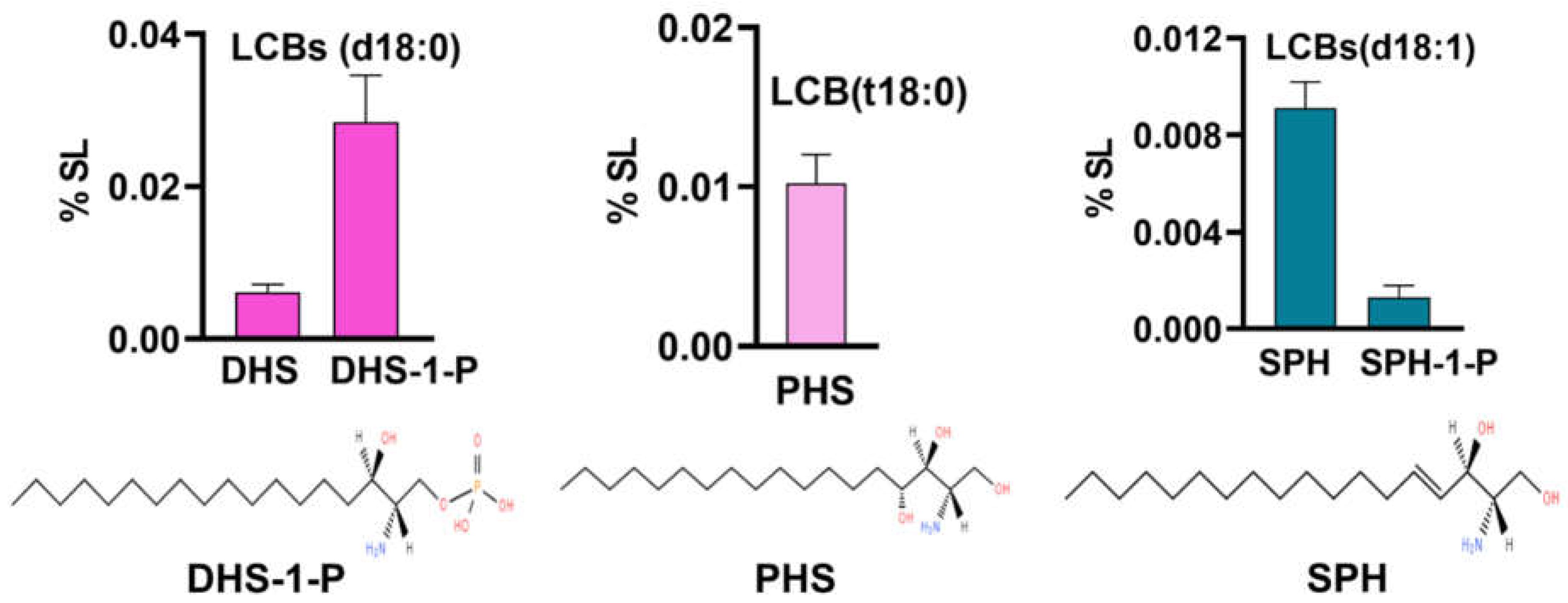
3.1.1. Long Chain Base (LCBs) Content Is Very Low with DHS-1-P as the Major Base.
Our analysis could detect all major LCBs including dihydrosphingosine (DHS), phytosphingosine (PHS), sphingosine (SPH), dihydrosphingosine-1-phosphate (DHS-1-P), sphingosine-1-phosphate (SPH-1-P). Notably, glucosyl-sphingosine (Glu-SPH) and phytosphingosine-1-phosphate (PHS-1-P) could not be detected in
R. delemar cells (
Figure 2). Combinedly, the total LCB content was very low (0.05 %) with DHS-1-P emerging as a major base (0.02%) followed by PHS (0.01%), both sharing approximately two-thirds of the LCB content between them. Other bases such as DHS, SPH and SPH-1-P were present in trace amounts ranging between 0.001% and 0.009%. In comparison with other yeasts such as
Candida and
Cryptococcus wherein LCBs ranged between 0.5% and 1.2%, its levels are very low in
R. delemar cells [
22,
26,
28].
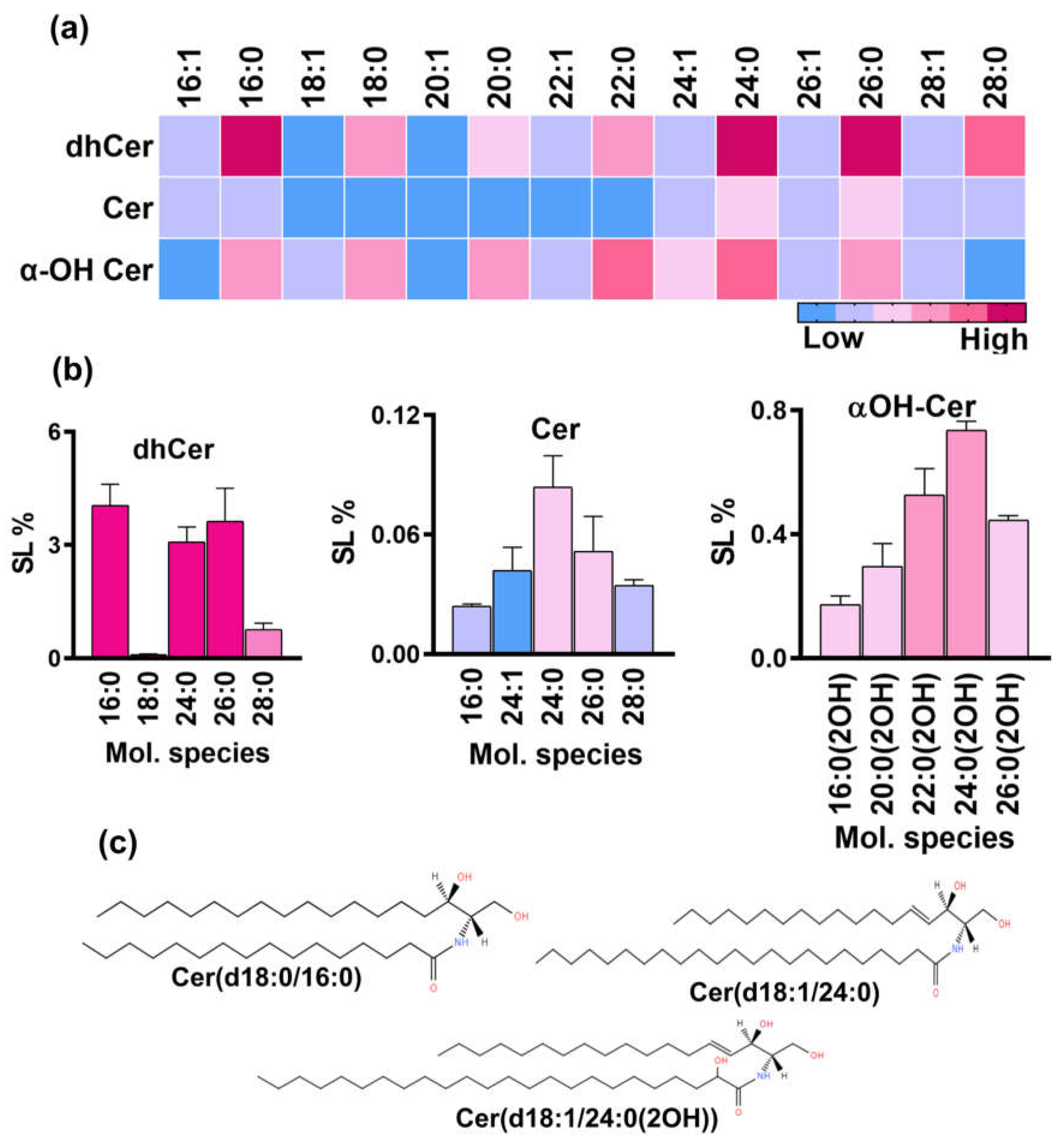
3.1.2. dhCer Synthesis Leads the Initiation of Neutral Pathway and 16:0 Is the Major Species.
dhCer structures are synthesized by the acylation of the sphingoid base, DHS, through the amine group present at C2-position of the base. These intermediates serve as starting precursors of the neutral branch of the fungal SL biosynthesis pathway. We could detect multiple species of dhCer. For the analysis, selected masses corresponding to molecular species with of 16 to 28 carbon long fatty acid chains were quantified (
Figure 3a). Total dhCer content was ~12% with 16:0 dhCer as the predominant species (
Figure 3b). Notably, the abundance of 16:0 species is different from other species of fungi such as
Candida, Cryptococcus where 18:0 dhCer predominates[
22,
28]. The species with longer chain lengths, 24:0, 26:0 and 28:0 shared 3%, 3% and 0.7%, respectively of the SL content. Other saturated fatty acid containing species such as 18:0, 20:0, 22:0 were present in very low amount, each having ≤ 0.1% contribution. Mono-unsaturated fatty acid containing species were present in trace amounts.
3.1.3. Cer and α-OH Cer Species Were Also Detected and 24:0 Is the Major Specie in Both Classes.
The desaturation of dhCer (d18:0 backbone) leads to the formation of Cer which is a central hub acting as a precursor of many simple to complex SL in eukaryotic cells. The total Cer content was ~0.3% mainly contributed by species with 16C to 28C long fatty acids, out of which 24:0 was the major species (0.08%) followed by 26:0, 24:1, 28:0, 26:1, 16:0 and 16:1 (ranging between 0.02 and 0.05%) (
Figure 3b). The other Cer species were found in trace amounts. Notably, mono-unsaturated fatty acid containing species were very low than the saturated ones with the same carbon number chain length. SLs with same backbone as that of Cer (d18:1), but having hydroxy-fatty acids most likely at the C2- position, known as αOH-Cer were also present. Total αOH-Cer was ~3.9 % of the total SL content with a wide range of species ranging from 14C to 30C long fatty acids. The major species were 24:0, 22:0, and 20:0 contributing 1.2%, 0.7%, 0.5% and 0.4%, respectively. The other prominent species were 20:0, 18:0, 16:0 and 14:0 ranging from 0.1% to 0.29%. Other species and the mono-unsaturated fatty acid containing species were present in very low amounts (<0.1%).
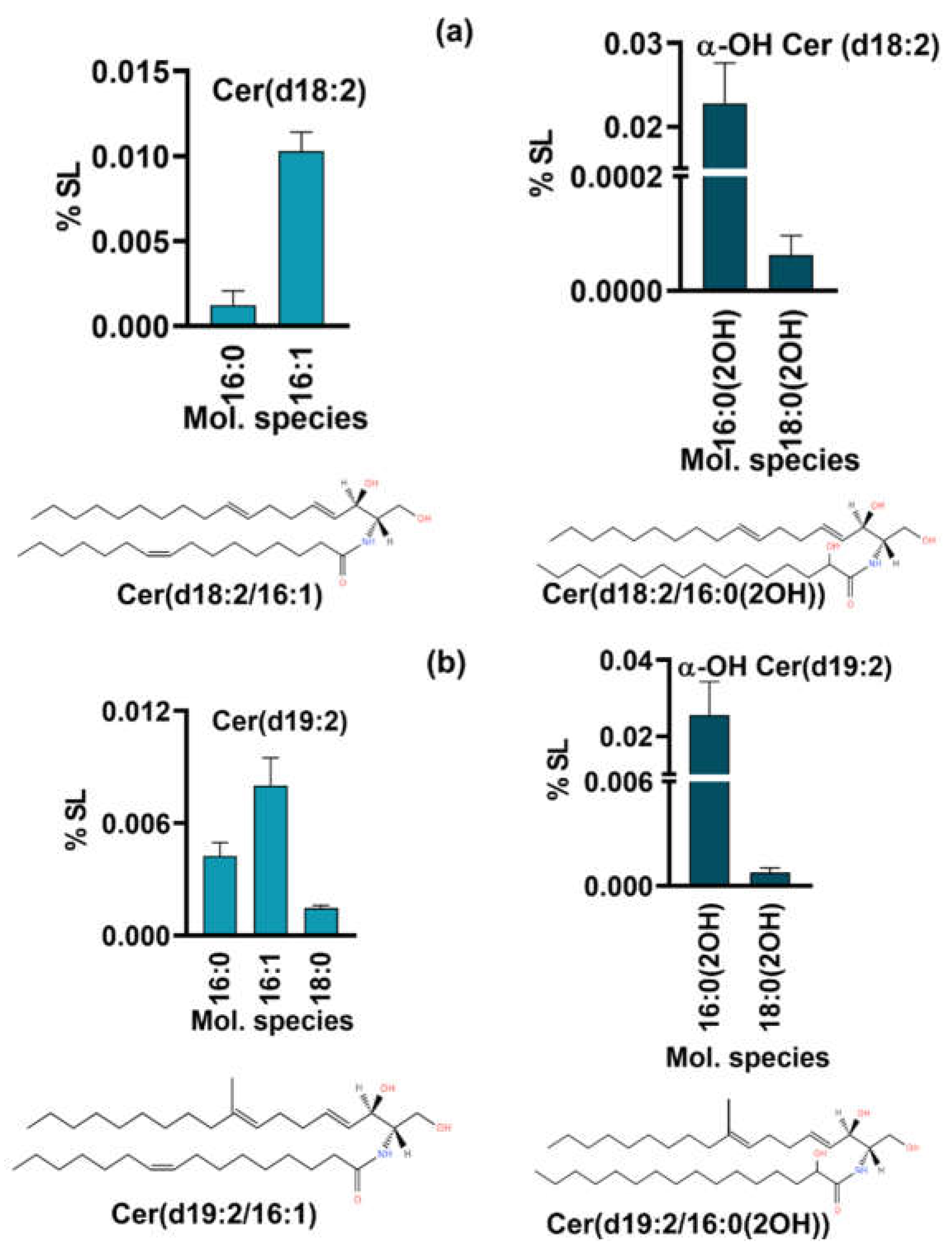
3.1.4. R. delemar Harbours Typical Fungal Specific Lipids
The fungal specific SLs, di-unsaturated sphingoid base, d18:2 or Δ8-Cer synthesized by desaturation of Cer at C8-position were detected (
Figure 4) along with its downstream intermediate, 9-methyl, Δ8-Cer having d19:2 backbone [
29]. Both types of SLs are unique to certain fungi such as
Candida and
Cryptococcus and are not reported in
S. cerevisiae and mammals [
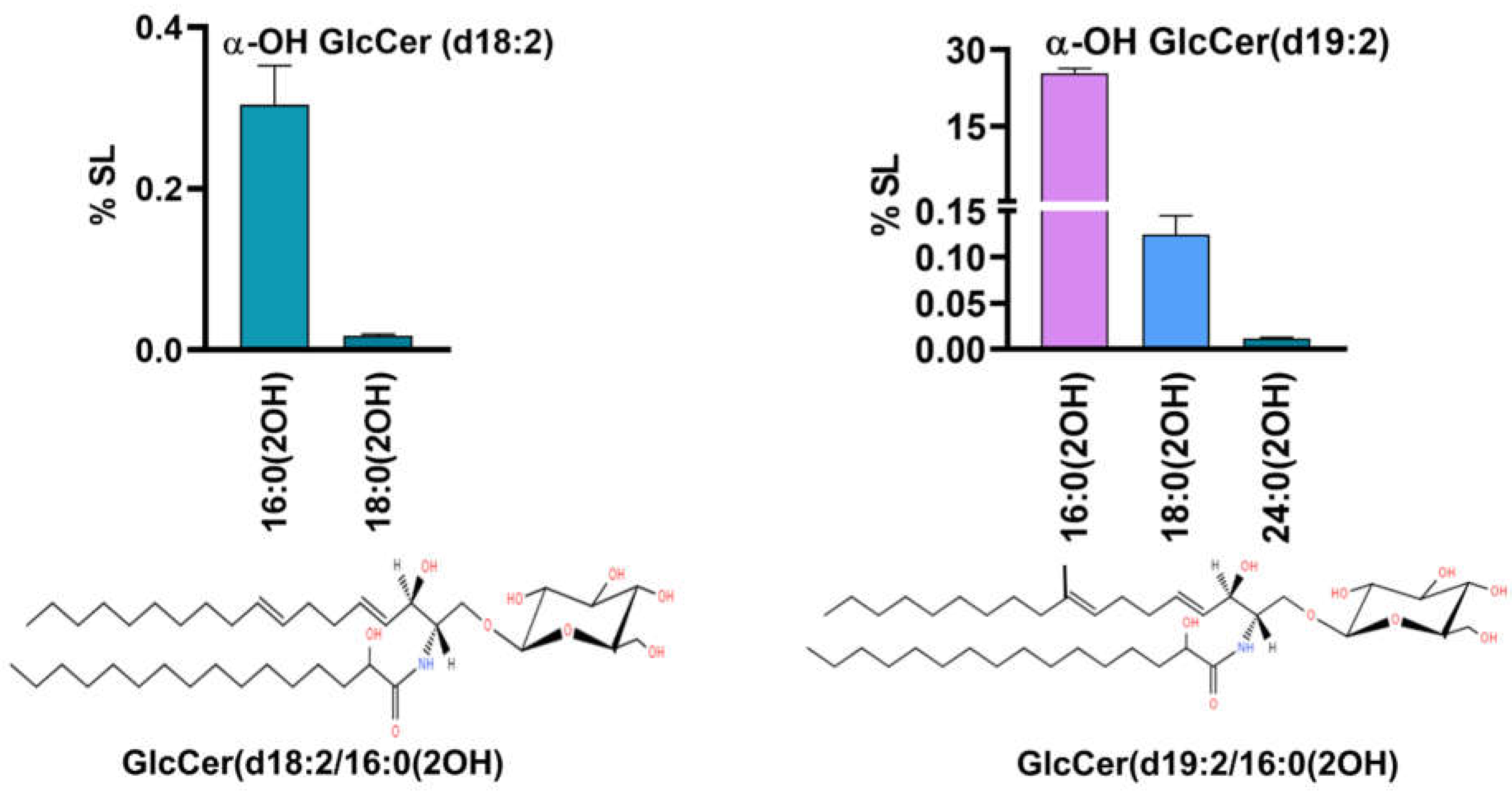
30]. In d18:2, two Cer species with non-hydroxy fatty acids, 16:0 and 16:1 and two species of αOH-Cer, 16:0(2OH) and 18:0(2OH) were quantifiable. The former two represented an amount of 0.001% to 0.01% while as the latter two were 0.02% and 0.0001%- thus again showing that 16C containing species predominate others as in dhCer. In 9-methyl, Δ8-Cer, five species were detected, out of which three were non-hydroxy fatty acid species (d19:2 Cer) and two were α-OH Cer species(d19:2 α-OH Cer). The d19:2 Cer species include 16:0, 16:1 and 18:0 representing 0.004%, 0.01% and 0.001%, respectively. The two α-OH Cer species 16:0(2OH) and 18:0(OH) were 0.02% and 0.0007% respectively. Species with d18:2 and d19:2 backbone are precursors of neutral complex SLs such as GlcCer.
3.1.5. Glucosylceramides Represent Second Most Abundant SL Class
As part of the neutral SL biosynthesis pathway, SL intermediates with d18:2 and d19:2 backbones are glycosylated at the C1-position to yield fungal complex SLs such as hexosylceramides with glucose as most common sugar in the headgroup. Our analyses detected α-OH GlcCer as a major complex SL representing ~26% of the total SL content, thus making it second most abundant SL class in
R. delemar after PCer. A total of five molecular species were detected that showed significant abundance (
Figure 5). Two GlcCer species from the d18:2 pool had 16(2OH) and 18:0(2OH) as fatty acid contributing 0.3% and 0.01%, respectively. In contrast, three GlcCer species from the d19:2 pool had cumulatively more abundance than the d18:2 pool and had 16:0(2OH), 18:0(2OH) and 24:0(2OH) as the major species sharing ~25%, 0.1% and 0.01% of the total SL content among them. Infact GlcCer d19:2/16:0(2OH) species was the single largest among all the species detected interms of quantity. This observation differs from other fungi such as
Candida where 18:0 (2OH) is the major GlcCer species [
22,
28]. GlcCer synthesis represents the terminal step in the neutral branch of the SL biosynthesis pathway.
3.1.6. PCer Is the Most Abundant SL Class While Its Terminal Acidic Intermediates Are Absent in R. delemar Cells
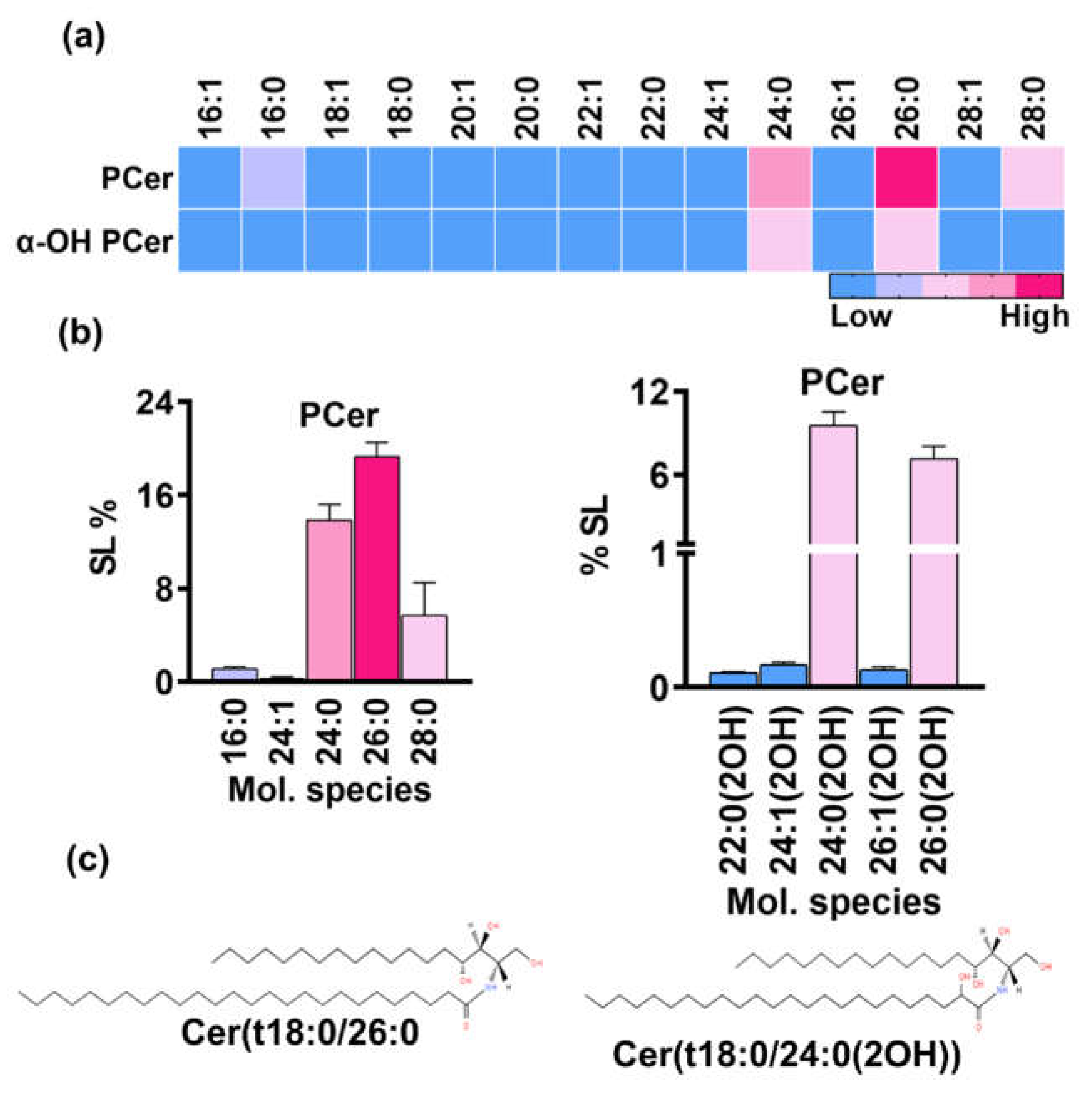
PCer is synthesized by acylation of PHS via amide linkage at C2-position of the PHS base, thus initiating the t18:0 branch of the SL biosynthesis pathway. It is the important intermediate of acidic SLs pathway. Scanning of the t18:0 backbone having m/z 282.2 yielded masses belonging to many SL classes (Supplementary file S1). Most mass signals corresponded to species belonging to PCer which upon quantification revealed PCer as the most abundant SL class with a proportion of 41% out of the total SL content. The detected PCer species prominently included even number of carbons containing fatty acids having chain length of 16 to 28 carbons (
Figure 6a). The significant species were 26:0, 24:0, 28:0, and 16:0, contributing 19.13%, 13.8%, 5.7%, and 1.1%, to the sphingolipid content, respectively (
Figure 6b). Other detected species such as 18:0, 20:0, 22:0 and mono-unsaturated fatty acid containing PCer species accounted for a very minute amount (<1%). Notably, species with saturated fatty acids were remarkably higher than the ones having unsaturated fatty acids.
Table 2. position of the fatty acids yields αOH-PCer which serve as precursor of inositol phosphorylceramides (IPCs) intermediates and represents the acidic branch of SLs biosynthesis in yeast and some other filamentous fungi. The acidic SLs are commonly found in several
Candida and in other fungal species; however, IPCs were not detected in
R. delemar. The analysis showed the accumulation of αOH-PCer which was ~17% of the total SLs and thus making it third most abundant SL class (
Figure 1b). Multiple molecular species of αOH-PCer with fatty acids of varying chain length (14C to 28C) were detected and quantified (
Figure 6a). Like PCer, major specie had similar number of carbons in fatty acids but hydroxylated such as 24:0(2OH), 26:0(2OH) representing 9.5% and ~7% of the total SL content, respectively (
Figure 6b). These were followed by 24:1(2OH), 26:1(2OH) and 28:0(2OH) with amount of 0.16%, 0.13% and 0.02%, respectively. Other species such as 14:0(2OH), 16:0(2OH), 18:0(2OH), 20:0(2OH), 22:0(2OH) and other mono-unsaturated species were only found in trace amounts (≤0.01%)
.
3.2. All Major Glycerophospholipds(GPL) Are Present in R. delemar.
Considering that GPL play diverse and important roles in the biology and pathogenesis of Mucorales, we analysed it in great detail wherein total extracted lipids were subjected to shotgun lipidomics in which different confirmatory scans targeting the polar headgroups of GPLs were used for detection of particular classes [
31]. All scans were performed in positive mode ([M+H]
+ or [M+NH
4]
+) and ranged between m/z 400 Da to 1000 Da covering all the known PL species. The different GPLs detected are given in
Figure 7.
Multiple species were detected that belonged to six classes of phospholipids (PLs). Approximately 200 top species were selected and quantified using MRM approach in which separate chromatograms were recorded for each specie and the identification was done on the basis of retention time with respect to the available natural standards of each class. Each class has a unique polar headgroup and one or two acyl chains linked to glycerol backbone via ester linkages. The complete list of quantified PL species is given in Supplementary file S2.
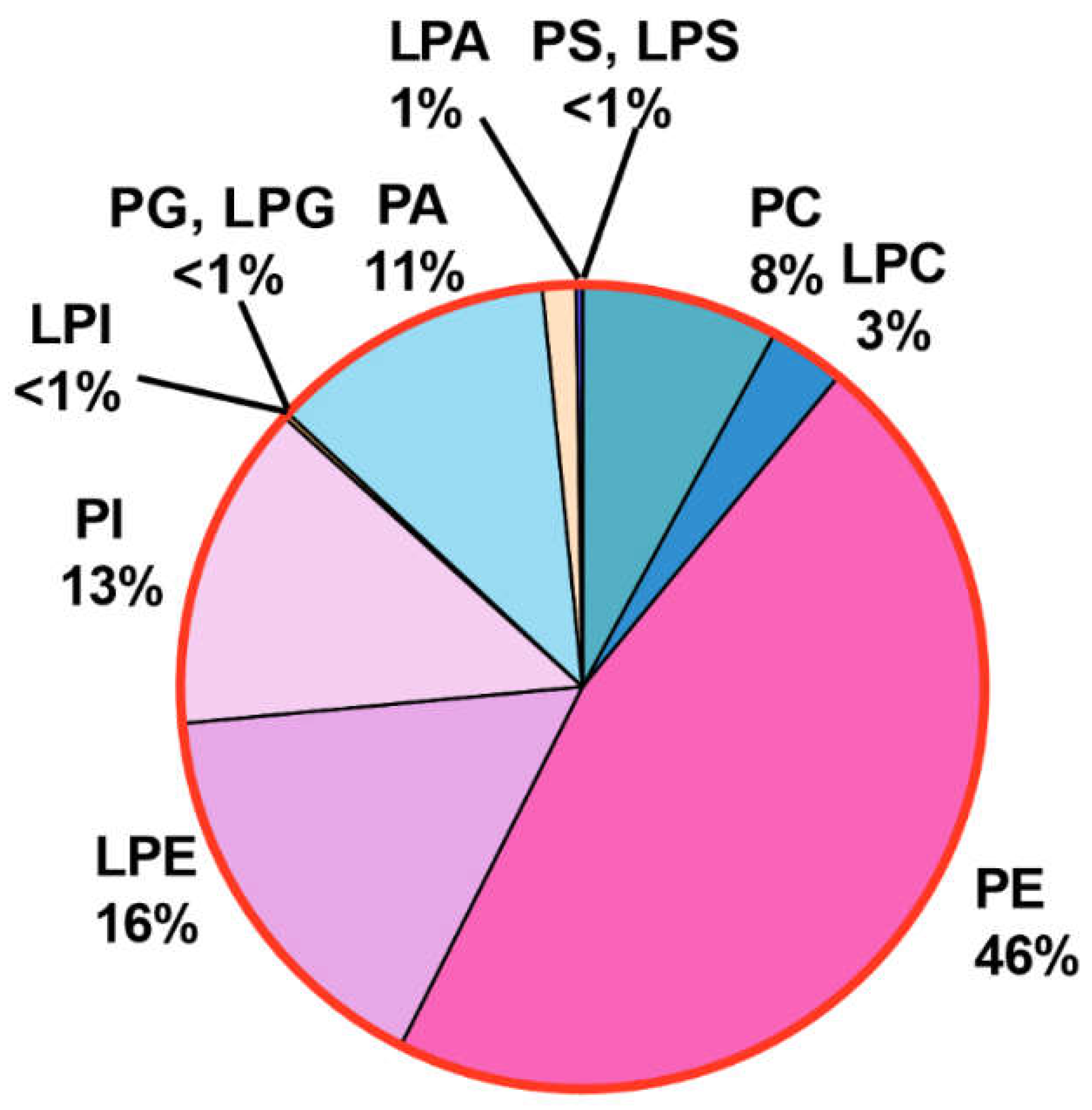
3.2.1. Phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) and Lysophosphatidylethanolamne (LPE) Constitute the Bulk of PL Content
PL classes with ethanolamine headgroup and having two acyl chains i.e; PE was found to be the most abundant PL class (46%). Together with LPE (16%) having only one acyl chain, these combinedly contribute bulk of the total PL content (
Figure 8). Both types of species were detected using a Neutral Loss Scan of 141 Da. While our analysis could detect numerous PE species, those with 30 to 38 carbons and having total double bonds ranging from 0 to 6 in both the acyl chains showed significant abundance and were quantified (
Figure 8a). Notably, species with unsaturated fatty acids were more abundant than those with saturated fatty acids. For instance, the major PE species found had combinedly 34C in the acyl chains such as PE 34:1(11.6%), 34:2(11.2%), 34:3(5.1%) (
Figure 8b). This was followed by species with 36C such as PE 36:2(4.4%), 36:4(3.4%), 36:3(3.2%), 36:1(~2%) and 36:5(1.8%) and 32:1(1.8%). All other species were <1%. Species with odd-chain fatty acids with total 33C and 35C were also detected and were present in low amounts.
LPE species were also present in high quantities (
Figure 8a). Five major species were detected, out of which 18C containg species predominated. LPE 18:1 was most abundant (7.3%) followed by 18:2 (5.4%) and 18:3 (1.36%) (
Figure 8b). Similarly 16C containing LPE 16:1 was the main specie followed by 16:0 sharing ~1% and 0.4% PL content, respectively.
3.2.2. PhosphatidylCholine (PC) Content Is Low
Unlike many fungal species, PC contents are low in
R. delemar cells. The precursor ion scan of phosphocholine headgroup (m/z 184.1 Da) revealed presence of species belonging to PC and LPC. Cumulatively, both types contributed ~11% to the PL content out of which PC was ~8% and LPC 3%. Like PE, species contained a total of 30C to 38C out of which 34C containg species, such as PC 34:1, 34:2 were most abundant, having a proportion of 1.7% and 1%, respectively (
Figure 8b). This was followed by species with 36C such as 36:1(~1%), 36:2(0.85%) and 36:3(0.73%). Two other significant species included 34:3(0.65%), 36:4(0.56%), 32:1 and 36:5 each sharing 0.3% of the total PL content. Other species including those with saturated fatty acids and with odd chain fatty acids of 31C, 33C and 35C were very low(≤0.1).
Similarly in LPC, species with saturated and unsaturated fatty acid chain length of 16C to 18C were detected in which LPC 18:1, 18:2 and 18:3 were major species with 1.8%, 0.8% and 0.4 % proportion, respectively, followed by LPC 16:0, 18:0 and 16:1 ranging from 0.12 % to 0.16% (
Figure 8b). Odd chain containing LPCs, 17:0 and 17:1 were found in trace amounts.
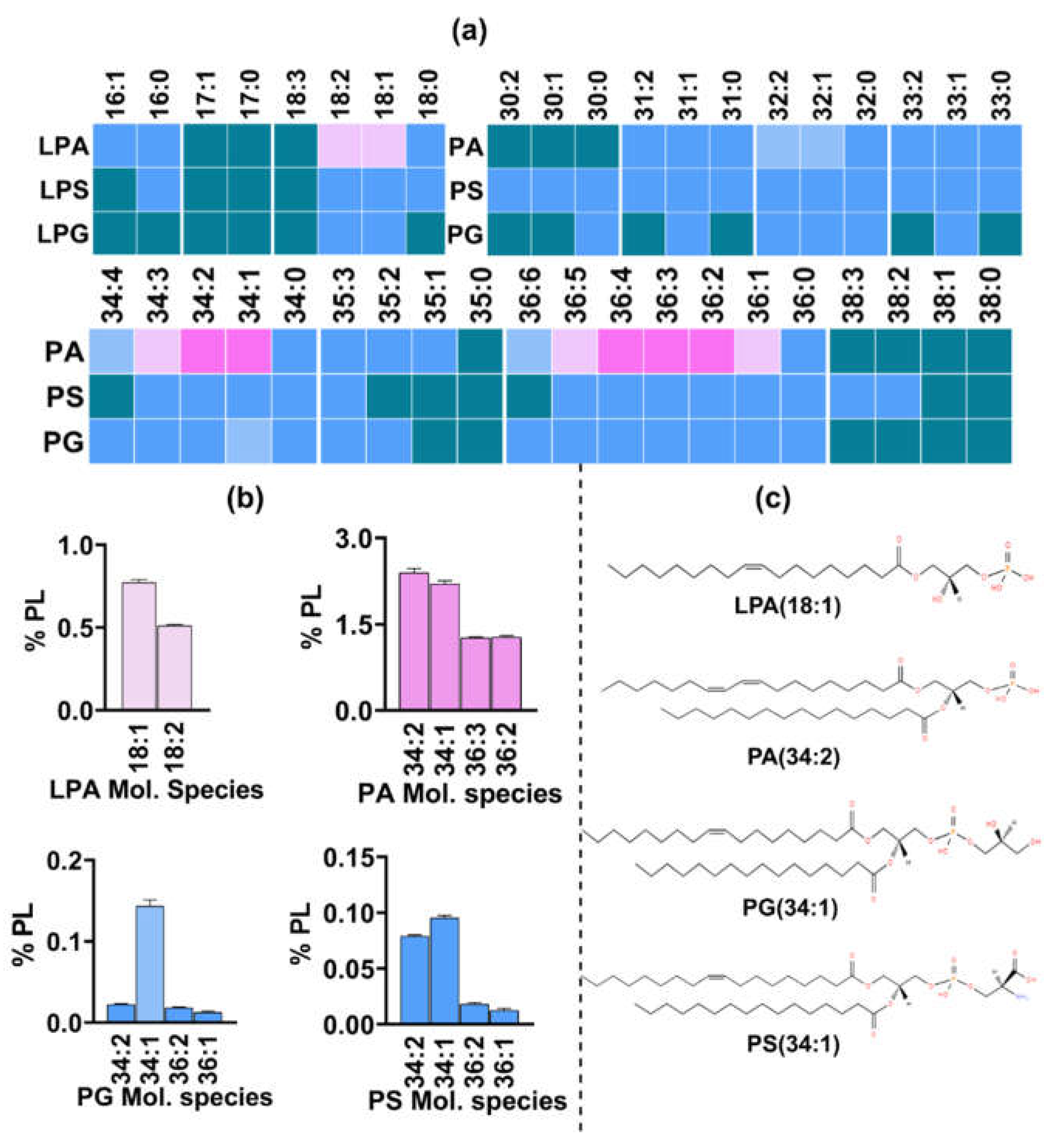
3.2.3. Phosphatidyl Inositol (PI) and Phosphatidic Acid (PA) Show Equal Abundance
Lipid species having inositol as a headgroup were detected using the confirmatory Neutral Loss scan of 277 Da in positive mode. Multiple species belonging to PI having two acyl chains were detected and quantified (
Figure 8a). However, lysophosphatidyl Inositol (LPI) which has only one acyl chain was scarce as only one LPI species showed significant presence. All PI and LPI species constituted about 13% of the total PL content. The major species among PI were those having a total of 34 carbons in both acyl chains, such as PI 34:1, 34:2 and 34:3 contributing 5.5%, 4.8% and 0.84%, respectively, to the total PL content (
Figure 8b). These were followed by 32C containing PI 32:1 and 32:2, having a proportion of 0.5% and 0.4%, respectively. Unlike PC and PE, 36C containing species were less abundant than those with 32C. Major species in 36C group were having one to five double bonds with their levels ranging from 0.05% to 0.2%. Other species including the odd chain fatty acid containing PI species and a single LPI species, LPI 18:1 were present in trace amounts.
Similarly lipid species with phosphate headgroup were detected by Neutral Loss of 115 Da scan and included PA and lyso-PA (
Figure 9a). Their combined abundance of 12.8% was nearly equal to PI and LPI (~13%). The major PA species were PA 34:2, 34:1 and 34:3 having proportion of ~2.4%, 2.2% and 0.7% respectively (
Figure 9b). These were followed by species having 36C and one to five double bonds with their proprtions ranging from 0.5% to 1.2%. Species from the 32C group, PA 32:1 and 32:2 were 0.45% and 0.3%, respectively. All other PA species were present in low amount (≤0.1%).
Unlike LPI, five species of LPA had significant presence with major species having 18C and 16C in their acyl chain. The major species were LPA 18:1(0.7%),18:2 (0.5%), 16:1(0.04%),16:0 (0.02%) and 18:0 (0.01%).
3.2.4. Phosphatidyl Serine (PS) and Phosphatidyl Glycerol (PG) Represent the Least Abundant GPLs.
In the positive mode, a neutral loss scan of 185 Da detected lipid species with serine headgroup.. Species belonging to PS with a total of 30C to 38C in their acyl chains showed significant presence (
Figure 9a). The pattern was similar as that of other PL classes with 34C containg species being more abundant than 36C and 32C containing species (
Figure 9b). The major species from the 34C group were PS 34:1, 34:2 and 34:3 having a proportion of 0.1%, 0.08% and 0.02%, respectively, followed by species within 36C group such as PS 36:2, 36:1, 36:3 with their respective amounts as 0.02%, 0.01% and 0.01%. Among the 32C group, PS 32:1 showed significant presence (0.01%). All other PS species including saturated and odd chain fatty acids were present in trace amounts (<0.01%). Four LPS species LPS 16:0, 18:0,18:1, and 18:2 were also found in minute amounts. PS and LPS combinedly constituted about 0.2% of the total PL content.
Species with glycerol as headgroup were also detected by Neutral loss of 189 Da scan, and belonged to either phosphatidyl glycerol (PG) with two acyl chains or lyso PG having only one acyl chain. Similar to PS and LPS, the total share of PG and LPG was found to be ~0.2%, hence making it the least abundant PL class. The compositional distribution of PG species also followed the same pattern as that of other PL classes with PG 34:1 and 34:2 being most abundant with their proportion as 0.1% and 0.02%, respectively (
Figure 9b). These were followed by PG 36:4 and 32:1 sharing 0.006% and 0.005%, respectively. All other species showed very low presence. Among LPG, two species, LPG 18:1 and LPG 18:2 were quantifiable and ranged between 0.001% to 0.008%
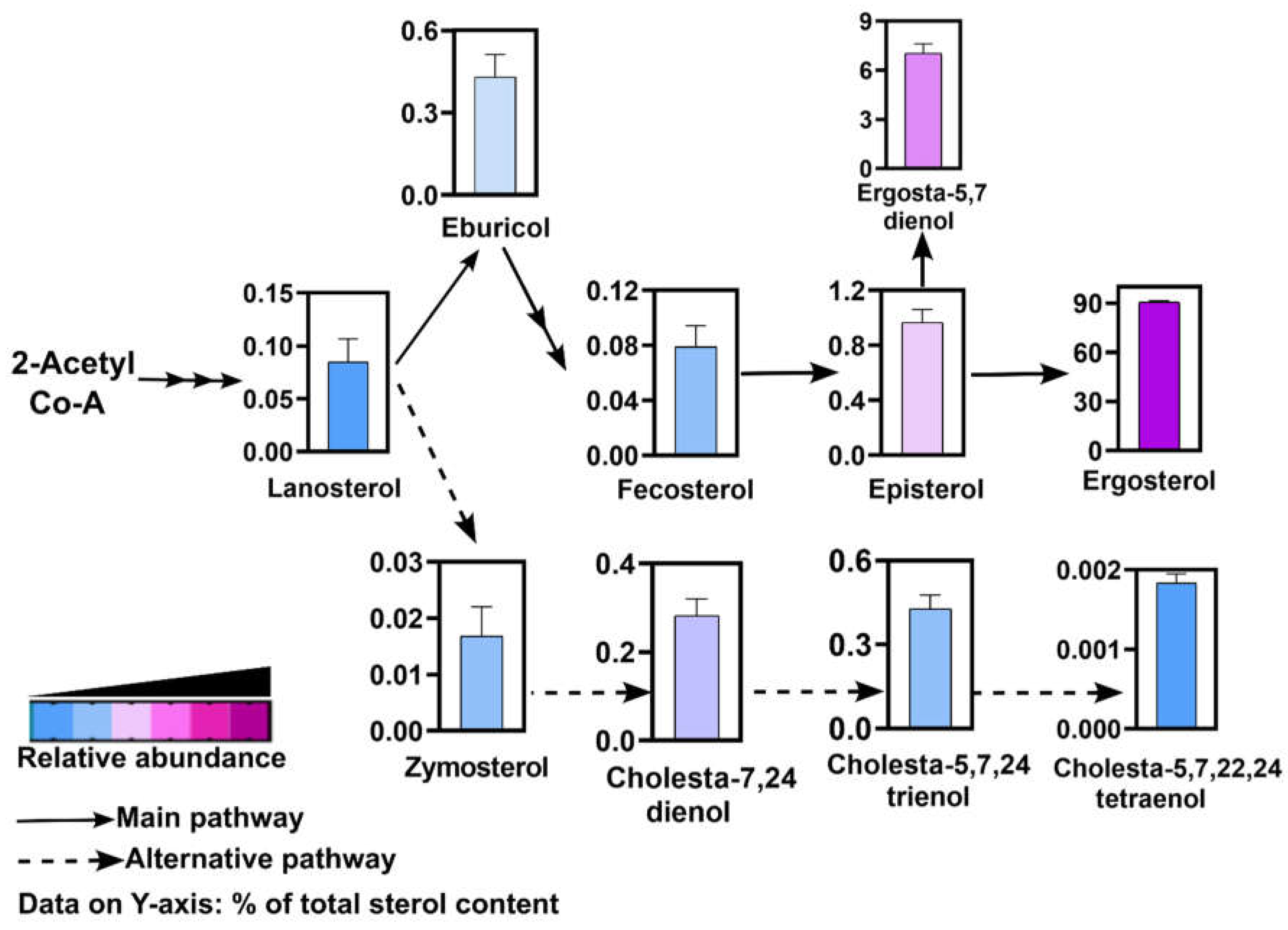
. 3.3. Ergosterol Is the Major Sterol and Alternative Sterol Biosynthesis Pathway Also Exists in R. delemar
We employed GCMS to detect and identify major intermediates in the sterol biosynthesis pathway in
R. delemar. Sterols were identified as TMS-derivatives and spectral pattern of each peak was searched against the spectral libraries of sterols [
25]. While we could detect a number of TMS-derivatized sterols, some non-derivatized and unidentified sterols were also detected. Here, we selected and quantified top sterol intermediates in which ergosterol was found to be the most abundant sterol (~90%), an observation widely found in fungal kingdom (
Figure 10). This was followed by ergosta-5,7 dienol (~7%) and its upstream intermediate, episterol (~1%). The first sterol in the fungal biosynthesis pathway sequence lanosterol was also detected. Its downstream products eburicol and zymosterol were also detected and also showed significant abundance. Both intermediates via fecosterol lead to synthesis of ergosterol through multiple steps.
Notably, cholesta type sterols synthesized from zymosterol were also detected. Major cholesta type sterols were cholesta-7,24 dienol, cholesta-5,7,24 trienol and cholesta-5, 7, 22, 24 tetraenol. These intermediates are part of the alternative pathway of ergosterol biosynthesis in
R. delemar (
Figure 10).
Discussion
Membrane lipids are targets of the common antifungal agents such as azoles and polyenes. Previous studies from others and our group suggest that perturbations in lipid profiles of fungi leads to antifungal resistance development [
32,
33,
34,
35,
36]. Conisdering the intricate relationship between lipids and drug resistance,
R. delemar 99-880, a genome sequenced [
21,
37,
38] and widely characterized representative of Mucorales was used to study compositional landscape of lipids. For the first time, we dissected three major lipid biosynthesis pathways such as SLs, PLs and sterols and not only detected major intermediates of their respective pathways, but also quantified major classes and their constituent molecular species that differed in carbon chain length, and enzymatic modifications such as hydroxylations and degree of unsaturation. The predicted biosynthetic pathways in
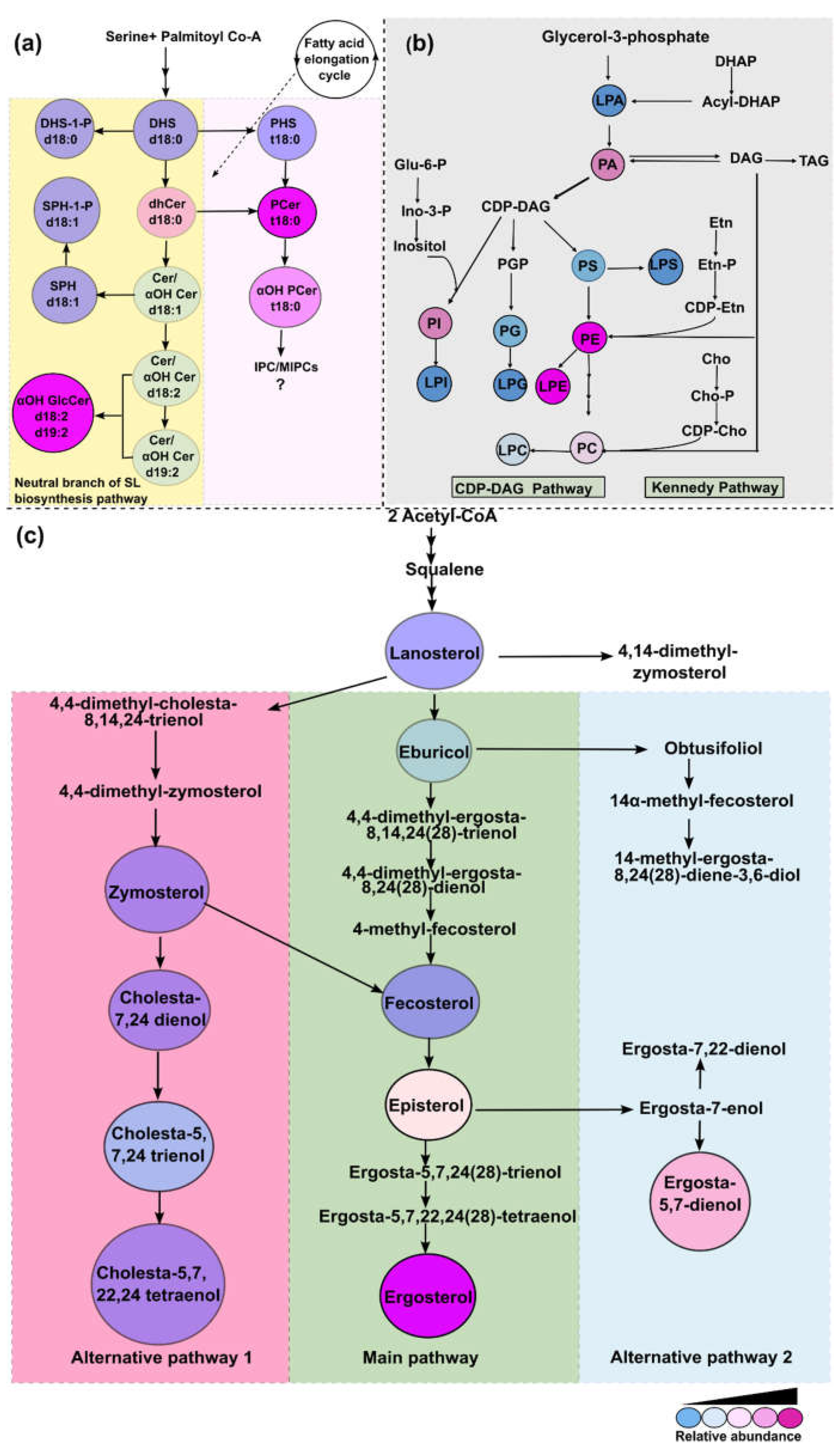
Figure 11, are based on detection of the lipid intermediates and their relative abundance.
Our analysis confirms an earlier study by Aoki et al., which demonstrated evidence of AbA resistance in many Mucorales species, as well as in ascomycete fungus
Hirsutella rhossiliensis and is due to absence of typical acidic SLs such as IPCs and mannosyl inositol phosphorylceramides (MIPCs) [
39,
40]. Also neutral SLs species having one to many sugar molecules in GlcCer have been described in the same study [
39]. However, information about their upstream precursors remained unexplored. In our analysis, we confirmed the presence of fungal specific SLs of the neutral pathway with d18:2 and d19:2 sphingoid backbones, that are precursors of complex GlcCers (
Figure 11a). GlcCer probably being the sole complex SL in
Rhizopus could play critical roles. In
Cryptococcus, GlcCer has already been shown to be a major virulence factor as its depletion rendered cells avirulent [
41]. In other filamentous fungi, GlcCer is required for polarized growth, spore germination and alkali tolerance while in
C. albicans, GlcCer mediates hyphal growth and also susceptibility towards SDS, and FLC [
30,
42,
43,
44]. Our recent studies have also suggested GlcCer compositional differences associated with drug resistance in clinical isolates of
C. auris [
26]. The lower abundance of upstream precursors such as d18:2 and d19:2 Cers and OH-Cer reinforces that these intermediates are highly fluxed towards synthesis of GlcCer to maintain its required proportion. Notably, exogenous GlcCer has been shown to antagonize the effects of the potential antifungal drug, miltefosine, in many species of Mucorales [
45]. Similarly, among LCBs, DHS-1-P was found to be major base compared to PHS and DHS which are found to be abundant in
Candida [
26,
46,
47]
. LCB4, encoding gene for LCB kinase is part of Tac1 regulon, which is one of the major determinats of azole resistance in
Candida [
48]. Phosphorylated bases are known to be involved in temperature tolerance in
S. cerevisiae, although their roles in other fungi are still unclear [
49].
Polar lipids such as PLs detected in our analysis were structurally similar to other eukaryotes. However, remarkable differences with regard to their relative composition among different PLs classes exist. For instance, the major characteristics observed in
R. delemar PLs is a high proportion of PE as compared to lower levels of PC, and high abundance of lyso-lipids (
Figure 11 b). Such apparent variations reflect a completely different physiological state of
R. delemar compared to other fungal pathogens, where PC usually predominates among all other lipid classes [
50]. Notably, a high PE content was seen to be associated with hyper-virulence in
C. albicans [
51]. In addition, a high PE:PC ratio is a major determinant of membrane rigidity that governs drug diffusion across the membrane and affects susceptibility [
36,
52]. Certain lyso-phospholipids were observed to be highly enriched in drug resistant
C. auris isolate [
46].The high abundance of lyso-lipids such as LPE in
R. delemar suggests strong phospholipase activity which impact fungal fitness and virulence. Lyso-lipids were also found in
Candida extracellular vesicles in reponse to oxidative stress [
53]. PLs are known to play roles in maintain membrane rigidity, cell cycle progression and also govern stress resistance. In one of our previous studies, drug resistant
C. auris isolate had higher PL levels compared to susceptible isolate [
54].
Sterol metabolism in fungi and its role in antifungal drug resistance has been a subject of research for a long time. As common antifungal drugs like azoles and polyenes target sterols, any alteration in sterol profile impacts drug susceptibility. Mutation in sterol biosynthesis genes such as
ERG6, HMG1 and ERG3 in
Candida,
Aspergillus,
Mucor lusitanicus and M. circinelloides impact susceptibility of azoles and polyenes [
55,
56,
57].
Erg6 deletion leads to the synthesis of cholesta-type lipids from zymosterol via an alternative ergosterol biosynthesis pathway-often associated with antifungal drug resistance. Genomic analysis of
R. oryzae (
R. delemar) [
21] also reveals presence of genes responsible for biosynthesis of alternative sterol intermediates, some of which were confirmed in our study as discussed earlier. Our analysis of measured sterol intermediates confirms all reported alternative sterol pathways which also appear to operate in
R. delemar (
Figure 11c). Also,
R. delemar genome contains multiple copies of several ergosterol biosynthesis genes such as
ERG11, ERG6, ERG3 and gene duplication of sterol biosynthesis genes has been linked to azole resistance [
21]. All these observations point towards potential resistance evolution in
Rhizopus clinical isolates.
In conclusion, our study presents the first draft landscape of all major classes of lipids in R. delemar, a reference species in Mucorale studies. Analyzing lipid composition among different Mucorales species, which exhibit varying levels of drug resistance, will be interesting since it could explain their diverse physiological roles and reveal their relevance in drug resistance. Nonetheless, the data provided here is expected to serve as a platform to stimulate further research on lipids, their physiological relevance, and their role in drug resistance.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.A., A.S. and R.P.; methodology, B.A., A.C., R.V,and A.S; software, B.A, and R.V.; validation, B.A., M.K.,R.V., A.S., and R.P.; formal analysis, B.A., P.K., H.C., C.L.R., S.M.R., and R.P.; investigation, B.A., A.S., A.S.I. and R.P.; resources, S.M.R., A.S.I., and R.P.; data curation, B.A., A.C., and M.K.; writing—original draft preparation, B.A.; writing—review and editing, M.K., A.S., A.S.I. and R.P.; visualization, B.A., A.S.I., and R.P; supervision, A.S., S.M.R., P.V.D., A.S.I., and R.P.; project administration, R.P.; funding acquisition, A.S., S.M.R., and R.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by the Science and Engineering Research Board (CRG/2022/001047) the Government of India, to R.P., S.M.R., and A.S. R.P. acknowledges the Department of Biotechnology support under Boost to University Interdisciplinary Life Science Departments for Education and Research Programme (DBT-Builder), and DBT-PG TEACHING support to Amity Institute of Biotechnology, Amity University, Haryana. BA acknowledges the Council of Scientifc and Industrial Research fellowship (09/263(1223)/2019-EMR-1). AC and PK acknowledge Indian Council of Medical Research, Government of India, for the award of Senior Research fellowships. M.K. acknowledges the award of the ICMR-Research Associateship Fellowship(Myco/fell/3/2022-ECD-II). BA, A.C, and PK acknowledge the support of the Amity Central Instrument Research facility (CIRF) and Amity Lipidomics Research Facility (ALRF) in carrying out this work. A.S.I. acknowledges his research support from the National Institutes of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID; R01 AI063503).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Jeong, W.; Keighley, C.; Wolfe, R.; Lee, W.L.; Slavin, M.A.; Kong, D.C.M.; Chen, S.C.-A. The Epidemiology and Clinical Manifestations of Mucormycosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Case Reports. Clinical Microbiology and Infection 2019, 25, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakrabarti, A.; Das, A.; Mandal, J.; Shivaprakash, M.R.; George, V.K.; Tarai, B.; Rao, P.; Panda, N.; Verma, S.C.; Sakhuja, V. The Rising Trend of Invasive Zygomycosis in Patients with Uncontrolled Diabetes Mellitus. Med Mycol 2006, 44, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, A.; Chatterjee, S.S.; Das, A.; Panda, N.; Shivaprakash, M.R.; Kaur, A.; Varma, S.C.; Singhi, S.; Bhansali, A.; Sakhuja, V. Invasive Zygomycosis in India: Experience in a Tertiary Care Hospital. Postgraduate Medical Journal 2009, 85, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roden, M.M.; Zaoutis, T.E.; Buchanan, W.L.; Knudsen, T.A.; Sarkisova, T.A.; Schaufele, R.L.; Sein, M.; Sein, T.; Chiou, C.C.; Chu, J.H.; et al. Epidemiology and Outcome of Zygomycosis: A Review of 929 Reported Cases. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2005, 41, 634–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.N.; Fothergill, A.W.; McCarthy, D.I.; Rinaldi, M.G.; Graybill, J.R. In Vitro Activities of Posaconazole, Itraconazole, Voriconazole, Amphotericin B, and Fluconazole against 37 Clinical Isolates of Zygomycetes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2002, 46, 1581–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebremariam, T.; Gu, Y.; Singh, S.; Kitt, T.M.; Ibrahim, A.S. Combination Treatment of Liposomal Amphotericin B and Isavuconazole Is Synergistic in Treating Experimental Mucormycosis. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 2021, 76, 2636–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, G.; Kiss, S.; Varghese, R.; Bauer, K.; Szebenyi, C.; Kocsubé, S.; Homa, M.; Bodai, L.; Zsindely, N.; Nagy, G.; et al. Characterization of Three Pleiotropic Drug Resistance Transporter Genes and Their Participation in the Azole Resistance of Mucor Circinelloides. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2021, 11, 660347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinel-Ingroff, A.; Chakrabarti, A.; Chowdhary, A.; Cordoba, S.; Dannaoui, E.; Dufresne, P.; Fothergill, A.; Ghannoum, M.; Gonzalez, G.M.; Guarro, J.; et al. Multicenter Evaluation of MIC Distributions for Epidemiologic Cutoff Value Definition To Detect Amphotericin B, Posaconazole, and Itraconazole Resistance among the Most Clinically Relevant Species of Mucorales. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2015, 59, 1745–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almyroudis, N.G.; Sutton, D.A.; Fothergill, A.W.; Rinaldi, M.G.; Kusne, S. In Vitro Susceptibilities of 217 Clinical Isolates of Zygomycetes to Conventional and New Antifungal Agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2007, 51, 2587–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Robbins, N.; Cowen, L.E. Molecular Mechanisms Governing Antifungal Drug Resistance. npj Antimicrob Resist 2023, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, A.; Kumar, P.; Chauhan, A.; Kumar, M.; Yadav, K.; Banerjee, A.; Sharma, R.D.; Rudramurthy, S.M.; Chakrabarti, A.; Sanyal, K.; et al. Directed Evolution Detects Supernumerary Centric Chromosomes Conferring Resistance to Azoles in Candida Auris. mBio 2022, 13, e0305222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, S.J.; Arendrup, M.C. Acquired Antifungal Drug Resistance in Aspergillus Fumigatus: Epidemiology and Detection. Medical Mycology 2011, 49, S90–S95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngamskulrungroj, P.; Chang, Y.; Hansen, B.; Bugge, C.; Fischer, E.; Kwon-Chung, K.J. Characterization of the Chromosome 4 Genes That Affect Fluconazole-Induced Disomy Formation in Cryptococcus Neoformans. PLoS One 2012, 7, e33022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodero, L.; Mellado, E.; Rodriguez, A.C.; Salve, A.; Guelfand, L.; Cahn, P.; Cuenca-Estrella, M.; Davel, G.; Rodriguez-Tudela, J.L. G484S Amino Acid Substitution in Lanosterol 14-Alpha Demethylase (ERG11) Is Related to Fluconazole Resistance in a Recurrent Cryptococcus Neoformans Clinical Isolate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2003, 47, 3653–3656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghannoum, M.A.; Rice, L.B. Antifungal Agents: Mode of Action, Mechanisms of Resistance, and Correlation of These Mechanisms with Bacterial Resistance. Clin Microbiol Rev 1999, 12, 501–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, X.; Al-Hatmi, A.M.S.; Vitale, R.G.; Lackner, M.; Ahmed, S.A.; Verweij, P.E.; Kang, Y.; de Hoog, S. Evolutionary Trends in Antifungal Resistance: A Meta-Analysis. Microbiology Spectrum 2024, 12, e02127–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caramalho, R.; Tyndall, J.D.A.; Monk, B.C.; Larentis, T.; Lass-Flörl, C.; Lackner, M. Intrinsic Short-Tailed Azole Resistance in Mucormycetes Is Due to an Evolutionary Conserved Aminoacid Substitution of the Lanosterol 14α-Demethylase. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 15898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chau, A.S.; Mendrick, C.A.; Sabatelli, F.J.; Loebenberg, D.; McNicholas, P.M. Application of Real-Time Quantitative PCR to Molecular Analysis of Candida Albicans Strains Exhibiting Reduced Susceptibility to Azoles. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2004, 48, 2124–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Q.; Yan, L.; Jiang, Y. The Synthesis, Regulation, and Functions of Sterols in Candida Albicans: Well-Known but Still Lots to Learn. Virulence 2016, 7, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoenigl, M.; Seidel, D.; Sprute, R.; Cunha, C.; Oliverio, M.; Goldman, G.H.; Ibrahim, A.S.; Carvalho, A. COVID-19-Associated Fungal Infections. Nat Microbiol 2022, 7, 1127–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.-J.; Ibrahim, A.S.; Skory, C.; Grabherr, M.G.; Burger, G.; Butler, M.; Elias, M.; Idnurm, A.; Lang, B.F.; Sone, T.; et al. Genomic Analysis of the Basal Lineage Fungus Rhizopus Oryzae Reveals a Whole-Genome Duplication. PLOS Genetics 2009, 5, e1000549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Singh, A.; Kumari, S.; Kumar, P.; Wasi, Mohd. ; Mondal, A.K.; Rudramurthy, S.M.; Chakrabarti, A.; Gaur, N.A.; Gow, N.A.R.; et al. Sphingolipidomics of Drug Resistant Candida Auris Clinical Isolates Reveal Distinct Sphingolipid Species Signatures. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids 2021, 1866, 158815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folch, J.; Ascoli, I.; Lees, M.; Meath, J.A.; LeBARON, N. Preparation of Lipide Extracts from Brain Tissue. J Biol Chem 1951, 191, 833–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morio, F.; Pagniez, F.; Lacroix, C.; Miegeville, M.; Le Pape, P. Amino Acid Substitutions in the Candida Albicans Sterol Δ5,6-Desaturase (Erg3p) Confer Azole Resistance: Characterization of Two Novel Mutants with Impaired Virulence. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 2012, 67, 2131–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, C.; Binder, U.; Bracher, F.; Giera, M. Antifungal Drug Testing by Combining Minimal Inhibitory Concentration Testing with Target Identification by Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry. Nat Protoc 2017, 12, 947–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, B.; Kumar, M.; Kumar, P.; Chauhan, A.; Usmani, S.A.; Rudramurthy, S.M.; Meis, J.F.; Chakrabarti, A.; Singh, A.; Gaur, N.A.; et al. Sphingolipid Diversity in Candida Auris: Unraveling Interclade and Drug Resistance Fingerprints. FEMS Yeast Res 2024, 24, foae008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ji, Z.; Feng, Y.; Yan, T.; Cao, Y.; Lu, H.; Jiang, Y. Myriocin Enhances the Antifungal Activity of Fluconazole by Blocking the Membrane Localization of the Efflux Pump Cdr1. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; MacKenzie, A.; Girnun, G.; Poeta, M.D. Analysis of Sphingolipids, Sterols, and Phospholipids in Human Pathogenic Cryptococcus Strains. J. Lipid Res 2017, 58, 2017–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usmani, S.A.; Kumar, M.; Arya, K.; Ali, B.; Bhardwaj, N.; Gaur, N.A.; Prasad, R.; Singh, A. Beyond Membrane Components: Uncovering the Intriguing World of Fungal Sphingolipid Synthesis and Regulation. Research in Microbiology 2023, 104087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poeta, M.D.; Nimrichter, L.; Rodrigues, M.L.; Luberto, C. Synthesis and Biological Properties of Fungal Glucosylceramide. PLOS Pathogens 2014, 10, e1003832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Prasad, T.; Kapoor, K.; Mandal, A.; Roth, M.; Welti, R.; Prasad, R. Phospholipidome of Candida: Each Species of Candida Has Distinctive Phospholipid Molecular Species. OMICS J. Integr. Biol 2010, 14, 665–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rybak, J.M.; Dickens, C.M.; Parker, J.E.; Caudle, K.E.; Manigaba, K.; Whaley, S.G.; Nishimoto, A.T.; Luna-Tapia, A.; Roy, S.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Loss of C-5 Sterol Desaturase Activity Results in Increased Resistance to Azole and Echinocandin Antifungals in a Clinical Isolate of Candida Parapsilosis. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 2017, 61, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbanek, A.K.; Muraszko, J.; Derkacz, D.; Łukaszewicz, M.; Bernat, P.; Krasowska, A. The Role of Ergosterol and Sphingolipids in the Localization and Activity of Candida Albicans’ Multidrug Transporter Cdr1p and Plasma Membrane ATPase Pma1p. IJMS 2022, 23, 9975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Wang, H.; Li, Z.; Wong, A.H.-H.; Wang, Y.-Z.; Guo, Y.; Lin, X.; Zeng, G.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; et al. Candida Albicans Gains Azole Resistance by Altering Sphingolipid Composition. Nat Commun 2018, 9, 4495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhopadhyay, K.; Prasad, T.; Saini, P.; Pucadyil, T.J.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Prasad, R. Membrane Sphingolipid-Ergosterol Interactions Are Important Determinants of Multidrug Resistance in Candida Albicans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2004, 48, 1778–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khandelwal, N.K.; Sarkar, P.; Gaur, N.A.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Prasad, R. Phosphatidylserine Decarboxylase Governs Plasma Membrane Fluidity and Impacts Drug Susceptibilities of Candida Albicans Cells. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr 2018, 1860, 2308–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebremariam, T.; Liu, M.; Luo, G.; Bruno, V.; Phan, Q.T.; Waring, A.J.; Edwards, J.E.; Filler, S.G.; Yeaman, M.R.; Ibrahim, A.S. CotH3 Mediates Fungal Invasion of Host Cells during Mucormycosis. J Clin Invest 2014, 124, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, S.S.M.; Baldin, C.; Gu, Y.; Singh, S.; Gebremariam, T.; Swidergall, M.; Alqarihi, A.; Youssef, E.G.; Alkhazraji, S.; Pikoulas, A.; et al. Mucoricin Is a Ricin-Like Toxin That Is Critical for the Pathogenesis of Mucormycosis. Nat Microbiol 2021, 6, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, K.; Uchiyama, R.; Yamauchi, S.; Katayama, T.; Itonori, S.; Sugita, M.; Hada, N.; Yamada-Hada, J.; Takeda, T.; Kumagai, H.; et al. Newly Discovered Neutral Glycosphingolipids in Aureobasidin A-Resistant Zygomycetes: IDENTIFICATION OF A NOVEL FAMILY OF GALA-SERIES GLYCOLIPIDS WITH CORE Galα1-6Galβ1-6Galβ SEQUENCES *. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2004, 279, 32028–32034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tani, Y.; Funatsu, T.; Ashida, H.; Ito, M.; Itonori, S.; Sugita, M.; Yamamoto, K. Novel Neogala-Series Glycosphingolipids with Terminal Mannose and Glucose Residues from Hirsutella Rhossiliensis, an Aureobasidin A-Resistant Ascomycete Fungus. Glycobiology 2010, 20, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rittershaus, P.C. Glucosylceramide Synthase Is an Essential Regulator of Pathogenicity of Cryptococcus Neoformans. Journal of Clinical Investigation 2006, 116, 1651–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levery, S.B.; Momany, M.; Lindsey, R.; Toledo, M.S.; Shayman, J.A.; Fuller, M.; Brooks, K.; Doong, R.L.; Straus, A.H.; Takahashi, H.K. Disruption of the Glucosylceramide Biosynthetic Pathway in Aspergillus Nidulans and Aspergillus Fumigatus by Inhibitors of UDP-Glc:Ceramide Glucosyltransferase Strongly Affects Spore Germination, Cell Cycle, and Hyphal Growth. FEBS Letters 2002, 525, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oura, T.; Kajiwara, S. Candida Albicans Sphingolipid C9-Methyltransferase Is Involved in Hyphal Elongation. Microbiology 2010, 156, 1234–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, C.M.; Goldman, G.H.; Del Poeta, M. Biological Roles Played by Sphingolipids in Dimorphic and Filamentous Fungi. mBio 2018, 9, e00642–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xisto, M.I.D. da S.; Rollin-Pinheiro, R.; Rochetti, V.P.; Castro-Almeida, Y. de; Borba-Santos, L.P.; Santos-Freitas, G.M.P. dos; Cypriano, J.; Abreu, F. de Á.; Rozental, S.; Barreto-Bergter, E. Miltefosine: A Repurposing Drug against Mucorales Pathogens. Journal of Fungi 2023, 9, 1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamith-Miranda, D.; Heyman, H.M.; Cleare, L.G.; Couvillion, S.P.; Clair, G.C.; Bredeweg, E.L.; Gacser, A.; Nimrichter, L.; Nakayasu, E.S.; Nosanchuk, J.D. Multi-Omics Signature of Candida Auris, an Emerging and Multidrug-Resistant Pathogen 2019, mSystems. 4, 00257–19, 4 4 00257-19.
- Healey, K.R.; Katiyar, S.K.; Raj, S.; Edlind, T.D. CRS–MIS in Candida Glabrata: Sphingolipids Modulate Echinocandin–Fks Interaction. Mol. Microbiol 2012, 86, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.T.; Znaidi, S.; Barker, K.S.; Xu, L.; Homayouni, R.; Saidane, S.; Morschhäuser, J.; Nantel, A.; Raymond, M.; Rogers, P.D. Genome-Wide Expression and Location Analyses of the Candida Albicans Tac1p Regulon. Eukaryot Cell 2007, 6, 2122–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrzypek, M.S.; Nagiec, M.M.; Lester, R.L.; Dickson, R.C. Analysis of Phosphorylated Sphingolipid Long-Chain Bases Reveals Potential Roles in Heat Stress and Growth Control in Saccharomyces. Journal of Bacteriology 1999, 181, 1134–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Kroon, A.I.P.M. Metabolism of Phosphatidylcholine and Its Implications for Lipid Acyl Chain Composition in Saccharomyces Cerevisiae. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids 2007, 1771, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tams, R.N.; Cassilly, C.D.; Anaokar, S.; Brewer, W.T.; Dinsmore, J.T.; Chen, Y.-L.; Patton-Vogt, J.; Reynolds, T.B. Overproduction of Phospholipids by the Kennedy Pathway Leads to Hypervirulence in Candida Albicans. Front Microbiol 2019, 10, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandelwal, N.K.; Chauhan, N.; Sarkar, P.; Esquivel, B.D.; Coccetti, P.; Singh, A.; Coste, A.T.; Gupta, M.; Sanglard, D.; White, T.C.; et al. Azole Resistance in a Candida Albicans Mutant Lacking the ABC Transporter CDR6/ROA1 Depends on TOR Signaling. J Biol Chem 2018, 293, 412–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trentin, G.; Bitencourt, T.A.; Guedes, A.; Pessoni, A.M.; Brauer, V.S.; Pereira, A.K.; Costa, J.H.; Fill, T.P.; Almeida, F. Mass Spectrometry Analysis Reveals Lipids Induced by Oxidative Stress in Candida Albicans Extracellular Vesicles. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahi, G.; Kumar, M.; Kumari, S.; Rudramurthy, S.M.; Chakrabarti, A.; Gaur, N.A.; Singh, A.; Prasad, R. A Detailed Lipidomic Study of Human Pathogenic Fungi Candida Auris. FEMS Yeast Research 2020, 20, foaa045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, K.; Rafael, B.; Vágó, B.; Kiss-Vetráb, S.; Molnár, A.; Szebenyi, C.; Varga, M.; Szekeres, A.; Vágvölgyi, C.; Papp, T.; et al. Characterization of the Sterol 24-C-Methyltransferase Genes Reveals a Network of Alternative Sterol Biosynthetic Pathways in Mucor Lusitanicus. Microbiol Spectr 2023, 11, e0031523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Mendoza, M.I.; Pérez-Arques, C.; Parker, J.; Xu, Z.; Kelly, S.; Heitman, J. Alternative Ergosterol Biosynthetic Pathways Confer Antifungal Drug Resistance in the Human Pathogens within the Mucor Species Complex. mBio 2024, e01661–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rybak, J.M.; Xie, J.; Martin-Vicente, A.; Guruceaga, X.; Thorn, H.I.; Nywening, A.V.; Ge, W.; Souza, A.C.O.; Shetty, A.C.; McCracken, C.; et al. A Secondary Mechanism of Action for Triazole Antifungals in Aspergillus Fumigatus Mediated by Hmg1. Nat Commun 2024, 15, 3642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
a. Susceptibility of R. delemar against SL inhibitors MYR and AbA. Approx. 103 spores were spotted on YPD plates with different concentrations of MYR and AbA. Plates were imaged after incubating at 30 °C for 48 hours. b. Pie-chart represents proportion of different SL intermedates in R. delemar. .
Figure 1.
a. Susceptibility of R. delemar against SL inhibitors MYR and AbA. Approx. 103 spores were spotted on YPD plates with different concentrations of MYR and AbA. Plates were imaged after incubating at 30 °C for 48 hours. b. Pie-chart represents proportion of different SL intermedates in R. delemar. .
Figure 2.
LCBs detected in R. delemar: DHS, DHS-1-P(d18:0), PHS(t18:0) and SPH, SPH-1-P(d18:1). Bar-graphs represent relative proportion of these bases out of total SL content. Structures represent top three major bases, each with different backbone.
Figure 2.
LCBs detected in R. delemar: DHS, DHS-1-P(d18:0), PHS(t18:0) and SPH, SPH-1-P(d18:1). Bar-graphs represent relative proportion of these bases out of total SL content. Structures represent top three major bases, each with different backbone.
Figure 3.
SL classes and molecular species of the neutral branch of SL biosynthesis pathway in R. delemar. a. Heatmap represents the relative representation of different molecular species of dhCer, Cer and αOH-Cer. b.Top five species of each class were quantified and represented by bar-graphs. c. Structures represent the major molecular species of each class.
Figure 3.
SL classes and molecular species of the neutral branch of SL biosynthesis pathway in R. delemar. a. Heatmap represents the relative representation of different molecular species of dhCer, Cer and αOH-Cer. b.Top five species of each class were quantified and represented by bar-graphs. c. Structures represent the major molecular species of each class.
Figure 4.
Fungal specific SL intermediates. a. having d18:2(Δ8-Cer) b. having d19:2 backbone (9Me,Δ8-Cer). Bars depict the top molecular species from each backbone type. The structure of one representative specie is depicted at the bottom of a and b panels.
Figure 4.
Fungal specific SL intermediates. a. having d18:2(Δ8-Cer) b. having d19:2 backbone (9Me,Δ8-Cer). Bars depict the top molecular species from each backbone type. The structure of one representative specie is depicted at the bottom of a and b panels.
Figure 5.
Five major species of αOH-GlcCer with d18:2 and d19:2 backbones acylated to fatty acids of varying chain lengths (x-axis). Structures of two major α-OH GlcCer species are drawn. GlcCer(d18:2/16:0(OH)) on the left has a backbone of 18 Carbons with double bonds at C-4 and C-8 position, glucose at C-1 position and hydroxyl group at C-2 position of the 16C fatty acid chain. Similarly on the right side, GlcCer(d19:2/16:0(OH)) is the major specie with methyl group at C-9 position of the sphoingoid base.
Figure 5.
Five major species of αOH-GlcCer with d18:2 and d19:2 backbones acylated to fatty acids of varying chain lengths (x-axis). Structures of two major α-OH GlcCer species are drawn. GlcCer(d18:2/16:0(OH)) on the left has a backbone of 18 Carbons with double bonds at C-4 and C-8 position, glucose at C-1 position and hydroxyl group at C-2 position of the 16C fatty acid chain. Similarly on the right side, GlcCer(d19:2/16:0(OH)) is the major specie with methyl group at C-9 position of the sphoingoid base.
Figure 6.
a. PCer and αOH-PCer, two major classes in the acidic branch and their molecular species. b. Bargraphs represents the relative amounts of top five molecular species from each class. At the bottom, structures of major species in each class are shown.
Figure 6.
a. PCer and αOH-PCer, two major classes in the acidic branch and their molecular species. b. Bargraphs represents the relative amounts of top five molecular species from each class. At the bottom, structures of major species in each class are shown.
Figure 7.
PL landscape of R. delemar with relative distribution of PL classes.
Figure 7.
PL landscape of R. delemar with relative distribution of PL classes.
Figure 8.
Major PL and Lyso-lipid species of different PL classes detected in R delemar. a. Heatmap represents relative abundance of molecular species in each class with varying number of carbons and double bonds in both acyl chains. b. Top molecular species from PC, PE, PI were quantified and represented by bar-graphs. c. Structures represent major molecular specie from each class.
Figure 9.
Major PL classes detected in R delemar and their Lyso-species. a. Heatmap represents relative abundance of molecular species in each class with varying number of carbons and double bonds in both acyl chains. b. Abundant molecular species from PA, PG, PS were quantified and represented by bar-graphs. c. Structures represent major molecular specie from each class.
Figure 9.
Major PL classes detected in R delemar and their Lyso-species. a. Heatmap represents relative abundance of molecular species in each class with varying number of carbons and double bonds in both acyl chains. b. Abundant molecular species from PA, PG, PS were quantified and represented by bar-graphs. c. Structures represent major molecular specie from each class.
Figure 10.
Major sterol intermediates in R delemar as detected by GCMS. Only the detected intermediates have been shown as bargraphs. Data on Y-axis represents % of each sterol intermediate of total sterol content.
Figure 10.
Major sterol intermediates in R delemar as detected by GCMS. Only the detected intermediates have been shown as bargraphs. Data on Y-axis represents % of each sterol intermediate of total sterol content.
Figure 11.
Putative lipid biosynthesis pathways in R. delemar. Relative abundance of each detected intermediate is depicted by different colurs. a. SL biosynthesis pathway based on the intermediates detected in our analyses. Description of SL class in circles is given by short abbreviations followed by characteristic backbone present. b. PL biosynthesis pathway and the major classes are given in circles. c. Sterol biosynthesis pathway as described in other fungi. Sterol intermediates in the circles are the abundant ones detected in our analysis. The intermediates in the central panel form the main pathway while as the right and the left are alternative pathways.
Figure 11.
Putative lipid biosynthesis pathways in R. delemar. Relative abundance of each detected intermediate is depicted by different colurs. a. SL biosynthesis pathway based on the intermediates detected in our analyses. Description of SL class in circles is given by short abbreviations followed by characteristic backbone present. b. PL biosynthesis pathway and the major classes are given in circles. c. Sterol biosynthesis pathway as described in other fungi. Sterol intermediates in the circles are the abundant ones detected in our analysis. The intermediates in the central panel form the main pathway while as the right and the left are alternative pathways.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).