1. Introduction
1.1. Global Energy Consumption: A Key Factor in Sustainable Building Practices
The importance of energy consumption and sustainability has reached a critical level on a global scale. As the primary source of emissions causing climate change, local and global communities worldwide must prioritize efforts to conserve energy in all aspects of our daily lives. Buildings are responsible for approximately 40% of all energy usage [
1], thus, they are an important area of concern when it comes to conservation efforts. It is necessary to focus on cutting down power consumption in buildings to save energy and reduce CO2 emissions at the same time. Nonetheless, the topic of energy conservation is specifically addressed by the UN Sustainable Goal number 7, where the goal is to ensure access to affordable, reliable, sustainable, and modern energy for everyone [
2].
The deficiency of consumption may be caused by different factors such as the building's physical characteristics, poor or outdated appliances, random and uncategorized human energy behaviour, and specified climate location-based characteristics could be considered among the critical influencing factors. [
3]
The architectural built artefact has to be considered as a sort of envelope for the indoor environment where one refers to the façade opening as the external cover of a building; subsequently, the presence of openings is a constant feature while the variability is manifested in their form, size, shape and position. The opening is the mean throughout occupants of a building, benefit of the outside view as well as profit of lighting conditions. However, poorly designed façades or improperly conceived openings can result in limited solar heat gain and inadequate natural ventilation, among other issues. The architectural and engineering factors have to be considered along with the in-situ characteristics of the place, as thermal environment conditions are noticeably different from region to region of different parts of the hemisphere.
1.2. Integrated Lighting and Daylighting
Daylighting has several benefits, from the early evidence connected to substantial findings that daylight has an enormous impact on human health and well-being [
4] among others and improves human biological and psychological aspects. From the early research about the optimal deployment of daylight in a large variety of uses of a period ranging of two decades, the main interest in using daylight has been redirected towards how it can be fully harvested to have beneficial indoor environments. These include an optimal indoor climate but also ideal lighting conditions that lead to a responsible use of artificial lighting and so, as a matter of consequence, energy saving.
Therefore, effective daylighting is only a practice that could be considered regarding new buildings, as the already dated and existing buildings do not satisfy the requirements to be “daylight retrofitted”, a process that refers to the modification of existing buildings, aimed to improve its daylighting capabilities, which is mainly appointed due to structural limitations and related costs.
As a matter of fact, the energy utilization level depends, amidst the rest, on the power consumption of lighting systems and the operating periods, where lamentably the worldwide residential sector still uses energy-inefficient lighting systems. Another factor is that in contemporary buildings, windows are the relevant means that influence energy consumption by either increasing or decreasing the need for cooling or heating. To control daylight, shading devices could be used but their proper and efficient employment could not rely on occupants, who only operate on them occasionally to mitigate excessive light conditions and therefore they do not frequently adjust shading devices, resulting in suboptimal energy consumption [
5].
Optimizing Energy Use: The Benefits of Solar Panels and Effective Daylighting
Hence a need for the technology field to seek and harness the ultimate strategies to supply a better life-cycle energy consumption, also concerning CO2 emissions.
The latest advancements in both engineering as well as lighting technology have also been responsible for reducing the energy consumption in buildings. This is the case of solar photovoltaic panels that absorb solar radiation and convert it into energy, which have been seen to reduce energy loss by up to 40% due to the reduction in artificial light usage [
6]. Today, daylighting must be re-considered into a beneficial medium throughout reaching the expected prevision of energy gaining. Studies have largely exposed the energy benefits from integration with daylighting in a wide range of different spaces, as an appropriate maximization of daylight within the spaces, can fully exploit the energy-saving potential of controls. According to IEA Task 61 [
7] buildings have frequently consumed more energy than necessary due to inadequate coordination of natural daylight and artificial lighting. The cause might be traced back to the lack of consideration on the sun´s position when designing light plans. As a result, with the missing integration between daylight and lighting, fixtures are not properly managed, leading to a considerable waste of energy. In this matter, researchers state that the present issue could be addressed by using integrated lighting control systems that can automatically adjust the amount of artificial light based on the amount of available natural light. The collection of 25 international case studies enabled Gentile et al. to gain a deeper understanding of how buildings can achieve energy-efficiency and human factor goals, their global deployment, and real-world performance [
8].
The research gives game-changing insights into how natural light and electrical lighting can be combined. Breakthroughs in technology have brought about LED lighting which uses minimal energy [
9,
10] while advanced systems for controlling shadows have been developed that reduce it even more. Prioritizing effective daylighting design and integration for energy-efficient integrated lighting solutions are key steps towards cutting down on power consumption. The value of natural light cannot be overstated when it comes to achieving energy efficiency; thus, Gentile et al. suggest that people should be allowed to control automated shading and lighting systems to improve their comfort and satisfaction levels [
11]. Consequently, there is a need for easy-to-use interfaces that come with clear instructions since this will help individuals familiarize themselves with these settings over time. It is important to note that in some parts of the world where there is little sunlight available throughout the year, reliance purely upon artificial illumination for physiological well-being may result in more usage of electricity. This means therefore that good planning of windows as well as sunscreens is necessary if we want to save energy [
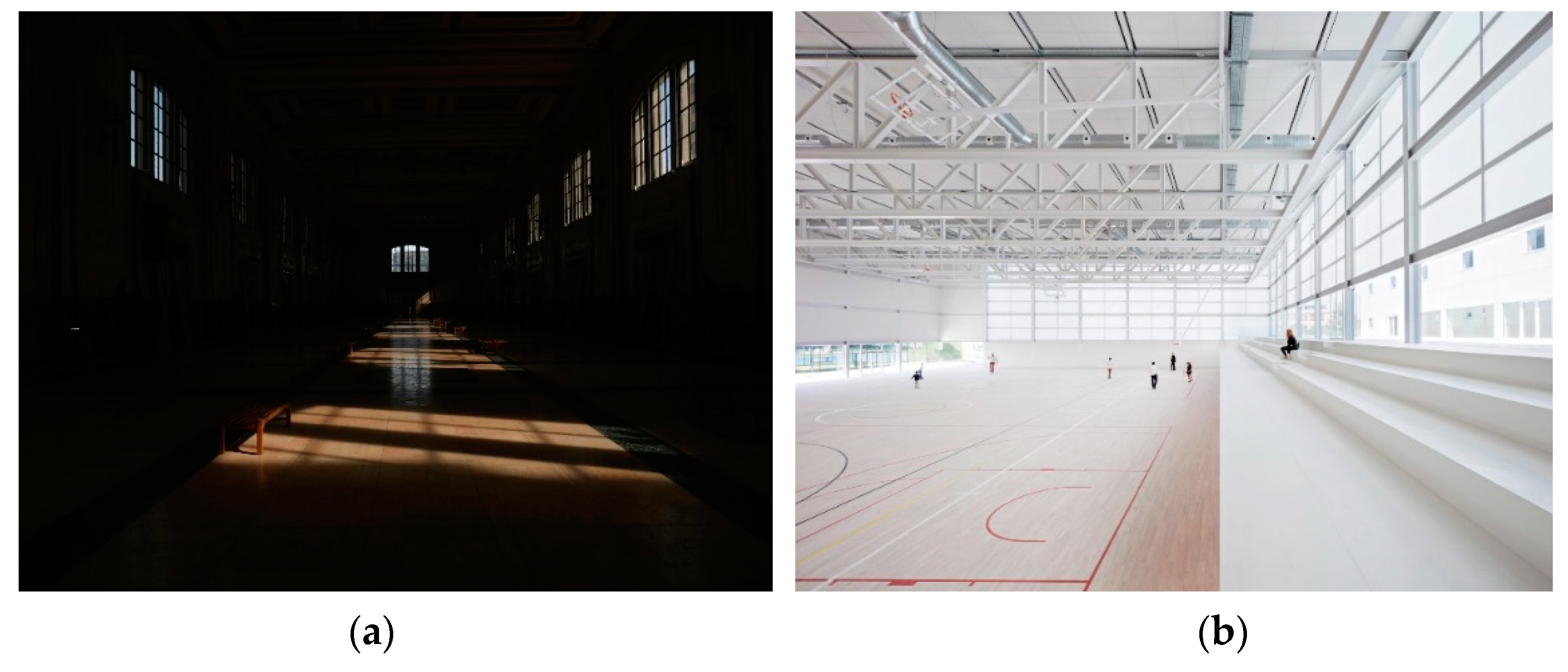
12] while at the same time maximizing the use of daylight in buildings, as exemplified in
Figure 1.
1.3. The Role of Building Information Modeling
Consequently, daylight should be appointed as one
of the most important variables in the design process in a very early stage, as it requires a deep understanding of the proper deployment of the building project, with a multitude of variables and parameters to be considered. To do and evaluate such performances, either virtual simulation modelling or manual measurements as well, could help the designers tackle the topic [
13]. Considering the problems experienced in construction and bad supervision that result in energy loss, it is important to discover how best natural light can be utilized in addition to cutting down on power consumption. Building Information Modeling, widely known as BIM, is a tool that yields much easier decision-making when designing buildings [
14,
15]. One of the biggest benefits of using BIM is that it makes it easy to compare different design options, especially in the early stages of a project, as illustrated in
Figure 3, where the nexus of BIM and smart buildings is depicted. By creating digital models of different design options, architects and designers can see how each option would work and then decide which one is best. This not only saves time but also eliminates the need to spend a lot of time manually looking at multiple designs. In addition, it offers a solution for optimizing daylighting in buildings and is widely recognized as a powerful tool for enhancing construction in numerous ways [
16].
BIM integrates a multitude of variables such as design, construction, and operation data, enabling stakeholders to analyze and visualize daylighting scenarios, precisely as
Figure 2. conveys in the image. This allows them to make informed decisions about building orientation, window placement, shading devices, and material selection. The goal is to maximize natural light penetration while minimizing energy demand, resulting in a more sustainable and comfortable indoor environment. Additionally, by maximizing daylight the major effect will be the reduction of the need for artificial lighting during daylight hours, leading to energy savings and by doing that, buildings can also lower their carbon footprint. Enhancing the scope of BIM, Digital Twins are considered an important step further in buildings' digital management based upon BIM. It was coined and introduced by Grieves in 2003 in the context of product lifecycle management in manufacturing engineering [
18].
A Digital Twin is essentially a copy of a physical building, system or process. The development of this type of virtual model has been possible since building information modelling has been merged with the Internet of Things platforms which have allowed for real-time data collection and monitoring processes, hence providing a clear overview of the buildings' performance and conditions. Decision-making capacity in these facilities is elevated by employing modeling and interaction with digital models in the real world which enables stakeholders to see and interact with the digital model in real time, which shows changes and updates from the physical environment. Nowadays, BIM is vastly used by architectural and engineering practices as an innovative technology that could manage various and multiple tasks, by in turn, allowing for more effective management, planning, and design of buildings [
19]. As society continues to face the pressing issue of environmental impact and the threat of global warming, it has become increasingly necessary to integrate BIM with building energy performance. Doing so is crucial for achieving lower building energy consumption throughout the entire project's life cycle. BIM could efficiently merge approaches and environmental aspects to significantly affect the environment, considering the mean throughout managing a better employment of the resources. In addition, the optimisation of the resources would allow to tackle the bad habits of the constructions which are appointed to be responsible for 37% of all energy-related CO2 emissions, according to the UN Environment Program [
20].
To achieve this goal is essential that BIM be used as a tool for the evaluation of energy during the initial design phase, by linking the structure of both future buildings and existing ones, to energy analysis tools. Only then, the idea of Green BIM be significantly predominant in all practices, as BIM and green buildings are the two essential factors that make it possible. This powerful tool could handle all the related sustainable aspects, such as energy, daylighting, ventilation and carbon emissions.
1.4. IoT in Building Management
Additionally, in the context of optimizing buildings, it's essential to explore the role of Internet of Things (IoT) technologies in managing lighting systems. IoT (Internet of Things) is a system where devices, or "things," have sensors and software that connect them to the internet. Through this connection, these devices can talk to each other and share information with other systems [
21]. While BIM provides valuable insights during the design phase, especially for daylighting strategies, the Internet of Things enables real-time monitoring, optimizes the performance of lighting in response to both environmental conditions and user needs as well and finally offers an adaptive control of lighting systems throughout a building's entire life cycle. Studies revolving around IoT-driven intelligent buildings have proven beneficial and efficient in diminishing greenhouse gas contributions and dealing with global heating issues. By incorporating IoT solutions, smart buildings can improve energy use, upgrade operational productivity, and activate responsive environmental observation and regulation systems [
22].
The rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) is seen as one of the newest developments, offering exciting chances for creating smart applications. However, many public lighting systems still use outdated and inefficient light sources. Therefore, this poses a challenge for public entities looking to improve their infrastructure and adopt energy-efficient lighting solutions. An intelligent lighting system among others could also be designed to optimize visual comfort, by prioritizing, for example, energy efficiency. The system usually incorporates advanced light sensors and subsequently analyses spectral data in real-time, ready to offer multiple applications and support communication via different protocols, by ultimately, enabling a precise spectral adjustment with remote monitoring and control through the Internet [
23].
In this regard, worth mentioning is how the IoT-connected lighting systems use sensors and network connectivity to change the intrinsic characteristics and the qualities of light, based on local variables, such as space occupancy, daylight provision and much more. As a natural consequence, the concept of a “smart city” could be introduced as the target enhancement idea in both the living standards and cost-effectiveness for its inhabitants [
24]. This notion is based on applying cutting-edge, sprouting technologies and reinventing new urban areas into self-reliant spaces.
The main objective of these is projected to play the important role of diminishing the ecological threats by developing better environmental solutions and cost-efficient technologies. With the effective integration of a multitude of elements, such as sensors with real-time monitoring and communication systems, smart cities will be able to supervise and control the infrastructures and in the last stage, it will consent for a wider resource distribution and reduction in the eco-impact, meaning also, a better living condition overall for their inhabitants [
25].
Due to technological progress spread in the last decades in the lighting design field, now able to accurately predict the light output of Light Emitting Diodes (LED), the idea that has risen is how to properly combine light fixtures to these systems and IoT devices [
26]. LEDs have proved to lower the demand in energy consumption, especially if the combined effect of light sources, advanced controls, and integration of daylighting and electrical lighting, are evaluated as a whole, thus drastically contributing to increasing the energy effectiveness of lighting [
27]. The use of LED-based systems for lighting has several benefits and advantages, both in current and future applications, making them an eco-friendly choice. This will significantly help to improve energy use, make people feel more comfortable, and make the lights last longer.
This convergence of Building Information Modeling and the Internet of Things, represents a holistic approach to building management, especially when enhanced and combined with Artificial Intelligence, that is taking rapidly in acceptance and widespread. In this regard, Wu et al. (2022) [
28] have shown how the adoption rate significantly increases when integrated with BIM and IoT.
Therefore, this literature review aims to deeply explore and discover the methods used for the integration of Building Information Modeling, and the Internet of Things, added to the latest advancements of integrated lighting solutions and the management of related systems. Advancing scholarly study, assessing data, and presenting pragmatic tips based on organized literature synthesis were the main points. The main objective is to uncover and deploy the current state of the art on how these technologies could join together in creating intelligent and energy-efficient buildings, to lead to innovative opportunities for the future of building systems. Furthermore, the predicted results would involve the development of effective methods to encourage the widespread use of low-carbon systems and innovative design techniques. This necessitates collaboration between higher education institutions and researchers. By working together, they can achieve the objective of developing buildings that are both sustainable and environmentally friendly
To better articulate the scope and structure of our literature review, a workflow diagram is presented in the introduction (
Figure 3). This diagram provides a visual representation of the key topics and subtopics explored, highlighting their hierarchical relationships and interconnections. It also emphasizes the importance of energy conservation and the integration of advanced technologies, such as Building Information Modeling (BIM), Internet of Things (IoT), and intelligent lighting solutions, in achieving sustainable building practices. By mapping out these areas, the diagram underscores the critical need for further investigation and innovation in creating energy-efficient and environmentally friendly buildings.
Figure 3.
Hierarchy diagram showing the workflow for the scope and structure of the literature review.
Figure 3.
Hierarchy diagram showing the workflow for the scope and structure of the literature review.
1.5. Existing Reviews on the Topic
The current section is being led by the examination of articles and the systematic review is based on a comprehensive literature search. A lot of studies were done with the help of Building Information Modeling, Artificial Intelligence and the Internet of Things in building constructions. However, none of them has attempted to provide an overview of the three main categories, the interest of the current review, seeking a circular integration of integrated lighting controls, BIM and IoT. For instance, Yang et al. (2021) [
17] carried out an extensive literature review proposing a framework with three dimensions for the integration of BIM applications in smart buildings, encompassing BIM advantages, attributes, applications project phases, and smart attributes. Despite mentioning that BIM is capable, through incorporated data, of performing energy simulations such as daylighting and electrical lighting, they did not delve into the specific feature for BIM to evaluate, based on its functions, the possibility of reducing energy consumption through integrated lighting analysis.
Concerning the sole focus on integrated lighting solutions, Thomson et al. (2021) [
29] highlighted the conflicting landscape within the ecosystem of daylighting and electric lighting systems in contemporary research, design, implementation and operation. They presented valuable tools and technical gaps that hinder the full integration of electrical lighting and daylighting with advanced façades, due to the lack of coordination between lighting and window research activities. Moreover, Plörer et al. (2021) [
30] identified current trends in control strategies. The results indicate that building controls are increasingly designed to address multiple objectives simultaneously, rather than focusing on a single goal. Proper control of daylight and electrical lighting systems by which a building's energy efficiency is optimized with comfort attributes is a hot topic of interest after their conducted review, although the other two area field subjects have just briefly mentioned as future directions for incorporating all relevant information. In the same way, Baghi et al. (2021) [
31] analysed technological innovations in the top five ranked sustainable net-zero houses in the Solar Decathlon competitions; in general, it was found that the majority of innovations were implemented in HVAC systems, architectural design, adaptability of building appliances to various lifestyles and climates, with limited references to integrated lighting solutions.
Noteworthy, Rangasamy and Yang (2024) [
32] highlighted in their review study, which hinged a three-stage methodology comprising a bibliometric study, the main fieldwork that brought to light the most recent developments in the domain of prefabrication (PC) assisted by the Building Information Modeling (BIM), the Artificial Intelligence (AI), and the Internet of Things (IoT) applications. The quantitative analysis pointed out major research patterns. On the other hand, it also proposes an alternative solution or combination of various technologies that can help in solving the problem in modern times.
Furthermore, the study accentuates the potential that these research directions have, for example, the advancement of automated design, the use of robots in fabrication, or the capability of different applications to work together, strategic decision-making, and the operation and maintenance of PC systems. Despite all the promising topics, the integrated lighting solutions or coexistence between daylighting and electrical lighting.
On a similar path, Mazhar et al. (2023) [
33] reviewed and analysed the challenges of the Internet of Things in a Smart grid, using Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning. The smart grid monitoring and its remote configuration systems can enhance both the security and comfort of building occupants and undeniably if paired with machine learning, as a result, the energy efficiency of smart buildings is improved by far. After all, connecting buildings to the IoT-smart grid has shown incredible advantages but also disadvantages, mainly due to the critical complexity of the models and algorithms and sometimes even low speediness; scarce mention of lighting and therefore integrated lighting control, which are known to be easily integrated with the aid of IoT in regard of the “smart lighting”.
Ultimately, regarding the integration of BIM in the architecture, engineering and construction sectors, Hauer et al. (2024) [
34] delved into the field of smart building and the implementation of Digital Twins as coupled with BIM methodologyin the construction and post-construction phases.
They highlighted major and substantial progress in areas such as fault detection, building control and facility management, although they noted that the development of integrative control strategies for daylight and artificial lighting systems within the BIM environment is still in its early stages
2. Research Objectives
In current literature research, it has been sought to answer the following research questions:
- −
How do the Integrated Light solutions positively impact energy consumption?
- −
How can the integration of BIM and IoT contribute to better lighting management and create synergies to maximize sustainability?
The primary question is investigated through a comprehensive examination. It involves scrutinizing the proliferation in the current state of research concerning Integrated daylight solutions and their related impact towards the reduction of the carbon footprint. Consequently, the secondary research question was solved using thematic examination which includes recognizing shared themes or areas within the Building Information Modeling (BIM) and the Internet of Things processes that align with sustainable practice and low energy demands; this in turn, enables the research to probe more specifically into some specific features of Building Information Modeling that support sustainable practices.
Examining the convergence of daylighting optimisation and Building Information Modeling (BIM) can offer substantial potential for enhancing energy efficiency in buildings. This literature review seeks to investigate the most recent research and developments in this area, with a particular focus on the application of BIM to enhance daylight performance and reduce energy usage. By unveiling contemporary trends regarding integrated lighting strategies through BIM and IoT, this review endeavors to contribute to the creation of environmentally conscious and sustainable built environments, offering a deeper understating of the key questions given in the introductory part of the paper.
This exploration is carried out through a bibliometric analysis of keyword co-occurrences, explaining the development of the prominent aspects of research, and articles that have a strong impact in the domain. Further, an exhaustive article review focuses on three areas with related sub-sections, including Integrated lighting controls, Building Information Modeling and IoT integration.
Finally, the paper offers an overview of the existing challenges and future directions in the field or further research. After this overview, the remainder of the paper is structured into the following sections: section 3 deploys the methodology to structure the following literature review, sections 4,5 and 6 present and qualitatively assess the relevant articles. Ultimately, section 7 outlines and discusses the potential directions for future research and section 8 concludes the study with the highlights.
3. Methods
3.1. Research Methodology
The aim of the current review was performed using the guidelines outlined in the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews (PRISMA) guidelines to conduct a scoping review. The most preferred method that was chosen involves a rigorous and systematic approach, by establishing a standardized process for conducting research step after step, data are found and thus analyzed on a particular topic [
35]. Whereas a conventional literature review aims to provide a clear framework for identifying and evaluating relevant studies in a structured and consistent manner.
This method, in return, provides an overview of collected information that settles a framework of a certain theory.
The search has been conducted on scientific databases (Scopus and Web of Science) mainly due to the broad selection of peer-reviewed journals they offer. The keywords used to prompt the search were about the connection of integrated lighting, Building Information Modeling and Internet of Things from 2019 to 2024. In conducting this literature review, a variety of important terms have been used, including those are shown in the table below,
Table 1.
To carry out the study, quantitative and qualitative data are converged, to fade away the unfavourable effects as a result of the biases and subjectivity in the data filtrations. Progress in the relevant domain is mirrored by the quantitative approach and the qualitative focus is a way of disclosing the research theme and also predicting the needs of future studies. The current system provides a thorough examination of the subject which discovers scientific inquiries, and research gaps and tries to address various keywords.
Each main keyword or phrase used in literature was searched in databases, and their synonyms were linked by logical OR. The OR terms generated were then linked using logical AND. The study concentrated on features of the constructed environment, such as the shading devices, the layout, the retrofitting of a building, the visual and thermal comfort, and the devices or strategies aimed to mitigate and lower energy consumption, to investigate their potential associations with promoting low carbon strategies. These terms were combined and utilized in the advanced search option across the three databases to identify relevant articles. Additionally, articles had to meet specific eligibility criteria such as the language of publication must be written in English, having a publication date from 2019 onwards and possibly being original research.
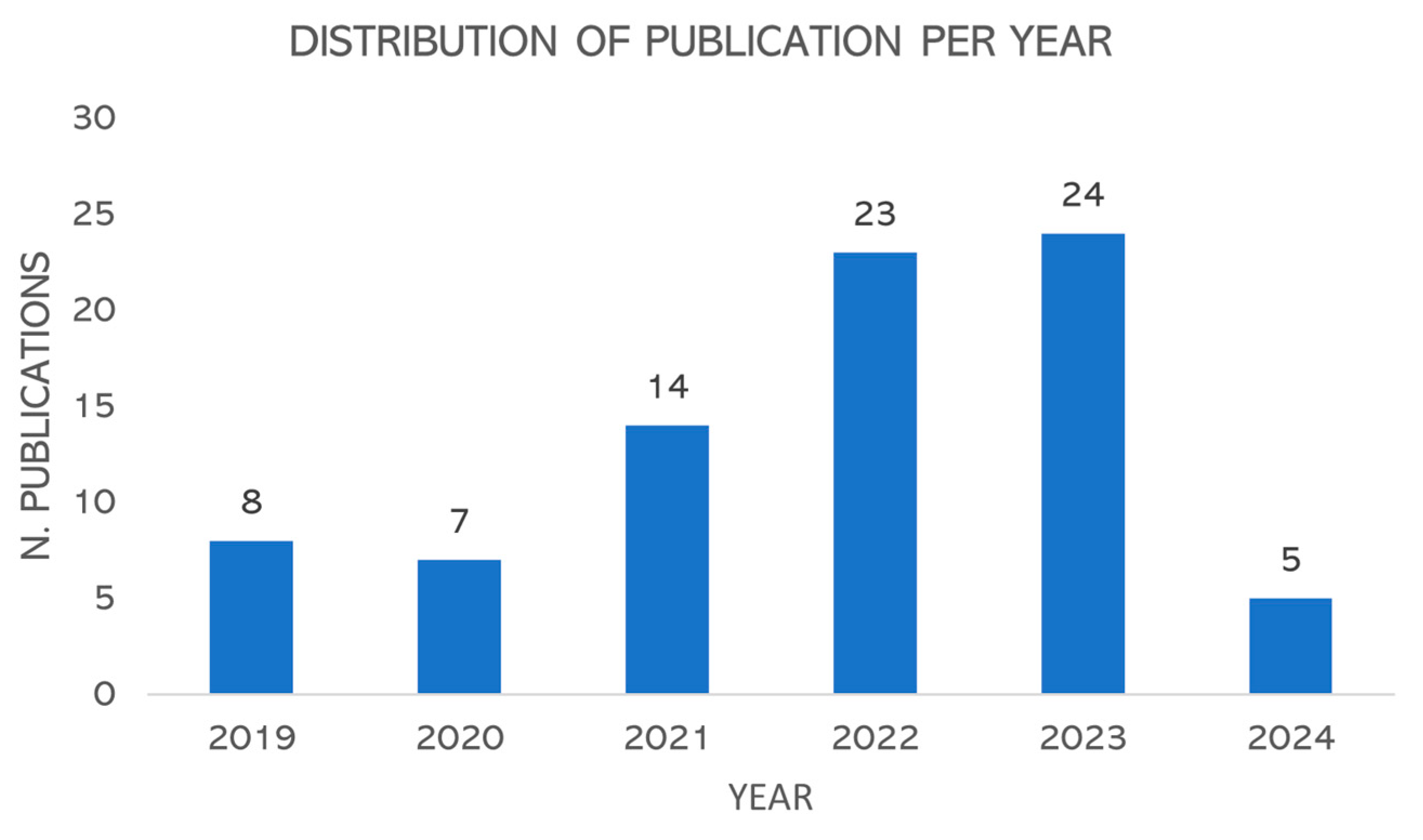
Interestingly, a tendency for the distribution of publications per year could be observed as the selected papers referred to a certain precise timescale. In recent years, after the first wave of the pandemic of coronavirus, there has been an engaging increase in topic relevance as shown in
Figure 4. which highlighted a slight rise from 2021. Little evidence was noted by 2019, the year after outlined a substantial drop in publications due to COVID-19. Nonetheless, early 2021 and ongoing research on these topics have shown a prominent increase because of the new strategies and opportunities brought after the COVID-19 pandemic period as new questions and goals that there is sustainability in all dimensions of life. The analysis then proceeded to categorize based on the authors' place of origin, to highlight territorial clusters related to the various topics under discussion.
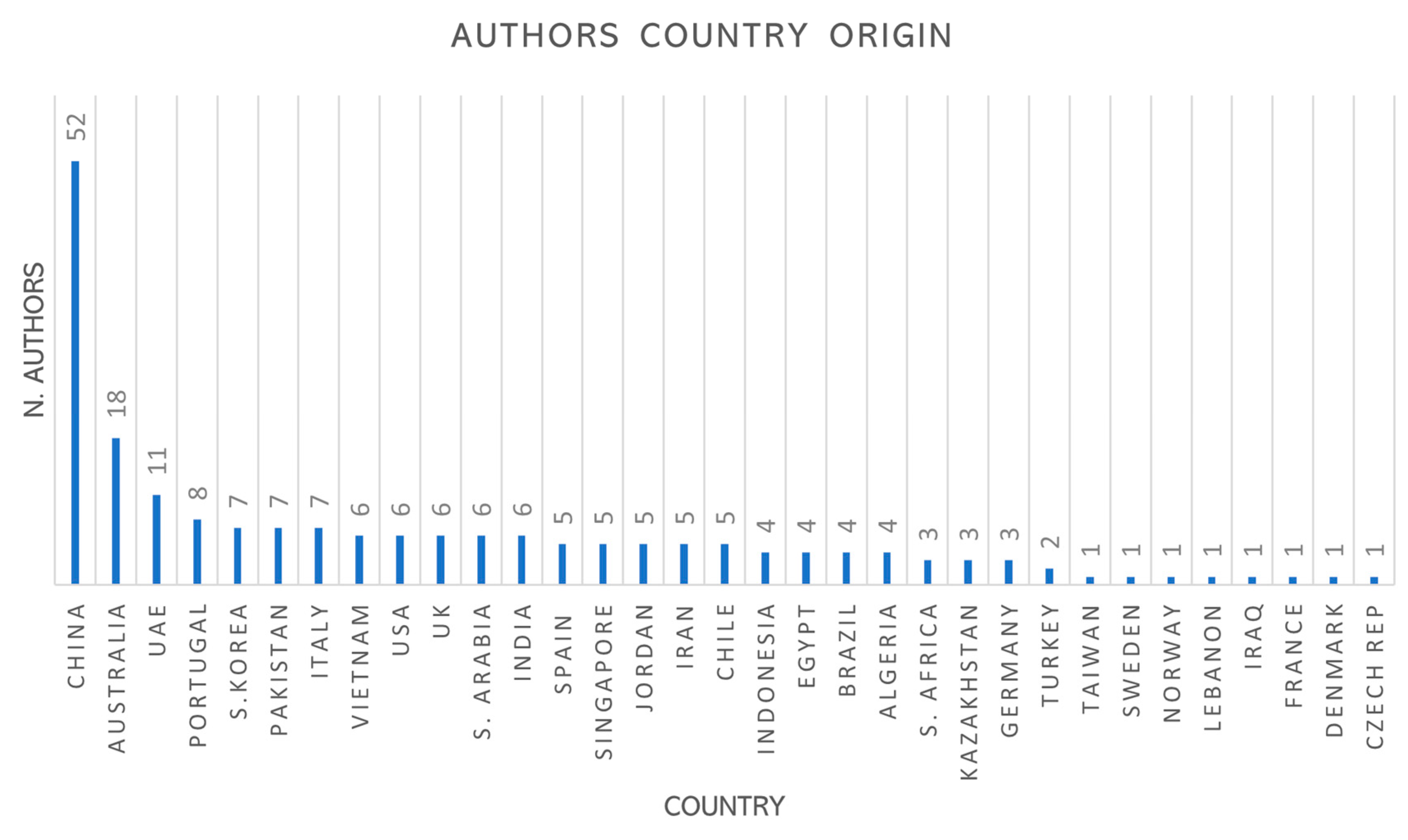
China had the most authors taking part in this study as pointed out in
Figure 5., 52 to be precise. It means they must have had a focus or specialization on those areas who participated in the reviewed studies. Then followed Australia, comprising 18 contributors, followed by the UAE. Other countries are also well represented, like Portugal, South Korea and Pakistan who demonstrated an interest in these regions, despite the severe climate conditions in those regions. After Italy, several nations are represented, pointing to a medium level of activity in this field. The general opinion from the distribution reveals Asia, especially China, as an extraordinarily strong actor in comparison to other countries. However, all countries from all continents appear to engage in the discussed themes to some extent.
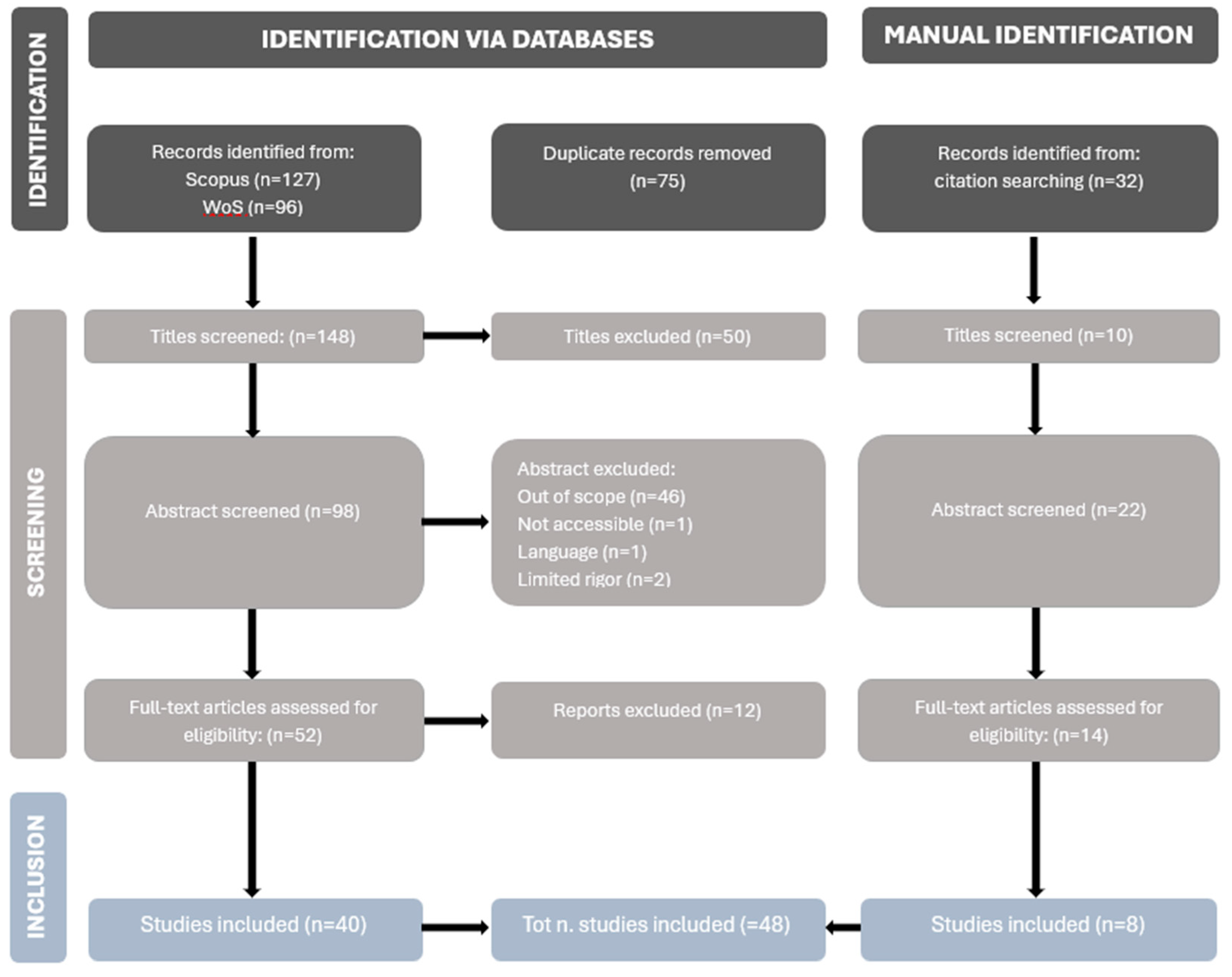
An aggregate of 223 articles were at first detected and appraised for further screening and additionally, another 32 records were identified throughout the citation scan, which gave upgrades to existing structures as shown in
Figure 6.
A first step of identification of the research was performed and aimed for a detailed analysis of the abstracts to recognize purposes, methods and results. Therefore, the papers, which were in line with the study objectives, were collected and processed. This procedure naturally produced a broad range of articles, which reported occasionally findings that were out of scope or even for duplicate presence and so led to the second necessary screening, where all the variables could be merged with the theme. In sum, a total of 158 articles from 255 initial ones were picked out, out of these, 50 were further excluded after the abstract thorough screening. 98 have been further processed by carefully reading the abstract and qualitatively discarding articles that were not compiled with the aim of the research.
Lastly, the assessment of the full-text eligibility gave a result of 52 titles to discharge so to obtain 40 articles to join over an additional 8 texts with an overall 48 studies to be included for the current review. To maintain a concentration on the first-hand process of the research, and to ensure a consistent contribution to the collection of the study's goals, the research eliminated non-original research materials like literature reviews and conference papers. The search then was conducted to thoroughly analyze the keywords and secondarily the eligibility of the collected articles was finally evaluated.
3.2. Bibliometric Analysis with VOSviewer
A bibliometric network, using VOSviewer [
36], advanced visualization techniques for evaluations, was performed. The choice of bibliometric networks is guided by the specific needs or by the statistical analyses and visualizations that most effectively highlight the study's critical findings. The major focus was particularly to be able to find connections between the thematic keywords so that the visualization tool could offer to a great extent, the level of strength and association between the relevant keywords. RefWorks was used to categorize and include all the keywords, that were extracted by the individual citation in the field of keywords from every article. Occasionally the range of those was enhanced by carefully reading the abstract and the methods, to further consolidate the pool of keywords. As a result, a detailed account of 248 keywords for the purpose of the research, was evaluated.
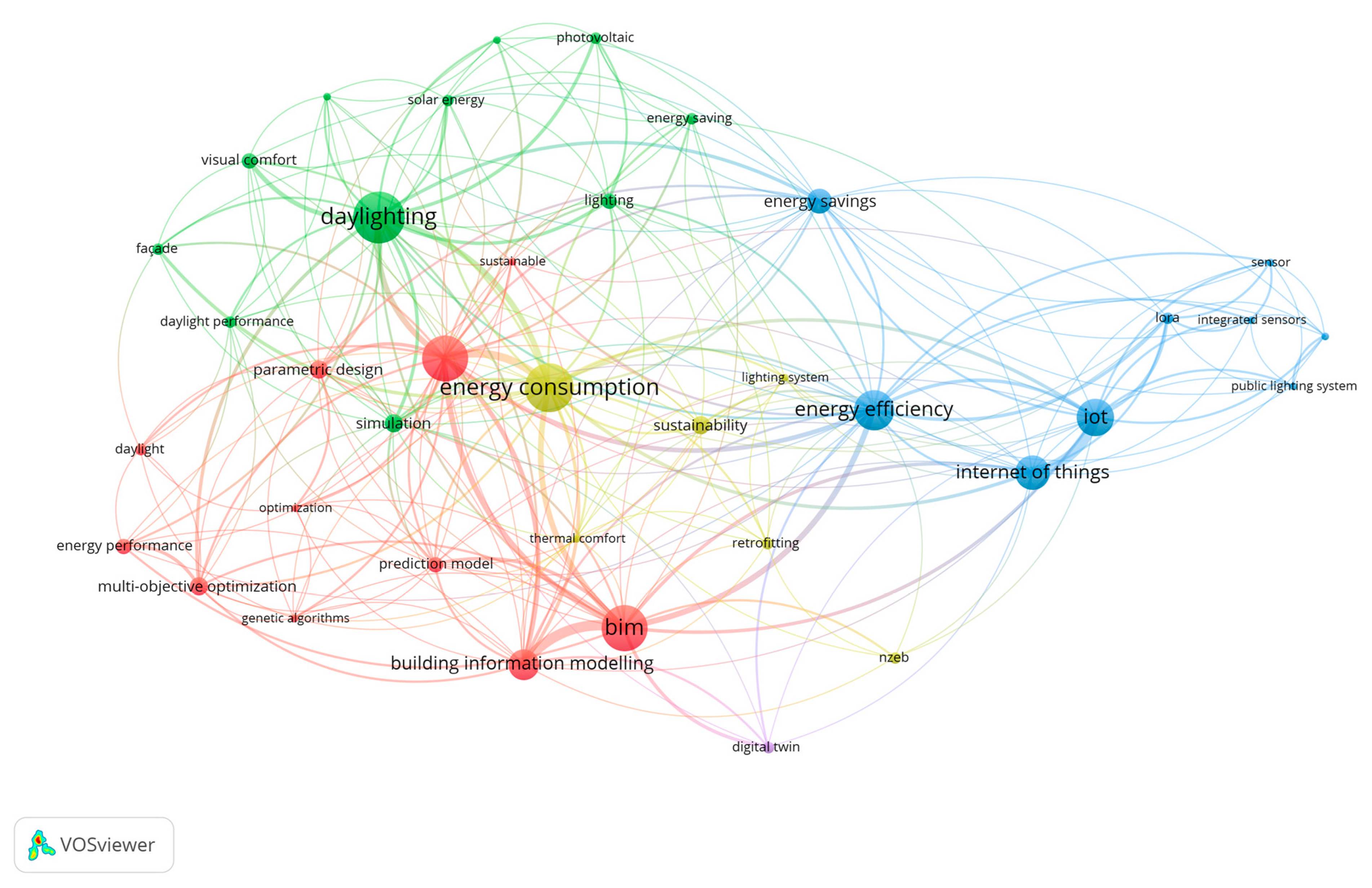
Based on a VOSviewer analysis of all 48 selected articles,
Figure 7. presents a clustering of the main keywords (represented as circles) and their interrelationships (depicted by connection lines). It was chosen to execute a “full counting” of the co-occurrence since every linkage has the same weight; the minimum time of occurrence was set to two so that the threshold could identify 50 keywords. The total-link strength appointed a value based on the most frequent interrelation between keywords and to further narrow down the analysis. It was decided to choose a total strength above eleven, therefore the analysis identified five clusters with 261 linkages and a total link strength of 413. The map's circles and lines represent the nodes and their connections. The larger the dimension, the more closely related the items are. The colours of the nodes indicate the clusters to which they belong. As for the first cluster, Buildings and Building Information Modeling appeared as the central focus; they are followed by Energy consumption and Sustainability which are representative of the second cluster of the literature search and effectively highlight the directly related topics. Another keyword that is emphasized as the largest item, is Daylight reflecting the third cluster, while Energy efficiency and Internet of Things are linked with the fourth, whereas Digital twin appears to be the last with a total strength of 11. Their increased frequency, particularly in "BIM", “Daylight” and "Internet of Things" underscores their foundational importance within the contexts of Buildings. Although “Integrated” or “Integrated controls” do not appear evidently, they are yielded in the sub-connections of the different linkages, hence appearing for instance in “integrated environmental solutions”, “lighting systems” and “integrated sensors”. Overall, all the mentioned efforts aimed not only to assess the current state of the art, and offer specific answers to specific research questions but also to identify gaps or insufficiently explored areas, while proposing potential strategies for future research or development.
4. Integrated Daylight Controls
In this section, the critical areas of innovation and advanced technologies that are shaping the future of building energy efficiency and sustainability will be presented structured into three main chapters: integrated lighting control, Building Information Modeling (BIM), and the Internet of Things (IoT).
The first chapter will explore the territory of Integrated Lighting Control, where innovation in lighting and daylight optimisation serves to maximize energy efficiency. The current study focuses on the optimisation of the building envelope and shading systems involving kinetic facades, adaptive shading, and photovoltaic solutions, among others.
The second chapter examines BIM's role in sustainable building practices and retrofitting buildings to achieve net-zero energy status, highlighting advanced BIM methods and the integration of parametric design to enhance energy efficiency. The final chapter delves into IoT smart building technologies, particularly smart lighting and adaptive controls, and discusses the synergy between IoT and BIM in energy monitoring and optimisation, showcasing practical IoT applications across various fields.
4.1. Innovation in Lighting and Daylight Optimisation
Overen et al. (2023) evaluated the daylight performance of a historic educational and office building, in Alice Town, eastern Cape, South Africa, using a quantitative approach, relying on building simulation software for analysis. [
37]. A climate-based daylight model (CBDM) was developed in Revit along with the Integrated Environmental Solutions Virtual Environment (IESVE) to perform simulations. According to the guidelines set by the Illuminating Engineering Society of North America (IESNA), the study aimed to achieve a minimum daylight illuminance of 300 lux. The analysis revealed that the south-facing ground floor area had the least amount of daylight hours with illuminance levels within UDI300-2000. However, the annual daylight analysis demonstrated that the points in the analyzed spaces met the UDI300-2000 criteria for more than 50% of the occupied hours throughout the year, with the building achieving a 100% sDA300,50% score. Additionally, discomfort glare was negligible, and the building's orientation was identified as a significant factor influencing the relationship between Daylight Glare Probability (DGP) and window placement. At the last, it could be noted that heritage buildings can effectively use daylight for daily activities, reducing the need for electric lighting and lowering the building's energy use, though this latter aspect was not further investigated.
On the same premises, stems the work of Piraei et al. (2022) who challenged the topic of the optimisation of daylight with empirical research and quantitative strategy through simulations to seek various alternative retrofitting solutions to achieve an optimisation of daylight by way of skylights and atria [
38]. Simulations were performed in Climate Studio [
39], calculating metrics like spatial daylight autonomy (sDA), annual sunlight exposure (ASE) and daylight factor; everything was conducted based on the configuration of six possible scenarios where multiple options for atria were proposed. Furthermore, the reliance on Ladybug and Honeybee, made it possible to accomplish optimal daylight optimisation. The results showed that the likelihood of roof lighting a building to maximize daylighting, utilizing a parametric approach, is trustworthy since all the metrics observed an increase; although none of the scenarios complied with the existing regulations standards, the optimized configuration will be built as daylighting was identified as a key factor.
Similarly, Xie et al. (2023) explored a new prediction method, for implementing daylight for high-speed railways station waiting halls, aiming to minimize the visual discomfort [
40]. Throughout a rigorous analysis with Honeybee and Ladybug tools, they evaluated the design metric and design parameters, leading to the proposal of the 'Gradient Boosted Regression Trees' (GBRT) This method aids in forecasting lighting levels using parametric datasets, offering quicker and more reliable alternative compared to old models, by ultimately improving the design process and reducing energy waste. It was found that the optimal orientation for the building to achieve an ideal daylight performance is the zero-degree angle, despite according to the GBRT model, this one has little influence on other design parameters; complimentary it was noted the relation with the building height impacts the natural light and greatly does with sDA with the opposite trend for UDI. As a third conclusion, one has to consider the skylight ratio which may trigger the increase in sDA, besides paying attention to the probability of uncomfortable glare that may rise.
Conversely, Garcia-Fernandez and Omar (2023), explored. three tangible ways to improve energy efficiency in a public library building in Egypt, focusing on challenges related to window size and lack of daylighting [
41]. The three main focus points were mostly about diagnosing the energy improvement by the replacement of the lighting system to enhance light quality and alignment with the visual task requirements and the third one, improving ergonomic safety and vision. And implementing proactive maintenance and protection measures. Results showed that integrating solar systems, replacing old lighting fixtures, and implementing two types of self-darkening glass with solar protection capabilities and an innovative lighting system using anidolic technology had in return reduced energy consumption in this space. Additionally, the proposal included. The goal throughout these three strategies, which can improve the building's performance without affecting none of its intrinsic characteristics, seemed very promising and feasible.
4.2. Parametric Design and Simulation for Energy Efficiency
In contrast, Sun et al. (2020) proposed an optimisation design model to replace the traditional, time-consuming and inefficient building performance simulations (BPS), integrating software and add-ons with Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) in a user-friendly interface for architects [
42]. The main benefit of the proposed workflow is its focus on accessibility and ease of use, to be used at different stages of the building design process to improve the building's performance. The multi-objective optimisation experiment was performed on a school library building in China, concentrating on refining the initial form and layout design of the structure, to lower energy usage and costs in buildings while improving the quality Among the others, objectives included Energy Use Intensity (EUI), and Building Envelope Cost, maximizing Spatial Daylight Autonomy (sDA) and Useful Daylighting Illuminance (UDI). In conclusion, the optimisation process has created several effective solutions, achieving significant energy savings and improvements in targeted metrics, alongside reductions in Building Envelope Cost (BEC).
Fang and Cho (2019), presented a method for optimizing building design in the early stages, using parametric design, daylight, energy simulations and genetic algorithms, to be tested on a small office building [
43]. The optimized design compared three climate zones across American cities, following four main steps: identifying the design variables to create a parametric design model, developing both daylight and energy models, combining the daylighting and energy simulation processes and finally, the process concluding with the multi-objective optimisation. The design solutions have shown significant performance improvements, from UDI with increased values, whereas the Energy Use Intensity (EUI) values have decreased, compared to the average performance across the three cities. The optimized design for the three climate conditions has highlighted some important factors with sometimes similarities occurring but providing specifications for the design variables. Lastly, findings have revealed that skylight width and length are the most significant variables across all locations. Additionally, it is noted that different design factors exert varying degrees of influence, with some having opposite effects on daylight and energy efficiency in different climate zones.
Another study, using a similar procedure including different major steps, introduced and modelling the scene in Rhinoceros and after that the Grasshopper plug-in, followed by the development and integration of daylight and energy simulation, concluding with a multi-objective optimisation and comparison was disseminated by Nasrollahzadeh Nasrollah (2021) [
44]. After evaluating daylight and electrical lighting with Radiance/DAYSIM and assessing the indoor thermal comfort using the Ladybug tool, analyzing the annual energy consumption in a multi-optimisation process. A residential duplex in Iran, with windows designed on the north and south sides and roof shading, served as the case study. The main goals of the study aimed to to create a framework that considers both thermal comfort and daylight and energy performance across various building envelope features, and to understand the impact of these features. Throughout the optimisation process, 2600 solutions were created, revealing a conflicting relationship between Energy Use Intensity (EUI) and Predicted Percentage of Dissatisfied (PPD), as well as between Useful Daylighting Illuminance (UDI) and PPD. Specifically, factors that positively affected energy use and daylight distribution often negatively impacted PPD, while EUI and UDI mostly displayed a complementary nature. One of the Models presented a significant improvement in all the metrics by meeting the daylight and energy requirements of LEED v4. Ultimately, the results and findings offer potential applications in diverse contexts, such as early-stage design, refurbishment, and renovation initiatives
4.3. Advanced Technologies for Building Energy Optimisation
Conversely, Karadag and Keskin (2021) developed a daylight simulation for the early stage of design using DaylightX, using Radiance, a tool that could perform and predict how daylight will be distributed in different architectural settings, running simulations much faster [
45]. The performance and features of the software have been extensively examined by conducting simulations, it certainly helps designers to display accurately the spread of daylight at any time, although, when analyzing indoor daylight levels over an entire year, this approach is ineffective. As a result, this must be due to static metrics and their limited flexibility in estimating the nuanced fluctuations in daylight levels what is more, there is a need to integrate dynamic daylighting analyses using advanced sky models.
Pompei et al. (2023) presented in their study a representative of a typical medium-sized commercial mall in Italy [
46]. The study examined the best lighting system for the case, by considering various factors, such as lighting controls, and energy-efficient lighting sources. By thoroughly evaluating these elements, the study aimed to recommend a lighting solution that optimizes performance, efficiency, and user comfort for the given case. The study examined different lighting methods, focusing on the benefits of spot relamping and integrating daylight using advanced lighting control systems. After evaluating the benefits of improving the baseline, a significant reduction in energy consumption was noted, beyond a return profit after 10 years after the retrofitting strategy. The goal was to evaluate the effectiveness of these strategies in improving illumination quality and energy efficiency and aimed to identify and inform the decision-making processes that can enhance sustainability and performance in buildings.
A new approach to designing and simulating buildings was proposed by Phuong et al. (2023) where the team focused on making buildings more energy-efficient, especially when it comes to lighting systems, by prioritizing sustainable lighting designs that could reduce and deploying the latest information technologies and software tools to streamline the design process [
47]. They considered its effectiveness through an application in a complex pilot building in Vietnam. The benefits of this approach would empower lighting designers and professional lighting experts to precisely simulate the amount of daylight entering different spaces within a building, before even designing artificial lighting systems. Implementing this approach is expected to significantly improve the building´s energy efficiency, reducing energy consumption for lighting by considerable amounts.
On the other hand, Dong et al. (2021) proposed an intelligent optimisation process involving several key steps: parametric modeling, which creates a detailed network of information, allowing for the exploration of different design options and their impacts, followed by performance automated simulations and multi-objective optimisation refine and optimize the design based on various criteria [
48]. This iterative, systematic approach helps create effective building designs with the help of a multi-objective optimisation module adopting the NSGA-II algorithm. An experiment has been then performed, to show how the intelligent optimisation framework is advanced, using the Revit-Dynamo platform: the former to build the model and the latter to consolidate the multilevel information within the model. The intelligent optimisation framework outperformed the other two methods in improving green performance metrics. This comparison provided clear, quantifiable insights into how much the intelligent optimisation framework enhances environmental sustainability and efficiency, showcasing its superior ability to guide more ecologically responsible and effective architectural design decisions. The trade-off capability of multi-objective was testified qualitatively regarding the performances of DA, UDI and EUI optimal solutions and confirmed to be better than subjective decision-making design and it is hence necessary to be discussed when compromising between daylighting and energy performance; Ultimately, the intelligent optimisation framework shows promise for automating the multi-objective optimisation process related to both daylighting and energy performance, offering architects a better balance of design accuracy and efficiency.
4.4. Building Envelope and Shading Optimisation
On the other hand, with an innovative parametric design, Bande et al. (2023) explored the possibilities of reducing the annual energy consumption of households in one of the largest cities in the Abu Dhabi Emirate [
49].
The article aimed to measure the power usage under assorted circumstances, particularly when installed with a shade mechanism, plus covering a multitude of parameters to deliver a comprehensive evaluation in different setups. By recruiting accessible and available villas in Al Ain, with existing plans for future renovations, the strategy included an analysis of a parametric shading structure, using traditional “Mashrabiya”, that could be considered as an architectural element of enclosed windows that protects from direct sunlight but also allows for privacy. Notably, it has acquired a substantial reduction in energy consumption of up to 55%, particularly in the first case compared to the base one, which could grow by another 10% if an additional shading device were provided. Therefore, the conclusions highlight the feasibility of adopting shading devices, as they are greatly beneficial for low-rise buildings located in severely arid zones like the one studied.
The study carried out by Reffat and Ahmad (2020) identified the best configurations for energy-efficient integrated Daylighting Systems within building windows, aiming. [
50] to maximize energy savings while also maintaining visual and thermal comfort for occupants. They analyzed six individual DLSs suitable for hot desert climate zones and proceeded to identify 51 office building cases to identify the optimal set of integrating Daylight Systems for optimizing energy efficiency, consisting of four phases. For instance, as reported, in the southern region, all but one DLS variation of DLSs has met the UDI threshold, with total energy consumption that has decreased by around 24% to 38%. However, some of the solutions did not meet the glare threshold and are therefore not recommended. As a result, a promising and comprehensive guide was created to assist designers in picking the right daylighting systems, to maximize their benefits, for their specific building orientation and location.
Based on their previous study, Xuan et al. (2022) introduced a new concept focused on the design of a new concept, aimed to generate electricity and provide daylight using solar energy, called lens-walled compound parabolic concentrator (LWCPC) [
51]. Through careful optimisation, the concept design was implemented and transformed into a transmitting entity TLWCPC which can efficiently capture sunlight for illumination but also highlights its potential for sustainable energy applications in various settings. Hence, the researchers explored the integration of a special type of design including a solar concentrator into an innovative smart skylight window design. This design aspired to intelligently manage light transmission using optical concentration and to accurately assess it, a ray-tracing simulation with Light tools was run. The impact of latitude on the yearly projected incidence angles of the TLWCPC was thoroughly evaluated by selecting five cities located at latitudes ranging from 20° to 60°. Findings showed that latitude had a significant influence on the performance of the TLWCPC. Specifically, east-west orientation, increases projected incidence angles with latitude, while north-south orientation, improves daylight efficiency despite reduced optical performance. Future research will focus on the TLWCPC-Photovoltaic/Daylighting skylight´s potential for annual energy savings in buildings, and glare analysis reduction, to evaluate the impact of the TLWCPC-PV/D skylight on the indoor visual environment.
4.5. Shading Devices
4.5.1. Kinetic Facades and Control Strategies
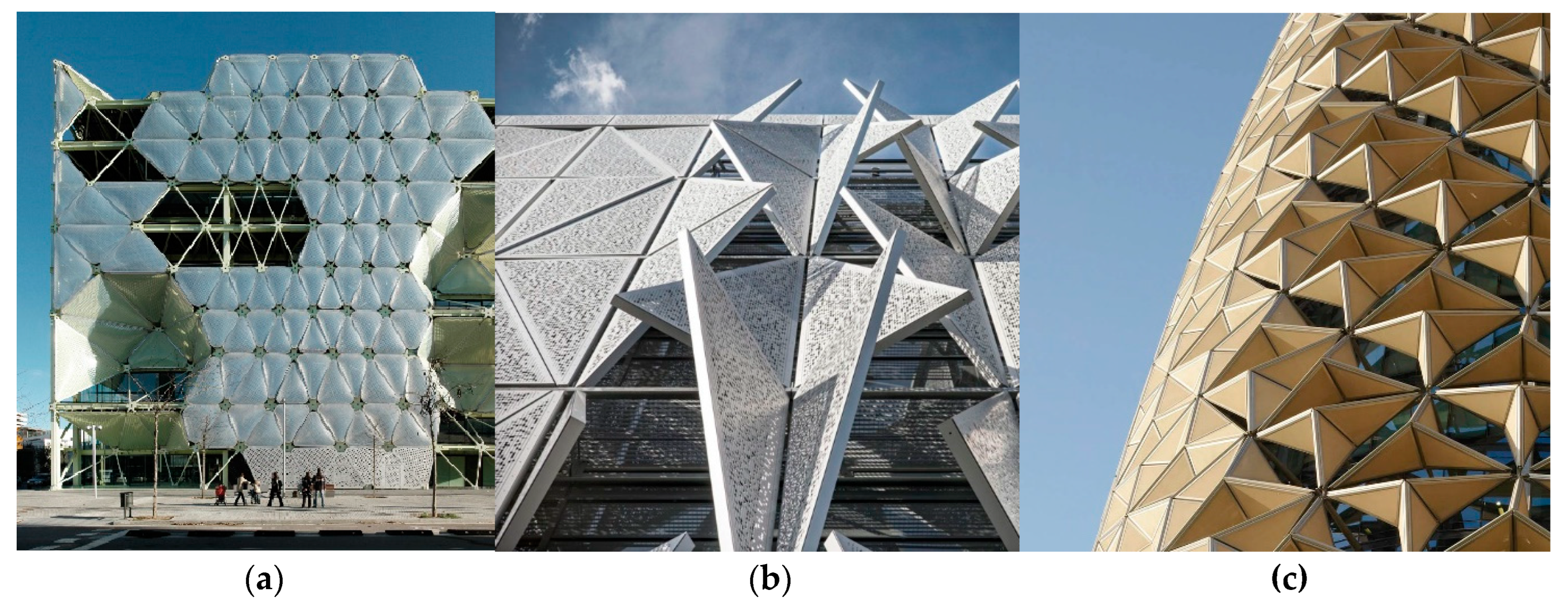
A novel framework for selecting a kinetic system was proposed by Alawaysheh et al. (2023) who discussed the important connection between using responsive kinetic systems and improving a building's energy efficiency, outlining the key principles of kinetic design that allow architects to create effective, practical, and innovative adaptive systems [
52]. The main goal was to develop design and evaluation methods for a kinetic facade using digital simulation tools. It also compared the energy performance of a kinetic facade against an existing building with fixed shading, using Integrated Design Solutions (IES) software, for its simulation capabilities, allowing for quick feedback on model adjustments. The study involved simulating three conditions using IES, the first was the base case, (the existing building), the second was a proposed redesign of the façade and finally, the third was the optimal kinetic design. To create the kinetic motion-based, a parametric model was developed to analyze the facade's behaviour using the ratios, to explore different motion scenarios and capture the exact facade configurations in real-time. The analysis revealed notable differences in electricity load savings, Specifically, reaching 32.2% in December and conversely in June showed the lowest electricity savings, averaging 22.8%. On average, across March, June, and December, the total electricity savings amounted to 27%. The annual energy savings across different months offered a cumulative reduction of up to 18% for cooling loads and 16% for total electricity loads. The indoor illuminance levels from daylight were evaluated to assess the effectiveness of the proposed kinetic scenarios, compared to the base case illuminance levels. Some of the kinetic systems are illustrated in
Figure 8.
Exterior shading devices can be a highly effective way to manage daylight and solar heat in glazed facades, ensuring thermal and visual comfort, in this regard, Uribe et al. (2019) assessed the influence of four different control strategies on a shading system with mobile curved and perforated louvres [
53]. The evaluation focused on the impact of these strategies on visual comfort and total energy consumption, including heating, cooling, and artificial lighting requirements in an office setting. Two orientations of the glazed façade were analyzed in three cities located in the northern hemisphere, specifically south and west, and the other two, north and east. The studied shading device is a Continuous Fin System (CFS) and it has movable horizontal louvres located outside a double-glazed window. These louvres were made of an aluminium-zinc alloy and have a curved shape with a 20% perforation rate, allowing the system to provide adjustable shading and light diffusion, improving the energy efficiency and comfort of the building where it is installed. Four different approaches to controlling lighting were explored: incident irradiance control, vertical eye illuminance-based control, cut-off angle control, and blocking control. The evaluation of different CFS used an integrated approach that involved using various software tools like Radiance and EnergyPlus so that it was possible to be accurately assessed. The study found that the best ways to reduce total energy use and ensure good lighting in office spaces varied depending on the city, where overall all four lighting control strategies met the SDA criteria. The findings highlighted the importance of tailoring shading and daylight control strategies to specific local climates and sun conditions to achieve both energy efficiency and visual comfort in office buildings.
Vanage et al. (2023) compared the differences between a vast variety of lighting and shading control strategies; this was due to the assumption that the baseline models usually differ considerably, as various daylight-based metrics are being evaluated in their performances in a real building [
54]. Hence the study established a common foundation to evaluate the differences among various lighting and shading control strategies currently in use, introducing an Integrated Control Strategy (ICS) that takes into account factors like occupancy, HVAC system status, incoming solar radiation, and time of day. A multi-phase- modelling approach combined daylighting and energy simulations, using RADIANCE and EnergyPlus. The small office building from the U.S. DOE Commercial Prototype Building models was used as the Baseline Model, with a focus redirected to the perimeter zones affected by shading controls. A range of control strategies included: the Baseline Model, (BAM) which served as the benchmark for comparison across all automated control strategies, two variants of the former, one called Manual Control Strategies (MCS), involving occupants manually adjusting the shading as they desired, the other one Independent Control Strategy (IDS) which uses a single variable as input to automate shading and light levels and lastly, the Integrated Control Strategy (IGS) that considered multiple variables to determine shading and light levels.
The study results revealed the main ability of the Manual Control Strategies (MCS) to yield a slight reduction in total energy consumption while enhancing visual comfort, particularly in mitigating glare. Moreover, the Integrated Control Strategy (IDS) with solar radiation-based control, exhibited superior energy efficiency and outdoor visibility. What is more, when employing glare-based control, it outperformed solar radiation-based IDS in terms of energy savings and glare reduction while also offering a total load reduction, of around 12%, with zero glare in a specific case. These findings provided a thorough comparison of various control strategies using roller shades, highlighting the importance of integrated controls and serving as a useful reference for future research on energy-efficient building design.
4.5.2. Photovoltaic and Energy-Generating Solutions
As already depicted in the three examples from
Figure 9., daylighting plays a crucial role in facilitating daily activities, so in this regard Wu et al. (2024) studied the utilization of semi-transparent photovoltaic glass within university gymnasiums, to effectively mitigate solar radiation while simultaneously harnessing solar energy to generate electricity [
55].
They studied six common skylight designs by running simulations to explore the effects of different configurations of Cadmium Telluride (CdTe) thin-film solar glass to balance energy generation and daylighting quality, while also assessing and integrating renewable energy, emphasizing and maintaining adequate daylighting for indoor sports facilities. The models were constructed using Rhinoceros and subsequently integrated into Ladybug and Honeybee, to evaluate daylighting within the actual design framework. This aspect made it possible to explore the design and iteration of various skylight configurations to enhance natural light distribution. The main goal of the simulation phase was to evaluate how well the CdTe thin film photovoltaic glass performed in providing daylighting in different skylight designs. The outcomes from the simulations revealed that distributed skylight designs, either horizontal or vertical strip skylights, achieved over 75% daylight autonomy (DA) with 80% light transmittance photovoltaic glass. Similarly, rectangular and ribbon skylights reached this DA level with 70-80% transmittance. However, the centralized X-shaped skylight did not consistently meet the 75% DA threshold. The findings suggest that distributed skylights offered more uniform daylight distribution, highlighting their potential for enhancing sustainable indoor lighting solutions. Accompanying a thorough analysis of the DA analysis the recommended higher transmittance of the photovoltaic panels as they led to a noticeable drop in the proportion of UDI values below 100 lux. On the other hand, the proportion of UDI values between 100 and 2000 lux initially rises before gradually decreasing, except for the centralized X-shaped skylight configuration. The simulation results indicated that different skylight designs have varying effects on dynamic daylighting metrics as the transmittance of photovoltaic glass increases. However, there are similar changing trends observed across the different configurations.
A 3D concentrator photovoltaic daylighting has been proposed, designed, built, and used in the Southwest region of China by Zhang et al. (2022) [
56]. The 3D CPVD window combines solar energy generation with natural lighting, providing an innovative solution for sustainable building design. Subsequently, a 3D model was developed and so the 3D CPVD window was placed to evaluate the daylighting performance of the CPV window integrated into the building facade. Given the complex structure of the concentrator and the extensive ray analysis required, ray tracing simulation was chosen as the preferred method for assessing concentrator performance. An outdoor artefact was also built to evaluate the real-scale 3D CPVD concentrator, building a rig, completed with tools for measuring illumination levels. This approach boosted the concentration ratio and provided better natural lighting for the building. Additionally, the 3D CPVD window angle can be adjusted, and the ideal angle for its electrical performance appears to be 60 degrees in middle and low latitudes. According to the daylighting analysis, the 3D CPVD window allows 9.46% more light to pass through compared to traditional PV windows. The simulations also show that the indoor lighting is more evenly distributed, with over 85% of UDI all year round. Lastly, the life cycle assessment showed that the energy payback time (EPBT) and greenhouse gas payback time (GPBT) of 3D concentrated photovoltaic devices were reduced by 19.5% and 23.5% respectively, compared to traditional photovoltaic (PV) systems. These findings confirm that 3D CPVD windows have advantages in energy savings and practical application.
On the subject of implementing strategies for energy efficiency in buildings to control the increase in energy demand, Fazelpour et al. (2022) used the concept of green roofs along with Double Skin Façade (DSF), in addition, to evaluate how the changes in leaf area index (LAI) would impact on the energy consumption [
57]. The investigation, which was conducted on a university building in Iran, examined the implementation of Photovoltaic Double-Skin Façade (PV-DSF) technology. To pursue that, a single floor of a building was simulated concurrently using DesignBuilder and Carrier Hap45 software, to ensure a thorough comparison and validation of the applied technique, ensuring the reliability and precision of the results. The study found that plants with a Leaf Area Index (LAI) of 2.15 used more energy compared to those with an LAI of 1.69, especially in one of the three cities taken into analysis. The energy consumption was 73.4 kWh higher for the plants with the higher LAI, even though the energy production rates were the same for both LAI values. In all three cities studied, both heating and cooling rates were significantly higher for the plants with the greater LAI. However, this increase in energy demand did not match a proportional increase in energy production, indicating a discrepancy between the growth rates of energy consumption and production. The orientation was also examined, as well as the yearly energy consumption, energy production, heating and cooling requirements across three cities, with a focus on Tehran. Buildings oriented at 90 degrees experienced higher energy consumption and significantly lower energy production compared to those oriented at 0 degrees. The decrease in energy production was substantial, indicating less efficiency in energy generation, suggesting that the effectiveness of such energy-saving measures can vary greatly depending on the geographical location and building orientation.
4.5.3. Adaptive Shading and Daylighting
Mashaly et al. (2021) suggested a system of optimisation for CFS (Complex fenestration systems) using simulations to create many design outcomes [
58], based on spatial needs and other conditions. It results in an innovative approach that could assist designers, by using Grasshopper, in exploring a multitude of design possibilities and in finding the most fitting solution. In substance, researchers have designed everything by prioritizing certain criteria, such as how to redirect panels to reduce sunlight falling on occupants, improving the daylighting distribution and uniformity, the useful amount of daylight in deep space and finally retaining the view towards the outside. Findings suggested that the refined CFS outperformed other CFS setups, due to both the given additional focus on daylight performance while optimizing the design with more advanced simulations. The creation and integration of these measures marked a notable bounce in Complex fenestrations system performance insight, and it’s been a promising tool for designers since the early stage of projects in assisting them, in particular when retrofitting a building after post-occupancy periods.
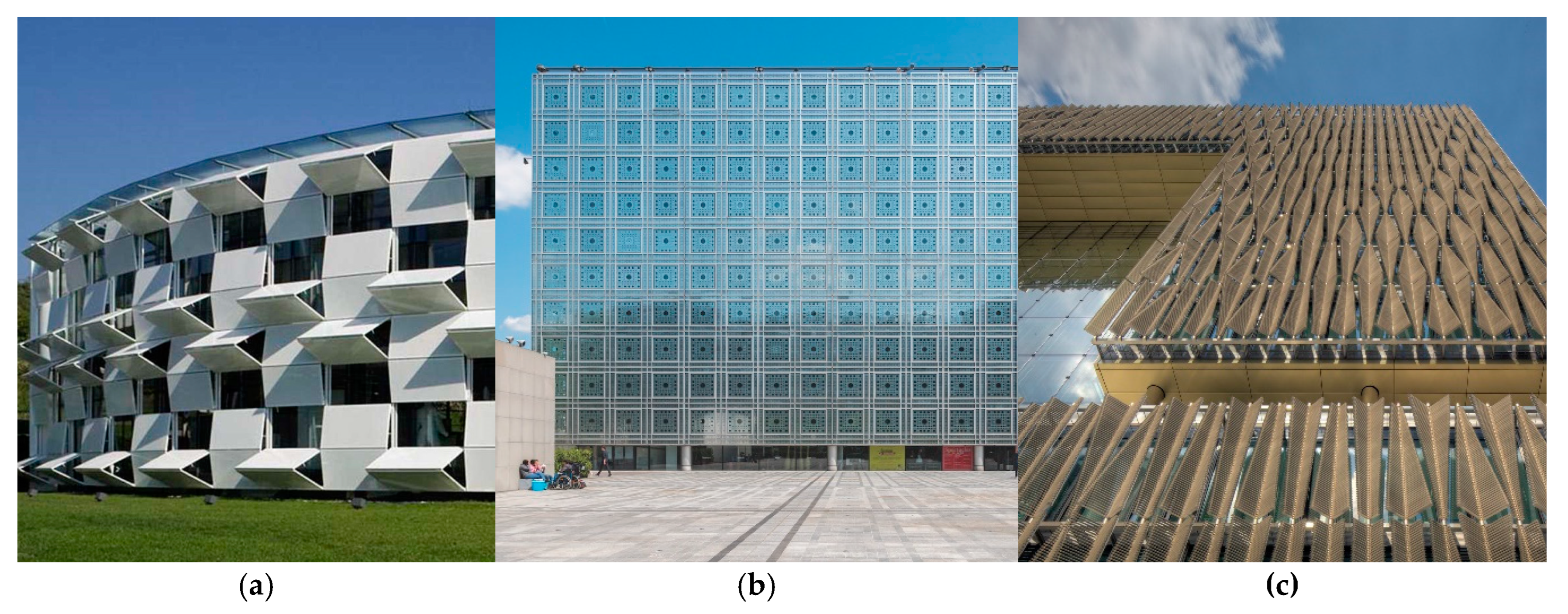
Figure 10.
Some representative built projects with adaptive shading controls (a) Kiefer Technic Showroom, Graz (AT), Project of Ernst Giselbrecht + Partner ZT GmbH, 2007 (b) Institut du Monde Arabe, Paris (FR), Project of Jean Nouvel, 1987 (c) Building, ThyssenKrupp Quarter, Essen (GR), Project of JSWD Architekten + Chaix & Morel et Associés, 2010.
Figure 10.
Some representative built projects with adaptive shading controls (a) Kiefer Technic Showroom, Graz (AT), Project of Ernst Giselbrecht + Partner ZT GmbH, 2007 (b) Institut du Monde Arabe, Paris (FR), Project of Jean Nouvel, 1987 (c) Building, ThyssenKrupp Quarter, Essen (GR), Project of JSWD Architekten + Chaix & Morel et Associés, 2010.
Jamala et al. (2023) aimed to assess how different shapes of building facades influence the distribution of daylight within the building, by considering five distinct facade forms: massive glass, sun shading vertical, horizontal, diagonal, and vertical diagonal models [
59]. The objective was to identify the facade model most effective in distributing daylight into the building, thereby minimizing energy consumption. They utilized quantitative methods, analyzing simulated data through SPSS software to understand variations in illuminance levels within the workspace, located in the coastal region of Makassar, Indonesia. Illuminance levels in Room A were carefully measured at specific points over three days, recording data in the morning, noon, and afternoon to evaluate changes throughout the day. The measurements showed that the amount of light, or illuminance, decreases from morning to afternoon and evening, especially in the area near the building's exterior walls. Similarly, the southwest-facing façade led to higher illuminance in the evening compared to the afternoon and morning. This analysis highlighted the influence of building orientation on the distribution of daylight within the room. Concerning the different facade models deployed, the vertical facade model proved to be optimal for allowing daylight, while the vertical-diagonal facades performed far better throughout the day.
In proceeding to lower the energy consumption of buildings, Jakubowsky and de Boer (2022) presented an innovative solution, with the development of a micro-structured system that redirects daylight in office spaces, where otherwise blocked by shading devices [
60]. The system is made using affordable UV printing or hot stamping methods and smoothly fitted into a regular three-panel window frame. The innovative lighting system used LED lights and a slim, see-through surface emitter, where the LED light is channelled into the surface, and then integrated into the building's facade design, using cylindrical microstructures that redirect the light upwards towards the ceiling, enhancing the light distribution in the space and significantly reducing direct glare. A series of empirical assessments compared two distinct testing environments to evaluate the effectiveness of the described systems. The experiment involved modifying the facade of one room to incorporate the systems under investigation (referred to as the "test room"), while the other room maintained a standard facade and conventional lighting solutions to serve as a benchmark. This analysis allowed for a comprehensive evaluation of the systems' performance, by directly comparing their outputs against traditional lighting setups under identical environmental conditions. The study showed a significant 58% energy saving in a test room using only 1.2 kWh on sunny days while providing 69% relative luminous exposure, in contrast to the reference room's 2.5 kWh and 13% exposure. Additionally, this system demonstrates the potential for wider application in cutting building sector CO2 emissions while ensuring adequate lighting.
Below is a comprehensive investigation of different integrated daylighting and lighting solutions, which also provide an extensive range of information about climate, methodological approach, function, destination, influential elements, and control strategies to achieve the set goals and building scale;
Table 2.
5. Building Information Modeling
5.1. BIM for Sustainable Building Practice and Net-Zero Retrofitting
As already mentioned, the construction industry is accounted for and responsible for an enormous variety of effects, thus Marzouk and Thabet (2023) set their goal to move towards more sustainable and eco-friendly building practices in Egypt [
61]. This system they proposed is focused on improving energy and resource efficiency, water conservation, and indoor environmental quality by connecting Building Information Modeling (BIM) with Egypt's sustainability rating criteria.
The study presented a new approach to incorporating BIM methods into sustainability evaluations throughout the design and construction stages of building projects. By using automated BIM tools and a customized Revit API plugin, the framework facilitated the adoption of sustainable construction practices, allowing seamless integration of data from different disciplines, leading to faster, more accurate, and more efficient assessments of sustainability aspects. As the study looked at a common office building in Cairo's new administrative centre, it also aimed to take advantage of green building benefits, suggesting energy-saving solutions through parametric-BIM software. The proposed framework combined BIM methodology and project management to streamline the evaluation and documentation processes of the Green Pyramid Rating System (GPRS). Consequently, it has proven effective in identifying optimal design retrofit solutions, achieving a Gold certification level for the case study. Furthermore, the framework enhanced collaborative efforts in design decision-making, promoting the adoption of green construction management practices. This structured approach empowers decision-makers to explore, analyze, enhance, and evaluate sustainability aspects efficiently, ensuring a comprehensive integration of sustainability.
In the pursuit of seeking to convert buildings into Net Zero Energy Buildings, Razzaq et al. (2023) examined various retrofitting techniques used in different buildings, climates, and industry standards [
62]. They aimed to transform an academic building into a net-zero energy facility to try to achieve Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) 7 and 13. The building's performance was evaluated using the Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED) rating system the building's energy consumption and CO2 emissions were compared before and after implementing the Indigenous retrofitting solutions, providing insights into their environmental impact and effectiveness. The study proceeded to gather existing data, including manually cataloguing appliances and their power ratings, documenting the building's construction materials, recording its elevation, and compiling details on all appliances that contribute to its energy use. This thorough data collection is crucial for accurately assessing the building's current energy usage and identifying opportunities for energy-saving retrofits. The current appliances in use were found to be outdated and inefficient, leading to substantial energy waste after analyzing the existing data. The building's energy consumption was significantly reduced after electrical retrofitting and improvements to its envelope. Also, an analysis of the building's CO2 emissions was conducted, considering its electrical energy consumption and the emission factor (EF), to evaluate the environmental impact of the retrofitting measures. As a result, the building's retrofitting led to a notable 32% drop in carbon dioxide emissions. The addition of solar photovoltaic panels on the rooftop further reduced emissions by 25.2 metric tons of CO2 per year. The transition to an energy-efficient building has proved to be a significant step towards achieving Sustainable Development Goals 7 and 13. After the retrofitting, the building qualified for a silver rating in LEED v4.1 O + M.
Shang Yuan Chen (2019), advocated for using Green Building Information Modeling (BIM) to help design zero-energy buildings (NZEBs) [
63]. Designing NZEBs involves two key tasks: First, evaluating and ensuring the building has high energy efficiency; second, integrating suitable renewable energy systems to meet the building's energy needs. As far as BIM technology is combined with Building Performance Analysis (BPA) tools, this helps to create an integrated design and decision-making process. The process involved repeated cycles of design and analysis, to optimize building development and improve environmental effectiveness. Important to note, that the analysis of building energy usage covered several key areas such as the Energy Use Intensity (EUI), the total energy consumption and costs over the building's lifetime. The study examined and therefore demonstrated the usefulness of BIM-Revit software's Energy Analysis and Solar Analysis modules, as an integrated design and analysis tool to improve the design iterations and achieve "net zero" performance goals.
5.2. Advanced BIM and Parametric Design for Energy-Efficiency Renovation
Further findings are supported by Carvalho et al. (2021) who attempted to bridge the gap in knowledge by working to create and deploy a Building Information Modeling (BIM) process uniquely suited to improve the thermal design of buildings in Portugal by also aiming to show how using this approach can improve the long-term environmental impact of buildings from the beginning of the design process [
64]. The primary goal of this study was to create and execute a BIM procedure that aided in the necessary evaluation of building energy performance in Portugal. In order to accomplish this, Revit and Cypetherm REH were selected to carry out the energy analysis. To conduct this assessment, two separate scenarios were selected: a pre-existing building and a new construction project. The pre-existing building under examination is a three-bedroom, single-family residence situated in Porto, Portugal. Before running any simulations, it was necessary to calculate the amount of renewable energy produced on-site, hence the research assumed that every roof of the structure would have a solar thermal collector. The energy renovation model, (of the existing building reference) was optimized to meet REH requirements and successfully cut the building's total primary energy needs by a remarkable 78.5%. The decrease in energy usage was mainly due to reduced heating needs, which were around 30% less than the optimized old model. The REH calculation procedure determined that the current reference model was given an F rating on the energy label. In contrast, after optimization, this model saw a notable improvement and was upgraded to a B rating. Additionally, the new building project model was awarded an impressive A rating on the national energy label. The use of BIM-based methodology in this research has proven to be seamlessly integrated into energy simulation and thermal project planning in the Portuguese context, showcasing enhanced reliability and accuracy compared to traditional calculation methods utilized in spreadsheets, although there is still room for enhancement in areas like the predefined reference U-value.
On another hand, Amoruso et al. (2019) developed an integrated approach that combines Building Information Modeling (BIM) and parametric techniques to renovate ageing apartment buildings in South Korea [
65]. The focus was on improving daylight conditions and a representative apartment building in Seoul was used as a case study to demonstrate this BIM-parametric framework. Using BIM software, the building was digitally recreated, and then a daylight simulation was conducted for a standard apartment unit within the building. This was done using parametric environmental analysis software. The energy and daylight simulations carefully examined the unique thermal and optical properties of the building materials. The renovation project using the BIM-parametric framework resulted in significant improvements in the apartment's daylight and visual comfort. Specifically, there was a 15% increase in Daylight Factor, a 30% enhancement in Daylight Autonomy, and a 15% rise in Useful Daylight Illuminance compared to the pre-renovation condition. By employing a parametric approach to define the construction details and optical characteristics of the windows, the study established a clear connection between the variable construction properties of different products and their impact on daylight and visual comfort. This method allowed for the- precise selection of optimal window components for the apartment renovation, notably based on the Life Cycle Assessment, to select them with the lowest environmental impact. Consequently, this research validated the effectiveness of the BIM parametric framework in developing on-site, sustainable renovation strategies aimed at enhancing the living environment.
Expanding on these findings Gan et al. (2023) investigated various ways to enhance future residential construction projects, from choosing materials to improving operational efficiency, by analyzing the carbon performance throughout the life cycle and assessing the potential for optimization through different materials and design techniques [
66]. Additionally, a new framework based on Building Information Modeling (BIM) predicted and improved the carbon footprint of the home, where the goal is to cut down on carbon emissions. Among the results, it is worth noting the use of alternative materials that can greatly reduce carbon emissions. For instance, they used green hydrogen steel, a new low-carbon material that uses hydrogen instead of coke in the manufacturing process to convert iron ore into iron, releasing water instead of carbon dioxide, which can reduce the initial carbon footprint by up to 10.9% and 44.4% respectively, and furtherly can cut carbon emissions by more than 50%. Reducing carbon emissions was also accomplished by adjusting certain architectural or structural design features, such as the building's orientation, which will optimize energy conservation, leading to lower energy consumption by providing occupants with better thermal comfort, thus reducing their reliance on mechanical heating and cooling systems. The research demonstrated how this approach can improve the design of eco-friendly buildings throughout their lifecycle analysis, thus offering guidance on energy-saving and carbon-reducing techniques.
Interestingly, Chen et al. deployed a Least Squares Support Vector Machine (LSSVM) as a fitness function, along with a Non-dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm II (NSGA-II), to propose a method for optimizing building energy consumption [
67]. The key research inquiries revolved around gathering useful data on building energy usage from a BIM model, of a case study for a university facility in China, creating a non-linear connection between energy usage and key factors related to the building's structure, and finding the best solutions for building design elements that consider energy usage and thermal comfort simultaneously. BIM-integrated energy simulation software such as EnergyPlus, which is known for its capability to take into account both the internal material properties of buildings and external environmental factors, was employed in this study, followed by DesignBuilder, a sophisticated platform that is based on EnergyPlus, to carry out thorough simulations of building energy usage.
Therefore, to significantly improve a building's energy efficiency through its outer layer, it is crucial to understand how each part of the layer affects the building's energy usage. In the winter period, external wall and roof U-values and window-to-wall ratio greatly impact in a positive way the energy consumption, while external wall and roof solar absorptances are negatively correlated. As conclusion, given the reliable dataset generated through simulation, the LSSVM model, which was trained to establish nonlinear relationships between energy consumption and influencing factors and lastly the LSSVM-NSGAII multi-objective optimization model constructed to determine the Pareto optimal front, which helped in selecting the optimal combination of building parameters using the ideal point method. In return, the new approach has shown significant progress in improving environmental protection and indoor comfort in buildings. To highlight key results, the LSSVM-NSGAII model efficiently optimized multiple goals, leading to a substantial 10.6% decrease in building energy consumption and a 32.2% increase in indoor thermal comfort compared to the original design.
5.3. BIM for Building Sustainability: Assessment, Challenges and Opportunities
Building upon the work of Shang Yuan Chen, Akhanova et al. (2021) presented the results of a study project that aimed to create the BIM-based Building Sustainability Assessment System (BSAS) by specifically targeting the Kazakhstani context, with a focus on commercial buildings [
68]. Their work outlined how this framework was further developed using multi-criteria decision-making methods to form a comprehensive sustainability assessment system. The study was focused on three main goals: to discover how BIM can improve building sustainability assessments; to assess how effective BIM is in enhancing the assessment indicators of the Kazakhstan Building Sustainability Assessment Framework (KBSAF) and to develop and validate a conceptual framework for a BIM-based building sustainability assessment system. The KBSAF consisted of nine assessment categories and 46 assessment indicators and to develop it, a Delphi study approach was used, which included selecting an expert panel, designing a questionnaire, conducting iterative scoring rounds, and analyzing survey data. A three-round Delphi survey was carried out to gather opinions from the expert panel on different aspects of the framework, using a five-point Likert scale, with responses from 1 to 5, to measure the panellists' views and assessments. The framework was validated through a three-round Delphi study and provided a detailed guide on the criteria for BIM modelling, building sustainability analysis, and integrating assessment indicators from the Kazakhstan Building Sustainability Assessment Framework. Examining the findings, it was found that out of the 46 assessment indicators in KBSAF, 24 could be tackled using BIM. Of these, 18 indicators could be fully addressed, while six could be partially addressed. The findings also showed that the framework successfully outlined the necessary phases and BIM functions for sustainability assessment in construction.
In contrast, Albdour et al. (2022) examined how implementing energy-saving guidelines can improve the energy efficiency of low-rise residential buildings in mild and dry climates, as it was noted and highlighted the pressing need to encourage energy conservation in current buildings [
69]. To select the case studies, the research used surveys to choose them diversely. According to the information given by the survey, the authors chose and simulated four typical low-rise residential buildings that are commonly built by most residents in the study area. The main focus was redirected to five important building energy systems: the building envelope, HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) system, daylighting and lighting, service water heating, and the plug load system. It was crucial to first start to validate energy simulation models by comparing annual results from simulated reference cases with real data, after setting up models in Revit and performing energy calculations in EnergyPlus. Two scenarios were assessed: first, comparing the average Energy Use Intensity (EUI) obtained from surveys with the simulated EUI for reference buildings, and second, comparing the average billed EUI for these buildings with their simulated EUI. In the first situation, the margin of error was around 12% when compared to the simulated results where on the other hand, In the second situation, the comparison showed a very accurate match, with a difference of less than 4% compared to the simulated outcomes. As a result, the heating requirements in Case 3 were the lowest among all cases, thanks to better wall insulation and more windows. However, the cooling needs in Case 3 went up by around 10% compared to the other cases. When Jordan's building energy code was implemented, there was a significant decrease in total energy consumption for all models except Case 3. Additionally, following ASHRAE Standard 90.2 led to even more reductions in energy when compared to the original buildings. Furthermore, applying ASHRAE Standard 90.2 to Case 3 resulted in up to an 18% improvement in energy efficiency.
On the other hand, González et al. (2021) explored to a greater extent the integration of Building Information Modeling (BIM) and Building Energy Modeling (BEM) [
70] This has been seen to be crucial for incorporating energy performance analysis in the initial phases of construction projects, for instance forecasting annual energy usage, and evaluating HVAC systems and appliances. Autodesk Revit was recognized once again as a valuable tool for enhancing interoperability between BIM and BEM methodologies by later, proposing an experimental design and statistical analysis, to simulate energy loads for houses in tropical and subtropical regions. Researchers focused on studying a high-standard residences in tropical and subtropical areas, analyzing features and consumption patterns typical of such homes. The selected five locations for their geographical and climatic relevance to the research, spanning from Brazil, Italy, Dominican Rep. to Emirates and Australia. The findings emphasized the importance of efficiency in appliance usage: better efficiency reduces Energy Use Intensity (EUI). When looking at different design factors in cities with diverse climates, it becomes clear that appliance energy consumption can differ greatly depending on location. Factors like air temperature, sunlight exposure, humidity, and precipitation are key in determining how buildings use energy because they impact electricity needs. Understanding these variables is crucial for improving energy efficiency and designing buildings suited to their environmental contexts. Evaluating energy usage offers opportunities to enhance efficiency and advance towards sustainability goals, such as Nearly Zero Energy Buildings (NZEB). By looking at and adjusting these aspects, buildings can make progress towards sustainability while reducing their impact on the environment.
On the line of assessing the Life Cycle Assessment for Buildings, Alotaibi et al. (2022) established a new approach to measure embodied carbon throughout all stages of a building's life, to provide an unbiased evaluation framework, eliminating the need for manual processes [
71]. The research sought to present a straightforward method to assess embodied carbon, which in turn can help in developing effective strategies for reducing carbon emissions and achieving net-zero goals in the construction industry. Integrating Building Information Modeling (BIM) with LCA was essential for accurately measuring material quantities and matching them with environmental impact data. The research followed a structured six-step strategy to conduct a thorough BIM-based LCA study, improving the accuracy and efficiency of environmental assessments in construction projects.
The process for conducting Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) using Building Information Modeling (BIM), of a sophisticated high-rise residential building in urban areas throughout India, consisted of various key phases. After all, the necessary data for the lifecycle inventory analysis were incorporated into the BIM environment. The main goal of the integration was to analyze the essential elements that contribute to the building's embodied carbon and to assess decarbonization strategies to reduce carbon emissions. The results indicated 414 kg CO2e/m²/year, which is crucial for assessing decarbonization approaches to reduce emissions during construction, operation, and demolition. The documented reduction of carbon emission in the case study was down to 135 kg CO2e/m2/year through different methods. Methods such as reusing and recycling materials, using low-carbon materials, sourcing locally to cut transportation emissions, utilizing renewable energy, and implementing water-efficient measures.
5.4. Integration of Digital Twins & BIM
As far as BIM cannot fully optimize building and facility management in totality due to some limitations, Opoku et al. (2024) introduced a digital twin for a civil engineering field in which Building Information Modeling is tightly integrated with the Internet of Things (IoT) Platform for real-time data acquisition [
72]. Essentially, the set goal was to give directions on how to choose an adequate dynamic and real-time data capture platform, how to select a proper visualization platform and how to combine live data with the visualization system to create a digital twin. A 4-tier architecture system was set to create a BIM-centered and IoT-empowered Digital Twin system for enhancing the livability of rooms within the “Living Lab” taking in the principles of simplicity, communication efficiency and the categories of sensor devices in use. The authors proposed a flexible, adjustable, and scalable workflow that integrates IoT and BIM within a digital twin. An experiment was conducted to test this system by gathering, processing, and representing real-time data to improve decision-making in the operational management of a library modelled in Revit. Since Raspberry Pi devices had limitations, it was necessary to find an alternate solution to address data acquisition in the library building. The selection of LoRa end devices (sensors) as a remedy helped solve these issues hence offering assurance concerning collection of information. Ultimately, the system benefits building managers by providing a comprehensive view of indoor environmental conditions, facilitating prompt decision-making and data-driven predictive measures and supporting improvements in occupant comfort and overall building performance
Gourlis and Kovacic (2022) in their work, represented the design of a complete Digital Twin-based framework that is specialized for the visualization, development, and simulation of industrial facilities units [
73].
The article refers specifically to the stipulated data exchange protocols that are to be adopted from the BIM models that will be used as some guiding principles for the simplification of the models. It furtherly examines the feasibility and methods for integrating building-related attributes, which are related to Building Energy Modeling (BEM), together with the modular hybrid simulation models through a semi-automated data acquisition workflow. It employs BIM models to acquire and parameterize building data, particularly through the BaMa (Balanced Manufacturing) digital twin ecosystem.
The framework involves visual programming methods to extract data from BIM models and integrate building aspects into the hybrid simulation room, establishing the building Digital Twin as outlined in the BaMa framework. First, the outcomes from the research, sought to answer three specific research questions and unveiled, through a comparative analysis, the feasibility of the suggested SADYN (semi-automated Dynamo-based workflow) workflow, despite the process is not entirely automated and requiring human intervention. The SADYN workflow eliminated the need for a separate BEM model for hybrid simulations and combines static information with the data that is continuously updated. Finally, the BEM representation proved the success of the workflow, cutting the energy consumption by one-third of the time when compared to other methods of simulation.
Considering the advantages of computer vision and digital twin technology, Tan et al. (2022) established a Visual Operation & Maintenance (VO&M) platform for a Digital Twin Lighting (DTL) system, integrating surveillance and lighting [
74].
It acquainted an extensive and smart approach to the control decision-making of lighting systems, coming along with the creation of the digital twin for the lighting system, which allows visualization of control operations on the remote end, which is a step towards a process of building a data-driven platform for the whole life cycle management of green smart buildings and lighting equipment. Moreover, it proved that using multi-sourcing types of heterogeneous data fusion from surveillance systems, lighting systems, and Building Information Modeling (BIM) significantly increases energy savings in intelligent buildings. The study used digital twins to create a new ingenious lighting system with a rigid setup to allow and provide the lighting quality which is purpose-fit and cut down on the usage of energy. Additionally, the authors were able to use pre-trained weights to pseudo-label, and thus annotate the pedestrian dataset to finally have implemented the YOLOv4 algorithm based on the deep learning framework. Creating a BIM model also allowed us to cover a wide range of possibilities, physical domains, scales, and probabilistic scenarios. This approach describes the whole life cycle of the equipment involved, which results in accurate mapping, virtual-real interaction, and intelligent lighting intervention. Thereafter, since classic desktop BIM models are not suitable for a remote, the BIM models have been compressed and converted to a lightweight format that is capable of web browsers. Lastly, they introduced a Virtual Operation and Maintenance (VO&M) platform tailored for the DTL system, which was structured into seven discrete modules, empowering administrators to remotely oversee the Real-Time Location (RL) system and access real-time data on energy consumption and hardware utilization via internet connectivity. The combination of Digital Twin and BIM was shown to have a positive impact on the system's intelligent decision-making capabilities for lighting control which resulted in lower energy consumption and costs, the proposed scheme allowed collective management of the lighting system and thus may cut the need for electric power and thus, electricity costs. Furthermore, the research appointed the benefit of decreased and facilitated Operation and Maintenance (O&M) expenses and running times. Besides, the digital twin properties, related to the smart lighting system and the large amount of lighting data, provided opportunities to implement complete life-cycle O&M practices for green intelligent buildings and equipment are among the advantages.
Table 3. summarizes the literature information from the BIM field, categorized into the novel approach, the various contributions have followed, certification assessment, the function, the destination, the aim or scope for which BIM was used and finally the assessment method and building variables.
6. Internet of Things
6.1. IoT-Enhanced Smart Lighting & Adaptive Controls
Here Sanchez-Sutil and Cano-Ortega (2021) proposed and developed a specialized measurement and control system for public lighting [
75], utilizing Long Range Low Power Wide Area Network (LoRa LPWAN). Their system utilized an Artificial Bee Colony (ABC) algorithm to vary the intensity of lighting to reduce electrical energy consumption. The system has an Operational Management Device for Smart Lighting (OMDSL) within the SL infrastructure which controls the light intensity and recorded electrical data. The collected information was sent through the Long-Range Low Power WideArea Network (LoRa LPWAN) to the Gateway for Smart Lighting Systems (GWSLS), which managed the LoRa LPWAN network to handle the data traffic and uploaded the information to the cloud. This framework ensured efficient operation, remote management capabilities, and compliance with regulations. The findings from a facility campus in Spain, for implementing the proposed system over the course of a year, were examined based on three distinct scenarios. The first scenario resulted in reaching the highest energy savings, totalling 248.392 kWh, in the summer. This trend highlights the seasonal variability in energy consumption patterns, with summer offering the greatest potential for efficiency gains thanks to the extended daylight hours. The ABC algorithm improved the response speed of the Smart Lighting Regulation (SLR) system, allowing it to quickly adapt to changing lighting needs throughout the day, week, and year. Ultimately, its implantation has led to substantial energy savings, amounting to 12,615.635 kWh in one year.
Interestingly, Chiradeja and Yoomak (2023) built their research to present a new approach to designing and developing public lighting systems that are enhanced by Internet of Things (IoT) technology in a smart city [
76]. The goal was to improve energy efficiency and provide additional functions for public lighting. These advanced public lighting solutions use LED bulbs combined with controllers that adjust brightness based on light levels and motion sensors. This enabled the illumination to be dynamically adjusted in different areas, meeting required standards while optimizing energy consumption. The design team then crafted lighting guidelines for the proposed smart public lighting system and thus simulated the system using DIALux software, to ensure not only the safety but also the visual performance of the lighting in different environmental conditions and scenarios. This process enabled the optimization of both energy efficiency and user experience, so the final illumination would meet all necessary standards for public use. Key components of the smart system included motion sensors to activate lights or alarms upon detecting movement, light intensity sensors to measure brightness, IP cameras for image analysis and security monitoring, and dust sensors to detect airborne particles. The experiment results were organized into three different operating modes: manual, scheduled, and automatic. The use of the Internet of Things seems to offer many benefits, as they can also detect pollution and improve safety through IP cameras. A key advantage is that the automatic mode, over the others, helped to conserve energy, as it can adjust brightness levels based on actual usage, optimizing energy consumption. However, the electronic switching devices used for light control can cause some current distortion in the electrical grid, but the distortion levels remain within acceptable standards, without any negative impact on the grid or other devices.
On the same premises of the previous findings, Gehlot et al. (2021) suggested and created a smart lamppost that can be used for various purposes such as smart lighting, environmental monitoring, electric vehicle charging, and Wi-Fi hotspots [
77]. All of these features are combined into one lamppost by additionally using IoT technology and fog and edge computing to make a versatile infrastructure element for smart cities, improving efficiency and connectivity in urban areas.
Streetlights were regulated by Light Dependent Resistor (LDR) sensors, which adjust brightness depending on surrounding light levels, making them very useful in streetlights and motion sensor circuits. In addition, moving objects are detected by Passive Infrared (PIR) sensors, saving energy by adjusting brightness based on both environmental light levels and activity. Streetlights were hence turned on at a particular dimming level depending on the time of day. The PIR sensor also adjusted the brightness of the streetlights according to the amount of natural light present, thus minimizing energy usage and providing sufficient illumination by the surroundings.
6.2. IoT and BIM for Energy Monitoring and Optimisation
Mataloto et al. (2019) a cost-effective LoRa/LoRAWAN solution to monitor building environments and enhance energy efficiency through a layered IoT-based architecture [
78]. The platform followed a system integration principle by providing a single platform for various devices, all transmitting data to the platform through IoT technologies. The system was divided into three layers: the Physical layer with sensors and actuators, the Network layer managing IP and LoRa communications, and the Application layer where data fusion, processing, and display take place. The savings method was put into action using pre-designed templates, which made it possible to create a data visualization tool which could help users at the local level interpret the gathered data and, using this visual representation, establish rules for automatic actions to save money. In the observed case study, a private kindergarten in Amadora, Lisbon, Portugal, the authors have recognized the potential of technology to help school owners achieve even greater savings and improve comfort. Finally, the data visualization and related actions taken over three years resulted in a significant decrease in overall energy usage, around 20% to 25% and the initial investment was recovered within the first year of implementation. When extended to larger buildings, this approach has the potential to generate even more substantial cost savings. On the wave of investigating the potential of Artificial Intelligence (AI), the primary focus of Garlik (2022), was to establish the conditions and requirements for implementing the Internet of Energy (IoE), given its substantial significance when referring to smart cities [
79]. The author´s strategy employed Energy Management Systems (EMS) using IoT technology and the control of devices such as KNX, FOXTRO, and ABB-free@home®, toward energy saving and thus decreasing CO2 emissions in the building. The installation of photovoltaic panels and micro-cogeneration on a Czech residential building, were a few other possible solutions to achieve, on the one hand, environmental burden abatement and the other, energy resilience enhancement in the urban clusters.
DesignBuilder and HOMER, enabled detailed analysis and optimization of energy performance in complex building clusters, by also allowing parallel simulation methods. Valuable insights were so gathered on various management strategies. However, despite these tools having some promising potential, they need to be further investigated in terms of their applicability. To sum up, although the latest achievements showed significant steps made towards the union of IoT technology and energy management to optimize the energy performance of buildings, research along with new research is necessary to develop a model, ensuring consistency in the validation of simulation outcomes against real-world data.
On the same premises, Canada-Bago et al. (2022) aimed to create and implement an IoT system that can control and monitor a stand-alone PV system in real-time; The main goal of this approach was to improve the overall efficiency of stand-alone PV systems by maximizing battery life and minimizing costs [
80]. The focus was turned on Photovoltaic systems and the integration of IoT devices since many IoT tools are equipped with solar power system to ensure uninterrupted operation. Particular attention was given to stand-alone solar power systems that work on their own, functioning without being linked to the grid, (the other type of PV system) and feature batteries to store the created energy, providing flexibility in using it during times of production and consumption.
The research project, after two experiments, created a powerful stand-alone solar energy system that was combined with an Internet of Things (IoT) device using limited resources, also designed with two knowledge-based controllers, including an IoT lighting application to demonstrate how the controllers could function on an IoT device to reduce costs as well as work smoothly in areas with limited resources. The findings showed that the knowledge-based controllers exceeded the performance of both commercial and basic controllers in experiments, displaying improved efficiency. Successfully using these controllers, especially in confined spaces, is a big step forward in using IoT for practical and efficient energy management and automation across different applications.
Similarly, Shao et al. (2023) also adopted a library for their case study, which aimed to integrate Distributed Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) with the Internet of Things (IoT) and Building Information Modelling technology to decrease power consumption via the implementation of smart illumination method [
81]. The main aim is to examine the plans and alternatives in developing an intelligent lighting system that is based on IoTs as well as BIMs and also look at its effects on the maintenance of a library. The whole system was designed so that it comprised a distributed wireless sensor network (WSN), luminaires, and sensors. Each luminaire had a sensor system that controlled the dimming level depending on the daylight amount, a predefined schedule and whether there were people of its presence. It used light sensors in the indoor sensor module lightest (closest to windows) to measure daylight intensity and then pass this information to the whole network; two similar rooms were used for testing this system. This system has been installed in one of these rooms as outlined, whereas the other one is simply a control room without any installation of the system Experimentation validated that the energy-saving control system could dynamically adjust brightness in library reading rooms. Thus, it continually adapts itself by means that encourage proper illumination while minimizing power use. Results showed clearly that the main control system was able to alter dynamically the consumption of energy for the library which in return leads to realizing all the energy-saving goals set by that particular system. With this in place, it allows the ability to switch according to various scenarios and types of usage to improve energy consumption.
Interestingly, Zou et al. (2024) presented a new method, D&S-HDA, which stands for “dynamic and static hybrid data analysis” for forecasting electricity usage in buildings [
82]. By merging dynamic and static data analysis techniques, D&S-HDA improves the accuracy and reliability of predictions by addressing outliers in dynamic data, unlike approaches relying solely on dynamic analysis.
The novelties and main contributions of the authors are several and could be highlighted among the others, the introduction of the D&S-HDA framework, which begins by using a dynamic data analysis model to make an initial estimation of electricity usage and then integrates static data from Building Information Modeling (BIM) to enhance these predictions on an hourly basis. Ultimately, the framework combines the dynamic data predictions with the static BIM data estimates to produce a more precise final prediction of electricity usage. The main problem to be tackled was that outliers in real-time data can compromise the accuracy and dependability of forecasts made using traditional techniques for predicting hourly electricity usage. The findings of the study suggest that using D&S-HDA can successfully minimize the negative impact of outliers in the time series of building energy use. This approach showed better prediction accuracy compared to methods solely based on dynamic data analysis for forecasting building electricity consumption
6.3. IoT Applications in Different Fields
Stevens et al. (2022) pursued their research on open-air Mobile Indoor Smart Hydroponics (MISH-O) systems, where plants can get natural (incorporating daylight harvesting methods) and artificial light [
83]. The goal was to make affordable IoT MISH systems that empower citizen science, hence they proposed Adaptalight, a cutting-edge Mobile Indoor Smart Hydroponics (MISH-O) system that improves upon existing IoT MISH systems; it utilizes accurate, direct pulse width modulation to control the LED power source. The effectiveness of this system was tested in a practical scenario in an apartment in Dubai, UAE. The results indicate that low-cost IoT sensors performed similarly to commercial sensors in measuring PAR in MISH systems. Furthermore, the findings suggest that the accuracy of the sensor in measuring PAR may be due to its calibration against high-quality instruments. Finally, there was no notable difference in plant yields compared to the controls, suggesting that the design of the system and the affordable PAR sensor alternative allow ordinary individuals to construct energy-efficient MISH-O systems for home food cultivation.
On the other hand, Kim et al. (2023) developed an indoor self-powered sensor module for real-time temperature measurement by integrating organic photovoltaic (OPV) modules with a voltage-boost converter [
84]. The study conducted real-time measurements of temperature changes using the self-powered sensor module integrated with an OPV module and an optimized converter. An innovative sensor module that can operate without external power sources has been developed for monitoring temperature in real-time, and such a module was powered by organic photovoltaic (OPV) modules that collect energy from indoor lighting. The generated electricity is transferred to a DC-DC converter which regulates the voltage to power the temperature sensor. The module was divided into three sections: an input power circuit, a converter circuit, and a temperature sensor circuit. Each part was tailored to perform a particular task, guaranteeing accurate and dependable real-time temperature readings from the sensor. Ultimately, organic solar cells made were used to efficiently convert electrical energy from indoor lighting. These OPV modules were designed to power indoor sensor applications and to achieve and ensure the temperature sensor operated reliably, it was important to optimize the voltage and power output of the modules, which can be done using a boost converter. In summary, the created sensor platform was able to generate its power to measure temperature in real-time, by combining OPV modules with a voltage-boost converter, the achievement of stable and accurate temperature measurements in indoor settings was possible. This advancement is likely to have a major impact on the widespread use of sensor systems and the growth of industries that rely on energy-harvesting technologies.
On the other hand, Chekired et al. (2022) focused on grid-connected PV, by presenting a one-tenth scale downsized UDES (Solar Equipment Development Unit) demonstrator, to explore integrated energy solutions [
85]. The demonstrator featured a grid-connected photovoltaic (PV) plant along with an energy storage system. The main goal was to reduce energy consumption and move towards energy self-sufficiency. The most important aspect of this study was the development of a comprehensive energy management system that is known for its strength, dependability, and affordability. The system was set up to use electricity generated by the PV panels to power the building, with any extra power going to charge the batteries. If the batteries are full, the surplus energy is sent to the grid. This setup boosted energy self-sufficiency and reduced reliance on the external power grid, promoting a more sustainable energy model for residential buildings. After a study phase, the energy system model was then implemented in a real-scale house in Algeria. It also considered a series of different aspects, providing a complete approach to managing buildings, taking into account various aspects of occupant health and environmental conservation. By utilizing intelligent lighting control, the energy used for lighting was decreased, resulting in a 15.88% increase in efficiency and so it was the total energy consumption in the home, that was lowered with the implementation of the smart control system.
Table 4. Provides the most crucial information to identify which type of network was used, the intelligent device that ensured the successful procedure, the technology and its application a finally the objective of IoT technology and its characteristics.
7. Discussion
7.1. Reflections upon the Reviewed Works
After reviewing studies on integrated lighting solutions, daylight optimisation and building performance, it has been discovered that there are several feasible approaches to improving energy efficiency and lighting quality in architectural designs. In addition to this, the research conducted into this area showed the considerable impact it can have in terms of energy consumption levels. Besides that, it is evident that advanced simulation tools coupled with parametric design techniques play a major role in improving daylighting as well as energy efficiency within architecture. As a result, many studies have been conducted to improve daylighting and such procedures applied to buildings, have demonstrated not only to reduce electricity consumption but also to foster the comfort and health of their occupants hence better daylighting as well as energy efficiency outcomes in buildings. Evidence showed that the best use of simulated tools will be to evaluate numerous factors like proper building orientation and design that help to achieve the right amount of natural light while minimizing discomfort caused by intense brightness. It is important to note that the preliminary stages of architectural planning can benefit a lot from multi-target optimisation as well as parametric designing which opens up many possibilities for designs thus saving energy and providing better lighting. In simpler terms, these findings indicate that architects and designers should use advanced simulation tools and optimisation techniques to make buildings more energy-efficient and improve lighting quality. It is important to balance these changes with considerations for occupant comfort and meeting regulations.
The impact of facade shapes on daylight distribution underscores the importance of facade design and orientation for energy efficiency and occupant well-being. Many studies have looked at diverse ways to incorporate innovative ideas for using daylight and energy-efficient technology in building design; among the others, kinetic facades have shown how adaptable they are to lower energy usage and enhance thermal efficiency and lastly, it was found a significant energy conservation benefit.
Regarding using comprehensive strategies for automation and control, further focused on the differences between manual and automated shading controls, the latter are more energy efficient and provide better outdoor visibility compared to manual methods, suggesting a new standard for automated shading controls. Even though some good things have been revealed to be useful, there are still areas in the research that need more exploration. A conflicting means of connection between energy usage and how comfortable the occupants feel would suggest whether focusing on improving one aspect could harm another. It demonstrates how challenging it can be to find a middle ground between saving energy and ensuring occupants are happy and content.
In addition, some research has proposed new strategies for maximizing daylight, while others have raised concerns about possible constraints, for example, certain software tools, such as DaylightX, could be limited in their ability to assess daylight levels throughout the year, highlighting the importance of using more flexible techniques. In general, the significance of a comprehensive approach to architectural design should be considered to balance energy efficiency, maximize daylight, and ensure occupant comfort all at once. Moving forward, it would be beneficial to find ways to overcome any constraints or gaps found in current research. In the construction industry, Building Information Modeling (BIM) and Digital twins are increasingly used to enhance sustainability and energy efficiency, with several studies which have demonstrated that BIM can effectively improve energy conservation, lower carbon emissions, improve cost estimation and optimize the overall building performance.
BIM showed the benefits of retrofitting a vast variety of buildings to achieve net-zero energy performance, lowering CO2 emissions and utilizing solar energy. Integrating daylighting analysis into the BIM environment enables stakeholders to make informed design choices, improving the efficiency and effectiveness of the architectural design process. The way a building uses energy depends on many variables such as systems, materials and architectural design. By carefully planning out the lighting, appliances, and HVAC systems, a building can significantly lower its energy needs. The improvement advocating a BIM framework has proved to emphasize daylight for visual and thermal comfort and support the designing of a net-zero energy building, where BIM can be integrated with tools for building performance analysis to enhance energy efficiency through an iterative approach in design. On the same premises, BEM and BIM offer an estimation of how much energy a building would use in various climates, with significant outcomes, underlining the importance of adapting construction plans to local environments. Moreover, a comprehensive assessment system can also be developed with the help of the BIM tool and support the Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) with decarbonization tactics during all phases of the building's life cycle. With the utilization of advanced modeling software together with innovative approaches, the construction industry could make a significant contribution to minimizing its environmental footprint as well as supporting global sustainable development goals. The Internet of Things (IoT) has transformed technology in various aspects, especially in the field of public lighting and energy control, leading the research to look for new methods of making intelligent illumination, with optimized algorithms systems that save power without depleting power sources. The outcomes surely have demonstrated to significantly reduce energy, by using environmental cues and traffic flow and dynamic LED controls based on movement and light thus meeting safety standards and energy consumption reduction. Components include movement detectors, light intensity sensors, IP cameras and dust sensors, enhancing smart lighting, and this indicated a high implementation of the systems with such components, based not only on environmental factors but also human behaviours.
As a result, integrating IoT technologies in a layered architecture makes it possible to minimise expenses while improving energy efficiency, while also considering an immediate return on investment. Other methods aimed to predict energy consumption in buildings by combining dynamic data analysis with static data from Building Information Modeling (BIM), where the accuracy was much higher than what one can get from conventional techniques. The many different studies on public lighting, energy management and similar topics show how the IoT can change these areas. IoT can provide more cost-effective lighting, save energy and be applicable in various spheres starting from smart cities and ending with greenhouses due to its novel algorithms and systems.
7.2. Development of a New Digitalized Design Procedure
With all being said, it is necessary to establish a new conceptual model, that would valuably help designers and related professional figures to approach and tackle the new integrated lighting projects.
Building upon the foundational work of Ehud Knoll, who proposed the “Conceptual method” that fundamentally describes the process of making and utilizing the basic principles that best define a product similar to a plan or a system [
86]
According to the model. The parameter analysis, in combination with the aid technology identification, allows to construction of the concept space. This latter is then merged through a realization (or particularization) process, into the configuration space. Through abstraction (or generalization) in the configuration space, it also iterates again.
This successive mechanism is a clear indication that the schematic design is still under revision and constant refinement. Therefore, the development of a new model. Undoubtedly, this approach is highly innovative as integrates the use of BIM (Building Information Modeling) and the use of the Internet of Things, to foster a more dynamic and interactive design environment.
The first step of the proposed model framework is the “Parameter Identification" phase, which involves the systematic identification of independent variables crucial for optimizing the design process. In the current phase, a range of independent variables is recognized, each of which may significantly impact the design outcome. These variables could include but are not limited to, the Window-to-Wall Ratio (WWR), shading devices, electrical lighting, building geometry, orientation, and another relevant factors. This initial phase is essential for setting the stage for effective optimisation and design innovation. The proposed model moves onto the second stage, called "Response", which involves the collection and examination of environmental quality data. In this phase, data related to both indoor and outdoor environments are collected, which play a crucial role in shaping the building's overall environmental quality. This information encompasses, among other things temperature, humidity, light levels, air quality, and user initial feedback obtained through IoT applications, (using artificial intelligence or surveillance cameras) and questionnaires. The insights gained from this data are very useful in grasping the environmental context in which the building operates, thereby influencing subsequent design decisions. This latter phase serves as a foundation for the next and most critical phase, known as "Sensing and Control". In this phase, the identified parameters and the environmental data are described and integrated to generate solution ideas that are both responsive to the gathered data and innovative in their approach. This stage is meaningful since it allows the decision-making process by synthesizing environmental data and identified parameters into actionable design strategies. Moreover, it involves a real-time assessment of all relevant variables, allowing designers or related professional figures to dynamically adjust and refine design solutions based on current conditions and evolving needs; notably, it is also called the “exploration” phase. Finally, towards the end of the process, the model proceeds to the “Evaluation” phase. This stage is noteworthy since it ensures that all the previously established goals are achieved and that the outcomes of the project are aligned with the intended objectives. In the process of Evaluation, the design solutions are considered to be effective or ineffective based on user satisfaction. Consequently, it becomes possible to comprehend user satisfaction as a successful representation and key indicator of the design and intelligent comprehension of the technology alongside the experiential and functional needs of the end-users. Once the evaluation shows that the goals have been satisfied, the process enters the final step of the "Adaptive Loop", also referred to as "Exploitation". In this final phase, the design process becomes iterative, continuously interacting with the changes in the environment and deploying new technologies as they become available. The Adaptive Loop ensures that the design remains dynamic and adaptable, to be able to respond and evolve in response to ongoing feedback and ambient conditions. It is a cyclical process that not only improves the existing design but also sets the basis of the system for future enhancements; in turn, this will help to sustain innovation and enable the system to operate with optimal performance over time.
This framework can be understood as a multi-step iterative process in which Building Information Modeling (BIM) plays a central role, controlling and coordinating the various stages. This initial level of control is referred to as the "Schematic Phase," and it represents a concrete parametric design approach. During this phase, BIM integrates all relevant parameters and variables, ensuring that the design process is both systematic and adaptable to changes in real time. The Internet of Things (IoT) goes beyond the Schematic Phase and spreads its model into the "Development Phase" or Adaptive Design, as well. In this phase, IoT technologies make it possible for the system to continuously work and communicate, especially in the "Sensing and Control" stage that goes on for some time. It provides immediate feedback and adjustments, which guarantees that the design evolves dynamically in response to the environment and its changes, as well as to user needs. The combination of BIM and IoT in this framework serves a rigid, adaptive system that does not only plan but permanently reconfigures and improves the performance of the building thus assuring that the outcome will be both cutting-edge and reacting to real-time situations. An exemplification of the newly developed procedure is illustrated in
Figure 11.
8. Conclusions
A variety of novel strategies were studied for light control handy energy consumption minimization, concentrating on integrated ways to collaborate in the realm of illumination and the bridging of Building Information Modeling (BIM) concerning the Internet of Things (IoT). The outcomes show that such techniques could make a substantial difference as far as effectiveness and environmental friendliness go across different settings.
The current literature review sought to answer two specific research questions: when it comes to the first research question on the impact of integrated lighting solutions on energy consumption, there is a consensus in most studies reviewed that new lighting solutions play a significant role in reducing energy use.
In summary, these studies suggest that successfully implementing energy-efficient solutions involves various factors such as building orientation, facade design, daylighting systems, and control strategies. Each factor has its benefits, but the main point is the need for customized solutions for different building types and locations. This thorough understanding can inform future research and the creation of innovative systems to enhance building performance and energy efficiency.
In addition, different orientations and climates called for specific shading techniques, highlighting the importance of unique solutions for each location to maximize natural light and energy efficiency. For instance, public lighting systems may see the integration of adaptive lighting controls that work to change the intensity of light based on environmental conditions as well as usage patterns such as the Artificial Bee Colony (ABC) optimisation algorithm resulting in a significant reduction of energy consumption. These integrated lighting solutions are not only making less use of electricity but also improving safety and comfort in public places.
Regarding the second research question (“How can the integration of BIM and IoT contribute to better lighting management and create synergies to maximize sustainability?”), studies have shown that BIM and IoT have the potential to create smart lighting systems that are better managed.
Comprehensive building data storage ability allows BIM to perform more correct simulations and light requirement analyses, while IoT enhances on-site management and monitoring capabilities additionally, the combination of IoT and lighting, connectivity and environmental monitoring can provide sustainable infrastructures not only in the building environment but also on the urban scale. The use of Building Information Modeling technology (BIM) has been crucial in driving the progress towards efficient and sustainable buildings, providing many advantages that enhance many different aspects IoT, on the other hand, ensures at any time an informed decision-making to tackle actions aimed at sustainability.
According to the review, the integration of BIM and IoT improves energy efficiency, sustainability and user experience through the incorporation of advanced lighting solutions while providing means for smarter, sustainable lighting systems by allowing remote controlling and extensive data analysis; hence, these technologies provide a way to create smarter and more sustainable lighting systems by enabling remote management.
In the future, there should be further exploration into the possible synergies that are possible between BIM and IoT. Increasingly important to this growing field is the need for solutions that can scale across many industries and urban areas. If these technologies are to realize their full potential in terms of energy conservation and sustainability, issues such as cost, interoperability and security in data storage must be addressed.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.Z.; methodology, G.Z., G.T. and M.H.; validation, G.T. and M.H.; formal analysis, G.T. and M.H.; investigation, G.Z., G.T. and M.H.; resources, G.Z., G.T. and M.H.; data curation, G.T. and M.H.; writing—original draft preparation, G.Z.; writing—review and editing, G.Z., G.T. and M.H.; visualization, G.Z.; supervision, G.T. and M.H.; project administration, G.T. and M.H.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.”
Funding
This research received no external funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge that this study is a part of our contribution to the project titled: "EUDP 2023-I Deltagelse i IEA SHC 70 Low carbon, High comfort integrated lighting”.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Cao, X., Dai, X., & Liu, J, “Building energy-consumption status worldwide and the state-of-the-art technologies for zero-energy buildings during the past decade”, Energy and Buildings, 2016, Vol. 128, pp. 198–213. [CrossRef]
- https://sdgs.un.org/goals/goal7.
- Yoshinoa, H., Hong, T., Nord, N., “IEA EBC annex 53: Total energy use in buildings—Analysis and evaluation methods”, Energy and Buildings, 2017, Vol. 152, pp. 124-136.
- Aries M., Aarts M., van Hoof J., “Daylight and health: A review of the evidence and consequences for the built environment”, Lighting Research & Technology, 2015, Vol.47, Issue 1, pp.6-27. [CrossRef]
- L. Sanati, M. Utzinger, “The effect of window shading design on occupant use of blinds and electric lighting”, Building & Environment, 2013, Vol. 64, pp.67–76. [CrossRef]
- Overen, O.K.; Meyer, E.L.; Makaka, G., “Daylighting Assessment of a Heritage Place of Instruction and Office Building in Alice, South Africa”, Buildings, 2023, Vol. 13, Issue 8, 1932. [CrossRef]
- https://task61.iea-shc.org/.
- Gentile, N., Lee, E.S., Osterhaus, W., Altomonte, S., David Amorim, C.N., Ciampi, G., Garcia-Hansen, V., Maskarenj, M., Scorpio, M., Sibilio, S., “Evaluation of integrated daylighting and electric lighting design projects: Lessons learned from international case studies”, Energy and Buildings, 2022, Vol. 268, 112191, ISSN 0378-7788. [CrossRef]
- Berardi, U.; Manca, M.; Casaldaliga, P.; Pich-Aguilera, F., “From High-Energy Demands to NZEB: The Retrofit of a School in Catalonia, Spain”, Energy Procedia, 2017, Vol. 140, pp. 141–150 . [CrossRef]
- Josijevic, M.; Gordic, D.; Milovanovic, D.; Jurisevic, N.; Rakic, N., “A Method to Estimate Savings of Led Lighting Instalation in Public Buildings: The Case Study of Secondary Schools in Serbia”, Thermal Science Journal, 2017, Vol. 21, pp. 2931–2943. [CrossRef]
- Gentile, N.,“Improving lighting energy efficiency through user response”, Energy and Buildings, 2022, Vol. 263, 112022. [CrossRef]
- Kima, S., Zadehb, P.A., Staub-Frenchc, S., Froesed, T., Cavka, B.L., “Assessment of the Impact of Window Size, Position and Orientation on Building Energy Load Using BIM”, Procedia Engineering, 2016, Vol. 45, pp. 1424-1431. [CrossRef]
- Kota, S., Haberl, J.S., Clayton, M.J., Yan W., “Building Information Modeling (BIM)-based daylighting simulation and analysis”, Energy and Buildings, 2014, Vol. 81, pp. 391-403. [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J., Lee, J. and Ham, Y., “Quantifying the impact of building envelope condition on energy use”, Building Research and Information, 2019, Vol. 47 No. 4, pp. 404-420. [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chen, Y.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, C., “Current Status and Future Directions of Building Information Modeling for Low-Carbon Buildings”, Energies, 2024, Vol.17, 143. [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhao, Z.; Xiao, J.; Tiong, R., “A Conceptual Framework for Estimating Building Embodied Carbon Based on Digital Twin Technology and Life Cycle Assessment”, Sustainability, 2021, Vol. 13, 13875. [CrossRef]
- Yang, A., Han, M., Zeng, Q., Sun, Y., “Adopting Building Information Modeling (BIM) for the Development of Smart Buildings: A Review of Enabling Applications and Challenges”, Advances in Civili Engineering, 2021, ID 8811476, 26 pages. [CrossRef]
- Grieves, M., “Digital twin: manufacturing excellence through virtual factory replication”. White Paper, 2014, Vol.1, p.1.
- Shukra, Z.A., Zhou, Y., "Holistic green BIM: a scientometrics and mixed review", Engineering, Construction and Architectural Management, 2021, Vol. 28 No. 9, pp. 2273-2299. [CrossRef]
- Building Sector Emissions Hit Record High, But Low-Carbon Pandemic Recovery Can Help Transform Sector—UN Report. 2020. Available online: https://www.unep.org/news-and-stories/press-release/building-sector-emissions-hit-record-high-low-carbon-pandemic (accessed on 5 March 2023).
- Adoghe, A.U., Owuama, E.C., Oguntosin, V., Morawo, B., “Design and Implementation of a Low-Cost Cloud-Powered Home Automation System”, Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Review, 2022, Vol. 15, Issue 3, pp.177-192.
- Verma, A., Prakash, S., Srivastava, V., Kumar, A. and Mukhopadhyay, S. C., "Sensing, Controlling, and IoT Infrastructure in Smart Building: A Review,", IEEE Sensors Journal, 2019, Vol. 19, no. 20, pp. 9036-9046, . [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, D, Abbadi, A.E., Emekci, F., Metwally, A. “Database management as a service: challenges and opportunities”, 2009 IEEE 25th International Conference on data engineering, 2009, pp 1709–1716. [CrossRef]
- Ahad, M.A.; Paiva, S.; Tripathi, G.; Feroz, N., “Enabling technologies and sustainable smart cities”, Sustainable Cities Society, 2020, Vol. 61, 102301.
- Zanella, A.; Bui, N.; Castellani, A.; Vangelista, L.; Zorzi, M., “Internet of things for smart cities”, IEEE Internet Things Journal, 2014, Vol.1, N. 1, pp. 22–32.
- Thirupathi, L., Rajesh, A., Sandeep, R.., “Internet of Lighting for Smart Cities”. In: Tiwari, M., Ismail, Y., Verma, K., Garg, A.K. (eds) International Conference on Optical and Wireless Technologies, 2023, OWT 2021. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, vol 892. Springer, Singapore. [CrossRef]
- 27. Annex 1a - Application form for IEA participation in Annexes and Task.
- Wu, L., Lu, W., Xue, F., Li, X., Zhao, R., Tang, M., “Linking permissioned blockchain to Internet of Things (IoT)-BIM platform for off-site production management in modular construction”, Computer in Industry, 2022, Vol. 135, 103573 . [CrossRef]
- Thomson, G.D.; Davis, R.G.; Fernandes, L.; Wang, T., “Achieving Integrated Daylighting and Electric Lighting Systems: Current State of the Art and Needed Research”, Energies, 2021, 14, 3833. [CrossRef]
- Plörer, D.; Hammes, S.; Hauer, M.; van Karsbergen, V.; Pfluger, R., “Control Strategies for Daylight and Artificial Lighting in Office Buildings—A Bibliometrically Assisted Review”, Energies, 2021, 14, 3852. [CrossRef]
- Baghi, Y.; Ma, Z.; Robinson, D.; Boehme, T., “Innovation in Sustainable Solar-Powered Net-Zero Energy Solar Decathlon Houses: A Review and Showcase”, Buildings, 2021, 11, 171. [CrossRef]
- Rangasamy, V., Yang, J-B., “The convergence of BIM, AI and IoT: Reshaping the future of prefabricated construction”, Journal of Building Engineering, 2024, Vol. 84, 108606. [CrossRef]
- Mazhar, T.; Irfan, H.M.; Haq, I.; Ullah, I.; Ashraf, M.; Shloul, T.A.; Ghadi, Y.Y.; Imran; Elkamchouchi, D.H., “Analysis of Challenges and Solutions of IoT in Smart Grids Using AI and Machine Learning Techniques: A Review”, Electronics, 2023, Vol. 12, 242. [CrossRef]
- Hauer, M.; Hammes, S.; Zech, P.; Geisler-Moroder, D.; Plörer, D.; Miller, J.; van Karsbergen, V.; Pfluger, R., “Integrating Digital Twins with BIM for Enhanced Building Control Strategies: A Systematic Literature Review Focusing on Daylight and Artificial Lighting Systems”, Buildings, 2024, 14, 805. [CrossRef]
- Booth A, Sutton A, Clowes M and Martyn-St James M., “Systematic approaches to a successful literature review”, SAGE Publications Ltd, 2021.
- van Eck, L.; Waltman, N.J. “VOSviewer Manual—Manual for VOSviewer Version 1.6.20. 2024. Available online: https://www. vosviewer.com.
- Overen, O.K.; Meyer, E.L.; Makaka, G. “Daylighting Assessment of a Heritage Place of Instruction and Office Building in Alice, South Africa”, Buildings, 2023, Vol. 13, 1932. [CrossRef]
- Piraei, F.; Matusiak, B.; Lo Verso, V.R.M., “Evaluation and Optimization of Daylighting in Heritage Buildings: A Case-Study at High Latitudes”, Buildings, 2022, Vol. 12, 2045. [CrossRef]
- https://www.solemma.com/climatestudio.
- Xie, F.; Song, H.; Zhang, H., “Research on Light Comfort of Waiting Hall of High-Speed Railway Station in Cold Region Based on Interpretable Machine Learning.”, Buildings, 2023, Vol. 13, 1105. [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Fernandez, B.; Omar, O.; “Integrated innovative solar lighting system for optimization of daylight utilization for public library in Alexandria, Egypt”, Ain Shams Engineering Journal, 2023, Vol. 14, Issue 1. [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Liu, Q.; Han, Y.; “Many-Objective Optimization Design of a Public Building for Energy, Daylighting and Cost Performance Improvement”, Applied Science, 2020, Vol. 10, 2435. [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Cho, S.; “Design optimization of building geometry and fenestration for daylighting and energy performance”, Solar Energy, 2019, Vol.191, pp.7-18. [CrossRef]
- Nasrollahzadeh; N.; “Comprehensive building envelope optimization: Improving energy, daylight, and thermal comfort performance of the dwelling unit”, Journal of Building engineering, 2021, Vol. 44. [CrossRef]
- Karadag, I.; Zeynep Keskin, Z.; “Development of a Daylight Simulation Software for Early Design Stage: A Case Study of a Container House”, Periodica Polytechnica Architecture, 2021, Vol. 52, Issue 1, pp. 102–111. [CrossRef]
- Pompei, L.; Nardecchia, F.; Viglianese, G.; Rosa, F.; Piras, G. “Towards the Renovation of Energy-Intensive Building: The Impact of Lighting and Free-Cooling Retrofitting Strategies in a Shopping Mall”, Buildings, 2023, Vol. 13, 1409. [CrossRef]
- Phuong, H.N.; Nguyen, L.D.L.; Nguyen, V.H.M.; Cuong, V.V.; Tuan, T.M; Tuan, P.A.; “A New Approach in Daylighting Design for Buildings”, Engineering, Technology & Applied Science Research, 2023, Vol. 13, n. 4, pp. 11344-11354. [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Sun, C.; Han, Y.; Liu, Q.; “Intelligent optimization: A novel framework to automatize multi-objective optimization of building daylighting and energy performances.”, Journal of Building Engineering, 2021, Vol. 43. [CrossRef]
- Bande, L.; Asmelash, Y.; Ahmad, A.; Cyiza, A.; Berengueres, J., “Evaluation of an Existing Validated Emirati House versus a New Parametric Design Based on the Local Social Environment through the Application of Advanced Tools” Buildings, 2023, Vol. 13, 2627. [CrossRef]
- Reffat, R.M.; Ahmad, R.M.; “Determination of optimal energy-efficient integrated daylighting systems into building windows”, Solar Energy, 2020, Vol. 209, pp. 258-277. [CrossRef]
- Xuan, Q., Li, G., Zhao, B., Jiang, B., Sun, D., Zhang, X., Tang, J., Zhuang, Y., Liu, J., Li, L.; “Evaluation of the smart daylighting control performance of the concentrating photovoltaic/daylighting system as the skylight in the building”, Solar Energy, 2022, Vol. 238, pp. 17-29. [CrossRef]
- Alawaysheh, A., Taleb, H., Kayed, M., “The impact of a kinetic façade on the lighting performance and energy efficiency of a public building: the case of Dubai frame”, International Journal of Sustainable Energy, 2023, Vol. 42, N. 1, pp. 1317-1363.
- Uribe, D., Vera, S., Bustamante, W., McNeil, A., Flamant, G., “Impact of different control strategies of perforated curved louvers on the visual comfort and energy consumption of office buildings in different climates”, Solar Energy, 2019, Vol. 190, pp. 495-510. [CrossRef]
- Vanage, S., Dong, H., Cetin, K., “Visual comfort and energy use reduction comparison for different shading and lighting control strategies in a small office building”, Solar Energy, 2023, Vol. 265, 112086. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, S.; Gao, X.; Fan, H. “Daylighting Performance of CdTe Semi-Transparent Photovoltaic Skylights with Different Shapes for University Gymnasium Buildings. Buildings, 2024, Vol. 14, 241. [CrossRef]
- Wei Zhang, W., Li, J., Xie, L., Hao, X., Mallick, T., Wu, Y., Baig, H., Shanks, K., Sun, Y., Yan, X., Tian, H., Li, Z., “Comprehensive analysis of electrical-optical performance and application potential for 3D concentrating photovoltaic window”, Renewable Energy, 2022, Vol. 189, pp. 369-382. [CrossRef]
- Farivar Fazelpour, F., Bakhshayesh, A., Alimohammadi, R., Saraei, A., “An assessment of reducing energy consumption for optimizing building design in various climatic conditions”, International Journal of Energy and Environmental Engineering, 2022, Vol. 13, pp. 319-329. [CrossRef]
- Mashaly, I. A., Garcia-Hansen, V., Cholette, M. E., Isoardi, G., “A daylight-oriented multi-objective optimisation of complex fenestration systems”, Building and Environment, 2021, Vol. 197, 107828. [CrossRef]
- Jamala, N., Hamzah, B., Mulyadi, R., Cahyani, I., “The Architectural Design of Building Façade Models Related to Optimizing Daylight Distribution”, Journal of Daylighting, 2023, Vol. 10, pp. 60-71, ISSN 2383-8701. [CrossRef]
- Jakubowsky, M., de Boer, J., “Façade elements for room illumination with integrated microstructures for daylight redirection and LED lighting”, Energy and Buildings, 2022, Vol. 266, 112106. [CrossRef]
- Marzouk, M.; Thabet, R. A “BIM-Based Tool for Assessing Sustainability in Buildings Using the Green Pyramid Rating System”, Buildings, 2023, Vol. 13, 1274. [CrossRef]
- Razzaq, I., Amjad, M., Qamar, A., Asim, M., Ishfaq, K., Razzaq, A., Mawra, K., “Reduction in energy consumption and CO2 emissions by retrofitting an existing building to a net zero energy building for the implementation of SDGs 7 and 13”, Frontiers in Environmental Science, 2023, Vol. 10. [CrossRef]
- Chen, S. Y., “Use of green building information modeling in the assessment of net zero energy building design”, Journal of Environmental Engineering and Landscape Management, 2019, Vol. 27, Issue 3, pp. 174-186. [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, J.P.; Almeida, M.; Bragança, L.; Mateus, R. “BIM-Based Energy Analysis and Sustainability Assessment—Application to Portuguese Buildings”. Buildings, 2021, Vol. 11, 246. [CrossRef]
- Amoruso, F. M., Dietrich, U., Schuetze, T., “Integrated BIM-Parametric Workflow-Based Analysis of Daylight Improvement for Sustainable Renovation of an Exemplary Apartment in Seoul, Korea”, Sustainability, 2019, Vol. 11, Issue 9, 2699. [CrossRef]
- Gan, J.; Li, K.; Li, X.; Mok, E.; Ho, P.; Law, J.; Lau, J.; Kwok, R.; Yau, R. “Parametric BIM-Based Lifecycle Performance Prediction and Optimisation for Residential Buildings Using Alternative Materials and Designs”. Buildings, 2023, Vol. 13, 904. [CrossRef]
- Chen, B., C., Liu, Q., Chen, H., Wang, L., Deng, T., Zhang, L., Wu, X., “Multi objective optimization of building energy consumption based on BIM-DB and LSSVM-NSGA-II”, Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, Vol. 294, 126153. [CrossRef]
- Akhanova, G.; Nadeem, A.; Kim, J.R.; Azhar, S.; Khalfan, M., “Building Information Modeling Based Building Sustainability Assessment Framework for Kazakhstan”. Buildings, 2021, Vol. 11, 384. [CrossRef]
- Albdour, M.S.; Shalby, M.; Salah, A.A.; Alhomaidat, F., “Evaluating and Enhancing the Energy Efficiency of Representative Residential Buildings by Applying National and International Standards Using BIM”, Energies, 2022, Vol. 15, 7763. [CrossRef]
- González, J.; Soares, C.A.P.; Najjar, M.; Haddad, A.N. “BIM and BEM Methodologies Integration in Energy-Efficient Buildings Using Experimental Design”, Buildings, 2021, Vol. 11, 491. [CrossRef]
- Alotaibi, B.S.; Khan, S.A.; Abuhussain, M.A.; Al-Tamimi, N.; Elnaklah, R.; Kamal, M.A., “Life Cycle Assessment of Embodied Carbon and Strategies for Decarbonization of a High-Rise Residential Building”, Buildings, 2022, Vol. 12, 1203. [CrossRef]
- De-Graft Joe Opoku, D.G.J., Perera, S., Osei-Kyei, R., Rashidi, M., Bamdad, K., Famakinwa, T., “Digital twin for indoor condition monitoring in living labs: University library case study”, Automation in Construction, 2024, Vol. 157, 105188. [CrossRef]
- Gourlis, G., Kovacic, I., “A holistic digital twin simulation framework for industrial facilities: BIM-based data acquisition for building energy modeling”, Frontiers in Built Environment, 2022, Vol. 8. [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y., Chen, P., Shou, W., Sadick, A-M., “Digital Twin-driven approach to improving energy efficiency of indoor lighting based on computer vision and dynamic BIM”, Energy and Buildings, 2022, Vol. 270, 112271. [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Sutil, F., Cano-Ortega, A., “Smart regulation and efficiency energy system for street lighting with LoRa LPWAN”, Sustainable City and Society, 2021, Vol. 70, 102912. [CrossRef]
- Chiradeja, P., Yoomak, S., “Development of public lighting system with smart lighting control systems and internet of thing (IoT) technologies for smart city”, Energy Reports, 2023, Vol. 10, pp. 3355-3372. [CrossRef]
- Gehlot, A.; Alshamrani, S.S.; Singh, R.; Rashid, M.; Akram, S.V.; AlGhamdi, A.S.; Albogamy, F.R. “Internet of Things and Long-Range-Based Smart Lampposts for Illuminating Smart Cities”, Sustainability, 2021, Vol. 13, 6398. [CrossRef]
- Mataloto, B., Ferreira, J.C., Cruz, N., “LoBEMS—IoT for Building and Energy Management Systems”, Electronics, 2019, Vol. 8, Issue 7, 763. [CrossRef]
- Garlik, B. “Energy Centers in a Smart City as a Platform for the Application of Artificial Intelligence and the Internet of Things”, Applied Science, 2022, Vol.12, 3386. [CrossRef]
- Canada-Bago, J.; Fernandez-Prieto, J.-A. “A Knowledge-Based Battery Controller for IoT Devices”, Journal Senor and Actuator Networks, 2022, Vol. 11, 76. [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z., Li, Y., Huang, P., Abed, A.M., Ali, E., Elkamchouchi, D.H., Abbas, M., Zhang, G., “Analysis of the opportunities and costs of energy saving in lightning system of library buildings with the aid of building information modelling and Internet of things”, Fuel, 2023, Vol. 352, 128918,. [CrossRef]
- Zou, R., Yang, Q., Xing, J., Zhou, Q., Xie, L., Chen, Q., “Predicting the electric power consumption of office buildings based on dynamic and static hybrid data analysis”, Energy, 2024, Vol. 290, 130149. [CrossRef]
- D. Stevens, J.; Murray, D.; Diepeveen, D.; Toohey, D., “Adaptalight: An Inexpensive PAR Sensor System for Daylight Harvesting in a Micro Indoor Smart Hydroponic System”, Horticulturae, 2022, Vol. 8, 105. [CrossRef]
- Kim, W:, Cho, K., Lee, J-H., Ko, D-h., Jung, S., “An Indoor Light-Powered Sensor System Integrated with Organic Photovoltaics”, Advanced Materials Technologies, 2023, Vol. 8, Issue 12, 2202040. [CrossRef]
- Chekired, F.; Taabli, O.; Khellili, Z.M.; Tilmatine, A.; de Almeida, A.T.; Canale, L. “Near-Zero-Energy Building Management Based on Arduino Microcontroller—On-Site Lighting Management Application”. Energies, 2022, 15, 9064. [CrossRef]
- Kroll, E., Condoor, S.S., Jansson, D.G., “Innovative Conceptual Design: Theory and Application of Parameter Analysis”, Cambridge University Press, 2001.
Figure 1.
(a) The hallway of Union Station, Kansas City, MO, US. Photo of Chad Stembridge, sourced from Unsplash; (b) Multi-Sport Pavillion Center, Francisco de Vitoria University, Madrid (ES), Project of Architect Alberto Campo Baeza, 2017.
Figure 1.
(a) The hallway of Union Station, Kansas City, MO, US. Photo of Chad Stembridge, sourced from Unsplash; (b) Multi-Sport Pavillion Center, Francisco de Vitoria University, Madrid (ES), Project of Architect Alberto Campo Baeza, 2017.
Figure 2.
A 3D view of the nexus of BIM and smart buildings as shown in [
17].
Figure 2.
A 3D view of the nexus of BIM and smart buildings as shown in [
17].
Figure 4.
Picture showing the distribution of publications per year.
Figure 4.
Picture showing the distribution of publications per year.
Figure 5.
Picture showing the author´s country of origin.
Figure 5.
Picture showing the author´s country of origin.
Figure 6.
PRISMA flow diagram.
Figure 6.
PRISMA flow diagram.
Figure 7.
Network visualization carried out on VOSviewer, applied to 48 articles based on a keyword-based occurrence.
Figure 7.
Network visualization carried out on VOSviewer, applied to 48 articles based on a keyword-based occurrence.
Figure 8.
Some representatives-built projects with responsive kinetic facades. (a) Media-ICT, Barcelona (ES), Project of Enric Ruiz Geli, 2010. (b) University of Southern Denmark, campus Kolding, Kolding (DK), Project of Henning Larsen Architects, 2014. (c) Al Bahar Towers, Abu Dhabi (UAE), Project of Aedas Architects, 2012.
Figure 8.
Some representatives-built projects with responsive kinetic facades. (a) Media-ICT, Barcelona (ES), Project of Enric Ruiz Geli, 2010. (b) University of Southern Denmark, campus Kolding, Kolding (DK), Project of Henning Larsen Architects, 2014. (c) Al Bahar Towers, Abu Dhabi (UAE), Project of Aedas Architects, 2012.
Figure 9.
Some representatives-built projects with photovoltaic energy-generating facades. (a) Copenhagen International School, Copenhagen (DK), Project of C.F. Møller, 2017. (b) EWE & Bursagaz Headquarter, Bursa (TR), Project of Tago Architects, 2016. (c) Green Dot Animo Leadership High School, Los Angeles (USA), Project of Brooks + Scarpa Architects, 2013.
Figure 9.
Some representatives-built projects with photovoltaic energy-generating facades. (a) Copenhagen International School, Copenhagen (DK), Project of C.F. Møller, 2017. (b) EWE & Bursagaz Headquarter, Bursa (TR), Project of Tago Architects, 2016. (c) Green Dot Animo Leadership High School, Los Angeles (USA), Project of Brooks + Scarpa Architects, 2013.
Figure 11.
The proposed design framework.
Figure 11.
The proposed design framework.
Table 1.
Overview of the main keywords used.
Table 1.
Overview of the main keywords used.
| Keywords |
1st Topic |
2nd Topic |
3rd Topic |
Goal |
Target |
| |
Integrated
lighting |
BIM |
IOT |
Energy efficiency |
Buildings |
| |
Lighting & Daylighting |
BIM software |
Internet of
Things |
Low carbon emission |
Built environment |
| |
Integrated controls |
Building Information Modeling |
Cloud management |
Carbon footprint |
Building sector |
| |
Shading devices |
|
|
|
|
| |
Integrated lighting solutions |
|
|
|
|
Table 2.
Integrated daylighting solutions and their methodological approach, functions and relation with the building form.
Table 2.
Integrated daylighting solutions and their methodological approach, functions and relation with the building form.
Daylight guide
system |
Year |
Climate |
Methodological approach |
Function |
Destination |
Influential element |
Control Strategies |
Building scale |
| Daylight performance of Heritage Building [38] |
2023 |
Cwb |
CBDM for daylight analysis |
DP; SSD |
U |
sDA300,50% throughout the year; UDI300-2000 |
Revit; Int. Env. Sol. Virt. Env. (IESVE) |
WB |
| Approach for roof lighting system [39] |
2022 |
Dfb |
Parametric analysis |
DP; SSD |
TB |
Skylights and core lighting systems |
Climate Studio, Ladybug, Honeybee and Galapagos |
R |
| Prediction method for quantitative analysis [40] |
2023 |
Dwa |
Optimisation
design / parametric simulations |
DP; GP; SSD; HI |
TB |
Interpretable Machine Learning for daylight optimisation |
Grasshopper, Ladybug, Honeybee / Machine Learning |
WB |
| Three ways for integrated light approach [41] |
2022 |
BWh |
Functional morphological approach |
DP; EE; SSD; HI |
PB |
Integration of a photovoltaic (PV) / change of nanomaterials/integration of a passive illumination. |
Passive solar system, designed as a hollow compound parabolic
concentrator |
WB |
| Many-objective optimisation design for Daylighting and Performance [42] |
2020 |
Dwa |
Parametric simulations / Optimisation engine |
DP; EE; CP |
PB |
Artificial neural network (ANN) |
Development of an optimisation
design model |
WB |
Design optimisation of geometry and
fenestration [43] |
2019 |
Am & Dfa |
Building performance optimisation process / Genetic algorithm |
DP; EE |
OF |
Multi-objective optimisation |
Energy simulation / genetic input of Octopus |
WB |
| Building envelope optimisation [44] |
2021 |
Csa |
Integration of daylight and energy
Simulation; thermal comfort
|
DP; EE |
RB |
Multi-objective optimisation analysis |
Critical parameters in energy performance |
WB |
| Development of a Daylight Simulation [45] |
2021 |
BWh |
Raytrace algorithm analysis |
DP; |
RB |
Daylight simulation software named DaylightX |
User-friendly interface and flexibility in the design process |
WB |
| Lighting and Free-Cooling Retrofitting [46] |
2023 |
Cfa |
Comparative analysis |
T; EE; LC; CP |
CB |
Strategies for improving illumination quality and energy efficiency |
Strategies for improving illumination quality and energy efficiency |
WB |
| Integration process of design and simulation [47] |
2023 |
Aw |
Integrated design-simulation
process |
DP; EE |
MB |
Calculations on the building envelope’s peripheral zones |
Daylighting coeff. as per local standards and the WWR per general international standards |
WB |
| Intelligent automatization performances [48] |
2021 |
Dwa |
Parametric programming and interface program |
DP; EE |
OF |
NSGA-II algorithm / SOM clustering |
User-friendly framework to
automatize the whole energy-efficient design process |
WB |
| Validated versus New Parametric Design-Based Social Env. [49] |
2023 |
BWh |
Parametric simulations / Comparative case analysis |
T; EE |
RB |
Strategies to control energy consumption with a comparative analysis |
Ladybug, Honeybee, Daysim, Pufferfish, Lunchbox |
F |
| Integrated daylighting systems into [50] |
2020 |
BWh |
Energy calculations/generation of the dataset |
T; DP; EE; GP |
OF |
Exploration of different configurations to generate an extensive set |
The optimal set of integrations is formulated into a multi-level utilization guide |
F |
| Daylighting controls and performance of the concentrating photovoltaic [51] |
2022 |
Am; Csa; Dwa; Dfb; Dfb |
Ray-tracing simulation / Optimisation and implementation |
DP; LC |
|
Regulate the indoor daylighting environment/generating renewable
electricity |
lens-walled compound parabolic concentrator (LWCPC) |
R |
| Kinetic façade on the lighting and energy performance [52] |
2022 |
BWh |
Field measurements / parametric simulations/simulation tools |
T; DP; CP |
SPB |
Performance framework for
Kinetic facade |
Integrated Environmental Solutions (IES) |
F |
| Control strategies of perforated curved louvers [53] |
2019 |
Am; Csb; Dfb; BSk |
Integrated thermal and lighting simulations |
T; EE; CP; LC |
OF |
Evaluate the impact of
different control strategies to a shading device. |
Inc. irrad. / Vertical eye illuminance / cut-off angle / blocking controls |
F |
Different shading and lighting control
strategies [54] |
2023 |
|
Multi-step modeling process |
T; DP; LC |
OF |
Common baseline evaluation |
Integrated Control Strategy (ICS) |
F |
| Daylighting Performance of CdTe Semi-transparent Photovoltaic Skylights [55] |
2024 |
Dwa |
Dynamic daylighting simulation / parametric simulations |
T; DP; SSD; LC |
U |
Evaluation of Semi-transparent photovoltaic Skylight optimal range |
Dyn.daylighting performance metrics DA, DAcon, DAmax, and UDI |
R |
| 3D concentrating photovoltaic window [56] |
2022 |
Cwa |
Ray-tracing simulation |
DP; SSD; CP; HI |
|
Design of 3D CPVD module |
cDA, UDI, sDA; DGP |
F |
| Optimizing building design reducing energy consumption [57] |
2022 |
BSk |
Numerical simulations / Criterion-related validation study |
T; EE |
U |
Use of the concept of green
roof in addition to DSF |
Double Skin Façade (DSF) |
F |
| Multi-objective optimisation of complex [58] |
2021 |
Cfa |
Multi-objective optimisation methodology / parametric simulations |
DP; SSD |
OF |
Multi-objective optimisation
analysis and multi-scenario |
Complex Fenestration System (CFS) |
F |
| Façade Models Related to Optimizing Daylight Distribution [59] |
2023 |
Aw |
Quantitative analysis/field measurements |
DP; SSD; VCE |
SPB |
Simulated data into a statistical program |
Radiance Illuminance Program |
F |
| Façade with integrated microstructures for daylight redirection [60] |
2022 |
Cfb |
Manufacturing methods for mass production |
DP; SSD; EE |
TR |
Optical raytracing simulation to design microstructures |
Microstructured system |
F |
Table 3.
Building Information Modeling strategies to achieve energy efficiency and their methodological approach, functions, certification assessments and use in relation with the building variables/forms.
Table 3.
Building Information Modeling strategies to achieve energy efficiency and their methodological approach, functions, certification assessments and use in relation with the building variables/forms.
| BIM Application |
Year |
Climate |
Methodological
approach |
Certification
Assessment |
Function |
Destination |
BIM use |
Assessment
method |
Building variables |
Building scale |
| Assessing Sustainability in Buildings using GPRS [61] |
2023 |
Bwh |
Quantitative calculations / comprehensive analysis for decision-making |
Green Pyramid Rating System |
EE; M; CP |
OF |
Interoperability design decisions/guides determination of building aspects |
Dynamo / Autodesk Revit / plug-ins using Revit API |
Level of details development (LOD) / life cycle assessment (LCA) |
WB |
| Retrofitting an existing building to a NZEB [62] |
2023 |
Cwa |
Manually cataloguing appliances/analysis of the building's CO2 emissions |
LEED rating tool |
T; EE; M; CP |
U |
Retrofitting to
NZEB |
Autodesk Revit / Helioscope tool |
SDGs 7 & 13 |
WB |
| BIM-Based Energy Analysis [63] |
2021 |
Csb |
Comparative analysis case |
Building Sustainability
Assessment method - SBToolPT-H |
T; EE; M |
RB |
BEM to analyze different design alternatives and improve building performances |
Autodesk Revit / Cypetherm REH |
P7 and P8 of SBToolPT-H |
WB |
| BIM-Parametric Workflow-Based Analysis of Daylight Improvement [64] |
2019 |
Dwa |
Parametric environmental analysis tools/energy and daylight simulations |
International standards |
DP; EE; VC |
RB |
Renovation of aged apartment buildings, focusing on daylight improvement |
Autodesk Revit / Ladybug and Honeybee / THERM 7.5 / WINODW 7.6 |
Removal of buffer zones/improv. of WWR / installation of window with higher g-values |
WB |
| BIM assessment of NZEB [65] |
2019 |
Cwa |
BIM combined with Building Performance Analysis (BPA) tools |
LEED rating tool |
T; M; EE; CP |
MB |
Support the design of zero-energy buildings |
Autodesk Revit /
in-built Energy analysis tools |
Ensuring high energy efficiency / integrating suitable renewable energy systems |
WB |
| Parametric BIM-Based Lifecycle Performance Prediction [66] |
2023 |
Cwa |
Parametric modeling / BIM-based framework / Life cycle assessment (LCA) |
Automated EC calculator/carbon assessment tool “CIC” |
T; EE; CP |
RB |
BIM-based lifecycle energy simulation
to predict carbon emissions |
Autodesk Revit |
Structural layout / Spatial Planning / Building usage pattern |
WB |
| BIM-DB and LSSVM-NSGA-II [67] |
2021 |
Cfa |
BIM / Least square support vector machine (LSSVM) / non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm-II (NSGA-II) |
Code for Thermal Design of Civil Buildings (GB50176-2016) |
T; EE |
U |
Minimizing BEC and maximizing indoor thermal comfort |
Autodesk Revit / Energy Plus |
Six building envelope parameters / WWR |
WB |
| BIM Sustainability Assessment Framework [68] |
2021 |
|
BIM-based BSAS
/ Delphi study approach |
BREEAM / LEED |
DP; EE; LC |
CB |
Conceptual framework for building sustainability
assessment |
Autodesk Revit / Daysim |
Nine assessment categories and 46 assessment indicators |
WB |
| Evaluating and Enhancing the Energy [69] |
2021 |
BSh |
Survey-based methodology |
ANSI/ASHRAE/IES Standard 90.1-2016 |
T; DP; M; EE |
RB |
BIM to apply national and international energy standards |
Autodesk Revit / Energy Plus |
building envelope / HVAC, daylight/lighting/water heating/plug load systems |
WB |
BIM and BEM
Methodologies [70] |
2021 |
Aw / CSa / BWh / Cfa |
Experimental Design / BIM and BEM / statistical analysis |
ISO 7730 / EN 15251 / ASHRAE 55-20 |
T; LC; EE |
RB |
Simulate facilities’ energy loads |
Autodesk Revit & Insight 360 / Green Building Studio |
Lighting efficiency / Plug-Load Efficiency / HVAC |
WB |
| LCA for Decarbonization [71] |
2022 |
|
Life cycle assessment (LCA) |
ISO-14040, 2006 / EN 15978 |
T; M; EE |
RB |
BIM to assess LCA and to
compare decarbonization |
Autodesk Revit |
Construction /
Operation / Demolition |
WB |
| Digital twin for indoor condition monitoring [72] |
2023 |
Cfb |
BIM visualization data / IoT
live data capture platform |
LEED V4 / ASHRAE 55 / 62 |
T; EE; RTDC; LC; DT |
U |
Develop DT of the library building / enhancing the
livability |
Autodesk Revit / LoRa end devices (sensors) |
Occupants-building interactions/sensors |
WB |
| BIM-based data acquisition [73] |
2022 |
Cfb |
Comparative analysis case / holistic modeling and simulation framework, |
|
T; EE; DT |
SPB |
Create and parametrize the
building-related part in the hybrid simulation environment |
Autodesk Revit / Dynamo / MATLAB |
State variables which refer to dynamic values, collected by sensors |
WB |
| Digital Twin driven approach with BIM [74] |
2022 |
Cfa |
Visualized operation and maintenance (VO&M) platform / DTL system based on dynamic BIM |
|
EE; LC; DT |
OF |
Complete multi-disciplinary, multi-physical, multi-scale, and multi-probability simulation |
Revit / YOLOv4 |
Surveillance system/video detections/lighting control system |
WB |
Table 4.
Internet of Things strategies applied on a variety of uses and their categorization of variables been adopted, such as type of network and intelligent device, functions, application and objective in the IoT and their advantages.
Table 4.
Internet of Things strategies applied on a variety of uses and their categorization of variables been adopted, such as type of network and intelligent device, functions, application and objective in the IoT and their advantages.
| IoT solution |
Year |
Type of Network |
Intelligent device |
Technology |
Function |
Application |
Characteristics |
The objective of IoT technology |
Advantages |
| Street lighting with LoRa LPWAN [75] |
2021 |
LoRa LPWAN network |
Gateway for Street Lights System (GWSLS) / Illumination Level Device (ILD) |
Operating and Monitoring Device for Street Lights (OMDSL) |
Design of a
measurement
and control system for public lighting |
Control, monitoring and energy-saving system for SLs |
The system adapts to different types of
lamps / can be configured with monitoring times |
Analyse the possibility of reducing electrical energy consumption |
Artificial Bee Colony
(ABC) which is fast, reliable and accurate |
| Public lighting systems with smart lighting control systems [76] |
2023 |
Mobile application via the Internet
communication network |
Controller based on light intensity and motion sensors |
The incorporated IoT technologies were also linked to the Blynk platform |
Design and development of public light systems integrated with the Internet of Things (IoT) |
Additional functionalities: Air quality detection and a security system with an IP camera are incorporated |
Designed to operate in three modes:
manual, scheduled, and auto modes |
Offer attractive roles for pollution detection/safety improvements using IP camera |
Higher pole spacing is recommended for
investment costs and energy savings |
| Long-Range-Based Smart Lampposts [77] |
2021 |
LoRa integrated with a Wi-Fi module |
Arduino UNO / LDR sensor / PIR sensor |
IoT-assisted Fog and edge node-based architecture |
A push-to-talk system, charging port infrastructure, Wi-Fi mobile and mesh. |
Enables to illuminate the light according to the light intensity that is around the lamppost |
Streetlights switch on at a particular dimming level as per the time scenario |
The flexibility of implementing a multitude of applications on a single system
|
Integration of advanced sensing-communication protocols / establish a smart infrastructure in smart cities |
| LoBEMS—IoT for BEMS [78] |
2019 |
LoRa/LoRAWAN |
4 different types of sensors |
Remote interaction with local A/C |
Helps local administration to identify savings |
Optimizing energy consumption / deploying an energy management system |
Novel MDA approach that provides automatic visualizations |
Management of energy systems using the current IoT |
The system provided, both student's and employees' sense of comfort has increased |
| AI and IoT for Smart cities [79] |
2022 |
ABB-free@home |
KNX/FOXTROT |
BEM integration with IoT |
Create conditions for reducing energy consumption |
Use of BEM along with an automated building control system |
Fulfil reference values of EPB (Energy Performance of Building) |
Definition of a smart grid, that relies on ICT and digital networks to collect data |
Build real consumption models to optimize the grid state in real-time |
| A Knowledge-Based Battery Controller for IoT Devices [80] |
2022 |
Wireless communication network / HTTP protocol |
Based on Arduino Micro / Arduino Nano 33IoT |
Allowed powering of both other components of the IoT application and IoT device |
Design and implement a battery controller integrated into a constrained resource |
Controls & monitors the PV system and executes other IoT applications |
Battery controller powering IoT device and other components |
Monitor and analyse the variables of IoT devices in near real-time |
The proposed controller achieved better performance than others |
| Costs of energy saving in lighting system [81] |
2023 |
Layer-by-layer breakdown of the Zigbee protocol |
PIR sensor / Daylight sensors / Micro-Doppler
occupancy sensors |
Distributed wireless sensor networks (WSN) |
Implementing a smart illumination technique |
The circuit design of an energy-saving system using IoT and BIM |
Integration of distributed Wi-Fi sensor networks and techniques with IoT and BIM approaches |
Intelligently manage the brightness in
response to changes in the surrounding environment |
BIM, and IoT-based systems to improve the effectiveness of services |
| Predicting the electric power consumption [82] |
2024 |
Improved TCN for parallel outputting data
samples |
D&S-HDA framework |
Dynamic and static hybrid data analysis |
Provide solutions with better prediction accuracy |
Accurately predicting building electricity consumption |
Time-by-hour basis, static data of BIM are used for analysis |
Building hourly power
consumption coefficient (BHPCC) |
TCN: longer memory / parallel convolutional layers / flexible convolution kernels / |
| A PAR Sensor System for Daylight Harvesting [83] |
2022 |
RPi that is running Raspberry Pi
OS and Node-RED |
AS7265x IoT sensor to measure PAR |
Micro Indoor Smart Hydroponics (MISH) |
Harvesting ambient light |
Flood and drain hydroponic technique |
Adaptalight MISH-O system, using inexpensive IoT sensors for measuring PAR |
Measuring PAR in MISH systems |
Reduce power consumption and costs |
| Light-Powered Sensor OPV [84] |
2023 |
Embedded device (myRIO-1900) |
OPV modules and a voltage-boost converter |
DC-DC converter |
Self-sustaining power source for sensors under low-intensity illumination |
IoT-based devices installed in homes |
Real-time temperature measurements |
Self-powered sensor
platform that can be used in smart home |
OPVs can absorb
energy within the visible-light range |
Near-Zero-Energy Building Management
[85] |
2022 |
Local
network or the internet |
Home Energy Management System (HEMS) device |
Solar Equipment Development Unit (UDES) |
Reducing energy consumption and achieving self-sufficiency |
Smart lighting system via a complete algorithm |
Can be managed and controlled remotely in real-time |
Provide comfort to the user / energy-saving |
Create a financially
accessible smart home
system |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).