Submitted:
05 September 2024
Posted:
06 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
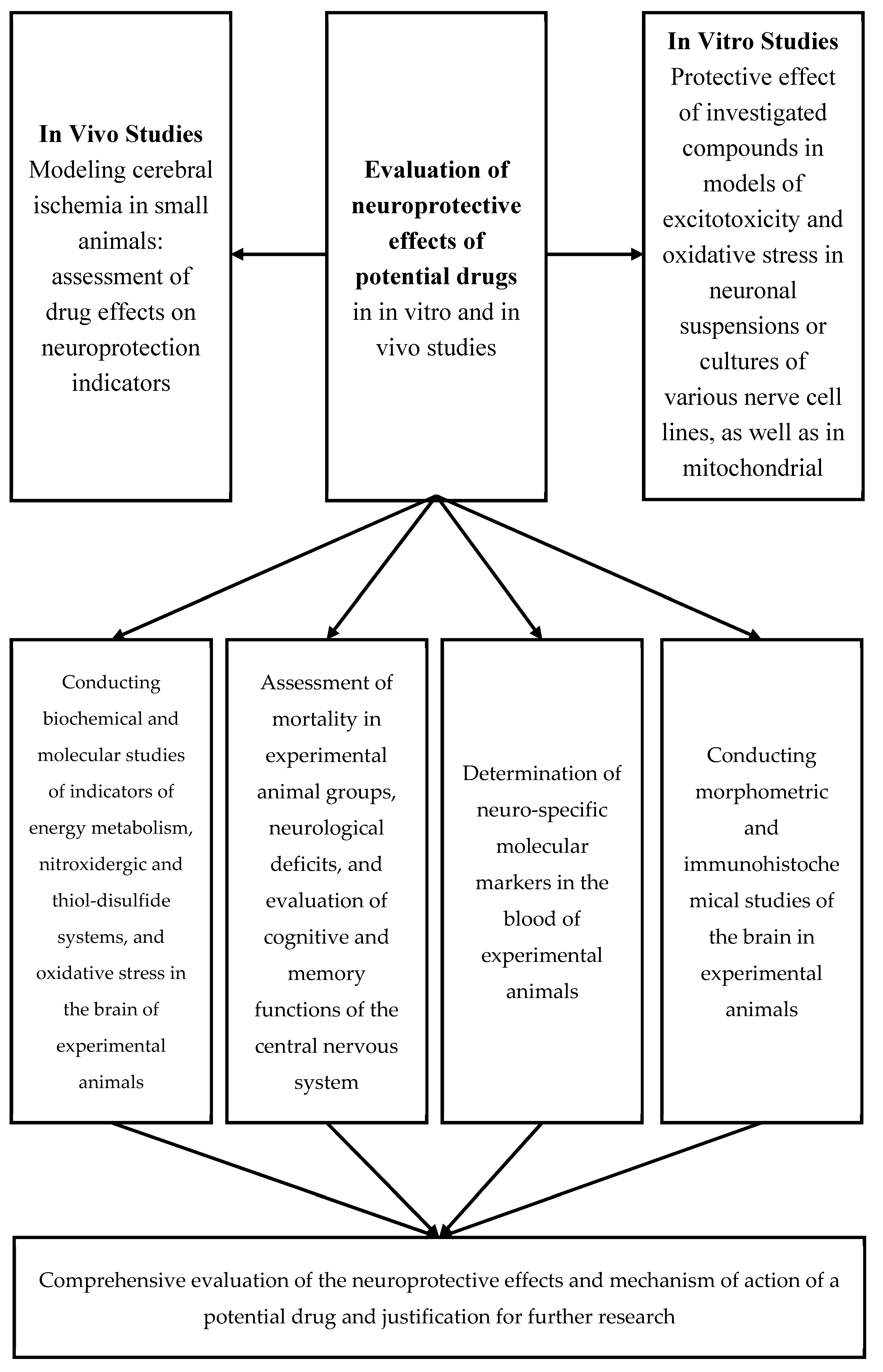
2. Preliminary Evaluation of the Neuroprotective Effects of Potential Drugs In Vitro
- MPTP (1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine)-induced opening of mitochondrial pores: add 40–60 µM MPTP to the incubation medium and after 5 minutes, add 50 µM CaCl₂.
- Ca²⁺-induced opening of mitochondrial pores: add 200 µM CaCl₂ to the incubation medium.
- NO-induced opening of mitochondrial pores: add 20–100 µM sodium nitroprusside to the incubation medium and after 2 minutes, add 50 µM CaCl₂.
- H₂O₂-induced opening of mitochondrial pores: add 50 mM hydrogen peroxide to the incubation medium and after 2 minutes, add 50 µM CaCl₂.
3. Preliminary Assessment of the Neuroprotective Effects of Potential Pharmaceutical Agents Using Various Models of Cerebral Ischemia
4. Assessment of Neurological Deficit in Animals with Experimental Cerebral Ischemia Serves as an Integrative Measure of the Neuroprotective Efficacy of Potential Pharmacological Agents
- Mild: 0 to 3 points;
- Moderate: 3 to 7 points;
- Severe: 7 points and above.
- Unilateral partial ptosis: 0.5 points;
- Unilateral ptosis: 1 point;
- Tremor: 0.5 points;
- Circling movements: 0.5 points;
- Paresis of limbs (per limb): 1 point;
- Paralysis of limbs (per limb): 2 points;
- Lateral positioning: 3 points;
- Inability to remain on the rotating rod (3 RPM) for 4 minutes: 3 points.
5. Determination of Oxidative Stress Markers and Antioxidant System Status
- Pentafluorophenylhydrazine (PFPH);
- Methylhydrazine (MH);
- 4-(2-phthalimidyl)benzohydrazine (FBH);
- 2,4-Dinitrophenylhydrazine (DNPH);
- o-(2,3,4,5,6-Pentafluorobenzyl)hydroxylamine hydrochloride (PFBH);
- tert-Butyldimethylchlorosilane (BDMCS);
- N,O-Di-(trimethylsilyl)-trifluoroacetamide (DTSFA);
- 2-Hydrazinobenzothiazole (HBT).
6. Determination of Antioxidant Enzyme Activity
7. α-Tocopherol
8. Determination of the Most Informative Indicators of the Thiol-Disulfide System
9. Indicators of the Nitric Oxide System in the Brain
10. Assessment of Brain Energy Metabolism Indicators
11. Morphometry of Various Brain Structures
- Density of Neurons, Glial Cells, Apoptotic, and Destructively Altered Neurons: Measured as the number of cells per 1 mm² of tissue section.;
- Cellular Composition: Determined as the percentage of neurons, glial cells, apoptotic, and destructively altered neurons in the IV-V layers of the cortex and the CA1 region of the hippocampus.;
- Area of Cell Bodies: Measured in µm² for neurons, glial cells, apoptotic, and destructively altered neurons;
- RNA Concentration: In neurons, glial cells, apoptotic, and destructively altered neurons, expressed in optical density units (ODU). This is calculated as the logarithm of the ratio of the optical density of the cell body to the optical density of the extracellular matrix;
- RNA Content: In neurons, glial cells, apoptotic, and destructively altered neurons, expressed in ODU. This is calculated as the product of RNA concentration and cell area.
- Neuron Survival Index: Assessed as the ratio of the number of neurons in experimental animals to the number of neurons in intact control animals.
11.1. Markers with Informational Value in CNS Pathology
11.1.1. Gold Dot (NR2 Antibody Detection)
- Independent Serum Marker: The level of antibodies to NR2 serves as an independent serum marker for cerebral ischemic events;
- Neurotoxicity Marker: NR2 antibodies are indicative of neurotoxicity associated with ischemic damage;
- Monitoring Tool: Tracking NR2 antibody levels enables monitoring the efficacy of pharmacological interventions for ischemic brain injury.
11.1.2. Neuron-Specific Enolase (NSE) (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay, Western Blot)
11.1.3. Myelin Basic Protein (MBP) (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay, Western Blot)
11.1.4. S-100 Protein (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay)
11.1.5. Galanin (Immunohistochemistry Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay, Western Blot)
11.1.6. Phosphorylated Neurofilament H (pNF-H) (Enzyme-Linked immunosorbent Assay, Western Blot)
11.1.7. Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein (GFAP) (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay)
11.2. Markers of Neuroplasticity
11.2.1. Neurotrophin-3 (NT3) and Neurotrophin-4/5 (NT4/5) (Immunohistochemistry, Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay, Western Blot)
11.2.2. Expression of c-fos and c-jun Proteins in the Brain (Immunohistochemistry; Western Blot)
11.2.2. Expression/Concentration of Heat Shock Proteins in the Brain (Immunohistochemistry, Western Blot, Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay)
11.2.3. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1α (HIF-1α) (Immunohistochemistry, Immunoblotting, Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay)
11.2.4. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) (Immunohistochemistry, Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay, Western Blot)
11.2.5. Ciliary Neurotrophic Factor (CNTF) (Immunohistochemistry, Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay, Western Blot)
11.2.6. Pigment Epithelium-Derived Factor (PEDF) (Immunohistochemistry, Western Blot)
11.3. Markers of Apoptosis
11.3.1. Annexin V (Immunohistochemistry, Western Blot)
11.3.2. Caspase-3 (Immunohistochemistry, Western Blot, Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay)
11.3.3. Cathepsins (Immunohistochemistry, Western Blot, Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay)
11.3.4. Procathepsin B (Immunohistochemistry, Western Blot, Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay)
11.3.5. DR5 (Death Receptor) (Immunohistochemistry, Western Blot)
11.3.6. Bcl-2 Family (Immunohistochemistry, Western Blot)
- Anti-apoptotic Subfamily: Includes close homologs such as Bcl-2, Bcl-XL, and Bcl-w, which inhibit apoptosis;
- Pro-apoptotic Subfamilies: Includes proteins such as Bax and members of the BH3-only group, which promote apoptosis.
- Perform Preliminary Screening**: Evaluate a large number of molecules while preserving animal lives.;
- Investigate Mechanisms**: Examine the impact of potential neuroprotectors on specific aspects of the ischemic brain damage pathogenesis, such as oxidative nitrosative stress, glutamate excitotoxicity, and thiol-disulfide balance shifts.
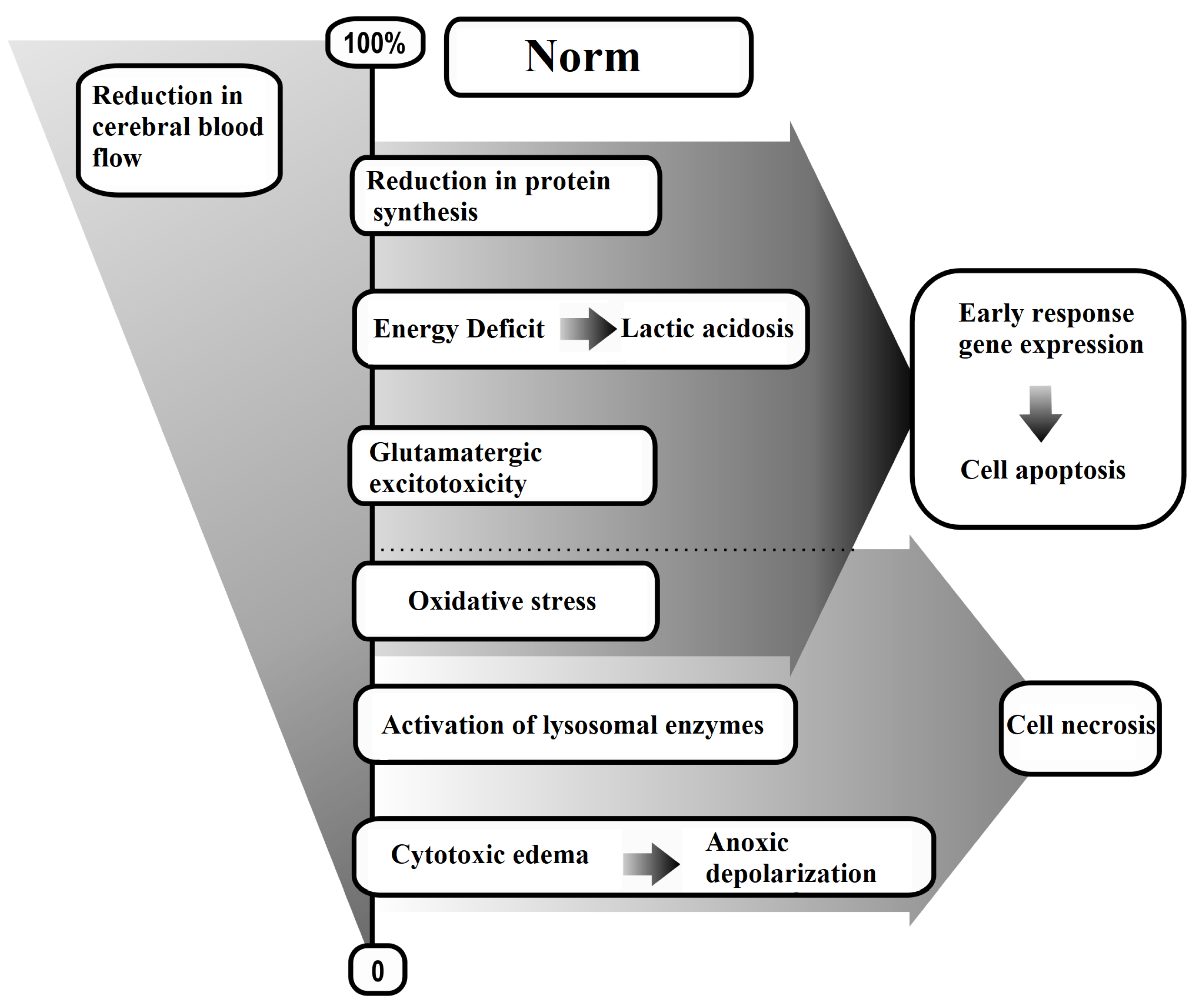
- Diffuse Decrease in Cerebral Blood Flow;
- Energy Deficit;
- Glutamate-Calcium Excitotoxicity;
- Oxidative Stress;
- Expression of Early Response Genes.
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Donkor, E.S. Stroke in the 21st Century: A Snapshot of the Burden, Epidemiology, and Quality of Life. Stroke Res Treat. 2018, 2018, 3238165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salaudeen, M.A.; Bello, N.; Danraka, R.N.; Ammani, M.L. Understanding the Pathophysiology of Ischemic Stroke: The Basis of Current Therapies and Opportunity for New Ones. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belov Kirdajova, D.; Kriska, J.; Tureckova, J.; Anderova, M. Ischemia-Triggered Glutamate Excitotoxicity From the Perspective of Glial Cells. Front. Cell Neurosci 2020, 14, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, C.; Arai, K.; Lo, E.H.; Hommel, M. Pathophysiologic Cascades in Ischemic Stroke. Int. J. Stroke 2012, 7, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Liu, J. New Role of Astrocytes in Neuroprotective Mechanisms After Ischemic Stroke. Arq. Neuropsiquiatr 2023, 81, 748–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Wang, X.; Chen, L.; Lenahan, C.; Fu, Z.; Fang, Y.; Yu, W. Crosstalk Between the Oxidative Stress and Glia Cells After Stroke: From Mechanism to Therapies. Front. Immunol 2022, 13, 852416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.; Candelario-Jalil, E. Emerging Neuroprotective Strategies for the Treatment of Ischemic Stroke: An Overview of Clinical and Preclinical Studies. Exp. Neurol 2021, 335, 113518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belenichev, I.F.; Cherniy, V.I.; Nagornaya, E.A.; Pavlov, S.V.; Cherniy, T.V. Neuroprotection and Neuroplasticity; Logos: Kyiv, 2015; p. 512. [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Shushan, S.; Miller, Y. Neuropeptides: Roles and Activities as Metal Chelators in Neurodegenerative Diseases. J. Phys. Chem. B 2021, 125, 2796–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belenichev, I.; Ryzhenko, V.; Popazova, O.; Bukhtiyarova, N.; Gorchakova, N.; Oksenych, V.; Kamyshnyi, O. Optimization of the Search for Neuroprotectors Among Bioflavonoids. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 2024, 17, 877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Wu, K.; Ye, X.Y.; Xie, T.; Zhang, P.; Blass, B.E.; Bai, R. Novel Druggable Mechanism of Parkinson's Disease: Potential Therapeutics and Underlying Pathogenesis Based on Ferroptosis. Med. Res. Rev. 2023, 43, 872–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.N.; Ngamnithiporn, A.; Du, E.; Stoltz, B.M. Recent Advances in the Total Synthesis of the Tetrahydroisoquinoline Alkaloids (2002-2020). Chem. Rev. 2023, 123, 9447–9496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
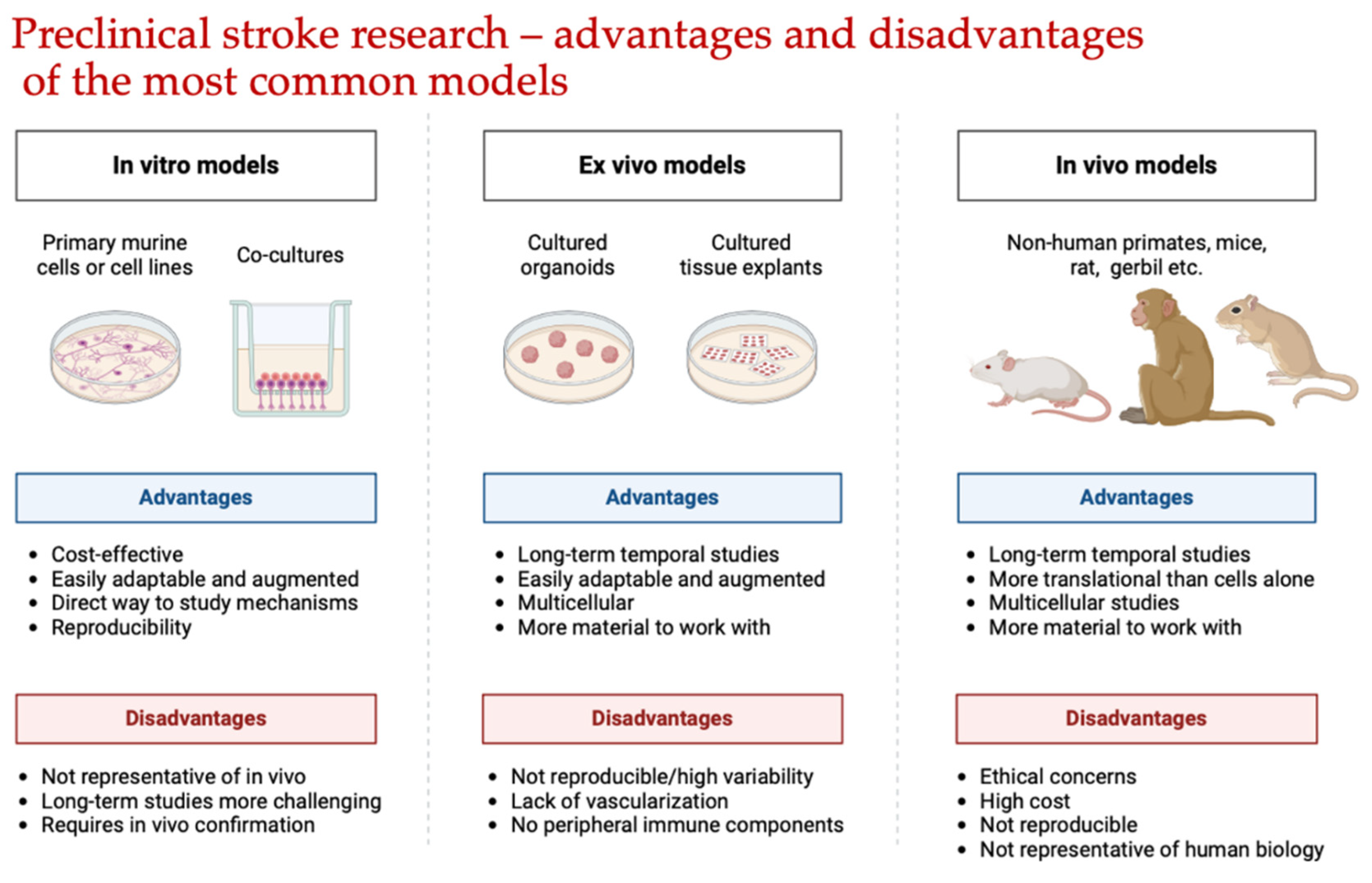
- Amado, B.; Melo, L.; Pinto, R.; Lobo, A.; Barros, P.; Gomes, J.R. Ischemic Stroke, Lessons from the Past Towards Effective Preclinical Models. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trotman-Lucas, M.; Gibson, C.L. A Review of Experimental Models of Focal Cerebral Ischemia Focusing on the Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion Model. F1000Res. 2021, 10, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belenichev, I.F.; Odnokoz, O.V.; Pavlov, S.V.; Belenicheva, O.I.; Polyakova, E.N. The Neuroprotective Activity of Tamoxifen and Tibolone During Glutathione Depletion in Vitro. Neurochem. J. 2012, 6, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kritis, A.A.; Stamoula, E.G.; Paniskaki, K.A.; Vavilis, T.D. Researching Glutamate-Induced Cytotoxicity in Different Cell Lines: A Comparative/Collective Analysis/Study. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2015, 9, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, X.; Gong, T.; Hong, Y. Hydrogen Peroxide Initiates Oxidative Stress and Proteomic Alterations in Meningothelial Cells. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ransy, C.; Vaz, C.; Lombès, A.; Bouillaud, F. Use of H2O2 to Cause Oxidative Stress, the Catalase Issue. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchgessner, A.L.; Liu, M.T.; Alcantara, F. Excitotoxicity in the Enteric Nervous System. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 8804–8816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Huang, H.; Wei, Q.; Ren, M.; Mburu, D.K.; Tian, X.; Su, J. Transcription Factors CncC/Maf and AhR/ARNT Coordinately Regulate the Expression of Multiple GSTs Conferring Resistance to Chlorpyrifos and Cypermethrin in Spodoptera exigua. Pest Manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 2009–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Wu, H.; Li, H.; Song, A.; Yin, W. The essential role of GSTP1 I105V polymorphism in the prediction of CDNB metabolism and toxicity: In silico and in vitro insights. Toxicol In Vitro 2023, 90, 105601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajpai, P.; Sangar, MC.; Singh, S.; Tang, W.; Bansal, S.; Chowdhury, G.; Cheng, Q.; Fang, JK.; Martin, MV.; Guengerich, F.P.; Avadhani, N.G. Metabolism of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine by mitochondrion-targeted cytochrome P450 2D6: implications in Parkinson disease. J Biol Chem. 2013, 288, 4436–4451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanova, A.; Galkin, A. Measurement of mitochondrial H2O2 production under varying O2 tensions. Methods Cell Biol 2020, 155, 273–293. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Saviani, E.E.; Orsi, C.H.; Oliveira, J.F.; Pinto-Maglio, C.A.; Salgado, I. Participation of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore in nitric oxide-induced plant cell death. FEBS Lett 2002, 510, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, S.; Shin, T.; Hirokata, Y.; Shigematsu, A. Inhibition of mitochondrial respiration by sodium nitroprusside and the mechanism of cyanide liberation. Br J Anaesth 1977, 49, 1239–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomeyer, C.A.; Bazil, J.N.; Stowe, D.F.; Pradhan, R.K.; Dash, R.K.; Camara, A.K. Dynamic buffering of mitochondrial Ca2+ during Ca2+ uptake and Na+-induced Ca2+ release. J Bioenerg Biomembr 2013, 45, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardi, P.; Di Lisa, F. The mitochondrial permeability transition pore: molecular nature and role as a target in cardioprotection. J Mol Cell Cardiol 2015, 78, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, C.J. Ischemic stroke: experimental models and reality. Acta Neuropathol 2017, 133, 245–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacigaluppi, M.; Comi, G.; Hermann, D.M. Animal models of ischemic stroke. Part two: modeling cerebral ischemia. Open Neurol J 2010, 4, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fluri, F.; Schuhmann, M.K.; Kleinschnitz, C. Animal models of ischemic stroke and their application in clinical research. Drug Des Devel Ther 2015, 9, 3445–3454. [Google Scholar]
- Traystman, R.J. Animal Models of Focal and Global Cerebral Ischemia. ILAR J 2003, 44, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netzley, A.H.; Pelled, G. The Pig as a Translational Animal Model for Biobehavioral and Neurotrauma Research. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovasova, V.; Bem, R.; Chlupac, J.; Dubsky, M.; Husakova, J.; Nemcova, A.; Fronek, J. Animal experimental models of ischemic limbs - A systematic review. Vascul Pharmacol 2023, 153, 107237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, P.; Kushwaha, V.; Shukla, V.; Kumar, A. Animal research ethics: an overview. Eur J Biomed Pharm Sci 2023, 10, 78–87. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, A.K. Animal Research. In The Moral Implications of Human and Animal Vulnerability; Palgrave Macmillan: Cham, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D. Genetic engineering of a mouse: Dr. Frank Ruddle and somatic cell genetics. Yale J Biol Med 2011, 84, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ruan, J.; Yao, Y. Behavioral tests in rodent models of stroke. Brain Hemorrhages 2020, 1, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellenbroek, B.; Youn, J. Rodent models in neuroscience research: is it a rat race? Dis Model Mech 2016, 9, 1079–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krafft, P.R.; Bailey, E.L.; Lekic, T.; Rolland, W.B.; Altay, O.; Tang, J.; Wardlaw, J.M.; Zhang, J.H.; Sudlow, C.L. Etiology of stroke and choice of models. Int J Stroke 2012, 7, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koukalova, L.; Chmelova, M.; Amlerova, Z.; Vargova, L. Out of the core: the impact of focal ischemia in regions beyond the penumbra. Front Cell Neurosci 2024, 18, 1336886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, J. Animal models of stroke. Animal Model Exp Med 2021, 4, 204–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicard, K.M.; Fisher, M. Animal models of focal brain ischemia. Exp Transl Stroke Med 2009, 1, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Hu, S.; Zeng, L.; Chen, R.; Li, H.; Yu, J.; Yang, H. Animal Models of Ischemic Stroke with Different Forms of Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion. Brain Sci 2023, 13, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowak, B.; Rogujski, P.; Guzman, R.; Walczak, P.; Andrzejewska, A.; Janowski, M. Animal models of focal ischemic stroke: brain size matters. Front Stroke 2023, 2, 1165231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, A.; Graham, D.I.; McCulloch, J.; Teasdale, G.M. Focal cerebral ischaemia in the rat: 1. Description of technique and early neuropathological consequences following middle cerebral artery occlusion. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 1981, 1, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, C.F.; Chuang, T.Y.; Hung, Y.W.; Lan, M.Y.; Tsai, C.H.; Huang, H.X.; Lin, Y.Y. Development of a Modified Surgical Technique for Simulating Ischemic Cerebral Cortex Injury in Rats. In Vivo 2019, 33, 1175–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunz, A.; Iadecola, C. Cerebral vascular dysregulation in the ischemic brain. Handb Clin Neurol 2009, 92, 283–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Windle, V.; Szymanska, A.; Granter-Button, S.; White, C.; Buist, R.; Peeling, J.; Corbett, D. An analysis of four different methods of producing focal cerebral ischemia with endothelin-1 in the rat. Exp Neurol 2006, 201, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Peng, C.; Guo, W.; Dong, Y.F.; Dong, X.H.; Sun, X.; Xie, H.H. A modified model of middle cerebral artery electrocoagulation in mice. CNS Neurosci Ther 2012, 18, 796–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.X.; Yang, Y.; Yang, T.; Shuaib, A. A focal embolic model of cerebral ischemia in rats: introduction and evaluation. Brain Res Brain Res Protoc. 2001, 7, 115–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justić, H.; Barić, A.; Šimunić, I.; Radmilović, M.; Ister, R.; Škokić, S.; Dobrivojević Radmilović, M. Redefining the Koizumi model of mouse cerebral ischemia: A comparative longitudinal study of cerebral and retinal ischemia in the Koizumi and Longa middle cerebral artery occlusion models. Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2022, 42, 2080–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahjouei, S.; Cai P., Y.; Ansari, S.; Sharififar, S.; Azari, H.; Ganji, S.; Zand, R. Middle cerebral artery occlusion model of stroke in rodents: A step-by-step approach. J Vasc Interv Neurol. 2016, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda, S.; del Zoppo, G.J. Models of focal cerebral ischemia in the nonhuman primate. ILAR J. 2003, 44, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Wang, H.; Chen, J.; Zhao, P.; Wen, M.; Bingwa L., A.; Jin, K.; Zhuge, Q.; Yang, S. Nonhuman primate models of ischemic stroke and neurological evaluation after stroke. J Neurosci Methods. 2022, 376, 109611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konstantinos M., Themistoklis; Themistoklis I., Papasilekas; Konstantinos S., Melanis; Konstantinos A., Boviatsis; Stefanos, I. Korfias; Konstaninos Vekrellis; Damianos E. Sakas. Transient intraluminal filament middle cerebral artery occlusion stroke model in rats: A step-by-step guide and technical considerations. World Neurosurgery 2022, 168, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, B.A.; Neuhaus A., A.; Couch, Y.; Balami J., S.; DeLuca G., C.; Hadley, G.; Harris S., L.; Grey A., N.; Buchan, A.M. The transient intraluminal filament middle cerebral artery occlusion model as a model of endovascular thrombectomy in stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2016, 36, 363–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemir, Y.G.; Bolay, H.; Erdem, E.; Dalkara, T. Occlusion of the MCA by an intraluminal filament may cause disturbances in the hippocampal blood flow due to anomalies of circle of Willis and filament thickness. Brain Res. 1999, 822, 260–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, B.D.; Dietrich, W.D.; Busto, R.; Wachtel, M.S.; Ginsberg, M.D. Induction of reproducible brain infarction by photochemically initiated thrombosis. Ann Neurol. 1985, 17, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalbetti, L.; Rozza, A.; Rizzo, V.; Favalli, L.; Scavini, C.; Lanza, E.; Savoldi, F.; Racagni, G.; Scelsi, R. Aminoacid recovery via microdialysis and photoinduced focal cerebral ischemia in brain cortex of rats. Neurosci Lett. 1995, 192, 153–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, H.; Hashimoto, A.; Matsumoto, Y.; Yao, H.; Miyakoda, G. Cilostazol, a phosphodiesterase inhibitor, attenuates photothrombotic focal ischemic brain injury in hypertensive rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2010, 30, 343–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atochin, D.N.; Chernysheva, G.A.; Aliev, O.I.; Smolyakova, V.I.; Osipenko, A.N.; Logvinov, S.V.; Zhdankina, A.A.; Plotnikova, T.M.; Plotnikov, M.B. An improved three-vessel occlusion model of global cerebral ischemia in rats. Brain Res Bull. 2017, 132, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, J.T.; Cohan, C.H.; Dave K., R.; Wright, C.B.; Perez-Pinzon, M.A. Global cerebral ischemia: synaptic and cognitive dysfunction. Curr Drug Targets. 2013, 14, 20–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansoorali, K.P.; Prakash, T.; Kotresha, D.; Prabhu, K.; Rama Rao, N. Cerebroprotective effect of Eclipta alba against global model of cerebral ischemia induced oxidative stress in rats. Phytomedicine. 2012, 19, 1108–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemoto, E.M.; Snyder, J.V.; Carroll, R.G.; Morita, H. Global ischemia in dogs: cerebrovascular CO2 reactivity and autoregulation. Stroke. 1975, 6, 425–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemoto, E.M.; Bleyaert, A.L.; Stezoski, S.W.; Moossy, J.; Rao, G.R.; Safar, P. Global brain ischemia: a reproducible monkey model. Stroke. 1977, 8, 558–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleyaert, A.; Safar, P.; Nemoto, E.; Moossy, J.; Sassano, J. Effect of postcirculatory-arrest life-support on neurological recovery in monkeys. *Crit Care Med.* 1980, 8, 153–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, K.R.; Della-Morte, D.; Saul, I.; Prado, R.; Perez-Pinzon M., A. Ventricular fibrillation-induced cardiac arrest in the rat as a model of global cerebral ischemia. Transl Stroke Res. 2013, 4, 571–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, G.; Yonchek, J.C.; Quillinan, N.; Strnad, F.A.; Exo, J.; Herson, P.S.; Traystman, R.J. A novel mouse model of pediatric cardiac arrest and cardiopulmonary resuscitation reveals age-dependent neuronal sensitivities to ischemic injury. J Neurosci Methods. 2014, 222, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kofler, J.; Hattori, K.; Sawada, M.; DeVries, A.C.; Martin, L.J.; Hurn, P.D.; Traystman, R.J. Histopathological and behavioral characterization of a novel model of cardiac arrest and cardiopulmonary resuscitation in mice. J Neurosci Methods. 2004, 136, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, A.H.; Erdogan, H.; Tasdemiroglu, E. Searching evidences of stroke in animal models: A review of discrepancies. Turk Neurosurg. 2017, 27, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodruff, T.M.; Thundyil, J.; Tang, S.C.; Sobey, C.G.; Taylor, S.M.; Arumugam, T.V. Pathophysiology, treatment, and animal and cellular models of human ischemic stroke. Mol Neurodegener. 2011, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahul, A.B.; Joshi, P.C.; Kumar, A.; Chakravarty, S. Transient global cerebral ischemia differentially affects cortex, striatum and hippocampus in bilateral common carotid arterial occlusion (BCCAo) mouse model. J Chem Neuroanat. 2018, 92, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Geng, Y.; Tang, X.; Guo, R.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, H.; Tian, X. A modified four vessel occlusion model of global cerebral ischemia in rats. J Neurosci Methods. 2021, 352, 109090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, D.; Wu, Y.; Qu, Y.; Shi, F.; Hu, J.; Gao, B.; Wang, B.; Gao, G.; He, S.; Zhao, T. A modified method to reduce variable outcomes in a rat model of four-vessel arterial occlusion. Neurol Res. 2016, 38, 1102–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radenovic, L. In Vivo Experimental Models of Cerebral Ischemia: Analysis, Translational Potential and Clinical Relevance. Cardiol Res Cardiovasc Med. 2024, 9, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGraw, C.P. Experimental cerebral infarction: effects of pentobarbital in Mongolian gerbils. Arch Neurol. 1977, 34, 334–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laas, R. Common carotid artery stump pressure in the gerbil stroke model. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1984, 47, 365–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Yue, Y.; Li, C.; Wu, X.; Park, S. Vagus nerve suppression in ischemic stroke by carotid artery occlusion: Implications for metabolic regulation, cognitive function, and gut microbiome in a gerbil model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belenichev, I.F.; Kolesnik, Y.M.; Pavlov, S.V.; Sokolik, E.P.; Bukhtiyarova, N.V. Malate-aspartate shunt in neuronal adaptation to ischemic conditions: Molecular-biochemical mechanisms of activation and regulation. Neurochem. J. 2012, 6, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlov, S.V.; Belenichev, I.F. Molecular and biochemical aspects of the neuroprotective effect of the selective estrogen receptor modulator tamoxifen in a model of acute cerebral ischemia. Neurochem. J. 2014, 8, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phaniendra, A.; Jestadi, D.B.; Periyasamy, L. Free radicals: properties, sources, targets, and their implication in various diseases. Indian J Clin Biochem. 2015, 30, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Cha, M.; Lee, B.H. Crosstalk between neuron and glial cells in oxidative injury and neuroprotection. Int J Mol Sci. 2021, 22, 13315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayala, A.; Muñoz, M.F.; Argüelles, S. Lipid peroxidation: production, metabolism, and signaling mechanisms of malondialdehyde and 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2014, 2014, 360438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordiano, R.; Di Gioacchino, M.; Mangifesta, R.; Panzera, C.; Gangemi, S.; Minciullo, P.L. Malondialdehyde as a potential oxidative stress marker for allergy-oriented diseases: An update. Molecules. 2023, 28, 5979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizzino, G.; Irrera, N.; Cucinotta, M.; Pallio, G.; Mannino, F.; Arcoraci, V.; Squadrito, F.; Altavilla, D.; Bitto, A. Oxidative stress: Harms and benefits for human health. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017, 2017, 8416763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jomova, K.; Raptova, R.; Alomar S., Y.; Alwasel S., H.; Nepovimova, E.; Kuca, K.; Valko, M. Reactive oxygen species, toxicity, oxidative stress, and antioxidants: chronic diseases and aging. Arch Toxicol. 2023, 97, 2499–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzaid, F.; Patel, V.B.; Preedy, V.R. Biomarkers of oxidative stress in blood. Biomarkers in Disease: Methods, Discoveries and Applications, 2015, 1-2, 567–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frijhoff, J.; Winyard, P.G.; Zarkovic, N.; Davies, S.S.; Stocker, R.; Cheng, D.; Knight, A.R.; Taylor, E.L.; Oettrich, J.; Ruskovska, T.; Gasparovic, A.C.; Cuadrado, A.; Weber, D.; Poulsen, H.E.; Grune, T.; Schmidt, H.H.; Ghezzi, P. Clinical relevance of biomarkers of oxidative stress. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2015, 23, 1144–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.C.W.; Furman, R.; Axelsen, P.H.; Shchepinov, M.S. Free radical chain reactions and polyunsaturated fatty acids in brain lipids. ACS Omega. 2022, 7, 25337–25345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guéraud, F.; Atalay, M.; Bresgen, N.; Cipak, A.; Eckl, P.M.; Huc, L.; Jouanin, I.; Siems, W.; Uchida, K. Chemistry and biochemistry of lipid peroxidation products. Free Radic Res. 2010, 44, 1098–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meagher, E.A.; FitzGerald, G.A. Indices of lipid peroxidation in vivo: strengths and limitations. Free Radic Biol Med. 2000, 28, 1745–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praticò, D. Lipid peroxidation in mouse models of atherosclerosis. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2001, 11, 112–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilska-Wilkosz, A.; Iciek, M.; Górny, M. Chemistry and biochemistry aspects of the 4-hydroxy-2,3-trans-nonenal. Biomolecules. 2022, 12, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abeyrathne, E.D.N.S.; Nam, K.; Ahn, D.U. Analytical methods for lipid oxidation and antioxidant capacity in food systems. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021, 10, 1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeb, A.; Ullah, F. A simple spectrophotometric method for the determination of thiobarbituric acid reactive substances in fried fast foods. J Anal Methods Chem. 2016, 2016, 9412767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grotto, D.; Santa Maria, L.D.; Boeira, S.; Valentini, J.; Charão, M.F.; Moro, A.M.; Nascimento, P.C.; Pomblum, V.J.; Garcia, S.C. Rapid quantification of malondialdehyde in plasma by high performance liquid chromatography-visible detection. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2007, 43, 619–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steghens, J.P.; van Kappel, A.L.; Denis, I.; Collombel, C. Diaminonaphtalene, a new highly specific reagent for HPLC-UV measurement of total and free malondialdehyde in human plasma or serum. Free Radic Biol Med. 2001, 31, 242–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendonça, R.; Gning, O.; Di Cesaré, C.; Lachat, L.; Bennett, N.C.; Helfenstein, F.; Glauser, G. Sensitive and selective quantification of free and total malondialdehyde in plasma using UHPLC-HRMS. J Lipid Res. 2017, 58, 1924–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Zhang, H.; Luo, J.; Li, L.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, R.; Liu, G. New method for HPLC separation and fluorescence detection of malonaldehyde in normal human plasma. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2006, 832, 103–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graille, M.; Wild, P.; Sauvain, J. .; Hemmendinger M.; Guseva Canu I.; Hopf N.B. Urinary 8-isoprostane as a biomarker for oxidative stress. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Toxicol Lett. 2020, 328, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlier, C.; Michaux, C. Dual inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and 5-lipoxygenase (5-LOX) as a new strategy to provide safer non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Eur J Med Chem. 2003, 38, 645–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, H.; Unoda, K.; Ito, T.; Kitaoka, H.; Kimura, F.; Hanafusa, T. The relation of urinary 8-OHdG, a marker of oxidative stress to DNA, and clinical outcomes for ischemic stroke. Open Neurol J. 2012, 6, 51–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makropoulos, W.; Kocher, K.; Heintz, B.; Schwarz, E.R.; Mertens, P.R.; Stefanidis, I. Urinary thymidine glycol as a biomarker for oxidative stress after kidney transplantation. Ren Fail. 2000, 22, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrera, G. Oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation products in cancer progression and therapy. ISRN Oncol. 2012, 2012, 137289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altomare, A.; Baron, G.; Gianazza, E.; Banfi, C.; Carini, M.; Aldini, G. Lipid peroxidation derived reactive carbonyl species in free and conjugated forms as an index of lipid peroxidation: limits and perspectives. Redox Biol. 2021, 42, 101899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chidambaram, S.B.; Anand, N.; Varma, S.R.; Ramamurthy, S.; Vichitra, C.; Sharma, A.; Mahalakshmi, A.M.; Essa, M.M. Superoxide dismutase and neurological disorders. IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2024, 16, 373–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukui, M.; Zhu, B.T. Mitochondrial superoxide dismutase SOD2, but not cytosolic SOD1, plays a critical role in protection against glutamate-induced oxidative stress and cell death in HT22 neuronal cells. Free Radic Biol Med. 2010, 48, 821–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauridsen, C.; Jensen S., K. α-Tocopherol incorporation in mitochondria and microsomes upon supranutritional vitamin E supplementation. Genes Nutr. 2012, 7, 475–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendonça, J.D.S.; Guimarães, R.C.A.; Zorgetto-Pinheiro, V.A.; Fernandes, C.D.P.; Marcelino, G.; Bogo, D.; Freitas, K.C.; Hiane, P.A.; de Pádua Melo, E.S.; Vilela, M.L.B.; Nascimento, V.A.D. Natural antioxidant evaluation: A review of detection methods. Molecules 2022, 27, 3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siluk, D.; Oliveira, R.V.; Esther-Rodriguez-Rosas, M.; Ling, S.; Bos, A.; Ferrucci, L.; Wainer, I.W. A validated liquid chromatography method for the simultaneous determination of vitamins A and E in human plasma. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2007, 44, 1001–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Go, Y.M.; Jones, D.P. Thiol/disulfide redox states in signaling and sensing. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2013, 48, 173–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashi, Y.; Aratake, T.; Shimizu, T.; Shimizu, S.; Saito, M. Protective role of glutathione in the hippocampus after brain ischemia. Int J Mol Sci. 2021, 22, 7765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewari, D.; Sah, A.N.; Bawari, S.; Nabavi, S.F.; Dehpour, A.R.; Shirooie, S.; Braidy, N.; Fiebich, B.L.; Vacca, R.A.; Nabavi, S.M. Role of nitric oxide in neurodegeneration: Function, regulation, and inhibition. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2021, 19, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contestabile, A.; Monti, B.; Contestabile, A.; Ciani, E. Brain nitric oxide and its dual role in neurodegeneration/neuroprotection: Understanding molecular mechanisms to devise drug approaches. Curr Med Chem. 2003, 10, 2147–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iova, O.M.; Marin, G.E.; Lazar, I.; Stanescu, I.; Dogaru, G.; Nicula, C.A.; Bulboacă, A.E. Nitric oxide/nitric oxide synthase system in the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative disorders—An overview. Antioxidants. 2023, 12, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belenichev, I.; Popazova, O.; Bukhtiyarova, N.; Savchenko, D.; Oksenych, V.; Kamyshnyi, O. Modulating nitric oxide: Implications for cytotoxicity and cytoprotection. Antioxidants (Basel) 2024, 13, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Apolito, E.; Sisalli, M.J.; Tufano, M.; Annunziato, L.; Scorziello, A. Oxidative metabolism in brain ischemia and preconditioning: Two sides of the same coin. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sifat, A.E.; Nozohouri, S.; Archie S., R.; Chowdhury E., A.; Abbruscato, T.J. Brain energy metabolism in ischemic stroke: Effects of smoking and diabetes. Int J Mol Sci. 2022, 23, 8512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belenichev, I.F.; Aliyeva, O.G.; Popazova, O.O.; Bukhtiyarova, N.V. Involvement of heat shock proteins HSP70 in the mechanisms of endogenous neuroprotection: The prospect of using HSP70 modulators. Front Cell Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1131683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khlyntsevaa, S.V.; Bazel Ya., R.; Vishnikin, A.B.; Andruch, V. Methods for the determination of adenosine triphosphate and other adenine nucleotides. J Anal Chem. 2009, 64, 657–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawabori, M.; Yenari, M.A. Inflammatory responses in brain ischemia. Curr Med Chem. 2015, 22, 1258–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawtharani, S.; Omeis, I. Acute ischemic stroke biomarkers: a new era with diagnostic promise? Acute Med Surg. 2021, 8, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Huang, Z.-X.; Liu, Z. Biomarkers and the outcomes of ischemic stroke. Front Mol Neurosci. 2023, 16, 1171101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- di Biase, L.; Bonura, A.; Pecoraro, P.M.; Carbone, S.P.; Di Lazzaro, V. Unlocking the potential of stroke blood biomarkers: Early diagnosis, ischemic vs. hemorrhagic differentiation and hemorrhagic transformation risk: A comprehensive review. Int J Mol Sci. 2023, 24, 11545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, E.J.; Reichardt, L.F. Neurotrophins: Roles in neuronal development and function. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2001, 24, 677–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawat, V.; Goux, W.; Piechaczyk, M.; Mello, S.R. c-Fos protects neurons through a noncanonical mechanism involving HDAC3 interaction: Identification of a 21-amino acid fragment with neuroprotective activity. Mol Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 1165–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krukoff T.L. c-Fos Expression as a Marker of Functional Activity in the Brain. In: Cell Neurobiology Techniques. Neuromethods, vol 33. Humana Press. [CrossRef]
- Miranda, M.; Morici, J.F.; Zanoni, M.B.; Bekinschtein, P. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor: A key molecule for memory in the healthy and the pathological brain. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019, 13, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquin, S.; Sharma, M.; Gauchat, J.F. Ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF): New facets of an old molecule for treating neurodegenerative and metabolic syndrome pathologies. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2015, 26, 507–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brook, N.; Brook, E.; Dharmarajan, A.; Chan, A.; Dass, C.R. Pigment epithelium-derived factor regulation of neuronal and stem cell fate. Exp Cell Res. 2020, 389, 111891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creeley, C.E. From Drug-Induced Developmental Neuroapoptosis to Pediatric Anesthetic Neurotoxicity—Where Are We Now? Brain Sci. 2016, 6, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.L.; Engle, J.T.; Griffin, E.A.; Miller, J.P.; Chu, W.; Zhou, D.; Mach, R.H. Imaging caspase-3 activation as a marker of apoptosis-targeted treatment response in cancer. Mol Imaging Biol. 2015, 17, 384–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingham, P.J.; Pocock, J.M. Microglial secreted cathepsin B induces neuronal apoptosis. J Neurochem. 2001, 76, 1475–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shlyakhtina, Y.; Pavet, V.; Gronemeyer, H. Dual role of DR5 in death and survival signaling leads to TRAIL resistance in cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, 3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lončarević-Vasiljković, N.; Milanović, D.; Pešić, V.; Tešić, V.; Brkić, M.; Lazić, D.; Avramović, V.; Kanazir, S. Dietary restriction suppresses apoptotic cell death, promotes Bcl-2 and Bcl-xl mRNA expression and increases the Bcl-2/Bax protein ratio in the rat cortex after cortical injury. Neurochem Int. 2016, 96, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Group of Oxidative Stress Reaction Products | Chemical Compounds | Detection Methods |
|---|---|---|
| I. Unstable (Radical Nature) | Alkyl, alkoxyl, peroxyl, nitrite, peroxynitrite radicals | Spontaneous CL, Fe2+ or H2O2-induced CL, EPR |
| II. Stable (Non-Radical Nature): | ||
| 1) Primary | Hydroperoxides, conjugated dienes, endoperoxides, dialkyl peroxides, epoxides | Polarography, iodometry, UV, IR, NMR, HPLC |
| 2) Secondary | Aldehydes (alkanal, alkenal), hydroxyalkenals, malondialdehyde, trienones, 8-isoprostanes, 8-hydroxy-2-deoxyguanosine, o-nitrotyrosine, o-chlorotyrosine, thymidine glycol | UV, HPLC, HPLC/Fluorescence, HPLC/UV, FS, TLC, GC, GC/MS |
| 3) End-Products | Gaseous products (pentane, heptane, etc.), Schiff bases, nitrates, and nitrites | FS, GRP |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





