Submitted:
05 September 2024
Posted:
05 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Data Collection
2.2. Cell Sorting
2.3. RNA Separation, Library Preparation and Next Generation Sequencing
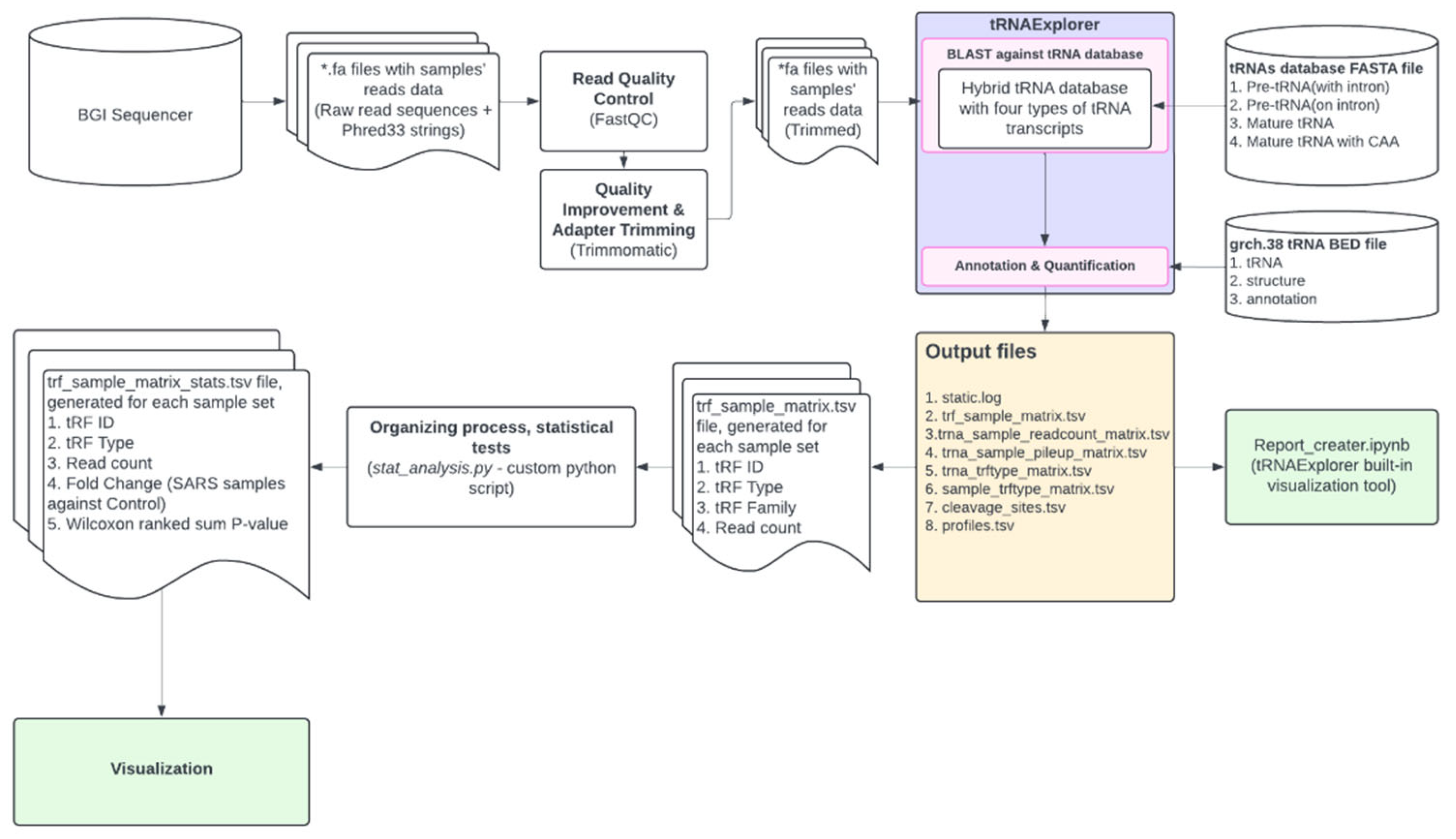
2.4. Bioinformatics
Read Quality Control
Adapter Trimming
Read Mapping, Count and Normalisation
2.5. Statistics
3. Results
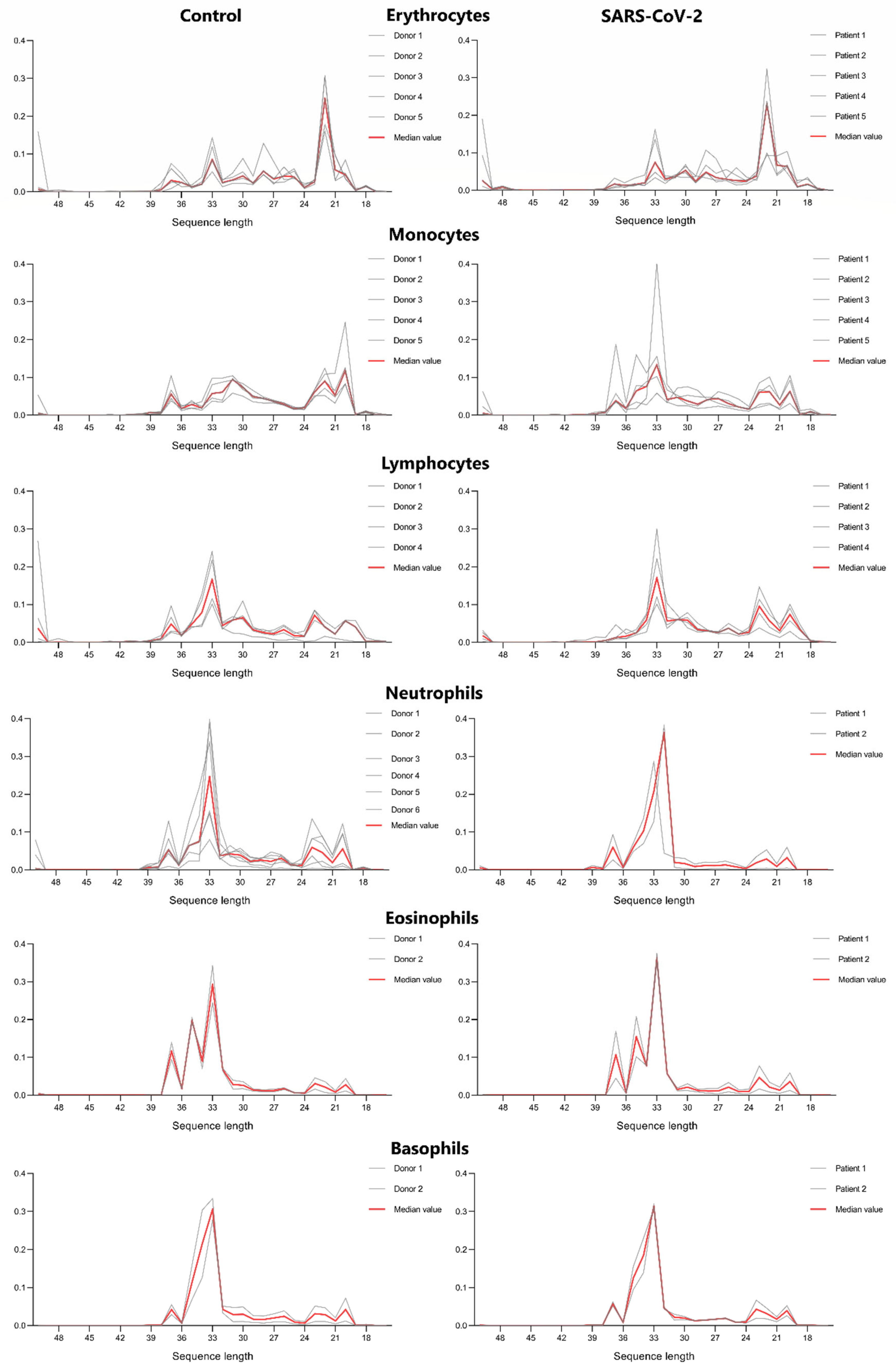
3.1. tRF Length Distribution in Main Cell Types
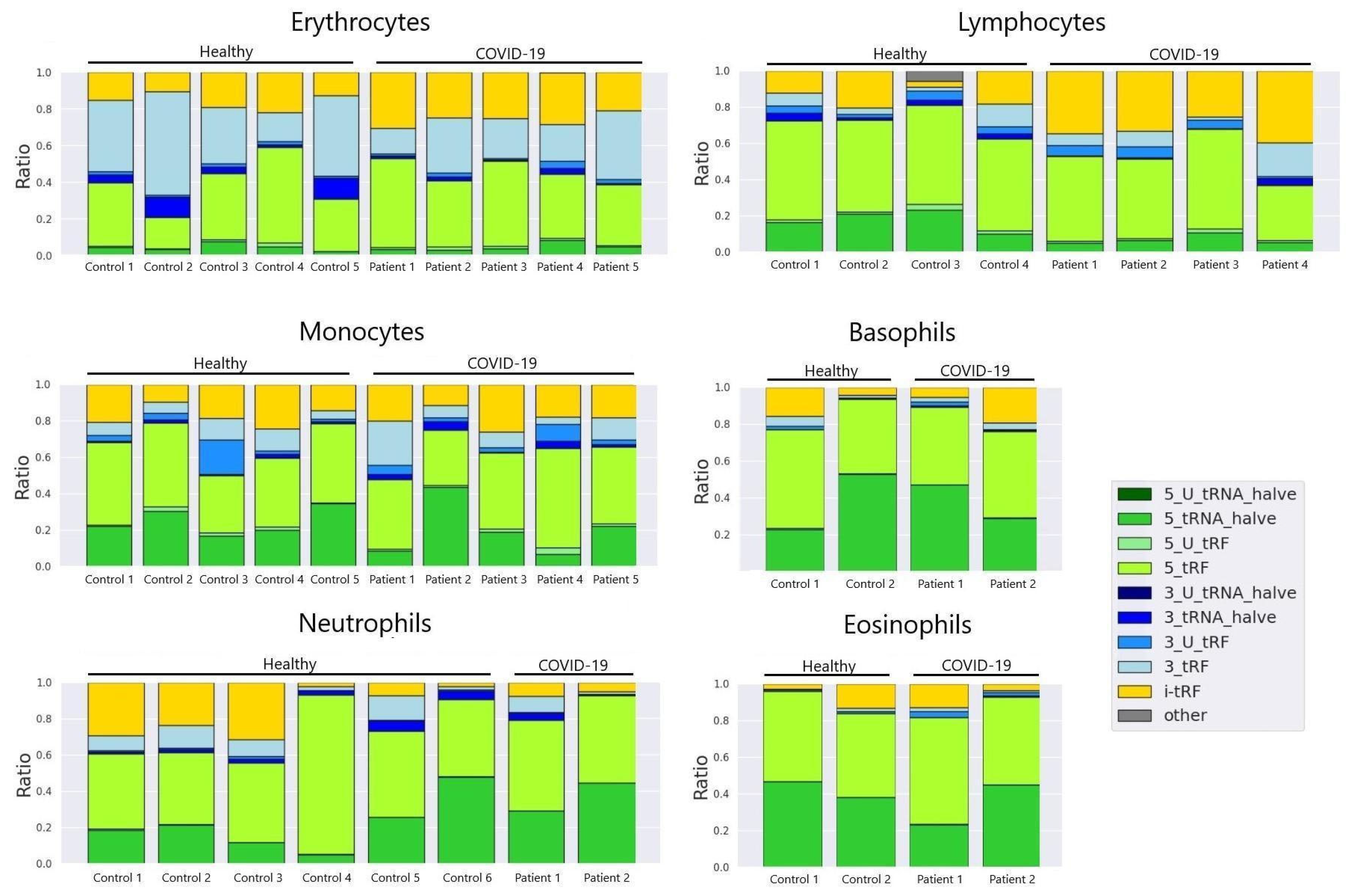
3.2. tRF Type Composition in Main Cell Types
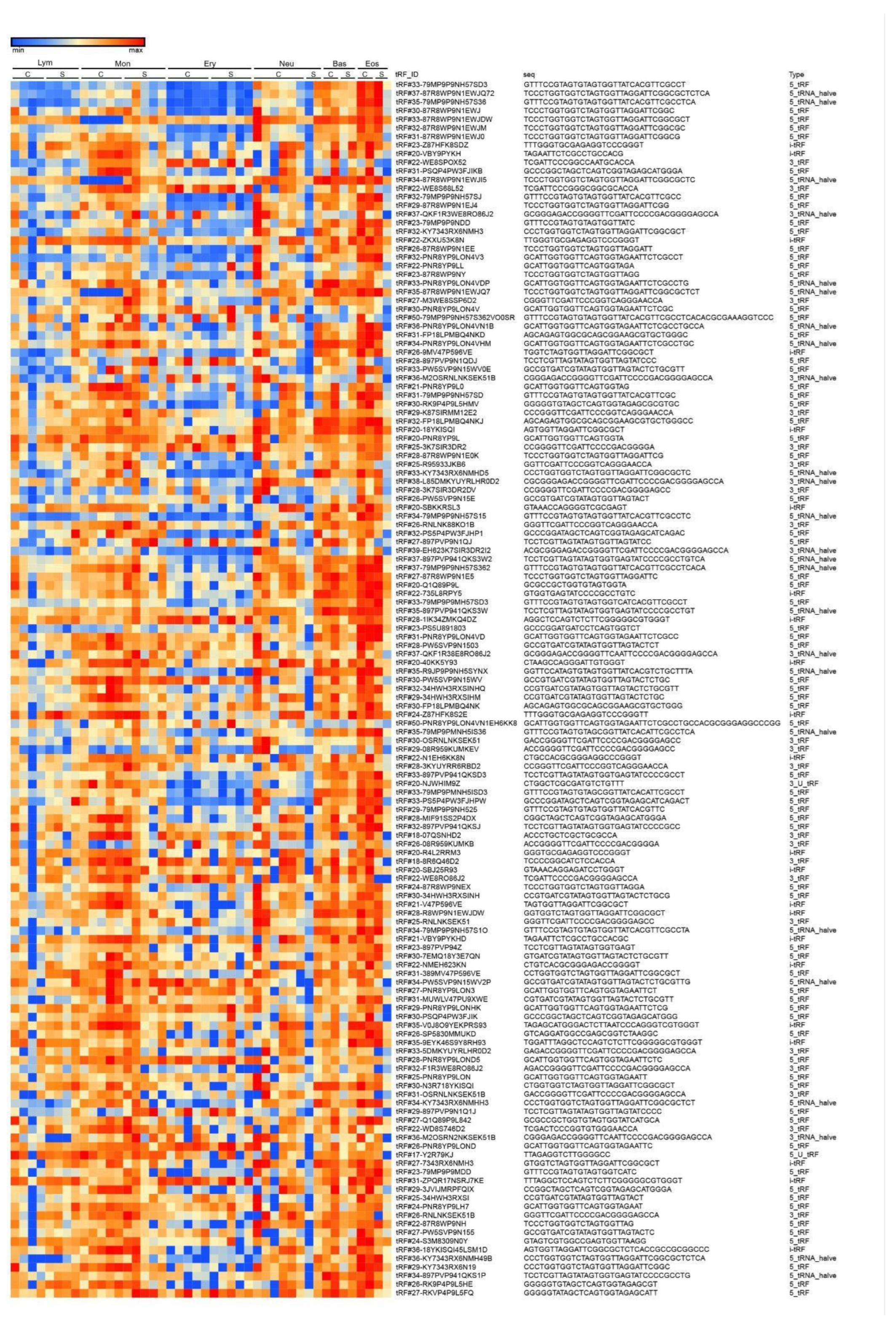
3.3. tRF Expression in Control Donors and Severe COVID-19 Patients
3.4. tRF Differential Expression in Erythrocytes
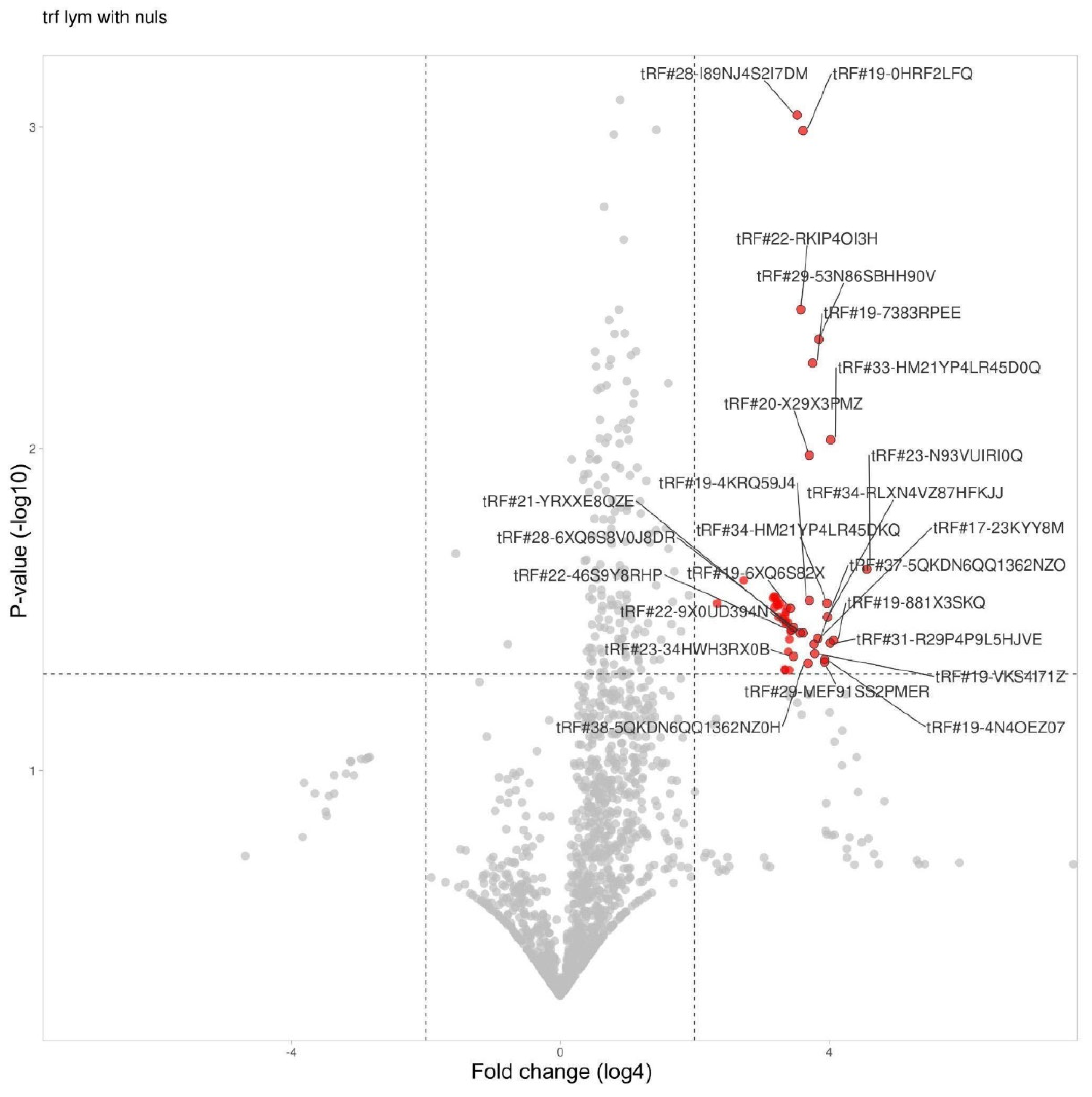
3.5. tRF Differential Expression in Lymphocytes
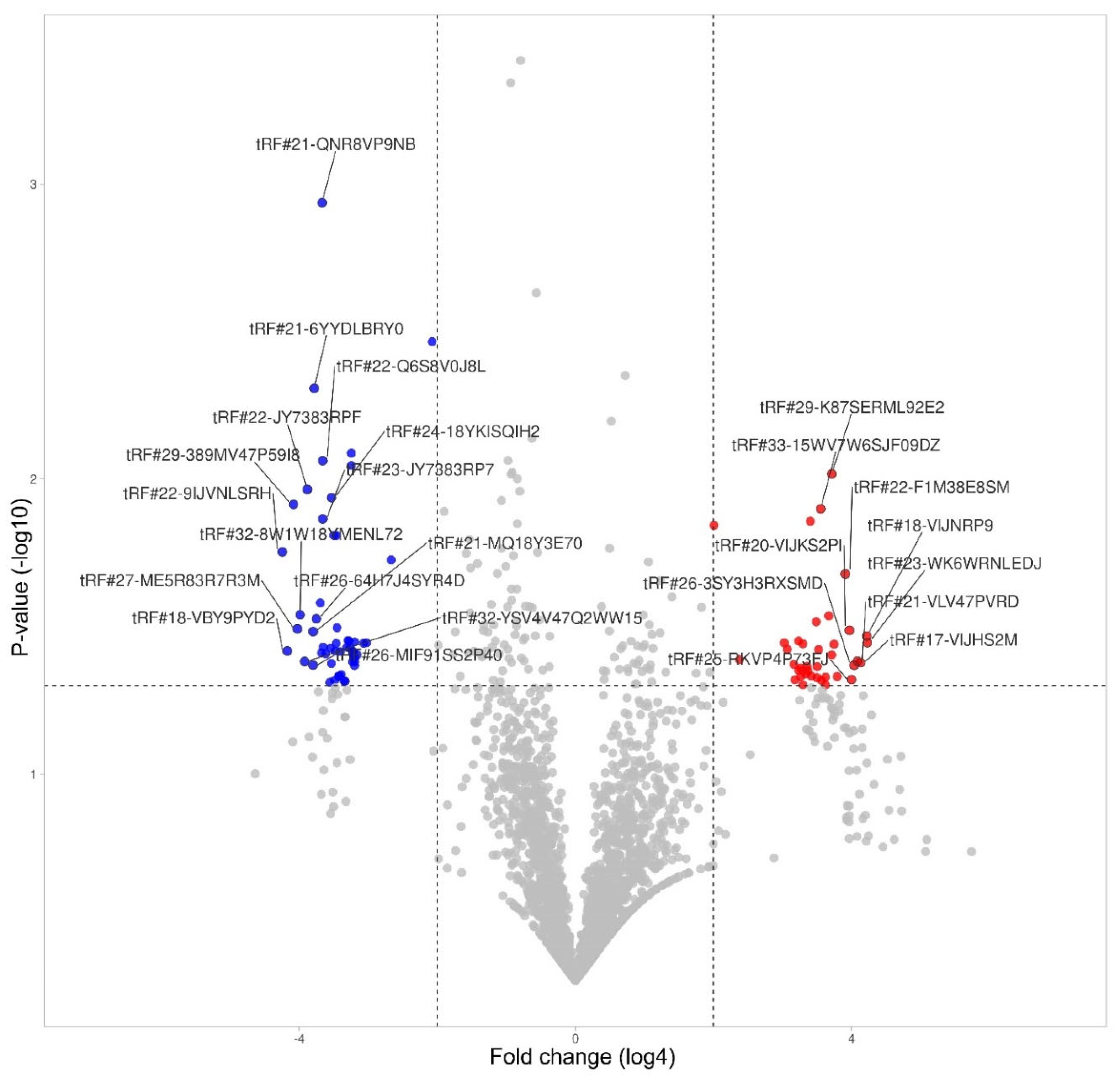
3.6. tRF Differential Expression in Monocytes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, V.N. Small RNAs: Classification, Biogenesis, and Function. Molecules and Cells 2005, 19, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, M.; Gu, J.; Wang, M.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, P.; Zhu, T.; Zhang, X. Emerging Roles of tRNA-Derived Fragments in Cancer. Molecular Cancer 2023, 22, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishna, S.; Raghavan, S.; DasGupta, R.; Palakodeti, D. tRNA-Derived Fragments (tRFs): Establishing Their Turf in Post-Transcriptional Gene Regulation. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 2607–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Choi, E.-J.; Wang, B.; Zhang, K.; Adam, A.; Huang, G.; Tunkle, L.; Huang, P.; Goru, R.; Imirowicz, I.; et al. Changes of Small Non-Coding RNAs by Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Infection. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, S.; Song, X.; Xiao, B.; Yan, Z. tRNA-Derived Fragments: Mechanisms Underlying Their Regulation of Gene Expression and Potential Applications as Therapeutic Targets in Cancers and Virus Infections. Theranostics 2021, 11, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondratov, K.A.; Artamonov, A.A.; Nikitin, Y.V.; Velmiskina, A.A.; Mikhailovskii, V.Y.; Mosenko, S.V.; Polkovnikova, I.A.; Asinovskaya, A.Y.; Apalko, S.V.; Sushentseva, N.N.; et al. Revealing Differential Expression Patterns of piRNA in FACS Blood Cells of SARS-CoV−2 Infected Patients. BMC Medical Genomics 2024, 17, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, S. FastQC: A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data. [Online] 2010. Available online at: http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/.
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A Flexible Trimmer for Illumina Sequence Data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic Local Alignment Search Tool. J Mol Biol 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Tan, J.; Zhao, M.; Peng, Q.; Zhou, M.; Zuo, S.; Wu, F.; Li, X.; Dong, Y.; Xie, M.; et al. Integrated Genomic Analysis Reveals Regulatory Pathways and Dynamic Landscapes of the tRNA Transcriptome. Sci Rep 2021, 11, 5226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yu, X.; Xie, Y.; Ye, G.; Guo, J. tRNA Derived Fragments:A Novel Player in Gene Regulation and Applications in Cancer. Front Oncol 2023, 13, 1063930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Kuscu, C.; Dutta, A. Biogenesis and Function of Transfer RNA Related Fragments (tRFs). Trends Biochem Sci 2016, 41, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, M.; Deng, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Ye, D. The Role and Mechanism of Action of tRNA-Derived Fragments in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Malignant Tumors. Cell Communication and Signaling 2023, 21, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGonagle, D.; Sharif, K.; O’Regan, A.; Bridgewood, C. The Role of Cytokines Including Interleukin-6 in COVID-19 Induced Pneumonia and Macrophage Activation Syndrome-Like Disease. Autoimmun Rev 2020, 19, 102537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzzi, N.; Cieśla, M.; Ngoc, P.C.T.; Lang, S.; Arora, S.; Dimitriou, M.; Pimková, K.; Sommarin, M.N.E.; Munita, R.; Lubas, M.; et al. Pseudouridylation of tRNA-Derived Fragments Steers Translational Control in Stem Cells. Cell 2018, 173, 1204–1216.e26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filetti, V.; La Ferlita, A.; Di Maria, A.; Cardile, V.; Graziano, A.C.E.; Rapisarda, V.; Ledda, C.; Pulvirenti, A.; Loreto, C. Dysregulation of microRNAs and tRNA-Derived ncRNAs in Mesothelial and Mesothelioma Cell Lines after Asbestiform Fiber Exposure. Sci Rep 2022, 12, 9181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Wang, X.; Cai, X.; Xiong, W.; Liu, Y.; Li, C.; Liu, Q.; Qin, J.; Li, Y. Identification of tRNAderived Fragments in Colon Cancer by Comprehensive Small RNA Sequencing. Oncology Reports 2019, 42, 735–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veneziano, D.; Tomasello, L.; Balatti, V.; Palamarchuk, A.; Rassenti, L.Z.; Kipps, T.J.; Pekarsky, Y.; Croce, C.M. Dysregulation of Different Classes of tRNA Fragments in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2019, 116, 24252–24258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umu, S.U.; Langseth, H.; Zuber, V.; Helland, Å.; Lyle, R.; Rounge, T.B. Serum RNAs Can Predict Lung Cancer up to 10 Years Prior to Diagnosis. eLife 2022, 11, e71035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olvedy, M.; Scaravilli, M.; Hoogstrate, Y.; Visakorpi, T.; Jenster, G.; Martens-Uzunova, E.S. A Comprehensive Repertoire of tRNA-Derived Fragments in Prostate Cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 24766–24777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbacher, C. Systemic and Local Mechanisms of Small Fiber Pathology in Female Patients with Fibromyalgia Syndrome, Universität Würzburg, 2023.
- Lyons, S.M.; Fay, M.M.; Ivanov, P. The Role of RNA Modifications in the Regulation of tRNA Cleavage. FEBS Letters 2018, 592, 2828–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazimierczyk, M.; Wojnicka, M.; Biała, E.; Żydowicz-Machtel, P.; Imiołczyk, B.; Ostrowski, T.; Kurzyńska-Kokorniak, A.; Wrzesinski, J. Characteristics of Transfer RNA-Derived Fragments Expressed during Human Renal Cell Development: The Role of Dicer in tRF Biogenesis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2022, 23, 3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Cao, J.; Wang, X.; Guo, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, T. Deciphering the tRNA-Derived Small RNAs: Origin, Development, and Future. Cell Death Dis 2021, 13, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Stanton, B.A. Transfer RNA-Derived Fragments, the Underappreciated Regulatory Small RNAs in Microbial Pathogenesis. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karanasios, E.; Simos, G. Building Arks for tRNA: Structure and Function of the Arc1p Family of Non-Catalytic tRNA-Binding Proteins. FEBS Letters 2010, 584, 3842–3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
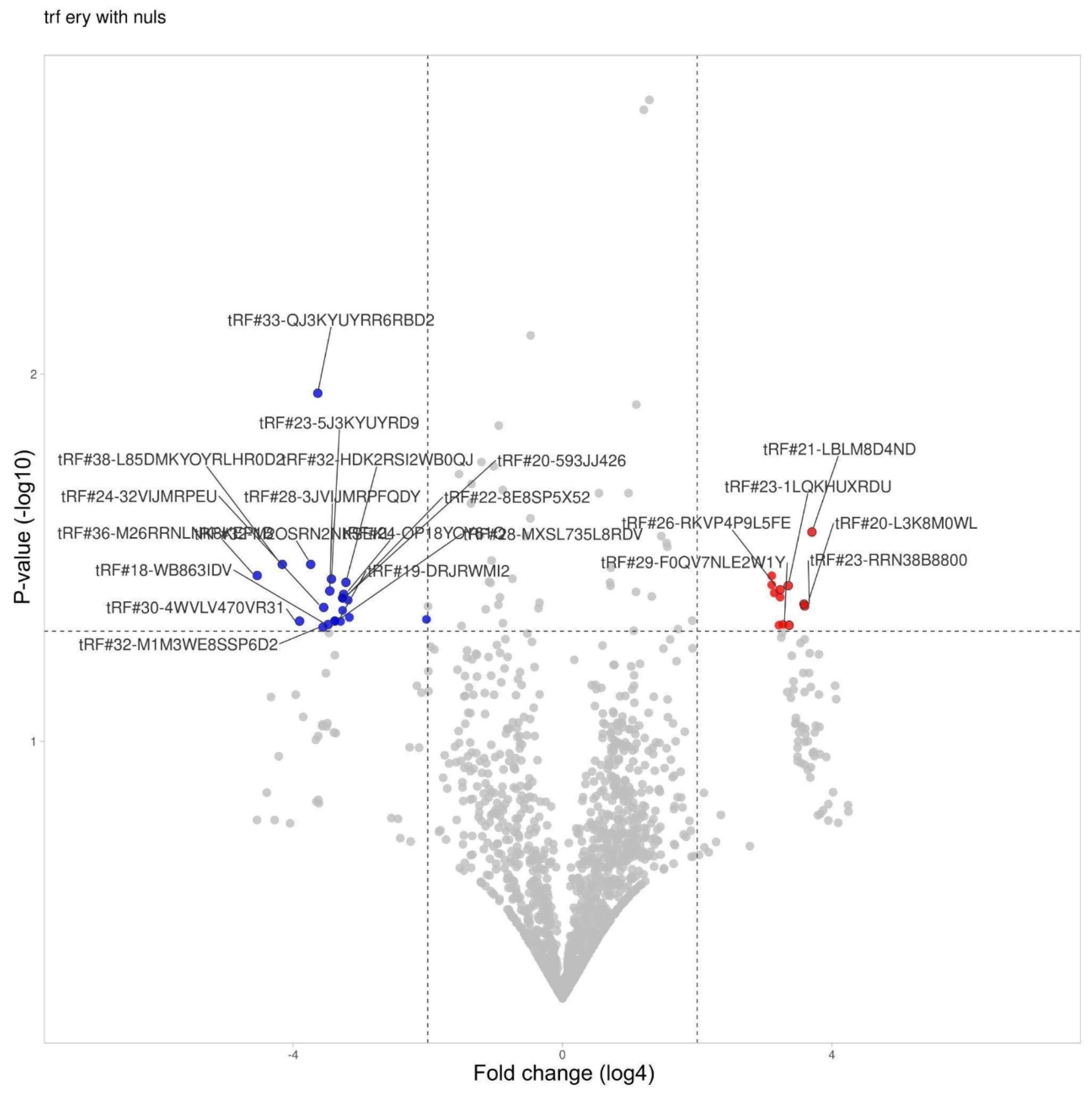
| Table 21. | Change | Fold change | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| tRF#21-LBLM8D4ND | Increased | 170 | 0,027 |
| tRF#23-RRN38B8800 | Increased | 146 | 0,043 |
| tRF#20-L3K8M0WL | Increased | 144 | 0,042 |
| tRF#29-F0QV7NLE2W1Y | Increased | 106 | 0,048 |
| tRF#23-1LQKHUXRDU | Increased | 104 | 0,038 |
| tRF#21-SRRN2EK8B | Increased | 94 | 0,048 |
| tRF#26-RKVP4P9L5FE | Increased | 88 | 0,039 |
| tRF#17-M3WE8SN | Increased | 88 | 0,040 |
| tRF#21-8PR9DM3WE | Increased | 86 | 0,048 |
| tRF#23-6KK87SIRD4 | Increased | 78 | 0,039 |
| tRF#33-73NK7F6Z2DNLDW | Increased | 74 | 0,035 |
| tRF#31-79MP9P9MH57SD | Increased | 74 | 0,037 |
| tRF#36-M26RRNLNK8KEP1B | Decreased | 536 | 0,035 |
| tRF#38-L85DMKYOYRLHR0D2 | Decreased | 320 | 0,033 |
| tRF#30-4WVLV470VR31 | Decreased | 224 | 0,047 |
| tRF#32-M2OSRN2NKSEKL | Decreased | 178 | 0,033 |
| tRF#33-QJ3KYUYRR6RBD2 | Decreased | 154 | 0,011 |
| tRF#32-M1M3WE8SSP6D2 | Decreased | 138 | 0,049 |
| tRF#24-32VIJMRPEU | Decreased | 136 | 0,043 |
| tRF#18-WB863IDV | Decreased | 124 | 0,048 |
| tRF#28-3JVIJMRPFQDY | Decreased | 120 | 0,039 |
| tRF#23-5J3KYUYRD9 | Decreased | 116 | 0,036 |
| tRF#19-DRJRWMI2 | Decreased | 108 | 0,047 |
| tRF#28-MXSL735L8RDV | Decreased | 108 | 0,047 |
| tRF#29-YP9LON4VN1EM | Decreased | 96 | 0,047 |
| tRF#20-593JJ426 | Decreased | 92 | 0,041 |
| tRF#22-8E8SP5X52 | Decreased | 92 | 0,041 |
| tRF#20-PW5SVP9N | Decreased | 92 | 0,044 |
| tRF#24-OP18YOY61Q | Decreased | 90 | 0,040 |
| tRF#32-HDK2RSI2WB0QJ | Decreased | 86 | 0,037 |
| tRF#21-1MQ8YUY60 | Decreased | 82 | 0,041 |
| tRF#37-WYL1M3WE8S68L52 | Decreased | 80 | 0,046 |
| tRF#28-3K76IR3DR2DV | Decreased | 16 | 0,047 |
| tRF id | Change | Fold change | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| tRF#23-N93VUIRI0Q | Increased | 557 | 0,024 |
| tRF#19-881X3SKQ | Increased | 280 | 0,039 |
| tRF#33-HM21YP4LR45D0Q | Increased | 265 | 0,009 |
| tRF#31-R29P4P9L5HJVE | Increased | 263 | 0,040 |
| tRF#34-RLXN4VZ87HFKJJ | Increased | 247 | 0,033 |
| tRF#34-HM21YP4LR45DKQ | Increased | 245 | 0,030 |
| tRF#29-MEF91SS2PMER | Increased | 233 | 0,046 |
| tRF#19-4N4OEZ07 | Increased | 233 | 0,045 |
| tRF#29-53N86SBHH90V | Increased | 207 | 0,005 |
| tRF#17-23KYY8M | Increased | 203 | 0,039 |
| tRF#19-VKS4I71Z | Increased | 190 | 0,043 |
| tRF#37-5QKDN6QQ1362NZO | Increased | 188 | 0,040 |
| tRF#19-7383RPEE | Increased | 183 | 0,005 |
| tRF#19-4KRQ59J4 | Increased | 170 | 0,030 |
| tRF#20-X29X3PMZ | Increased | 170 | 0,010 |
| tRF#38-5QKDN6QQ1362NZ0H | Increased | 165 | 0,046 |
| tRF#28-6XQ6S8V0J8DR | Increased | 150 | 0,037 |
| tRF#19-0HRF2LFQ | Increased | 150 | 0,001 |
| tRF#22-RKIP4OI3H | Increased | 143 | 0,004 |
| tRF#22-9X0UD394N | Increased | 140 | 0,037 |
| tRF#28-I89NJ4S2I7DM | Increased | 133 | 0,001 |
| tRF#21-YRXXE8QZE | Increased | 123 | 0,036 |
| tRF#23-34HWH3RX0B | Increased | 123 | 0,044 |
| tRF#22-46S9Y8RHP | Increased | 118 | 0,037 |
| tRF#19-P7M84I2Q | Increased | 115 | 0,037 |
| tRF#19-6XQ6S82X | Increased | 115 | 0,031 |
| tRF#20-1QKS3W2V | Increased | 113 | 0,049 |
| tRF#19-MIF91S2H | Increased | 113 | 0,039 |
| tRF#21-WRD81H93E | Increased | 110 | 0,043 |
| tRF#21-9L5H52NL0 | Increased | 110 | 0,035 |
| tRF#22-W60XY9BIQ | Increased | 108 | 0,031 |
| tRF#23-R9J89O9N9 | Increased | 105 | 0,035 |
| tRF#19-8NWE6WIZ | Increased | 105 | 0,035 |
| tRF#28-Z3R918VBY9DV | Increased | 105 | 0,032 |
| tRF#23-9M8O90Q4DZ | Increased | 103 | 0,049 |
| tRF#22-Z3FJ6KEWH | Increased | 103 | 0,049 |
| tRF#23-9N1QKS3WD1 | Increased | 103 | 0,033 |
| tRF#22-7EMQ18Y31 | Increased | 98 | 0,034 |
| tRF#21-7O3B1NR8E | Increased | 93 | 0,030 |
| tRF#22-282K63ZNQ | Increased | 90 | 0,033 |
| tRF#18-7383RP7 | Increased | 90 | 0,031 |
| tRF#23-RPM8309M0F | Increased | 88 | 0,030 |
| tRF#22-6LQ6S8V02 | Increased | 88 | 0,030 |
| tRF#35-S4I7LZM3Q01M3K | Increased | 85 | 0,029 |
| tRF#25-QSD2NSWWDZ | Increased | 83 | 0,031 |
| tRF#23-1E6SF8WOD9 | Increased | 83 | 0,029 |
| tRF#22-2EJ1OWZIQ | Increased | 80 | 0,029 |
| tRF#34-5QKDN6QQ1362HQ | Increased | 44 | 0,026 |
| tRF#35-5QKDN6QQ1362NZ | Increased | 25 | 0,030 |
| tRF id | Change | Fold change | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| tRF#23-WK6WRNLEDJ | Increased | 352 | 0,036 |
| tRF#18-VIJNRP9 | Increased | 348 | 0,034 |
| tRF#17-VIJHS2M | Increased | 306 | 0,042 |
| tRF#21-VLV47PVRD | Increased | 288 | 0,041 |
| tRF#26-3SY3H3RXSMD | Increased | 270 | 0,043 |
| tRF#25-RKVP4P73FJ | Increased | 256 | 0,048 |
| tRF#20-VIJKS2PI | Increased | 246 | 0,033 |
| tRF#22-F1M38E8SM | Increased | 226 | 0,021 |
| tRF#44-K8HJ83ML5F82NZD7HY | Increased | 192 | 0,047 |
| tRF#25-RKILQ673FJ | Increased | 180 | 0,036 |
| tRF#28-R1RXQ678Y2D8 | Increased | 172 | 0,039 |
| tRF#29-K87SERML92E2 | Increased | 172 | 0,010 |
| tRF#31-ZPQR16ZSIJ7KE | Increased | 162 | 0,029 |
| tRF#22-WEK6S1852 | Increased | 152 | 0,047 |
| tRF#23-K8HJ83MLDS | Increased | 152 | 0,050 |
| tRF#18-VIJKS2DU | Increased | 140 | 0,048 |
| tRF#33-15WV7W6SJF09DZ | Increased | 138 | 0,013 |
| tRF#25-P21MNKYUPR | Increased | 132 | 0,038 |
| tRF#38-Y2R79K3BEE4O3Q03 | Increased | 128 | 0,043 |
| tRF#24-PS5U8918JP | Increased | 128 | 0,047 |
| tRF#21-W60XY9BIE | Increased | 126 | 0,030 |
| tRF#30-6Q46D6PUMZQZ | Increased | 114 | 0,046 |
| tRF#22-9LON4VN11 | Increased | 112 | 0,014 |
| tRF#34-IEWS7YRR50SRIZ | Increased | 106 | 0,045 |
| tRF#18-HSQSD2D2 | Increased | 104 | 0,043 |
| tRF#32-ZPQR17NSRJ7KQ | Increased | 102 | 0,046 |
| tRF#26-R3HJ83RPFQE | Increased | 96 | 0,036 |
| tRF#19-K876IR19 | Increased | 96 | 0,050 |
| tRF#37-9EUK46S9Y8RH93Q | Increased | 92 | 0,044 |
| tRF#20-9VWVEH93 | Increased | 92 | 0,047 |
| tRF#28-WS3V2VR0PSDZ | Increased | 88 | 0,035 |
| tRF#20-SVKKN27F | Increased | 88 | 0,044 |
| tRF#32-FN5KYUSRYWRSJ | Increased | 82 | 0,048 |
| tRF#27-WN1Q18Y3HRK | Increased | 80 | 0,042 |
| tRF#20-3K7SIR3D | Increased | 70 | 0,038 |
| tRF#22-WEPSJR852 | Increased | 66 | 0,036 |
| tRF#21-MXSL73VLE | Increased | 27 | 0,041 |
| tRF#25-QNR8ZP9LON | Increased | 16 | 0,014 |
| tRF#22-9IJVNLSRH | Decreased | 360 | 0,018 |
| tRF#18-VBY9PYD2 | Decreased | 326 | 0,038 |
| tRF#29-389MV47P59I8 | Decreased | 288 | 0,012 |
| tRF#27-ME5R83R7R3M | Decreased | 266 | 0,032 |
| tRF#32-8W1W18YMENL72 | Decreased | 252 | 0,029 |
| tRF#32-YSV4V47Q2WW15 | Decreased | 230 | 0,042 |
| tRF#22-JY7383RPF | Decreased | 218 | 0,011 |
| tRF#26-MIF91SS2P40 | Decreased | 194 | 0,043 |
| tRF#21-MQ18Y3E70 | Decreased | 194 | 0,033 |
| tRF#21-6YYDLBRY0 | Decreased | 190 | 0,005 |
| tRF#26-64H7J4SYR4D | Decreased | 182 | 0,030 |
| tRF#21-MUWLV47PE | Decreased | 168 | 0,026 |
| tRF#21-R84QPYVMD | Decreased | 164 | 0,039 |
| tRF#21-QNR8VP9NB | Decreased | 162 | 0,001 |
| tRF#22-Q6S8V0J8L | Decreased | 160 | 0,009 |
| tRF#23-JY7383RP7 | Decreased | 160 | 0,014 |
| tRF#33-1MN0YU09FKRFD2 | Decreased | 158 | 0,037 |
| tRF#22-9P9NH57SJ | Decreased | 150 | 0,039 |
| tRF#23-RXSINHZ4DV | Decreased | 138 | 0,049 |
| tRF#24-941QKS3WF8 | Decreased | 136 | 0,037 |
| tRF#20-J87383RP | Decreased | 134 | 0,042 |
| tRF#24-18YKISQIH2 | Decreased | 134 | 0,012 |
| tRF#38-ML5F924ZDRJKW4DZ | Decreased | 128 | 0,016 |
| tRF#21-9P4P9L5HE | Decreased | 126 | 0,048 |
| tRF#24-Z3RQ18YJFH | Decreased | 124 | 0,038 |
| tRF#23-J87383RP7 | Decreased | 122 | 0,036 |
| tRF#20-RK9P4P9L | Decreased | 122 | 0,016 |
| tRF#22-MQ18Y3E7M | Decreased | 120 | 0,032 |
| tRF#28-RUPLQVNRDF0E | Decreased | 116 | 0,047 |
| tRF#22-73H3RXPLM | Decreased | 114 | 0,046 |
| tRF#24-94SX73V2KK | Decreased | 112 | 0,038 |
| tRF#21-MIF91SS20 | Decreased | 110 | 0,046 |
| tRF#24-04SXQ3V2KJ | Decreased | 104 | 0,048 |
| tRF#21-9LV470JPD | Decreased | 102 | 0,048 |
| tRF#20-1PSJPM17 | Decreased | 98 | 0,037 |
| tRF#34-JY7383RPD9W1JV | Decreased | 96 | 0,035 |
| tRF#24-YDLBRY73JL | Decreased | 94 | 0,035 |
| tRF#21-3P47M26YB | Decreased | 92 | 0,037 |
| tRF#22-6YR29P4PP | Decreased | 90 | 0,008 |
| tRF#21-WB8689SVD | Decreased | 90 | 0,009 |
| tRF#21-WLV47PU9E | Decreased | 88 | 0,039 |
| tRF#21-N1EH6KK80 | Decreased | 88 | 0,042 |
| tRF#18-SR99RHD2 | Decreased | 86 | 0,038 |
| tRF#33-5F924ZDRJKW4DZ | Decreased | 86 | 0,039 |
| tRF#22-5721V98B3 | Decreased | 84 | 0,036 |
| tRF#26-MY73H3RXPL0 | Decreased | 84 | 0,040 |
| tRF#22-J4S2I7L7M | Decreased | 84 | 0,042 |
| tRF#28-RKVP4P9L5F0Q | Decreased | 84 | 0,043 |
| tRF#26-94SL735FVI0 | Decreased | 80 | 0,039 |
| tRF#18-6M0Y1MY | Decreased | 70 | 0,036 |
| tRF#24-MY73H3RXII | Decreased | 66 | 0,036 |
| tRF#33-1N3KYUSR681SD2 | Decreased | 40 | 0,019 |
| tRF#25-R8VP9NFQFY | Decreased | 18 | 0,003 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





