Submitted:
04 September 2024
Posted:
09 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Study Group
MLPA
RNA-Sequencing
Bioinformatics and Statistical Analysis
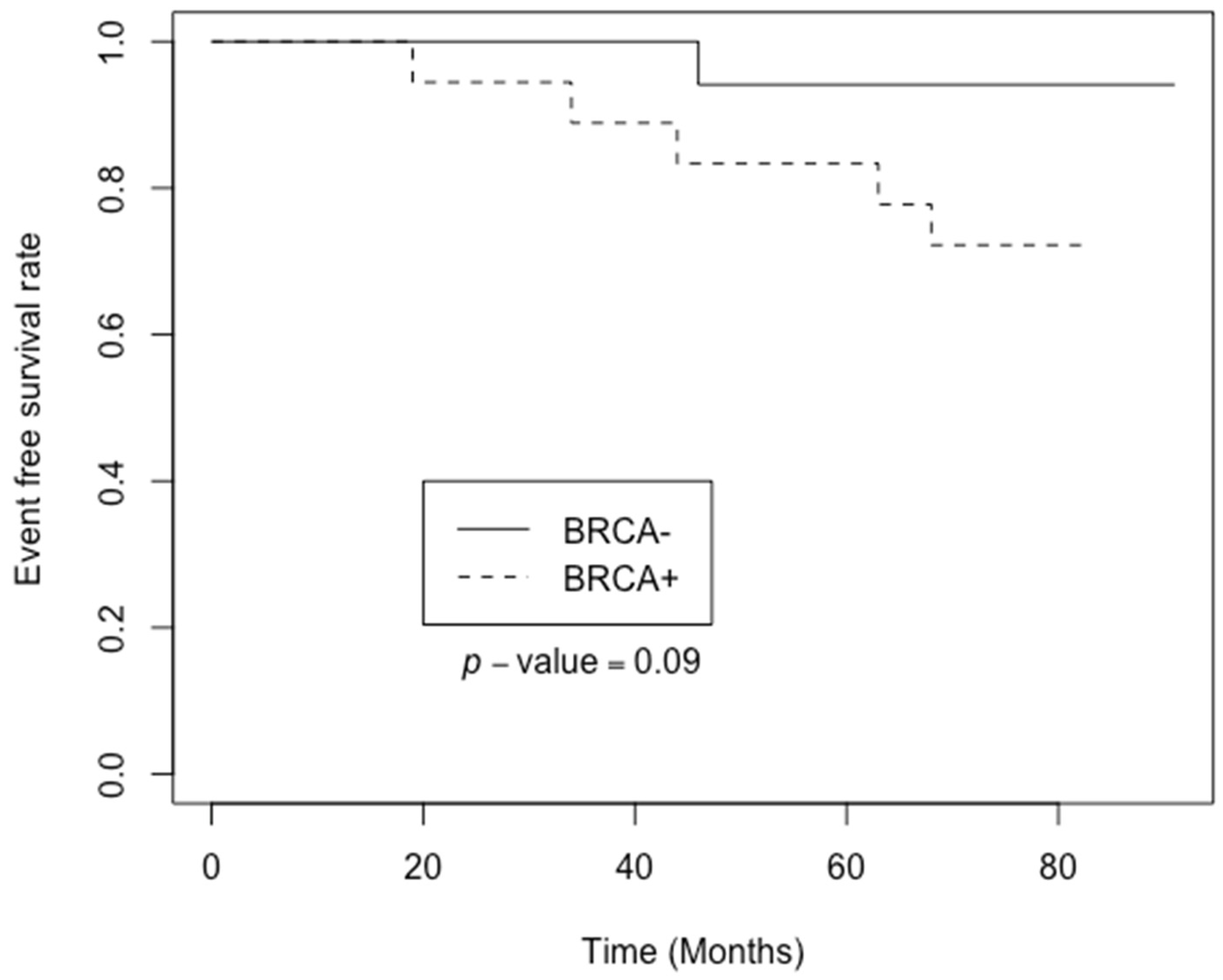
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Characteristic | Study population (n=36) | BRCA1 - group (n=17) | BRCA1 + group (n=19) | p-value |
| Age, median (range) | 59.5 (37-81) | 58 (38-81) | 68 (37-76) | |
| T stage, n (%) | 0.16 | |||
| Tis | 1 (2.8) | 0 (0) | 1 (5) | |
| T1 | 10 (27.8) | 4 (24) | 6 (32) | |
| T2 | 21 (58.3) | 13 76) | 8 (42) | |
| T3 | 3 (8.3) | 0 (0) | 3 (16) | |
| T4 | 1 (2.8) | 0 (0) | 1 (5) | |
| N stage, n(%) | 0.24 | |||
| N0 | 26 (72.2) | 13 (76.5) | 13 (68.4) | |
| Nmic | 2 (5.6) | 2 (11.8) | 0 (0) | |
| N1 | 7 (19.4) | 2 (11.8) | 5 (26.3) | |
| N3 | 1 (2.8) | 0 (0) | 1 (5.3) | |
| Clinical stage | n (%) | 0.25 | ||
| 0 | 1 (2.8) | 0 (0) | 1 (5.2) | |
| IA | 9 (25) | 3 (17.6) | 6 (31.8) | |
| IB | 1 (2.8) | 1 (5.9) | 0 (0) | |
| IIA | 14 (38.9) | 10 (58.9) | 4 (21.1) | |
| IIB | 8 (22.1) | 3 (17.6) | 5 (26.3) | |
| IIIA | 1 (2.8) | 0 (0) | 1 (5.2) | |
| IIIB | 1 (2.8) | 0 (0) | 1 (5.2) | |
| IIIC | 1 (2.8) | 0 (0) | 1 (5.2) | |
| Grade | n (%) | 0.74 | ||
| G1 | 5 (13.9) | 3 (17.6) | 2 (10.5) | |
| G2 | 22 (61.1) | 10 (58.8) | 12 (63.2) | |
| G3 | 6 (16.7) | 2 (11.8) | 4 (21.1) | |
| not known | 3 (8.3) | 2 (11.8) | 1 (5.3) | |
| Ki67 index: | n (%) | 0.34 | ||
| <20% | 15 (41.7) | 5 (29.4) | 10 (52.6) | |
| >20% | 15 (41.7) | 9 (52.9) | 6 (31.6) | |
| Unknown | 6 (16.7) | 3 (17.6) | 3 (15.8) | |
| Molecular type: | n (%) | 0.28 | ||
| Luminal A | 10 (27.8) | 3 (17.6) | 7 (36.8) | |
| Luminal B | 13 (36.2) | 6 (35.3) | 7 (36.8) | |
| TNBC | 7 (19.4) | 4 (23.5) | 3 (15.8) | |
| HER2 positive | 3 (8.3) | 3 (17.6) | 0 (0) | |
| Unknown | 3 (8.3) | 1 (5.9) | 2 (10.5) | |
| Adjuvant treatment: | n | |||
| Chemotherapy | 14 | 7 | 7 | |
| Endocrine therapy (Tamoxifen or AI) | 13 | 6 | 7 | |
| Radiotherapy | 26 | 11 | 15 | |
| Trastuzumab | 2 | 2 | 0 | |
References
- Y. Feng et al., “Breast cancer development and progression: Risk factors, cancer stem cells, signaling pathways, genomics, and molecular pathogenesis,” Genes Dis, vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 77–106, Jun. 2018. [CrossRef]
- Q. Jiang and R. A. Greenberg, “Deciphering the BRCA1 Tumor Suppressor Network,” Journal of Biological Chemistry, vol. 290, no. 29, pp. 17724–17732, Jul. 2015. [CrossRef]
- B. W. X. Lim et al., “Somatic inactivation of breast cancer predisposition genes in tumors associated with pathogenic germline variants,” JNCI: Journal of the National Cancer Institute, vol. 115, no. 2, pp. 181–189, Feb. 2023. [CrossRef]
- R. D. Nindrea, W. A. Harahap, T. Aryandono, and L. Lazuardi, “Association of BRCA1 Promoter Methylation with Breast Cancer in Asia: A Meta- Analysis.,” Asian Pac J Cancer Prev, vol. 19, no. 4, pp. 885–889, Apr. 2018. [CrossRef]
- G. Arpino et al., “Tumor characteristics and prognosis in familial breast cancer,” BMC Cancer, vol. 16, no. 1, p. 924, Dec. 2016. [CrossRef]
- P. C. Fong et al., “Inhibition of Poly(ADP-Ribose) Polymerase in Tumors from BRCA Mutation Carriers,” New England Journal of Medicine, vol. 361, no. 2, pp. 123–134, Jul. 2009. [CrossRef]
- N. Turner, A. Tutt, and A. Ashworth, “Hallmarks of ‘BRCAness’ in sporadic cancers,” Nat Rev Cancer, vol. 4, no. 10, pp. 814–819, Oct. 2004. [CrossRef]
- S. Nik-Zainal et al., “Landscape of somatic mutations in 560 breast cancer whole-genome sequences,” Nature, vol. 534, no. 7605, pp. 47–54, Jun. 2016. [CrossRef]
- E. M. Walsh et al., “Olaparib Use in Patients With Metastatic Breast Cancer Harboring Somatic BRCA1/2 Mutations or Mutations in Non-BRCA1/2, DNA Damage Repair Genes,” Clin Breast Cancer, vol. 22, no. 4, pp. 319–325, Jun. 2022. [CrossRef]
- J. Ledermann et al., “Olaparib maintenance therapy in patients with platinum-sensitive relapsed serous ovarian cancer: a preplanned retrospective analysis of outcomes by BRCA status in a randomised phase 2 trial,” Lancet Oncol, vol. 15, no. 8, pp. 852–861, Jul. 2014. [CrossRef]
- K. P. Pennington et al., “Germline and Somatic Mutations in Homologous Recombination Genes Predict Platinum Response and Survival in Ovarian, Fallopian Tube, and Peritoneal Carcinomas,” Clinical Cancer Research, vol. 20, no. 3, pp. 764–775, Feb. 2014. [CrossRef]
- J. MAKSIMENKO et al., “Prognostic role of BRCA1 mutation in patients with triple-negative breast cancer,” Oncol Lett, vol. 7, no. 1, pp. 278–284, Jan. 2014. [CrossRef]
- D. Szklarczyk et al., “STRING v11: protein–protein association networks with increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide experimental datasets,” Nucleic Acids Res, vol. 47, no. D1, pp. D607–D613, Jan. 2019. [CrossRef]
- D. F. Quail and J. A. Joyce, “Microenvironmental regulation of tumor progression and metastasis,” Nat Med, vol. 19, no. 11, pp. 1423–1437, Nov. 2013. [CrossRef]
- E. Kuzņecova et al., “Identification of Altered Transcripts and Pathways in Triple Negative Breast Cancer,” Proceedings of the Latvian Academy of Sciences. Section B. Natural, Exact, and Applied Sciences., vol. 77, no. 1, pp. 33–40, Feb. 2023. [CrossRef]
- J.-P. Kankkunen, I. T. Harvima, and A. Naukkarinen, “Quantitative analysis of tryptase and chymase containing mast cells in benign and malignant breast lesions,” Int J Cancer, vol. 72, no. 3, pp. 385–388, Jul. 1997. [CrossRef]
- A. Iamaroon, S. Pongsiriwet, S. Jittidecharaks, K. Pattanaporn, S. Prapayasatok, and S. Wanachantararak, “Increase of mast cells and tumor angiogenesis in oral squamous cell carcinoma,” Journal of Oral Pathology & Medicine, vol. 32, no. 4, pp. 195–199, Apr. 2003. [CrossRef]
- J. Wedemeyer and S. J. Galli, “Decreased susceptibility of mast cell-deficient Kit/Kit mice to the development of 1, 2-dimethylhydrazine-induced intestinal tumors,” Laboratory Investigation, vol. 85, no. 3, pp. 388–396, Mar. 2005. [CrossRef]
- M. Furuhashi, S. Saitoh, K. Shimamoto, and T. Miura, “Fatty Acid-Binding Protein 4 (FABP4): Pathophysiological Insights and Potent Clinical Biomarker of Metabolic and Cardiovascular Diseases,” Clin Med Insights Cardiol, vol. 8s3, p. CMC.S17067, Jan. 2014. [CrossRef]
- S. Liu et al., “FABP4 in obesity-associated carcinogenesis: Novel insights into mechanisms and therapeutic implications,” Front Mol Biosci, vol. 9, Aug. 2022. [CrossRef]
- J. Zeng, E. R. Sauter, and B. Li, “FABP4: A New Player in Obesity-Associated Breast Cancer,” Trends Mol Med, vol. 26, no. 5, pp. 437–440, May 2020. [CrossRef]
- J. Hao et al., “Expression of Adipocyte/Macrophage Fatty Acid–Binding Protein in Tumor-Associated Macrophages Promotes Breast Cancer Progression,” Cancer Res, vol. 78, no. 9, pp. 2343–2355, May 2018. [CrossRef]
- K. Kast et al., “Associations of height, body mass index, and weight gain with breast cancer risk in carriers of a pathogenic variant in BRCA1 or BRCA2: the BRCA1 and BRCA2 Cohort Consortium,” Breast Cancer Research, vol. 25, no. 1, p. 72, Jun. 2023. [CrossRef]
- D. J. Brennan et al., “The cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript mediates ligand-independent activation of ERα, and is an independent prognostic factor in node-negative breast cancer,” Oncogene, vol. 31, no. 30, pp. 3483–3494, Jul. 2012. [CrossRef]
- H. J. Kang, Y. W. Yi, H. J. Kim, Y. B. Hong, Y. S. Seong, and I. Bae, “BRCA1 negatively regulates IGF-1 expression through an estrogen-responsive element-like site,” Cell Death Dis, vol. 3, no. 6, pp. e336–e336, Jun. 2012. [CrossRef]
- R. Roy, J. Yang, and M. A. Moses, “Matrix Metalloproteinases As Novel Biomarker s and Potential Therapeutic Targets in Human Cancer,” Journal of Clinical Oncology, vol. 27, no. 31, pp. 5287–5297, Nov. 2009. [CrossRef]
- M. K. Jena and J. Janjanam, “Role of extracellular matrix in breast cancer development: a brief update,” F1000Res, vol. 7, p. 274, Jun. 2018. [CrossRef]
- K. Dzobo and C. Dandara, “The Extracellular Matrix: Its Composition, Function, Remodeling, and Role in Tumorigenesis,” Biomimetics, vol. 8, no. 2, p. 146, Apr. 2023. [CrossRef]
- M. D. Martin and L. M. Matrisian, “The other side of MMPs: Protective roles in tumor progression,” Cancer and Metastasis Reviews, vol. 26, no. 3–4, p. 717, Dec. 2007. [CrossRef]
- H. Huang, “Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) as a Cancer Biomarker and MMP-9 Biosensors: Recent Advances,” Sensors, vol. 18, no. 10, p. 3249, Sep. 2018. [CrossRef]
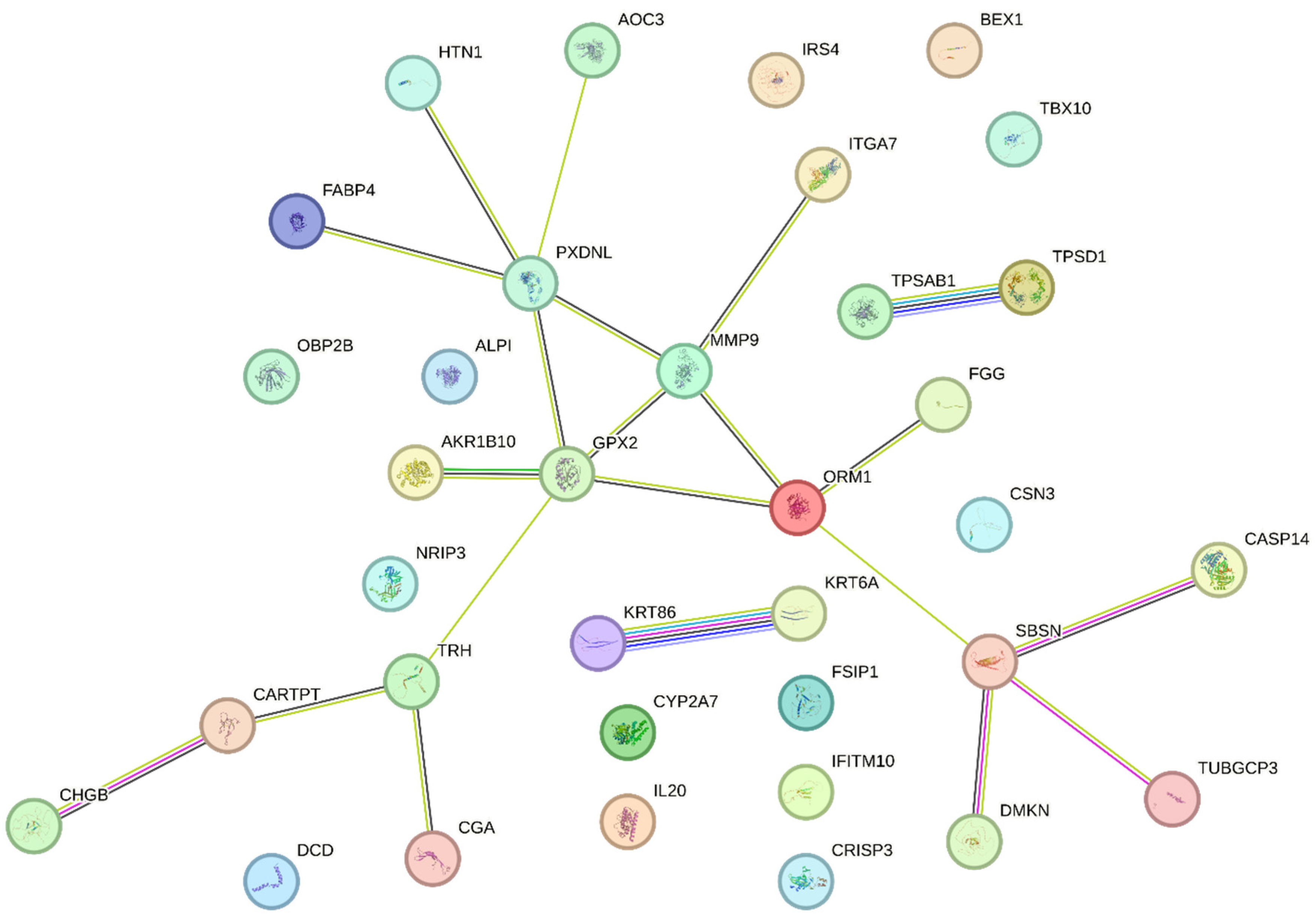
| Gene | Log₂ fold change | Fold change | p-value | HGNC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NRIP3 | 2.37 | 5.17 | 1.81E-08 | HGNC:1167 |
| TUBGCP3 | 2.42 | 5.37 | 7.66E-08 | HGNC:18598 |
| GPX2 | 2.72 | 6.60 | 6.25E-08 | HGNC:4554 |
| PXDNL | 2.84 | 7.15 | 3.21E-07 | HGNC:26359 |
| FSIP1 | 3.06 | 8.32 | 5.6E-09 | HGNC:21674 |
| IL20 | 3.35 | 10.22 | 1.31E-07 | HGNC:6002 |
| MMP9 | 3.75 | 13.46 | 6.45E-08 | HGNC:7176 |
| TPSD1 | 3.81 | 14.06 | 3.6E-07 | HGNC:14118 |
| TPSAB1 | 3.85 | 14.43 | 1.45E-08 | HGNC:12019 |
| TRH | 4.36 | 20.56 | 2.56E-10 | HGNC:12298 |
| AKR1B10 | 4.37 | 20.75 | 5.45E-07 | HGNC:382 |
| ORM1 | 4.52 | 22.86 | 4.8E-07 | HGNC:8498 |
| CGA | 4.75 | 26.90 | 1.18E-06 | HGNC:1885 |
| BEX1 | 4.87 | 29.27 | 5.66E-10 | HGNC:1036 |
| TBX10 | 5.72 | 52.82 | 9.21E-10 | HGNC:11593 |
| FGG | 5.81 | 56.16 | 5.42E-08 | HGNC:3694 |
| CASP14 | 6.27 | 77.34 | 4.16E-10 | HGNC:1502 |
| CRISP3 | 7.06 | 133.61 | 1.41E-16 | HGNC:16904 |
| CSN3 | 7.10 | 137.58 | 1.92E-10 | HGNC:2446 |
| HTN1 | 9.80 | 891.01 | 1.74E-12 | HGNC:5283 |
| ALPI | 10.61 | 1566.05 | 4.67E-16 | HGNC:437 |
| Gene | Log₂ fold change | Fold change | p-value | HGNC |
| CARTPT | -9.88 | -944.90 | 4.29E-20 | HGNC:24323 |
| SBSN | -8.98 | -504.29 | 2.71E-19 | HGNC:24950 |
| IRS4 | -8.00 | -256.83 | 1.06E-16 | HGNC:6128 |
| CHGB | -7.93 | -243.21 | 2.68E-17 | HGNC:1930 |
| CYP2A7 | -7.44 | -173.43 | 4.19E-22 | HGNC:2611 |
| KRT6A | -5.37 | -41.46 | 4.43E-10 | HGNC:6443 |
| DCD | -5.27 | -38.53 | 4.59E-09 | HGNC:14669 |
| OBP2B | -4.04 | -16.48 | 1.14E-10 | HGNC:23381 |
| KRT86 | -3.62 | -12.30 | 7.03E-09 | HGNC:6463 |
| DMKN | -3.30 | -9.83 | 1.16E-08 | HGNC:25063 |
| FABP4 | -3.09 | -8.49 | 2.55E-07 | HGNC:3559 |
| IFITM10 | -2.23 | -4.68 | 3.22E-08 | HGNC:40022 |
| AOC3 | -2.03 | -4.08 | 3.7E-07 | HGNC:550 |
| ITGA7 | -1.85 | -3.61 | 1.25E-06 | HGNC:6143 |
| #Category | Term ID | Term description | Genes from input | Strength | False discovery rate | Matching proteins in the network (labels) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO Component | GO:0005576 | Extracellular region | 23/4175 | 0.49 | 3.74e-05 | TPSD1, FABP4, ORM1, ALPI, CARTPT, TRH, CSN3, FGG, DMKN, TPSAB1, PXDNL, AKR1B10, IL20, MMP9, CHGB, KRT6A, CRISP3, DCD, HTN1, SBSN, KRT86, CGA, OBP2B |
| GO Component | GO:0005615 | Extracellular space | 20/3247 | 0.54 | 5.90e-05 | TPSD1, FABP4, ORM1, CARTPT, CSN3, FGG, DMKN, TPSAB1, PXDNL, IL20, MMP9, CHGB, KRT6A, CRISP3, DCD, HTN1, SBSN, KRT86, CGA, OBP2B |
| COMPARTMENTS | GOCC:0005576 | Extracellular region | 17/2079 | 0.66 | 4.18e-05 | FABP4, ORM1, ALPI, CARTPT, TRH, CSN3, FGG, TPSAB1, PXDNL, AKR1B10, IL20, MMP9, CHGB, CRISP3, DCD, HTN1, CGA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





