1. Introduction
Proprioception, a crucial sensory process for normal human body function, is mediated by proprioceptors—mechanosensory neurons located in muscles, tendons, and joints. These receptors are active during various behaviors and provide essential information about limb speed, movement, load, and limits. The central nervous system integrates proprioceptive information with other sensory systems, such as vision and the vestibular system, to create a comprehensive representation of the body’s position, movement, and acceleration. Proprioception is crucial for everyday activities like walking or maintaining balance in complete darkness without losing orientation [
1].
In addition to maintaining balance, the vestibular system collects information necessary for movement control and reflex actions, facilitating the body’s adjustment to positional changes [
2]. This interaction between proprioception and vestibular information is vital for optimal body function, facilitating motor coordination. Studies have shown that deficits in proprioception or vestibular function can significantly impact a patient’s ability to move and maintain balance, underscoring the need for an integrated approach in medical rehabilitation [
3].
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV), the most common cause of vertigo, has a prevalence of 2.4% and an annual incidence of 0.6%, affecting a significant population worldwide [
4]. In the United States, between 17% and 42% of patients presenting with dizziness are diagnosed with BPPV, highlighting the significant public health impact of this condition [
5]. Moreover, BPPV significantly impairs a patient’s ability to perform daily activities, greatly diminishing their quality of life. In the absence of treatment, BPPV may persist for approximately 15 days on average, with a recurrence rate of 15% per year, and half of the patients are prone to recurrences [
6]. Although in many cases the etiology of BPPV remains unknown, there are precipitating factors that can trigger this condition, including head trauma, viral infections, and Ménière’s disease [
4].
Traditional treatment for BPPV includes physical maneuvers aimed at repositioning the otoconia back into the utricle [
7]. However, a significant percentage of patients continue to experience residual symptoms after treatment, emphasizing the need for additional rehabilitation methods [
8]. Vestibular rehabilitation thus becomes an essential component of treatment, aiming to facilitate the physiological compensation process in cases of peripheral vestibular lesions [
9]. Vestibular rehabilitation programs not only accelerate the recovery process but also significantly improve patients’ quality of life [
10].
The importance of physical therapy rehabilitation in managing patients with BPPV is well-documented in the literature [
6]. Vestibular exercises are designed to improve gaze stability, coordination, and balance [
10]. Additionally, proprioceptive training interventions are integrated to restore the perception of limb position and movement, ensuring a full recovery [
7]. The rehabilitation of patients with BPPV through physical therapy is crucial not only for alleviating vestibular symptoms but also for fully restoring motor and proprioceptive function [
8]. Studies have shown that an integrated approach combining vestibular rehabilitation with proprioceptive training techniques can provide the best outcomes in terms of restoring motor function, preventing recurrences, and improving quality of life [
9].
The main objective of this study is to evaluate the effectiveness of an integrated vestibular rehabilitation program in enhancing balance, motor control, and proprioceptive function in patients diagnosed with BPPV. By highlighting the impact of a multidisciplinary approach that incorporates various rehabilitation methods, this study aims to optimize patient outcomes and reduce recovery time. Focusing on the specific challenges posed by BPPV, this research seeks to provide a comprehensive understanding of how tailored interventions can improve patient recovery and minimize the likelihood of symptom recurrence.
2. Materials and Methods
We conducted a prospective observational study involving 107 subjects diagnosed with Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV). The participants were recruited from the EMT Department of the Municipal Hospital in Sighisoara, Romania. All patients exhibiting symptoms indicative of BPPV, such as intense and brief episodes of dizziness, nystagmus, nausea, vomiting, and balance disturbances, underwent an ENT consultation and a comprehensive evaluation to confirm the diagnosis of BPPV diagnosis. In addition, all participants had coexisting orthopedic issues, specifically affecting either the knee or shoulder.
The study was conducted over a period of 4 years and 6 months, from September 2019 to April 2024.
Informed consent for study participation and data publication was obtained from each subject of the study.
Inclusion criteria: confirmed diagnosis of BPPV, willingness to participate in the study, and compliance with the recovery program.
Exclusion criteria were cervical spondylosis, any form of cancer, conditions contraindicating physical therapy, refusal to participate in the study, or non-compliance with the recovery protocol.
2.1. Study Design
In order to relieve specific symptoms caused by BPPV we appleid the following methods: Epley maneuver (particularly effective for BPPV, symptoms may begin to improve after a few days of regular practice); Brandt-Daroff Exercices (noticeable improvements can occur after a few weeks of daily practice); Cawthrone-Cooksey exercises (symptoms reliev may begin to be noticed after 3-4 weeks of daily exercises); , Gaze stabilization and balance exercises (positive results typically appear after a few weeks of consistent practice).
In the recovery process, a stationary bicycle, balance cushions and boards, low-resistance elastic bands, and balance exercises were also utilized. These were typically introduced on average starting from week 5.
The duration of the recovery program varied from individual to individual, but on average, it ranged between 8 and 10 weeks.
The interdisciplinary character of the study results from precise evaluations carried out by otorhinolaryngologists and the follow-up of kinetic assessments and program by the physiotherapist, including the adaptation of the recovery program according to the needs of the individual.
2.2. Physiotherapy Assessments Applied to Study Subjects:
During the study, the Dynamic Gait Index (DGI) and the Balance Beam Test were utilized to assess dynamic balance. These assessments were conducted both at the beginning and at the end of the recovery program, providing a comprehensive evaluation of the subjects’ progress over time.
The score (expressed in points) and interpretation for DGI stages 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7 are as follows: 0 points indicate complete inability to perform the task; 1 point represents uncertain performance with frequent loss of balance; 2 points signify performance with minor balance issues; and 3 points indicate performance without balance problems. The maximum possible score is 15 points. The Balance Beam Test results were expressed in terms of time (seconds) and the number of balance disturbances, providing a detailed measure of the participants’ stability and coordination during the assessment.
The Balance Beam Test results were expressed in terms of time (seconds) and the number of balance disturbances, conducted on a 2-meter surface, providing a detailed measure of the participants’ stability and coordination during the assessment
2.3. Recovery Program Design
Recovery procedures can commence immediately after obtaining the specialist’s approval. Patients with inner ear disorders, exhibiting symptoms such as vertigo, are advised to be accompanied to the rehabilitation sessions. The room should be well-ventilated, preferably cool (around 20°C), and vital signs—blood pressure, pulse, blood glucose levels, and oxygen saturation—should be monitored. These measures help to reduce patient discomfort and eliminate other factors that could trigger dizziness, confusion, or similar symptoms.
These patients should be approached with great calm and patience. In the initial sessions, some patients may require more time, longer breaks, or may experience anxiety. In such cases, they might need to talk to alleviate their concerns and become comfortable with the environment. Any of these approaches to patient care is appropriate.
The first rehabilitation session focuses on assessment, designing a recovery plan with short-term and long-term objectives, and generally explaining to the patient what to expect during the process. After each session, the patient will be assigned home exercises. During the following session, the patient will be reevaluated to determine whether the rehabilitation program can progress to the next phase or if it should remain at the current level of difficulty.
The rehabilitation program, including the exercises, is tailored to the patient’s specific needs, while adhering to the general principles of physiotherapy. The program may evolve differently for each patient, but to ensure a structured approach and logical progression, the following phases of vestibular rehabilitation have been outlined:
phase I: Epley maneuver. The goal of this phase is to reposition the otoconia, those small calcium particles that dislodge and move into the semicircular canals of the inner ear, causing vertigo. The Epley maneuver is designed to guide these particles back into the utricle, rapidly reducing vertigo symptoms. This phase is essential for quickly alleviating symptoms and providing the comfort necessary to proceed with the subsequent phases of rehabilitation.
Phase II: Brandt-Daroff exercises and initiation of transfer exercises from supine to sitting positions. The objective of this phase is to adapt and desensitize the vestibular system to positional changes. These exercises are used to reduce sensitivity to vertigo, and the transfer exercises from supine to sitting help individuals regain confidence in their ability to rise and change positions without triggering vertigo. Phase II is crucial for stabilizing symptoms and initiating the re-education of daily movements.
Phase III: Cawthorne-Cooksey exercises and initiation of head and neck mobilization exercises from a seated position. The aim of this phase is to improve coordination between head movements and visual perception, thereby reducing dizziness. Cawthorne-Cooksey exercises are used to enhance motion tolerance and to train the brain to compensate for vestibular deficits. Head and neck mobilization from a seated position helps improve postural control and balance.
Phase IV: Gaze stabilization and balance exercises, along with strengthening exercises for the lower limb muscles. In this phase, the focus is on improving balance and postural control through gaze stabilization and balance exercises. Strengthening the lower limb muscles is also important to support the patient’s overall stability and prevent falls. Phase IV helps consolidate the results achieved so far and prepares the patient for more complex exercises.
Phase V: initiation of gait training. This phase focuses on rehabilitating the patient’s ability to walk without experiencing vertigo or imbalance. Gait exercises are progressive, starting with simple steps and increasing in complexity as the individual gains confidence and stability. Phase V is essential for restoring basic walking function and ensuring a smooth transition to daily activities.
Phase VI: complex exercises that demand attention, coordination, concentration, and balance. The final phase of the program aims to refine and integrate all the skills acquired in the previous phases. The complex exercises are designed to challenge and strengthen the individual’s coordination, attention, and balance in situations that simulate complex daily activities. Phase VI helps prepare the patient for full socio-professional reintegration.
Progressing from one phase of the rehabilitation program to the next does not entail the discontinuation of the previously implemented procedures, but rather their integration into a more comprehensive recovery regimen.
In terms of session frequency, the rehabilitation sessions initially take place twice a week under the supervision and guidance of the physical therapist. As the patient advances to phase IV of the rehabilitation program, the frequency increases to three times a week, reflecting the program’s intensification.
In our study, the vestibular rehabilitation process consists of six phases, with the duration of each phase potentially varying based on the severity of the symptoms. Key indicators such as the patient’s comfort during exercises, the absence or reduction of dizziness and vertigo, and an overall sense of security determine the appropriate timing to initiate and advance to the next phase of the rehabilitation program.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
The collected data were processed in MS Excel, and the statistical analysis was conducted using SPSS (Statistical Package for the Social Sciences). Descriptive statistics for the entire sample of 107 subjects, as well as for those with vestibular system impairment (BPPV), are presented in terms of central numerical values (mean and median), variability (standard deviation), and extremes (minimum and maximum). Additionally, the data are divided into four equal segments (quartiles). These statistics include the results of tests conducted at two evaluations: initial and final.
3. Results
The study included 107 subjects aged between 22 and 74 years, of which 45 (42.05%) were male and 62 (57.94%) were female. Among the study participants, 68 (63.6%) were professionally active in a dynamic environment, 57 (53.3%) engaged in recreational physical activities regularly, including four (3.7%) who were professional athletes—handball players. Out of the 107 study participants, 30 (28%) had comorbidities such as hypertension, tachycardia, osteoporosis, type II diabetes, or rheumatologic conditions.
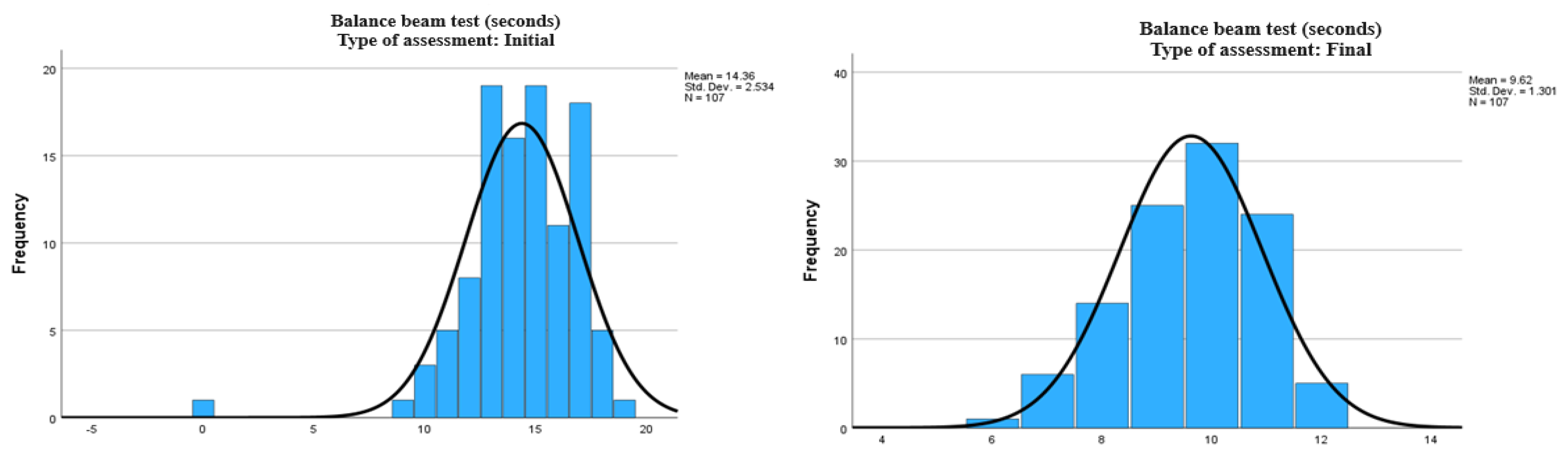
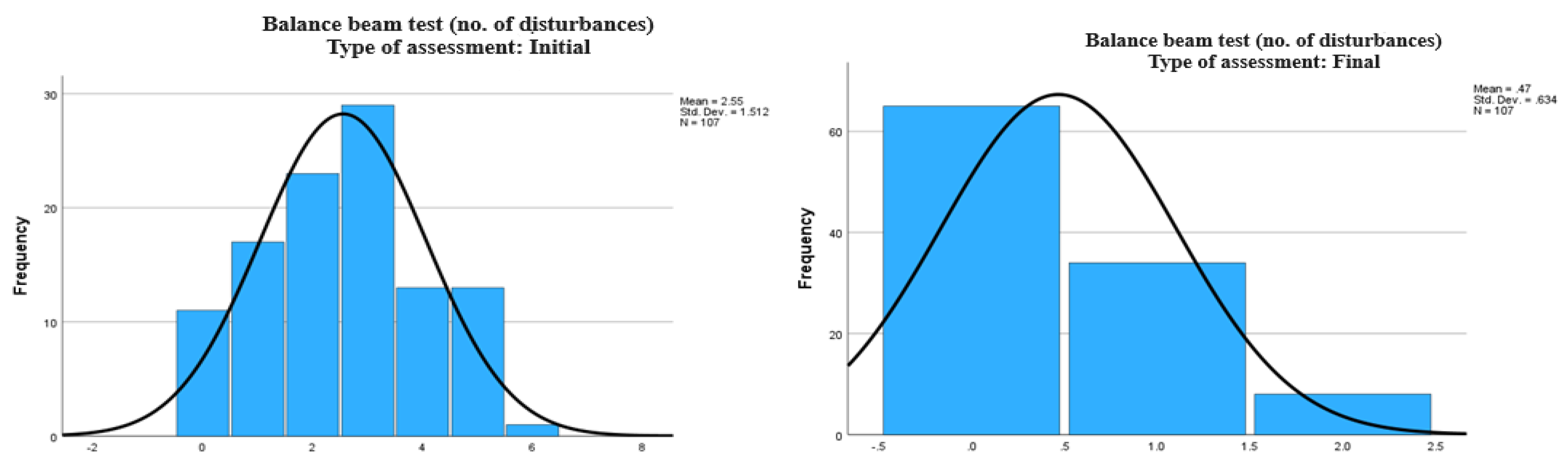
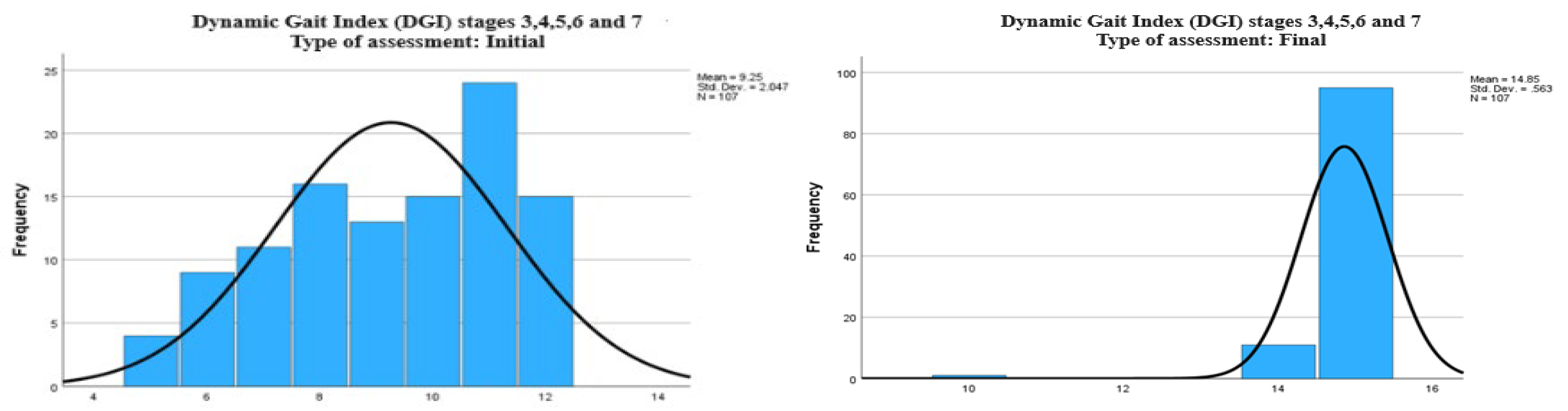
Table 1 indicates a significant improvement in balance and dynamic motor performance following the rehabilitation intervention. This is evidenced by the decrease in the time required to complete the Balance Beam test (with an average time of 14.36 seconds at the initial assessment, a minimum of 0 seconds for subjects unable to complete the test, and a maximum of 19 seconds, compared to an average of 9.62 seconds at the final assessment, with a minimum of 6 seconds and a maximum of 12 seconds). Additionally, there was a reduction in the number of balance disturbances (from an average of 2.55 disturbances at the initial assessment to an average of 0.47 disturbances at the final assessment) and an increase in DGI scores (with a median of 9 points at the initial assessment and 15 points at the final assessment).
We graphically represented the results obtained from the Balance Beam and Dynamic Gait Index (DGI) tests, both at the initial and final evaluations, to highlight the evolution of balance and dynamic motor performance following the rehabilitation intervention.
The first graph shows the distribution of balance times, with an average of 14.36 seconds and a standard deviation of 2.534 seconds. Following the rehabilitation intervention, the final assessment (
Figure 1) demonstrates a significant reduction in the average balance time to 9.62 seconds, accompanied by a lower standard deviation of 1.301 seconds, indicating a notable improvement in balance.
Regarding the number of balance disturbances during the Balance Beam test (
Figure 2), the initial evaluation revealed an average of 2.55 disturbances, with a standard deviation of 1.512. In the final evaluation (
Figure 3), the graph shows a dramatic reduction in the number of disturbances, with an average of only 0.47 and a standard deviation of 0.634, reflecting significantly improved stability.
For the DGI scores, the graph from the initial evaluation (
Figure 3) shows an average of 9.25 points, with a standard deviation of 2.047 points. After the intervention, the graph of the final evaluation (
Figure 3) indicates a notable increase in the average score to 14.85 points, with a standard deviation of 0.563 points, suggesting a significant improvement in dynamic motor function.
Graphs 1, 2 and 3 demonstrate considerable improvements in the balance and dynamic motor performance of patients following the rehabilitation program, highlighting the effectiveness of the physicaltherapy intervention in alleviating symptoms associated with BPPV.
We used the One-Sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov test to determine whether the continuous variables in the study followed a normal distribution. This was essential for deciding whether to apply parametric or non-parametric statistical methods. The results, presented in the following table, indicate that only the variable ‘age’ exhibited a normal distribution.
According to the results presented
Table 2, the variable ‘age’ is the only one that follows a normal distribution, with a statistical significance of .200, allowing us to retain the null hypothesis. In contrast, the variables related to balance tests and DGI scores demonstrated a significant deviation from normality (p < .001), leading us to reject the null hypothesis for these variables. This suggests that the distribution of these data is non-normal, thereby justifying the use of non-parametric statistical methods in the subsequent analysis.
The statistical hypothesis H0 was tested using the Student’s t-test to determine if there were statistically significant differences between the mean scores of the tests at the final assessment compared to the mean scores at the initial assessment for the entire sample (n=107).
Table 3 presents the descriptive statistics for each type of assessment (initial and final), while
Table 4 displays the results of the Student’s t-test for comparing the means.
The descriptive statistics table (
Table 3) indicates the means, standard deviations, and standard errors for each of the three assessments: the Balance Beam Test expressed in seconds, the Balance Beam Test expressed in the number of balance disturbances, and the scores obtained on the Dynamic Gait Index (DGI) for stages 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7. The mathematical differences between the initial and final means are evident, reflecting significant improvements following the rehabilitation intervention.
The results of the Student’s t-test (
Table 4) indicate that for all three tests, there were statistically significant differences (p-value < 0.001) between the means at the final assessment and those at the initial assessment. For all tests, the p-value was well below 0.05, providing strong evidence against the null hypothesis and confirming the effectiveness of the rehabilitation program.
The observed differences between the initial and final means for all three tests demonstrate a significant improvement in balance and dynamic motor performance, highlighting the effectiveness of the rehabilitation intervention.
To test whether there are statistically significant differences between men and women regarding the effectiveness of the treatment (final assessment), we applied the independent samples t-test for comparing the means of the two groups.
Table 5 presents the descriptive statistics for the two groups (men and women), while
Table 6 shows the results of the t-test.
Table 5 provides descriptive statistics for three key assessments: the Balance Beam test (measured both in seconds and the number of disturbances) and the Dynamic Gait Index (DGI) scores, all categorized by gender (male and female).
In the Balance Beam test (seconds), the mean time required for test completion is slightly lower in males (Mean = 9.36 seconds) compared to females (Mean = 9.81 seconds). The standard deviation is also marginally higher in males (Std. Deviation = 1.351) than in females (Std. Deviation = 1.239), indicating a slightly greater variability in male performance.
For the Balance Beam test (number of disturbances), the mean number of disturbances is very similar between males (Mean = 0.49) and females (Mean = 0.45), with standard deviations that are almost identical across both groups.
Regarding the Dynamic Gait Index (DGI), the mean scores for males (Mean = 14.87) and females (Mean = 14.84) are nearly identical, suggesting comparable performance between the two genders.
Table 6 presents the results of the Student’s t-test, which was conducted to compare the performance of male and female participants across three key measurements: the Balance Beam Test (measured in seconds), the Balance Beam Test (measured by the number of disturbances), and the Dynamic Gait Index (DGI).
For the Balance Beam Test (seconds), the Levene’s test for equality of variances revealed no significant difference between the variances of male and female participants (Sig. = 0.147), suggesting that the variability in performance was consistent across both groups. The subsequent t-test indicated a statistically significant difference between genders (p = 0.038 for a one-tailed test and p = 0.077 for a two-tailed test). This finding suggests that, on average, male participants completed the test slightly faster than their female counterparts. However, the difference in mean completion times, while statistically significant, was relatively modest, amounting to just -0.451 seconds.
In the case of the Balance Beam Test (number of disturbances), the Levene’s test again confirmed equal variances between males and females (Sig. = 0.953). The t-test results showed no statistically significant difference between the genders (p = 0.383 for a one-tailed test and p = 0.766 for a two-tailed test), indicating that the number of disturbances experienced during the test was similar for both male and female participants, with no significant gender-based variation.
Regarding the Dynamic Gait Index (DGI), the analysis followed a similar pattern. The Levene’s test indicated that the variances between the male and female groups were equal (Sig. = 0.537). The t-test results did not reveal a significant difference between males and females in terms of DGI scores (p = 0.401 for a one-tailed test and p = 0.801 for a two-tailed test), suggesting that both groups performed similarly on this measure, with no significant gender-related differences observed.
Overall, the analysis indicates that while there is a small yet statistically significant difference in the Balance Beam Test (measured in seconds) between males and females, no significant differences were found in the number of disturbances during the Balance Beam Test or in the DGI scores. This suggests that gender may have a minor influence on the speed of task completion but does not significantly affect overall balance performance or dynamic gait control.
3.1. Correlations
To analyze whether there are correlations between the results of the three tests at each of the two evaluations points, namely the initial and final assessments, we applied Pearson correlations, with the results presented in
Table 7 and
Table 8.
There is a strong and statistically significant positive correlation between the time required to complete the Balance Beam Test and the number of balance disturbances, both at the initial (
Table 7) and at the final (
Table 8) assessment. This suggests that as the time needed to complete the test increases, so does the number of disturbances. This relationship is expected and confirms that the measurements were performed correctly and are consistent with the anticipated behavior of the subjects, demonstrating the validity of the applied test.
The initial assessment (
Table 7) also shows a moderate and statistically significant negative correlation between the Dynamic Gait Index (DGI) scores and the Balance Beam test duration, with a Pearson coefficient of -0.423 (p < 0.001). This relationship implies that higher DGI scores, indicative of better performance, are associated with shorter completion times for the Balance Beam test, highlighting a clear link between improved dynamic gait control and enhanced balance efficiency.
In contrast, the correlation between the Dynamic Gait Index (DGI) and the number of disturbances during the Balance Beam test at the final assessment (
Table 8) is very weak and not statistically significant, with a Pearson coefficient of -0.093 (p = 0.340). This lack of a significant relationship suggests that DGI scores do not strongly correspond to the number of disturbances encountered during the Balance Beam test in the final assessment, indicating no clear association between these variables.
Regarding the final assessment, the analysis between the Balance Beam test duration (seconds) and the number of disturbances (
Table 8) uncovered a moderate and statistically significant positive correlation, evidenced by a Pearson coefficient of 0.299 (p = 0.002). This finding indicates that as the time taken to complete the Balance Beam test increases, so does the number of disturbances. Although the relationship remains significant, its strength has diminished compared to the initial assessment, hinting at an improvement in balance efficiency following the intervention.
The relationship between the Dynamic Gait Index (DGI) and the Balance Beam test time at the final assessment (
Table 8) displays a weak negative correlation, with a Pearson coefficient of -0.156 (p = 0.108). This result suggests that the inverse correlation observed between these variables is less pronounced during the final evaluation, with the lack of statistical significance at the p < 0.05 level indicating that higher DGI scores do not strongly correlate with a reduction in the time required to complete the Balance Beam test in this scenario.
Examining the correlation between the Dynamic Gait Index (DGI) and the number of disturbances in the Balance Beam test at the final assessment (
Table 8) reveals a very weak negative correlation, represented by a Pearson coefficient of -0.093 (p = 0.340). This weak association, which is not statistically significant, suggests that there is no strong or meaningful relationship between DGI scores and the number of disturbances encountered during the Balance Beam test in the final evaluation, indicating a lack of interdependence between these variables in the post-intervention context.
4. Discussions
Our study demonstrated significant improvements in balance and motor control in patients diagnosed with benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) following the application of an integrated vestibular rehabilitation program. The average time required to complete the Balance Beam test decreased considerably from the initial to the final assessment, indicating a clear enhancement in the dynamic balance of the participants. Additionally, the number of disturbances during the test significantly decreased, suggesting increased stability post-intervention. These results are further supported by the increase in Dynamic Gait Index (DGI) scores, reflecting an improvement in motor control and the ability to perform complex balance tasks while in motion. These findings emphasize the potential for targeted interventions to improve specific aspects of motor function, reinforcing the need for a tailored approach to rehabilitation. Therefore, these findings underscore the effectiveness of the integrated vestibular rehabilitation program in alleviating symptoms and restoring motor and proprioceptive function in patients with BPPV.
The correlation analysis between the Balance Beam test and the number of disturbances reveals a strong and statistically significant relationship. This suggests that as the time needed to complete the test increases, so does the number of disturbances. This expected relationship indicates that measurements were accurately conducted and are consistent with the anticipated behavior of patients, highlighting the validity of the applied tests. Such insights are crucial in clinical settings, where understanding these correlations can inform the design of more effective rehabilitation programs. For instance, interventions could be adapted based on these findings to include additional stability and balance exercises for patients who demonstrate greater difficulties.
Our study’s findings align with existing literature on the benefits of vestibular rehabilitation in patients with BPPV. Similar to the improvements reported by Herdman et al. (2007) [
11] and Chang et al. (2008) [
10], we observed significant enhancements in balance and motor control, as evidenced by improved DGI scores and reduced balance disturbances during the Balance Beam test.
The outcomes of our study are consistent with those reported by Badke et al. (2004), who found that integrating vestibular rehabilitation with proprioceptive training significantly reduces dizziness and improves balance metrics in BPPV patients [
9]. Additionally, Herdman et al. (2007) confirmed the utility of the DGI in monitoring balance improvements, supporting the relevance of our findings [
8].
While our study showed significant improvements across all metrics, the degree of change in the Balance Beam test was somewhat less pronounced than in the study by Fife et al. (1998). This discrepancy could be attributed to differences in patient populations or rehabilitation protocols [
7].
The findings of our study emphasize the clinical value of integrated vestibular rehabilitation programs for patients with BPPV. The significant improvements in balance and motor control observed in our cohort suggest that such programs should be a cornerstone of treatment strategies for these patients. Moreover, the study revealed slight differences in Balance Beam test performance between men and women. These differences, although not statistically significant for most measurements, might suggest that male and female patients could respond differently to certain aspects of the rehabilitation program. This opens up avenues for further exploration on whether gender-specific adjustments could enhance rehabilitation outcomes. Clinicians should consider incorporating proprioceptive exercises alongside traditional vestibular rehabilitation techniques to optimize patient outcomes. Our study highlights the importance of early and consistent intervention, which can lead to quicker recovery and a reduction in the recurrence of symptoms.
The practical implications of these findings extend beyond just confirming the benefits of vestibular rehabilitation. The observed improvements, particularly in dynamic gait control, suggest that such interventions can significantly reduce the risk of falls, enhance patient independence, and improve overall life quality. Clinicians should be encouraged to integrate these findings into practice, tailoring rehabilitation programs to the individual needs of patients to maximize recovery and minimize the recurrence of symptoms.
Despite the significant contributions of this study, there are several limitations that need to be considered. First, the relatively modest sample size of 107 subjects limits the ability to generalize the results to a broader population. A larger sample size would have allowed not only for more robust statistical analysis but also for greater statistical power, which would have strengthened confidence in the conclusions drawn.
Second, the absence of a control group is another significant limitation. Without a control group that did not receive the applied intervention, it becomes challenging to assess the exclusive impact of the vestibular rehabilitation program compared to other treatment methods or the absence of any intervention. Such a group would have provided a more rigorous framework for evaluating the intervention’s effectiveness.
Additionally, the variable duration of the intervention for each participant, ranging from 8 to 10 weeks, may influence the final outcomes. Although the study was conducted over a total period of 4 years and 6 months, a longer-term monitoring of patients would have allowed for the evaluation of the lasting effects of vestibular rehabilitation and the identification of any symptom recurrences.
Another aspect to consider is the uncontrolled unfavorable factors, such as variations in patient compliance or the presence of comorbidities, which could have influenced the results. Furthermore, the use of a limited set of measurement tools, although appropriate for the study’s objectives, could be considered a limitation, as the inclusion of additional tools would have allowed for a more detailed assessment of the improvements achieved through vestibular rehabilitation.
Building on the findings and limitations of this study, several avenues for future research can be identified. Firstly, expanding the sample size in subsequent studies would be essential to enhance the generalizability of the results. A larger cohort would allow for more nuanced subgroup analyses, potentially uncovering variations in treatment efficacy across different demographics or clinical characteristics.
Secondly, the inclusion of a control group in future studies is crucial. By comparing outcomes between those who receive vestibular rehabilitation and those who do not, or who receive alternative treatments, researchers can more accurately determine the specific impact of the rehabilitation program. Such comparative studies could also help identify the most effective components of the rehabilitation protocol, leading to optimized treatment strategies.
Longitudinal studies with extended follow-up periods are another important direction for future research. While this study provided valuable insights into the short-term benefits of vestibular rehabilitation, understanding the long-term sustainability of these benefits is equally important. Future research should aim to track patients over several years to evaluate the persistence of improvements and the potential for symptom recurrence.
Moreover, exploring the integration of additional measurement tools and outcome indicators could provide a more comprehensive evaluation of vestibular rehabilitation’s effectiveness. Future studies could incorporate advanced imaging techniques, biomechanical assessments, or patient-reported outcome measures (PROMs) to capture a broader range of recovery dimensions, including patient satisfaction and quality of life.
Finally, future research should also consider the role of individualized treatment plans tailored to specific patient needs. Investigating the effectiveness of personalized rehabilitation protocols, perhaps based on initial patient assessments or predictive analytics, could lead to more effective and efficient rehabilitation outcomes.
5. Conclusions
At the initial assessment, the correlations between the analyzed tests were stronger and statistically significant, indicating clear relationships between balance performance and DGI scores. However, at the final assessment, these correlations weakened and, in most cases, were not statistically significant, suggesting that the rehabilitation intervention led to a more individualized improvement in participants’ performance and balance. This could imply that the rehabilitation program was effective in addressing the specific needs of each patient, leading to a decoupling of previously correlated variables.
These results highlight the effectiveness of the vestibular rehabilitation program in improving balance and motor control in patients with BPPV, regardless of gender. The findings suggest that both men and women responded similarly to the intervention, with no significant differences in treatment outcomes. This underscores the potential of vestibular rehabilitation to provide equitable benefits across different patient groups.
The practical implications of this study are significant for clinical practice. The reduction in the correlation between variables at the final assessment suggests that patients may experience more tailored improvements, which could enhance their overall recovery process. These findings support the continued use and further development of vestibular rehabilitation programs in treating BPPV, with the potential to improve patient outcomes and reduce the risk of symptom recurrence.
While the study offers valuable insights, it is important to consider the limitations, such as the relatively small sample size and the absence of a control group. Future research with larger, more diverse populations and controlled study designs will be essential to validate these findings and explore the long-term effects of vestibular rehabilitation.
In conclusion, this study contributes to the growing body of evidence supporting vestibular rehabilitation as a crucial intervention for patients with BPPV. By tailoring treatment to individual patient needs, clinicians can optimize recovery and enhance the quality of life for those affected by this condition.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: Patricia-Maria Crișan-Mălăncrăvean, Gheorghe Mühlfay and Klara Brînzaniuc; Methodology, Patricia-Maria Crișan-Mălăncrăvean, Gheorghe Mühlfay and Klara Brînzaniuc; Software, Patricia-Maria Crișan-Mălăncrăvean; Validation, Gheorghe Mühlfay and Klara Brînzaniuc;Formal analysis, X.X.; Investigation: Patricia-Maria Crișan-Mălăncrăvean; Resources, Patricia-Maria Crișan-Mălăncrăvean; Data curation, Patricia-Maria Crișan-Mălăncrăvean; Writing—original draft preparation: Patricia-Maria Crișan-Mălăncrăvean;Writing—review and editing, Gheorghe Mühlfay and Klara Brînzaniuc; Visualization: Gheorghe Mühlfay and Klara Brînzaniuc; Supervision: Gheorghe Mühlfay and Klara Brînzaniuc; Project administration, Patricia-Maria Crișan-Mălăncrăvean; Funding acquisition, This project was carried out without financial assistance from any organization or institution. “All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.”
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Informed Consent Statement
“Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.”
Conflicts of Interest
“The authors declare no conflicts of interest.”
Appendix A
| Nr.Crt. |
Initiale name and surename |
Gender |
Age |
Athlete (YES/NO) |
Systematic Physical Activity (NO/YES) |
Occupation (Static or Dynamic Work Environment) |
INITIAL |
FINAL |
| BALANCE BEAM TEST (no. disturbances) |
BALANCE BEAM TEST (seconds) |
DGI stages 3,4,5,6 and 7 (points) |
BALANCE BEAM TEST (no. disturbances) |
BALANCE BEAM TEST (seconds) |
DGI stages 3,4,5,6 and 7 (points) |
| 1. |
O.M |
M |
57 |
NO |
NO |
STATIC |
5 |
12 |
6 |
1 |
12 |
15 |
| 2. |
A.C |
M |
38 |
NO |
YES |
STATIC |
0 |
7 |
12 |
0 |
7 |
15 |
| 3. |
N.C |
M |
30 |
NO |
YES |
STATIC |
3 |
8 |
7 |
0 |
8 |
15 |
| 4. |
V.L |
M |
40 |
NO |
NO |
DYNAMIC |
3 |
8 |
9 |
0 |
8 |
15 |
| 5. |
D.M |
F |
43 |
NO |
YES |
DYNAMIC |
1 |
10 |
9 |
0 |
10 |
15 |
| 6. |
R.H |
M |
50 |
NO |
NO |
STATIC |
0 |
9 |
8 |
0 |
9 |
15 |
| 7. |
M.T |
F |
31 |
NO |
YES |
DYNAMIC |
5 |
7 |
5 |
0 |
7 |
15 |
| 8. |
D.I |
F |
53 |
NO |
NO |
STATIC |
3 |
11 |
6 |
0 |
11 |
14 |
| 9. |
M.R |
F |
22 |
YES |
YES |
DYNAMIC |
0 |
6 |
11 |
0 |
6 |
15 |
| 10. |
B.C |
F |
44 |
NO |
YES |
STATIC |
3 |
9 |
5 |
1 |
9 |
15 |
| 11. |
I.S |
M |
43 |
NO |
NO |
STATIC |
5 |
10 |
7 |
0 |
10 |
15 |
| 12. |
C.M |
F |
58 |
NO |
NO |
DYNAMIC |
5 |
11 |
8 |
0 |
11 |
15 |
| 13. |
H.D |
F |
51 |
NO |
YES |
STATIC |
4 |
11 |
7 |
1 |
11 |
15 |
| 14. |
P.M |
F |
45 |
NO |
YES |
STATIC |
1 |
9 |
6 |
0 |
9 |
15 |
| 15. |
D.A |
M |
71 |
NO |
NO |
STATIC |
5 |
11 |
6 |
2 |
11 |
15 |
| 16. |
S.R |
M |
49 |
NO |
NO |
DYNAMIC |
1 |
10 |
8 |
1 |
10 |
15 |
| 17. |
K.R |
F |
32 |
NO |
YES |
STATIC |
2 |
10 |
10 |
0 |
10 |
15 |
| 18. |
A.I |
F |
38 |
NO |
YES |
STATIC |
3 |
9 |
11 |
0 |
9 |
15 |
| 19. |
F.C |
M |
41 |
NO |
YES |
DYNAMIC |
2 |
8 |
8 |
0 |
8 |
15 |
| 20. |
P.M |
M |
56 |
NO |
YES |
STATIC |
3 |
11 |
6 |
0 |
11 |
14 |
| 21. |
S.C |
M |
68 |
NO |
NO |
STATIC |
1 |
10 |
8 |
1 |
10 |
15 |
| 22. |
K.J |
F |
37 |
NO |
YES |
DYNAMIC |
0 |
9 |
12 |
0 |
9 |
15 |
| 23. |
R.F |
M |
33 |
NO |
YES |
DYNAMIC |
3 |
10 |
12 |
0 |
10 |
15 |
| 24. |
D.A |
M |
42 |
NO |
NO |
STATIC |
3 |
8 |
10 |
1 |
8 |
15 |
| 25. |
U.T |
F |
54 |
NO |
NO |
STATIC |
3 |
9 |
7 |
1 |
9 |
15 |
| 26. |
D.E |
F |
70 |
NO |
NO |
STATIC |
4 |
10 |
5 |
1 |
10 |
14 |
| 27. |
A.B |
M |
58 |
NO |
NO |
DYNAMIC |
4 |
9 |
6 |
0 |
9 |
15 |
| 28. |
M.G |
F |
46 |
NO |
NO |
STATIC |
4 |
10 |
8 |
1 |
10 |
15 |
| 29. |
H.M |
M |
39 |
NO |
YES |
STATIC |
2 |
10 |
8 |
0 |
10 |
15 |
| 30. |
P.R |
M |
40 |
NO |
NO |
DYNAMIC |
0 |
8 |
11 |
0 |
8 |
15 |
| 31. |
S.R |
M |
23 |
YES |
YES |
DYNAMIC |
0 |
7 |
12 |
0 |
7 |
15 |
| 32. |
M.A |
F |
62 |
NO |
NO |
STATIC |
6 |
9 |
7 |
2 |
9 |
14 |
| 33. |
P.P |
F |
30 |
NO |
YES |
STATIC |
2 |
9 |
12 |
0 |
9 |
15 |
| 34. |
M.C |
M |
47 |
NO |
YES |
STATIC |
3 |
10 |
12 |
0 |
10 |
15 |
| 35. |
F.R |
F |
59 |
NO |
YES |
STATIC |
5 |
11 |
8 |
0 |
11 |
15 |
| 36. |
W.J |
M |
56 |
NO |
NO |
STATIC |
1 |
10 |
9 |
1 |
10 |
15 |
| 37. |
P.T |
F |
42 |
NO |
YES |
DYNAMIC |
3 |
10 |
10 |
1 |
10 |
15 |
| 38. |
B.S |
F |
30 |
NO |
NO |
DYNAMIC |
1 |
9 |
11 |
0 |
9 |
15 |
| 39. |
P.L |
F |
34 |
NO |
YES |
STATIC |
2 |
9 |
11 |
0 |
9 |
15 |
| 40. |
A.D |
F |
56 |
NO |
YES |
STATIC |
2 |
12 |
6 |
0 |
12 |
15 |
| 41. |
L.T |
F |
53 |
NO |
NO |
STATIC |
1 |
9 |
11 |
1 |
9 |
15 |
| 42. |
T.S |
M |
66 |
NO |
NO |
STATIC |
3 |
11 |
7 |
1 |
11 |
15 |
| 43. |
V.A |
F |
50 |
NO |
NO |
DYNAMIC |
2 |
10 |
10 |
0 |
10 |
15 |
| 44. |
O.R |
F |
37 |
NO |
YES |
DYNAMIC |
2 |
9 |
10 |
0 |
9 |
15 |
| 45. |
N.M |
M |
74 |
NO |
YES |
STATIC |
5 |
12 |
7 |
2 |
12 |
14 |
| 46. |
M.D |
M |
60 |
NO |
NO |
DYNAMIC |
3 |
11 |
11 |
0 |
11 |
15 |
| 47. |
G.C |
F |
33 |
NO |
YES |
STATIC |
4 |
10 |
12 |
2 |
10 |
15 |
| 48. |
M.L |
F |
51 |
NO |
YES |
STATIC |
3 |
11 |
9 |
1 |
11 |
15 |
| 49. |
A.S |
M |
62 |
NO |
NO |
STATIC |
4 |
11 |
7 |
1 |
11 |
14 |
| 50. |
P.N |
F |
48 |
NO |
YES |
DYNAMIC |
1 |
9 |
11 |
0 |
9 |
15 |
| 51. |
T.L |
F |
69 |
NO |
NO |
STATIC |
3 |
11 |
9 |
0 |
11 |
15 |
| 52. |
G.V |
M |
48 |
NO |
YES |
STATIC |
3 |
7 |
8 |
1 |
7 |
15 |
| 53. |
M.M |
F |
52 |
NO |
YES |
STATIC |
2 |
11 |
8 |
1 |
11 |
15 |
| 54. |
T.F |
F |
64 |
NO |
NO |
STATIC |
1 |
10 |
10 |
0 |
10 |
10 |
| 55. |
P.S |
F |
57 |
NO |
NO |
STATIC |
5 |
9 |
7 |
0 |
9 |
15 |
| 56. |
G.A |
F |
66 |
NO |
YES |
STATIC |
2 |
10 |
10 |
1 |
10 |
15 |
| 57. |
A.A |
F |
43 |
NO |
YES |
DYNAMIC |
3 |
9 |
6 |
1 |
9 |
15 |
| 58. |
P.K |
M |
50 |
NO |
YES |
STATIC |
4 |
10 |
8 |
1 |
10 |
15 |
| 59. |
O.M |
F |
51 |
NO |
NO |
STATIC |
3 |
10 |
12 |
0 |
10 |
15 |
| 60. |
S.V |
F |
48 |
NO |
YES |
DYNAMIC |
3 |
11 |
12 |
0 |
11 |
15 |
| 61. |
D.O |
M |
55 |
NO |
YES |
STATIC |
0 |
8 |
11 |
0 |
8 |
14 |
| 62. |
I.S |
M |
33 |
NO |
YES |
DYNAMIC |
5 |
8 |
11 |
1 |
8 |
15 |
| 63. |
B.S |
F |
24 |
YES |
YES |
DYNAMIC |
1 |
7 |
11 |
0 |
7 |
15 |
| 64. |
A.M |
F |
40 |
NO |
NO |
STATIC |
2 |
11 |
10 |
0 |
11 |
15 |
| 65. |
V.O |
M |
38 |
NO |
YES |
DYNAMIC |
2 |
8 |
11 |
0 |
8 |
15 |
| 66. |
C.D |
F |
36 |
NO |
NO |
DYNAMIC |
4 |
10 |
11 |
1 |
10 |
15 |
| 67. |
M.D |
F |
32 |
NO |
NO |
STATIC |
2 |
10 |
11 |
0 |
10 |
15 |
| 68. |
A.D |
M |
29 |
NO |
YES |
STATIC |
0 |
8 |
11 |
0 |
8 |
15 |
| 69. |
F.R |
M |
55 |
NO |
NO |
DYNAMIC |
5 |
11 |
11 |
1 |
11 |
15 |
| 70. |
D.I |
M |
63 |
NO |
NO |
STATIC |
4 |
11 |
9 |
2 |
11 |
14 |
| 71. |
P.M |
F |
56 |
NO |
NO |
STATIC |
2 |
11 |
12 |
0 |
11 |
15 |
| 72. |
S.B |
M |
35 |
NO |
YES |
STATIC |
0 |
9 |
11 |
0 |
9 |
15 |
| 73. |
S.Z |
M |
27 |
NO |
YES |
DYNAMIC |
2 |
9 |
8 |
1 |
9 |
15 |
| 74. |
C.R |
M |
30 |
NO |
YES |
DYNAMIC |
1 |
10 |
12 |
1 |
10 |
15 |
| 75. |
H.D |
M |
72 |
NO |
NO |
STATIC |
4 |
11 |
8 |
1 |
11 |
14 |
| 76. |
P.N |
F |
47 |
NO |
NO |
STATIC |
3 |
10 |
7 |
2 |
10 |
15 |
| 77. |
P.D |
F |
38 |
NO |
YES |
STATIC |
2 |
9 |
12 |
0 |
9 |
15 |
| 78. |
K.H |
F |
43 |
NO |
YES |
STATIC |
5 |
9 |
8 |
0 |
9 |
15 |
| 79. |
S.B |
F |
51 |
NO |
NO |
STATIC |
3 |
11 |
7 |
0 |
11 |
15 |
| 80. |
R.G |
F |
49 |
NO |
NO |
DYNAMIC |
2 |
10 |
9 |
0 |
10 |
15 |
| 81. |
S.C |
F |
55 |
NO |
YES |
DYNAMIC |
2 |
12 |
9 |
1 |
12 |
15 |
| 82. |
B.C |
F |
56 |
NO |
YES |
STATIC |
3 |
11 |
10 |
2 |
11 |
15 |
| 83. |
B.A |
M |
34 |
NO |
YES |
DYNAMIC |
1 |
8 |
11 |
0 |
8 |
15 |
| 84. |
M.C |
F |
45 |
NO |
NO |
STATIC |
5 |
11 |
6 |
2 |
11 |
14 |
| 85. |
H.M |
F |
50 |
NO |
YES |
STATIC |
2 |
12 |
9 |
0 |
12 |
15 |
| 86. |
C.MA |
F |
58 |
NO |
YES |
STATIC |
2 |
10 |
8 |
0 |
10 |
15 |
| 87. |
O.I |
F |
44 |
NO |
YES |
STATIC |
3 |
10 |
10 |
1 |
10 |
15 |
| 88. |
P.E |
F |
60 |
NO |
NO |
STATIC |
2 |
8 |
10 |
1 |
8 |
15 |
| 89. |
G.B |
M |
48 |
NO |
NO |
DYNAMIC |
1 |
9 |
10 |
0 |
9 |
15 |
| 90. |
T.V |
M |
59 |
NO |
NO |
STATIC |
3 |
10 |
11 |
0 |
10 |
15 |
| 91. |
B.D |
M |
42 |
NO |
YES |
STATIC |
3 |
9 |
10 |
1 |
9 |
15 |
| 92. |
P.T |
M |
31 |
NO |
NO |
DYNAMIC |
1 |
9 |
11 |
0 |
9 |
15 |
| 93. |
D.P |
F |
56 |
NO |
NO |
DYNAMIC |
1 |
10 |
9 |
0 |
10 |
15 |
| 94. |
K.E |
F |
44 |
NO |
NO |
DYNAMIC |
3 |
9 |
11 |
0 |
9 |
15 |
| 95. |
R.A |
F |
46 |
NO |
YES |
DYNAMIC |
2 |
10 |
11 |
0 |
10 |
15 |
| 96. |
N.C |
F |
52 |
NO |
NO |
STATIC |
3 |
10 |
8 |
1 |
10 |
15 |
| 97. |
G.I |
F |
31 |
NO |
NO |
STATIC |
3 |
8 |
9 |
0 |
8 |
15 |
| 98. |
H.S |
M |
46 |
NO |
YES |
DYNAMIC |
4 |
10 |
10 |
1 |
10 |
15 |
| 99. |
U.M |
F |
53 |
NO |
NO |
STATIC |
2 |
11 |
11 |
1 |
11 |
15 |
| 100. |
P.C |
F |
63 |
NO |
NO |
STATIC |
4 |
10 |
5 |
1 |
10 |
15 |
| 101. |
P.F |
F |
23 |
YES |
YES |
DYNAMIC |
3 |
7 |
12 |
0 |
7 |
15 |
| 102. |
Z.V |
M |
31 |
NO |
YES |
STATIC |
0 |
9 |
9 |
0 |
9 |
15 |
| 103. |
T.S |
M |
46 |
NO |
NO |
DYNAMIC |
1 |
10 |
9 |
0 |
10 |
15 |
| 104. |
S.S |
F |
48 |
NO |
NO |
STATIC |
4 |
11 |
12 |
0 |
11 |
15 |
| 105. |
I.G |
F |
70 |
NO |
YES |
STATIC |
5 |
11 |
10 |
0 |
11 |
14 |
| 106. |
D.S |
M |
33 |
NO |
YES |
STATIC |
1 |
8 |
12 |
0 |
8 |
15 |
| 107. |
M.A |
M |
30 |
NO |
YES |
DYNAMIC |
2 |
8 |
11 |
0 |
8 |
15 |
References
- Proske, U.; Gandevia, S.C. The proprioceptive senses: Their roles in signaling body shape, body position and movement, and muscle force. Physiol. Rev. 2012, 92, 1651–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelaki, D.E.; Cullen, K.E. Vestibular System: The Many Facets of a Multimodal Sense. Annual Review of Neuroscience. 2008, 31, 125–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shumway-Cook, A.; Woollacott, M. Motor Control: Translating Research into Clinical Practice, 5th ed.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2017; pp. 125–138. [Google Scholar]
- Lempert, T.; Neuhauser, H. Epidemiology of vertigo, migraine and vestibular migraine. Journal of Neurology 2009, 256, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharyya, N.; Gubbels, S.P.; Schwartz, S.R.; Edlow, J.A.; et al. Clinical practice guideline: Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (update) executive summery. Otolaryngol - Head Neck Surg. 2017, 156, S1–S47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herdman, S.J.; Hall, C.D.; Schubert, M.C.; Das, V.E.; Tusa, R.J. Recovery of dynamic visual acuity in bilateral vestibular hypofunction. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2007, 88, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fife, T.D.; Iverson, D.J.; Lempert, T.; Furman, J.M.; Baloh, R.W.; Tusa, R.J.; Hain, T.C.; Herdman, S.; Morrow, M.J.; Gronseth, G.S. Practice parameter: Therapies for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (an evidence-based review): Report of the quality standards subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 2008, 70, 2067–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herdman, S.J.; Clendaniel, R.A.; Mattox, D.E.; Tusa, R.J.; Herdman, N.T. Vestibular Rehabilitation Therapy for Patients With Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo. Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery 2007, 137, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badke, M.B.; Shea, T.A.; Miedaner, J.A.; Grove, C.R. Outcomes after rehabilitation for adults with balance dysfunction. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2004, 85, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, W.-C.; Yang, Y.-W.; Hsu, L.-C.; Chern, C.-M.; Wang, R.-Y. Balance improvement in patients with benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Clin. Rehabil. 2008, 22, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herdman, S.J.; Hall, C.D.; Schubert, M.C.; Das, V.E.; Tusa, R.J. Recovery of dynamic visual acuity in bilateral vestibular hypofunction. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2007, 88, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).