1. Introduction
Human Papillomavirus (HPV) infection is recognized as a significant etiological factor in developing various cancers. HPV-related malignancies constitute a distinct subgroup of epithelial carcinomas, commonly manifesting in anatomical sites such as the cervix, anogenital regions, and the head and neck (H&N) area [
1,
2]. Epidemiological data indicate that the prevalence of HPV-associated cervical cancer reaches 86%, while approximately 28% of head and neck cancers are attributable to HPV infection [
3]. Recent advancements have led to the development of salivary-based assays for detecting HPV-related oral cancer [
4]. Moreover, the established biological linkage between HPV and carcinogenesis has facilitated the development of prophylactic vaccines [
5] and the enhancement of therapeutic strategies, including novel immunotherapies [
6]. Reflecting the prognostic significance of HPV-driven carcinogenesis, the revised 8th edition of the UICC/AJCC cancer staging system now stratifies oropharyngeal cancer patients based on HPV status, distinguishing between HPV-positive and HPV-negative cases [
7]. Notably, HPV-positive tumors often exhibit increased radiosensitivity, which is potentially linked to the retention of wild-type p53 during the oncogenic process [
8]. Consequently, HPV-related tumors demonstrate improved outcomes following postoperative radiotherapy in patients with oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma (OPSCC) [
9].
The molecular mechanisms underlying HPV-driven carcinogenesis are well-documented. Recognizing the potential of HPV-related biomarkers, we propose that both E6/E7 oncoproteins and anti-E6/E7 antibodies could serve as reliable saliva-based biomarkers for simultaneous detection. The E6 oncoprotein plays a pivotal role in malignant transformation, primarily through the degradation of p53 and the functional inactivation of the Rb protein by the E7 oncoprotein [
10]. The expression of E6 oncoprotein increases progressively from precancerous lesions to malignant cells, underscoring its role in HPV-induced carcinogenesis [
11]. Consequently, E6/E7 oncoproteins have been identified as ideal targets for detecting and diagnosing HPV-related cancers [
12,
13]. Given the crucial role of HPV 16-derived oncoproteins in oncogenesis, it has been suggested that detecting E6/E7 oncoproteins may be more informative than HPV DNA detection, as oncoproteins provide direct evidence of HPV-driven carcinogenesis [
10,
12,
14,
15].
Supporting this view, research by Holzinger et al. has shown that seropositivity for anti-HPV antibodies is a reliable diagnostic marker for HPV 16-related head and neck cancers, demonstrating superior sensitivity and specificity compared to traditional diagnostic methods [
16,
17]. Several case-controlled studies have corroborated these findings, showing elevated levels of antibodies against E6/E7 in both serum [
18,
19,
20,
21] and oral rinse fluid [
22] of patients with cervical and OPSCC [
23]. These studies collectively indicate that higher antibody titers against E6/E7 in serum or saliva are associated with improved treatment outcomes, thereby positioning anti-HPV antibodies as valuable biomarkers for diagnosis and prognostication in head and neck cancer patients.
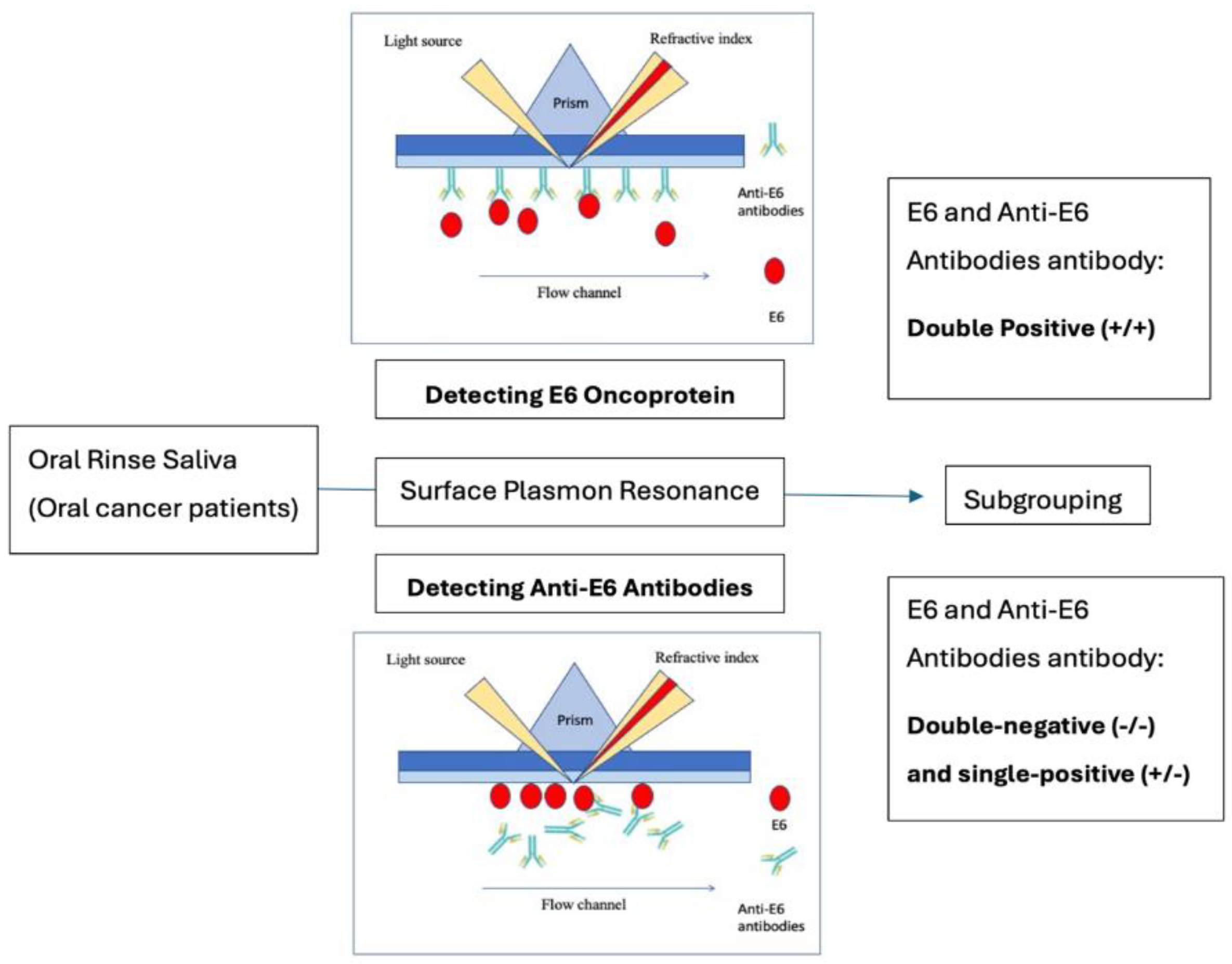
We hypothesize that dual positivity for these antigenic and antibody biomarkers may enhance the accuracy of HPV-related cancer diagnosis and offer complementary prognostic value. To test this hypothesis, we explored the feasibility of using a dual-panel biomarker approach in oral cancer patients. In this study, we employed surface plasmon resonance (SPR) technology to detect these biomarkers in saliva oral rinses using immune-based biosensor technology (
Figure 1).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects and Collection of Oral Rinse Saliva
This study used oral rinse samples from 13 healthy subjects and 30 patients diagnosed with oral cancer. The samples from healthy subjects were utilized to establish the cut-off levels for distinguishing between positive and negative results. Participants were recruited from the Division of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery at the Veterans General Hospital in Taichung. The inclusion criteria for healthy subjects included individuals over 18 years old with no history of neoplastic diseases. The oral cancer patients selected for this study were those with untreated, advanced stage III/IV disease, classified according to the 8th edition of the AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. Ethical approval for the study protocol was obtained from the Ethics Committee on Human Research at Veterans General Hospital (IRB approval #SE13339b#1). All participants provided written informed consent for sample collection and survival outcome analysis.
The collection of oral rinse samples involved an initial gentle gargle with 20 to 30 mL of sterile distilled water to serve as a pre-collection rinse. Subsequently, 5 mL of sterile water was used for a second gargle, lasting one minute, and the resulting oral rinse was collected in an empty centrifuge tube. A protease inhibitor (Protease Cocktail Inhibitor; Complete Tablets, Mini, EASYpack, Roche, Switzerland) was added to the collected fluid, which was then centrifuged at four °C at 3,000 rpm. The supernatant was aliquoted and stored at -80°C for subsequent analysis.
2.2. Determination of Total Protein Levels in Oral Rinse Saliva
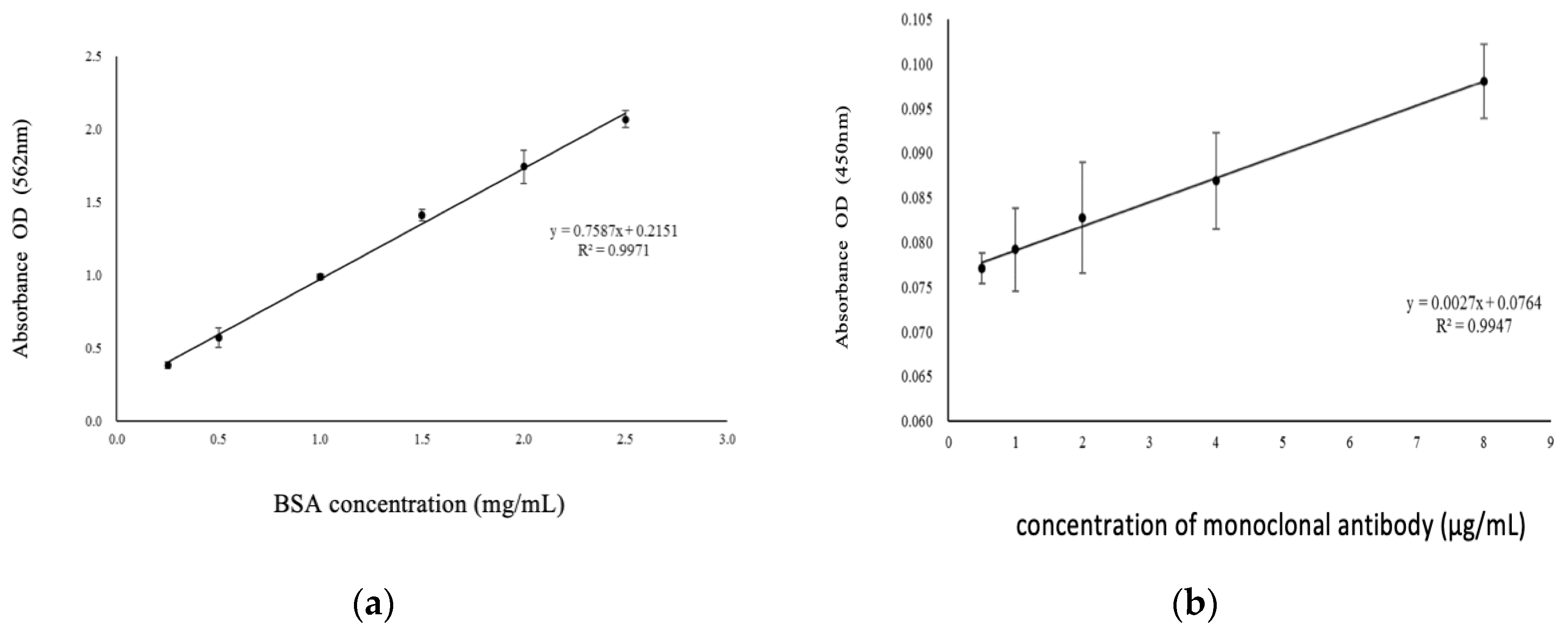
Total protein levels in the oral rinse samples were quantified using the bicinchoninic acid (BCA) assay. The samples were thawed on ice and centrifuged at 4°C at 3,000 rpm. Standard curves were generated using bovine serum albumin at concentrations of 2.5, 2, 1.5, 1, 0.5, and 0.25 mg/mL. The total protein level for each subject was estimated using the BCA assay, and all samples were diluted to a 1.5x concentration for consistent protein level estimations. The standard curve utilized for protein level estimation is depicted in
Figure 2a.
(a)
(b)
2.3. Indirect ELISA for Determination of Anti-E6 Antibody Titer
The titers of anti-E6 antibodies were measured using an indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). This assay employed commercially available rabbit anti-HPV16 E6 antibody and corresponding standard E6 oncoprotein. Briefly, 100 μL of standard E6 oncoprotein and 100 μL of chicken anti-E6 antibody were added to microtiter wells on the ELISA plate. Each well then received 100 μL of goat anti-chicken-HRP conjugate reagent, and the mixture was incubated with mechanical shaking (750 rpm) at room temperature for 90 minutes. After incubation, the wells were rinsed five times with 1x wash buffer and dried on paper towels. Subsequently, 100 μL of 3,3′,5,5′-Tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) reagent was added to each well, mixed gently, and incubated in the dark at room temperature for 20 minutes with mechanical shaking (750 rpm). The reaction was stopped by adding 100 μL of 1 N hydrochloric acid, which changed the color from blue to yellow. Absorbance at 450 nm was measured within 15 minutes using a VERSAmax™ microplate reader (Molecular Devices, Boston, MA, USA). Antibody concentrations were determined by serially diluting monoclonal antibodies, starting from 8 μg/mL and diluting to 4, 2, 1, and 0.5 μg/mL, followed by ELISA detection. The linear relationship between antibody and antigen detection from 0.5 to 8 μg/mL is shown in
Figure 2b, with an optimal antibody concentration of 8 μg/mL selected for further experiments.
2.4. Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) Analysis for E6 Oncoprotein and Anti-E6 Antibody in Saliva
Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) was employed to detect E6 oncoprotein in the oral rinse samples. Initially, anti-E6 antibodies were immobilized on biochips using a two-channel SPR sensor CM5. The BIAcore 3000 system was used for SPR immunoassays, following the manufacturer's guidelines (GE Healthcare Biosciences, AB. Biacore™ Assay Handbook). The assay began with pH optimization using sodium acetate buffer at pH 3.5, and HBS buffer was used as a flow buffer at 5 μL/min. A mixture of 200 μL NHS (0.05 M) and EDC (0.2 M) (50:50, v/v) was injected to activate carboxymethylated dextran into NHS-esters, which were subsequently deactivated with 100 μL of ethanolamine hydrochloride (1 M, pH 8.5) to block nonspecific binding. Anti-E6 antibodies were covalently immobilized on the sensor chip surface using EDC/NHS activation. A sensorgram was generated by analyzing a 1:2 diluted saliva sample from each of the 43 subjects. Samples were diluted with HBS buffer and analyzed using the Biacore 3000 at a flow rate of 20 μL/min.
Following the analysis of E6 oncoprotein in oral rinse samples, the detection of anti-E6 antibodies in saliva was performed by immobilizing E6 oncoproteins on the sensor chip. The final concentrations of E6 oncoprotein and anti-E6 antibody were 0.03 μg/mL and 10 μg/mL, respectively. The final ΔRU was calculated as the difference between SPR angles before and after sample flow through the channel.
2.5. Competitive Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) for E6 Oncoprotein Verification in Oral Rinse Samples
A competitive ELISA was performed to verify E6 oncoprotein in oral rinse samples. Antibodies and antigens were immobilized on a 96-well plate at 4°C for at least 16 hours. The plate surface was washed multiple times with PBS and blocked for one hour. The primary antibody (rabbit anti-HPV16 E6 antibody) was diluted 1:200 as per the manufacturer’s instructions, followed by adding the antibody-saliva mixture. Each antibody-saliva mixture concentration was assayed in triplicate. The remaining antibody was allowed to react with the plate surface antigen for 90 minutes at room temperature. A secondary antibody (goat anti-rabbit-HRP) was then added to react with the primary antibody on the well plate. After the final addition of TMB substrate, absorbance (OD450) was measured using a microplate reader at a wavelength of 450 nm.
2.6. Statistical Analyses
The mean (x̄) and standard deviation (s) of SPR values from control samples were initially calculated to assess the positivity of the two biomarkers in oral rinse samples. These values were used to construct a box plot and interpret the differences in HPV E6 and anti-E6 antibody levels. Extreme outliers were excluded, and a 99% confidence interval was applied to define positivity. Kaplan-Meier survival plots were generated to represent the overall survival of oral cancer patients, and log-rank tests were conducted to compare the two groups. Patient demographic characteristics were reviewed and summarized. All statistical analyses were performed using Microsoft Office 2016 Excel and SAS software version 9.4.
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Clinical Characteristics
A total of 29 patients were included in the final analysis, with one patient excluded due to loss of follow-up after surgical intervention (
Table 1). The follow-up duration ranged from 15 to 46 months, with a mean follow-up time of 31.9. The mean age of the cohort was 55.4 years, with the double-positive group having a mean age of 60.1 years, compared to 54.0 years in the single-positive and negative group. Most patients were male (89.6%), with 100% of the double-positive group male and 86.3% in the single-positive and negative group.
Regarding the primary tumor sites, 41.3% of cases involved the buccal mucosa, followed by 24.1% in the gingiva, 20.6% in the tongue, 6.9% in the palate, and 6.9% in the floor of the mouth. Regarding clinical staging, 69.9% of the patients were in Stage IV, while 30.1% were in Stage III. Surgical intervention was performed in all cases, with 37.9% undergoing surgery alone and 62.0% receiving a combination of surgery with concurrent chemoradiotherapy (CCRT).
E6 oncoprotein and anti-E6 antibody levels were higher in oral cancer patients than in control subjects. Among the 29 patients with advanced T3/T4 oral cancer, 37.9% (11/29) were positive for the E6 oncoprotein, and 31.0% (9/29) showed increased expressions of anti-E6 antibodies. Notably, 24.1% (7/29) of these patients exhibited double positivity in their oral rinse samples (
Table 1). In contrast, within the control group, the positivity rates for E6 oncoprotein and anti-E6 antibodies were 7.7% and 15.4%, respectively.
3.2. Analyses of Biomarkers in Saliva Samples Using SPR (HPV E6 Oncoprotein, Anti-E6 Antibody)
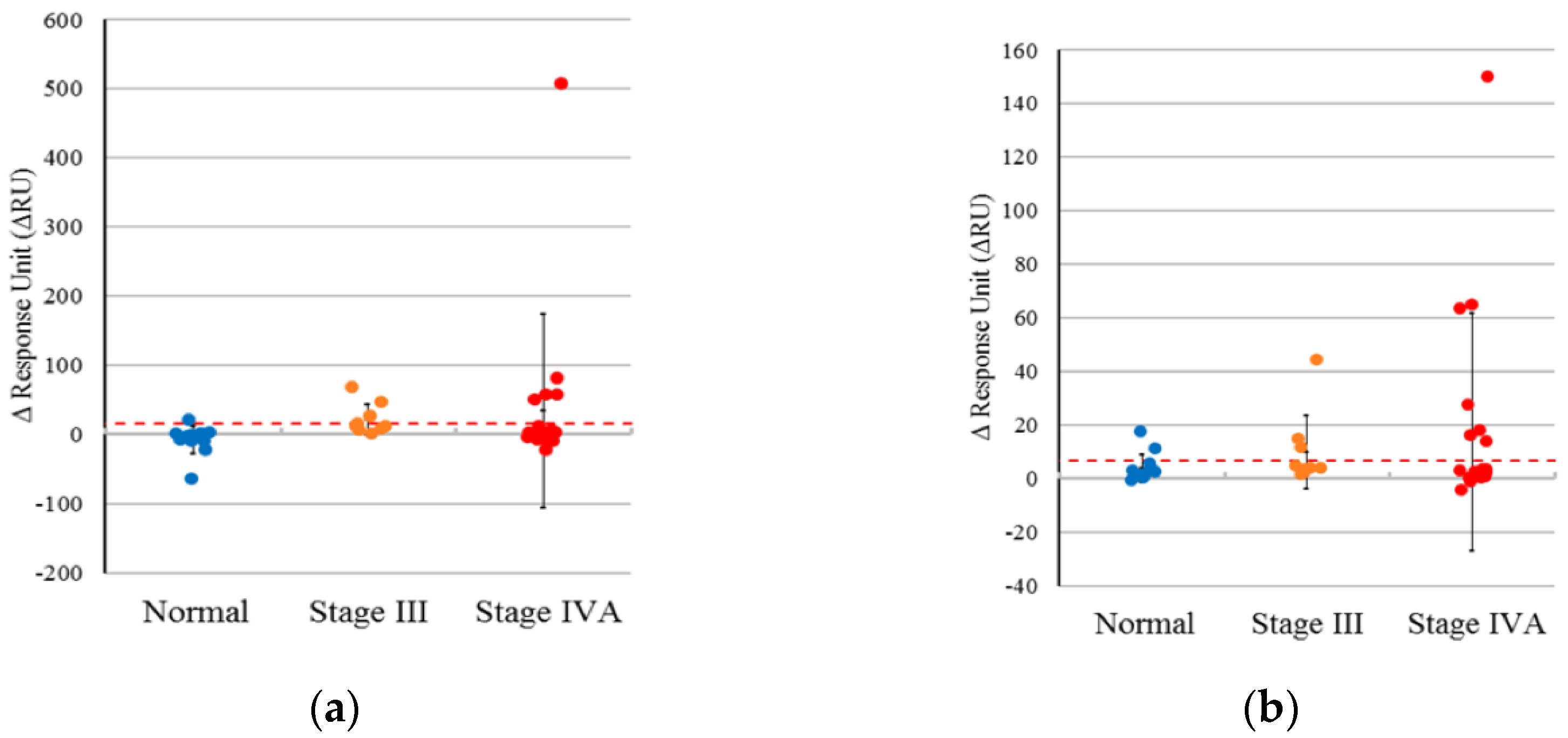
3.2.1. HPV E6 Oncoprotein
After removing extreme outliers (samples N12 and N20) based on the quartile method, the mean signal strength for E6 oncoprotein in non-oral cancer subjects was calculated as -4.109, with a standard deviation of 7.561. The 99% confidence interval ranged from -23.617 to 15.399. Consequently, we conservatively classified sample results as positive if the signal strength exceeded 15.399 (
Figure 3a).
3.2.2. Anti-E6 Antibody
Following a similar approach as previously described, extreme outliers (samples N20 and N26) were excluded using the quartile method. The criterion for positivity to the anti-E6 antibody was defined as a signal strength greater than 6.894 (
Figure 3b). For non-oral cancer subjects, the average signal strength for anti-E6 antibody was 2.184, with a standard deviation of 1.826, yielding a 99% confidence interval of -2.526.
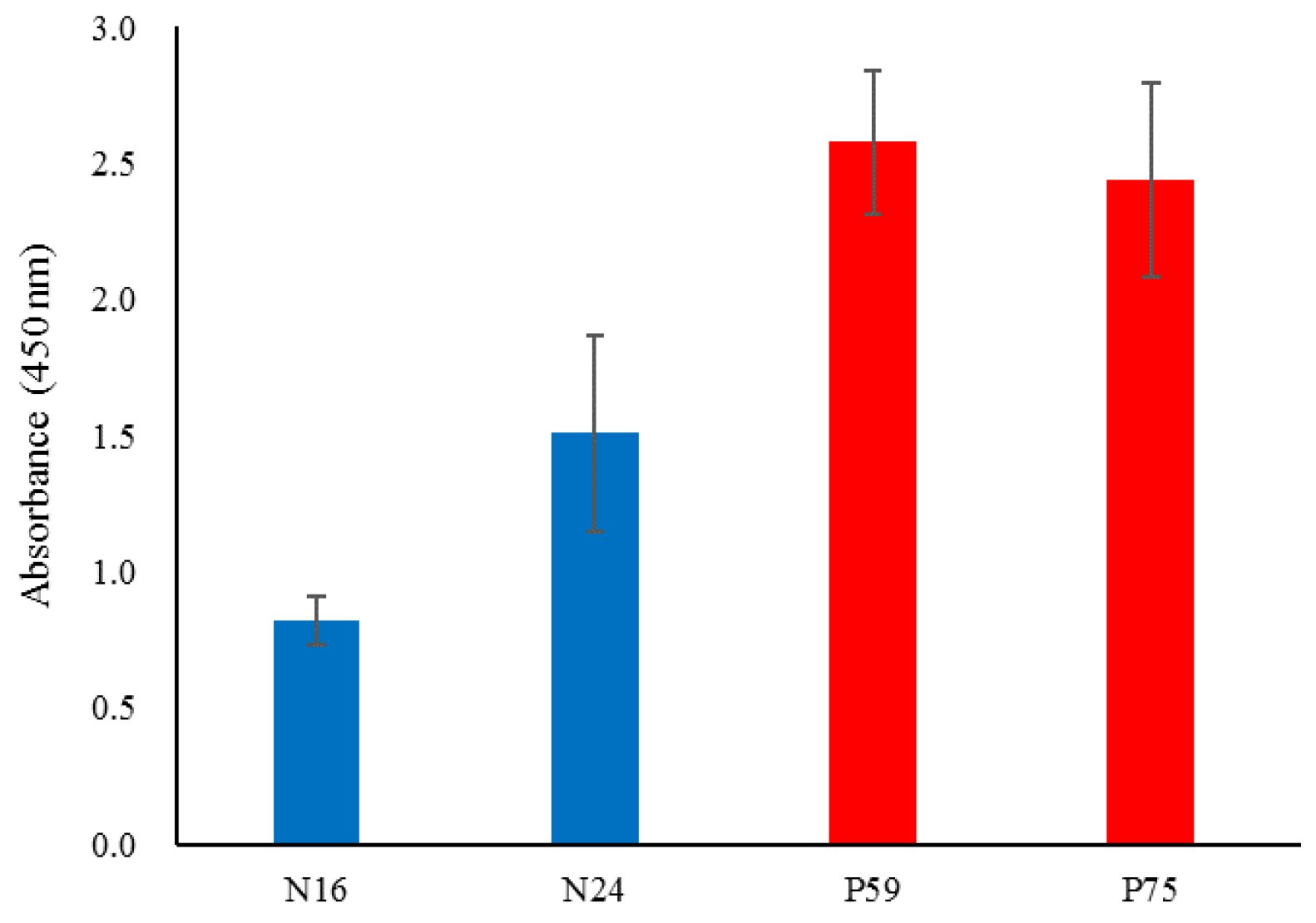
3.3. Verification of SPR E6 Oncoprotein Positivity by Competitive ELISA
This verification step aimed to confirm the consistency between SPR data and competitive ELISA results. The findings demonstrated that the positive and negative results were concordant when comparing immobilizations using E6 protein antigen and anti-E6 antibody. Specifically, the results for saliva samples P59 and P75 (patients) and N16 and N24 (normal) were representative of this consistency. The data trends observed for samples N16, N24, P59, and P75 aligned with the SPR results (
Figure 4).
3.4. Overall Survival Rate Comparison between Patients with Double Positivity (E6 Oncoprotein and Anti-E6 Antibody) and Those with Single Positivity or Negative Status
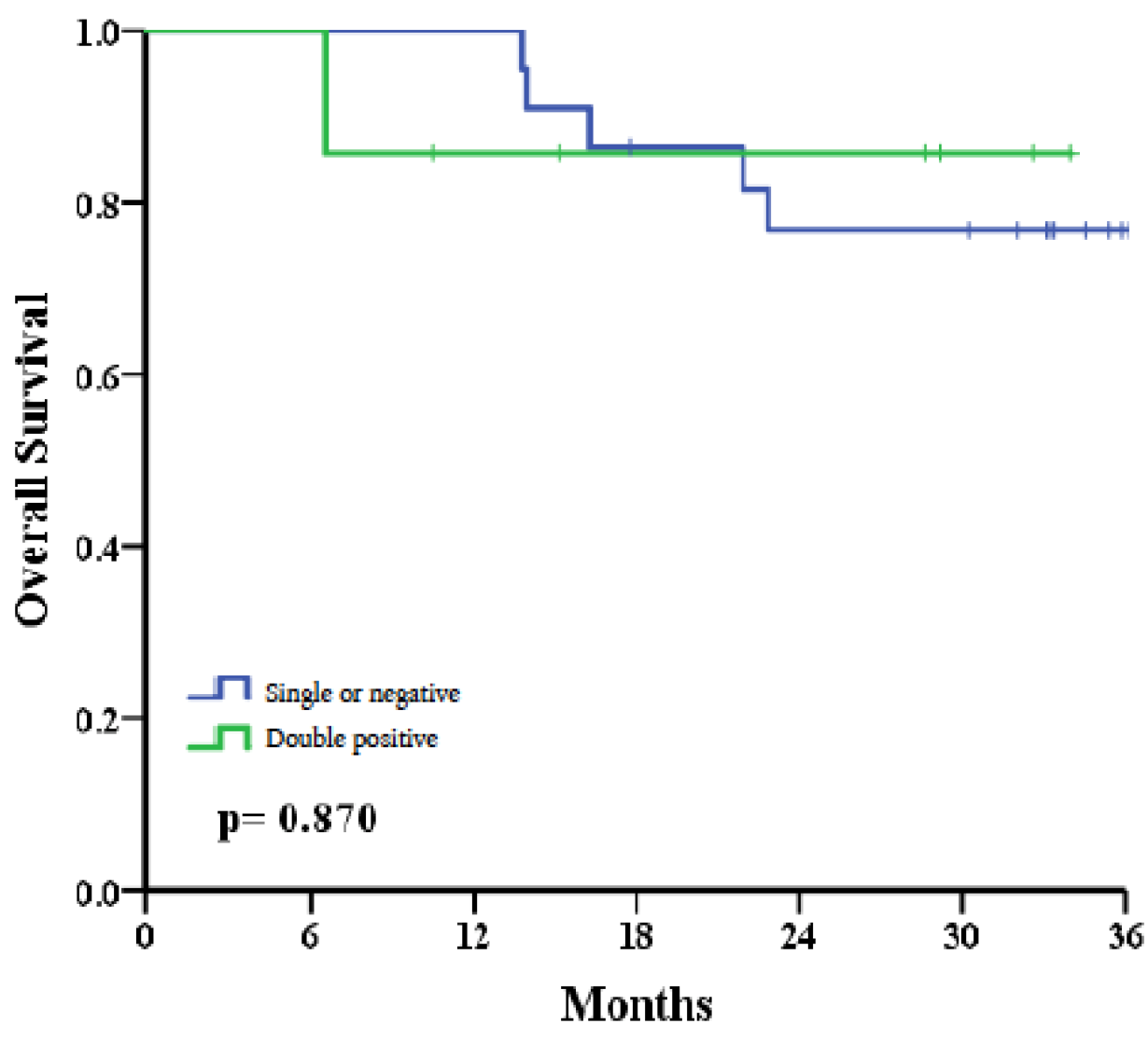
Survival analysis showed that 85.7% of patients in the double-positive group were alive at the end of the follow-up period, compared to 78.6% in the single-positive and negative group. This preliminary study reported that six patients succumbed to treatment failure, with uncontrolled recurrences leading to death within the three-year follow-up period. The causes of death included metastasis to the lungs (n=1), bones (n=1), and local recurrences (n = 4). Within the double positivity group, 1 out of 7 patients (14.3%) died. Conversely, in the combined group of single positivity and negativity, 5 out of 22 patients (22.7%) died within three years post-treatment. Although the sample size is limited and lacks sufficient statistical power, an observed trend indicates that patients with double positivity had better survival outcomes than those with single positivity or double negativity (85.7% vs. 76.8%, p=0.870) (
Figure 5).
4. Discussion
This study demonstrated the feasibility of utilizing a dual biomarker approach—measuring both E6 oncoprotein and anti-E6 antibodies in saliva samples—using the SPR biosensor technique. Our findings revealed that approximately one-third of patients with advanced oral cavity cancer exhibited significant expression levels of E6 oncoprotein (37.9%) and anti-E6 antibody (31.0%) in their oral rinse saliva. Notably, 24.1% of these patients showed double positivity for both biomarkers, and this subgroup exhibited a trend toward better 3-year survival outcomes compared to the combined subgroups of single positivity or negativity. Although the limited sample size in this preliminary study precluded statistically significant results, the observed association suggests that this saliva-based dual biomarker assay may provide valuable prognostic information for predicting survival outcomes in patients with advanced oral cancer.
The significance of E6 oncoproteins and anti-E6 antibodies in predicting survival outcomes can be understood in the context of the carcinogenic pathways associated with HPV. The overexpression of E6 oncoprotein and elevated levels of anti-E6 antibodies in patients aligns with the natural progression of HPV-related cancers, which typically begin with a transient viral infection. Viral oncogenes integrate into host cell DNA as the infection persists, driving the malignant transformation. Furthermore, high anti-E6 antibody levels suggest an ongoing immune response that began during the initial viral infection and continues through the progression to cancer. Based on these mechanisms, we hypothesize that the observed double positivity for these HPV-related biomarkers confers a survival advantage. This may be due to a combination of more effective therapeutic responses, the natural radiosensitivity of HPV-positive tumors, and a robust long-term immune response against tumor cells. Together, these factors may contribute to better therapeutic outcomes and improved overall survival in patients exhibiting double positivity.
Previous studies have established that non-HPV-associated tumors often exhibit more aggressive behavior, characterized by a wide range of phenotypes and diverse malignant behaviors. In contrast, HPV-related cancer cells, marked by the overexpression of E6/E7 oncoproteins, demonstrate distinctive genetic alterations and functional expressions compared to non-HPV-associated cancer cells [
24]. The detection of E6 oncoprotein has been suggested as a more reliable biomarker than p16INK4a for diagnosing HPV-related cancers, as it reflects real-time overexpression of E6 oncoprotein, which correlates with better survival outcomes in HPV-positive patients [
25,
26]. Clinically, HPV-positive head and neck cancer patients who retain wild-type p53 during carcinogenesis often show increased radiosensitivity and improved survival outcomes [
27]. For instance, Ang et al. reported that advanced HPV-positive cases had a significantly higher 3-year overall survival rate compared to HPV-negative cases (82.4% vs. 57.1%) following intensive radiation therapy and chemotherapy [
9].
Another survival benefit linked to HPV-related biomarkers is the presence of higher levels of anti-E6 antibodies [
28]. These antibodies, typically IgA and IgG, emerge as part of the immune response to HPV infection, persisting through HPV-associated carcinogenesis [
29]. High anti-E6 antibody levels often coexist with detectable E6 oncoproteins in the tumor and surrounding tissues, including saliva [
22]. Studies have reported strong correlations between anti-E6 seropositivity and improved survival outcomes [
21,
23,
30], suggesting that these antibodies may contribute to an antiviral immune response that also exerts anti-tumor effects. This concept has been explored in studies aiming to develop monoclonal antibodies targeting E6/E7 oncoproteins to inhibit tumor growth [
31].
Given these insights, there is a compelling need to explore the clinical value of saliva-based HPV biomarkers, particularly E6 oncoproteins and anti-E6 antibodies, in oral cancer patients [
32]. Detecting E6 oncoprotein in body fluids is challenging due to its low abundance, but recent advances in biosensor techniques, such as surface plasmon resonance (SPR), offer promising solutions [
33,
34]. SPR has proven to be an effective tool for detecting cancer biomarkers, and its application in "Lab-on-a-Chip" or "Point-of-Care Testing" (POCT) models makes it a non-invasive, patient-friendly option for real-time monitoring of biomarkers in clinical settings [
25,
35,
36,
37].
Traditionally, p16 and HPV DNA are the standard assays for diagnosing HPV-related cancers. Immunohistochemical (IHC) assessment of p16 in surgical specimens is a critical surrogate biomarker for diagnosing HPV-related cervical and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma (OPSCC) [
9,
38]. Some studies have suggested that combining p16 and HPV DNA positivity in tumor cells offers greater accuracy in diagnosing and predicting outcomes of HPV-related cancers [
39,
40]. However, in saliva or oral rinses, HPV DNA detection has been the mainstream method for identifying HPV-associated biomarkers [
17]. Nevertheless, the presence of HPV DNA alone does not necessarily confirm the causality of cancer [
41], as it cannot distinguish between transient viral infection and malignant transformation driven by the integration of viral genes into the host genome [
11]. Therefore, the expression of HPV E6/E7 oncoproteins serves as more direct evidence of the carcinogenic role of HPV [
13]. Given this, developing saliva-based biomarker assays to detect E6/E7 proteins could provide a practical approach for diagnosing and monitoring oral cavity cancers, particularly since HPV-related particles or exosomes can be readily obtained from saliva through oral rinses [
43].
This study has several limitations that should be acknowledged. First, there is currently no universally accepted consensus tool for verifying HPV-related oral cavity cancer, which presents challenges in standardizing diagnostic approaches. Although the competitive ELISA used in this study technically provided confidence in confirming SPR results for selective patients, it is not without its limitations. Additionally, the study was conducted with a relatively small sample size of cancer patients and a follow-up period of only three years. To obtain more robust and statistically significant findings, future studies will require larger sample sizes and longer observation periods. These enhancements would help to strengthen the evidence supporting the utility of HPV-related biomarkers in predicting survival outcomes in oral cavity cancer patients.
5. Conclusions
In this preliminary study, our findings suggest that the simultaneous detection of E6 oncoproteins and anti-E6 antibodies in saliva may serve as a valuable dual biomarker for diagnosing and predicting the overall outcomes of HPV-related oral cancers. Given the distinct pathogenesis of HPV-related cancers, where infectious and neoplastic processes diverge, diagnostic tests should focus on detecting oncoproteins rather than merely identifying the presence of the virus. The observed increase in E6 oncoproteins in cancer patients indicates that these biomarkers can help identify a subgroup of HPV-related cases with better prognoses, likely due to increased radiosensitivity. Moreover, elevated anti-E6 antibody levels may imply an ongoing immune response capable of inhibiting persistent tumor growth. Ultimately, the goal of a saliva-based HPV detection approach extends beyond laboratory research, aiming to design and develop simple, convenient platforms suitable for chair-side practices. We believe that oral cavity cancer, due to its accessibility for sample collection, may be particularly well-suited for the development of such saliva-based biomarker detection assays, offering a practical and non-invasive tool for clinical use.
Funding
This work was funded by the Ministry of Health and Welfare, Taiwan (Grant number MOHW105-TDU-B-211-134002 (1-2-1).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee on Human Research at Veterans General Hospital (IRB approval #SE13339b#1).”.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- van Dam, P.A.; Rolfo, C.; Pauwels, P.; Van Berchelaer, C.; Trinh, X.B.; et al. Potential new biomarkers for squamous carcinoma of the uterine cervix. ESMO Open 2018, 3, e000352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otter, S.; Whitaker, S.; Chatterjee, J.; Stewart, A. The Human Papillomavirus as a Common Pathogen in Oropharyngeal, Anal and Cervical Cancers. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol) 2019, 31, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Sanjosé, S.; Serrano, B.; Tous, S.; Alejo, M.; Lloveras, B.; Quirós, B.; et al. Burden of Human Papillomavirus (HPV)-Related Cancers Attributable to HPVs 6/11/16/18/31/33/45/52 and 58. JNCI Cancer Spectr 2018, 2, pky045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.D.; Kenny, L.; Frazer, I. H.; Punyadeera, C. High-risk human papillomavirus detection in oropharyngeal cancers: Comparison of saliva sampling methods. Head Neck 2019, 41, 1484–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Bonito, P.; Accardi, L.; Galati, L.; Ferrantelli, F.; Federico, M. Anti-Cancer Vaccine for HPV-Associated Neoplasms: Focus on a Therapeutic HPV Vaccine Based on a Novel Tumor Antigen Delivery Method Using Endogenously Engineered Exosomes. Cancers (Basel) 2019, 11, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, C.; Cohen, R.B.; Morrow, M.P.; Kraynyak, K.A.; Sylvester, A.J.; Knoblock, D.M.; et al. Immunotherapy Targeting HPV16/18 Generates Potent Immune Responses in HPV-Associated Head and Neck Cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2019, 25, 110–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lydiatt, W.M.; Patel, S.G.; O'Sullivan, B.; Brandwein, M.S.; Ridge, J.A.; Migliacci, J.C.; et al. Head and Neck cancers-major changes in the American Joint Committee on cancer eighth edition cancer staging manual. CA Cancer J Clin 2017, 67, 122–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, K.K.; Sturgis, E.M. Human papillomavirus as a marker of the natural history and response to therapy of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Semin Radiat Oncol 2012, 22, 128–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, K.K.; Harris, J.; Wheeler, R.; Weber, R.; Rosenthal, D.I.; Nguyen-Tan, P.F.; et al. Human papillomavirus and survival of patients with oropharyngeal cancer. N Engl J Med 2010, 363, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doorbar, J.; Egawa, N.; Griffin, H.; Kranjec, C.; Murakami, I. Human papillomavirus molecular biology and disease association. Rev Med Virol 2015, 25 Suppl 1, 2–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezhake, R.; Hu, S.Y.; Zhao, S.; Xu, X.Q.; Zhao, X.L.; Zhang, L.; et al. Eight-type human papillomavirus E6/E7 oncoprotein detection as a novel and promising triage strategy for managing HPV-positive women. Int J Cancer 2019, 144, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellsague, X.; Alemany, L.; Quer, M.; Halec, G.; Quirós, B.; Tous, S.; et al. HPV Involvement in Head and Neck Cancers: Comprehensive Assessment of Biomarkers in 3680 Patients. J Natl Cancer Inst 2016, 108, djv403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.J.; Cao, X.C.; Zheng, X.Y.; Wang, H.Y.; Li, Y.W. Feasibility study of a human papillomavirus E6 and E7 oncoprotein test for the diagnosis of cervical precancer and cancer. J Int Med Res 2018, 46, 1033–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Sanjose, S.; Brotons, M.; Pavon, M.A. The natural history of human papillomavirus infection. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol 2018, 47, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussu, F.; Ragin, C.; Boscolo-Rizzo, P.; Rizzo, D.; Gallus, R.; Delogu, G.; et al. HPV as a marker for molecular characterization in head and neck oncology: Looking for a standardization of clinical use and of detection method(s) in clinical practice. Head Neck 2019, 41, 1104–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzinger, D.; Wichmann, G.; Baboci, L.; Michel, A.; Hofler, D.; Wiesenfarth, M.; et al. Sensitivity and specificity of antibodies against HPV16 E6 and other early proteins for the detection of HPV16-driven oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer 2017, 140, 2748–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirghani, H.; Lang Kuhs, K.A.; Waterboer, T. Biomarkers for early identification of recurrences in HPV-driven oropharyngeal cancer. Oral Oncol 2018, 82, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D'Souza, G.; Kreimer, A. R.; Viscidi, R.; Pawlita, M.; Fakhry, C.; Koch, W. M.; et al. Case-control study of human papillomavirus and oropharyngeal cancer. N Engl J Med 2007, 356, 1944–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koslabova, E.; Hamsikova, E.; Salakova, M.; Klozar, J.; Foltynova, E.; Salkova, E.; et al. Markers of HPV infection and survival in patients with head and neck tumors. Int J Cancer 2013, 133, 1832–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreimer, A.R.; Johansson, M.; Waterboer, T.; Kaaks, R.; Chang-Claude, J.; Drogen, D.; et al. Evaluation of human papillomavirus antibodies and risk of subsequent head and neck cancer. J Clin Oncol 2013, 31, 2708–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broglie, M.A.; Jochum, W.; Michel, A.; Waterboer, T.; Foerbs, D.; Schoenegg, R.; et al. Evaluation of type-specific antibodies to high risk-human papillomavirus (HPV) proteins in patients with oropharyngeal cancer. Oral Oncol 2017, 70, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanna, G.J.; Sridharan, V.; Margalit, D.N.; La Follette, S.K.; Chau, N.G.; Rabinowits, G.; et al. Salivary and serum HPV antibody levels before and after definitive treatment in patients with oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Biomark 2017, 19, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahlstrom, K.R.; Anderson, K.S.; Cheng, J. N.; Chowell, D.; Li, G.; Posner, M. , et al. HPV Serum Antibodies as Predictors of Survival and Disease Progression in Patients with HPV-Positive Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Oropharynx. Clin Cancer Res 2015, 21, 2861–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, B.; Young, R.J.; Rischin, D. Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Genomics and emerging biomarkers for immunomodulatory cancer treatments. Semin Cancer Biol 2018, 52, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, R.C.; Lim, Y.; Frazer, I.H.; Wan, Y.; Perry, C.; Jones, L.; et al. A pilot study to compare the detection of HPV-16 biomarkers in salivary oral rinses with tumour p16(INK4a) expression in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma patients. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zafereo, M.E.; Xu, L.; Dahlstrom, K.R.; Viamonte, C.A.; El-Naggar, A.K.; Wei, Q.; et al. Squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity often overexpresses p16 but is rarely driven by human papillomavirus. Oral Oncol 2016, 56, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, A.C.; Briolat, J.; Millon, R.; de Reyniès, A.; Rickman, D.; Thomas, E.; et al. Biological and clinical relevance of transcriptionally active human papillomavirus (HPV) infection in oropharynx squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer 2010, 126, 1882–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, E.M.; Rubenstein, L.M.; Ritchie, J.M.; Lee, J. H.; Haugen, T. H.; Hamsikova, E.; et al. Does pretreatment seropositivity to human papillomavirus have prognostic significance for head and neck cancers? Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2008, 17, 2087–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westrich, J.A.; Warren, C.J.; Pyeon, D. Evasion of host immune defenses by human papillomavirus. Virus Res 2017, 231, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlstrom, K.R.; Anderson, K.S.; Field, M.S.; Chowell, D.; Ning, J.; Li, N.; et al. Diagnostic accuracy of serum antibodies to human papillomavirus type 16 early antigens in the detection of human papillomavirus-related oropharyngeal cancer. Cancer 2017, 123, 4886–4894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Albanese, J.; Kesterson, J.; Warrick, J.; Karabakhtsian, R.; Dadachova, E.; et al. Monoclonal Antibodies Against Human Papillomavirus E6 and E7 Oncoproteins Inhibit Tumor Growth in Experimental Cervical Cancer. Transl Oncol 2019, 12, 1289–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bussu, F.; Ragin, C.; Boscolo-Rizzo, P.; Rizzo, D.; Gallus, R.; Delogu, G.; et al. HPV as a marker for molecular characterization in head and neck oncology: Looking for a standardization of clinical use and of detection method(s) in clinical practice. Head Neck 2019, 41, 1104–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayanthi, V.; Das, A.B.; Saxena, U. Recent advances in biosensor development for the detection of cancer biomarkers. Biosens Bioelectron 2017, 91, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergara, D.; Bianco, M.; Pagano, R.; Priore, P.; Lunetti, P.; Guerra, F.; et al. An SPR based immunoassay for the sensitive detection of the soluble epithelial marker E-cadherin. Nanomedicine 2018, 14, 1963–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malamud, D. Saliva as a diagnostic fluid. Dent Clin North Am 2011, 55, 159–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steckl, A.J.; Ray, P. Stress Biomarkers in Biological Fluids and Their Point-of-Use Detection. ACS Sens 2018, 3, 2025–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonaka, T.; Wong, D.T.W. Liquid Biopsy in Head and Neck Cancer: Promises and Challenges. J Dent Res 2018, 97, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, J.S. Jr.; Beadle, B.; Bishop, J.A.; Chernock, R.D.; Colasacco, C.; Lacchetti, C.; et al. Human papillomavirus testing in head and neck carcinomas: guideline from the College of American Pathologists. Arch Pathol Lab Med 2018, 142, 559–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mena, M.; Taberna, M.; Tous, S.; Marquez, S.; Clavero, O.; Quiros, B.; et al. Double positivity for HPV-DNA/p16(ink4a) is the biomarker with strongest diagnostic accuracy and prognostic value for human papillomavirus related oropharyngeal cancer patients. Oral Oncol 2018, 78, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coordes, A.; Lenz, K.; Qian, X.; Lenarz, M.; Kaufmann, A.M.; Albers, A.E. Meta-analysis of survival in patients with HNSCC discriminates risk depending on combined HPV and p16 status. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 2015, 273, 2157–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinath, D.; Kunnath Menon, R. The significance of an algorithm for human papillomavirus detection in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. J Oral Pathol Med 2018, 47, 540–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillison, M.L.; Alemany, L.; Snijders, P.J.; Chaturvedi, A.; Steinberg, B.M.; Schwartz, S.; et al. Human papillomavirus and diseases of the upper airway: head and neck cancer and respiratory papillomatosis. Vaccine 2012, 30 Suppl, F34–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harden, M.E.; Munger, K. Human papillomavirus 16 E6 and E7 oncoprotein expression alters microRNA expression in extracellular vesicles. Virology 2017, 508, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).