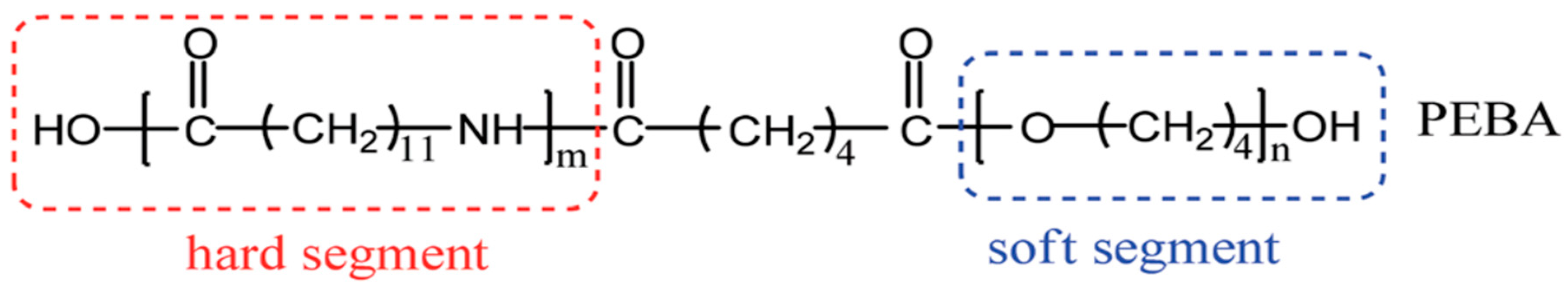4. Conclusion
A series of studies were conducted to offer comprehensive insights into the effects of addition of inorganic fillers on the processing and material properties of Polyether block amide (PEBA). BaSO4 and BiOCl were selected as the fillers of choice as they have garnered wide use in the manufacture of medical tubing, praised for their excellent x-ray contrast properties. The investigation looked closely at the effects of addition level of these inorganic fillers on PEBA, as PEBA is a widely used polymer in the development of cardiovascular tubing. Pebax® 6333 SA01 MED is of particular interest, as this material is commonly used for various types of medical devices, possessing many desirable characteristics required for medical tubing. The investigations carried out encompassed twin screw extrusion and injection moulding processing, as well as mechanical, rheological, thermal, density and ash content analysis of the various composites.
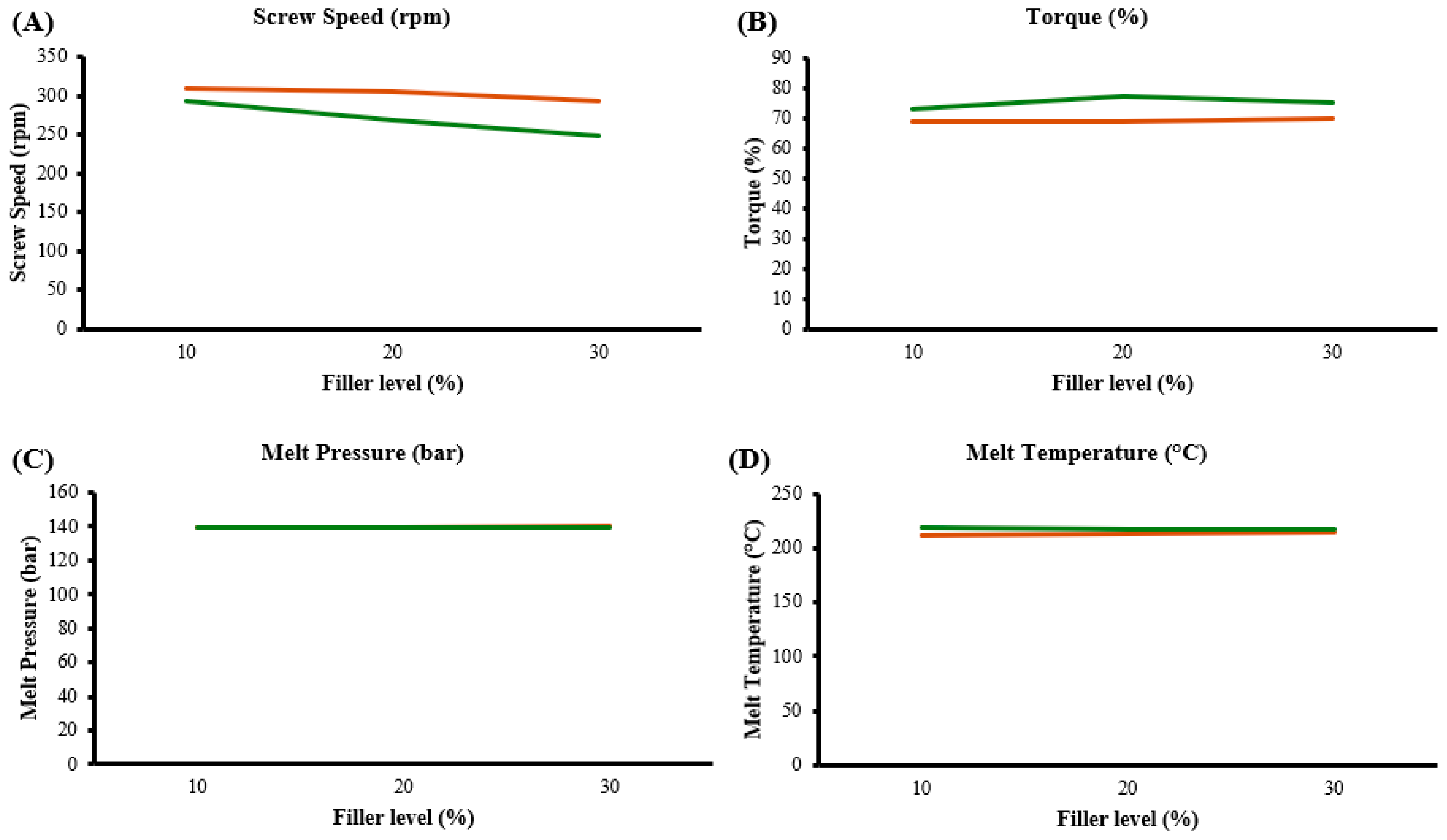
During the extrusion trials, the impact of the filler type and concentration on processing parameters such as screw speed, torque, melt pressure and temperature were studied. It was observed that higher filler levels, particularly in the case of BiOCl, led to an increase in torque, necessitating a reduction in screw speed to maintain stable processing conditions. The higher torque requirement for PEBA/BiOCl composites indicated a greater mechanical demand during processing to achieve adequate mixing and dispersion of filler throughout the polymer when compared to BaSO4. Interestingly, the melt temperatures for PEBA/BiOCl composites were consistently higher than those for PEBA/BaSO4 composites, likely due to the higher thermal conductivity of BiOCl, which, leads to more heat absorption by the composite. The appearance of the extruded material, namely colour and opacity, varied depending on the filler and the addition level. The BiOCl composites displayed a greater degree of opaqueness, with greater whiteness, while the BaSO4 appeared to have less opacity, with a creamy tint to the colour. These findings on the extrusion of composites highlight that, while BaSO4 ensure consistent processing with minor adjustments, BiOCl, although requiring parameter adjustments for consistency, delivers superior aesthetic properties.
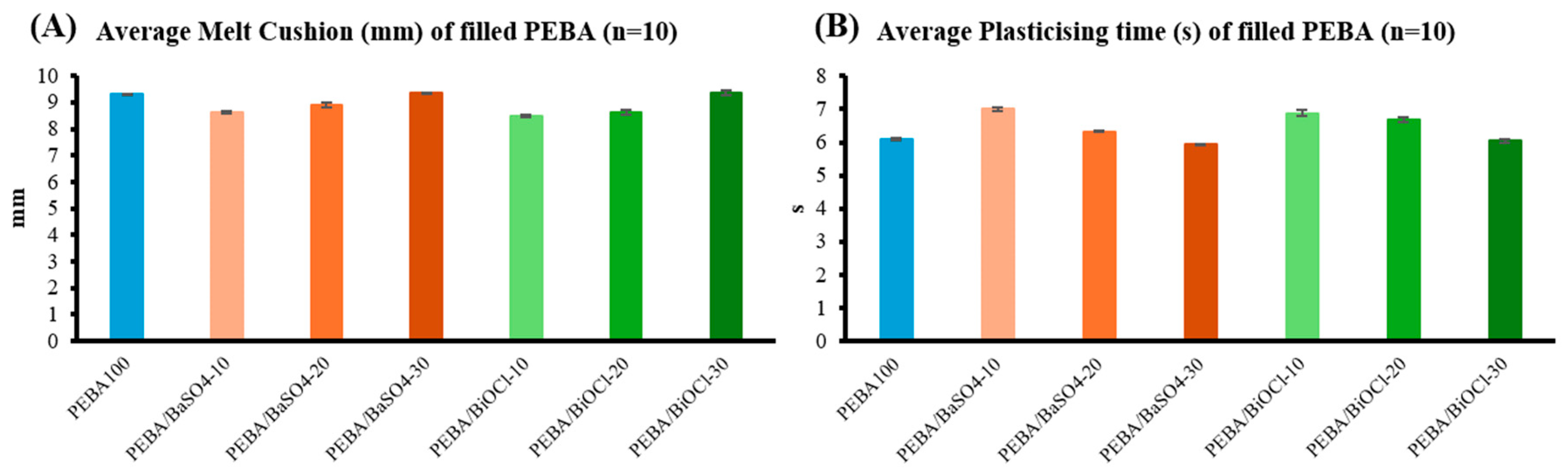
The injection moulding trials gave an insight into the behaviour of the composites when moulded. It was established that with an increase in filler level for both composites, there was a clear increase in melt cushion and a decrease in plasticising time during production. These phenomena may be as a result of the changing viscosity and density of the composites due to the additional heat history of the composites in extrusion and the incorporation of inorganic filler at various loadings. With the various polymer composites exposed to shear in the compounding process, this led to a reduction in the viscosity of the various resins as seen from the melt flow analysis. It was found that as the filler level increased, the viscosity reduced, which provides merit to the reduction in molecular weight theory that would affect the melt cushion and plasticising time as discussed previously. The consistency throughout the processes depicts excellent dispersion and addition of filler in the respective composites, suggesting that both BaSO4 and BiOCl fillers, despite their impact on the processing parameters, can be effectively integrated into the injection moulding processes with predictable results.
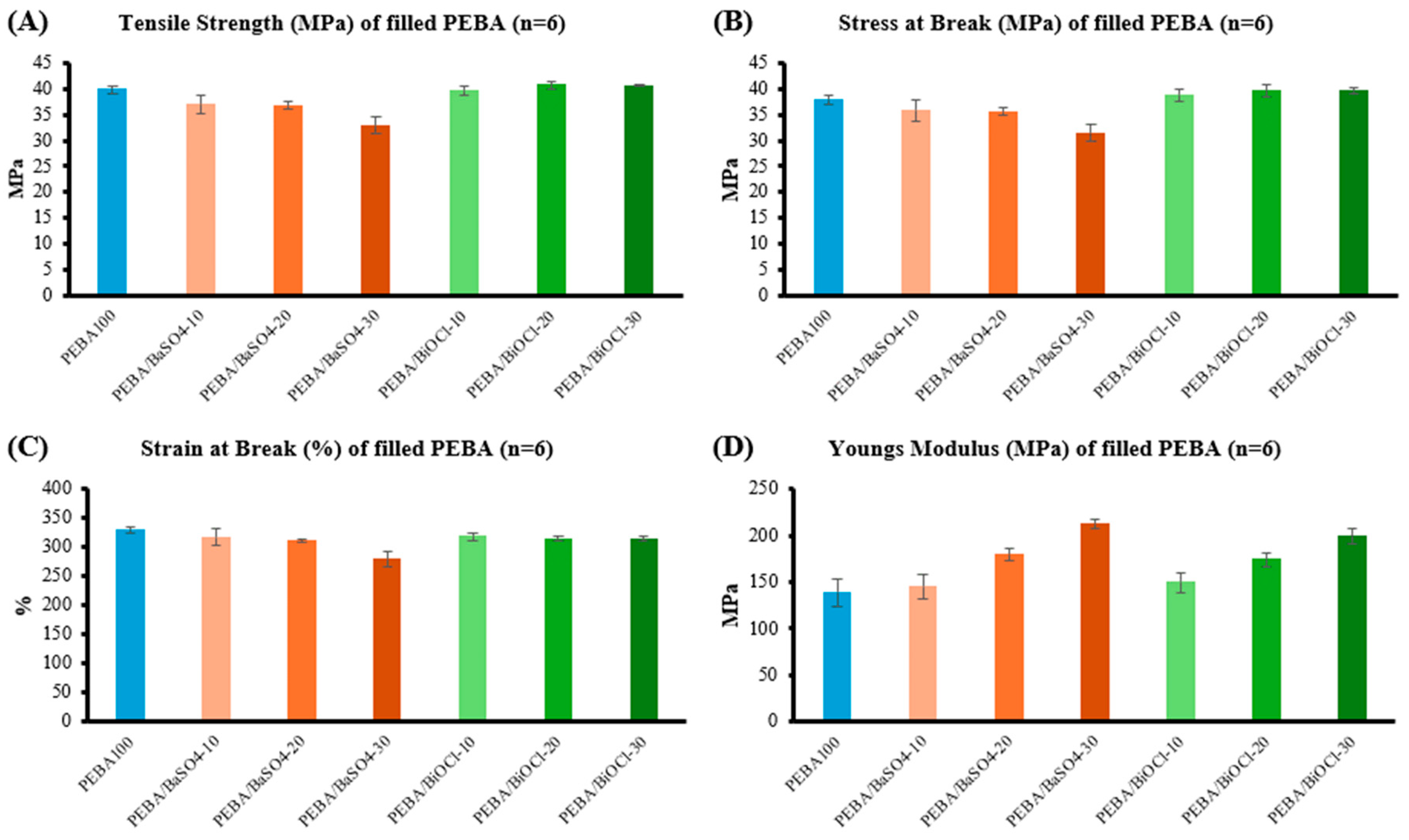
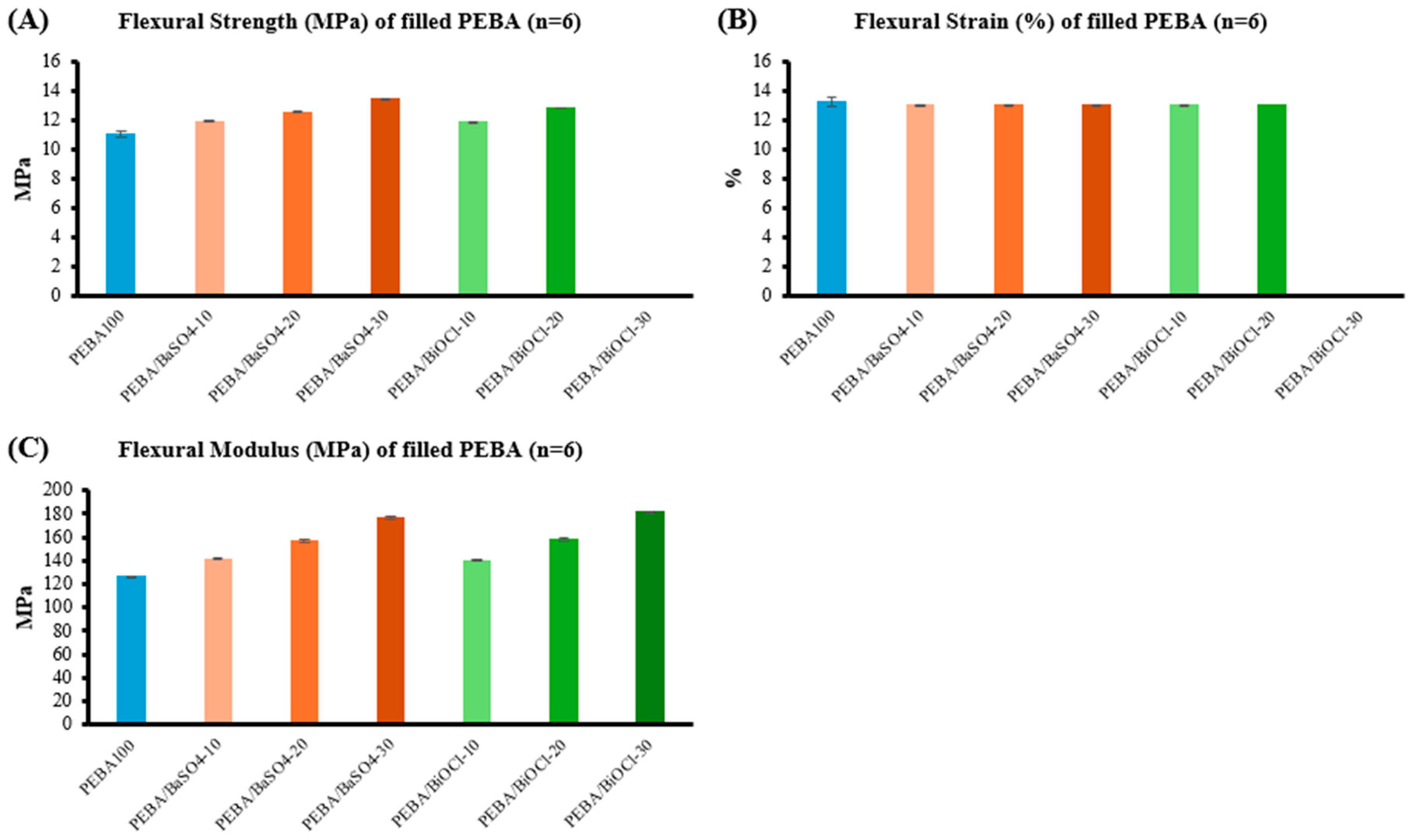
The tensile properties of the PEBA composites were significantly influenced by the type and loading of fillers. Both fillers led to a reduction in tensile strength, with BaSO4 showing a more pronounced decrease, especially at higher loading levels. This reduction in strength is attributed to a combination of higher volumetric content of BaSO4, which likely increases the brittleness of the composite, and chain scission as a result of shear which occurs in both the extrusion and injection moulding process. In contrast, the PEBA/BiOCl composites retained tensile properties close to those of the unfilled PEBA, indicating less of a detrimental impact from the addition of filler, in part, due to the lower volumetric addition rate. It was, however, observed that the incorporation of both respective fillers led to an increase in the stiffness of the composites (Young’s modulus). The BaSO4 displayed a more substantial increase in stiffness, which is likely due to the large volume of filler in the composite in comparison to BiOCl. The flexural behaviour of the composites mirrored the trends observed during tensile testing, with both fillers enhancing the stiffness of the material as evidenced by increased flexural strength and modulus. Notably, the PEBA/BiOCl composites exhibited slightly higher flexural moduli at higher loadings when compared to the PEBA/BaSO4 composite of same loading, suggesting greater stiffness. Despite the increased stiffness of the composites, they largely retain their flexibility, indicating that the addition of filler did not extensively compromise the materials ability to deform under bending loads. This retention of flexibility, despite filler addition, is particularly valuable in medical tubing applications, where both stiffness and flexibility are required.
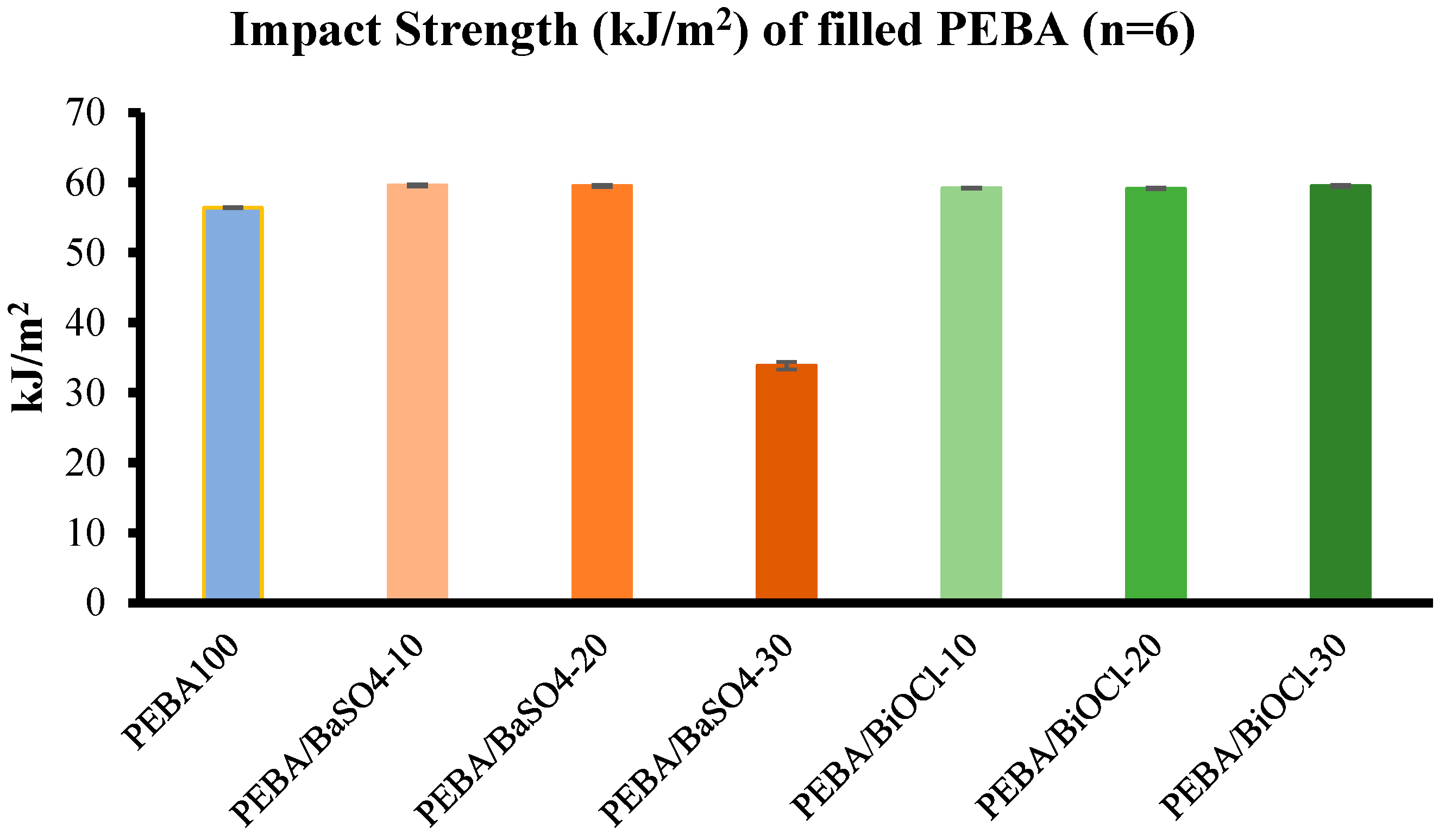
The impact strengths of the composites were not significantly enhanced with the addition of inorganic fillers at various loading levels, with an overall improvement of impact strength for all composites (apart from PEBA/BaSO4-30) ranging from 4.7 % to 5.33 %, with no breakage, in comparison to PEBA100. However, at the highest addition level of BaSO4, there was a significant reduction in impact strength, resulting in breakage of the samples. This reduction in impact strength, and breakage of samples, was likely due to the brittleness imparted into the composite due to the excessive loading of BaSO4 filler by volume. The excessive loading would likely lead to poor particle-matrix interaction, causing stress concentration in these areas of poor interfacial adhesion. The PEBA/BiOCl composites maintained consistent impact strength across all filler loadings, suggesting that the BiOCl composites do not reach the same critical brittleness threshold as the PEBA/BaSO4-30. The ability of the PEBA/BiOCl composites to retain toughness at the higher filler loadings make BiOCl filled composites a more suitable choice for applications that require greater radiopacity, while not compromising the rigidity and impact resistance of the composite. A key observation made was the effects of the compounding process on the mechanicals and thermal properties of the composites. The dynamic mechanical properties of amorphous polymers can be changed by the thermal history of the sample, but the effects are generally much less prominent that with the crystalline polymers (Nielsen, 1974). The evaluation of the rheological properties of the various composites, while not as straight forward as expected, was important to analyse the effects of filler loading and the shear from twin screw extrusion. It was initially expected that the incorporation of filler at high loading levels would lead to an increase in viscosity, reduction in melt flow. This, however, was not the case.
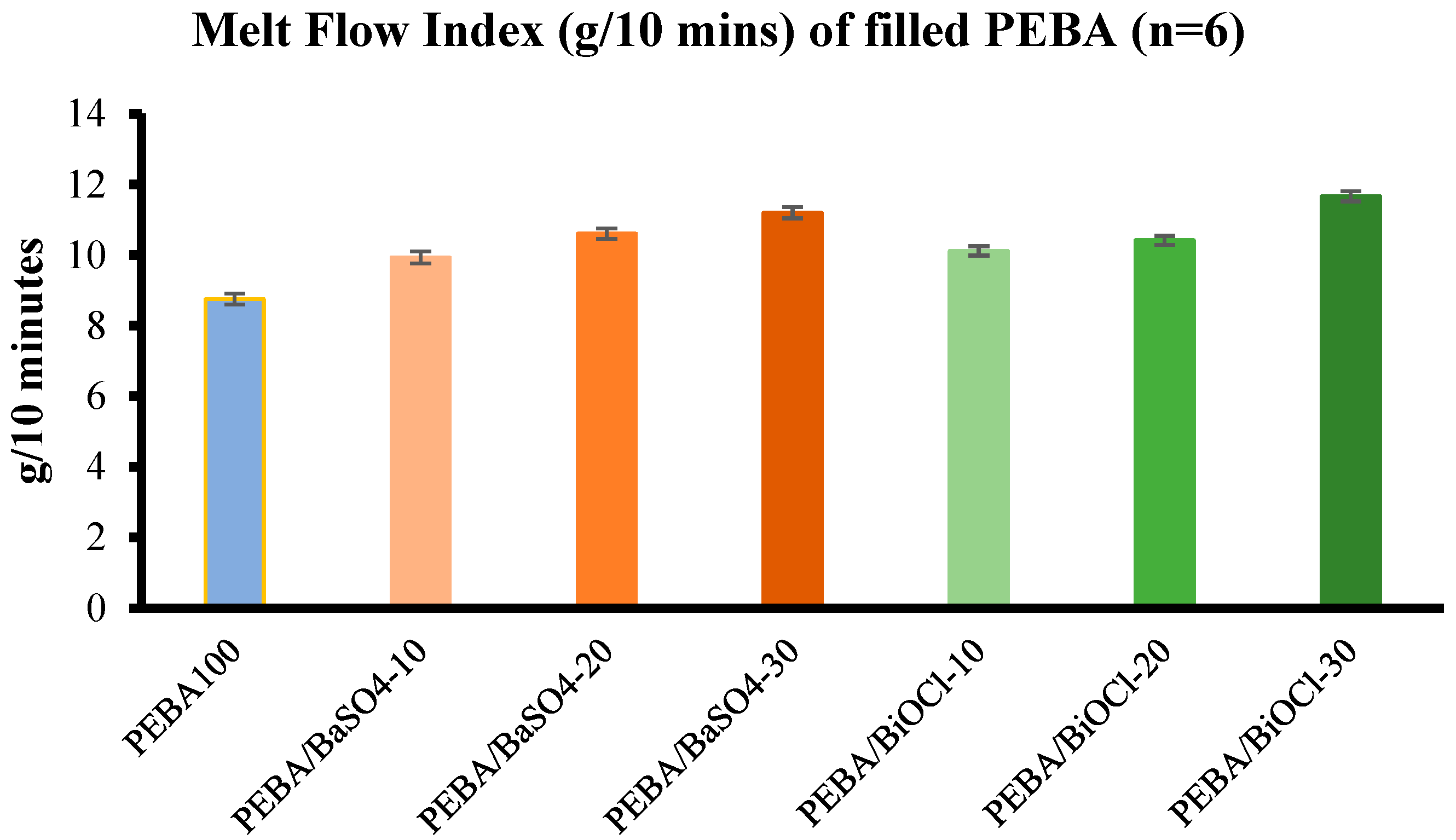
The MFI analysis revealed that as the filler level increased in the composites, the melt flow also increased across all composites. While this enhanced flowability is advantageous for processing methods such as injection moulding and extrusion, the findings challenged the conventional expectations that fillers increase viscosity. Instead of the conventional theories, it highlighted the complex interplay between filler content, shear forces during processing, and the resultant molecular weight reduction, which collectively influence the melt flow characteristics. This increased melt flow indicated that these composites of various filler loadings could be processed more efficiently, however, it would be important to avoid excessive shear during processing, as this does in fact lead to a reduction in the mechanical properties of the composite.
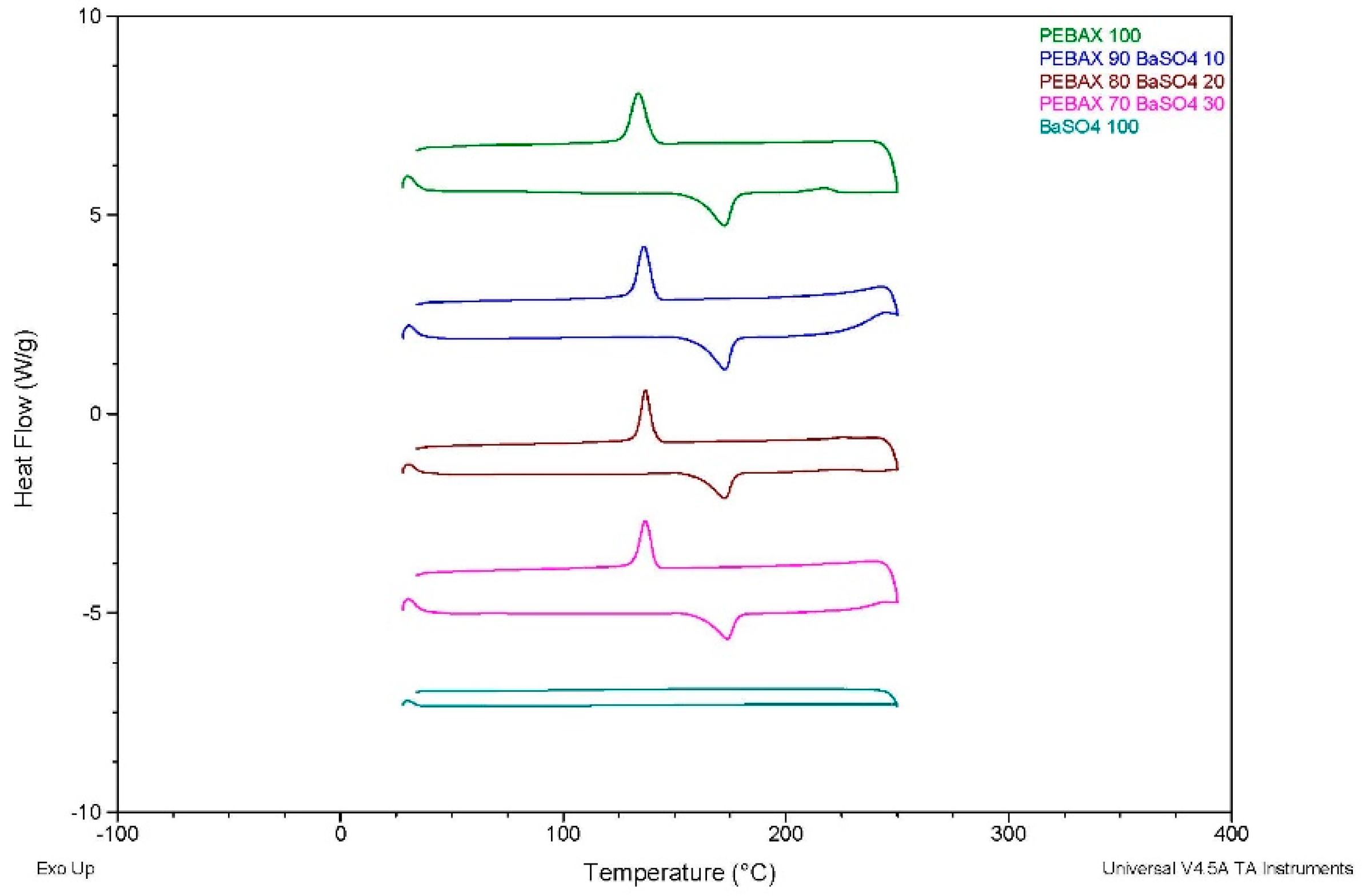
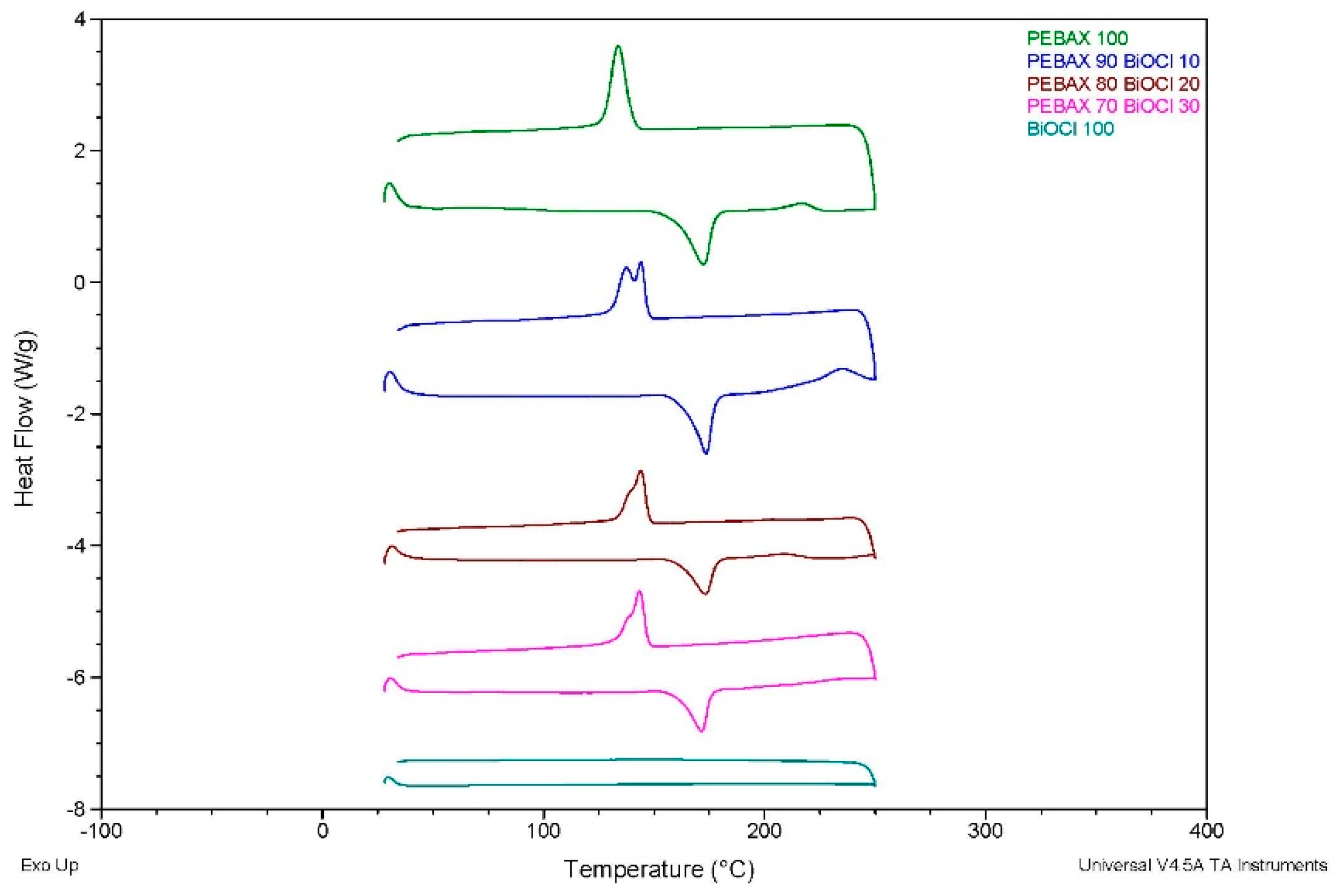
The DSC offered valuable insights into the thermal behaviour of the various composites. It was established that the addition of inorganic filler significantly affected the crystallinity of the PEBA composites, with the incorporation of BiOCl into the polymer resulting in a greater reduction in crystallinity when compared to the PEBA/BaSO4 of the same filler content. Despite this reduction, the melting temperatures remained largely unchanged, indicating that the fillers do not significantly alter the thermal stability of the PEBA matrix. The reduction in crystallinity suggests that these composites may experience less shrinkage during processing, which could have its advantages in applications requiring dimensional stability.
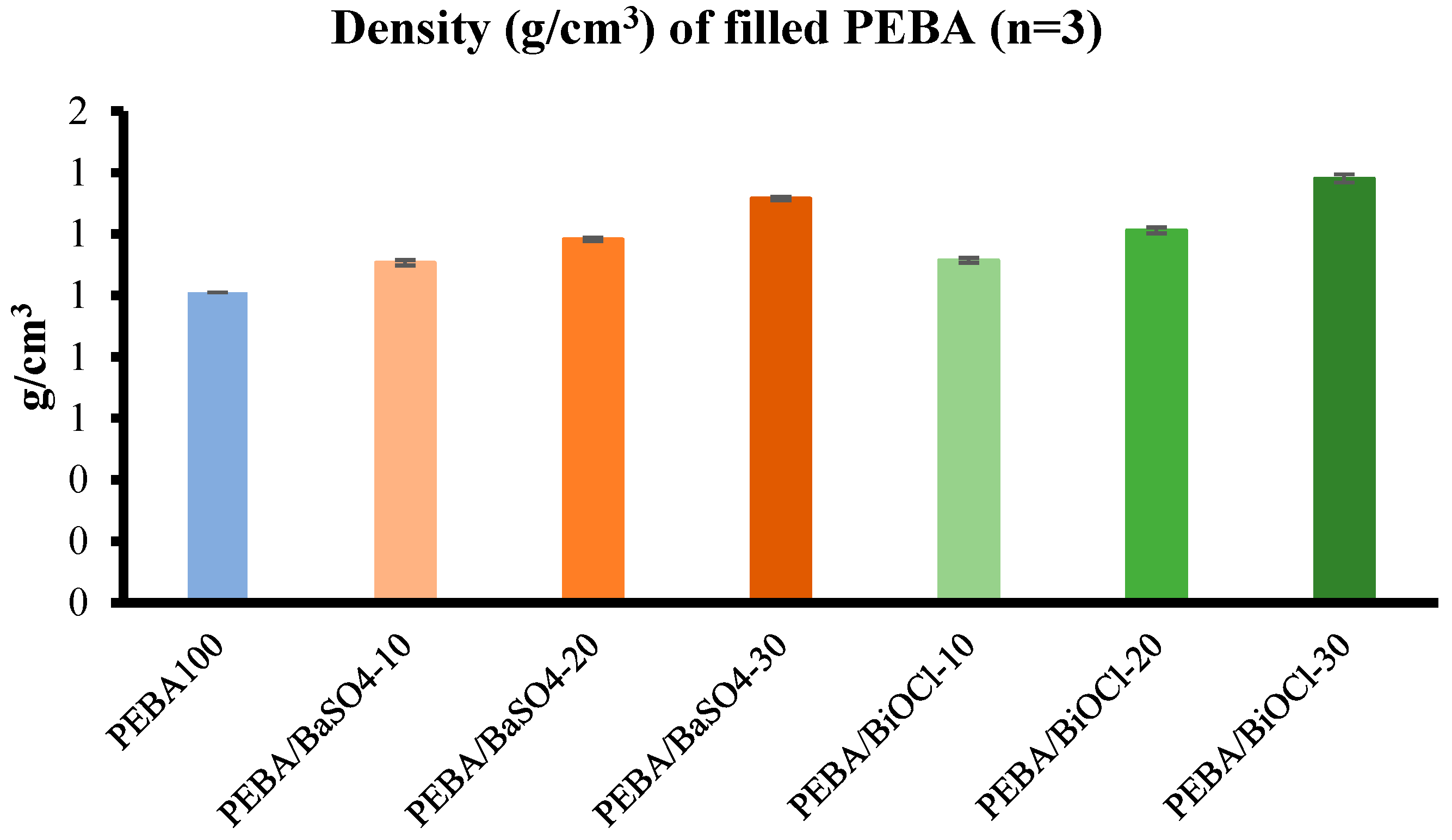
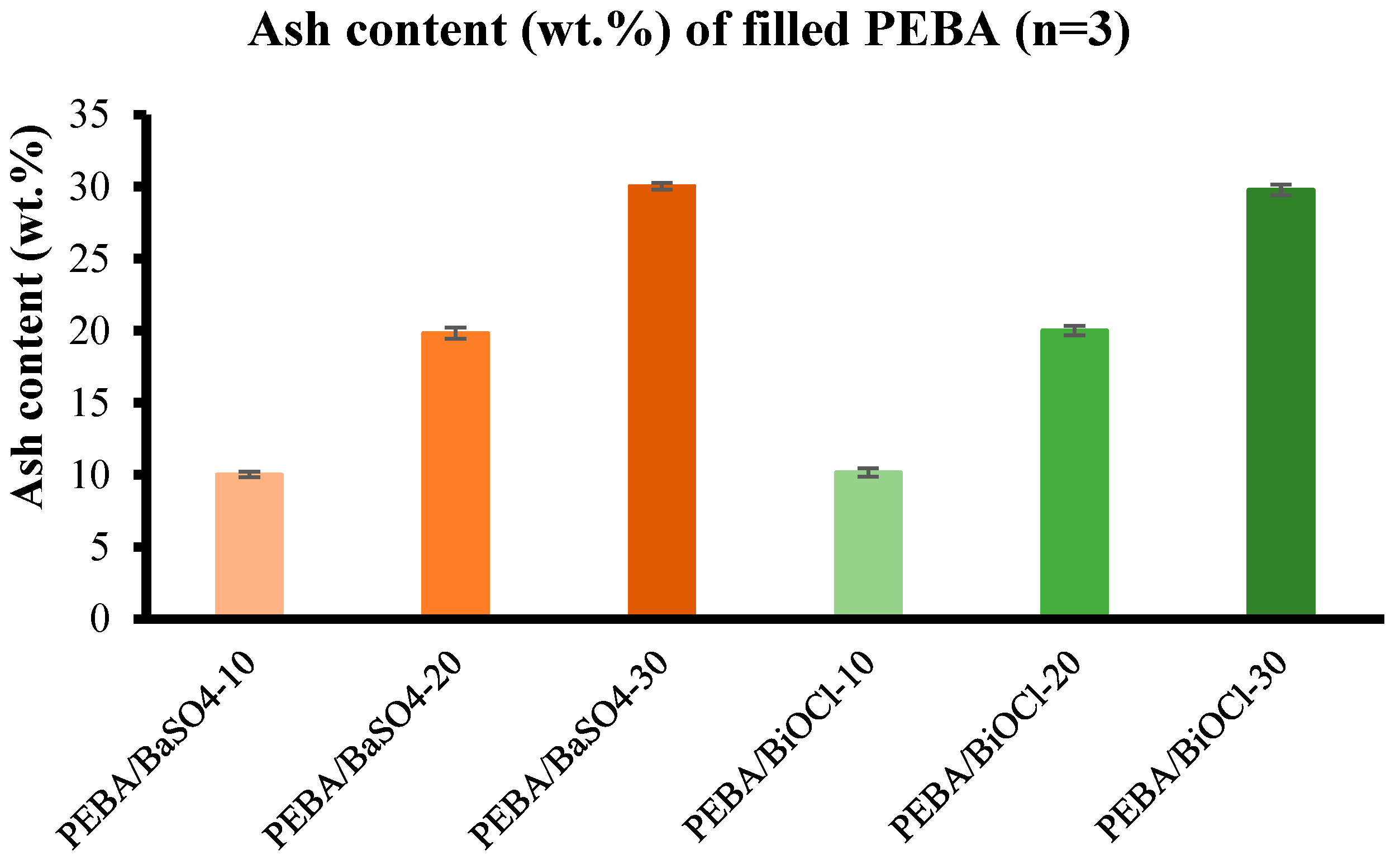
Density analysis was conducted to evaluate the actual practical density of the various composites, while also evaluating the actual filler content by means of ash content testing. It was established through ash content testing, that the compounding process was very accurate, with an average tolerance of 0.66 %. The incorporation of fillers led to a significant increase in the density of the respective composites, with the PEBA/BiOCl composites resulting in greater densities in comparison to the PEBA/BaSO4 at equivalent loadings. Evaluation of these composite densities is crucial for understanding the behaviour of the composite during processing and for design of medical tubing, where the weight of a component is critical in specific applications. These are considerations that must be made when evaluating a particular inorganic filler for composites, where the balance between density, mechanical strength, processability and radiopacity are critical. In conclusion, this study provides a detailed understanding of how inorganic fillers such as BaSO4 and BiOCl, and additional thermal history from compounding affect the processing, mechanical, thermal, and rheological properties of a PEBA composite.
While both fillers offer their respective benefits, it was observed throughout the study that with the incorporation of BiOCl at the various filler loadings, there were generally more balanced enhancement of properties with less adverse effects on the mechanical properties such as tensile strength, flexibility and impact resistance. The findings of this study emphasise the important of optimising the filler concentration, irrespective of the chosen filler, along with the processing conditions to achieve a desired polymer composite for specific applications. Particularly in the medical field, where precision and performance are paramount.