Submitted:
04 September 2024
Posted:
09 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
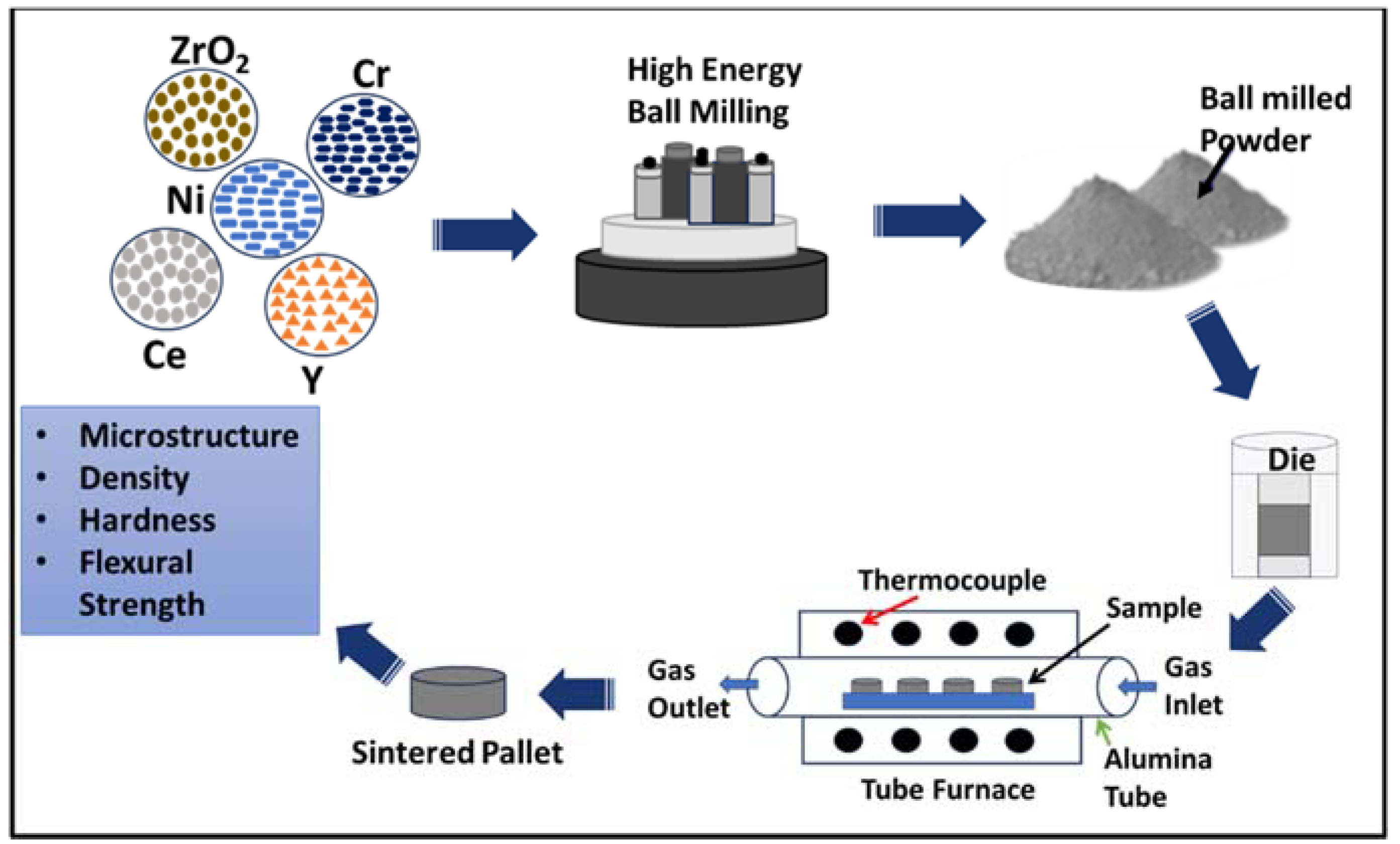
2. Materials and Methods
3. Characterization and Testing Technique
3.1. SEM Analysis
3.2. Density:
- ρex: Density of Sintered Sample
- Wa: Weight in air
- Ww: Weight in water
- The rule of mixtures was utilized to compute the theoretical density of each fabricated composite. The inverse rule of mixtures is expressed as follows:
3.3. Mechanical Testing:
3. Results and Discussion
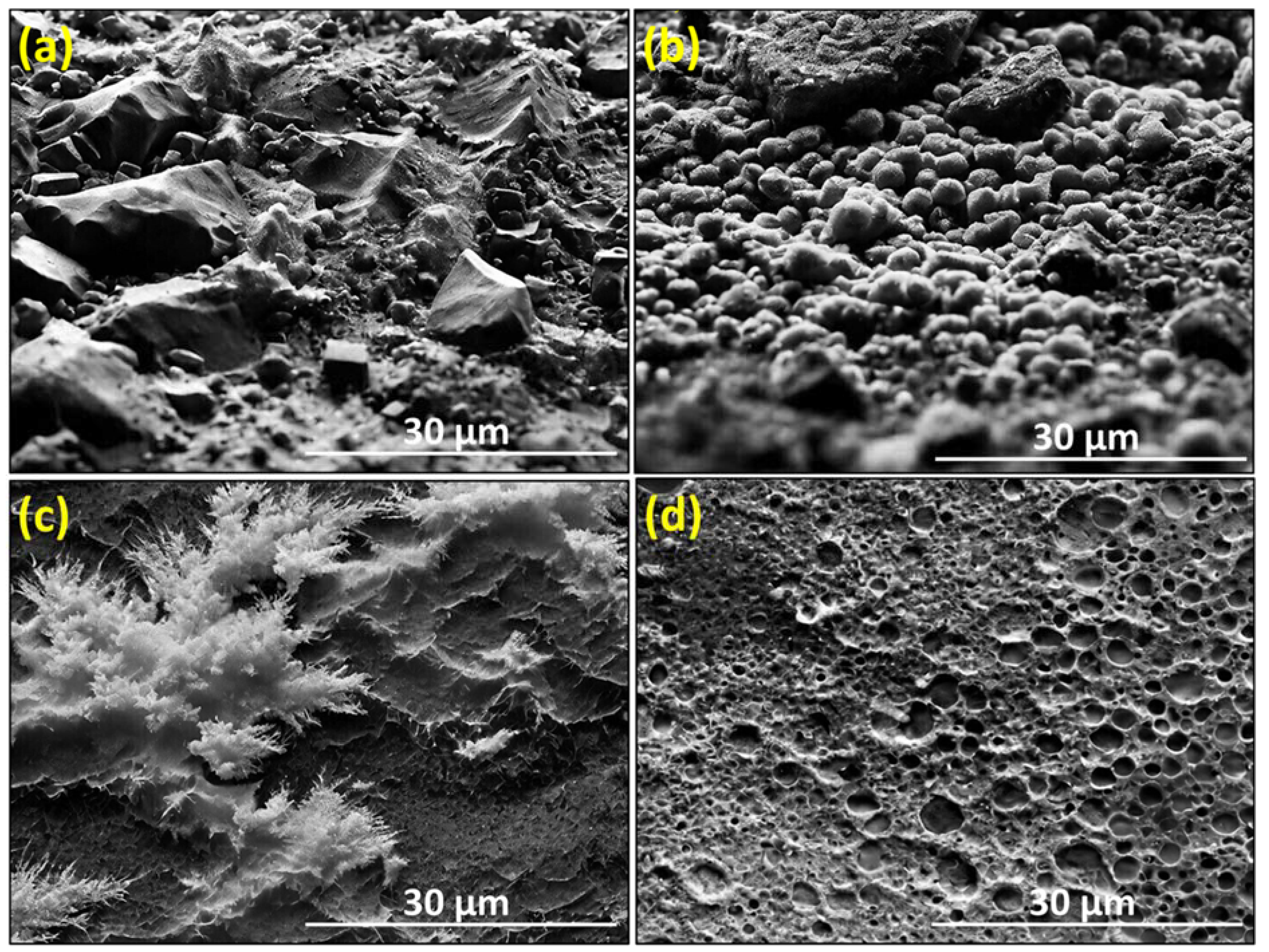
3.1. Microstructural Analysis
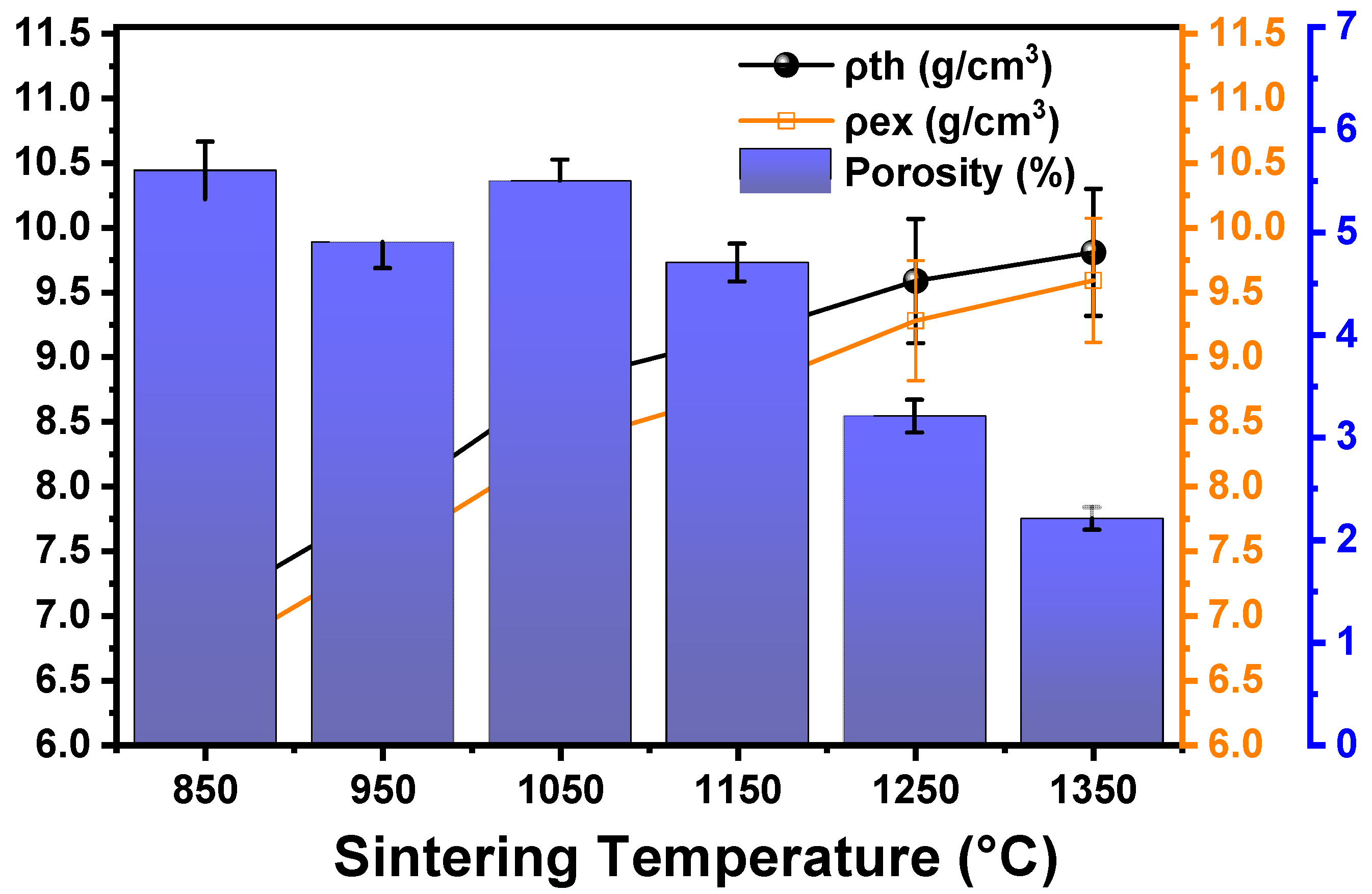
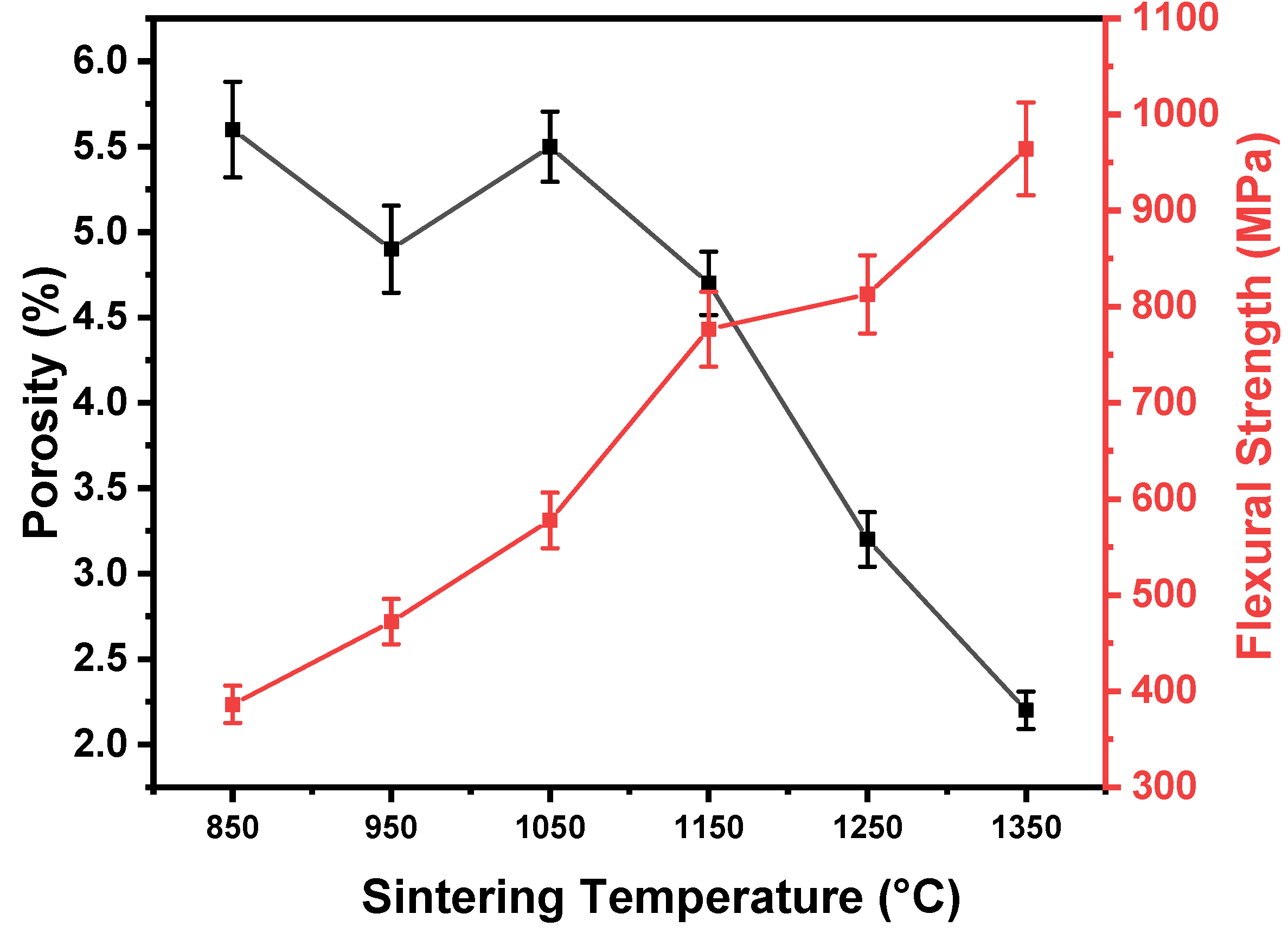
3.2. Density
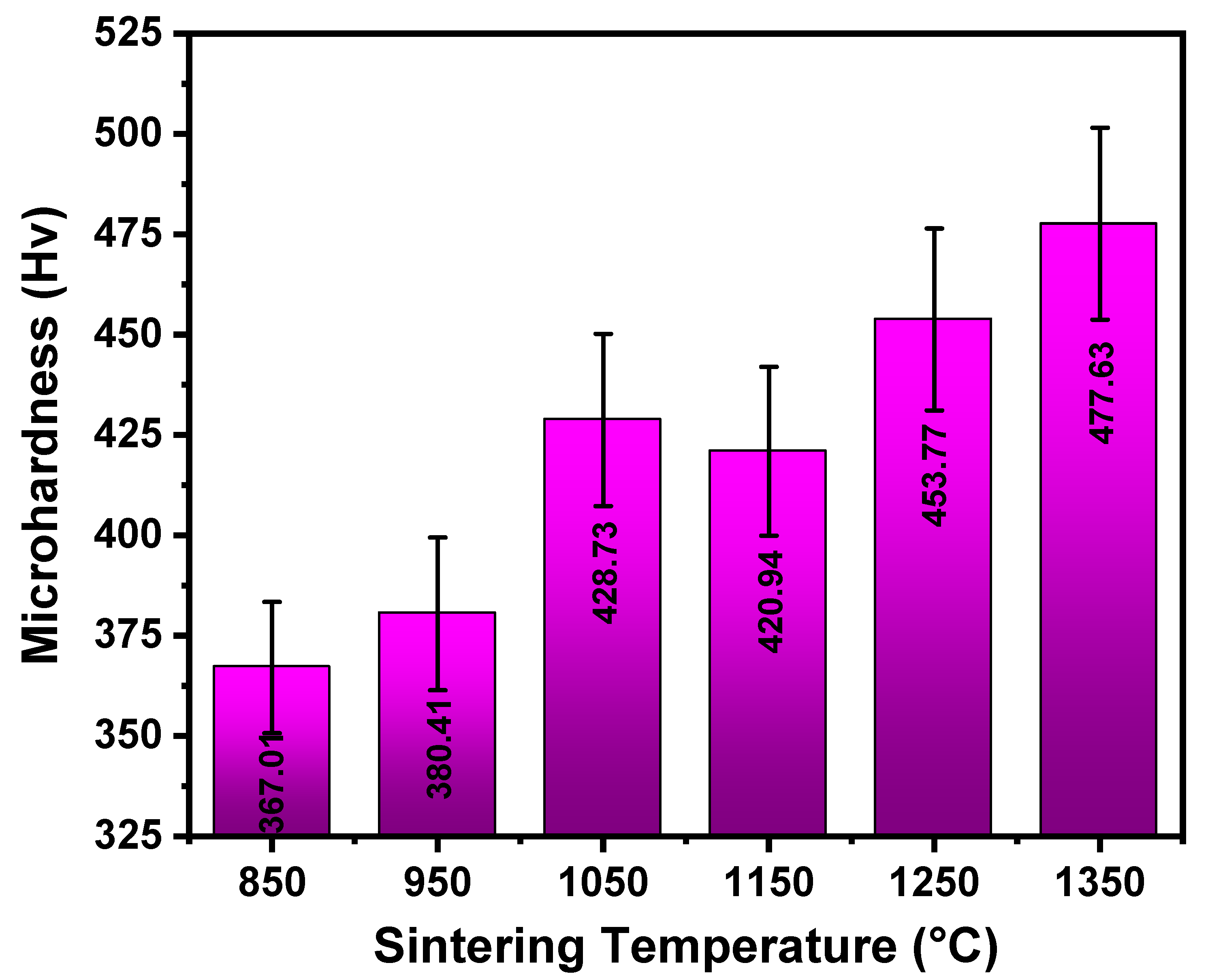
3.3. Hardness
3.4. Flexural Strength
5. Conclusions
- SEM micrographs show a homogeneous distribution of ZrO2, Cr, Ni, Ce, and Y phases, indicating effective fabrication. At lower sintering temperatures (850°C to 950°C), the microstructure features stone-shaped structures due to slow fusion rates, which evolve into smaller forms between 1050°C and 1150°C.
- The composite microstructure evolved from coarse, stone-shaped structures at lower temperatures to finer, layered formations at higher temperatures, culminating in a dense, compact structure at 1350°C.
- Density increased with temperature, primarily due to pore filling by liquid Ce phase, but was counteracted by pore formation from Ce diffusion at higher temperatures.
- Hardness generally improved with temperature, influenced by solid solution strengthening and grain refinement.
- Flexural strength steadily increased with temperature, reaching a peak at 1350°C, demonstrating the composite's potential for high-performance applications.
- The addition of Ce and Y played a crucial role in enhancing mechanical properties through solid solution strengthening and pore filling.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- J. Cho, J. Li, H. Wang, Q. Li, Z. Fan, A.K. Mukherjee, W. Rheinheimer, H. Wang, and X. Zhang, Mater Res Lett 7, 194-202 (2019).
- J. Li, Z. Hao, Y. Shu, and J. He, Journal of Materials Research and Technology 9, 14792-14798 (2020).
- J. Tian, D. Zhang, Y. Chen, G. Zhang, and J. Sun, Vacuum 170, 108779-108788 (2019).
- Y. Wu, Q. Yan, and X. Zhang, Int J Refract Metals Hard Mater 86, 105093-105103 (2020).
- B. Zhu, M. Duke, L. Dumée, A. Merenda, E. des Ligneris, L. Kong, P. Hodgson, and S. Gray, Membranes (Basel) 8, 83-110 (2018).
- Y. Chen, X. Hou, M. Liao, W. Dai, Z. Wang, C. Yan, H. Li, C.-T. Lin, N. Jiang, and J. Yu, Chemical Engineering Journal 381, 122690-122697 (2020).
- Zhang, Yang, Li, and Wu, Metals (Basel) 9, 961-976 (2019).
- T. Sun, Z. Zhao, Z. Liang, J. Liu, W. Shi, and F. Cui, Appl Surf Sci 416, 656-665 (2017).
- S.-Y. Jian, Y.-C. Tzeng, M.-D. Ger, K.-L. Chang, G.-N. Shi, W.-H. Huang, C.-Y. Chen, and C.-C. Wu, Mater Des 192, 108707-108721 (2020).
- Y. Ikoma, T. Toyota, Y. Ejiri, K. Saito, Q. Guo, and Z. Horita, J Mater Sci 51, 138-143 (2016).
- R. Kumar, E. Jordan, M. Gell, J. Roth, C. Jiang, J. Wang, and S. Rommel, Surf Coat Technol 327, 126-138 (2017).
- X. Deng, Y. Wang, Y. Chen, Z. Cui, and C. Shi, J Solid State Chem 275, 206-209 (2019).
- Y. Wang, B. Gao, S. Li, B. Jin, Q. Yue, and Z. Wang, Chemosphere 218, 974-983 (2019).
- J. Zhou, Y. Yang, Y. Yang, D.S. Kim, A. Yuan, X. Tian, C. Ophus, F. Sun, A.K. Schmid, M. Nathanson, H. Heinz, Q. An, H. Zeng, P. Ercius, and J. Miao, Nature 570, 500-503 (2019).
- R.I. Shakirzyanov, N.O. Volodina, A.L. Kozlovskiy, M. V. Zdorovets, D.I. Shlimas, D.B. Borgekov, and Y.A. Garanin, Journal of Composites Science 7, 411-430 (2023).
- T.S. Natarajan, V. Mozhiarasi, and R.J. Tayade, Photochem 1, 371-410 (2021).
- G.R. Xu, J.L. Zou, and G.B. Li, J Hazard Mater 150, 394-400 (2008).
- S.A. McDonald, C. Holzner, E.M. Lauridsen, P. Reischig, A.P. Merkle, and P.J. Withers, Sci Rep 7, 5251-5262 (2017).
- L. Wang, B. Ma, X. Ren, C. Yu, J. Tian, C. Liu, C. Deng, C. Hu, Z. Liu, J. Yu, and Z. Jiang, Mater Today Commun 30, 103032-103042 (2022).
- A.M. Khalil, A. V. Pozdniakov, A.N. Solonin, T.S. Mahmoud, M. Alshah, and A.O. Mosleh, Materials 16, 5477-5490 (2023).
- L. CHANG, B. JIA, S. LI, X. ZHU, R. FENG, and X. SHANG, Journal of Rare Earths 35, 1029-1034 (2017).
- Z. Shen, Y. Zhen, K. Wang, and J. Li, Journal of the American Ceramic Society 92, 1748-1752 (2009).
- M.A. Almomani, A.M. Shatnawi, and M.K. Alrashdan, Adv Mat Res 1064, 32-37 (2014).
| Powder | Supplier | Purity (%) | Particle size (μm) | Apparent Density (g/cm3) | Density (ρ) (g/cm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZrO2 | Sood Chemicals | 95.01 | 1-5 | 5.5 | 5.89 |
| Cr | Sood Chemicals | 95.16 | 1-5 | 7.10 | 7.19 |
| Ni | Sood Chemicals | 95.10 | 1-5 | 8.02 | 8.91 |
| Yttrium (Y) | Nano laboratories | 98.20 | 1-5 | 4.4 | 6.96 |
| Cerium (Ce) | Nano Laboratories | 99.02 | 40 | 6.23 | 6.77 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





