1. Introduction
Caproic acid, a precursor to ethyl hexanoate-the main flavor compound in Nongxiangxing Baijiu-is produced by specific bacteria during fermentation(Wan et al., 2024). These caproic acid-producing bacteria are crucial functional microorganisms in the production of Nongxiangxing Baijiu(Guan et al., 2023; Ren et al., 2024c). They utilize substrates such as lactic acid, D-glucose, ethanol, and D-galactose to synthesize caproic acid. This process involves oxidizing metabolites like ethanol and lactic acid to produce acetyl-CoA and acetic acid(Dong et al., 2023; Ren et al., 2024b). Acetyl-CoA then enters the reversed β-oxidation pathway, where it first combines with other coenzyme A derivatives to form longer-chain coenzyme A derivatives(Yuan et al., 2022). In each cycle of reversed β-oxidation, acetyl-CoA extends the carbon chain of acetic acid by two carbons to produce butyric acid. Subsequently, butyric acid is extended by two more carbons to form caproic acid(orline Nzeteu et al., 2022).
Numerous caproic acid-producing bacteria have been identified(Hu et al., 2015; Liu et al., 2022), with key genera including Clostridium(Li et al., 2023b; Yan & Dong, 2018), Ruminococcaceae(Flaiz et al., 2020), Bacillus(Luo et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2021), and Megasphaera(Jeon et al., 2016; Jeon et al., 2017). Among these, Clostridium is particularly significant. It is a strict anaerobe capable of producing high-value compounds such as butanol, butyric acid, caproic acid, and octanoic acid, often in co-culture systems with other bacteria like Bacillus, Thermoanaerobacterium, and Methanogen(Cui et al., 2021; Du et al., 2020).
Sub-high-temperature Daqu, a saccharification and fermentation agent used in Nongxiangxing Baijiu production(Li et al., 2023a; Ren et al., 2024a), is traditionally exposed to natural inoculation over an extended period(Ren et al., 2024c; Zheng et al., 2011). This practice enriches a diverse range of microorganisms beneficial to the liquor’s quality(Xu et al., 2017). Daqu has historically been regarded as “the bone of liquor” due to its critical role in fermentation(Xue et al., 2023). While research on caproic acid-producing bacteria has focused largely on pit mud and fermented grains, there is limited investigation into their composition within Daqu itself. Studying caproic acid-producing bacteria in Daqu is challenging due to their low abundance, the dormant state of microbial community, and insufficient sequencing data.
In this study, we selected four sub-high-temperature Daqu samples from various regions of Sichuan. By enriching the Daqu samples and using caproic acid content as an indicator, we extracted metagenomic DNA from both the Daqu samples and the enrichment cultures. High-throughput sequencing of 16S rRNA gene amplicons was then employed to analyze the composition of caproic acid-producing bacteria in Daqu and to investigate differences among the Daqu samples.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
Daqu samples were collected from four high-quality wineries across different regions of Sichuan. The samples were labeled as follows: No. 1 Daqu, sourced from eastern Sichuan, was designated Q1; No. 2 Daqu, from southern Sichuan, was labeled Q2; No. 3 Daqu, from western Sichuan, was designated Q3; and No. 4 Daqu, from northern Sichuan, was labeled Q4. Each Daqu sample was crushed, divided into quarters, and then reduced to 1000 g for analysis. Three replicates of each Daqu sample were prepared, packed into sterile bags, and transported to the laboratory. The samples were stored at 4 °C until further use.
The main experimental reagents used in the study included: n-hexanoic acid, chromatographic grade (Shanghai Anpu Experimental Technology Co., Ltd.); 2-ethylbutyric acid, chromatographic grade (Chengdu Kelong Chemicals Co., Ltd.); biotin, analytical grade (Chengdu Kelong Chemicals Co., Ltd.); p-aminobenzoic acid, analytical grade, (Chengdu Kelong Chemicals Co., Ltd.); DNA extraction kit (Thermo Corporation, USA).
2.2. Instruments and Equipment
High-speed refrigerated centrifuge (Thermo Company, USA); gel imaging system (Bio-Rad, USA); 7890B-7000D gas chromatograph-mass spectrometer (Agilent, USA); DHD electric constant temperature blast drying oven (Chengdu Shengjie Technology Co., Ltd.); MYP11-2A constant temperature magnetic stirrer (Shanghai Meiyingpu Instrument Manufacturing Co. Ltd.); LRH-250 biochemical incubator (Shanghai Qixin Scientific Instrument Co., Ltd.); CI54DS vertical pressure steam sterilizer (Xiamen Instrument Co., Ltd.); SHZ-D (III) circulating water multi-purpose vacuum pump (Shanghai Lichen Bangxi Instrument Technology Co., Ltd.).
2.3. Enrichment Culture Medium
Based on the carbon source utilization characteristics of caproic acid bacteria, mCGM-lactic acid culture medium (lactic acid as carbon source), ethanol yeast powder culture medium (ethanol as carbon source), caproic acid bacteria isolation culture medium (mainly containing sodium acetate, trace ions, etc.), and enhanced Clostridium culture medium (glucose as carbon source) were used to culture Daqu anaerobically. The culture medium was sterilized at 121 °C for 20 min. The specific compositions of these media are listed below.
(1) mCGM-lactic acid medium (mCGM, g/L): peptone 10, yeast extract powder 10, ammonium sulfate 2, sodium dihydrogen phosphate 1, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 0.5, magnesium sulfate 0.1, ferrous sulfate heptahydrate 0.015, manganese sulfate 0.01, cobalt chloride 0.01, zinc sulfate 0.002, lactic acid 18, sodium acetate 2.5, calcium carbonate 10, p-aminobenzoic acid 0.01, biotin 0.0005, pH adjusted to 5.5.
(2) Ethanol yeast powder medium (YJ, g/L): yeast powder 6; calcium carbonate 30 (added after sterilization), 40 mL anhydrous ethanol (added after sterilization), p-aminobenzoic acid 0.01, biotin 0.0005, natural pH.
(3) Caproic acid-producing bacteria isolation medium (JF, g/L): sodium acetate 8; magnesium chloride 0.0025; ammonium chloride 0.0005; magnesium sulfate 0.0025; calcium sulfate 0.01; ferrous sulfate 0.005; sodium molybdate 0.0025, p-aminobenzoic acid 0.01, biotin 0.0005, natural pH.
(4) Reinforced Clostridium medium (RCM, g/L): peptone 10, beef extract 10, yeast extract 3, glucose 5, soluble starch 1, sodium chloride 5, anhydrous sodium acetate 3, L-cysteine hydrochloride 0.5, p-aminobenzoic acid 0.01, biotin 0.0005, pH adjusted to 5.5.
2.4. Caproic Acid Detection Method
Pretreatment of fermentation broth: Take 1 mL of fermentation broth, add 100 μL of formic acid for acidification and 1 mL of 2-ethylbutyric acid (5 g/L) as internal standard calibration, and dilute to 5 mL with anhydrous ethanol. After thorough mixing, centrifuge at 12000 r/min for 5 min, filter the supernatant with a 0.22 μm filter membrane to remove live bacteria, and take 1 mL of the filtrate for gas chromatography (GC) detection.
GC conditions: capillary column is LZP-930 (30 m × 0.32 mm × 1.0 µm); injection volume is 1 µL; injection port temperature is 230 °C; program temperature rise: 50 °C for 6 min, 5 °C /min to 170 °C, and keep for 5 min; carrier gas: high-purity nitrogen; carrier gas pressure: 0.05 MPa.
The external standard method is used for quantification, and the peak area of the sample is calculated by the regression equation of the caproic acid standard curve to obtain the caproic acid content of the measured sample.
2.5. Enrichment of Caproic Acid-Producing Bacteria in Daqu
The anaerobic fermentation device uses a 100 mL blue-capped bottle with a rubber inner stopper and a perforated outer cover for easy vacuuming and sealing. The blue-capped bottle containing 50 mL of sterilized culture medium. After the culture medium is cooled, 1% (m/V) Daqu powder was inoculated. The vacuum pump is used to exhaust the air to ensure that the bottle is in an anaerobic environment, and the bottle is placed in a biochemical incubator for constant temperature enrichment culture.
2.6. DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification, and Sequencing of Genomic DNA from Daqu and Its Enrichment Solution
Genomic DNA from Daqu and its enrichment solutions were extracted using the Dnasy PowerSoil soil microbial DNA extraction kit according to the operating instructions. Primers 338F (5’-ACTCCTACGGGAGGCAGC-3’) and 806R fusion primers (5’-7 bp barcode + GGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT-3’) were used to amplify the V4 variable region in the 16S rRNA sequence of the Daqu genome in the mixed sample. The extracted DNA was tested for quality by agarose gel electrophoresis and then constructed and sequenced by Shanghai Meiji Biotechnology Co., Ltd.
2.7. Data Analysis
The experimental results are expressed as mean ± standard deviation, and each group of experiments was repeated 3 times. SPSS 19.0 software was used for one-way analysis of variance, and Origin 2022 software was used for plotting data. The original sequencing data was quality controlled and filtered using Fastp v0.19.6, and the sequences were merged using Flash v1.2.7 to obtain the optimized data after quality control splicing. Then, DADA2 was used to denoise the data to obtain the amplicon sequence variant (ASV) representative sequence and abundance information, and finally annotated using RDP’s RNA database (Silva v138). Based on the microbial diversity QIIME2 process of Shanghai Meiji Biocloud Platform and the ASV representative sequence and abundance information, alpha diversity analysis, Venn diagram drawing, abundance level curve drawing, and principal coordinate analysis (PCA) were performed.
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Different Culture Media on Caproic Acid Production by Daqu
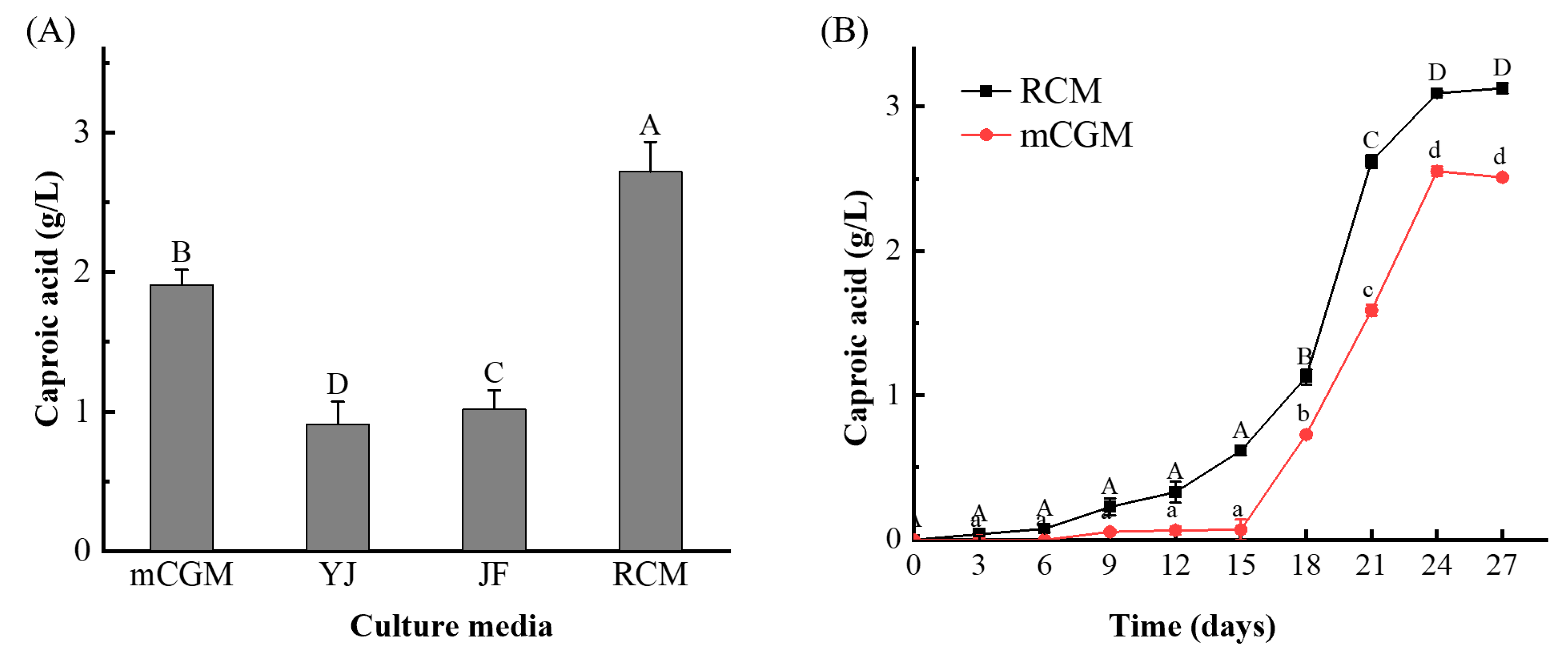
The enrichment method was optimized using Q1 Daqu as the target. Daqu was inoculated into four different culture media and incubated at 37 °C. Given that butyric acid is an intermediate in the synthesis of caproic acid by microorganisms, with caproic acid being synthesized subsequently(Khor et al., 2017), the culture period was set to 20 days, and the caproic acid content in the enriched solutions was measured.
As shown in
Figure 1A, there were significant differences in the caproic acid content among the four culture media (P < 0.05). The media were ranked from highest to lowest caproic acid production as follows: RCM > mCGM > YJ > JF. RCM medium and mCGM-lactic acid medium exhibited the best performance, with caproic acid contents reaching 2.72 g/L and 1.91 g/L, respectively. The other two media also supported caproic acid production, but to a lesser extent. This indicates that Daqu can produce caproic acid under anaerobic conditions and may contain functional microorganisms capable of caproic acid production.
The variation in caproic acid content among the enriched solutions is likely due to differences in nutrient composition among the culture media, which affects caproic acid production processes and pathways, as well as enzyme activities (Tang et al., 2014). Therefore, RCM medium and mCGM-lactic acid medium were selected as the optimal enrichment media for isolating caproic acid-producing bacteria from medium-high temperature Daqu.
To investigate the temporal changes in caproic acid production in medium-high temperature Daqu, Q1 Daqu was inoculated into the enrichment medium and cultured anaerobically at 37 °C. Caproic acid content in the enrichment solution was measured every 3 days.
As shown in
Figure 1B, the caproic acid content in both culture media exhibited an initial gradual increase followed by a peak. During the first 6 days of fermentation, the microorganisms in Daqu were adapting to their environment, and the nutrients in the culture medium were not fully utilized. As a result, caproic acid production was either negligible or exhibited a slow increase. From the 15th day of fermentation, caproic acid content in both culture media increased logarithmically, reaching its peak on the 24th day. At this point, the caproic acid content in the RCM medium reached 3.03 g/L, while the content in the mCGM-lactic acid medium reached 2.52 g/L. Following this peak, the caproic acid content gradually stabilized. Thus, 24 days was determined to be the optimal culture time for enriching caproic acid-producing bacteria in Daqu.
3.2. Effect of Fermentation Temperature on Caproic Acid Production in Daqu
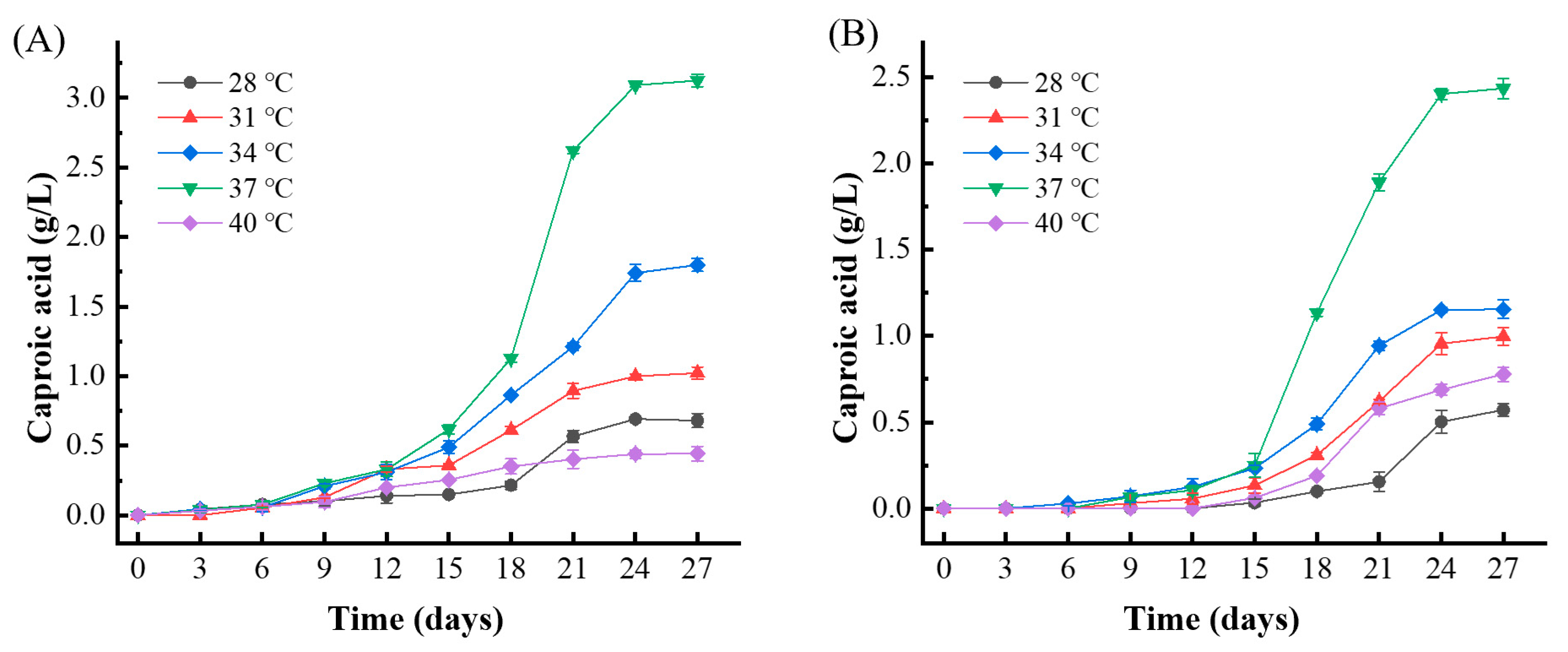
To assess the impact of temperature on caproic acid production in medium-high temperature Daqu fermentation, five different temperature settings were tested for the enrichment of caproic acid-producing bacteria. Q1 Daqu was inoculated into the enrichment medium and cultured anaerobically at these various temperatures. The caproic acid content in the enrichment solution was measured every 3 days.
Figure 2A,B illustrate that, across all temperatures, both culture media began to produce a small amount of caproic acid between 6 to 12 days. Significant increases in caproic acid content were observed after 15 days, with the highest production reaching a peak at 24 days. The optimal temperature for caproic acid production was found to be 37 °C. Under these conditions, the caproic acid content in the RCM medium reached 3.13 g/L, while in the mCGM-lactic acid medium, it reached 2.43 g/L. Therefore, 37 °C was identified as the optimal temperature for enriching caproic acid-producing bacteria in Daqu.
3.3. Enrichment of Caproic Acid-Producing Bacteria in Daqu
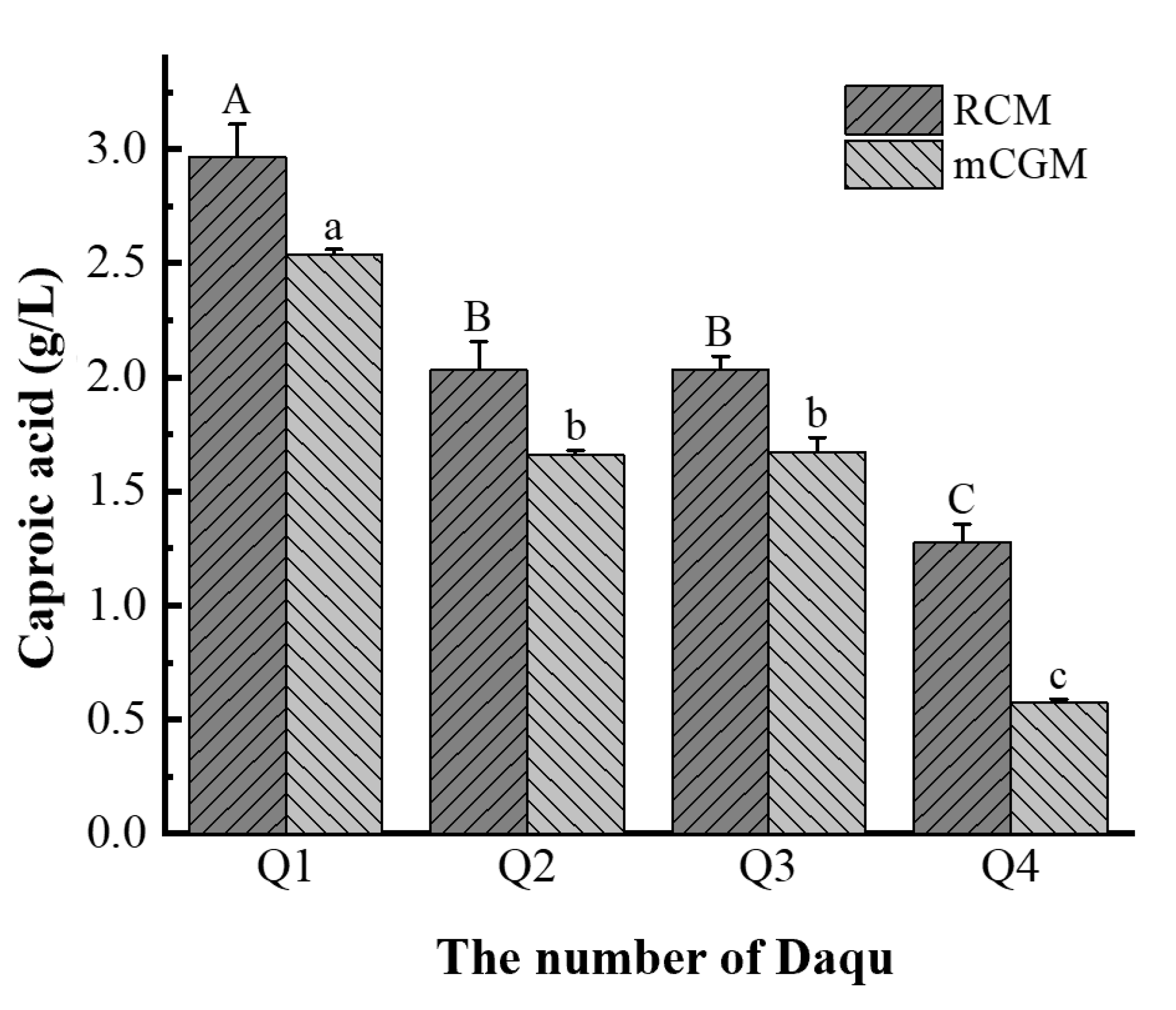
According to the optimal enrichment conditions for caproic acid-producing bacteria previously determined, the caproic acid content in each enrichment solution after culturing four types of Daqu is shown in
Figure 3. Among the four enrichment solutions using RCM culture medium, the caproic acid content, ranked from highest to lowest, is Q1 (2.97 g/L) > Q3 (2.04 g/L) > Q2 (2.03 g/L) > Q4 (1.28 g/L). The difference in caproic acid content among the collection solutions was not significant (P > 0.05), except for the significant difference between Q1 and Q4 Daqu enrichment solutions (P < 0.05). For the four enrichment cultures using mCGM-lactic acid medium, the caproic acid content in Daqu enrichment solutions ranked from highest to lowest is Q1 (2.53 g/L) > Q3 (1.67 g/L) > Q2 (1.66 g/L) > Q4 (0.57 g/L). The differences in caproic acid content between the enrichment solutions were not significant (P > 0.05), with the exception of the significant difference between Q1 and Q4 Daqu enrichment solutions (P < 0.05).
The four medium- and high-temperature Daqu types exhibit varying abilities to produce caproic acid under anaerobic conditions, which may be attributed to differences in the abundance and composition of the caproic acid-producing bacteria in Daqu(Liu et al., 2014; Zhou et al., 2024). It is evident that there are differences in caproic acid production among Daqu in different media and at varying temperatures. The RCM medium proves to be more effective for the enrichment of caproic acid-producing bacteria and the synthesis of caproic acid. All Daqu enrichment solutions produced caproic acid, indicating that caproic acid-producing bacteria have been successfully enriched and can be used for further analysis of the composition of the caproic acid-producing bacterial community.
3.4. Analysis of the Microbial Diversity of Daqu and Its Enrichment Solutions
After sequencing the 12 mixed samples from repeated experiments, a total of 254,812 sequences were obtained, and cluster analysis yielded 1,984 OTU (operational taxonomic unit) classifications. As shown in
Table 1, compared with the 12 samples before and after Daqu enrichment, the Ace index and Chao index decreased, indicating that the richness of the Daqu microbial community decreased after enrichment. This reduction may be attributed to the selective enrichment conditions of the medium. Based on the Shannon index and Simpson index, it is observed that the species diversity of Daqu did not change significantly after enrichment with mCGM-lactic acid medium, whereas it decreased after enrichment with RCM medium. The Coverage index of the 12 samples was close to 100%, indicating that the sequencing results accurately reflect the real composition of the samples. Overall, the richness and diversity of the microbial flora changed to some extent after Daqu enrichment, confirming that the enrichment effect was achieved.
3.5. Analysis of Bacterial Microbial Community Structure in Daqu Enrichment Solutions
The bacterial microbial community composition of Daqu samples was analyzed at the genus level. Bacterial genera with a relative abundance greater than 1% were plotted in community stacking bar graphs, while those with relative abundance less than 1% were classified as “Others”. As shown in
Figure 4A, the most abundant bacterial genus in Q2 Daqu was
Weissella (38.97%), in Q4 Daqu and Q1 Daqu was
Rhodococcus (30.37% and 35.35%, respectively), and in Q3 Daqu was
Thermoactinomyces (56.99%).
After enrichment, the dominant bacterial genus was mainly
Clostridiaceae under the phylum Firmicutes. Specifically, after enrichment with RCM medium, the dominant bacterial genera in the enrichment solution were mainly
Clostridium_sensu_stricto_18 (2.19%-63.04%),
Bacillus (4.27%-17.15%),
Tissierellales (11.36%-14.50%),
Caldicoprobacter (0.03%-16.00%),
Caproiciproducens (0.02%-10.11%),
Eubacterium (2.47%-7.72%),
Sporanaerobacter (0%-4.66%),
Tepidimicrobium (2.09%-3.51%), and
Clostridium_sensu_stricto_1 (0.97%-2.91%) (
Figure 4A).
After enrichment with mCGM-lactic acid medium, the dominant bacterial genera in the enrichment solution included
Clostridium_sensu_stricto_18 (4.92%-21.63%),
Sporanaerobacter (14.15%-43.03%),
Bacillus (3.42%-12.5%),
Caldicoprobacter (2.86%-7.07%),
Tissierellales (4.87%-15.34%),
Clostridium_sensu_stricto_1 (2.01%-17.36%),
Eubacterium_fissicatena_group (1.46%-15.82%),
Enterococcus (1.01%-18.17%),
Caproiciproducens (2.19%-8.17%),
Clostridium_sensu_stricto_15 (3.54%-7.65%), and
unclassified_f_lachnospiraceae (2.43%-7.67%) (
Figure 4A).
Comparing the bacterial microbial composition of four medium- and high-temperature Daqu from different regions of Sichuan before and after enrichment reveals significant changes in the microbial populations. Before enrichment, the dominant bacterial genera in Daqu were mainly concentrated in Actinobacteriota, Firmicutes, and Proteobacteria. Potential caproic acid-producing bacteria, such as Clostridium_sensu_stricto_18 (10.87%) in Q4 Daqu and Caproiciproducens (3.48%) and Clostridium_sensu_stricto_12 (1.17%) in Q2 Daqu, were not found in other Daqu samples. This may be due to their low abundance, which caused them to be classified under the “Others” category.
Thus, it is necessary to enrich Daqu to increase the content of potential caproic acid-producing bacteria and to compare the differences in the bacterial composition of these bacteria in different medium- and high-temperature Daqu. After enrichment with two culture media, the diversity of potential caproic acid bacteria in Daqu increased, including genera such as
Clostridium_sensu_stricto_18,
Caproiciproducens,
Clostridium_sensu_stricto_15,
Clostridium_sensu_stricto_12,
Clostridium_sensu_stricto_1,
Clostridium_sensu_stricto_10, and
Clostridium_sensu_stricto_7. Except for
Caproiciproducens, these all belong to the
Clostridium genus in the strict sense and are speculated to be caproic acid producers in Daqu. Among them,
Caproiciproducens,
Clostridium_sensu_stricto_18, and
Clostridium_sensu_stricto_12 are commonly found in pit mud and fermented grains and are reported to be important for caproic acid production in these environments(Mao et al., 2023).
Clostridium_sensu_stricto_12 can convert lactic acid into caproic acid and promote the formation of various volatile compounds, showing a significant positive correlation with caproic acid, butyric acid, and 2,3-butanediol (
Figure 4A).
Comparing the bacterial microbial community structure of different Daqu enrichment solutions, the main caproic acid-producing bacteria identified include Clostridium_sensu_stricto_1, Caproiciproducens, and Clostridium_sensu_stricto_18 in Q2 Daqu; Clostridium_sensu_stricto_18 and Clostridium_sensu_stricto_1 in Q4 Daqu; Clostridium_sensu_stricto_18 and Caproiciproducens in Q3 Daqu; and Clostridium_sensu_stricto_18 and Clostridium_sensu_stricto_15 in Q1 Daqu. Generally, enrichment with RCM medium resulted in higher abundance and diversity of caproic acid-producing bacteria compared to mCGM-lactic acid medium.
The Rank-Abundance curves depicted in
Figure 4B illustrate the species abundance and evenness. The curves for the four Daqu samples show a large and gentle span, indicating high species evenness and abundance before enrichment, which decreases post-enrichment. Principal coordinate analysis (PCA) of the bacterial communities at the genus level (
Figure 4C) shows that Q2 and Q3 are very similar, whereas Q1 and Q4 are more distinct, reflecting that Q2 and Q3 have a more similar bacterial community composition compared to Q1 and Q4.
After enrichment, the confidence ellipses for the microbial communities enriched in RCM and mCGM-lactic acid media were quite distinct from those of the original Daqu samples, indicating significant changes in microbial community structure. Enrichment with RCM medium resulted in RQ2 being close to RQ3 but distant from RQ1 and RQ4, while enrichment with mCGM-lactic acid medium resulted in mQ4 being close to mQ3 but distant from mQ1 and mQ2. The PCA results confirm that different enrichment media lead to distinct bacterial microbial community structures in Daqu.
3.6. Analysis of Bacterial Microbial Species Composition in Daqu Enrichment Solutions
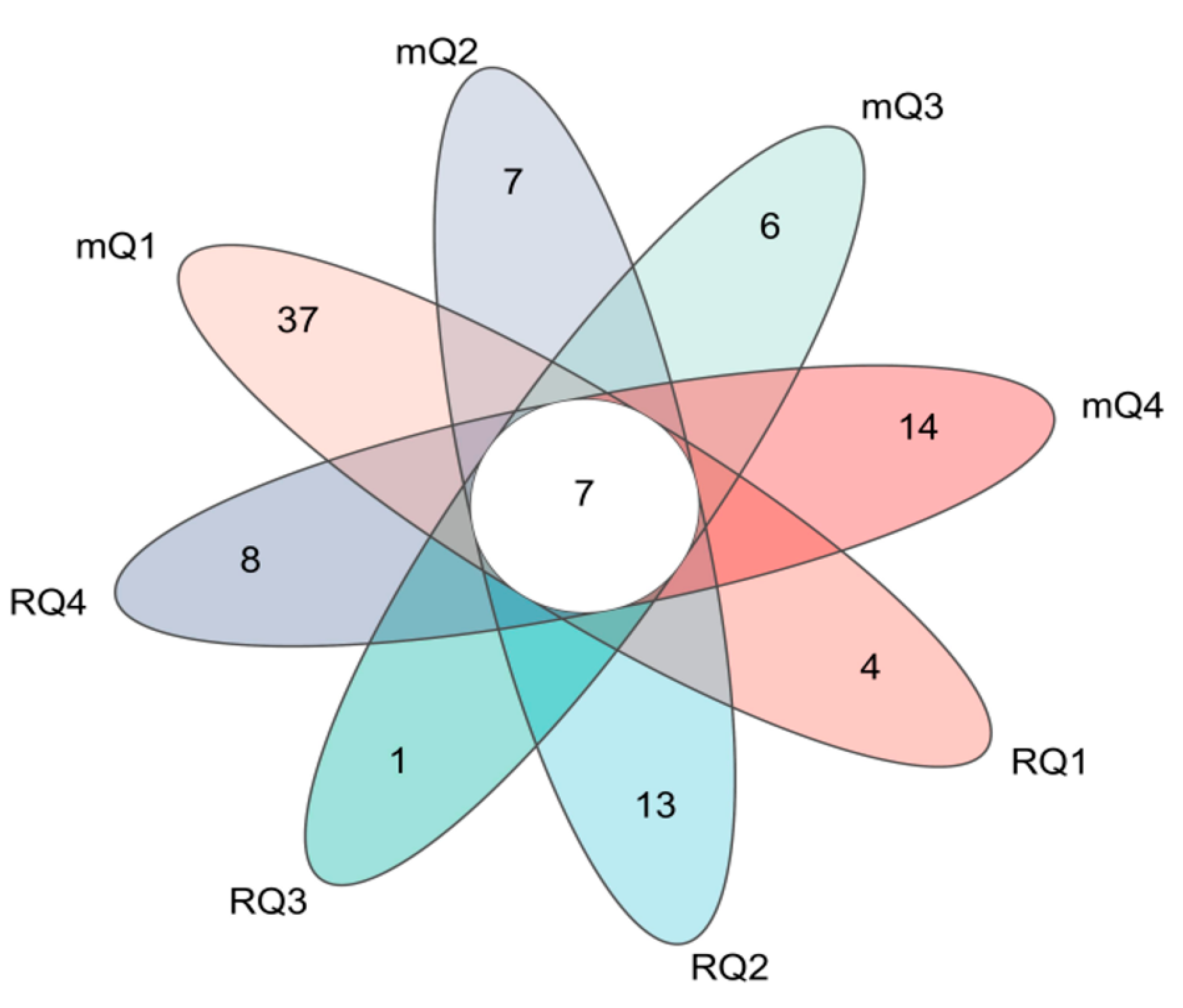
To identify common and unique bacterial species in Daqu enrichment from different regions, the bacterial community was analyzed at the genus level using a Venn diagram. As shown in
Figure 5, different colors represent bacterial genera from Daqu enrichment solutions across various regions and culture media conditions. The overlapping sections denote common genera, while the non-overlapping sections represent unique genera. The numbers indicate the corresponding counts of these genera.
It is observed that all Daqu enrichment solutions contain a total of 92 bacterial genera. Among these, 7 bacterial genera are shared, accounting for a total abundance ranging from 11.59% to 83.89%. The dominant bacterial genera include Clostridium_sensu_stricto_18 (2.19% to 63.04%), Bacillus (3.42% to 17.15%), Enterococcus (0.05% to 18.17%), and Clostridium_sensu_stricto_1 (0.31% to 17.37%). In the Daqu enrichment solutions using mCGM-lactic acid medium, the only dominant bacterial genus is Rummeliibacillus (0.31% to 17.37%). Conversely, in the Daqu enrichment solutions using RCM medium, the sole dominant bacterial genus is Lachnoclostridium (0.31% to 17.37%).
4. Conclusions
In single-factor experiments, caproic acid production from medium-high temperature Daqu was highest after 24 days of culture at 37 °C in RCM medium and mCGM-lactic acid medium, indicating the best enrichment effect. The results demonstrated the presence of caproic acid-producing bacteria in medium-high temperature Daqu. Enrichment of these bacteria was most effective when cultured in RCM medium and mCGM-lactic acid medium. The dominant bacterial genera in Daqu were primarily Actinobacteriota, Firmicutes, and Proteobacteria. After enrichment, the dominant genera shifted to Clostridiaceae, with variations in caproic acid-producing bacteria composition among different Daqu samples. Overall, enrichment in RCM medium yielded higher abundance and diversity of caproic acid-producing bacteria compared to mCGM-lactic acid medium. Medium-high temperature Daqu is a crucial source of microorganisms in the fermentation of Nongxiangxing Baijiu. Analyzing the composition of caproic acid-producing bacteria in Daqu provides a theoretical basis for targeted research on these bacteria and their role in improving the fermentation process.
Author Contributions
Zhiqiang Ren, Data visualization, Writing - Original Draft, Writing - Review & Editing, Funding acquisition, Resources; Shuqin Huang, Data Curation, Formal analysis; Huang Zhiguo, Writing - Review, Resources.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Open Fund Project of the Sichuan Key Laboratory of Brewing Biotechnology and Application (NJ2022-07), awarded to Zhiqiang Ren.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
References
- Cui, Y., Yang, K.-L., Zhou, K. 2021. Using co-culture to functionalize Clostridium fermentation. Trends Biotechnol., 39(9), 914-926. [CrossRef]
- Dong, W., Yang, Y., Liu, C., Zhang, J., Pan, J., Luo, L., Wu, G., Awasthi, M.K., Yan, B. 2023. Caproic acid production from anaerobic fermentation of organic waste-Pathways and microbial perspective. Renew Sustain Energy Rev., 175, 113181. [CrossRef]
- Du, Y., Zou, W., Zhang, K., Ye, G., Yang, J. 2020. Advances and applications of Clostridium co-culture systems in biotechnology. Front Microbiol, 11, 560223. [CrossRef]
- Flaiz, M., Baur, T., Brahner, S., Poehlein, A., Daniel, R., Bengelsdorf, F.R. 2020. Caproicibacter fermentans gen. nov., sp. nov., a new caproate-producing bacterium and emended description of the genus Caproiciproducens. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 70(7), 4269-4279. [CrossRef]
- Guan, T., Wu, X., Hou, R., Tian, L., Huang, Q., Zhao, F., Liu, Y., Jiao, S., Xiang, S., Zhang, J. 2023. Application of Clostridium butyricum, Rummeliibacillus suwonensis, and Issatchenkia orientalis for Nongxiangxing baijiu fermentation: Improves the microbial communities and flavor of upper fermented grain. Food Res. Int., 169, 112885. [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.-l., Du, H., Xu, Y. 2015. Identification and quantification of the caproic acid-producing bacterium Clostridium kluyveri in the fermentation of pit mud used for Chinese strong-aroma type liquor production. Int. J. Food Microbiol., 214, 116-122. [CrossRef]
- Jeon, B.S., Choi, O., Um, Y., Sang, B.-I. 2016. Production of medium-chain carboxylic acids by Megasphaera sp. MH with supplemental electron acceptors. Biotechnol Biofuels., 9, 1-9. [CrossRef]
- Jeon, B.S., Kim, S., Sang, B.-I. 2017. Megasphaera hexanoica sp. nov., a medium-chain carboxylic acid-producing bacterium isolated from a cow rumen. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 67(7), 2114-2120. [CrossRef]
- Khor, W.C., Andersen, S., Vervaeren, H., Rabaey, K. 2017. Electricity-assisted production of caproic acid from grass. Biotechnol Biofuels., 10, 1-11. [CrossRef]
- Li, H., Liu, S., Liu, Y., Hui, M., Pan, C. 2023a. Functional microorganisms in Baijiu Daqu: Research progress and fortification strategy for application. Front Microbiol, 14, 1119675. [CrossRef]
- Li, M., Li, T., Zheng, J., Qiao, Z., Zhang, K., Luo, H., Zou, W. 2023b. Genome Analysis and Optimization of Caproic Acid Production of Clostridium butyricum GD1-1 Isolated from the Pit Mud of Nongxiangxing Baijiu. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 33(10), 1337. [CrossRef]
- Liu, C., Du, Y., Zheng, J., Qiao, Z., Luo, H., Zou, W. 2022. Production of caproic acid by Rummeliibacillus suwonensis 3B-1 isolated from the pit mud of strong-flavor baijiu. J. Biotechnol., 358, 33-40. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y., Tang, T.-X., Pei, X.-Q., Zhang, C., Wu, Z.-L. 2014. Identification of ketone reductase ChKRED20 from the genome of Chryseobacterium sp. CA49 for highly efficient anti-Prelog reduction of 3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)acetophenone. J. Mol. Catal. B: Enzym., 102, 1-8. [CrossRef]
- Luo, H., Li, T., Zheng, J., Zhang, K., Qiao, Z., Luo, H., Zou, W. 2022. Isolation, Identification, and Fermentation Medium Optimization of a Caproic AcidProducing Enterococcus casseliflavus Strain from Pit Mud of Chinese Strong Flavor Baijiu Ecosystem. Polish J. Microbiol., 71(4), 563. [CrossRef]
- Mao, F., Huang, J., Zhou, R., Qin, H., Zhang, S., Cai, X., Qiu, C. 2023. Succession of microbial community of the pit mud under the impact of Daqu of Nongxiang Baijiu. J. Biosci. Bioeng., 136(4), 304-311. [CrossRef]
- orline Nzeteu, C., Coelho, F., Trego, A.C., Abram, F., Ramiro-Garcia, J., Paulo, L., O’Flaherty, V. 2022. Development of an enhanced chain elongation process for caproic acid production from waste-derived lactic acid and butyric acid. J Clean Prod., 338, 130655. [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z., Chen, Q., Tang, T., Huang, Z. 2024a. Unraveling the water source and formation process of Huangshui in solid-state fermentation. Food Sci. Biotechnol., 1-11. [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z., Liu, L., Tang, T., Huang, K., Huang, Z. 2024b. Effectively Increase the L(+)-Isomer Proportion of Ethyl Lactate in Baijiu by Isolating and Applying L(+)-Lactic Acid-Producing Bacteria. in: Preprints, Preprints.
- Ren, Z., Xie J., Tang T., & Huang Z. (2024). Short-Chain Carboxylates Facilitate the Counting of Yeasts in Sub-High Temperature Daqu. Pol J Microbiol, 73, 167-176. [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.-X., Liu, Y., Wu, Z.-L. 2014. Characterization of a robust anti-Prelog short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase ChKRED20 from Chryseobacterium sp. CA49. J. Mol. Catal. B: Enzym., 105, 82-88. [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y., Huang, J., Tang, Q., Zhang, S., Qin, H., Dong, Y., Wang, X., Qiu, C., Huang, M., Zhang, Z. 2024. Characterizing the Contribution of Functional Microbiota Cultures in Pit Mud to the Metabolite Profiles of Fermented Grains. Foods, 13(11), 1597. [CrossRef]
- Wang, H., Gu, Y., Zhou, W., Zhao, D., Qiao, Z., Zheng, J., Gao, J., Chen, X., Ren, C., Xu, Y. 2021. Adaptability of a caproate-producing bacterium contributes to its dominance in an anaerobic fermentation system. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 87(20), e01203-21. [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y., Sun, B., Fan, G., Teng, C., Xiong, K., Zhu, Y., Li, J., Li, X. 2017. The brewing process and microbial diversity of strong flavour Chinese spirits: a review. J. Inst. Brew., 123(1), 5-12. [CrossRef]
- Xue, W., Jian, L., Qian, W., Xueli, P., Qifa, Z., Wei, L., Dewen, H., Yang, N.J.F.S. 2023. Research Progress on the effect of Bacillus on flavor substances of Maotai flavor Baijiu. Food Science and Technology, 43, e101422. [CrossRef]
- Yan, S., Dong, D. 2018. Improvement of caproic acid production in a Clostridium kluyveri H068 and Methanogen 166 co-culture fermentation system. Amb Express, 8, 1-13. [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S., Jin, Z., Ali, A., Wang, C., Liu, J. 2022. Caproic acid-producing bacteria in Chinese Baijiu brewing. Front Microbiol, 13, 883142. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.W., Tabrizi, M.R., Nout, M.R., Han, B.Z. 2011. Daqu—a traditional Chinese liquor fermentation starter. J. Inst. Brew., 117(1), 82-90. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L., Tang, T., Deng, D., Wang, Y. & Pei, D. (2024). Isolation and Electrochemical Analysis of a Facultative Anaerobic Electrogenic Strain Klebsiella sp. SQ-1. Polish Journal of Microbiology, 73(2) 143-153. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).