1. Introduction
Freshwater and marine ecosystems are vital for the human survival and evolution and are frequently being studied through targeted or shotgun metagenomics. Metagenomics studies of these environments involve extracting genomic DNA (gDNA) from samples and analyzing the diverse organisms present, including bacteria, archaea, eukaryotes and viruses and/or their underlying functional characteristics.
Regardless of methods, study designs and goals, samples of various water volumes are collected, transported to laboratories and optimally processed immediately. The initial step of most bacterial metagenomics studies on water samples involves extracting the biomass (also called enrichment) from the water content. Most often, water samples include small particles such as soil, rocks, plant residues which could be extracted as well due to microorganisms and/or extracellular DNA adhere to those particles or floating free as planktonic forms. In the case of larger sample debris, additional steps are implemented to remove them prior to the biomass extraction. Three main techniques have been developed and used to varying extents for biomass extraction, namely vacuum filtration (VF), ultracentrifugation (UC) and skimmed milk flocculation (SMF). VF is mainly used for characterization of bacterial and fungal communities and is by far considered the gold standard. UC is almost exclusively applied for viral and phage metagenomics, whereas SMF was originally developed to concentrate viruses from coastal waters [
1].
Filtration is a straightforward size exclusion or inclusion method used in metagenomics to separate microbial cells and sample debris from the water by vacuum as pressure-driven factor. However, there are numerous factors influencing the filterability during vacuum filtration such as the membrane protein binding affinity, surface charge, hydrophobicity, pore size and structure, and roughness. Additionally, cell size, shape, flexibility, charge and hydrophobicity also influence the potential of bacteria to flow though the filter, and lastly, the particulate nature of the sample suspension itself [
2]. For those reasons, research in filtration methods is still evolving. On the other hand, SMF is used mainly for concentrating viruses such as SARS-CoV-2 [
3], and others [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6]. SMF is straightforward, affordable, quick to perform, and requires simple laboratory equipment. The flocculation is achieved at 3.5-4.0 pH, where the casein proteins (net positive charge) interact with viral particles from the water samples, which carry a net negative charge due to their functional surface groups like carboxylates and phosphates. The reaction solution is usually agitated at low rpm for approx. 2h, during which through electrostatic interactions, flocs (virus-protein complexes or aggregates) are formed and settle out of the solution either naturally or facilitated through centrifugation at 3500 x g for 30 min [
7]. Previously, SMF has been used for simultaneous concentration and quantification of water-borne viruses, bacteria and protozoa [
8] mainly for water control purposes and microbial risk assessment studies. However, there is a literature gap regarding its applicability in bacterial microbiome studies. Therefore, we used both 16S rRNA and shotgun metagenomics data to observe microbial differences in the taxonomic composition to assess the applicability of SMF for bacterial metagenomics.
Another critical step is the gDNA extraction from filters or precipitates. Numerous studies have assessed the impact of various DNA extraction protocols on the quantitative analysis of bacterial biomass [
9,
10,
11,
12,
13], highlighting the necessity for a standardized protocol yielding reproducible results to facilitate cross-study comparisons, especially in research areas with future health diagnostic perspectives such as human gut microbiota profiling. For instance, according to the largest current comparative study based on shotgun sequencing evaluating the bacterial extraction performance of 21 faecal DNA extraction protocols [
9], the Protocol Q, which is a slightly modified version of Qiagen’s QIAamp DNA Stool Mini Kit, has been proposed as the standard protocol providing the best results for bacterial DNA extraction from human faeces. To date, there is no equivalent DNA extraction protocol for aqueous environmental samples. In addition, due to limited availability or costs, not all studies could afford to use the same protocol, especially commercial ones. For this, we optimised an in-house protocol that involves elements from other published protocol and compared it with four other commercial DNA extraction kits on Mock community standard samples to inform future study designs.
In the case of targeted bacterial metagenomics, after sequencing and the initial quality control of the sequencing data, 16S rRNA databases (DB) are utilised to infer bacterial taxonomic composition. While
de novo clustering approach is often the choice for studies for initial observation it is not directly influenced by 16S databases, closed or open reference clustering approaches utilise 16S rRNA DBs for clustering and are still preferred widely. As a result, 16S rRNA DBs influence the final taxonomic composition. Several studies benchmarked their performance previously [
13,
14,
15,
16], but they undergo constant updates which prompts additional evaluation. Herein, we present a small-scale easy-to-perform benchmarking of six well-established as well as more recently published 16S rRNA DBs on the same set of Mock samples extracted by the five different DNA protocols to evaluate the extent of bias introduced by the choice of 16S rRNA DBs.
This study showed results from comparison of different techniques spanning the three most common critical steps in each metagenomics study: the applicability of SMF for the use of bacterial metagenomics on real samples; the evaluation of a novel DNA extraction method on Mock community standard and on real samples through comparative analysis with other commercially available DNA extraction protocols; and comparison of 16S rRNA databases for taxonomic assignments.
2. Results
First, we evaluated the bias introduced by different DNA extraction protocols and the 16S rRNA DBs on the 16S metagenomics Mock community datasets (
n=8). In total, we scored factors such as DNA yield, A
260/280nm, A
260/230nm, Species-level Taxon accuracy rate (TAR), Genus-level Taxon detection rate (TDR), Measurement Integrity Quotient score (MIQ), percent of reads that mapped to the reference sequences, failed quality filter, failed to merge, or are chimeric (
Supplementary Table S6). The in-house method yielded the highest amount of DNA, whereas highest purity was achieved with the EurX and EZNA kits. EurX kit yielded an overall good results, compared to the other mock samples and at the time of assessment was considered for the shotgun studies.
2.1. MIQ Score Variability in DNA Extraction Protocols
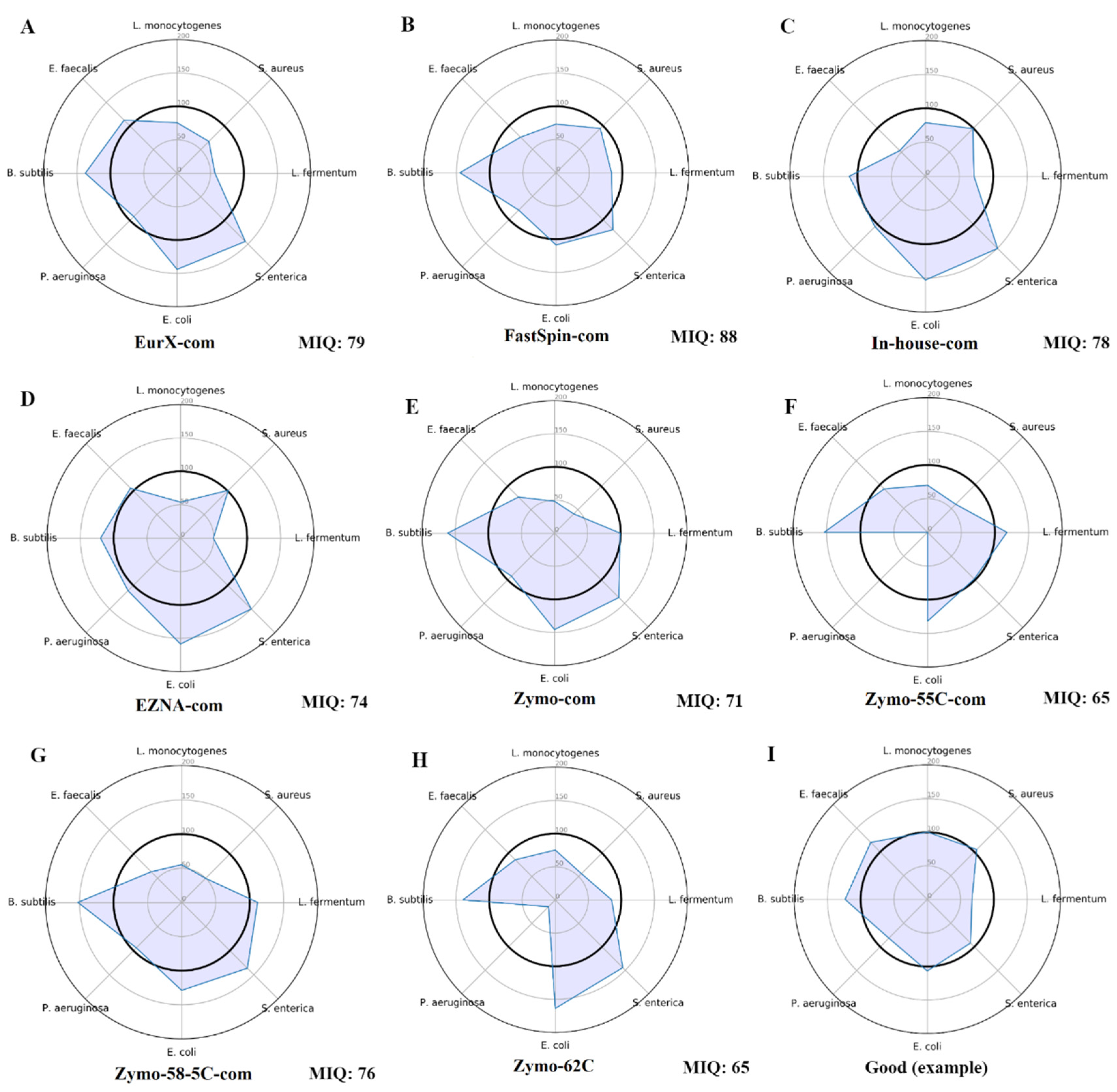
The tool miqScore16SPublic (2.6.) provided by Zymo was used to establish the bias introduced by DNA kits. The complete reports are available in Suppl. File S1, and only the radar plots were provided in
Figure 1. Results indicate that the samples isolated by the FastSpin Soil kit showed the least bias scoring 88 MIQ, followed by EurX, and the in-house method, whereas the worst MIQ scores were in Zymo kit and its datasets with the varying annealing temperatures.
2.2. Bias Introduced by 16S rRNA DBs and/or DNA Extraction Kits on Closed-Reference Clustered Mock Samples
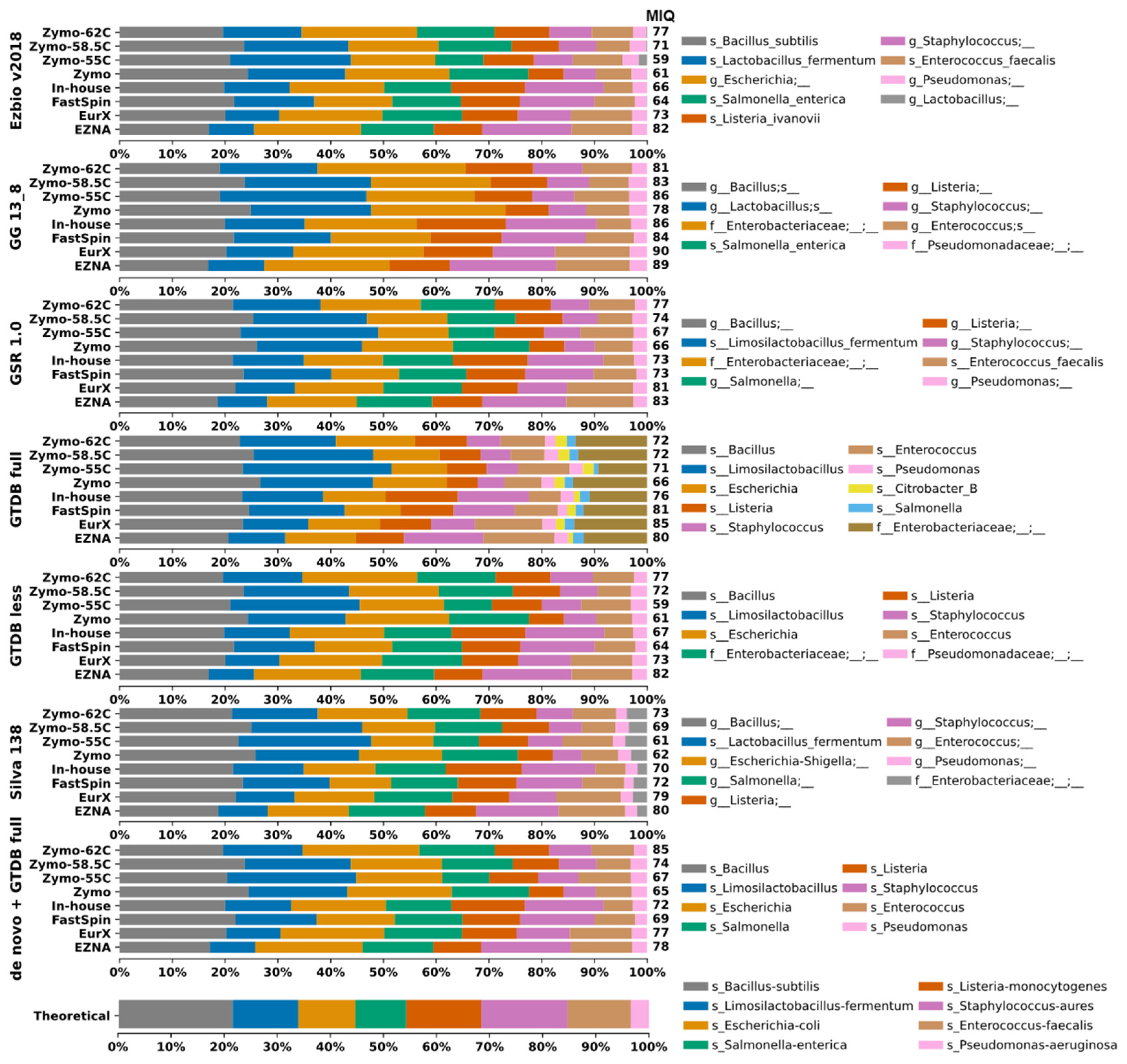
Herein we assessed to what extent the DB could bias the taxonomic composition. For this, closed-reference 99% OTU clustering was applied by using each DB reference sequences. Taxonomic composition plots of all mock samples are visualized on
Figure 2. The DBs GTDB-full and Silva generated more OTUs compared to the remaining DBs. This could be considered both beneficial and negative depending on the study purpose. However, in this case the additional OTU Citrobacter_B in GTDB-full that should not be present in the mock sample is skewing the results, resulting in lower MIQ scores (
Figure 2 and
Figure 4).
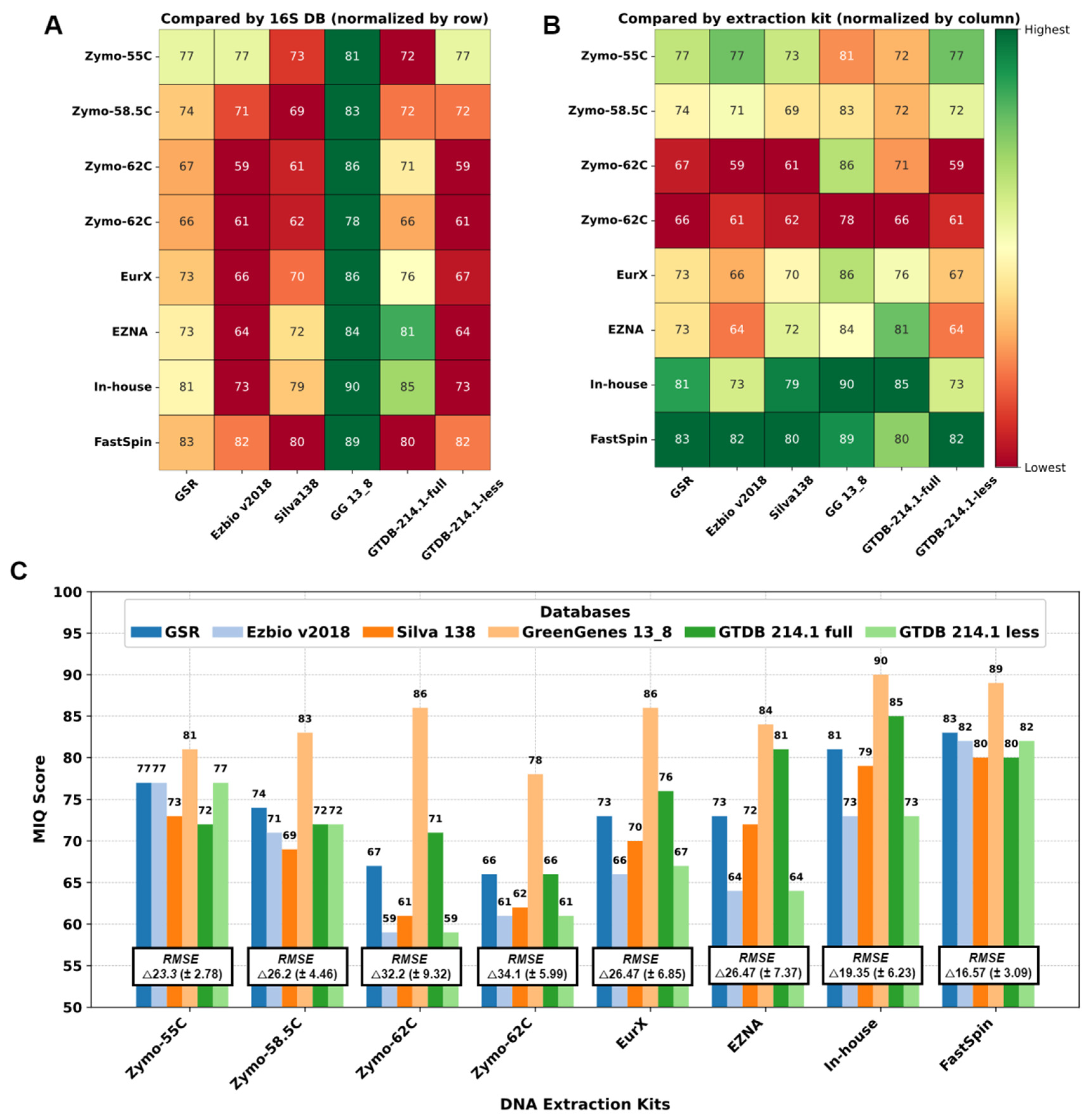
We compared the 16S rRNA DBs and the DNA extraction protocols by MIQ scores in parallel and the results are shown in
Figure 3. First, 16S rRNA DBs were compared (
Figure 3A), and the best theoretical compositions with the least bias were yielded by GG 13_8, followed by GSR and GTDB-214.1-full. Interestingly, GreenGenes database yielded an OTU at family level
Enterobacteriaceae, failing to differentiate
Escherichia coli and
Salmonella enterica. Unfortunately, there was no adequate approach to separate this 99%-clustered OTU for the MIQ calculator to precisely calculate the bias for each microorganism. Therefore, for GG_13.8 specifically, we considered both
E. coli and
S. enterica as a single organism, and adjusted the reference theoretical composition in the MIQ score script. As a result, all the MIQ scores for GG_13.8 DB are elevated compared to the remaining DBs and should be interpreted with caution. We then compared different DNA extraction kits (
Figure 3B), regardless of DB used. Except for ZymoBIOMICs with primer annealing temperature 55°C all the Zymo variants performed worse compared to the others. FastSpin kit yielded the highest MIQs scores (82.6 on average) with all DBs. Second best results were scored by our in-house protocol.
Interestingly, all the 16S DBs except GG_13.8 yielded comparable results with each DNA extraction kits ranging from 59-71 in the worst performing sample (Zymo-62C) up to 80-83 in the best sample (FastSpin). These results suggest that the DNA extraction kit had the largest impact on the final mock composition. The bias in mock samples could not be compensated with the use of a better performing 16S DB (as in the case of both repetitions Zymo-62C in
Figure 3C) and vice versa – a sample treated with good performing DNA extraction kit yields comparable taxonomic compositions resembling the theoretically expected one regardless of the 16S DB used.
Figure 2.
Taxa bar plots of the eight mock samples analyzed with closed-reference clustering with each 16S rRNA Database separately and de novo clustered datasets identified with GTDB-full. A database-specific legends with taxa identification (lowest rank) were provided on the right side. For easier interpretation the resulting MIQ score was provided right next to the bars. Higher MIQ score represents taxonomic composition closer to the theoretically expected one (bottom).
Figure 2.
Taxa bar plots of the eight mock samples analyzed with closed-reference clustering with each 16S rRNA Database separately and de novo clustered datasets identified with GTDB-full. A database-specific legends with taxa identification (lowest rank) were provided on the right side. For easier interpretation the resulting MIQ score was provided right next to the bars. Higher MIQ score represents taxonomic composition closer to the theoretically expected one (bottom).
Figure 3.
Performance of DNA extraction kits and 16S DBs by MIQ score. A. Comparison of 16S DB. B. Comparison of DNA extraction kits/annealing temperatures. Green is better and red is worse. C. Bar graph with the MIQ scores and average root mean square error (RMSE) values.
Figure 3.
Performance of DNA extraction kits and 16S DBs by MIQ score. A. Comparison of 16S DB. B. Comparison of DNA extraction kits/annealing temperatures. Green is better and red is worse. C. Bar graph with the MIQ scores and average root mean square error (RMSE) values.
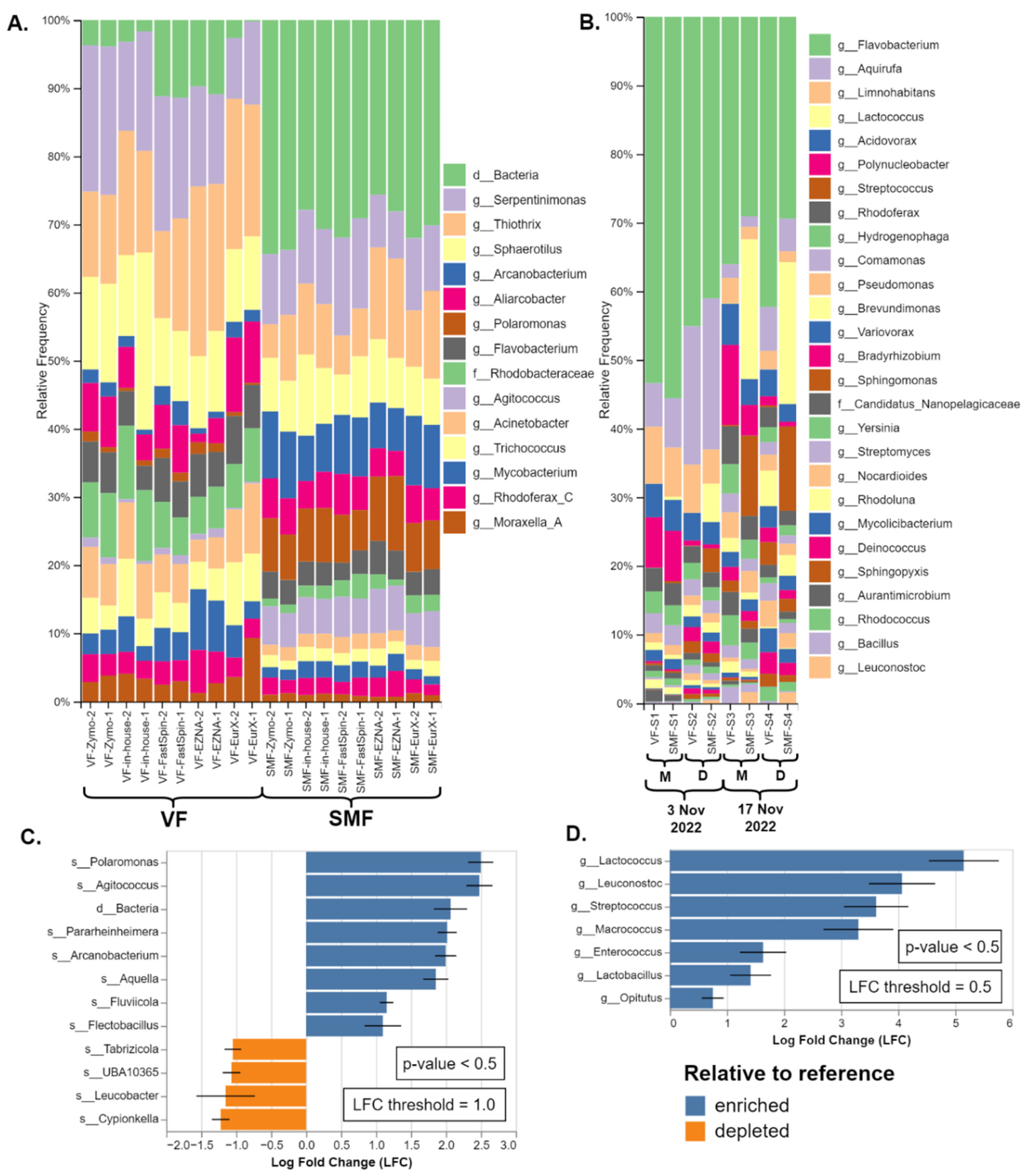
Figure 4.
Comparison of taxonomic composition of SMF and VF. (A) Duplicate datasets from the amplicon metagenomics samples from River Perlovska per DNA Extraction kit. (B) Datasets from the shotgun metagenomics samples from River Iskar. Sample pairs (VF and SMF treated) were ordered by sampling date and location (M - villa area Mechka, D - Dragushinovo village). Differential abundance analysis of the (C) amplicon and (D) shotgun samples with all VF samples pooled as a reference compared to the SMF samples. Only taxa with p value < 0.5 and with log fold change (LFC) ≥ 1.0 (C) and 0.5 (D) were presented.
Figure 4.
Comparison of taxonomic composition of SMF and VF. (A) Duplicate datasets from the amplicon metagenomics samples from River Perlovska per DNA Extraction kit. (B) Datasets from the shotgun metagenomics samples from River Iskar. Sample pairs (VF and SMF treated) were ordered by sampling date and location (M - villa area Mechka, D - Dragushinovo village). Differential abundance analysis of the (C) amplicon and (D) shotgun samples with all VF samples pooled as a reference compared to the SMF samples. Only taxa with p value < 0.5 and with log fold change (LFC) ≥ 1.0 (C) and 0.5 (D) were presented.
2.3. Taxa Identification Efficiency of 16S DBs on de novo Clustered Mock Samples
While taxonomic composition is the first criterion to assess the bias in mock samples, taxon accuracy rating (TAR) and taxon detection rate (TDR) are two important factors which essentially, evaluate how a 16S rRNA DB performs the taxonomical identification. Although, we presented the results as values for each DB, one should note that they are heavily influenced by the amplified region, the choice of OTU vs. ASV approach and should not be considered entirely as drawbacks to the 16S DBs.
The taxon accuracy rating (TAR) and taxon detection rate (TDR) results were calculated with data from 99% de novo clustered OTUs. The 99% OTU-generated results tend to underrepresent
Enterococcus faecalis by splitting it into two separate OTUs
g_Enterococcus and
s_Enterococcus-faecalis with similar relative frequency values in all extraction kits, thus skewing the total microbial composition. For a small Mock community standard with only 8 bacterial strains, results did not vary drastically, and also TAR and TDR scores at each taxonomic level were identical. At species-level the accurate identification varied from 1/8 bacteria for Silva, 2/8 for GSR, and up to 4/8 for Ezbio, while for genus-level was between 6/8 to 8/8 (
Figure 2 and
Suppl. Table S7). GreenGenes 13_8 and GTDB 214.1 were designed for genus-level identification, therefore species-level resolution was not possible and not discussed. Only one case of misclassification was recorded, namely
Listeria monocytogenes identified as
Listeria ivanovii by Ezbio. Underclassifications by two taxonomic levels were observed for
Salmonella enterica in GTDB and Silva, for
Escherichia coli in GreenGenes and GSR. Additionally,
P. aeruginosa was underclassified by two ranks by GreenGenes (
Suppl. Figure S7).
2.4. Evaluation of Skimmed Milk Flocculation
SMF and VF were compared only on real samples as the Zymo Mock standards are not designed to be pre-treated prior to DNA extraction as cells are stored in DNA/RNA Shield
TM and are partially lysed. The relative taxonomic composition of both types of datasets were presented in
Figure 4A and
Figure 5B. Full length figures of the DAA results are available in
Supplementary Figure S2 and S3. In all sample pairs (a pair being VF and SMF treated) noticeable differences were observed by the separation of SMF- and VF-treated samples in the PCoA plots (
Supplementary Figure S4).
In the 16S rRNA amplicon datasets (River Perlovska), genus
Polaromonas, Agitococcus and an unidentified OTU were observed to be overrepresented in the SMF treated samples. In Green Genes and the GSR DBs the
Polaromonas was identified to species-level as
P. naphtalenivorans, while the unidentified OTU was either left at domain
Bacteria, order
Bacteroidales, or identified as family
Saprospiraceae by EzbioCloud (both the free DB v2018 and their website non-free latest DB v2023.08.23). All three taxa and a few more were also shown to be significantly enriched (
p < 0.5) with log fold change (LFC) of 2.0 and above as shown by the DAA in
Figure 4C.
Similar trend was observed in the shotgun metagenomics datasets (River Iskar) but with different enriched taxa. Not all enriched taxa were visible on the bars except for the genera
Streptococcus (brown) and
Lactococcus (pale yellow) in SMF-S2, SMF-S3 and SMF-S4 in
Figure 4B. Sankey plots were provided for better visualization of all taxa in
Supplementary Figure S1. According to the DAA the lactic acid bacteria members
Lactococcus,
Leuconostoc,
Streptococcus,
Enterococcus, and
Lactobacilus were significantly enriched (
p < 0.5) with LFC between 1.75 - 5.0 in the SMF-treated samples. Lastly, the genus
Macrococcus was also significantly overrepresented and Bracken species-level hits are mostly
Macrococcus caseolyticus. Interestingly, genus
Streptococcus was also detected in the amplicon metagenomics samples but was not overrepresented. The complete non-filtered taxonomy tables are available as
supplementary Table S7, S8 and S9.
3. Discussion
This section may be divided by subheadings. It should provide a concise and precise description of the experimental results, their interpretation, as well as the experimental conclusions that can be drawn. This is the first study to evaluate the applicability of SMF in bacterial metagenomics. Despite the small scale of the study design, with the use of DAA analysis it was clearly shown that SMF has skewed the taxonomic composition of real water samples, therefore rendering the SMF technique inapplicable for bacterial enrichment in metagenomics. Interestingly, not all taxa were altered, rather only specific ones. According to a previous study on the concentration of specific species such as
Escherichia coli and
Helicobacter pylori SMF has provided comparable results as expected [
8] and could be used for detection of specific pathogens or indicator species.
Skimmed milk consists mainly of protein (casein and whey) and lactose in addition to other nutrients and minerals that could act as growing factors for bacteria and is usually supplied in culture media. In this regard, it was previously shown that the genus
Polaromonas was enriched in dairy products removal tanks [
17], while other studies have identified it as the third most abundant genus in the mixed-species dairy biofilm on a biofilter [
18]. Genus
Agitococcus was also significantly enriched in SMF-treated samples and while no species level identification was achieved,
Agitococcus lubricus, a species described in 1981 was tested positive for skim milk proteolysis [
19], and members of the genus
Agitococcus would likely be positive as well. Unfortunately, the largest significantly enriched OTU namely the f_
Saprospiraceae (EzbioCloud) or o_
Bacteroidales (Green Genes) or d_
Bacteria (GTDB-full) remained unidentified and no conclusion about its SMF utilization could be drawn. Similarly, in the shotgun datasets from River Iskar, all of the enriched lactic acid bacteria are usually found in decomposing plants and milk products, which produce lactic acid as the major metabolic end product of carbohydrate fermentation by utilizing the lactose from the skimmed milk. The acidification of samples (pH=3.5) during the SMF which facilitates the flocculation process might be advantageous to their replication. Lastly, according to the Bracken reports, most of the
Macrococcus read hits were
Macrococcus caseolyticus, which is again shown to efficiently hydrolyse casein and is a natural component of the secondary microflora in cheeses and sausages [
20,
21]. In conclusion, the skimmed milk was highly likely metabolized during the 2 h. incubation protocol resulting in replication of specific taxa and skewing significantly the final taxonomic composition of SMF-treated samples.
DNA extraction is a critical step in a metagenomics workflow and it is known to be influenced by numerous parameters, which are challenging to evaluate comprehensively. In addition, the choice of the DNA extraction method strongly affect the detection and composition of bacterial communities [
22,
23]. Moreover, in-house methods and protocols and or commercial products are constantly being developed and used widely, therefore cross-study comparison is difficult and either updated benchmarking studies are required or standardization. While, we developed a good performing DNA extraction protocol, further improvements are needed to match the performance of the EurX kit used here. Nevertheless, budget study design could implement the in-house method. Surprisingly, EZNA Universal Pathogen kit is not designed for metagenomics and certainly is not optimized to extract DNA equally from Gram positive and Gram negative as the cell wall of Gram-positive bacteria is composed of a thick layer of peptidoglycan. Nevertheless, it performed more or less equally to other kits such as ZymoBIOMICs, EurX without implementing a bead-beating step, which is presently widely adopted and recommended to facilitate balanced lysis [
24].
Next, our meticulously optimized 16S rRNA amplicon library sequencing protocol has shown good results, yielding MIQ scores ≥ 80 with most of DNA Extraction kits and the in-house method, which according to the Zymo miqScore16SPublic calculator were considered good and validates the real sample results. Nevertheless, benchmarking of sequencing datasets from simultaneous 16S amplicon libraries generating protocols or commercial kits are required to fully evaluate the applicability of the 16S protocol.
In regard to the 16S DBs comparison, we aimed to present the most sample- and primer pairs-specific taxonomic identification by first truncating the reference sequences to the primer regions with the use of in-silico PCR and then building a classifier. This way, the detection and the accuracy of identification of each 16S DB have been adjusted specifically to the used primer pair, thus allowing for normalized comparison. TAR and TDR values were not as informative as initially perceived mainly due to the small number of bacteria included in the Microbial community standard. 16S DB results presented here should be interpret together with the amplified region as identification is also heavily influenced by the amplified region. TAR of resulting OTUs clustered at threshold equal or below 99% usually suffered from identification bias [
25] and as anticipated no 8/8 TAR was achieved with OTUs. While most reliable identification is usually achieved with amplicon sequence variants (ASV), a large portion of studies still rely on OTU clustering [
26,
27].
A few limitations of the study could be listed. The SMF protocol applied in this study was originally optimized for virus concentration. In the literature, SMF protocols adopted or adjusted for bacteria are lacking and additional pre-treatment steps could be implemented to inhibit bacteria growth. Ideally, microbial community standards with higher number of bacteria (20+) would present more insightful results compared to the 8 bacteria community standard used here.
4. Materials and Methods
Both 16S and shotgun metagenomics sets were included in the current study. Chronologically, 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing was performed first. Initially, a novel in-house method for DNA extraction for metagenomics was optimized. Then, Mock Community Standard together with real water samples were used to evaluate and compare the new protocol for metagenomics to other commercial DNA extraction kits followed by a small-scale 16S rRNA databases comparison. Next, the applicability of SMF for both 16S amplicon and shotgun metagenomics was analysed on real water samples only and separately from the comparative studies on mock samples. For the shotgun samples, only one DNA extraction protocol was applied.
4.1. Samples
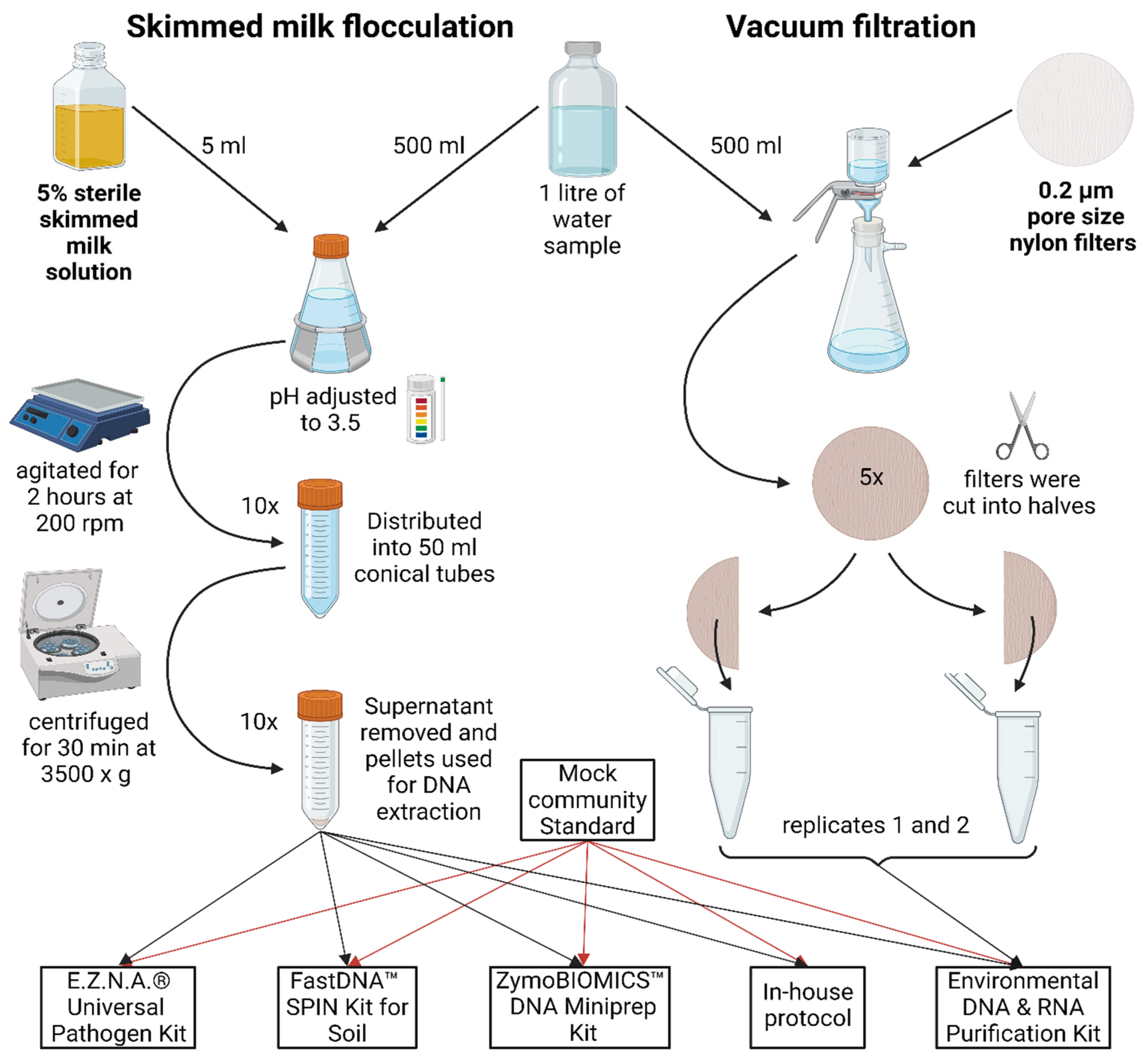
Two different sets of water samples were collected and processed separately. For shotgun metagenomic sequencing four composite water samples (1 litre each) were collected in pairs along the River Iskar from the two locations (42.367698, 23.555463 – Dragushinovo village and 42.431095, 23.531900 – villa area “Mechkata”) with an automatic sampler over the period of 24 h to avoid day-night bias on 3rd Nov 2022 and 17th Nov 2022. They were transferred to the laboratory within 6 h and immediately processed. For 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing one non-composite water sample (1 litre) was collected in a sterile HDPE plastic container from a small urban River Perlovska at location 42.692164, 23.343892 and transported within 30 min to the laboratory. All samples were divided into two equal parts (500 ml) for SMF and VF steps as described in
Figure 5. SMF and VF was applied on both set of samples to analyse the applicability of SMF in both 16S and shotgun bacterial metagenomics.
Figure 5.
Graphical representation of the SMF and VF water treatment steps. In brief, the sample was divided into equal parts. For SMF, the sample was adjusted to 0.05% skimmed milk, with pH 3.5-4.0, agitated at slow speed for 2 h, aliquoted and centrifuged at 3500 x g for 30 min. For VF, the sample was further divided into 100 ml portions and filtered through 0.2 µm nylon filters, aseptically cut into smaller pieces and added to DNA extraction tubes. A pair of two tubes with pellets / filters were resuspended in lysis buffer from each kit / protocol.
Figure 5.
Graphical representation of the SMF and VF water treatment steps. In brief, the sample was divided into equal parts. For SMF, the sample was adjusted to 0.05% skimmed milk, with pH 3.5-4.0, agitated at slow speed for 2 h, aliquoted and centrifuged at 3500 x g for 30 min. For VF, the sample was further divided into 100 ml portions and filtered through 0.2 µm nylon filters, aseptically cut into smaller pieces and added to DNA extraction tubes. A pair of two tubes with pellets / filters were resuspended in lysis buffer from each kit / protocol.
4.2. Skim Milk Flocculation
For SMF a previously described protocol was used [
7]. In brief, 5% skim milk (HiMedia Laboratories) was autoclaved for 15 minutes at 115°C, 18 psi. Five ml of the 5% pre-flocculated skim milk solution was added to 500 ml sample to achieve 0.05% final skim milk concentration. The sample pH was adjusted to 3.5-4.0 with 1M HCl, placed on a horizontal shaker and agitated at 200 rpm for 2 h at room temperature. It was then distributed into 50 ml conical tubes, and centrifuged at 3500 x g for 30 min at 4⁰C. The supernatant was decanted and tubes left upside down to drain residual water for 5 min. Pellets were subjected to DNA extraction (see 2.4.).
4.3. Vacuum Filtration
The samples were subjected to VF through 47 mm diameter 0.2 µm pore size nylon filters (Cytiva, Whatman™), using Lafil 400 - LF 30 Filtration System (Rocker). The sample from River Perlovska (16S amplicon metagenomics) was divided among five filters (100 ml each) and subjected to the five DNA extraction kits (2.4.), while for River Iskar samples (shotgun metagenomics), the entire volume of 500 ml was filtered through one filter and extracted with only one DNA extraction kit (see 2.4). Regardless of the sample sets, each filter was cut sterilely in two equal halves to be further extracted in pairs. Each half was further cut into smaller pieces for better homogenization and directly added to extraction tubes (see 2.4.).
4.4. DNA Extraction
The four DNA extraction kits and the in-house protocol, were evaluated in parallel only on the Perlovska River and Mock samples in duplicates. The following kits used were by adhering to the manufacturer instructions: 1) E.Z.N.A. Universal Pathogen Kit (OMEGA Bio-Tek, Inc., USA); 2) ZymoBIOMICS DNA Miniprep Kit (Zymo Research, USA); 3) FastDNA Spin Kit for Soil (MP Biomedicals, LLC, Germany); and 4) Environmental DNA & RNA Purification Kit (EURx Sp. z o.o., Poland). The in-house protocol was developed by combining elements from other published protocols [
28] with slight modifications and optimised locally. Complete detailed protocol and reagents are provided in Suppl.
Tables S1. The Microbial Community Standard used herein was (ZymoBIOMICS, Zymo Research, cat. D6300), from which we obtained five DNA samples. The Perlovska River water sample was split into SMF-treated and VF-treated portions, and each was subjected to five DNA extraction methods, resulting in ten DNA samples (
Figure 5). Next, DNA from the Iskar River samples were extracted with Environmental DNA & RNA Purification Kit (EURx Sp. z o.o., Poland).
4.5. 16S rRNA and “Shotgun” Metagenomics
16S rRNA metagenomics was applied on Perlovska river samples and Mock community standard samples. The 16S rRNA V3-V4 region was amplified with previously published primer pairs Pro341F and Pro805R [
29] and with a rigorously optimized 16S rRNA amplification protocol described in
Suppl. Tables S2÷S5. Sequencing was carried out on Illumina MiSeq V3 (2x300bp). Additionally, for the Zymo miniprep DNA kit we used the same DNA sample in three additional amplification reactions with primer annealing temperature gradient (55℃, 58.5℃, 62℃), therefore resulting in 8 Mock Community Standard and ten Perlovska River datasets.
Shotgun metagenomics was applied on Iskar River samples and a single Mock community standard (used for pre-sequencing quality control). NGS libraries were constructed Illumina DNA Prep kit (Illumina, Inc., San Diego, California, U.S.) with 50 ng genomic DNA input. The libraries were pooled and sequenced on NextSeq 550 with V2.5 Mid Output kit (2 x 150 bp) (Illumina, San Diego, California, U.S.).
4.6. Bioinformatic Analysis
For DNA extractions and 16S rRNA DBs comparisons with Mock samples we used the Qiime2 platform [
30] and miqScore16SPublic tool (
https://github.com/Zymo-Research/miqScore16SPublic, accessed on 22.07.2024) to determine which DNA extraction kit yields microbial composition of mock samples closest to the “ground truth”. Raw reads were automatically demultiplexed and trimmed from adapters in BaseSpace. Next, cutadapt v4.6 was used to remove the 16S rRNA primers and trim low quality bases (<20 Q at 5’end, and <15 Q at 3’end). We used six 16S rRNA DBs and trained classifiers (n=6) locally. First, full-length 16S DBs (Silva 138-99%-OTU, GSR-99%-OTU, GTDB-214.1-99%-OTU-less, GTDB-214.1-99%-OTU-full, GreenGenes-13_8-99%-OTU, EzBio-Cloud-v.2018) were downloaded. Reference sequences were extracted based on
in-silico PCR with the 16S primer pairs, and used as input for the Naïve-bayes algorithm within sk-learn to train personalized classifiers with default parameters, used later for taxonomic assignments with confidence index at 0.7 (default). Both
de novo and
closed-reference clustered (for each 16S rRNA DB) OTUs were obtained at 99% for each mock dataset.
De novo clustered OTUs provided an equal starting basis to efficiently compare the identification accuracy and detection limits of each 16S rRNA DBs, as the taxonomic composition of all resulting OTUs is the same regardless of the DB. For this we used the “evaluate-composition” plugin [
31] in Qiime2 to compare the expected and observed features, the taxon detection and taxon accuracy rates.
On the other hand,
closed-reference OTUs are clustered according to each 16S rRNA DB and thus influence the final taxonomic composition. To evaluate the composition the miqScore16SPublic tool was used, as it calculates a MIQ score (ranging from 0 to 100), a numeric value to assess the bias between the observed and the theoretically expected microbial profile. However, it was designed to function only with raw reads and performs amplicon sequence variants (ASV) instead of OTUs. And while we used to as is and considered the obtained MIQ scores as reference, it could not be used with OTU tables obtained from our
closed-reference clustered OTUs. For this we used the miqScore16SPublic intrinsic formula for MIQ score calculation in a separate Python script (
https://github.com/maddne/MIQ-calc-from-OTU-tables), which accepts OTU tables as input regardless of their origin.
Next, for comparison of SMF and VF we used differential abundance analysis (DAA). Taxonomic assignment to raw reads was performed with Kraken2 v2.1.2 [
32] with the PlusPF (Standard plus Refeq protozoa & fungi), built in January 2023, followed by Bracken v2.8 [
33] as described in protocol [
34]. The resulting OTU count tables were imported into Qiime2 platform, filtered from low count taxa (
n=20 in at least 3 samples), and used for differential abundance analysis with ANCOM-BC2 plugin [
35].
5. Conclusion
In this study, we systematically evaluated the effectiveness of SMF for bacterial metagenomics, introduced and benchmarked a novel in-house DNA extraction method against four commercial kits, and assessed the performance of six 16S rRNA databases for taxonomic identification.
The findings reveal that skimmed milk flocculation is unsuitable for bacterial microbiome studies as it significantly alters the microbial composition due to the proliferation of lactic acid or casein utilizing bacteria, leading to an increased relative abundance compared to the traditional vacuum filtration method. Our in-house DNA extraction protocol demonstrated competitive performance, particularly in comparison to the commercial kits, which were rigorously optimized for minimal bias. This in-house protocol provides a cost-effective alternative for researchers with limited access to commercial kits, offering robust and reliable results for metagenomic studies.
Lastly, the evaluation of 16S rRNA databases showed that while there are variances in taxonomic assignments, the choice of DNA extraction protocol has a more pronounced impact on the microbial composition than the choice of 16S rRNA database. This underscores the importance of selecting an appropriate DNA extraction method to minimize biases in metagenomic studies. This comprehensive benchmarking study offers critical insights for designing future water metagenomic studies, emphasizing the importance of method selection at various stages to ensure accurate and reliable microbial community profiling.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on
Preprints.org. Suppl. File 1: Mock-standard-reports-from-miqScore16SPublic; Suppl. Figure S1: Sankey plots of Bracken Genus-level reports; Suppl. Figure S2: Differential abundance analysis in full length of the 16S amplicon metagenomics; Suppl. Figure S3: Differential abundance analysis in full length of the shotgun metagenomics; Suppl. Figure S4: PCoA plots separating the SMF-treated and VF-treated samples; Suppl. Table S1: In-house DNA extraction protocol suitable for metagenomic studies; Suppl. Table S2: 16S rRNA amplification with Pro primers; Suppl. Table S3: 16S amplicon clean-up; Suppl. Table S4: index PCR 16S rRNA Pro; Suppl. Table S5: 16S amplicon clean-up and double size selection; Suppl. Table S6: DNA extraction kits on Mock community samples; Suppl. Table S7: Amplicon metagenomics - River Perlovksa - 99OTUs-GTDB-full; Suppl. Table S8: mpa-style species-level Bracken combined reports from shotgun metagenomic samples from River Iskar; Suppl. Table S9: mpa-style genus-level Bracken combined reports from shotgun metagenomic samples from River Iskar
Author Contributions
“Conceptualization, D.D. and I.I.; methodology D.D. and I.I.; software, D.D. and I.S.; validation, D.D. and I.I. and I.S.; formal analysis, D.D.; investigation, D.D. and I.I.; resources, I.I. and A.D.; data curation, D.D. and I.S.; writing—original draft preparation, D.D.; writing—review and editing, I.I., I.S., A.D.; visualization, D.D. and I.S.; supervision, I.I.; project administration, I.I. and A.D.; funding acquisition, I.I. and A.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.”
Funding
This research was funded by the European Regional Development Fund through the Operational Program Science and Education for Smart Growth 2014–2020; Grant BG05M2OP001-1.002-0001-C04 “Fundamental Translational and Clinical Research in Infection and Immunity” and Biocampus Sofia Association. The article processing charges was covered by ELTA 90 M.
Data Availability Statement
All used data is included in the main text and in the
Supplementary Materials. Shotgun metagenomic data is available under the Bioproject PRJNA1071831. Amplicon metagenomic data is available under the Bioproject PRJNA1138176. Generated information and/or datasets analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Acknowledgement
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support provided by Biocampus Sofia Association (
https://biocampus.bg/), a Bulgaria-based non-profit organization dedicated to advancing biotechnologies, life sciences, and digital health ecosystems, fostering industry-academia collaboration, and promoting scientific innovation. The authors would like to thank the Biocampus Sofia and Sofiyska Voda AD for arranging the sampling, storage and transport to the laboratory of the River Iskar samples subjected to shotgun metagenomics.
Conflicts of Interest
The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- B. Calgua, A. Mengewein, A. Grunert, et al., “Development and application of a one-step low cost procedure to concentrate viruses from seawater samples,” J. Virol. Methods, vol. 153, no. 2, pp. 79–83, Nov. 2008 (PMID:18765255) URL: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18765255/.
- C. F. Nnadozie, J. Lin, and R. Govinden, “Selective isolation of bacteria for metagenomic analysis: Impact of membrane characteristics on bacterial filterability,” Biotechnol. Prog., vol. 31, no. 4, pp. 853–866, Jul. 2015 (PMID:26018114) URL: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/btpr.2109.
- S. E. Philo, A. Q. W. Ong, E. K. Keim, et al., “Development and Validation of the Skimmed Milk Pellet Extraction Protocol for SARS-CoV-2 Wastewater Surveillance,” Food Environ. Virol., vol. 14, no. 4, Dec. 2022 (PMID:35143035) URL: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35143035/.
- K. Yanaç, J. Francis, J. Zambrano-Alvarado, Q. Yuan, and M. Uyaguari-Díaz, “Concentration of Virus Particles from Environmental Water and Wastewater Samples Using Skimmed Milk Flocculation and Ultrafiltration,” JoVE (Journal Vis. Exp., vol. 2023, no. 193, p. e65058, Mar. 2023 (PMID:37010296) URL: https://www.jove.com/v/65058/concentration-virus-particles-from-environmental-water-wastewater.
- A. S. F. Assis, M. H. Otenio, B. P. Drumond, T. M. Fumian, M. P. Miagostovich, and M. L. da Rosa e Silva, “Optimization of the skimmed-milk flocculation method for recovery of adenovirus from sludge,” Sci. Total Environ., vol. 583, pp. 163–168, Apr. 2017 (PMID:28094048) URL: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28094048/.
- E. Borgmästars, S. Persson, M. Hellmér, M. Simonsson, and R. Eriksson, “Comparison of Skimmed Milk and Lanthanum Flocculation for Concentration of Pathogenic Viruses in Water,” Food Environ. Virol., vol. 13, no. 3, pp. 380–389, Sep. 2021 (PMID:33974212) URL: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12560-021-09477-x.
- D. Abraham, V. R. Mohan, and G. Kang, “Skimmed Milk Flocculation Technique for Waste Water,” May 2021 URL: https://www.protocols.io/view/skimmed-milk-flocculation-technique-for-waste-wate-buzmnx46.
- E. Gonzales-Gustavson, Y. Cárdenas-Youngs, M. Calvo, et al., “Characterization of the efficiency and uncertainty of skimmed milk flocculation for the simultaneous concentration and quantification of water-borne viruses, bacteria and protozoa,” J. Microbiol. Methods, vol. 134, pp. 46–53, Mar. 2017 (PMID:28093213).
- P. I. Costea, G. Zeller, S. Sunagawa, et al., “Towards standards for human fecal sample processing in metagenomic studies,” Nat. Biotechnol. 2017 3511, vol. 35, no. 11, pp. 1069–1076, Oct. 2017 (PMID:28967887) URL: https://www.nature.com/articles/nbt.3960.
- A. Wesolowska-Andersen, M. I. Bahl, V. Carvalho, et al., “Choice of bacterial DNA extraction method from fecal material influences community structure as evaluated by metagenomic analysis,” Microbiome, vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 1–11, Jun. 2014 URL: https://microbiomejournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/2049-2618-2-19.
- M. Y. Lim, E. J. Song, S. H. Kim, J. Lee, and Y. Do Nam, “Comparison of DNA extraction methods for human gut microbial community profiling,” Syst. Appl. Microbiol., vol. 41, no. 2, pp. 151–157, Mar. 2018 (PMID:29305057) URL: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29305057/.
- J. P. Shaffer, C. S. Carpenter, C. Martino, et al., “A Comparison of Six DNA Extraction Protocols for 16S, ITS and Shotgun Metagenomic Sequencing of Microbial Communities,” Biotechniques, vol. 73, no. 1, pp. 34–46, Jun. 2022 (PMID:35713407) URL: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.2144/btn-2022-0032.
- C. Elie, M. Perret, H. Hage, et al., “Comparison of DNA extraction methods for 16S rRNA gene sequencing in the analysis of the human gut microbiome,” Sci. Reports 2023 131, vol. 13, no. 1, pp. 1–12, Jun. 2023 (PMID:37355726) URL: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-023-33959-6.
- K. Dixit, D. Davray, D. Chaudhari, et al., “Benchmarking of 16S rRNA gene databases using known strain sequences,” Bioinformation, vol. 17, no. 3, p. 377, Mar. 2021 (PMID:34092959) URL: /pmc/articles/PMC8131573/.
- A. Hiergeist, J. Ruelle, S. Emler, and A. Gessner, “Reliability of species detection in 16S microbiome analysis: Comparison of five widely used pipelines and recommendations for a more standardized approach,” PLoS One, vol. 18, no. 2, p. e0280870, Feb. 2023 (PMID:36795699) URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0280870.
- L.-A. G. Molano, S. Vega-Abellaneda, and C. Manichanh, “GSR-DB: a manually curated and optimized taxonomical database for 16S rRNA amplicon analysis,” mSystems, vol. 9, no. 2, Feb. 2024 (PMID:38189256) URL: https://journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/msystems.00950-23.
- B. Gil-Pulido, E. Tarpey, W. Finnegan, X. Zhan, A. D. W. Dobson, and N. O’Leary, “Dominance of the genus Polaromonas in the microbial ecology of an Intermittently Aerated Sequencing Batch Reactor (IASBR) treating dairy processing wastewater under varying aeration rates,” J. Dairy Res., vol. 85, no. 3, pp. 388–390, Aug. 2018 (PMID:30088464) URL: https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/journal-of-dairy-research/article/abs/dominance-of-the-genus-polaromonas-in-the-microbial-ecology-of-an-intermittently-aerated-sequencing-batch-reactor-iasbr-treating-dairy-processing-wastewater-under-varying-aeration-rates/408F705A2F5326C109608BE1B424098F.
- L. Yuan, H. Dai, G. He, Z. Yang, and X. Jiao, “Invited review: Current perspectives for analyzing the dairy biofilms by integrated multiomics,” J. Dairy Sci., vol. 106, no. 12, pp. 8181–8192, Dec. 2023 (PMID:37641326).
- P. D. Franzmann and V. B. D. Skerman, “Agitococcus lubricus gen. nov. sp. nov., a lipolytic, twitching Coccus from freshwater,” Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol., vol. 31, no. 2, pp. 177–183, Apr. 1981 URL: https://www.microbiologyresearch.org/content/journal/ijsem/10.1099/00207713-31-2-177.
- S. Mazhar, K. N. Kilcawley, C. Hill, and O. McAuliffe, “A Systems-Wide Analysis of Proteolytic and Lipolytic Pathways Uncovers The Flavor-Forming Potential of The Gram-Positive Bacterium Macrococcus caseolyticus subsp. caseolyticus,” Front. Microbiol., vol. 11, Jul. 2020 URL: /pmc/articles/PMC7358451/.
- J. E. Keller, S. Schwendener, J. Neuenschwander, G. Overesch, and V. Perreten, “Prevalence and characterization of methicillin-resistant Macrococcus spp. in food producing animals and meat in Switzerland in 2019,” Schweiz. Arch. Tierheilkd., vol. 164, no. 2, pp. 153–164, 2022 (PMID:35103598).
- K. B. E., B. Lasse, M. Patrick, et al., “Impact of Sample Type and DNA Isolation Procedure on Genomic Inference of Microbiome Composition,” mSystems, vol. 1, no. 5, p. 10.1128/msystems.00095-16, Oct. 2016. [CrossRef]
- F. Fouhy, A. G. Clooney, C. Stanton, M. J. Claesson, and P. D. Cotter, “16S rRNA gene sequencing of mock microbial populations-impact of DNA extraction method, primer choice and sequencing platform,” BMC Microbiol., vol. 16, no. 1, pp. 1–13, Jun. 2016 (PMID:27342980) URL: https://link.springer.com/articles/10.1186/s12866-016-0738-z.
- N. A. Kennedy, A. W. Walker, S. H. Berry, et al., “The Impact of Different DNA Extraction Kits and Laboratories upon the Assessment of Human Gut Microbiota Composition by 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing,” PLoS One, vol. 9, no. 2, p. e88982, Feb. 2014 (PMID:24586470) URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0088982.
- R. C. Edgar, “Accuracy of taxonomy prediction for 16S rRNA and fungal ITS sequences,” PeerJ, vol. 2018, no. 4, 2018 URL: /pmc/articles/PMC5910792/.
- B. J. Callahan, P. J. McMurdie, and S. P. Holmes, “Exact sequence variants should replace operational taxonomic units in marker-gene data analysis,” ISME J. 2017 1112, vol. 11, no. 12, pp. 2639–2643, Jul. 2017 (PMID:28731476) URL: https://www.nature.com/articles/ismej2017119.
- M. Chiarello, M. McCauley, S. Villéger, and C. R. Jackson, “Ranking the biases: The choice of OTUs vs. ASVs in 16S rRNA amplicon data analysis has stronger effects on diversity measures than rarefaction and OTU identity threshold,” PLoS One, vol. 17, no. 2, p. e0264443, Feb. 2022 (PMID:35202411) URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0264443.
- P. Harkes, A. K. A. Suleiman, S. J. J. van den Elsen, et al., “Conventional and organic soil management as divergent drivers of resident and active fractions of major soil food web constituents,” Sci. Reports 2019 91, vol. 9, no. 1, pp. 1–15, Sep. 2019 (PMID:31534146) URL: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-019-49854-y.
- S. Takahashi, J. Tomita, K. Nishioka, T. Hisada, and M. Nishijima, “Development of a Prokaryotic Universal Primer for Simultaneous Analysis of Bacteria and Archaea Using Next-Generation Sequencing,” PLoS One, vol. 9, no. 8, p. e105592, Aug. 2014 (PMID:25144201) URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0105592.
- E. Bolyen, J. R. Rideout, M. R. Dillon, et al., “Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2,” Nat. Biotechnol. 2019 378, vol. 37, no. 8, pp. 852–857, Jul. 2019 (PMID:31341288) URL: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41587-019-0209-9.
- N. A. Bokulich, B. D. Kaehler, J. R. Rideout, et al., “Optimizing taxonomic classification of marker-gene amplicon sequences with QIIME 2’s q2-feature-classifier plugin,” Microbiome, vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 1–17, May 2018 (PMID:29773078) URL: https://microbiomejournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s40168-018-0470-z.
- D. E. Wood, J. Lu, and B. Langmead, “Improved metagenomic analysis with Kraken 2,” Genome Biol., vol. 20, no. 1, pp. 1–13, Nov. 2019 (PMID:31779668) URL: https://genomebiology.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13059-019-1891-0.
- J. Lu, F. P. Breitwieser, P. Thielen, and S. L. Salzberg, “Bracken: Estimating species abundance in metagenomics data,” PeerJ Comput. Sci., vol. 2017, no. 1, p. e104, Jan. 2017 URL: https://peerj.com/articles/cs-104.
- J. Lu, N. Rincon, D. E. Wood, et al., “Metagenome analysis using the Kraken software suite,” Nat. Protoc. 2022 1712, vol. 17, no. 12, pp. 2815–2839, Sep. 2022 (PMID:36171387) URL: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41596-022-00738-y.
- H. Lin and S. Das Peddada, “Analysis of compositions of microbiomes with bias correction,” Nat. Commun., vol. 11, no. 1, Dec. 2020 (PMID:32665548) URL: /pmc/articles/PMC7360769/.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).