Submitted:
06 September 2024
Posted:
06 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- -
- Evaluate potential correlations between unipolar and bipolar depression with total calcium and thyrotropin (TSH) levels, free T4, (FT4; thyroxine), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), and reactive C protein (CRP) values in patients accessing the University Psychiatry Unit of Varese (ASST, Azienda Socio-Sanitaria Territoriale Sette Laghi-Varese) and Como (ASST, Azienda Socio-Sanitaria Territoriale Lariana);
- -
- Compare two patient subgroups (unipolar depression vs. bipolar depression) in terms of alterations in calcium, TSH, ESR, and CRP levels;
- -
- Assess potential correlations between suicidal ideation and calcium levels, TSH, ESR, and CRP in patients accessing the University Psychiatry Unit of Varese and Como.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
- -
- Diagnosis of major depressive disorder and bipolar disorder in the depressive phase according to the diagnostic criteria of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5);
- -
- Age ≥ 18 years;
- -
- Provision of written informed consent for the use of anonymous data for scientific scope;
- -
- CGIs ≥ 3.
- -
- Patients were excluded from the study based on the following exclusion criteria:
- -
- Age < 18 years;
- -
- Refusal to participate in the study;
- -
- Neurocognitive deficits that impair the understanding of assessment tools;
- -
- Inflammatory diseases and current infectious;
- -
- Language barriers that impair the understanding of assessment tools.
2.3. Assessment Tools
- -
- Patient demographic form: standardized instrument to collect essential information from patients and clarify the demographic profile (age, gender, marital status, education level, employment status, and other relevant demographic details). Collected information can be used to identify potential correlations between demographic factors and health outcomes;
- -
- Beck Depression Inventory-II (BDI-II): widely used self-report questionnaire designed to assess the severity of depression. Developed by Aaron T. Beck and colleagues, the BDI-II consists of 21 items, each rated on a 4-point scale, which reflects the intensity of depressive symptoms experienced over the past two weeks. It covers various aspects of depression, including mood, cognitive function, physical symptoms, and behavior. The BDI-II is a reliable and valid tool for both clinical and research settings [9];
- -
- The Orbach & Mikulincer Mental Pain Questionnaire (OMMP): used to measure psychological pain or mental anguish, distinct from physical pain. It assesses intensity, frequency, and duration of mental pain, including feelings of hopelessness, loss, and emotional turmoil. The OMMP helps clinicians identify the depth of mental suffering that may not be captured by traditional measures of depression or anxiety [10];
- -
- Beck Anxiety Inventory (BAI): 21-item self-report inventory designed to measure the severity of an individual's anxiety. Each item describes a common symptom of anxiety, which the respondent rates based on their experience over the past week. The BAI covers various domains of anxiety, including physiological, cognitive, and affective symptoms, and is useful in both clinical and research contexts for diagnosing and monitoring treatment progress [11];
- -
- Reasons for Living Inventory (RFL): self-report instrument developed to assess cognitive and motivational factors that prevent individuals from attempting suicide. It includes a series of statements reflecting reasons for living, such as fear of social disapproval, moral objections, and survival and coping beliefs. The RFL helps identify protective factors that may mitigate the risk of suicidal behavior [12,13].
- -
- Clinical Global Impressions Severity (CGIs): used to assess the severity of a patient's mental illness. It involves a single-item rating, where the clinician evaluates the patient’s current state on a scale from 1 (normal, not at all ill) to 7 (among the most extremely ill patients). The CGIs is widely used in clinical practice and research due to its simplicity and effectiveness in providing a global assessment of patient severity [14,15].
2.4. Laboratory Tests
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Data Protection
3. Results
3.1. Socio-Demographic and Clinical Characteristics of the Sample
3.2. Data Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Teraiza, E.; Meza, R. Depression as a Medical-Psychiatric Entity. Rev colomb psiquiatr 2008, 37, 220–235. [Google Scholar]
- Baumeister, D.; Russell, A.; Pariante, C.M.; Mondelli, V. Inflammatory biomarker profiles of mental disorders and their relation to clinical, social and lifestyle factors. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 2014, 49, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasparini, A.; Callegari, C.; Lucca, G.; Bellini, A.; Caselli, I.; Ielmini, M. Inflammatory Biomarker and Response to Antidepressant in Major Depressive Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Psychopharmacol Bull 2022, 52, 36–52. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lang, U.E.; Beglinger, C.; Schweinfurth, N.; Walter, M.; Borgwardt, S. Nutritional aspects of depression. Cell Physiol Biochem 2015, 37, 1029–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutschenbaur, L.; Beck, J.; Kiyhankhadiv, A.; Mühlhauser, M.; Borgwardt, S.; Walter, M.; Hasler, G.; Sollberger, D.; Lang, U.E. Role of calcium, glutamate and NMDA in major depression and therapeutic application. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2016, 4, 325–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, U.E.; Borgwardt, S. Molecular mechanisms of depression: Perspectives on new treatment strategies. Cell Physiol Biochem 2013, 31, 761–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ielmini, M.; Lucca, G.; Trabucchi, E.; Aspesi, G.L.; Bellini, A.; Caselli, I.; Callegari, C. Assessing Mental Pain as a Predictive Factor of Suicide Risk in a Clinical Sample of Patients with Psychiatric Disorders. Behav Sci (Basel) 2022, 12, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, I.G.; Machado-Vieira, R.; Soares, J.C.; Teixeira, A.L. The immunology of bipolar disorder. Neuroimmunomodulation 2014, 21, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, A. T.; Steer, R. A.; Brown, G. Beck Depression Inventory–II (BDI-II), 1996.
- Orbach, I.; Mikulincer, M.; Sirota, P.; Gilboa-Schechtman, E. Mental Pain: A Multidimensional Operationalization and Definition. Suicide and Life-Threatening Behavior 2003, 33, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, A. T.; Steer, R. A. Beck Anxiety Inventory manual. Psychological Corporation, San Antonio, TX, 1993.
- Linehan, M.M.; Goodstein, J.L.; Nielsen, S.L.; Chiles, J.A. Reasons for Staying Alive When You Are Thinking of Killing Yourself: The Reasons for Living Inventory. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 1983, 51, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, A. , Jones, K., & Osman, J. R. The Reasons for Living Inventory: Psychometric Properties. Psychological Reports 1991, 69, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guy, W. Assessment Manual for Psychopharmacology. Editor. ECDE, 1976.
- Busner, J.; Targum, S.D. The clinical global impressions scale: Applying a research tool in clinical practice. Psychiatry (Edgmont) 2007, 4, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stern, J.E.; Guinjoan, S.M.; Cardinali, D.P. Correlation between serum and urinary calcium levels and psychopathology in patients with affective disorders. Short communication. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 1996, 103, 509–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steardo, L., Jr.; Luciano, M.; Sampogna, G.; Carbone, E.A.; Caivano, V.; Di Cerbo, A., Giallonardo; Palummo, C.; Vece, A. Del Vecchio, V.; De Fazio, P.; Fiorillo, A. Clinical Severity and Calcium Metabolism in Patients with Bipolar Disorder. Brain Sci 2020, 10, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IBM Corp. IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 28.0. Armonk, NY, IBM Corp. (SCIRP), 2021.
- DL n.211 of 24 June 2003 (and DM 17 December 2004).
- Bosc, M. Assessment of social functioning in depression. Compr Psychiatry 2000, 41, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NIHM, 2020. Available online: https://www.nimh.nih.gov/.
- Köhler-Forsberg, O.; Sylvia, L.G.; Ruberto, V.L.; Kuperberg, M.; Shannon, A.P.; Fung, V.; Overhage, L.; Calabrese, J.R.; Thase, M.; Bowden, C.L.; Shelton, R.C.; McInnis, M.; Deckersbach, T.; Tohen, M.; Kocsis, J.H.; Ketter, T.A.; Friedman, E.S.; Iosifescu, D.V.; McElroy, S.; Ostacher, M.J.; Nierenberg, A.A. Familial severe psychiatric history in bipolar disorder and correlation with disease severity and treatment response. J Affect Disord 2020, 1, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moncrieff, J.; Cohen, D.; Porter, S. The psychoactive effects of psychiatric medication: The elephant in the room. J Psychoactive Drugs 2013, 45, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dome, P.; Rihmer, Z.; Gonda, X. Suicide Risk in Bipolar Disorder: A Brief Review. Medicina (Kaunas) 2019, 55, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilcox, H.C.; Conner, K.R.; Caine, E.D. Association of Alcohol and Drug Use Disorders and Completed Suicide: An Empirical Review of Cohort Studies. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2004, 76, 9–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Onofrio, S.; Mahaffey, S.; Garcia-Rill, E. Role of calcium channels in bipolar disorder. Curr Psychopharmacol 2017, 6, 122–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talaei, A.; Rafee, N.; Rafei, F.; Chehrei, A. TSH cut off point based on depression in hypothyroid patients. BMC Psychiatry 2017, 17, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
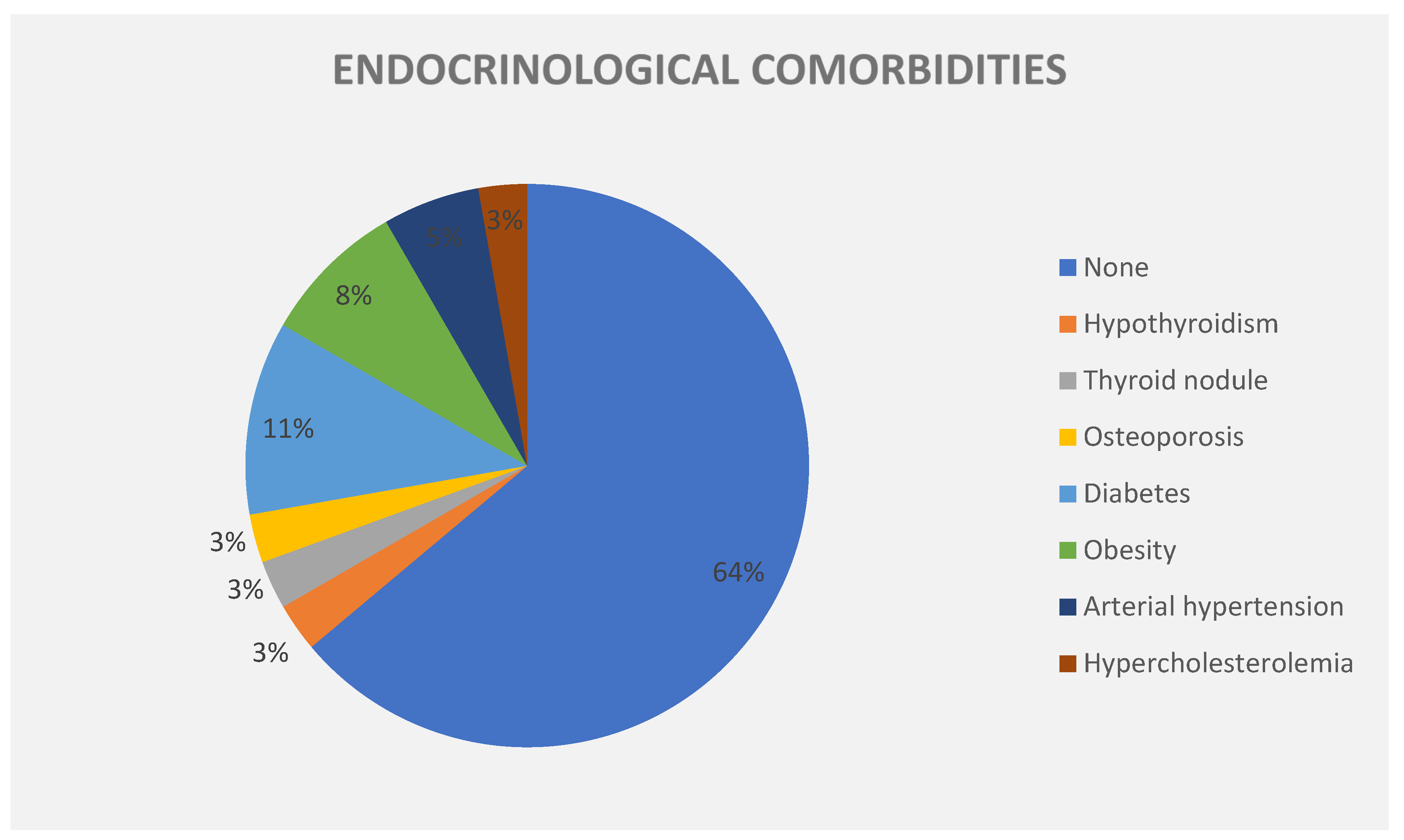
| Male (N) | Female (N) | Total (N) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 17 | 19 | 36 | |
| Marital status | |||
| Married Single Divorced Widowed |
7 4 3 3 |
12 3 4 - |
19 (58.2%) 7 (19.4%) 7 (19.4%) 3 (8.3%) |
| Education | |||
| Elementary school Middle school High school Degree Missing data |
2 9 3 2 1 |
- 7 7 5 - |
2 (5.7%) 16 (45.7%) 10 (28.6%) 7 (20%) - |
| Employment | |||
| Occupied Unoccupied Retired Invalid Missing data |
5 4 6 1 1 |
8 3 5 2 1 |
13 (38.2%) 7 (20.6%) 11 (32.4%) 3 (8.8%) - |
| Main psychiatric diagnosis | N (%) | Psychiatric comorbidities | N (%) |
| Major Depressive Disorder | 16 (45%) | None | 22 (61.1%) |
| Reactive Depression with Adjustment Disorder and Adjustment Disorder with depressive mood | 5 (14%) | Substance abuse | 3 (8.3%) |
| Bipolar Disorder Type 1 | 3 (8%) | Adjustment Disorder | 1 (2.8%) |
| Bipolar Disorder Type 2 | 12 (33%) | Personality disorder NOS | 9 (25.0%) |
| Eating disorder | 1 (2.8%) | ||
| Total | 36 (100.0%) | Total | 36 (100.0%) |
| Pearson chi-square | Exact Fisher test | Cramer V | |
| Calcium and UD | 0.233 | 0.233 | 0.233 |
| Calcium and BD | 0.050 | 0.115 | 0.378 |
| CPR and UD | 0.592 | 0.592 | 0.592 |
| CPR and BD | 0.017 | 0.017 | 0.017 |
| Actual substance abuse | No actual substance abuse | Total | P value | |
| Current suicidal intention |
2 |
16 |
18 |
=.0275 |
| No current suicidal intention |
9 |
9 |
18 |
|
| Total | 11 | 25 | 36 |
| Group | DDU BRLF | DB BRLF | P value |
| Media | 45.52 | 35.47 |
=.0126 |
| SD | 12.36 | 9.55 | |
| SEM | 2.70 | 2.47 | |
| N | 21 | 15 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





