1. Introduction
Nowadays, the major challenges affecting the worldwide are the global warming and the climate change caused by the rise of global population, and the massive exploration and use of fossil fuels. The energy sector is the main contributor to global warming, accounting for exceeding two-thirds of universal greenhouse gas emissions. The reduction of GHG emissions from power sector through rising the share of green and renewable energy resources is regarded as efficient solution to cope with the effects of the climate warming. Nevertheless, the irregularity of renewable energy slows down the full carbon depletion of the energy sector. Storing energy is viewed as a vital solution to rise the deployment of renewable energy through storing the energy during the high supply period and reuse it during the high demand period. Storing the energy in Li-ion battery is a good option since it has high energy efficiency and can utilize existing charging infrastructure, however, energy density is low and it has a limited charging rate, rending it unfeasible for large applications. Recently, hydrogen got more attention as a promising sustainable and carbon-neutral energy supply. Hydrogen has attractive advantages such as energy supply with high energy density up to 140 MJ/kg, compared to hydrocarbon fuels with an energy density of 50 MJ/kg. In addition, hydrogen has high charging rate, making it practical to be used in large applications. Many renewable and non-renewable energy resources could be used to generate hydrogen like fossil fuels, biomass, biological sources, and water electrolysis.
The hydrogen derived from water by using energy generated from renewable resources is known as green hydrogen. The use of green hydrogen to stock the surplus of energy generated from renewable energy sources in order to use it at peak period, is deemed as an efficient technology thanks to its numerous benefits. Besides its potential to be used as energy storage, it is a sustainable and clean fuel with zero emissions, it can be used as fuel cells to generate electricity, it has high calorific combustion value, and it is able to fight against global warming since it can substitute the fossil fuels. The water electrolysis is used to produce green hydrogen by decomposing the water into hydrogen and oxygen. The operating principle of electrolysis is fundamentally similar, while electrolysers are differentiated by the kind of electrolyte materials and the working temperature. The electrolyser is categorized into two categories: low temperature electrolyser, and high temperature electrolyser. The low temperature electrolysers are commercially available and involve proton exchange membrane (PEM), alkaline electrolysis, and anion exchange membrane (AEM). Proton exchange membrane (PEM) and alkaline water electrolysis are the technologies that are only commercially available [
1]. However, the high temperature electrolysers are still under research and development phase. The technology of AEMWE is mature and cheaper, while it has many issues related to the slow start-up, several components, corrosion, and a difficult maintenance.
PEM electrolyser has lately earned traction and popularity owing to its various advantages in comparison to the conventional alkaline water electrolysers. It is safer, with a great reliability, high hydrogen purity, lower power usage, and operability at high current density [
2,
3]. Also, PEM water electrolysis is distinguished by a capability to fast accelerate and decelerate, and a large working range of 0-100%, contributing to be a functional solution to deal with the irregularity issues of renewable energy resources. Also, PEM water electrolysis is convenient for off-grid, it is powerful, compact, with reduced maintenance, and it is appropriate for small to medium industrial applications. Whilst the cost of PEM electrolsyer is higher compared to alkaline owing to the utilization of noble metals, such as Pt/Pd, as electrocatalysts. In addition, the large amount of water and its purification, demanded to run PEM water electrolysis, rises its capital cost. Also, PEM electrolsyer experiences difficulties in terms of acidic environment and low endurance. The cost of PEM electrolyser is accounted mainly by the cost of bipolar plate with 48%. Recently, several studies are performed to boost the performance and lower the price of PEM electrolysis by finding a replacement bipolar plates, catalyst, and PEM based membrane electrode. Fundamentally, there are two methods to minimize the cost of PEMWE, with keeping a high performance. Replacing expensive stack materials, like Ir and Ti, is one of the options to minimize the cost of PEMWE, but it affects the endurance and the efficiency of PEMWE. The second option, which is more realistic than the first one, is based on operating the electrolyser under convenient circumstances to achieve a high rate of H
2 generation. The following operation approaches are essential for a performance improvement:
- Rising current density to increase hydrogen generation rates.
- Rising working temperature to improve cell performance.
- Rising hydrogen output pressure to prevent the need of mechanical compressions and thus minimizing cost and improving efficiency of the system.
[
4] examined and studied the lifespan, capital cost and efficiency of PEMWE. Findings pointed out that a transference from alkaline electrolysis membrane (AEM) to PEMWE will happen by 2030 owing to its various benefits when it comes to coupling with renewable energy resources. Besides, a reduction of the investment cost has already recorded by 2020 compared to 2016, and the reduction of price with the larger functional flexibility would achieve a commercial profit by 2030.
The current paper aims at presenting a review on PEM water electrolyser (PEMWE). The efficiency of PEMWE and the different conceptual and functional factors affecting its performance are extensively discussed and presented in this paper. In addition, the recent developed technologies to enhance the efficiency of PEMWE are highlighted. This study might support researchers to enhance the efficiency of PEM through rising the amount of hydrogen generated and the safety and lowering the price of hydrogen production
2. Background of PEM Water Electrolysis
The PEM was initially launched in 1960s by General Electric for fuel cell usage and then for electrolyser usage [
5]. In 1987, the first PEMWE was implemented by a metallurgical company (Stellram) in Nyon, Switzerland, that was intended to supply 20Nm
3 h
-1 of hydrogen at a pressure of 1-2 bars. Currently, the PEMWE is used in many sectors like hydrogen generation, hydrogen welding, pure substance generation utilized in pure metals, electronic industry, and metallurgy of alloys.
2.1. Operating Principle of PEMWE
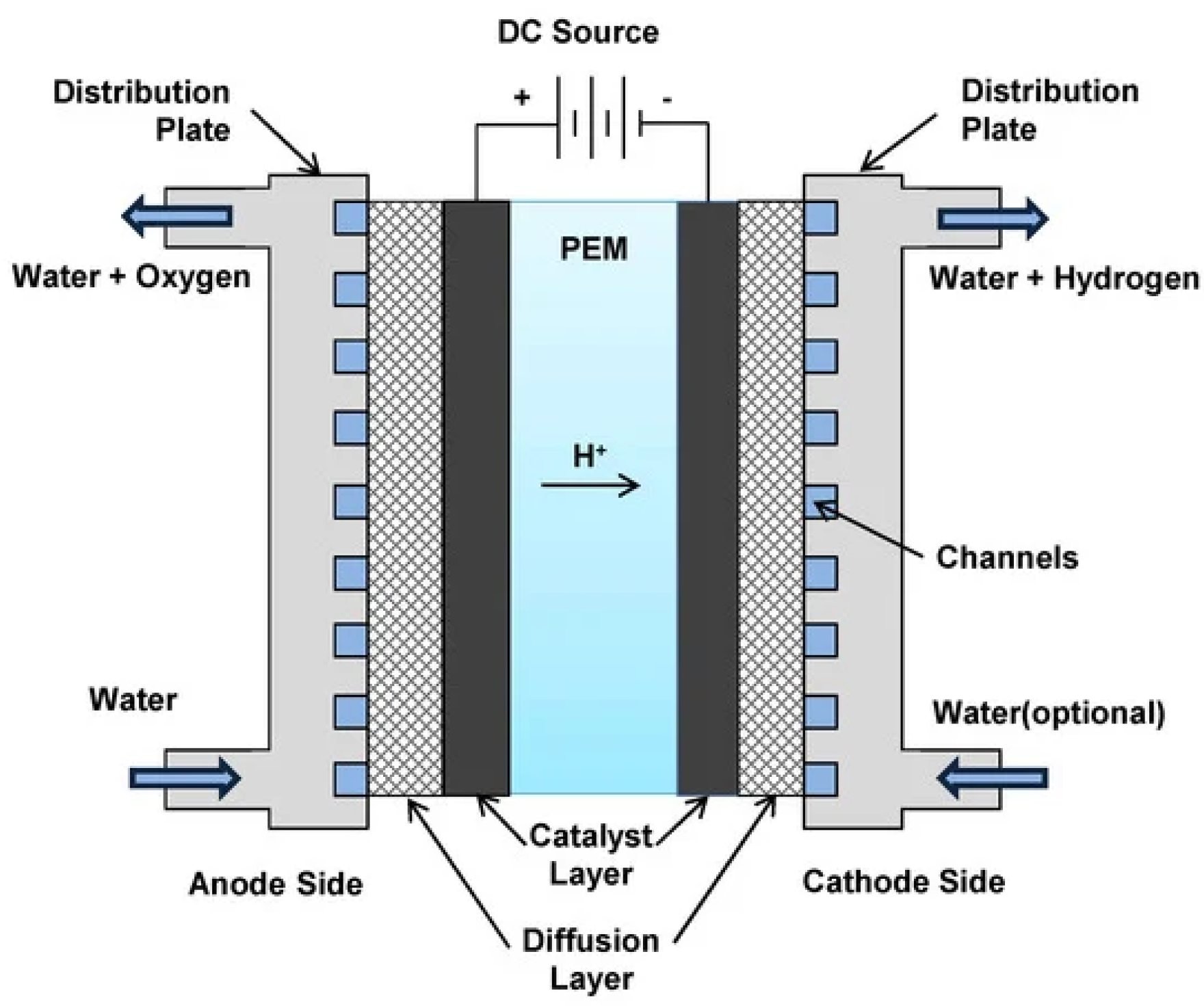
The main components of PEMWE are membrane electrode assembly (MEA), compression plate, gas diffusion layer (GDL), anode and cathode chambers, and bipolar plates (BPP). The compression plate is formed from aluminum alloy and employed to fix the whole electrolysis cell. The MEA comprises of a proton-conducting layer coated with porous electrocatalyst layers on both the anode and cathode areas which present the essential component of the electrolyzer, in which water is broken down into gaseous hydrogen and oxygen by electric current. The bipolar plates (BBP) are flat separator plates, and used to conduct electric current between cells, spread equally air and fuel gas, eliminate heat from the active region, and avoid seepage of gases and coolant. The gas diffusion layer (GDL), is known also as current collector PTL, is an electronic conductor between BPP and MEA. It is used to maintain an efficient mass transfer of gases and liquids between the BPP and the electrodes.
The working principle of PEMWE is based on applying an external supply of energy (minimum potential of 1.23 V) through the electrochemical cell to kickoff electrochemical reactions at the cathode and anode electrodes (Figure. 1). In order to accelerate the reaction, catalysts should be utilized. The catalysts utilized are primarily few noble metals, namely platinum and iridium. The procedure commences by injecting water at the anode, and then the water molecules are decomposed into protons (H+), oxygen, and electrons (e-) at the anode by dint of the electric field and catalyst. The water is transmitted from the path of the BPP to the catalyst coat on the layer through the current collector. After that, the protons stir to the cathode area through the MEA, which permits only protons to spout. At the cathode side, an external power is used to incorporate the protons with the electrons aiming to compose hydrogen gas molecules. Electrons come from the catalyst coat on the anode region and permeate the current collector and BPP to reach the cathode region. The overall reaction, the anode and the cathode reactions are presented below:
Figure 1.
Visual representation of PEMWE [
6].
Figure 1.
Visual representation of PEMWE [
6].
Anode reaction (oxidation):
Cathode reaction (oxidation):
The use of noble metals, namely IrO2/RuO2 in the oxygen evolution reaction (OER) at the anode, and Pt/Pd in the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) at the cathode, are the main drawbacks of PEMWE. The hydrogen and the oxygen molecules are not able to be merged owing to the impenetrability of the layer to oxygen and hydrogen molecules. Nevertheless, water is flowed with proton through the layer and this situation is named electro-osmotic drag. The efficiency of PEMWE and the yield of hydrogen generation depends on membrane, temperature, pressure, cell voltage, and current density. Additionally, membrane hydration is a critical factor affecting the PEMWE. For an efficient proton conductivity and a higher cell’s efficiency, the membrane should maintain hydrated. Thus an efficient water management and a proper pressure and temperature management should be considered in order to avoid dehydration of the membrane.
2.2. Types of Electrolyser Performance
The component of electrolyzer efficiency comprises three efficiencies named hydrogen generation efficiency, Faradaic efficiency, and the effort needed to compress the output hydrogen gas.
Hydrogen generation efficiency
The process of decomposing water into hydrogen and oxygen in the electrolysis process requires energy. The magnitude of needed energy is assessed by the enthalpy change
(ΔH) which is the combination of Gibbs free energy (
ΔG) and heat energy. Gibbs free energy is utilized to estimate the least needed decomposition voltage to operate the electrochemical reaction given that it matches the demanded energy to made water molecule using gases of oxygen and hydrogen. The evaluation of Gibbs free energy under standard environment is performed by:
where
N is the number of involved electrons,
F is the Faraday’s constant (96500 C.mol
-1), and
Vreversible is the reversible voltage and it is described as the least demanded voltage to breakdown the water into oxygen, and hydrogen, and it is equivalent to 1.23 V [
7,
8].
The entropy
TΔS presents the heat energy. The enthalpy variation is 85.84 kJmol-1 at standard circumstances. consequently, the thermal-neutral voltage, which is the lowest demanded voltage, for the electrolysis might evaluated by [
9]:
The used potential must transcend the reversible voltage to promote the charge transmission in the MEA of an electrolyzer, considering there is a proportional relation between the current density and the rate of hydrogen generation. The estimation of hydrogen generation efficiency is performed using the output of electrical energy transformed to chemical energy. Consequently, the estimation of hydrogen generation performance is performed by the higher heating value of hydrogen. The calculation of hydrogen efficiency is performed by dividing the thermo-neutral voltage (V
TN) by the measured cell voltage (V
cell) [
1]:
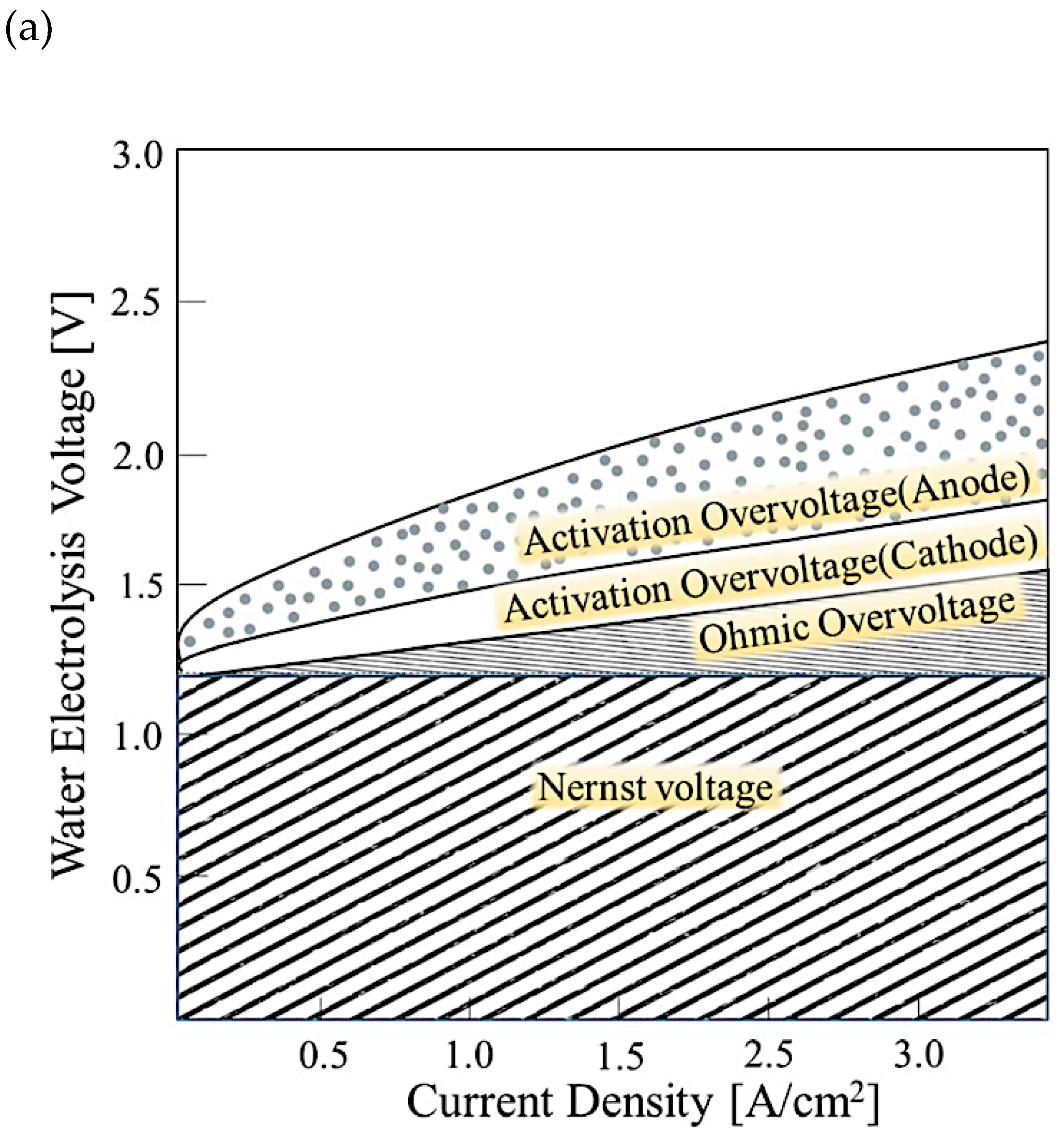
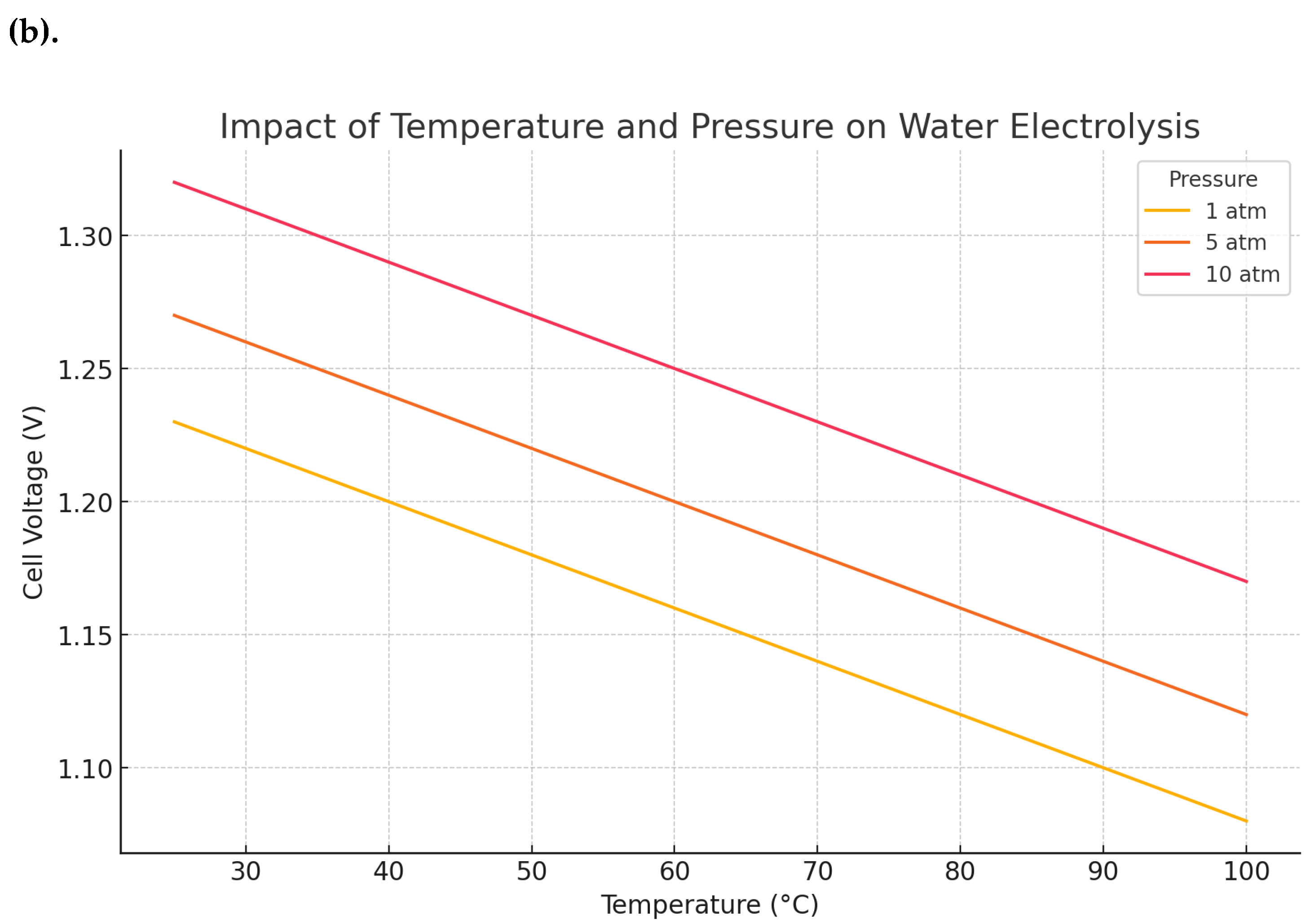
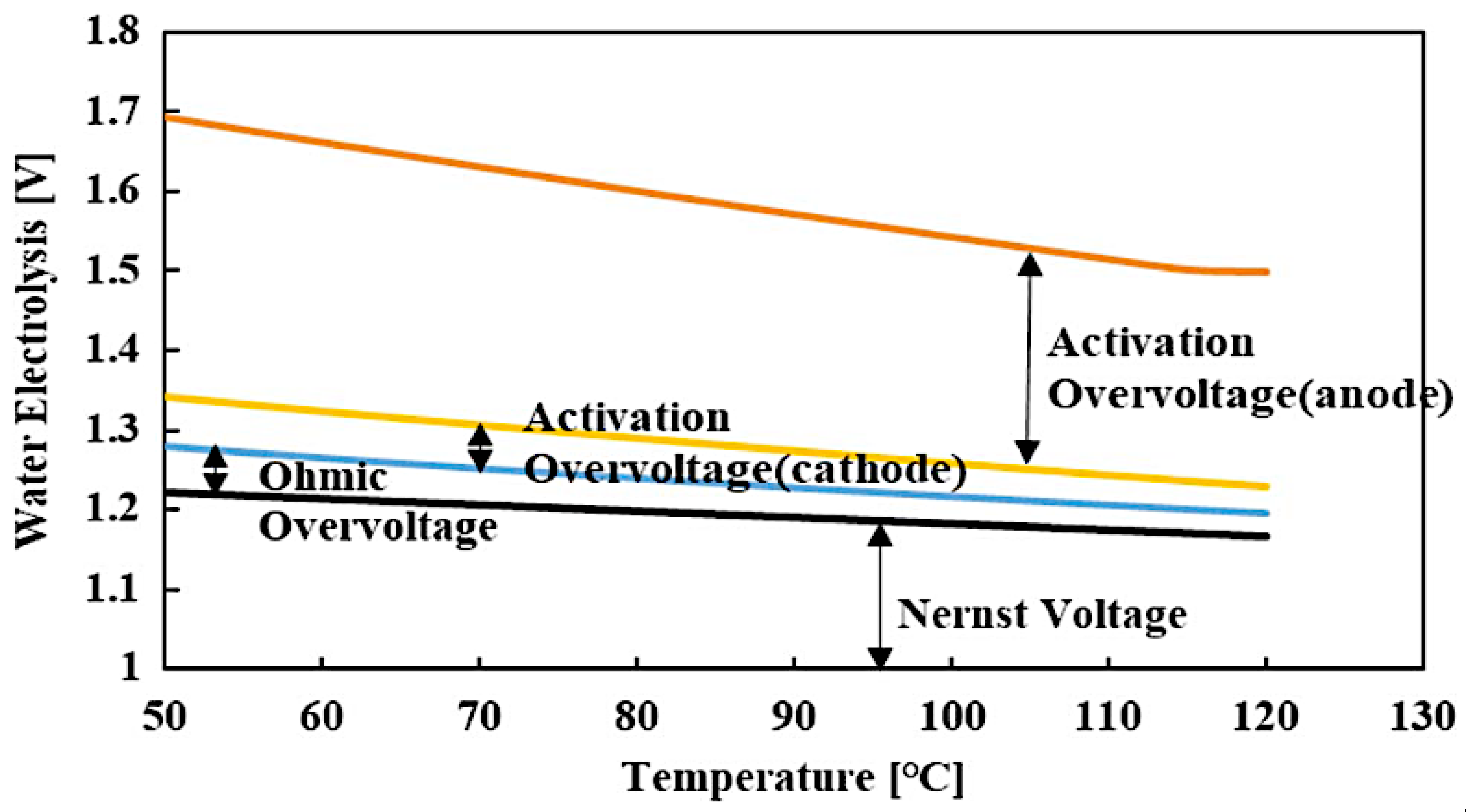
The cell voltage relies on pressure, temperature, and current density, and it encompasses four elements: the reversible cell voltage (the Nernst voltage), the oxygen evolution reaction (OER) charge transfer overpotential at anode, the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) charge transfer overpotential at cathode, and the overall ohmic potential drop in the cell (Figure. 2a). The difference within the experimental observed potential and the value estimated thermodynamically is called overpotential, and it encompasses all the electrical and catalytic losses. The ion transport resistance in the layer beside the catalyst activation control the overpotential cell voltage. The impact of pressure and temperature on the voltage of water electrolysis is displayed in Figure (2b). The rise of temperature increases the reaction kinetic and thus minimize the required voltage. However, the rise of pressure increases the required voltage, but it improves gas management, which is beneficial for the overall efficiency.
Figure 2.
a) I-V characteristic curves of the constituents of the water electrolysis [
10], (b) Impact of temperature and pressure on water electrolysis
.
Figure 2.
a) I-V characteristic curves of the constituents of the water electrolysis [
10], (b) Impact of temperature and pressure on water electrolysis
.
The cell voltage is estimated by [
11]:
where Ri (Ω.cm2) is the surface resistance of the ith cell element (including ionic and electronic conduction), ηH2 (in V) is the absolute value of HER overpotential, and ηO2 (in V) is the OER overpotential. This correlation might be utilized for any value of current density.
Faradaic efficiency
Actually, there is a mismatch between the amount of hydrogen that could be stocked and the quantity of generated hydrogen. The estimation of the amount of output hydrogen pursuant to the provided power and energy efficiency is performed and presented by Faradaic efficiency. It is expressed as the ratio of the measured quantity of output hydrogen and the theoretically quantity of output hydrogen:
An evaluation of the theoretical volume of gas is performed by using the Faraday’s second law. The estimation of volume of gas relies on many factors, including current density, working surrounding (pressure and temperature), electrode area, and electrolysis duration. Water-gas displacement or gas chromatography could be used to evaluate the experimental developed volume of gas.
Under low current density, the Faradaic losses are more recognizable, and the increase of the hydrogen pressure leads to lower the Faraday’s efficiency [
12]. However, there is no influence of temperature on the Faraday’s efficiency [
9]. The layer wideness and the Faraday’s performance are proportional, the reduction of layer wideness lowers the Faraday’s efficiency. This may be attributed to the phenomenon named gas cross over, wherein a part of hydrogen formed at the cathode under unstable high pressure is repelled to the anode, provoking a reduction of Faraday’s performance.
Compression effort
Compressions effort is a performance loss induced by system. The compression process of the produced gas is included in the performance of the system, and it is termed the effort for gas compression (
ηc, H2). It is estimated by dividing the demanded work to compress the hydrogen by the quantity of hydrogen that might be stocked taking into account the mechanical performance of the compressor [
13].
The power demanded for compression is calculated by:
where is the needed power for on single compression stage, and ns is the phase number.
The overall performance of the PEM system relies on the hydrogen performance, the Faradaic performance, and the work done to compress the hydrogen. It is estimated by [
14]:
The total performance of PEMWE is predominately prevailed by the hydrogen generation performance Scheepers, Stähler, Stähler, Rauls, Müller, Carmo and Lehnert [
14].
3. Parameters Influencing the Performance of PEMWE
Several conceptual and functional parameters affect the efficiency of PEMWE, such as current density, temperature, water flow, pressure at anode and cathode sides, conceptual design of layer, and catalyst.
3.1. Functional Parameters
3.1.1. Effects of Temperature on the Efficiency of PEMWE
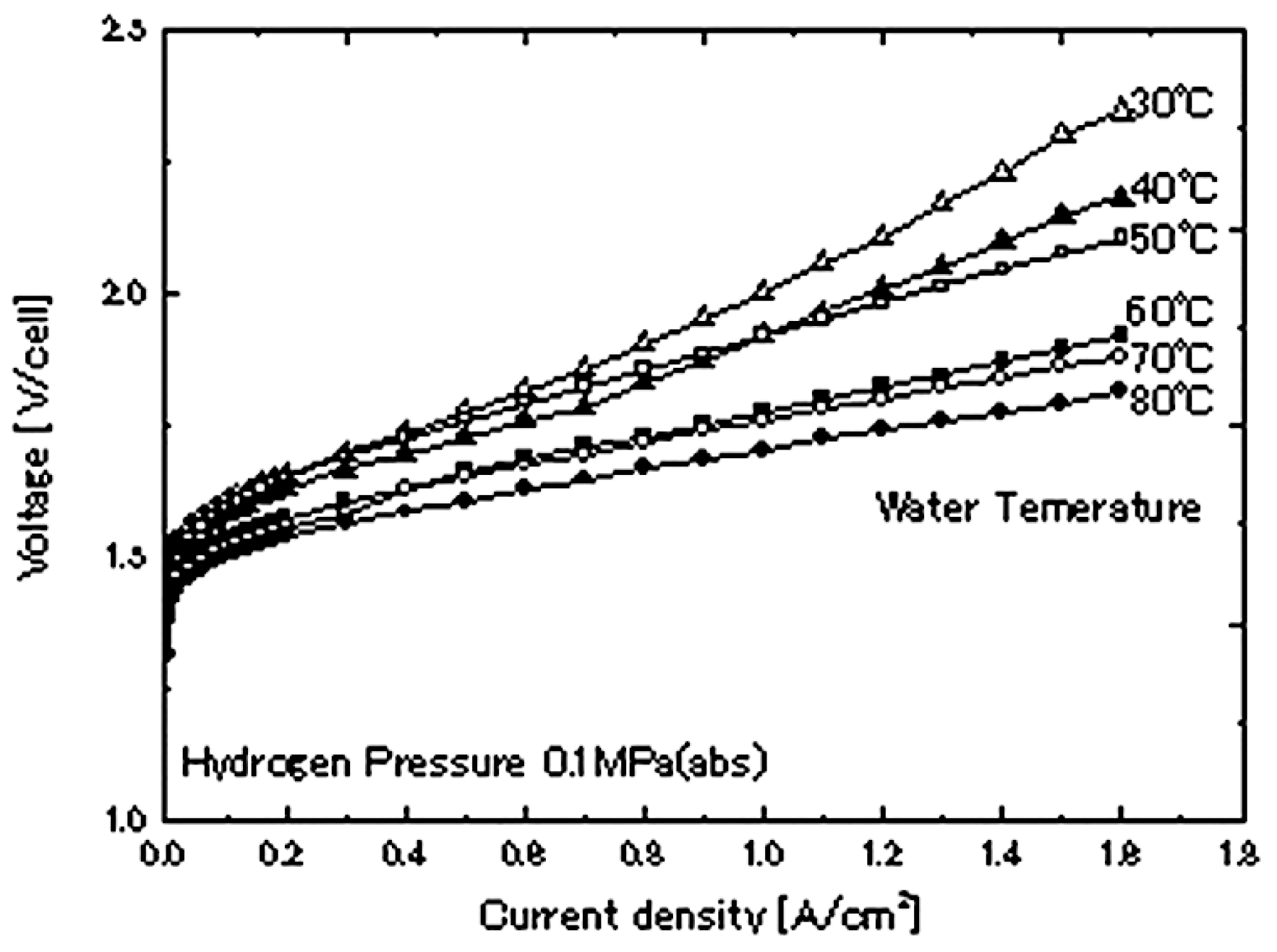
Electrolyzers should be ran under high temperature conditions to achieve a high performance. The working temperature influences the performance of PEM through affecting the reversible voltage, and ohmic and charge transfer overpotential at the cathode and anode sides (
Figure 3). The rise of temperature minimizes the ohmic overvoltage, the reversible voltage, and the activation overvoltage at cathode and anode regions.
The reaction rate increases at the electrode with the rise of temperature, leading to a rise of exchange current density, that reduces the activation overpotential. Several investigations have been conducted to study the influence of temperature on the performance of PEMWE. The influences of current density and temperature on 1D PEMWE, that has been designed to include a chemical deterioration, have been studied by [
15]. The study was based on measuring the time change in layer wideness with the change of temperature in the situation of a constant current density. Results proved that lowering the membrane wideness below 50% requires a time 35,000 to 8700 h for an increase of temperature from 333 K to 353 K. The decrease of membrane width with the rise of temperature can be explained by the chemical degradation, mechanical stress and creep, and dehydration and water content loss. The rising of temperature can accelerate the degradation of membrane material due to thermal stress, resulting in thinning the membrane over the time. Also, the rise of temperature can induce mechanical stress in the membrane owing to the thermal expansion between the membrane and other component of the eletrolyser. leading to reduce its thickness. Additionally, the rise of temperature can cause a dehydration of membrane if the working conditions are not carefully controlled, resulting in decrease membrane’s thickness since the polymer structure collapse slightly in case of insufficient water to maintain its swollen state. The diminution of layer wideness leads to hydrogen and oxygen crossover, that can cause an explosion. [
16] investigated the effect of temperature on ion conductibility and resistance of the polymer electrode, and on working cell voltage with the aid of an evolved model. The simulation results reported a reduction of ohmic resistance from 0.198 Ω/cm
2 to 0.125Ω/cm
2 with a rise of the temperature from 40°C to 80°C. Also, a decrease of operating cell voltage from 2.13 V to 1.98 as the temperature raises from 40°C to 80°C, under a current density, has been recorded. In contrast, the working temperature does not influence Faraday’s efficiency, according to a study conducted by [
17]. [
18] developed a mathematical model to discuss the leverage of several parameters on the efficiency of PEMWE. Results revealed a decrease of voltage by 8.3% and an enhancement of energy and exergy efficiency by 5.6% and 5.8%, consecutively, as the temperature rises from 313 K to 353 K, at current density of 1.2 A.cm
2. An electrochemical investigation on the leverage of temperature on the efficiency of PEMWE has been conducted by [
19]. Results reported that the rise of temperature induces a change of current density under the same MEA conditions, and a rise of ionic conductibility that has a substantial positive leverage on the effectiveness of PEMWE. The ion conductibility recorded an increase from 0.191 S.cm
-1 to 0.211 S.cm
-1 as the temperature increases from 75 to 85 ºC. In addition, the increase of temperature reduces the activation potential, resulting in an exponential amelioration of efficiency. [
18] conducted a numerical study, based on an evolved CFD model, to study the effect of temperature on the efficiency of PEM under a temperature range of 293-373K. Results revealed that the rise of working temperature decreases the demanded energy to obtain the same density, contributing to enhance the PEM effectiveness. It could be interpreted by considering that the rise of temperature enhances ionic conductibility and electrochemical activities. Also, findings showed that the impact of temperature becomes significant under high current density (
Figure 4).
Nevertheless, the improvement of cell performance with the rise of temperature has a limit due to the vaporization of electrolyte at working temperatures passing 100 ºC. Since water evaporates at temperature more than 373 K, the temperature should not be increased to transcend 373 K, and water is required to be liquified to conserve the ionic conductibility at the electrolyte layer. The rise of temperature above 100 ºC leads to minimize liquid saturation, and water shortage deficiency, that could be prevented through a pressurized operation. In addition, Water is required to be purified before using it in PEMWE since unpurified water can lead to degrade the materials and components of PEMWE. The quality of water is usually specified by commercial manufacturers regarding conductivity and a total organic carbon content. The feasibility of pressurized operation on preventing the reduction of liquid saturation has been studied by [
10]. Results reported that the increase of temperature to 120 ºC and the pressure to 0.22 MPa restrained the saturation under 0.3 and decreased the overvoltage from 1.57 V to 1.51V. The rise of temperature above the accepted limit does not affect only the liquid saturation, but it can degrade the layer. In such circumstance, a cooling system should be combined to maintain the temperature under 373 K and robust materials mish be needed. An analysis study conducted by [
14] on the influence of temperature on the effectiveness of PEMWE demonstrated that the low stack temperature has more effect compared to high temperature. It has been reported that a decrease of the penetrability of gas through the membrane with the decrease of temperature, leads to reduce the quantity of hydrogen that permeates via the layer. This is considering as safer as per the fact that the rise of hydrogen volume fraction in the oxygen above 4% leads to rise the security issues, owing to the formation of explosive gases on the oxygen area. Additionally, the study pointed out that the value of the optimal temperature lessens to reach the ambient temperature with low current densities. In addition, there will be no need for durable materials, that are required in the case of high temperature.
3.1.2 Effect of Cathode Pressure on the Effectiveness of PEM
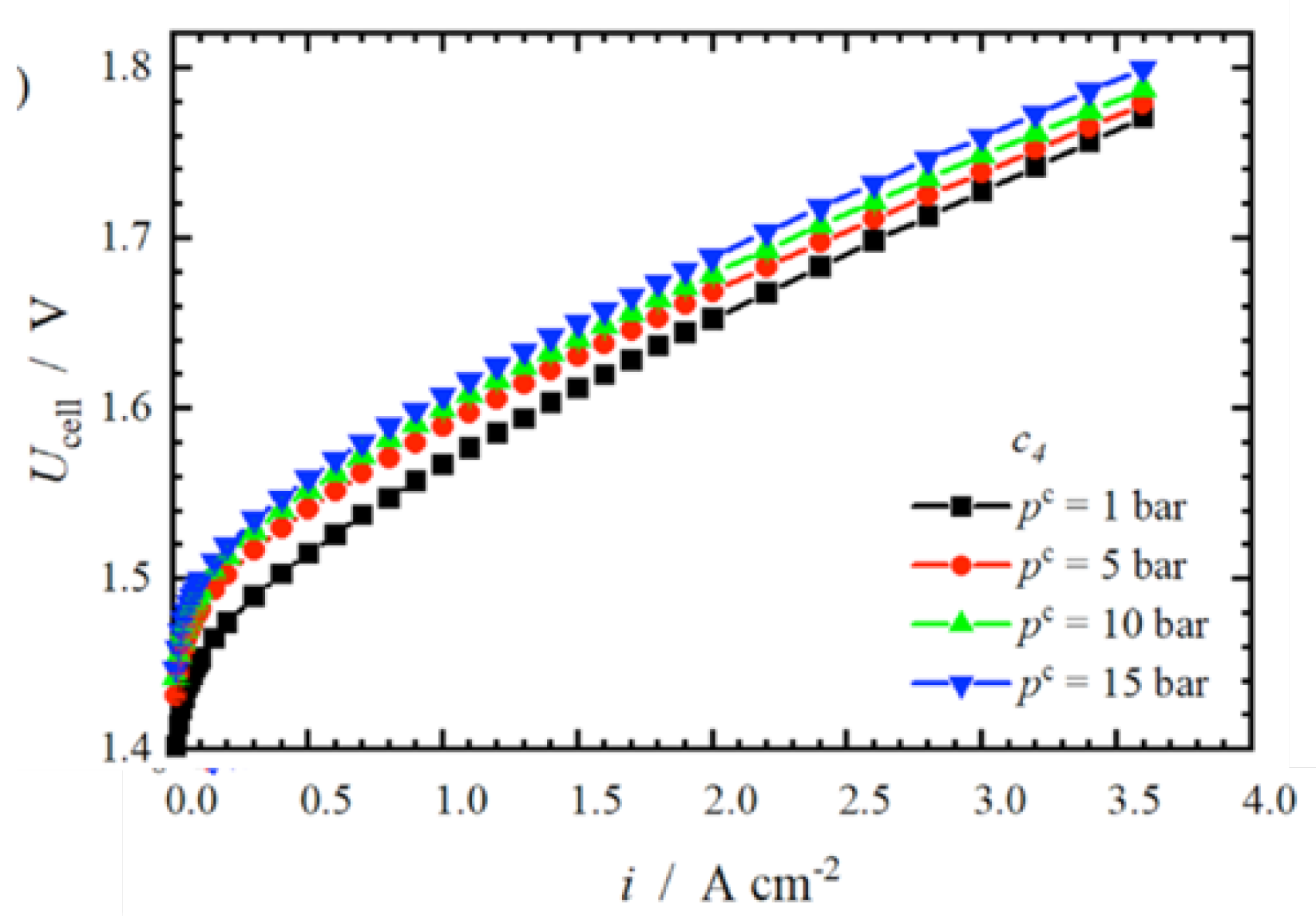
Cathode pressure has a significant effect on minimizing the needed energy to compress the output of hydrogen to store it. In addition, generation of pressurized hydrogen could minimize cost and rise efficiency of the system. Nevertheless, an inverse displacement of H+ ions from the anode to the cathode is caused by the rise of pressure at the cathode, leading to rise the over-voltage and to decelerate the electrochemical reactions (Figure. 5). Consequently, the rise of pressure at the cathode adversely influences the exergy and the energy performances of the PEMWE.
Figure 5.
I-V characteristic curve for various cathode pressures [
21]
.
Figure 5.
I-V characteristic curve for various cathode pressures [
21]
.
The impact of pressure change, in the cathode area, on the efficiency of PEMWE, with retaining the pressure at anode area at atmospheric pressure, has been investigated by [
22]. Results revealed a decrease of the PEMWE efficiency with the rise of pressure, the leverage of pressure on the augmentation of reversible cell voltage under high current density is more pronounced than that of the lowering on the overvoltage, evoking in rising the required cell voltage as the cathode pressure rises. Besides, the input current increases as the pressure increases from 1000 kPa to 2000 kPa. Additionally, a study has been carried out by [
18] to analyze the effect of cathode pressure on the performance of PEM revealed that the reduction of cathode pressure from 4 bar to 1 bar leads to minimize the voltage of PEM by 4.8%. Moreover, as reported by Yodwong, et al Yodwong, Guilbert, Phattanasak, Kaewmanee, Hinaje and Vitale [
12], the increase of hydrogen pressure decreases the Faraday’s performance.
The gas permeation phenomena of two types of layer, Nafion 212 and Nafion 117, operated at high pressure of 30 bar has been examined by [
23]. Nafion 212 is thinner (51 µm thick) than Nafion 117 (178 µm thick). Results showed a higher current density with Nafion 212 compared to Nafion 117 under normal circumstances. The rise of operating pressure from 1 to 30 bar rises the hydrogen concentration in oxygen, which is quicker in the case of Nafion 212 in comparison to Nafion 117 under low current density. The higher performance in the case of thinner Nafion is due to the reduction of the proton transport resistance in thinner membrane. However, the thinner membrane leads to rise gas crossover and affects the lifespan of the membrane. Results showed also that the concentration of hydrogen in oxygen is under 2% for the two types of layers under high current density circumstance of 4000 mA/cm
2 or more.
A PEMWE system constitutes of five-cell PEMWE stack able to resist 50 bar and a catalyst coated proton exchange membrane to create a membrane electrode assembly has been evolved by [
24]. This developed PEMWE stack can generate a constant scale of hydrogen within the limits of 0 to 50 bar without any deemed variation. A diminution of the contact resistance within the metal bipolar plate and membrane electrode assembly is achieved in this design. Also, the effect of the pressurized gas generated on the efficiency of PEMWE is insignificant.
A numerical model based on Nernst equation was developed by [
25] to evaluate the performance of PEMWE under pressure conditions of 1 and 90 bar and at temperature 52° C and 90°C. Additionally, it has been demonstrated the possibility of generating high-pressure hydrogen without the need of mechanical compressor since there is no deemed change in cell efficiency, owing to the pressure difference.
3.1.3 Impact of Current Density
The permeation of hydrogen is actively affected by the current density. [
26], reported that a rise of current density to 1 A/cm
2 could rise the hydrogen permeation at a similar way as the rise of cathode pressure to 20 bar and many decenniums rise of temperature. The rise of current density induces a reduction of the stack voltage, leading to improve the cell performance. This might be assigned to the fact that the rise of current density increases the kinetics reaction on the electrodes, resulting in lessening the charge transfer resistance and thus enhancing the cell performance [
27]. In contrast, the high current densities produce large amounts of gas, causing a collection of
O2 that can generate two distinct phase flow regimes and protect the anode electrode from water. It should be mentioned that the generated gas mass transport and the water could be afflicted by these problems. The accretion of produced gas in PEMWE when the gas generation in the catalyst’s region transcends the gas sweep capability of the flow channels, cause blister obstruction. The leading reasons for the blister obstruction are the crosses sectional and the water’s flow rate via the ducts. An investigation study of the behavior of the two-phase flow in the anode flux channel of a PEMWE with the aid of an optical visualization, has been conducted by [
28]. Results revealed that a delay from bubbly to slug transition is provoked by high water flux rate and leads to create tinier blister and reduced slugs. Additionally, the working temperature plays a significant role on the effect of water flux on cell performance. The behaviors of two-phases flow and gas blister in the anode area of PEMWE, using high speed optical imaging and under different operating circumstances has been carried out by [
29]. The study reported a high efficiency with the anode parallel flow field design in comparison to the single serpentine flow-field. Also, the long channel length increases the gas accumulation and channel blocking, leading to lessen the performance of PEMWE.
3.1.4. Impact of Flow Rate
The flow rate is one of the parameters influencing the effectiveness of PEMWE. The impact of flow rate on the performance of PEMWE by using magnetic flux density has been studied by [
30]. Results showed a rise of 33% in the current density under a flow rate of 300 mL/min and 0.5 T magnetic flux density, and at 2.5 V. The magnetic flux density rises the flow rate, that positively affects the performance beside its role in accelerating product outgassing from the electrode surface, resulting in minimizing mass transport losses [
31].
An investigation study on the influence of different values of flow rate on the efficiency of PEMWE was performed by [
19]. Results reported a rise of current density with the reduction of flow rate at the same voltage. [
32] pointed out that the rise of flow rate reduces the effectiveness. The highest current density was obtained at 1.0 mL/min and a decrease of efficiency is achieved with the rise of flow rate. The conditions of porous transport layers take a significant part role in determining the maximum current density. Consequently, the value of highest flow rate, that determines the highest current density, depends on the structure of the PEMWE.
3.2 Conceptual Parameters
The layer and electrode wideness, and the porosity of cathode and anode are conceptual parameters influencing the performance of PEMWE.
3.2.1 The Layer and Electrode Wideness
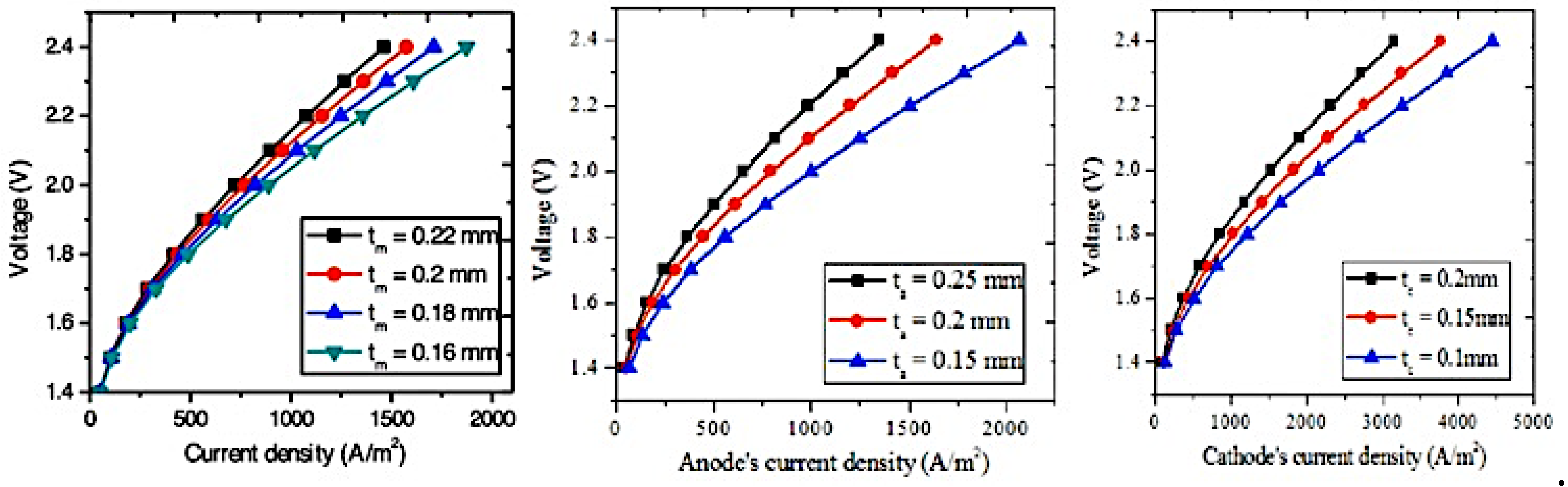
The layer wideness is regarded as a crucial conceptual parameter influencing the efficiency of PEMWE. The leverage of layer and electrode wideness on the effectiveness of PEM is investigated and analyzed by [
33]. Results reported a decrease of the performance of PEMWE with the rise of layer wideness because the ionic and electric resistance boost with the extension of the layer wideness and lead to lower the voltage and thus increase ohmic loss. Additionally, the rise of the anode gas diffusion layer ‘s wideness and the cathode gas diffusion layer ‘s wideness reduce voltage, and the high current densities cause a significant reduction of voltage. The rise of layer wideness entails to rise the ohmic resistance, and to rise the needed power [
22]. In addition, the high current density intensifies the impact of layer wideness on the voltage. The Faraday’s performance diminishes with the reduction of membrane wideness and the effect is more prominent at high cathode pressure. This is attributed to the reduction of the hydrogen’s flux densities through the membrane and output rates when the layer wideness decreases, contributing to lower the Faraday’s performance.
Figure 6.
Impact on the efficiency of (a) the layer wideness (b) the anode GDL’s wideness of GDL (c) the cathode GDL’s wideness of GDL [
33]
.
Figure 6.
Impact on the efficiency of (a) the layer wideness (b) the anode GDL’s wideness of GDL (c) the cathode GDL’s wideness of GDL [
33]
.
[
18] Conducted a parametric study to analyze the impact of layer wideness and the channel dimensions on the voltage and on the exergy and energy efficiencies of PEMWE. Results reported a decrease of voltage and a rise of energy and exergy efficiencies with the decrease of layer wideness and the dimensions of the channel. The rise of the width and height of the channel augment the ohmic resistant and the electrolyser’s voltage. The cross-sectional area increases with the rise of the width and height of the channel, provoking a reduction of water velocity and reaction rate, and a rising of cell voltage. Consequently, A reduction of layer wideness is needed to minimize the ohmic resistance, the needed power, and the price. However, an immoderation diminution of the layer wideness might negatively influence its endurance and result in a penetration of reactive gases.
3.2.2 The Porosity of Cathode and Anode
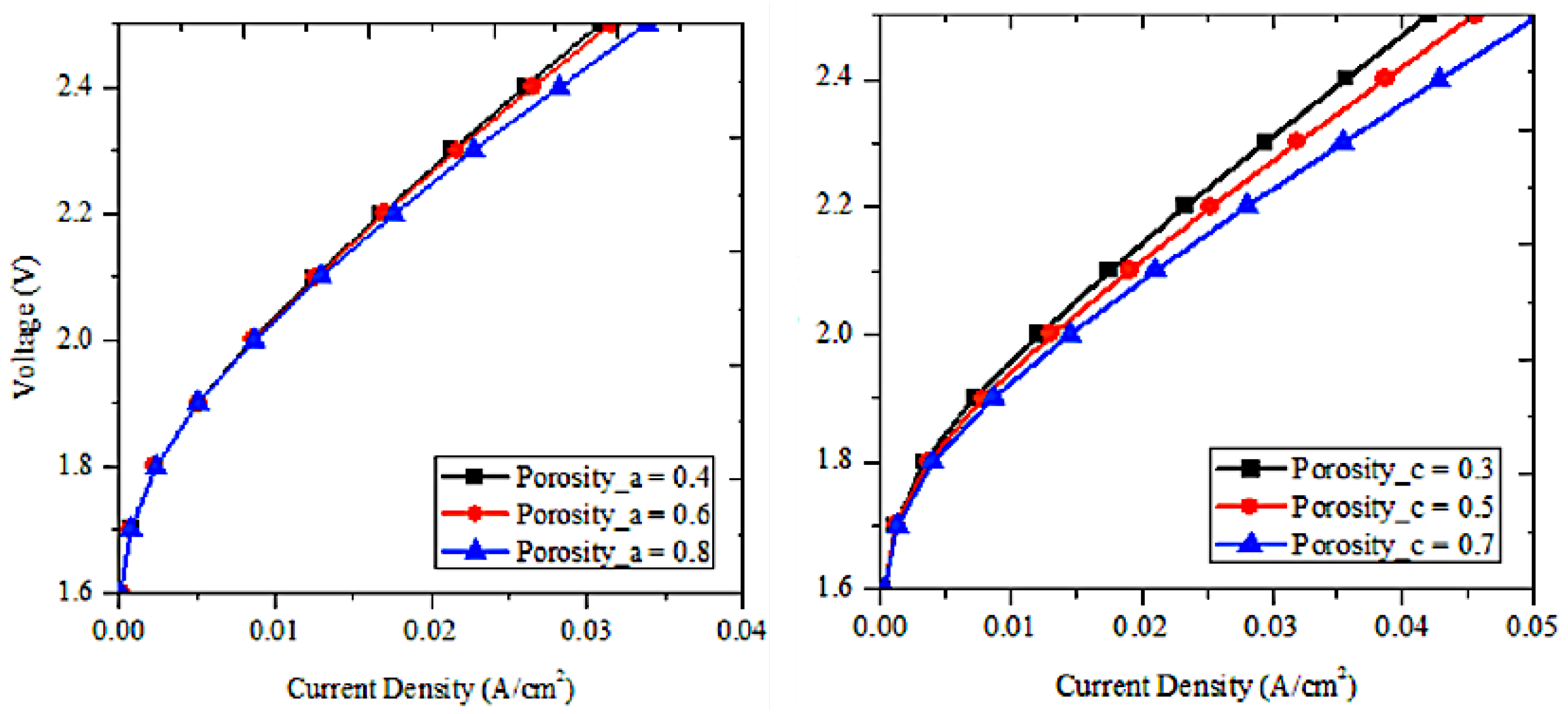
The porosities of cathode and anode influence the efficiency of PEMWE. A study conducted by [
33] to analyze this effect through changing the porosity of one electrode with maintaining the porosity of second electrode constant. Results are displayed in Figure. 7 and reported an improvement of PEMWE with the rise of porosity at high voltage and this effect is important for the cathode. This can be interpreted by the electric resistance that is low at high porosity since it has low volume fraction. In addition, the diffusion loss diminishes as the porosity rises, contributing to enhance the PEMWE performance. Rising porosity in both anode and cathode allows a better gas diffusion and mass transport, leading to a easier access of reactants (water at the anode and hydrogen ions at the cathode) to reaction sites, and output products, oxygen and hydrogen, could be easily removed. Additionnally, the rise of porosity increases the elecrochemical surface area, leading to rise the number of active sites for the electrochemical reaction, resulting in enhancing efficiency of PEMWE. However, the rise of porosity above the optimal range negatively affect the mechanical stability and minimize the contact between the catalyst and the membrane, causing a lower efficiency. The rise of porosity at the anods side ensure a better water distribution, ensuring hydroation of the membrane, which is fundemental for proton conductivity. On the other hand, the rise of porosity at the cathode side helps on the removal of hydrogen gas, resulting in an efficient gas removal and thus prevent flooding, that negatively affects the efficiency.
Figure 7.
Impact on the PEMWE efficiency of (a) porosity of anode (b) porosity of cathode [
33]
.
Figure 7.
Impact on the PEMWE efficiency of (a) porosity of anode (b) porosity of cathode [
33]
.
3.2.3 Gas Diffusion Layers (GDL)
GDL are one of the components of PEM that sandwiches MEA from both parts. It is used to conduct electrons between cathode and anode, to transport water into the MEA, and to transfer gases from the catalyst layer toward MEA. GDL used in PEM is based on carbon materials like carbon cloth or carbon paper. The carbon based materials have several issues related to their high sensitivity to be oxidized at the anode side with a potency of releasing CO
2 by reason of high oxygen revolution reaction at the anode [
34]. The metallic based GDL is viewed as a suitable candidate thanks to their high mechanical robustness and conductibility. Porous titanium mesh and felt have the benefit of corrosion-resistant in acidic environment, making them an ideal option for anode GDL [
35,
36]. However, during the operation, the impedance of titanium GDL rises because of the creation of TiO
2 passivation layer, that rises the connection impedance within the GDL and other elements of PEM [
37]. Coating GDL with Pt or IrO
2 layers are one of the existing options to reduce this effect. However, it rises the cost of GDL and consequently, the cost of PEM electrolyser will be higher [
38].
A uniform contact between the GDL and MEA should be applied to prevent an irregular current distribution, that leads to rise the degradation of the layer. Titanium is made of sintering titanium particles with rough surface and weak contact. Microporous layers of Ti are based on depositing smaller particles of Ti on Ti GDL and are used to enhance the connection between GDL and the MEA, and to control the porosity of Ti GDL, that affects the mass transport of water and O2 and H2 generated at MEA.
The GDL requires special exigencies like corrosion impedance, with high conductibility, and low mass transfer losses [
39]. The mass transfer impedance and interaction impedance between MEA and GDL depend on the porosity, composition, and wideness of the GDL [
40]. An optimization of titanium current collector by conglomerating Ti particles with changing size has been performed and analyzed by [
41]. Results reported that the optimum particles size were 50-75 µm with a pore size of 12-13 µm. An antimony-doped tin oxide (ATO) blended with Nafion solution over titanium felt is used and studied by [
35]. Results revealed an improvement in the electrolyser activity in the voltage range influenced by charge transfer kinetics.
3.2.4 Bipolar Plates (BPs)
Bipolar plates offer many functions such as heat transfer, retaining the separating between O
2 and H
2 in the cell, mass transport, and ensuring a structural stability for electrolyser systems operating at high pressure [
42]. The materials used for the BPs requires specific high conductibility properties, meaning low intersectional contact resistance and bulk resistance. The BPs at the anode side should be invulnerable to the oxidizing medium because the oxidation at the anode provokes the oxidation of metallic BPs. At the cathode area, the corrosion of BPs is less compared to anode area. While, the absorption of hydrogen on the metal causes hydrogen embrittlement [
43]. Many approaches have been discussed in the literature to minimize the passivation and resistance of the materials used in BPs through deposition of metal oxide films and noble metals sheets.
Titanium based BPs
Titanium -based bipolar plates are oxidized owing to the high oxidizing medium and formed the TiO2 layer that has low electrical conductibility, resulting in rising intersectional contact impedance between BPs and the gas diffusion layer. Many investigation studies have been conducted to avoid the passivation on the BPs through coating them by noble metals like Ta2O5, Pt, and Au. The coating methods used in the literature are vapor phase deposition, electrodeposition, and sputtering.
Titanium coated with Pt is usually used but it increases the cost of PEMWE. TiN-based coating is one of options used to coat Ti-BPs through plasma and thermal methods. According to a study conducted by [
44] on the effect of TiO2 deposits on the TiN coating, the operation of oxidation of the TiN coating is long and the H
2 embrittlement reduced, that could also minimize the capability of Ti uptake owing to TiH figuration.
Electrodeposition of platinum on Ti-based BPs is an option used to reduce the cost coating technique. It minimizes the corrosion and the oxidation, and decreases the ohmic resistance. [
45] proved that electrodeposition of platinum on Ti-BPs could enhance the performance of electrolysis.
Vacuum sputtering is also used to manufacture gold-coated Ti BPs. The advantage of gold coating educes from its capability to reduce the creation of passive layer on the surface. The ideal gold loading to achieve a stable electrolysis efficiency is 1 µm [
46].
A coating film formed of Ag nanoparticles and TiN applied on Ti BPs showed a high corrosion resistance at high potential and in oxidation medium due to high electro conduction of Ag and the corrosion -resistant characteristic of TiN.
Stainless steel BPs
Stainless steel is used as material for BPs thanks to its low price, simpler to machine, and less vulnerable to hydrogen embrittlement [
47]. However, stainless has low corrosion resistant compared to titanium under electrolysis circumstances. In the purpose of protecting BPs from passivation, a dense titanium coating is placed on stainless steel BPs through the vacuum plasma spraying process, and a thin film of platinum is placed on Ti by using the plasma vapor deposition process. This coating proved a good protection of stainless-steel area against corrosion. The optimal wideness to minimize the wideness of the layer and the price of the total stack is 30 µm [
48].
A coating of Au/Ti is also tested by depositing Ti using vacuum thermal spraying with electrodeposition of Au. Results showed a reduction of interfacial contact resistance, and the steepness of Ti ensures a good cohesion to the electrodeposited Au nano particles. The coating was examined in a simulated mash that imitated the PEMWE anode medium [
49]. Results revealed a long-time protection on stainless-steel BPs.
RuO
2 was used to be located on the ferric stainless steel based BPs by using the electrodeposition technique [
50]. The interfacial contact resistance (ICR) measurement was used and proved a positive impact of the deposition of RuO
2 on stainless steel and led to lower the interfacial contact resistance.
An assessment study of cheap material that could be used for BPs, including stainless steels (SS316L, SS321 and SS904L), was conducted by [
51]. Coating layers of Ti, CrN/TiN, TiN, and Ti/TiN on stainless steel BPs was performed by using the physical vapor technique. In the purpose of determining the best substrate/coating compound for BPs, a corrosion test was used in anodic PEMWE circumstances. In addition, the ICR was measured following the corrosion test. Results revealed that Ti/TiN multi-layered coating on SS 321 recorded the best efficiency with -0.02% weight loss and ICR of 9.9 mΩ cm
2 after the corrosion test.
3.3. Impacts of Catalysts
Catalyst is deemed as a significant parameter influencing the efficiency of PMEWE. Enhancing catalysts activity leads to reduce the activation overpotential especially at the anode side. In the activation part of the polarization curve, the factors that determine the efficiency of PEMWE are the catalysts kind and loading, the stability of the catalyst, and the electrochemical active area. The electrocatalysts utilized in PEMWE are usually noble metals based, like RuO
2/IrO
2 catalysts as anode for oxygen evolution reaction (OER) and Pt/Pd- based catalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) [
52,
53]. The drawback of these metals is the high cost, resulting in raising the price of PEMWE. Moreover, the price of precursor salt needed in the initial coating process leads to higher the price of PEMWE. Several investigations have been performed to evolve alternative and cheaper electrocatalysts for HER and OER.
3.3.1. Hydrogen Evolution Reaction Catalysts
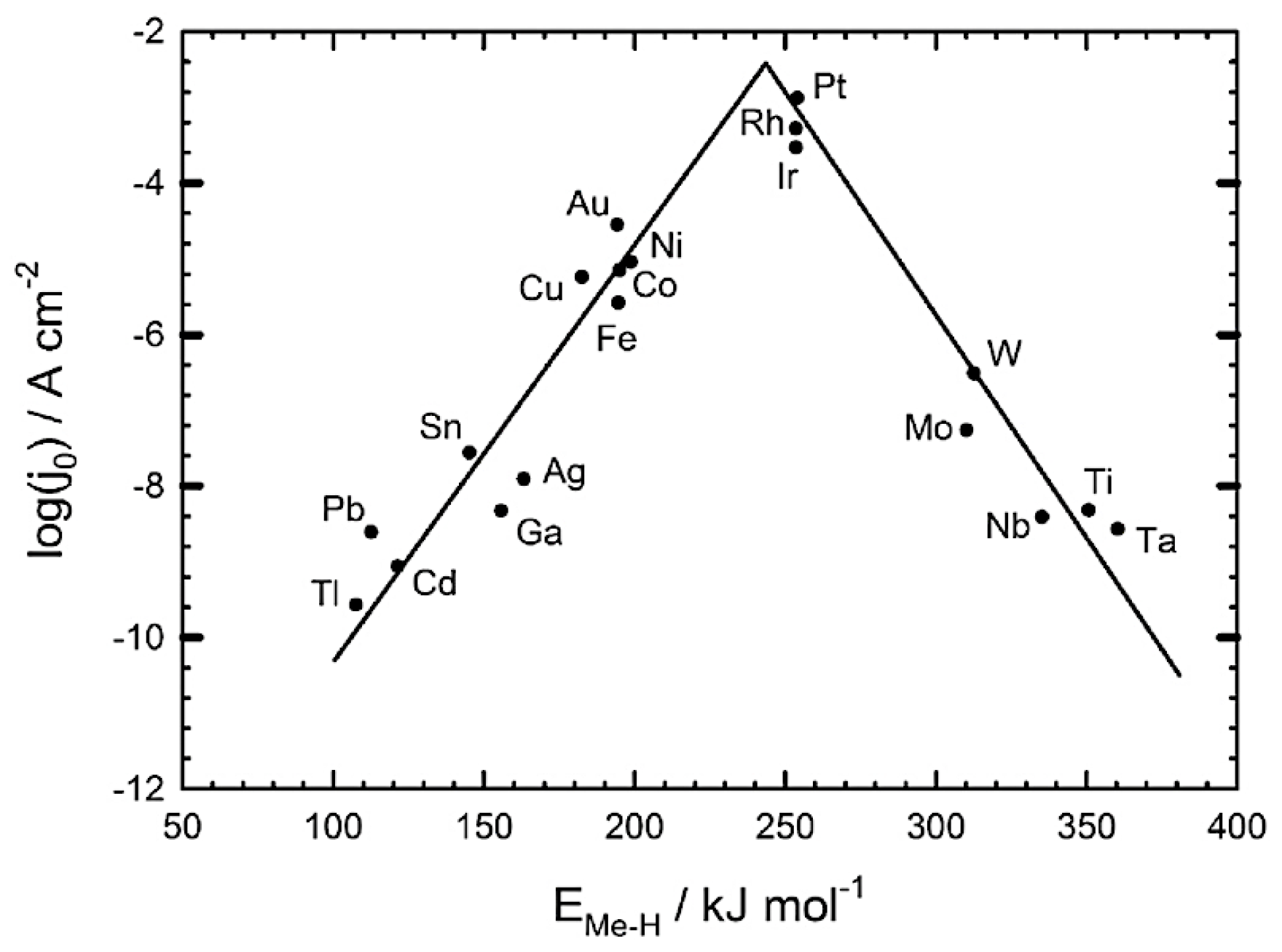
The hydrogen evolution reaction has an electrocatalyst activity that relies on the strength of the Me-H bond. The plot ‘Volcano’ presents the relation between the strength of Me-H and the current density of the HER [
54]. It may be viewed from Figure.8 that the highest HER efficiency can be achieved through noble metals, since they own hydrogen binding energy within reach of optimum, leading to making the thermodynamic transition from reactants to products easier.
Figure 8.
Volcano-plot to express the correlation between the exchange current density and the Me-H bond strength [
54]
.
Figure 8.
Volcano-plot to express the correlation between the exchange current density and the Me-H bond strength [
54]
.
Platinum-group noble metals are regarded as the most active candidate to be used as catalyst in the HER. Despite the high catalytic effectiveness of the Pt, their scarcity and high cost make them inconvenient to be used in large industrial applications [
55]. Many investigations have been conducted to optimize the geometric parameters of Pt-based catalyst with keeping electrocyclic activity. Backing platinum nanoparticles on a high surface carbon is a cheap and an easy approach to make active electrocatalysts. The frequently used method is 20 wt% Pt placed on carbon black (Pt/C) and it could accomplish one of the smallest values of overpotential of 46 mV under 10 mA/cm
2 [
56,
57]. The atomic layer deposition (ALD) technique is also one of the options utilized to lessen the use of precious metal. It is based on the elaboration of Pt nanoparticle, monolayers and nanoclusters of an accurately controlled size [
58,
59]. This technique could significantly minimize the quantities of noble metal (up to 1/10th of a standard Pt loading of approximately 300 μg cm
2) [
60].
The feasibility of using MoS
2 electrocatalyst in the HER has been tested by [
61]. Results demonstrated that the MoS
2 might be utilized as electrocatalyst in the HER. An incorporation of MoS
2 with RuS
2 has been suggested by [
62] to be used as catalyst and results reported excellent output of this combination like satisfactory over potential and Volmer Tafel behavior, and high exchange current density. The benefit of this combination is the ability to enhance the hydrogen production to attain 1.2 l/h under an operated current density of 1 A/cm
2, a power of 41.8 W, energy utilization of 3.8 kWh/Nm
3, and a performance of 93%.
Palladium is regarded as another nominee for electrocatalyst thanks to its remarkably electrocatalytic effectiveness, its reduced cost compared to platinum, and it is presented in abundance in earth [
63]. The utilization of carbon supported electrocatalysts, such as Ni
2P/CNTs, , Mo
2C/CNTs, A- Ni-C, WO
2/C nano-wires, Co-doped FeS
2/CNTs, and CoFe nanoalloys embedded in N-doped graphene, have been enormously studies to examine and asses their abilities to substitute Pt in HER and lower the price of catalysts utilized in HER [
64,
65,
66,
67,
68]. In addition, many studies have been performed to investigate the utilization of alternative catalysts to Pt-based catalysts for HER in-PEM electrolysis. Findings showed that the catalysts MoSx and Pd-based nano carbon are the best electrocatalysts in terms of electro catalytic effectiveness and endurance.
Recently, the use of non-precious metals, their compounds and allows as catalyst in HER has been received a significant attention and progress. The main factors influencing the catalytic effectiveness are auspicious harmonious effect between different metal, anion/cations relation, catalyst support kind with high geometric design, and core architecture of the nominated catalyst. Minimizing the use of precious metal through alloying it with cheaper metals is a successful approach and has been used. The use of one or more metals owing a further benefit on the catalytic effectiveness of the precious metal is an excellent method. [
69] conducted a study to examine allowing cheap metal, Co, Ru, Au, Fe, and Cu, with Pt. Results demonstrated the feasibility of using these metals and presented the reasons behind the improvement of their performances compared to Pt nanoparticle-based catalyst. A ‘lattice strain effect’ affects the surface Pt-Pt bond gap by reason of introducing another metal [
70]. A ‘ligand effect’ is attributed to the variation of the electronic features of the active areas of one transition metal by inserting different metal [
71]. Even though the allowing approach could reduce the cost of catalyst with maintaining the cell efficiency, the rarity and the pricey of the precious metals are still deemed as dominant barriers for a mass extension in manufactory.
3.3.2. Oxygen Evolution Reaction Catalyst
The oxygen evolution reaction comprises four electrons with bigger overpotential compared to HER. However, the kinetic of HER is quicker compared to OER. The OER in PEM occurs in an acidic condition and needs a catalyst to be effective and stable under corrosive circumstance. The loading needs of OER catalyst should be minimized with attaining high activity aiming to minimize the overall cost of PEMWE. Many transition metals, involving noble and non-noble materials, have been studied and tested to be used as electrocatalyst in OER. The two metal oxides IrO
2 and RuO
2 have showed bigger metallic conductibility among the metal oxides [
72]. Iridium offers a good balance between activity and stability owing to its inherent characters, allowing it to be a suitable candidate as electrocatalyst in OER. However, its use faces a challenge due to its high cost and rarity. RuO
2 has proved better effectiveness for OER, and more effective than IrO2, but unstable by reason of corrosion induced by the high acidity of the perfluoro-sulfonic layer and high anodic potential at OER [
52]. Nevertheless, IrO
2 recorded a larger impendence to PER in acidic environment and poor performance [
73].
Several investigations have been carried out to evolve approaches and alternates catalysts for OER with high stability and functioning, and cheaper to reduce the use Ir. The developed approaches are nano structuring of Ir, fixing Ir on supporting substrates, and combining Ir with hetero metals.
Nano structuring of Ir is based on depositing thin layer of Ir with low amount on the GDL and it proved its ability to reduce the use of catalyst with maintaining a high activity [
74]. The electrodeposition technology is viewed as an efficient technology to assemble a catalyst on the GDL since it can lessen the quantity of catalyst due to good scattering of catalyst. In addition, it has been utilized to place IrO
2 on various substrates, like gold, titanium, and carbon paper. A unique catalyst formed of nano-porous Ir nanosheets was suggested by [
75] through alloying Ni with Ir in the shape of thin film and dealloyed in acidic environment. This combination proved a significant performance compared to a commercial IrO
2 nanoparticle catalyst.
Fixing Ir on supporting substrates is one of the approaches used to lower the quantity of noble metal used in catalyst. This approach offers several benefits such as rising the active surface of the catalyst, boosting electrical conductibility by strong interconnection between the fixed materials and the supporting, and steadying the active species and avoiding it from grave accumulation. [
76] tested the use of boron carbide (B
4C) as supporting substrate for Ir and demonstrated its highly effectivity and endurance for OER. Compared to carbon materials, B
4C has an important electrochemical stability beside its high electrical conductibility. Tungsten oxide nanorod was also examined to be used as supporting substrate for defective thin Ir sheet by [
77]. A hydrothermal reaction was used to prepare an ordered array of tungsten oxide, and then depositing Ir on the surface through electrodeposition process to form nanorods. Results showed a reduction of the mass transport and the total loading of Ir (0.14 mg Ir/cm
2) during the functioning of PEMWE. Moreover, TiO
2 proved its ability to be a good candidate as a supporting material for Ir thanks to its low price, high stability and availability [
78]. A physical mixing of IrO
2 catalyst with Ti metal support was prepared and tested by [
53]. Results showed a rising of the scattering of IrO
2 over Ti particles was achieved with a high activity when it is employed as anode in PEMWE.
Alloying Ir with hetero metal (M, Ni, Cu, Co, Fe) could optimize the surface chemical characteristics due to the change of charge distributions, with morphological benefits, and electronic structure adjustment. The core-shell structure is effective in obtaining an adequate match between effectivity and the constancy of electrocatalysts in PEMWE. [
79] developed a self-build RuO2@IrOx core-shell nanostructure in the purpose of attaining a high stability and activity. The self-assembled RuO2@IrOx showed a lower overpotential of 215 mV at 10 mA/cm
2 compared to RuO
2 (260 mV at 10 mA/cm
2) and IrO
2 (316 mV at 10 mA/cm
2). Moreover, this designed core shell proved a good stability at 1 A/cm
2, owing to the efficient protection supplied by IrO
2 shell.
The structure of catalysts particles, including size and distribution, has a significant effect on the available surface area for the electrochemical reactions and thus, directly affect the mass transfer [
80,
81]. In term of size, catalysts with smaller particles offer a larger surface area for the chemical reaction, leading to rise the number of reaction sites, and thus enhancing the use of catalysts. Despite that, smaller particles catalyst can cause a denser packing, leading to decrease porosity and block mass transfer. Regarding the distribution, a uniform distribution is essential to ensure the complete access of reactants on all parts of the catalyst layer. Thus, it reduces the dead spots, where reactions are occurring, decreasing gradients and overpotential, and enhancing the overall efficiency of the PEMWE.
4. Conclusions
PEM electrolyser is regarded as an efficient technology to produce green hydrogen thanks to its various benefits. Nevertheless, the high price, the reduced endurance, the acidic corrosive environment, and the requirement of high quantity of purified water are the main disadvantages of PEM. The current paper presented the efficiency of electrolyser that entails the hydrogen production efficiency, the Faradaic efficiency, and the effort power to compress the output hydrogen. The hydrogen generation efficiency is the highest efficiency. Several operating and conceptual factors influencing the efficiency of PEMWE, like catalyst, temperature, current density, cathode pressure, and layer wideness. The effect of these factors is reviewed and discussed in this paper.
Enhancing the performance of PEMWE could be achieved through optimizing its operating circumstances. Operating the PEMWR under high temperature rises the quantity of hydrogen produced through minimizing the overvoltage, while it can decay the layer and lessen the lifespan of the PEMWE.
Increasing the cathode pressure minimizes the quantity of power demanded to compress the hydrogen to stock it and thus decrease the cost of generated hydrogen, while this increase negatively affects the efficiency of PEMWE. Thus, pressure should be adapted according to the features of the layer. Also, in the purpose of avoiding explosion, the density of oxygen in the hydrogen should be examined.
The rise of current density improves the efficiency of PEM electrolysis, while the high current density causes blister obstruction and two phases-flow, that decrease the effectiveness of PEM electrolysis.
The design of gas diffusion layer, which is an essential element of PEMWE, affects the effectiveness of PEMWE. Several methods and designs of GDL have been developed and showed an enhancement of the performance of PEMWE. The decrease of the cost of PEMWE besides improving its stability require the use of cheap and low-corrosion-resistant GDL. MPL with micron size is one of the designs that rises the contact between the layer and GDL. Electrodeposition of a catalyst on GDL proved its ability to enhance catalyst distribution and reduce the corrosion of GDL. Pore-graded GDL at the catalyst layer with the current collector is an effective approach to enhance catalyst distribution on the GDL and prevent catalyst low, owing to the lading of big pores in foam-based GDL. Also, a thin tunable GDL design could optimize the ohmic contact and enhance the overall efficiency of PEMWE. Designing GDL with very low wideness with maintaining same or better mass transport, electrical, and corrosion -resistant properties requires more development and research.
The reduction of layer wideness can improve the PEMWE. However, an excessive decrease of layer wideness affects its endurance and leads to a permeation of reactive gases. The intensity of the influence of layer wideness, cathode pressure, and temperature on the PEMWE efficiency relies on the current density. The increases of cathode and anode porosity boost the PEMWE efficiency at high voltage and this effect is more pronounced for the cathode.
The catalyst plays a considerable role in enhancing the PEMWE performance. The used catalysts in OER and HER are noble metals, that are costly, resulting in raising the cost of PEMWE. Several alternative cheaper catalysts have been evolved and proved a high power as cheap electrocatalysts. In the OER, iridium-based catalyst is used as anode catalyst thanks to its high stability and competent activity. Several studies have been conducted to enhance the robustness and decrease the loading mass of Ir to minimize the cost of PEMWE. The developed and suggested methods are nano structuring, deposition on conductive substrates, and alloying with hetero metals. The deposition of Ir on conductive substrate improves the active surface species and boosts the conductibility of the catalyst. The alloying of Ir makes the iridium existing in different oxidation states and reduces the binding energy of oxygen intermediates in the surface. More research is required to improve the alloyed and supported catalyst and to develop more design approaches to ameliorate the catalytic effectiveness of the OER like trimetallic catalytic systems.
Author Contributions
All works have been done by Gaydaa ALZohbi
Funding
This research received no external funding
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest
References
- Kumar, S.S.; Himabindu, V. Hydrogen production by PEM water electrolysis–A review. Materials Science for Energy Technologies 2019, 2, 442–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, S.; Salzano, F.J. Prospects for hydrogen production by water electrolysis to be competitive with conventional methods. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy 1977, 2, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, A.; Børresen, B.; Hagen, G.; Tsypkin, M.; Tunold, R. Hydrogen production by advanced proton exchange membrane (PEM) water electrolysers—Reduced energy consumption by improved electrocatalysis. Energy 2007, 32, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, O.; Gambhir, A.; Staffell, I.; Hawkes, A.; Nelson, J.; Few, S. Future cost and performance of water electrolysis: An expert elicitation study. International journal of hydrogen energy 2017, 42, 30470–30492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millet, P.; Andolfatto, F.; Durand, R. Design and performance of a solid polymer electrolyte water electrolyzer. International journal of hydrogen energy 1996, 21, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sood, S.; Prakash, O.; Boukerdja, M.; Dieulot, J.-Y.; Ould-Bouamama, B.; Bressel, M.; Gehin, A.-L. Generic dynamical model of PEM electrolyser under intermittent sources. Energies 2020, 13, 6556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Zhang, Y. Noble metal-free hydrogen evolution catalysts for water splitting. Chemical Society Reviews 2015, 44, 5148–5180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.; Monirul, U.K.; Juodkazis, S.; YOKOTA, Y.; MISAWA, H. Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications 243, 2001.
- Kurzweil, P.B. Grundlagen, Komponenten, Systeme, Anwendungen. 2013.
- Kai, J.; Saito, R.; Terabaru, K.; Li, H.; Nakajima, H.; Ito, K. Effect of temperature on the performance of polymer electrolyte membrane water electrolysis: numerical analysis of electrolysis voltage considering gas/liquid two-phase flow. Journal of The Electrochemical Society 2019, 166, F246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villagra, A.; Millet, P. An analysis of PEM water electrolysis cells operating at elevated current densities. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 9708–9717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yodwong, B.; Guilbert, D.; Phattanasak, M.; Kaewmanee, W.; Hinaje, M.; Vitale, G. Faraday’s efficiency modeling of a proton exchange membrane electrolyzer based on experimental data. Energies 2020, 13, 4792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzimas, E.; Filiou, C.; Peteves, S.; Veyret, J. Hydrogen storage: state-of-the-art and future perspective. EU Commission, JRC Petten, EUR 20995EN 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Scheepers, F.; Stähler, M.; Stähler, A.; Rauls, E.; Müller, M.; Carmo, M.; Lehnert, W. Temperature optimization for improving polymer electrolyte membrane-water electrolysis system efficiency. Applied Energy 2021, 283, 116270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandesris, M.; Médeau, V.; Guillet, N.; Chelghoum, S.; Thoby, D.; Fouda-Onana, F. Membrane degradation in PEM water electrolyzer: Numerical modeling and experimental evidence of the influence of temperature and current density. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 1353–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, A.A.; Tijani, A.S.; Shukri, F.H. Simulation analysis of the effect of temperature on overpotentials in PEM electrolyzer system. Journal of Mechanical Engineering 2015, 12, 47–65. [Google Scholar]
- Tijani, A.S.; Rahim, A.A. Numerical modeling the effect of operating variables on Faraday efficiency in PEM electrolyzer. Procedia Technology 2016, 26, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nafchi, F.M.; Afshari, E.; Baniasadi, E.; Javani, N. A parametric study of polymer membrane electrolyser performance, energy and exergy analyses. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 18662–18670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Lee, W.; Na, Y. Effect of gravity and various operating conditions on proton exchange membrane water electrolysis cell performance. Membranes 2021, 11, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, T.; Nagata, Y.; Endo, N.; Ishida, M. Effect of water electrolysis temperature of hydrogen production system using direct coupling photovoltaic and water electrolyzer. Journal of International Council on Electrical Engineering 2016, 6, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.; Trinke, P.; Stähler, M.; Stähler, A.; Scheepers, F.; Bensmann, B.; Carmo, M.; Lehnert, W.; Hanke-Rauschenbach, R. The Effect of Cell Compression and Cathode Pressure on Hydrogen Crossover in PEM Water Electrolysis. Journal of The Electrochemical Society 2022, 169, 014502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, M.; Kim, A.; Paramanantham, S.S.; Kim, H.; Lim, D.; Lee, S.; Moon, S.; Lim, H. Three-dimensional CFD simulation of proton exchange membrane water electrolyser: Performance assessment under different condition. Applied Energy 2022, 306, 118016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernt, M.; Schröter, J.; Möckl, M.; Gasteiger, H. Analysis of gas permeation phenomena in a PEM water electrolyzer operated at high pressure and high current density. Journal of The Electrochemical Society 2020, 167, 124502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, W.; Yang, W.; Liu, W.; Min, F.; Mao, S.S.; Xie, J. Catalyst-coated proton exchange membrane for hydrogen production with high pressure water electrolysis. Applied Physics Letters 2021, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiber, S.; Balzer, H.; Wierhake, A.; Wirkert, F.J.; Roth, J.; Rost, U.; Brodmann, M.; Lee, J.K.; Bazylak, A.; Waiblinger, W. Porous transport layers for proton exchange membrane electrolysis under extreme conditions of current density, temperature, and pressure. Advanced Energy Materials 2021, 11, 2100630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinke, P.; Bensmann, B.; Hanke-Rauschenbach, R. Current density effect on hydrogen permeation in PEM water electrolyzers. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 14355–14366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon Araya, S.; Juhl Andreasen, S.; Knudsen Kær, S. Parametric Sensitivity Tests—European Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cell Stack Test Procedures. Journal of Fuel Cell Science and Technology 2014, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouri-Khorasani, A.; Ojong, E.T.; Smolinka, T.; Wilkinson, D.P. Model of oxygen bubbles and performance impact in the porous transport layer of PEM water electrolysis cells. International journal of hydrogen energy 2017, 42, 28665–28680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majasan, J.O.; Cho, J.I.; Dedigama, I.; Tsaoulidis, D.; Shearing, P.; Brett, D.J. Two-phase flow behaviour and performance of polymer electrolyte membrane electrolysers: Electrochemical and optical characterisation. international journal of hydrogen energy 2018, 43, 15659–15672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, M.F.; Demir, N.; Rees, N.V.; El-Kharouf, A. Improving PEM water electrolyser’s performance by magnetic field application. Applied Energy 2020, 264, 114721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeh, M.A.; Arlt, T.; Manke, I.; Banhart, J.; Fritz, D.L.; Maier, W.; Lehnert, W. In operando synchrotron X-ray radiography studies of polymer electrolyte membrane water electrolyzers. Electrochemistry communications 2015, 55, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopata, J.; Kang, Z.; Young, J.; Bender, G.; Weidner, J.; Shimpalee, S. Effects of the transport/catalyst layer interface and catalyst loading on mass and charge transport phenomena in polymer electrolyte membrane water electrolysis devices. Journal of The Electrochemical Society 2020, 167, 064507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tugirumubano, A.; Shin, H.J.; Kwac, L.K.; Kim, H.G. Numerical simulation of the polymer electrolyte membrane electrolyzer. IOSR 2016, 13, 94–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzo-Robledo, A.; Boucher, A.C.; Pastor, E.; Alonso-Vante, N. Electro-oxidation of Carbon Monoxide and Methanol on Carbon-Supported Pt–Sn Nanoparticles: a DEMS Study. Fuel cells 2002, 2, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polonský, J.; Kodým, R.; Vágner, P.; Paidar, M.; Bensmann, B.; Bouzek, K. Anodic microporous layer for polymer electrolyte membrane water electrolysers. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry 2017, 47, 1137–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siracusano, S.; Hodnik, N.; Jovanovic, P.; Ruiz-Zepeda, F.; Šala, M.; Baglio, V.; Aricò, A.S. New insights into the stability of a high performance nanostructured catalyst for sustainable water electrolysis. Nano Energy 2017, 40, 618–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bystron, T.; Vesely, M.; Paidar, M.; Papakonstantinou, G.; Sundmacher, K.; Bensmann, B.; Hanke-Rauschenbach, R.; Bouzek, K. Enhancing PEM water electrolysis efficiency by reducing the extent of Ti gas diffusion layer passivation. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry 2018, 48, 713–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, S.; Lee, B.-S.; Cho, M.K.; Kim, H.-J.; Henkensmeier, D.; Yoo, S.J.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Park, H.S.; Jang, J.H. Electrodeposited IrO2/Ti electrodes as durable and cost-effective anodes in high-temperature polymer-membrane-electrolyte water electrolyzers. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental 2018, 226, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Z.; Yang, G.; Mo, J.; Yu, S.; Cullen, D.A.; Retterer, S.T.; Toops, T.J.; Brady, M.P.; Bender, G.; Pivovar, B.S. Developing titanium micro/nano porous layers on planar thin/tunable LGDLs for high-efficiency hydrogen production. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 14618–14628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lettenmeier, P.; Kolb, S.; Burggraf, F.; Gago, A.; Friedrich, K.A. Towards developing a backing layer for proton exchange membrane electrolyzers. Journal of Power Sources 2016, 311, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigoriev, S.; Millet, P.; Volobuev, S.; Fateev, V. Optimization of porous current collectors for PEM water electrolysers. International journal of hydrogen energy 2009, 34, 4968–4973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Sabir, I. Review of bipolar plates in PEM fuel cells: Flow-field designs. International journal of hydrogen energy 2005, 30, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lettenmeier, P.; Wang, R.; Abouatallah, R.; Saruhan, B.; Freitag, O.; Gazdzicki, P.; Morawietz, T.; Hiesgen, R.; Gago, A.; Friedrich, K. Low-cost and durable bipolar plates for proton exchange membrane electrolyzers. Scientific Reports 2017, 7, 44035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toops, T.J.; Brady, M.P.; Zhang, F.-Y.; Meyer III, H.M.; Ayers, K.; Roemer, A.; Dalton, L. Evaluation of nitrided titanium separator plates for proton exchange membrane electrolyzer cells. Journal of Power Sources 2014, 272, 954–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.-Y.; Huang, S.-Y.; Popov, B.N. High-durability titanium bipolar plate modified by electrochemical deposition of platinum for unitized regenerative fuel cell (URFC). Journal of Power Sources 2010, 195, 1950–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.-Y.; Huang, S.-Y.; Ganesan, P.; Popov, B.N. Performance of gold-coated titanium bipolar plates in unitized regenerative fuel cell operation. Journal of Power Sources 2009, 194, 972–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lettenmeier, P.; Wang, R.; Abouatallah, R.; Burggraf, F.; Gago, A.; Friedrich, K. Coated stainless steel bipolar plates for proton exchange membrane electrolyzers. Journal of The Electrochemical Society 2016, 163, F3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langemann, M.; Fritz, D.L.; Müller, M.; Stolten, D. Validation and characterization of suitable materials for bipolar plates in PEM water electrolysis. International journal of hydrogen energy 2015, 40, 11385–11391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gago, A.S.; Ansar, A.S.; Gazdzicki, P.; Wagner, N.; Arnold, J.; Friedrich, K.A. Low cost bipolar plates for large scale PEM electrolyzers. ECS Transactions 2014, 64, 1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Ricketts, M.; Hirano, S. Ex situ evaluation of nanometer range gold coating on stainless steel substrate for automotive polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell bipolar plate. Journal of Power Sources 2010, 195, 1401–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, N.; Sánchez-Molina, M.; Sevilla, G.; Amores, E.; Almandoz, E.; Esparza, J.; Vivas, M.R.C.; Colominas, C. Coated stainless steels evaluation for bipolar plates in PEM water electrolysis conditions. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 25929–25943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Scott, K. The effects of ionomer content on PEM water electrolyser membrane electrode assembly performance. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 12029–12037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozain, C.; Mayousse, E.; Guillet, N.; Millet, P. Influence of iridium oxide loadings on the performance of PEM water electrolysis cells: Part I–Pure IrO2-based anodes. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental 2016, 182, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendt, H.; Spinacé, E.V.; Oliveira Neto, A.; Linardi, M. Electrocatalysis and electrocatalysts for low temperature fuel cells: fundamentals, state of the art, research and development. Química Nova 2005, 28, 1066–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapountzi, F.M.; Gracia, J.M.; Fredriksson, H.O.; Niemantsverdriet, J.H. Electrocatalysts for the generation of hydrogen, oxygen and synthesis gas. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science 2017, 58, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, B.; Liu, X.; Hu, G.; Gul, S.; Yano, J.; Jiang, D.-e.; Sun, Y. Universal surface engineering of transition metals for superior electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution in neutral water. Journal of the American Chemical Society 2017, 139, 12283–12290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Chen, B.; Mei, D.; Liang, X. The OH−-driven synthesis of Pt–Ni nanocatalysts with atomic segregation for alkaline hydrogen evolution reaction. Journal of Materials Chemistry A 2019, 7, 5475–5481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.-J.; Wan, Z.; Kim, C.-M.; Oh, I.-K.; Harada, R.; Suzuki, K.; Choi, E.-A.; Kwon, S.-H. Atomic layer deposition of Pt thin films using dimethyl (N, N-dimethyl-3-butene-1-amine-N) platinum and O2 reactant. Chemistry of Materials 2019, 31, 5056–5064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Gan, J.; Huang, Z.; Chen, W.; Qian, G.; Zhou, X.; Duan, X. Boosting HER performance of Pt-based catalysts immobilized on functionalized vulcan carbon by atomic layer deposition. Frontiers in Materials 2019, 6, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adzic, R.R.; Zhang, J.; Sasaki, K.; Vukmirovic, M.B.; Shao, M.; Wang, J.; Nilekar, A.U.; Mavrikakis, M.; Valerio, J.; Uribe, F. Platinum monolayer fuel cell electrocatalysts. Topics in Catalysis 2007, 46, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinnemann, B.; Moses, P.G.; Bonde, J.; Jørgensen, K.P.; Nielsen, J.H.; Horch, S.; Chorkendorff, I.; Nørskov, J.K. Biomimetic hydrogen evolution: MoS2 nanoparticles as catalyst for hydrogen evolution. Journal of the American Chemical Society 2005, 127, 5308–5309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarno, M.; Ponticorvo, E. High hydrogen production rate on RuS2@ MoS2 hybrid nanocatalyst by PEM electrolysis. international journal of hydrogen energy 2019, 44, 4398–4405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, B.T.X.; Chiku, M.; Higuchi, E.; Inoue, H. Preparation of PdAg and PdAu nanoparticle-loaded carbon black catalysts and their electrocatalytic activity for the glycerol oxidation reaction in alkaline medium. Journal of Power Sources 2015, 297, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-F.; Wang, C.-H.; Sasaki, K.; Marinkovic, N.; Xu, W.; Muckerman, J.T.; Zhu, Y.; Adzic, R. Highly active and durable nanostructured molybdenum carbide electrocatalysts for hydrogen production. Energy & Environmental Science 2013, 6, 943–951. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, L.; Liu, P.F.; Yan, X.; Gu, L.; Yang, Z.Z.; Yang, H.G.; Qiu, S.; Yao, X. Atomically isolated nickel species anchored on graphitized carbon for efficient hydrogen evolution electrocatalysis. Nature communications 2016, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.-Y.; Gong, M.; Chou, H.-L.; Pan, C.-J.; Chen, H.-A.; Wu, Y.; Lin, M.-C.; Guan, M.; Yang, J.; Chen, C.-W. Highly active and stable hybrid catalyst of cobalt-doped FeS2 nanosheets–carbon nanotubes for hydrogen evolution reaction. Journal of the American Chemical Society 2015, 137, 1587–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, B.B.; Nanda, K. CoFe Nanoalloys Encapsulated In N-doped Graphene Layers As Pt-Free Multi-Functional Robust Catalyst: Elucidating The Role Of Coalloying and N-doping. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering 2018, 6, 12736–12745. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, R.; Zhang, J.; Shi, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhang, B. Metallic WO2–carbon mesoporous nanowires as highly efficient electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction. Journal of the American Chemical Society 2015, 137, 6983–6986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scofield, M.E.; Zhou, Y.; Yue, S.; Wang, L.; Su, D.; Tong, X.; Vukmirovic, M.B.; Adzic, R.R.; Wong, S.S. Role of chemical composition in the enhanced catalytic activity of Pt-based alloyed ultrathin nanowires for the hydrogen oxidation reaction under alkaline conditions. ACS Catalysis 2016, 6, 3895–3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Q.; Liang, W.; Bates, M.K.; Mani, P.; Lee, W.; Mukerjee, S. Activity descriptor identification for oxygen reduction on platinum-based bimetallic nanoparticles: in situ observation of the linear composition–strain–activity relationship. ACS nano 2015, 9, 387–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitchin, J.; Nørskov, J.K.; Barteau, M.; Chen, J. Modification of the surface electronic and chemical properties of Pt (111) by subsurface 3d transition metals. The Journal of chemical physics 2004, 120, 10240–10246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trasatti, S.; Buzzanca, G. Ruthenium dioxide: a new interesting electrode material. Solid state structure and electrochemical behaviour. Journal of electroanalytical chemistry and interfacial electrochemistry 1971, 29, A1–A5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Xu, K.; Fleischer, C.; Liu, X.; Grandcolas, M.; Strandbakke, R.; Bjørheim, T.S.; Norby, T.; Chatzitakis, A. Earth-abundant electrocatalysts in proton exchange membrane electrolyzers. Catalysts 2018, 8, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Guo, L.; Pan, L.; Yan, T.; He, Z.; Li, Y.; Shi, C.; Huang, Z.F.; Zhang, X.; Zou, J.J. Advances in oxygen evolution electrocatalysts for proton exchange membrane water electrolyzers. Advanced Energy Materials 2022, 12, 2103670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Peng, X.; Intikhab, S.; Zeng, G.; Kariuki, N.N.; Myers, D.J.; Danilovic, N.; Snyder, J. Nanoporous iridium nanosheets for polymer electrolyte membrane electrolysis. Advanced Energy Materials 2021, 11, 2101438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, J.; Kim, S.-K.; Thien, P.T.; Kim, M.-J.; Cho, H.-S.; Cho, W.-C.; Kim, C.-H.; Lee, C.; Lee, J.H. Enhancing the activity and durability of iridium electrocatalyst supported on boron carbide by tuning the chemical state of iridium for oxygen evolution reaction. Journal of Power Sources 2021, 512, 230506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Yu, H.; Li, Y.; Yao, D.; Chi, J.; Sun, S.; Shao, Z. Low-loading and highly stable membrane electrode based on an Ir@ WO x NR ordered array for PEM water electrolysis. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces 2021, 13, 15073–15082. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, H.-S.; Nong, H.N.; Reier, T.; Bergmann, A.; Gliech, M.; Ferreira de Araújo, J.; Willinger, E.; Schlögl, R.; Teschner, D.; Strasser, P. Electrochemical catalyst–support effects and their stabilizing role for IrO x nanoparticle catalysts during the oxygen evolution reaction. Journal of the American Chemical Society 2016, 138, 12552–12563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Shao, C.; Zhou, W.; Shen, X.; Xue, M.; Zhang, C. Self-assembled RuO2@ IrOx core-shell nanocomposite as high efficient anode catalyst for PEM water electrolyzer. Applied Surface Science 2020, 514, 145943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Chen, M.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Ye, S.; Xu, S.; Wang, H.; Li, H. Bridging the gap between highly active oxygen reduction reaction catalysts and effective catalyst layers for proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Nature Energy 2021, 6, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Wang, S.; Sun, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, C. Anode catalyst layer with hierarchical pore size distribution for highly efficient proton exchange membrane water electrolysis. Journal of Power Sources 2023, 564, 232878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).