1. Introduction
Medical errors are the third largest cause of death in the world [
1], and within that, diagnostic errors kill or permanently disable 800,000 people each year in the United States [
2]. Research by The National Academy of Medicine as well as Newman-Toker et al. estimated that diagnostic errors are responsible for approximately 10% of patient deaths [
3,
4] and 6-17% of hospital complications [
3]. 75% of diagnostic errors are cognitive errors [
5] most commonly caused by premature closure, the failure to consider alternatives after an initial diagnosis has been established. Cognitive errors are also naturally linked to the overload and stress physicians have been experiencing with current burnout rates reaching the highest ever levels recorded [
6]. Given the recent progress in Artificial Intelligence, large language models (LLMs) have been proposed to help with various aspects of clinical work, including diagnosis [
7]. GPT-4, a LLM developed by OpenAI has shown promise in medical applications with its ability to pass medical board exams in multiple countries and languages [
8,
9,
10,
11].
Only a handful number of studies have attempted to compare the diagnostic ability of LLMs mostly on New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM) Case Challenges or clinical vignettes. Khan et al. [
12] used the former and compared GPT-3.5, GPT-4 (Bing) and Gemini 1.5 diagnoses in 10 clinical cases with the help of 10 physicians who filled out a grading rubric. Chiu et al. [
13] used 102 case records to compare the performance of Bard, Claude 2 and GPT-4 using the ICD-10 hierarchy. Others have compared LLM capabilities for a given specialty, such as otolaryngology [
14] and radiology [
15].
NEJM Case challenges are notoriously hard, and they most often have a single definitive diagnosis. Eriksen et al. [
16] asked GPT-4 to choose one from 6 diagnostic options for each of the 38 case challenges whereas Kanjee et al. [
17] asked GPT-4 to first, state the most likely diagnosis (in 27 out of the 70 cases the LLM got it right) and second, give a list of differentials: manual review by the authors concluded that in 45 out of the 70 cases the correct answer was included in the differentials. Hirosawa et al. [
18] compared 2 physicians and GPT-4 in their ability to extract correct final diagnoses from GPT-4, Bard and LlaMA2-generated differential diagnoses. Shieh et al. [
19] used 63 case report vignettes and asked GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 for its top 3 differentials with the latter including the correct answer in 47 out of its 63 generated differentials.
These evaluation strategies work for case challenges but would not suffice for a cohort of highly comorbid real patients, such as in MIMIV-IV [
20]. To solve this, our previous study outlined a methodology to use AI-Assisted evaluation to quickly estimate the diagnostic accuracy of different models on a set of highly comorbid real hospital patients [
21]. This automated evaluation not only allows for evaluating on larger datasets (we increased the sample size 10-fold from the <100 typically seen in clinical vignettes to 1000), but also facilitates quick benchmarking of multiple models, which is our goal in this study. Our automated evaluation gave reliable estimates as judged by three medical doctors in our previous study [
21], and as AI models improve, we only expect this to become better.
2. Methods
2.1. Models
We compared the following models for diagnosis in our analysis: Gemini 1 (gemini-pro-vision via Google Vertex AI API used on 2024/03/26 with temperature set to zero), Gemini 1.5 (Gemini-1.5-pro-preview-0409 via Google Vertex AI API used 2024/05/08, temperature set to zero), MedLM (medlm-medium via Google Vertex AI API used 2024/05/08, temperature: 0.2, top_p: 0.8, top_k: 40), LlaMA 3.1 (Meta-Llama-3.1-405B-Instruct deployed on Microsoft Azure used via API on 2024/08/22), Mistral 2 (Mistral-large-2407 deployed on Microsoft Azure used via API on 2024/08/22), Command R Plus (command-r-plus via Cohere API used 2024/06/24), GPT-4-Turbo (gpt-4-1106-preview via OpenAI API used 2024/02/14), GPT-4o (gpt-4o via OpenAI API used 2024/08/29, temperature set to zero), Claude 3.5 Sonnet (claude-3-5-sonnet-20240620 via Anthropic API used 2024/07/23, temperature set to zero). The automated evaluation was done by GPT-4-Turbo (gpt-4-1106-preview via OpenAI API, temperature set to zero) on the same day when the diagnostic models were run. Note: when parameters are not mentioned, they were not explicitly set, and their default values have been used. The reported hit rate is the average across all the ground truth diagnoses of the 1000 sample patients.
GPT-4o with retrieval augmented generation (RAG) was implemented via Azure Cognitive Search. A document containing Laboratory Test Reference Ranges from The American Board of Internal Medicine updated January 2024 [
22] was vectorized (embedded by the
Ada-002 model from OpenAI) and indexed to be used for RAG with default overlap and chunk size (1024). The 5 closest matches were retrieved using the cosine similarity metric and the output was generated on 2024/06/26 with
temperature of zero,
strictness parameter of 3 and the
inScope flag set to False.
2.2. Diagnosis and Automated Evaluation
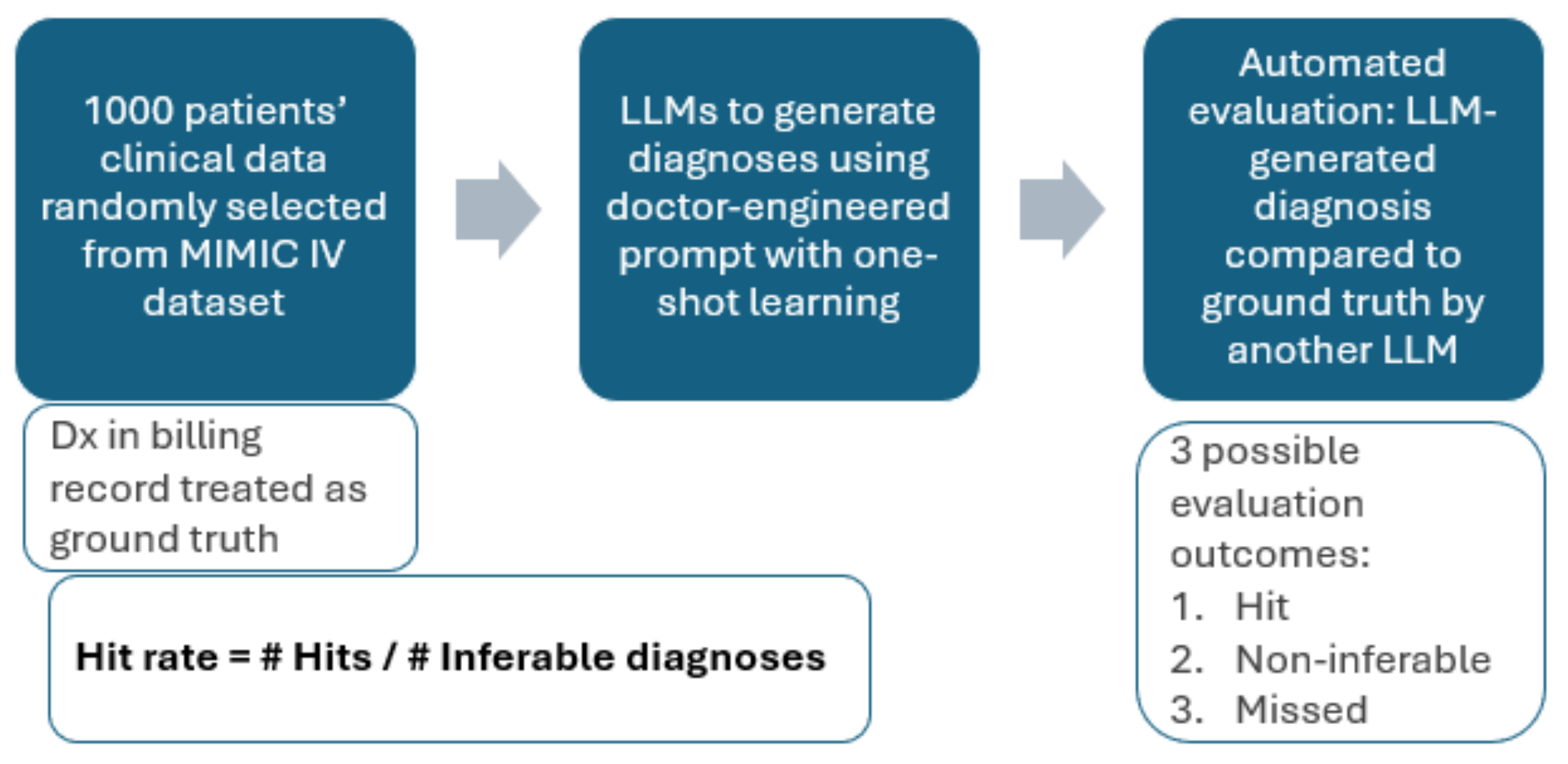
The MIMIC-IV data sample containing 1000 hospital admissions and the diagnostic and evaluation prompts were taken from [
20]. The evaluation methodology is summarized in
Figure 1.
Our initial idea was to simply compare the predicted ICD codes to the ICD codes extracted from the patients’ billing reports (ground truth) and examine what proportion was guessed correctly. However, the MIMIC-IV data did not contain patient history (previous diagnoses, medications), patient physical examinations and other useful measurements such as ECG. Of course, without medication records, we would not know if the patient is suffering from a coagulation disorder or is taking anticoagulants and without ECG we cannot diagnose atrial fibrillation. Hence, such diagnoses are not inferable from the data, and we exclude them. Further, given the lack of patient diagnostic history and the very specific ICD code names, it may not be possible to distinguish between diseases with different onsets (acute vs chronic) or between diseases with differing degrees of severity. Hence, we deem the prediction correct if the predicted and the ground truth diagnoses are two related diseases (e.g., caused by the same pathogen, affecting the same organ) which are indistinguishable given the patient data. In this case, the further tests the LLM is instructed to suggest [
20] are of crucial importance to understand to exact disease pathology. There are also ICD codes that do not correspond to diagnoses (e.g., Do Not Resuscitate, homelessness, unemployment) and we exclude such codes from this study. We define a correct prediction as a ‘hit’, and the failure to predict a ground truth diagnosis as a ‘miss’.
In terms of the evaluation metrics, we solely focus on hit rate (also called recall, true positive rate, sensitivity) in this study. The rationale is as follows: for every single disease in the world, the patient may have it or not have it. As such, when making predictions, the LLM is effectively executing binary classifications for every single disease. Of course, even a highly comorbid patient will not have 99.99%+ of the possible diseases and hence the metrics related to negative selected elements, such as specificity are very close to 1 by default and are not meaningful to report. As a result, the meaningful metrics here are precision and hit rate. However, a good quantification of precision is challenging in this case because false positives are difficult to establish as not every single medical condition ends up on the billing report of the patient. Hence, it’s unclear and subjective whether certain well-reasoned diagnostic predictions should be marked false positives just because they did not show up on the patient’s billing report. As a solution, we report the hit rate while (1) indirectly constraining the number of predictions by limiting the LLM output tokens to 4096 and (2) ensuring explainability by asking the LLM to reason why it predicted certain conditions.
3. Results
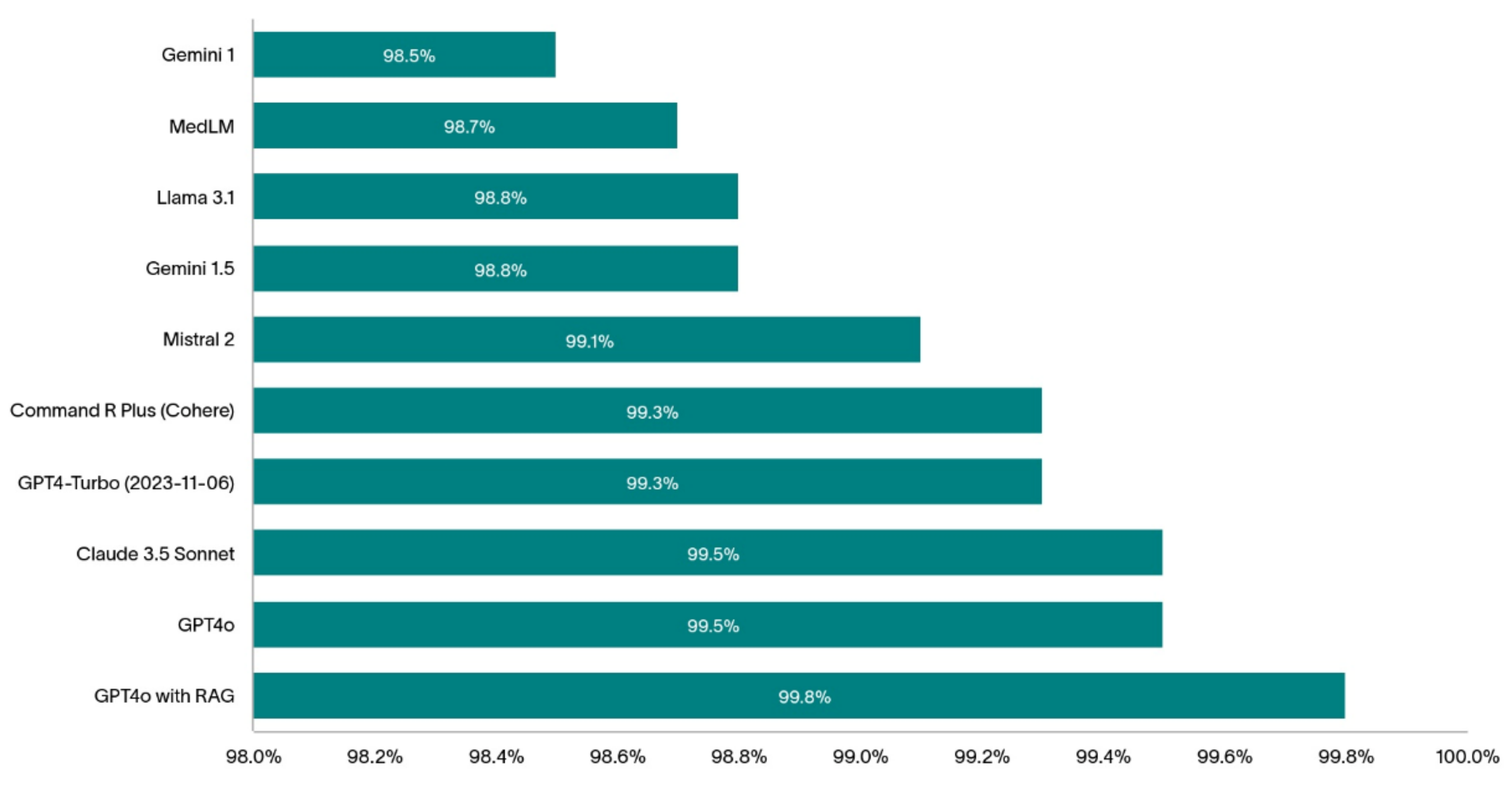
The 1000 randomly selected patients are highly comorbid with an average of 14.4 distinct diagnostic codes per patient (min:1, max: 39, IQR: 10). The bar chart on
Figure 2 shows the diagnostic hit rate of the models we tested in this study.
The top-performing models (without RAG) assessed in this study were GPT-4o and Claude 3.5 Sonnet with both achieving 99.5% hit rate.
Table 1 summarizes the most common hits and misses by these two top-performing LLMs.
To boost the diagnostic hit rate of one of the best performing models, GPT-4o, we reduced the errors in the predictions by plugging the knowledge gaps in the model using RAG. GPT-4o with RAG achieved a stunning 99.8% hit rate. A more detailed analysis of this result is reported in [
23].
4. Discussion
In this paper we compared the diagnostic ability of multiple large language models using a previously established method on a subset of the MIMIC-IV dataset. The method uses the ICD codes from the patient record as the ground truth and (1) removes not inferable diagnoses and (2) accepts similar ICD diagnoses as correct predictions when there’s not enough data to infer the exact code.
Others have used ICD chapters [
13] and 515 CCSR categories and 22 CCSR bodies [
24] to compare the diagnostic predictions to the ground truth and reported accuracies at these different levels. While this method is very much helpful for creating a fast and objective evaluation framework, it does not consider if the data available is enough to arrive to the ground truth diagnosis (or to a similar one within the same CCSR category) resulting in a more conservative reported diagnostic accuracy. In other words, by using this method, one assumes that the information in the data used (MIMIC-III in the case of [
24]) is sufficient to make the reported ICD diagnoses. In addition, one major drawback of attempting to predict ICD chapters and CCSR categories is that two physiologically very different diseases may end up in the same category. For example, ‘Type 1 diabetes mellitus without complications’ (ICD-10 code:
E109) and ‘Type 2 diabetes mellitus without complications’ (ICD-10 code
E119) belong to the same CCSR category 1 of
END002. This means that if the LLM predicted type 1 diabetes, but the patient was suffering from type 2 diabetes, the prediction would be deemed correct, even though in practice this would be a serious misdiagnosis. Ironically, closely related conditions may end up in different CCSR categories: ‘chronic kidney disease, stage 1’ (ICD-10 code
N181) is in the
GEN003 CCSR category whereas ‘Hypertensive chronic kidney disease with stage 1 through stage 4 chronic kidney disease, or unspecified chronic kidney disease’ (ICD-10 code
I129) is in the
CIR008 CCSR category. This means that we would penalize the LLM if it does not know that the chronic kidney disease was of hypertensive origin even if it does not have access to the patient history proving so (note that patient blood pressure may appear normal in hypertensive kidney disease due to medication).
Our method uses a more subjective assessment, where we let the LLM agent conducting the evaluation decide whether the prediction is acceptable based on its similarity to the ground truth and given the available data. For example, mixing up type 1 and type 2 diabetes would be considered a miss if there is relevant antibody and C peptide data. At the very least, the model would suggest a further C peptide test (as instructed via the prompt in [
21]) if not already in the data, to confirm the diagnosis. Another advantage of our approach is that it makes the reported hit rate less data dependent by removing the non-inferable diagnoses. However, in an ideal case, complete and detailed patient EHR data is available from multiple hospitals, locations and demographics to test the diagnostic ability of LLMs. While the hit rate of these LLMs on such dataset might be different, we would expect the relative rankings of these models to stay the same.
Throughout our analysis, we took care to report the exact dates when the experiments were conducted to account for potential silent model changes that have happened since. Note that due to the stochastic nature of the LLMs, the same model ran twice may give different results. However, repeating experiments (and the evaluation) have resulted in very similar results without a change to the first number after the decimal point. Hence, we chose the report hit rates with one decimal precision.
RAG is helpful for boosting hit rate as it allows the model to refer to up-to-date clinical reference ranges and diagnostic guidelines: whenever there’s a blood result or symptom mentioned in the text, the LLM receives further information on the diagnostic guidelines resulting in fewer hallucinations [
25] and more consistent output. For example, using RAG helped the GPT-4o model accurately diagnose dehydration which was the top missed diagnosis as reported in
Table 1. We presume this is because of the serum and plasma osmolarity reference ranges in the document used for RAG. We expect fine-tuning these models with a medic-curated dataset will further increase their diagnostic abilities and this is something we’re currently experimenting with.
Finally, we would like to draw attention to the shortcomings of this study: first, we only considered one single dataset, coming from a single hospital. This dataset didn’t contain all information that doctors normally use for diagnosing patients, resulting in excluding some important diagnoses from the analysis as they were deemed non-inferable. In fact, in practice, decision making goes beyond text-based data from the electronic patient record and without an AI system taking multimodal inputs sitting alongside a doctor as part of a proper hospital pilot, it’ll be very difficult to truly compare diagnostic ability of LLMs to that of doctors. In this study we allowed LLMs to make many predictions, however, in practice doctors may need to rely on one single diagnosis and treatment plan, which is their current best estimate. In addition, evaluation was done by an LLM and has not been reviewed manually by a human, let alone a clinician. Moreover, this paper did not assess model biases in the predictions made by the different models, which would be an essential first step towards hospital deployment of LLMs.
5. Conclusions
In this study we compared the diagnostic ability of 9 different LLMs from 6 different companies on 1000 electronic patient records. We found that GPT-4o from OpenAI and Claude Sonnet 3.5 from Anthropic were the top performers with them only missing 0.5% of ground truth conditions that were clearly inferable from the available data. Open-source models, such as Mistral 2 and LlaMA 3.1 performed reasonably well, better than the closed-source models from Google, but worse than alternatives from Cohere, Anthropic and OpenAI. We showed how retrieval augmented generation further improved the hit rate of GPT-4o and even though the numbers look very promising, we cautioned against drawing conclusions about the diagnostic abilities of these models in a real hospital setting.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
References
- Sameera V, Bindra A, Rath GP. Human errors and their prevention in healthcare. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2021 Jul-Sep;37(3):328-335. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman-Toker DE, Nassery N, Schaffer AC, et al. Burden of serious harms from diagnostic error in the USA BMJ Quality & Safety 2024;33:109-120.
- National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. 2015. Improving Diagnosis in Health Care. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press. [CrossRef]
- Newman-Toker DE, Wang Z, Zhu Y, Nassery N, Saber Tehrani AS, Schaffer AC, et al. Rate of diagnostic errors and serious misdiagnosis-related harms for major vascular events, infections, and cancers: toward a national incidence estimate using the “Big Three”. Diagnosis. 2020; 8(1): 67–84.
- Thammasitboon S, Cutrer WB. Diagnostic decision-making and strategies to improve diagnosis. Curr Probl Pediatr Adolesc Health Care. 2013; 43(9): 232–241.
- Wise J. Burnout among trainees is at all time high, GMC survey shows BMJ 2022; 378 :o1796.
- Topol, J.E. Toward the eradication of medical diagnostic errors. Science. 2024;383:1.
- Madrid-García A, Rosales-Rosado Z, Freites-Nuñez D, et al. Harnessing ChatGPT and GPT-4 for evaluating the rheumatology questions of the Spanish access exam to specialized medical training. Sci Rep. 2023;13;22129.
- Rosoł, M., Gąsior, J.S., Łaba, J. et al. Evaluation of the performance of GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 on the Polish Medical Final Examination. Sci Rep 2023;13;20512.
- Brin, D., Sorin, V., Vaid, A. et al. Comparing ChatGPT and GPT-4 performance in USMLE soft skill assessments. Sci Rep 2023;13;16492.
- Kung TH, Cheatham M, Medenilla A, Sillos C, De Leon L, et al. (2023) Performance of ChatGPT on USMLE: Potential for AI-assisted medical education using large language models. PLOS Digital Health 2(2): e0000198.
- Khan MP and O’Sullivan ED (2024) A comparison of the diagnostic ability of large language models in challenging clinical cases. Front. Artif. Intell. 7:1379297. [CrossRef]
- Chiu W, Ko W, Cho W, Hui S, Chan W, Kuo M Evaluating the Diagnostic Performance of Large Language Models on Complex Multimodal Medical Cases J Med Internet Res 2024;26:e53724.
- Warrier A, Singh R, Haleem A, Zaki H, Eloy JA. The Comparative Diagnostic Capability of Large Language Models in Otolaryngology. Laryngoscope. 2024 Sep;134(9):3997-4002. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonoda, Y., Kurokawa, R., Nakamura, Y. et al. Diagnostic performances of GPT-4o, Claude 3 Opus, and Gemini 1.5 Pro in “Diagnosis Please” cases. Jpn J Radiol (2024). [CrossRef]
- Eriksen, Alexander & Möller, Sören & Ryg, Jesper. (2023). Use of GPT-4 to Diagnose Complex Clinical Cases. NEJM AI. 1. [CrossRef]
- Kanjee Z, Crowe B, Rodman A. Accuracy of a Generative Artificial Intelligence Model in a Complex Diagnostic Challenge. JAMA. 2023;330(1):78–80. [CrossRef]
- Hirosawa T, Harada Y, Mizuta K, Sakamoto T, Tokumasu K, Shimizu T Evaluating ChatGPT-4’s Accuracy in Identifying Final Diagnoses Within Differential Diagnoses Compared With Those of Physicians: Experimental Study for Diagnostic Cases JMIR Form Res 2024;8:e59267.
- Shieh, A., Tran, B., He, G. et al. Assessing ChatGPT 4.0’s test performance and clinical diagnostic accuracy on USMLE STEP 2 CK and clinical case reports. Sci Rep 14, 9330 (2024).
- Johnson AEW, Bulgarelli L, Shen L, Gayles A, Shammout A, Horng S, et al.: MIMIC-IV, a freely accessible electronic health record dataset. Sci Data 10(1), 1 (2023).
- Sarvari P, Al-fagih Z, Ghuwel A, Al-fagih O.: A systematic evaluation of the performance of GPT-4 and PaLM2 to diagnose comorbidities in MIMIC-IV patients. Health Care Sci. 3, 3–18 (2024).
- ABIM laboratory reference ranges. Available online: https://www.abim.org/Media/bfijryql/laboratory-reference-ranges.pdf (accessed on 9 March 2024).
- Sarvari, P.; Al-fagih, Z.; Abou-Chedid, A. Rhazes: A generative-AI powered web app to handle all the paperwork and analytical tasks in medicine. Submitted to Diagnostics, manuscript id: diagnostics-3210068.
- Shah-Mohammadi, F.; Finkelstein, J. Accuracy Evaluation of GPT-Assisted Differential Diagnosis in Emergency Department. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang C, Ong J, Wang C, Ong H, Cheng R, Ong D. Potential for GPT Technology to Optimize Future Clinical Decision-Making Using Retrieval-Augmented Generation. Ann Biomed Eng. 2023; 1: 1.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).