1. Introduction
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a systemic autoimmune disease characterized by chronic inflammation, abnormal synovial proliferation, and the formation of pannus [
1]. These manifestations mainly apparent in the synovial joints, ultimately resulting in the destruction of diarthrodial joints [
2]. Condition of RA progressively worsens follows a pattern of alternating between periods of disease quiescence and progression, as well as activity and remission [
3]. One key aspect of the development of RA involves the proliferation of stressed cells, while evading immune destruction and apoptosis is crucial [
4]. As inflammatory infiltration increases, there is irreversible destruction of articular cartilage and bone tissue. Failure to address this promptly in the joint can lead to chronicity with resultant joint damage and deformity [
5]. The long-term consequences of the disease are, characterized by significant morbidity, loss of functional capacity, permanent disability, and increased mortality, presenting a significant challenge for contemporary society [
6].
The treatment of RA has undergone two significant paradigm shifts, greatly improving the quality of life for patients. The first shift occurred with the development of disease-modifying drugs, which not only alleviated symptoms but also slowed down or even prevented joint damage [
7]. The second came with the introduction of targeted therapy through the use of biologic agents [
8,
9]. Currently, the therapeutic goal of rheumatologists is the implementation of drug-free remission [
10]. Ultimately, of course, achieving prolonged or life-long drug-free remission would essentially be equivalent to a cure [
11]. While presently therapies have shown success in achieving drug-free remission in some patients, they are not effective for all individuals and were not originally designed with the goal of achieving this outcome in mind [
12]. Newer therapies are being intentionally designed to leverage the body’s natural ability to reduce immune-mediated inflammation [
13]. These approaches involve developing therapies that enhance the quantity or function of regulatory cells to facilitate the re-establishment and restoration of immunological tolerance, along with the administration of natural anti-inflammatory and/or pro-resolution molecules [
14]. Despite these advances in the management of RA, the significant unmet need remains the development of therapies that can induce a cure: prolonged periods of drug-free remission [
15].
Currently, clinical treatment measures for early stages of RA are still quite limited, with options mainly focused on relieving clinical symptoms [
16]. Research efforts have led to some progress in developing treatments for RA, however, despite following current management recommendations and trying multiple treatment options, many patients still struggle to effectively control the activity and progression of the disease [
17]. The emergence of serious symptoms or refractory RA may occur as a consequence, potentially requiring end-stage joint replacement surgery, thereby placing considerable strain and burden on individuals, their families, and the society [
18]. The complexity of RA pathogenesis and the multifaceted nature of its treatment present ongoing challenges in this field [
19]. The theoretical framework surrounding RA is still evolving and lacks a unified consensus [
20]. Additionally, clinical manifestations in RA patients exhibit both similarities and differences, encompassing disease activity, progression, treatment approaches, and prognostic outcomes [
3]. The pathogenic process is most probably initiated by the presentation of an autoantigenic peptide by an antigen presenting cell to a T-helper cell, leading to a pro-inflammatory cascade of cytokine release and bystander interactions [
21]. Pathogenesis is driven by an imbalance in secretion of pro-/anti-inflammatory cytokines, induction of pro-inflammatory mediators such as stress proteins, reactive oxygen species (ROS) and enzymes, and ultimately dysregulation of bone metabolism resulting in bone erosion [
22,
23].
The resolution of acute inflammation and reinstatement of immunological homeostasis following an immune response are essential for preventing chronic inflammation in RA [
10]. Therefore, a sophisticated network of anti-inflammatory, pro-resolution and immunoregulatory cells and molecules counteract the predominantly inflammatory networks initiated following immunological recognition of pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) and/or damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) [
10]. DAMPs are endogenous intracellular molecules that are specifically and rapidly released into the surrounding extracellular space at times of cellular stress or damage to serve as danger signals to the immune system, alerting it of a threat to tissue viability and initiating inflammation. DAMPs are integral part of immune response. At low concentrations, these molecules help regulate homeostasis and correct altered physiological states. However, when present in high amounts, DAMPs can intensify and spread inflammatory responses. Excessive release of DAMPs resulting from trauma or inflammation can induce immune activation in surrounding cells and recruitment of distant cells. This causes further tissue damage, thus creating vicious cycles of injury, ultimately contributing to the development of chronic inflammation [
24]. The DAMP family consists of various molecules such as high mobility group box protein 1 (HMGB1), adenosine triphosphate (ATP), uric acid, heat shock protein 70 (HSP70), and the S100 calcium-binding proteins family [
10,
25]. These DAMPs have the ability to activate and sustain immune responses in the absence of infectious agents, making them critical to the sterile inflammation observed in many pathologies like trauma, ischemia, allergies, cancers, neurodegenerative diseases, and autoimmune diseases [
26,
27]. While sterile inflammatory processes are necessary for maintaining immunological balance, they can also contribute to the development of autoimmune disorders, such as RA [
25].
Immune mechanisms in RA are regulated by a diverse group of endogenous proteins [
14]. These proteins can be broadly categorized into two main groups: pro-inflammatory DAMPs and anti-inflammatory resolution-associated molecular patterns (RAMPs) [
10]. However, it is important to note that there is significant overlap in the activities of some molecules, exhibiting both DAMP- and RAMP-like properties. RAMPs, a heterogeneous collection of molecules, resemble DAMPs in that they are released from injured cells and frequently engage with pattern-recognition receptors (PRRs) on neighboring cells [
10]. Nevertheless, unlike DAMPs, the predominant cellular effect of RAMPs is to suppress the secretion of cytotoxins and pro-inflammatory agents by immune cells [
10]. This positions most RAMPs as pivotal in modulating the immune response, facilitating the resolution of inflammation, and contributing significantly to homeostasis maintenance within the body [
28]. The RAMPs deliver anti-inflammatory and pro-resolution signals into immune networks when decompartmentalized from within the cell [
10]. Additionally, through their ability to promote the resolution of inflammation, RAMPs may herald novel immunotherapeutics, capable of inducing drug-free remission in patients with autoinflammatory disease [
10,
29].
Molecular chaperones are now acknowledged as key regulators of cellular homeostasis in both health and disease, extending beyond their originally identified function as protein foldases [
30]. One important immunomodulating chaperone involved in cellular stress response is the 78-kDa glucose-regulated protein (GRP78), also referred to as binding immunoglobulin protein (BiP), which is coded by the HSPA5 gene and belongs to HSP70 family. What sets GRP78/BiP apart from other HSP70 members found in cytosol is its signal sequence that targets it to endoplasmic reticulum (ER) [
31]. As a prominent ER chaperone, GRP78/BiP is well established to have a crucial role in the folding and processing of newly synthesized membrane-bound or secretory proteins [
31]. Through interacting with the transmembrane ER stress sensors, GRP78/BiP further serves as a vital regulator of the unfolded protein response (UPR), a mechanism that allows cells to adjust to proteotoxic stress [
31]. This response is evolutionarily conserved and is frequently observed in conditions such as oncogenic, metabolic, neurological disorders, and autoinflammatory diseases [
32]. The conventional perception of GRP78/BiP and other ER chaperones solely as luminal ER proteins has transformed with the revelation that ER stress not only boosts their expression to regulate ER protein quality control but also actively promotes their relocation to other cellular sites, where they perform novel regulatory functions beyond the ER [
33]. This paradigm shift in perspective signifies a substantial evolution in understanding the roles of GRP78/BiP [
34].
The ER lumen contains a single Hsp70 chaperone, GRP78/BiP, which operates through reversible chaperone repression as the regulatory principle of UPR activity [
33]. However, the specific impact of GRP78/BiP on its target cells remains to be determined, as a putative receptor for GRP78/BiP has not yet been identified [
35]. Interestingly, despite belonging to a member of HSP70 family and sharing 60% to 70% homology with this molecule, GRP78/BiP does not bind to any of the multiple receptors identified for HSP70 [
33]. This highlights the fact that although extracellular activity of HSP70 is typically proinflammatory, GRP78/BiP actually exhibits significant anti-inflammatory effects [
33]. Evidence is emerging that during physiological stress or necrosis, the same stressed cells release other endogenous molecules like GRP78/BiP [
32,
35,
36,
37]. These molecules may be released simultaneously or later in a sequence of events, ultimately facilitating the termination of inflammation [
36]. Unlike other passively DAMPs, these molecules function in an autocrine and paracrine manner, exerting an opposing effect. Through the induction of anti-inflammatory mediators, and actively, via deactivation of inflammatory mediators and cells, they promote the resolution of acute inflammation [
10].
GRP78/BiP is one of a group of intracellular stress proteins which have recently been recognized as another type of RAMPs [
28]. Moreover, GRP78/BiP is involved in most of the stress response, providing immunoregulatory and pro-resolution signals into immune networks [
10]. Notably, GRP78/BiP has the ability to translocate from ER to nucleus as well as to cell surface, indicating its versatility in different cellular functions [
38]. The evidence suggests that the intracellular GRP78/Bip, located within the cell, plays a crucial role in protein folding as a chaperone in ER [
38]. Apart from its function as an antiapoptotic protein and a major pro-survival component of UPR, intracellular GRP78/Bip is also a regulator of apoptotic drivers through direct or indirect interactions [
38]. Conversely, extracellular GRP78/Bip located outside of the cell exhibits significant immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory effects [
38]. The dual functionality of GRP78/Bip greatly broadens our comprehension of the role that stress proteins play within different cellular environments. This adaptability underscores its significance in maintaining immune homeostasis and facilitating resolution processes during various biological contexts [
38]. Therefore, GRP78/Bip exemplifies a bona fide moonlighting protein, as it performs two distinct roles in vivo. This protein’s involvement in modulating immune responses indicates its potential as a target for therapeutic interventions aimed at regulating inflammatory processes and promoting resolution of immune-related disorders [
35,
36,
38,
39].
There is mounting evidence that GRP78/BiP can be overexpressed in saliva [
40], synovium [
41,
42,
43,
44,
45,
46], serum [
10,
42,
45,
46,
47,
48,
49,
50,
51,
52,
53,
54,
55,
56], and synovial fluid (SF) [
47,
49,
57,
58,
59] in RA, acting as an autoantigen in the disease. In a Phase I/IIA clinical trial conducted on RA, GRP78/Bip was found to be both safe and well-tolerated among participants. The findings from this biomarker analysis revealed a considerable anti-inflammatory effect associated with GRP78/Bip, indicating its potential to provide meaningful clinical benefits for individuals suffering from RA [
60]. However, the current research on GRP78/Bip is fragmented and lacks a comprehensive perspective, as existing studies on RA primarily focus on the role and targeted intervention of GRP78/Bip in either serum, SF, or synovium, without considering disease activity status and progression stage. This limited literature overlooks the systemic complexity of disease development and the changes that occur in RA. The existing literature does not provide adequate information regarding the differential expressions of intracellular or extracellular GRP78/Bip in relation to both the disease activity and progression of RA, as well as any potential associations that may exist between the statuses and stages of RA and the accompanying presence of GRP78/Bip within cells or in the extracellular space. Furthermore, the regulatory functions of GRP78/Bip under different cellular environments and during various conditions within RA have not yet been documented. Specially, it remains unclear whether the expression of GRP78/Bip changes with disease activity status and progression stage in RA, and what role different forms of GRP78/Bip play in different conditions of RA. This absence of comprehensive information emphasizes a critical gap in our current understanding of how this protein interacts and exerts its influence within the framework of the disease. Addressing these questions is essential for a more complete perspective on the roles that GRP78/Bip may play in the pathophysiology of RA and could potentially pave the way for a more personalized therapy targeting GRP78/Bip in RA. Thus, the aim of this study was to investigate the differential expression of GRP78/Bip in serum, SF, and synovium, as well as to explore the association of intracellular and extracellular GRP78/Bip with disease activity and progression in patients diagnosed with RA. A better understanding of the function of intracellular and extracellular forms of GRP78/Bip, along with the mechanisms regulating GRP78/Bip-induced immune responses, may result in innovative strategies to the management of RA and possibly other inflammatory diseases.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
The experiment was carried out in accordance with the ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects set forth in the Helsinki Declaration. All participants were fully informed about the process and possible adverse effects of the investigation and instructed to report any adverse reaction to researchers during the experiment. All testing was voluntary, confidential, and undertaken with the patient’s written informed consent, and the rights of the participants were protected. In the course of the experiment, they were advised that they could withdraw from the study at any time. Coding is used in the data analysis process, instead of participant’s personal details. All data were managed by a blinded author, and statistical analyses were done by a statistician.
2.2. Study Design and Setting
Participants were consecutively recruited over a period from June 2020 to June 2023 through a convenient sampling method. Patients with knee RA were diagnosed based on the 2010 American College of Rheumatology (ACR)/European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology (EULAR) classification criteria [
61]. Patients with knee OA were diagnosed based on the 2019 ACR recommendations [
62]. Patients with traumatic meniscal injury (TMI) were diagnosed based on MRI description of Fischer grading criteria [
63].
In the study, patients with TMI who did not exhibit radiographic signs of OA were incorporated into the control (CON) group. It is assumed that these knees were in a healthy state prior to the trauma and without any post-traumatic or OA-related abnormalities other than TMI. Patients diagnosed with OA were incorporated into the inflammation control (iCON) group. In every instance of RA assessed in the study, disease activity was evaluated using DAS28 criterion (Disease activity scores in 28 joints), while disease progression was assessed using Steinbrocker classification grade. Patients with RA were stratified accordingly in six distinct groups based on disease activity and progression: disease activity coupled with early-stage progression in RA (aES RA) group, disease activity coupled with moderate-stage progression in RA (aMS RA) group, disease activity coupled with severe-stage progression in RA (aSS RA) group, disease remission coupled with early-stage progression in RA (rES RA) group, disease remission coupled with moderate-stage progression in RA (rMS RA) group, disease remission coupled with severe-stage progression in RA (rSS RA) group.
Disease onset was defined as the day of diagnosis, as documented in participant medical records. Only cases with a minimum of one year since diagnosis were considered for inclusion. The inclusion criteria were primary diagnosed RA, OA or TMI. Specifically, for patients diagnosed with RA and OA, it was essential that they had no presence of fibrous or bony ankylosis, which is classified as Stage IV in the STEINBROCKER classification system. Moreover, patients with TMI were required to present with a grade 3 meniscal tear, as defined by the Fischer grading criteria, and to be free from any joint or connective tissue disorders. All patients included exhibited knee synovitis at the outset of the study and had not received intraarticular injections of steroids or chondroprotectors for at least three months prior to the study. The participants subsequently underwent either joint replacement or arthroscopic surgery for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.
Exclusion criteria for this study included a diagnosis of autoimmune diseases other than RA, engaging in intense or competitive activity for more than 1 hour per week within the past 3 months, use of glucocorticoids or biological disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs, presence of haemophilia, congenital patellar dysplasia, or other congenital knee deformities, acute and chronic infections, malignant diseases, severe lung, liver, kidney or endocrinological disorders, age younger than 18 or older than 80. Additionally, patients with OA or TMI were excluded if they had an acute knee injury.
In total, 186 consecutive patients met the 2010 ACR/EULAR criteria, 2019 ACR recommendations, and Fischer grading criteria. These individuals were screened according to the specific inclusion and exclusion criteria within the outpatient department, resulting in 165 patients (88.71%) being categorized into the predefined groups. Each group of RA patients was enrolled in a 1:1 ratio matched according to their gender. Similarly, for each case in CON group, we enrolled a 1:6 match with RA patients according to gender. Specifically, in iCON group, each case was enrolled in a 1:6 ratio matched with RA patients based on age (± 5 years) and gender. This study ultimately involved 128 patients (68.82 %), with 16 patients in each of the following groups: CON group, iCON group, aES RA group, aMS RA group, aSS RA group, rES RA group, rMS RA group, and rSS RA group. All the enrolled 128 patients were tested for serum GRP78/Bip.
Although enrolment was continued for 3 years, only 50 patients proceeded to surgical intervention. Subsequently, participants from each group were further enrolled in a 1:1 ratio matched according to their gender. Within the same group, patients were then further screened based on their median serum levels of GRP78/Bip. Ultimately, 24 patients were involved, with 3 patients from each group included in the follow-up study.
2.3. Determination of RA Disease Activity
The DAS28 criterion was used to carry out the groups based on disease activity status. DAS28 is calculated from four components, swollen joint count (SJC), tender joint count (TJC) of 28 joints, ESR (mm/h) as a marker of systemic inflammation, and global health assessment indicated by the visual analog scale (VAS). RA patients are distributed into two subgroups according to their DAS28 status: disease activity (DAS28 > 2.6) and disease remission (DAS28 ≤ 2.6) patients.
2.4. Determination of RA Disease Progression
The Steinbrocker classification grade was used to carry out the groups based on the severity of disease progression (
Table 1). In order to ensure a more precise and dependable classification, specific characteristics of the disease, focusing on the joints and nearby structures, were utilized to differentiate between the different stages of disease progression. These stages can be divided into four categories based on clinical signs and radiographic changes. Specifically, patients with RA in Stage IV of the Steinbrocker classification were excluded from this study.
RA patients exhibit varying statuses of disease, which can be categorized as either active or in remission. In cases where the disease is active, it is noteworthy that spontaneous remission can still take place, irrespective of the severity of disease progression. Moreover, different statuses of RA are characterized by specific clinical and laboratory features that help to define the levels of disease activity. These features are not fixed and can be present in any stages of disease progression. However, it is important to recognize that as disease develops and inflammatory changes persist, certain characteristics may become more pronounced, further complicating the clinical picture.
At any point during the course of RA, certain objective features may be present and clinically recognized, such as persistent joint swelling with or without effusion, tenderness, stiffness, and limitation of motion. Furthermore, specific characteristics regarding the severity of disease progression, particularly those related to structural changes, play a significant role in distinguishing between different conditions of the disease. For a more comprehensive understanding,
Table 1 provides a detailed outline that encapsulates these key distinguishing characteristics. In clinical observations, any two or more of these stages may occur simultaneously at different joints within the same patient, but usually the process advances to an approximately similar extent in multiple joints. Since it is not practical to evaluate the disease according to the stage of each affected joint separately, it is efficient to classify each case based on the condition of the specific joint under investigation, such as the knee joint in this particular study. It is crucial to recognize that the status of RA can be classified as either active or in remission at any given stage of disease progression.
2.5. Sample Collection and Preparation
Fasting blood samples were collected from participants in the morning using serum separator tubes under standard conditions. The samples were allowed to clot for 30 minutes at room temperature, followed by centrifugation at 1,000 g for 10 minutes. The serum samples were then promptly aliquoted, kept on ice throughout the process, and stored at -80℃.
SF samples were aspirated from the knee joint of patients prior to surgical procedures and extracted during capsular cutting in the surgical procedures. The samples were collected in heparinized containers to prevent coagulation and subsequent cell damage. After centrifugation at 1,000g for 20 minutes, the cell-free SF was aliquoted and stored at -80℃.
The diseased synovium samples were collected during surgical procedures after ruling out infection. To minimize protein degradation, the samples were processed immediately, kept on ice, and stored at -80℃ for future use. Diseased synovium samples from CON group were collected during the procedure of arthroscopic synovectomy, while samples for iCON group were gathered during joint replacement surgeries. Samples from aES RA and rES RA groups were collected during the procedure of arthroscopic synovectomy, while samples for aMS RA, aSS RA, rMS RA, and rSS RA groups were gathered during joint replacement surgeries.
2.6. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
Levels of GRP78/Bip, tumor necrosis factor -α (TNF-α), and interleukin-10 (IL-10) in serum, SF, and synovium tissue homogenates were examined using ELISA kits (Jonin Biotech, Shanghai, China). All experimental protocols were strictly adhered to in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions to ensure the integrity and accuracy of the results. The ELISA experiment was conducted by a proficient laboratory technician, with meticulous control over each step of the test. The experiment was repeated three times for each sample, and the results were then averaged.
2.7. Western Blot (WB)
Synovium lysates or SF samples were electrophoresed on 10% sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gels and transferred onto nitrocellulose membranes. Following non-specific blocking, the membranes were incubated and probed with an anti-BiP or anti-Caspase-3 monoclonal antibody (Cell Signaling Technology, Beverly, Mass., USA). Subsequently, antigen–antibody complexes (Santa Cruz, Calif., USA) were then applied. The purified protein’s molecular weight was determined by SDS polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, and the band was excised for protein identification using a chemiluminescence detection system (Cell Signaling Technology). Band density was analyzed with ImageJ 1.41 (National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Md., USA).
2.8. Statistical Analysis
All data were presented as mean ± standard deviation (x̄ ± s) or as median and interquartile range (IQR). The Shapiro-Wilk test was conducted to assess normal distribution of the data. Independent Student’s t test was used to compare the differences between two independent groups, and one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was applied to compare the differences among ≥3 independent groups. Spearman correlation coefficients were calculated to investigate the relationship between disease activity/severity status and the levels of GRP78/Bip, TNF-α, IL-10, or Caspase-3. Statistical significance was defined as P < 0.05 for both differences and correlations.
4. Discussion
RA is a widespread inflammatory autoimmune disorder that affects approximately 1%–2% of the world’s population [
65]. The incidence of RA is steadily rising by 8.2% annually [
65]. This condition is characterized by a multifaceted clinical profile, encompassing abnormal immune responses, inflammatory pathways, genetic and epigenetic factors, as well as the regulation of immunometabolism [
66]. If left untreated, RA can frequently result in bone erosion and eventual joint destruction. It can also affect extra-articular organs such as the heart, lungs, eyes, and blood vessels, potentially reducing the lifespan of RA patients [
67]. Therefore, early and accurate diagnosis of RA is essential to decrease functional disability and enhance quality of life. Uncovering the pathogenesis of RA and expediting clinical transformation are imminently in need [
68]. However, RA can be challenging to diagnose in its early stages when typical disease features are not yet apparent [
61]. Diagnosis involves a complex process that integrates various data points, surpassing simplistic algorithm-based criteria. Hence, establishing definitive diagnostic criteria for RA is not straightforward. Recommendations and guidelines have been developed to aid in the management and treatment of RA [
69]. Importantly, classification criteria are not intended to be used for diagnosis. Nonetheless, they are commonly used to support the diagnostic process in clinical decision-making and facilitate the timely implementation of therapeutic measures. Classification criteria, on the other hand, are used to serve as a standardized method for selecting a well-defined group of patients in clinical studies, ensuring better comparability between studies. [
69,
70].
The current recommended standard for RA diagnosis was the 2010 ACR/EULAR classification criteria [
61]. These criteria include clinical assessments such as joint counts, acute phase reactants (APR) like inflammation markers (C reactive protein and erythrocyte sedimentation rate), and crucially, the identification of rheumatoid factor (RF) and anticitrullinated protein/peptide antibodies (ACPAs), which were the hallmark autoantibodies in RA. RF and ACPAs were commonly utilized as serological biomarkers in the diagnosis of RA, each playing a significant role in the pathogenic process. The 2010 ACR/EULAR classification criteria were also proposed as a tool to take advantage of therapeutic interventions in the early stages of RA. On the other hand, these new criteria emphasized the significance of utilizing biomarkers to guide therapeutic decisions in clinical practice. In the realm of clinical findings, RF, ACPA, and APR stood out as the most frequently used biomarkers in clinical settings for guiding the diagnosis and prognosis of RA. RF, which was first described in 1940, remains a cornerstone laboratory tool for diagnosis and prognosis of RA in its early stages [
71]. Nevertheless, the utilization and interpretation of RF have been conditioned by the emergence of ACPAs [
14,
50]. The sensitivity of RF in diagnosing RA ranges from 30% to 70% in early cases and increases to 80%-85% in progressive cases, but its specificity is ~40% as it could also be present in patients with other diseases and even in healthy individuals [
14,
50]. In contrast, ACPAs exhibited a sensitivity of 60~80% and a high specificity of 95%~98% [
14]. Despite their widespread use, both RF and ACPA, along with APR (which are not specific to RA and may not change with disease progression), have proven to be inadequate in satisfactorily responding to the high heterogeneity of RA [
20,
72]. Clinical practice still faced challenges with misdiagnosis and missed diagnoses, which could result in unwarranted initiation of DMARD therapy [
20,
72]. Therefore, issues arose on how comprehensive the criteria should be and whether they should be updated and adapted to findings from the past two decades that might increase both their specificity and sensitivity [
20,
72]. Additionally, the added value of other antimodified protein antibodies or biomarkers to the increased sensitivity and/or specificity of the criteria remains a topic of debate [
20,
72].
Biomarkers are defined as interaction parameters that provide objective information on measurable changes in physiology, biochemistry, or morphology, which are evaluable at the molecular, biochemical, or cellular level [
73]. These biomarkers serve as indicators of functional biological processes, pathogenic states, or responses to medical interventions [
74]. Biological markers are considered as physiological signals induced by exposure to a foreign substance, such as cellular exposure, precocious cellular response, or inherent/acquired susceptibility [
75]. Biomarkers are classified based on their specific nature and the type of biological study they originate from. One primary classification is omics, which encompasses genomics for genetic research, proteomics for the study of proteins, and metabolomics for the analysis of metabolites [
14]. Another category is epigenetics, which involves DNA alterations related to certain pathologies [
76,
77]. Biomarkers also include microRNA molecules, which exhibit varying levels of expression in either normal or cancerous cells (genomics/transcriptomics) [
78]. Additionally, the Food and Drug Administration further categorizes biomarkers as diagnostic biomarker, prognostic biomarker, safety biomarker, monitoring biomarker, and pharmacodynamic response biomarkers [
79]. Ideal biomarkers should be able to provide diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic information [
14]. They should be obtainable from a patient’s clinical data and possess specific chemical-analytical characteristics [
14]. These characteristics include high specificity, where the measurement of a biomarker must be specific to a disease; specimen collection should be minimally invasive, with saliva being preferred over urine and urine over blood; representativeness, meaning levels of biomarkers in the sample should be representative of levels in the organism; and stability, where the kinetics must be known [
14].
Multiple studies have provided evidence of significant differences in the functions of GRP78/BiP depending on its extracellular or intracellular location [
32,
34,
36,
37,
80,
81]. This versatility allows GRP78/BiP to be classified as a true moonlighting protein, with two distinct roles in vivo [
38]. The intracellular form of GRP78/BiP serves as a critical chaperone in protein folding within ER and possesses anti-apoptotic properties, aiding in cell protection under stressful conditions. Conversely, the extracellular form of GRP78/BiP exhibits potent immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory effects, although the specific cell-surface receptor through which it acts remains unidentified, with expression being mainly on monocytes. This dual role of GRP78/BiP underscores its importance in both intracellular and extracellular processes, highlighting its potential as a therapeutic target for various conditions [
82]. During the pathogenesis process of RA, GRP78/BiP appears as a product of stress response and patients are likely to develop autoantibodies to GRP78/BiP [
82]. Many studies have confirmed the elevated levels of GRP78/BiP and anti-GRP78/BiP antibodies in RA patients [
42,
47]. Additionally, the upregulation of GRP78/BiP seems to be distinctive of RA and independent of drug treatment [
83]. Antibodies to BiP have also been detected in the sera of individuals antedating the onset of RA [
47]. These findings suggest that GRP78/BiP or anti-GRP78/BiP antibodies could be explored as a potential biomarker to enhance the diagnostic algorithms for RA.
Various techniques have been applied to characterize the proteomic profile of saliva [
40], synovium [
41,
42], serum [
42,
47], and SF [
47,
58] in RA, yielding promising outcomes. The use of mass spectrometry (MS) and WB techniques in evaluating the diagnostic value of RA in saliva indicated that GRP78/BiP exhibited high specificity (0.95), sensitivity (0.83), pooled positive likelihood ratio (16.66), and diagnostic odds ratio (94.77) [
40].The potential applicability of the findings deriving from this study will be represented by the possibility of identifying novel, non-invasively collected salivary proteomic biomarkers in order to significantly improve the diagnostic algorithms of RA. Antibodies to GRP78/BiP in serum, as measured by ELISA, exhibit a sensitivity of 73% and a specificity of 71% for established RA, and 66% and 65% for early RA, respectively [
47]. The antibody levels to GRP78/BiP increased as the patient approaches the onset of arthritis, with a significant rise in anti-GRP78/BiP antibodies by the time of early RA diagnosis compared to controls. Anti-GRP78/BiP antibodies were also found in SF of RA patients at levels similar to those in serum, significantly higher than in control SF [
47]. A study demonstrated that the dominant immunoreaction in the majority of tested RA serum was with a 68 kDa antigen known as GRP78/BiP, which was probably ubiquitously expressed [
42]. Antibodies targeting GRP78/BiP autoantigen were present in both serum and synoviocytes in 64% of 167 RA patients tested via WB, and could also be found in seronegative RA patients, but were rarely present in patients with other rheumatic diseases (1% out of 98 patients) [
42]. Notably, these antibodies were absent in 55 healthy controls. Antibodies to a GRP78/BiP antigen with sensitivities comparable to that of the synovial GRP78/BiP antigen (64%) were observed in lymphocyte and HeLa total protein preparations (75% and 58%) [
42]. These findings suggested that anti-GRP78/BiP antibodies were produced in both primary and secondary lymphoid organs as well as the joint, potentially serving as a diagnostic biomarker for identifying RA in patients with early arthritis. Cell-free GRP78/BiP, as measured by WB, has been identified in SF of patients with RA, with a higher prevalence in SF samples (72%) compared to samples from patients with other inflammatory joint diseases (38%) [
58]. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) responded to GRP78/BiP by secreting an anti-inflammatory profile of cytokines. Although GRP78/BiP stimulated the early production of inflammatory cytokine TNF-α, the predominant cytokine induced was the anti-inflammatory IL-10. These results indicated that cell-free GRP78/BiP did indeed occur and could have biological effects by interacting with cells. Extracellular GRP78/BiP may stimulate immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory pathways, which were only partly attributed to the production of IL-10 [
58]. GRP78/BiP was significantly upregulated in synovial sections from RA patients, in stark contrast to control sections [
58]. GRP78/BiP-specific autoantibodies were present in 63% of 400 RA patients, 7% of 200 individuals with other rheumatic diseases, and in none of the healthy subjects [
41]. Interestingly, researchers observed a distinct alteration in GRP78/BiP-specific T cell reactivity in RA patients [
41]. Unlike healthy individuals and patients with other rheumatic diseases where measurable GRP78/BiP reactive T cells were undetectable, RA patients exhibited pronounced T cell reactivity to GRP78/BiP [
41]. Notably, this reactivity could be induced by specifically blocking antigen presentation to potentially regulatory T cells. Since overexpression of GRP78/BiP has been demonstrated to reduce the sensitivity of cells to cytotoxic T cell-mediated killing, GRP78/BiP overexpression and GRP78/BiP-specific autoimmunity may be involved in the pathogenesis of RA [
41]. Consequently, the detection of GRP78/BiP-specific autoantibodies has emerged as a novel diagnostic tool, potentially serving as both a preclinical indicator [
41,
47] and an improved diagnostic biomarker [
14] for RA.
The data from the ’Duisseldorf Rheumaregister’ retrieval study included analysis of 277 RA patients and 893 patients with other rheumatic diseases to identify the presence of RF [
42]. The anti-GRP78/BiP antibody demonstrated equal sensitivity (66% vs 68%) and higher specificity (99% vs 76%) compared to the RF. It is important to note that 5% of the apparently healthy population also yield positive results for RF. The high specificity of GRP78/BiP or anti-GRP78/BiP antibodies significantly exceeded that of RF based on research findings [
42,
48,
72]. Unlike RF, which targets the Fc portion of IgG and formulates the immune complexes that exceed the process of RA as well as other rheumatoid diseases, GRP78/BiP antibodies exhibited a more focused immune response. This enhanced specificity was crucial in distinguishing between RA and other rheumatoid diseases. ACPAs have been identified as highly specific biomarkers for diagnosing RA and were believed to be closely linked to the pathogenesis of arthritis. Notably, the presence of anti-CCP antibodies could be detected several years before the onset of joint inflammation [
50]. Given the high specificity of ACPAs in RA diagnosis, their role in the pathogenesis of RA has become the focus of active investigation. Similarly, GRP78/BiP or anti-GRP78/BiP antibodies showed comparable sensitivity to ACPAs (67% vs. 67%) and slightly lower specificity (92% vs. 95%) [
72]. This resemblance may stem from their similar role in the pathogenesis of RA. With moderate sensitivity and high specificity, GRP78/BiP or anti-GRP78/BiP antibodies could serve as a valuable supplement to existing diagnostic methods. Given their distinct roles in RA pathogenesis, a combination of GRP78/BiP and anti-GRP78/BiP antibodies with RF or ACPAs could provide even more reliable and accurate results for the clinical diagnosis of RA. Their different roles in the pathogenesis of RA made them complementary to each other, enhancing the overall effectiveness of diagnostic testing. The combination of anti-GRP78/BiP antibodies and anti-CCP antibodies could obtain higher specificity than that of anti-CCP antibodies detected individually [
48]. This tandem combination approach has demonstrated good clinical value in differentiating RA from other autoimmune diseases. These findings highlighted the importance of considering multiple biomarkers and combined detection in diagnostic testing for RA, as the presence of both anti-GRP78/BiP and anti-CCP antibodies together could provide more accurate and specific results.
Research on potential clinical biomarkers in RA has been a prominent topic over the past two decades, yielding numerous significant findings [
2,
3,
14]. However, there remain several unresolved questions in this area. What exact role do these potential biomarkers play in the pathogenesis and development of RA? How do biomarkers fluctuate during different disease activity statuses and progression stages of RA? And is there any therapeutic benefit in targeting biomarker-positive RA patients under different conditions and courses of the disease?
The existing research on the potential clinical biomarker GRP78/Bip in RA has primarily limited to isolated examinations of either synovium [
41,
42,
43,
44,
45,
46], serum [
10,
42,
45,
46,
47,
48,
49,
50,
51,
52,
53,
54,
55,
56], or SF [
47,
49,
57,
58,
59]. However, no studies have comprehensively examined GRP78/Bip across serum, SF, and synovium collectively. Due to the insufficiency of relevant studies, current research has not conducted stratified analyses on specific subgroups such as the serum, SF, and synovium. Understanding the pathogenesis and progression of RA requires an analysis of both systemic and local immune responses, which are intricately linked. Investigating the changes and interconnections of GRP78/Bip in different intracorporeal environments, including serum, SF, and synovium, is essential for gaining a comprehensive understanding of its role as a potential biomarker in RA. By adopting a holistic approach to study GRP78/Bip, researchers may uncover valuable insights into its significance and implications for RA treatment and management. Furthermore, RA is a complex systemic disease characterized by gradual advancement and deterioration as development in the stage of disease progression and the status of disease activity [
11,
66,
84]. Despite this understanding, there has been a lack of comprehensive research into the fluctuations of GRP78/Bip levels in relation to different statuses and stages of RA. The potential role and specific regulatory effects of GRP78/Bip in different cellular environments, as well as under different statuses and stages of RA, have not been fully explored or documented. Further investigation into these factors is necessary to gain a better understanding of the role of GRP78/Bip in the pathogenesis of RA. Hence, this study delves into the differential expressions of GRP78/Bip in serum, SF, and synovium under various stages of disease progression and different statuses of disease activity in RA. The research also seeks to explore the associations between GRP78/Bip expression, disease activity and progression of RA, as well as the levels of predominant inflammatory cytokine TNF-α and anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 for the first time. This study aims to elucidate the potential interconnectedness of these factors in the context of RA.
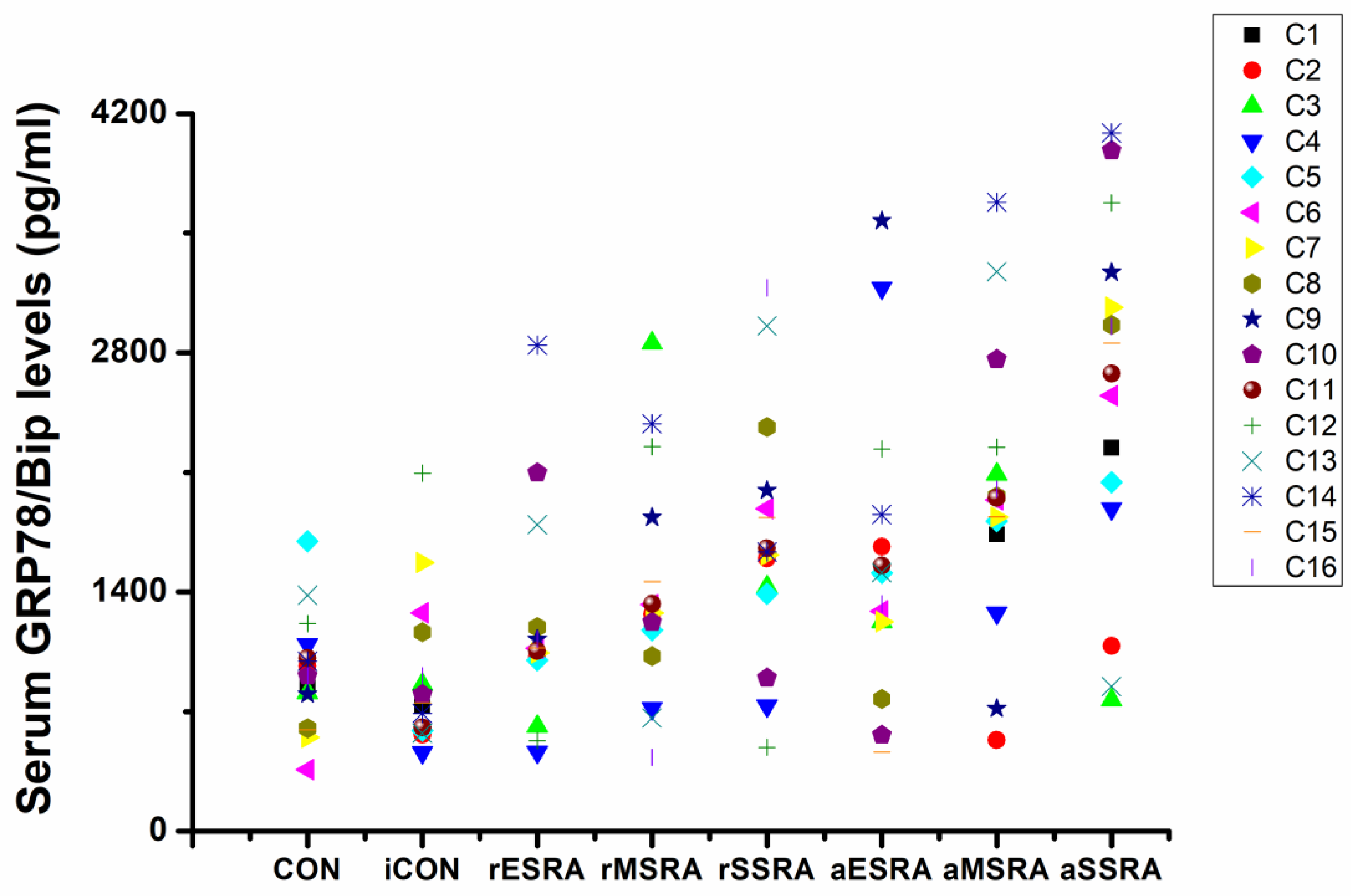
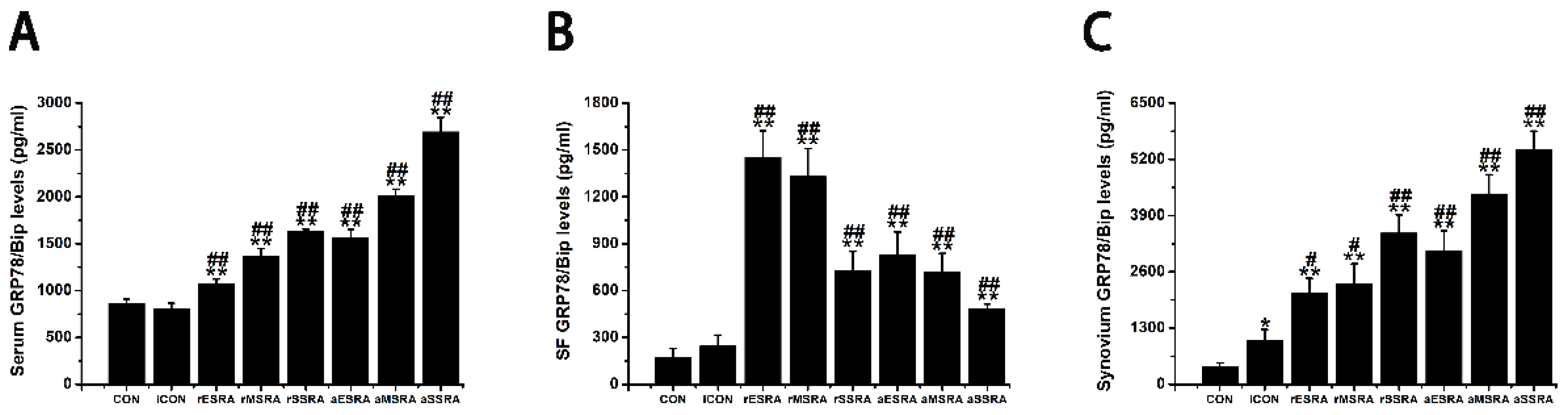
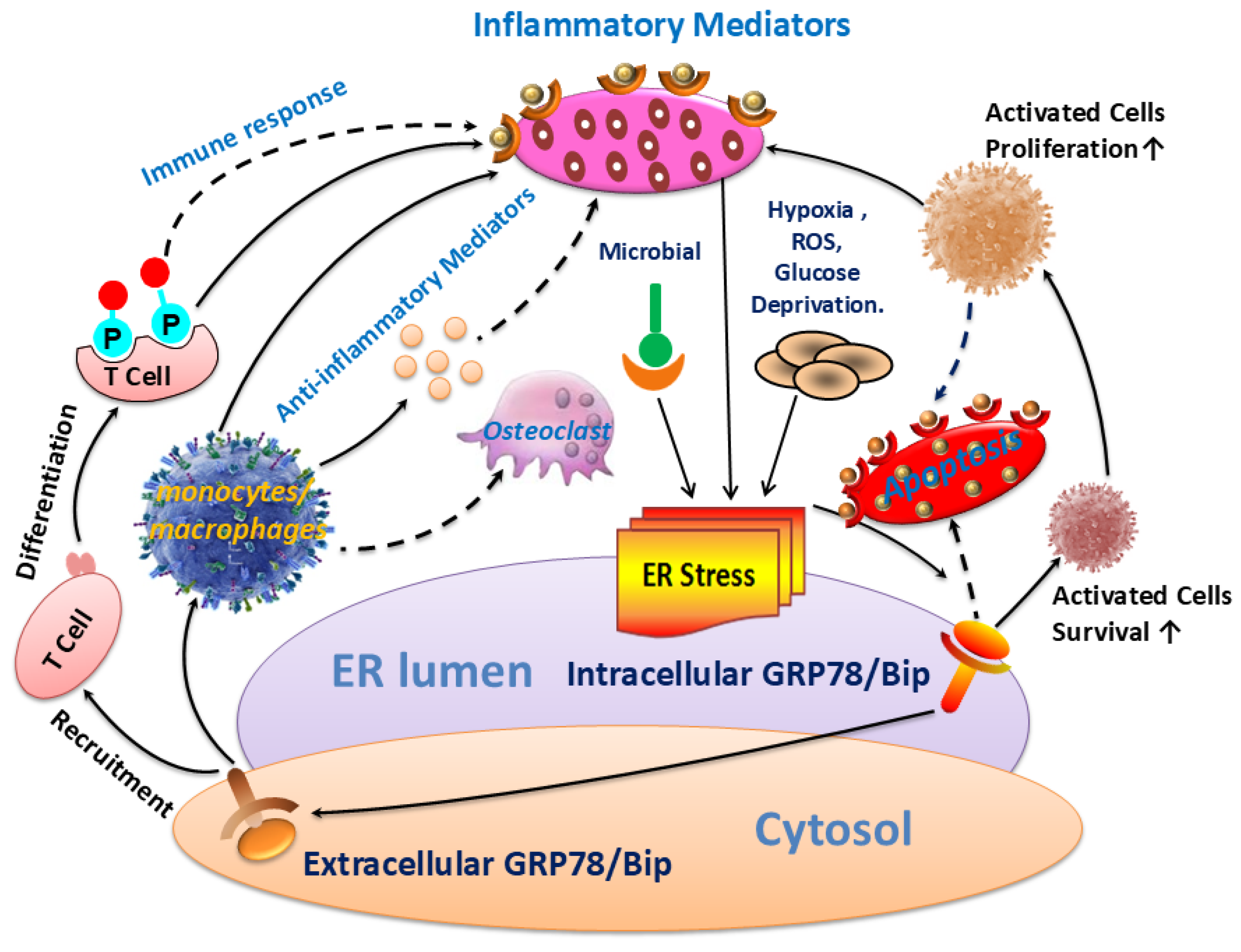
The results of this study revealed that GRP78/Bip was consistently present in both intracellular (synovium) and extracellular (cell-free serum and SF) RA lesions, with variations in expression levels closely linked to disease activity and progression of RA. The disease activity statuses and progression stages of RA were found to align with the expressions of GRP78/Bip in serum and synovium, but differed significantly from those in SF. This study emphasized the critical role of GRP78/Bip in disease activity and progression of RA, noting that its function could vary depending on different intracorporeal environment or status and stage of RA. The findings underscore the significance of GRP78/Bip in the pathogenesis of RA, suggesting that its expression levels could serve as valuable indicators of disease activity and progression. The differing expressions of GRP78/Bip among different RA lesions implied that it may play a unique role in disease activity and progression of RA within the synovium compared to the SF and serum, aligning with previous literature on the subject [
41,
42]. To further explore the underlying causes of these substantial discrepancies, an extensive analysis was carried out, incorporating insights from previous research in the field [
10,
32,
33,
36,
38,
82,
83,
85,
86,
87,
88,
89,
90](
Figure 5).
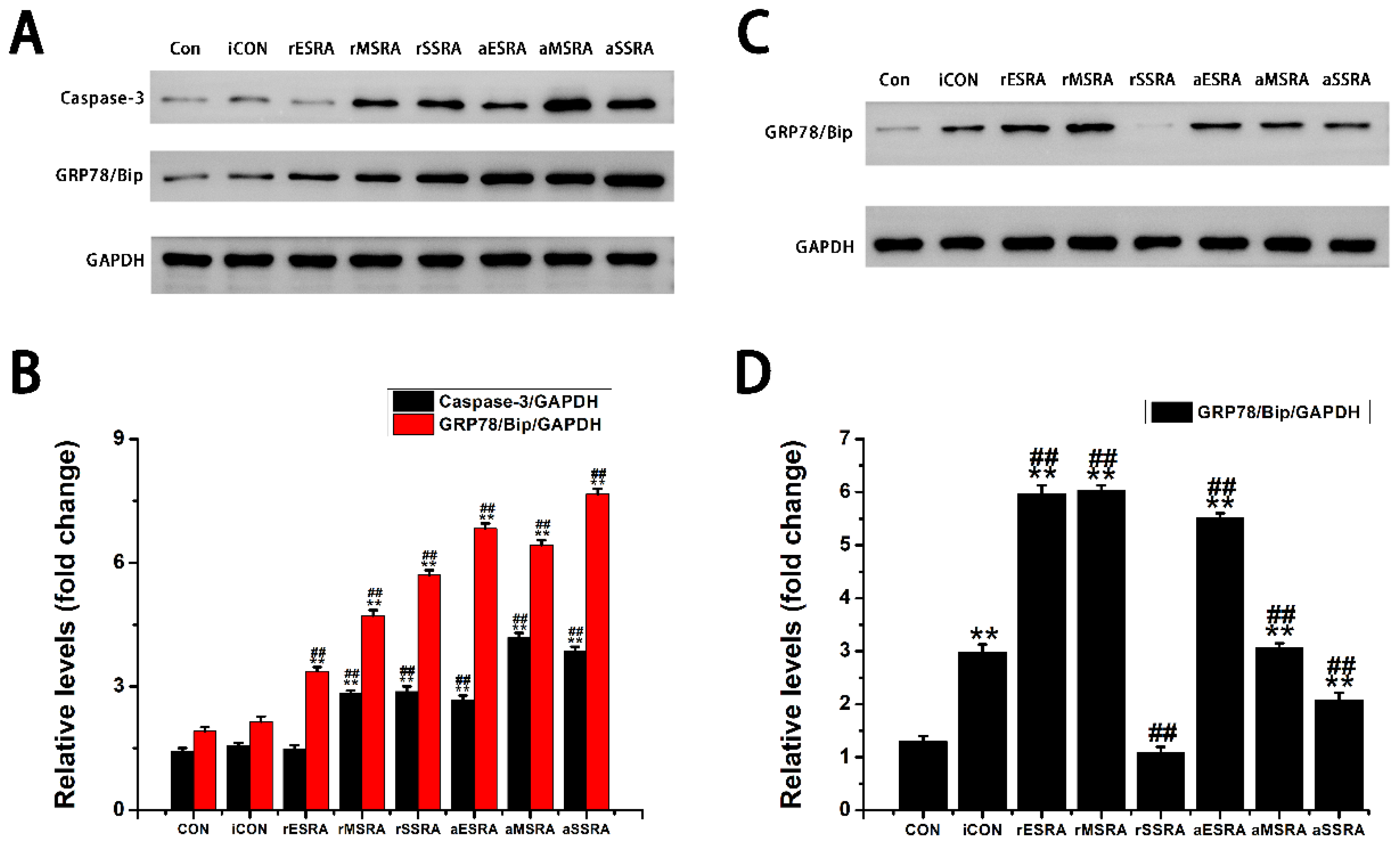
Exploring the role of GRP78/Bip in synovium during disease activity and progression of RA was conducted. Upon the onset of RA, heightened levels of intracellular GRP78/Bip are generated in response to stress signals, aiming to counteract ERS disturbances. This process aids in re-establishing ER functionality, reducing cellular harm, and supporting cell viability. As ERS persists and disease advances, the body increasingly activates stress response mechanisms in the affected cells. This process aims to prevent irreversible damage and apoptosis of these affected cells through the expression of intracellular GRP78/Bip. Consequently, the expression of GRP78/Bip in synovium increases gradually with the severity of the disease. Specifically, in this research, the levels of intracellular GRP78/Bip expression in synovium were found to be highest at severe-stage, followed by moderate-stage, and lowest in early-stage. In the context of RA, disease activity resembles an acute exacerbation, characterized by heightened apoptosis and intensified inflammatory reactions in synovium. Specifically, in this research, elevated levels of caspase-3 expression were observed during disease activity as opposed to disease remission, with higher expression levels in severe- and moderate-stages compared to early-stage. This RA activity status also witnesses an aggravated inflammatory response and a rapid increase in the expression and synthesis of intracellular GRP78/Bip. This upregulation in intracellular GRP78/Bip serves as a protective mechanism against further disease progression of the inflammatory disease. Conversely, during the remission status of RA, the inflammatory response is alleviated, leading to a decrease in intracellular GRP78/Bip expression, but still remains relatively high compared to healthy and disease control individuals. The results of this research demonstrated that the expression levels of GRP78/Bip in synovium were consistently greater during disease activity status compared to those in remission.
Investigation was additionally focused on the role of GRP78/Bip in SF with respect to disease activity and progression of RA. In the context of RA onset, GRP78/Bip experiences a shift in location and function within the cell. Normally residing in ER, GRP78/Bip can avoid ER "reattachment" by binding to unfolded proteins. However, during the development of RA, GRP78/Bip can translocate to the cytoplasm and cell membrane along with these unfolded proteins. As ERS disrupts ER structure, GRP78/Bip is released into the extracellular space. This results in the loss of its anti-apoptotic effect within the cell but leads to its involvement in the immune response and anti-inflammatory response outside the cell as extracellular GRP78/Bip and autoantigens. As the disease progresses and worsens, some intracellular GRP78/Bip have already depleted due to apoptosis before metastasizing to the extracellular space, further decreasing the extracellular expression. However, the disruption of homeostatic function and the increase of apoptosis in stressed cells will in turn exacerbate protein misfolding and accumulation and further increase the intensity of ERS response, thus leading to a vicious cycle and accelerating cell dysfunction and lesion progression. As ERS persists and disease advances, the ability to maintain homeostasis diminishes, resulting in an increased demand for intracellular GRP78/Bip. Consequently, there is a reduced release of intracellular GRP78/Bip into the extracellular space. When ER stress-induced apoptosis exceeds its protective capabilities and causes irreversible damage, apoptotic signals are activated to remove stressed cells if normal function cannot be restored. This helps maintain a delicate balance between cell survival and apoptosis. In such situations, some intracellular GRP78/Bip may have been lost due to apoptosis prior to metastasizing to the extracellular space, further reducing its expression outside the cell. This disruption of homeostatic function, coupled with an increase in apoptosis in stressed cells, will exacerbate protein misfolding and accumulation, intensify ER stress response, creating a harmful cycle that accelerates cell dysfunction and disease progression. Therefore, the aforementioned scenario presents a negative correlation between extracellular GRP78/Bip levels and severity of RA progression. This study further confirmed the presence of extracellular GRP78/Bip in SF of patients with RA at different disease progression stages, with levels decreasing from early- to moderate- and then to severe-stages. On the other hand, during active RA, intracellular GRP78/Bip was presented to be significantly elevated, resulting in a relatively lower extracellular GRP78/Bip level in SF. Specifically, in this research, the extracellular levels of GRP78/Bip in SF followed the pattern of disease remission being greater than disease activity in RA patients.
GRP78/Bip serves as a reactive protective mechanism in cells, emphasizing its essential role in maintaining cellular function and viability. The presence of both intracellular and extracellular GRP78/Bip has been shown to work together to exhibit synergistic effects, further highlighting the significance of this protein in cellular homeostasis. As RA develops, there is a gradual increase in the body’s requirement for GRP78/Bip to cope with the ongoing inflammatory processes. In response to this heightened demand, the immune system is activated to increase the production of GRP78/Bip at the affected area. This results in elevated levels of GRP78/Bip in the bloodstream, reflecting the body’s efforts to counteract the inflammatory response associated with RA. However, achieving remission in RA is contingent upon striking a delicate balance between intracellular and extracellular GRP78/Bip expression at the affected site. This equilibrium is essential for resolving inflammation and restoring normal cellular function. Ultimately, the body’s demand for circulating GRP78/Bip must be maintained at a relatively balanced state to facilitate recovery from RA and promote overall well-being. Consequently, the findings of this research revealed distinct patterns in GRP78/Bip expression in RA serum: disease activity surpassed disease remission status, severe- surpassed moderate-stage and moderate- surpassed early-stage.
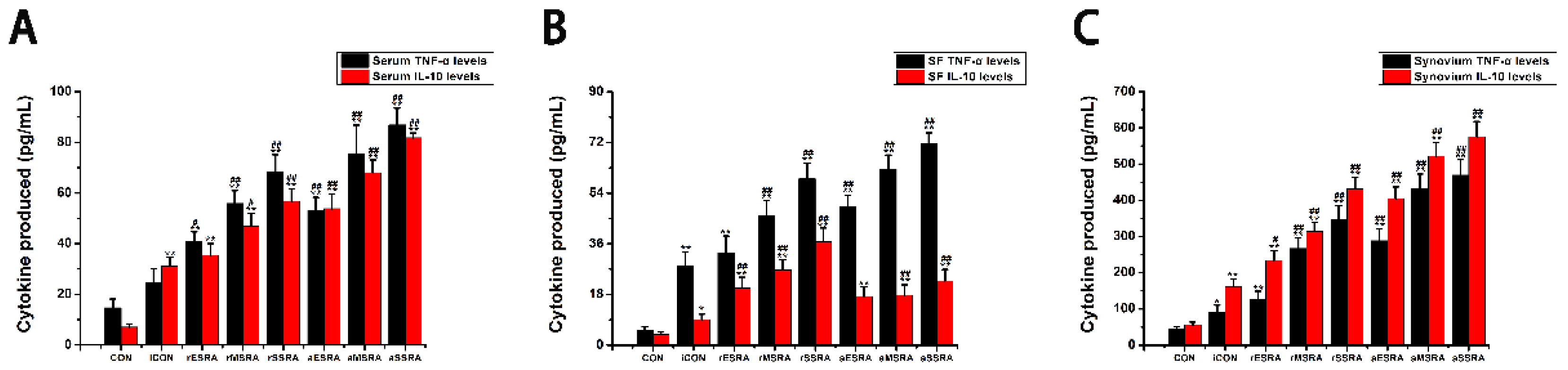
Additionally, a study was performed to evaluate the fluctuations in both inflammatory and anti-inflammatory factors present within serum, SF, and synovium. The results indicated that the levels of inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines in individuals with RA varied depending on their disease activity statues and progression stages. As ERS persists and RA lesions aggravate gradually, the inflammatory response intensifies both locally and systemically. This escalation results in elevated expression of both inflammatory and anti-inflammatory factors in various areas such as serum, SF, and synovium. Specifically, the levels of TNF-α and IL-10 in these areas followed a pattern of increasing expression with disease progression, with the highest levels observed in severe-stage of RA, followed by moderate-stage, and then early-stage. This suggests that as RA develops, the inflammatory response becomes more pronounced at different levels within the body. During activity status of RA, the disease reaches a phase of acute exacerbation. In this condition, both local and systemic inflammatory responses become significantly more severe compared to the remission status. This heightened inflammatory activity leads to a significant increase in the secretion of inflammatory factors by the body. In the scope of this research, the TNF-α levels in serum, SF, and synovium were notably higher during disease activity as opposed to remission status. In the acute exacerbation state of disease activity, the local inflammatory response is notably more intense than the anti-inflammatory response. To counteract this, the body mobilizes both local and systemic cellular immune systems to alleviate the inflammation. This process results in the secretion of numerous anti-inflammatory factors from synovium and blood, which are rich in cellular components. It was observed that the level of anti-inflammatory factor IL-10 in synovium and blood was higher during disease activity when compared to the remission status. However, the production of IL-10 in SF, which contains fewer cells, was limited. During disease remission status, the body maintains a dynamic balance between local and systemic inflammatory and immune responses. Although the local inflammatory response remains high, there is a relatively balanced interplay between inflammatory and anti-inflammatory factors. This equilibrium is achieved by enhancing local immune responses, leading to increased production of anti-inflammatory factors. For example, in this research, it was observed that the levels of IL-10 in SF were elevated during periods of disease remission when contrasted with disease activity status.
This research indicated that patients with RA experience a shift in the balance between inflammatory and anti-inflammatory factors under different environmental conditions. Specifically, TNF-α was recognized as the primary factor present in SF, and was found at higher levels in the bloodstream compared to IL-10. Nonetheless, there were comparatively minor discrepancies in the levels of TNF-α and IL-10 when present in synovium. Simultaneously, this research demonstrated that alterations in caspase-3 levels corresponded with the changes observed in GRP78/Bip within the affected synovium. Additionally, alterations in IL-10 levels in serum, SF, and affected synovium closely mirrored the patterns noted in GRP78/Bip, supporting the anti-inflammatory properties of extracellular GRP78/Bip. These findings implied that GRP78/Bip might play a role in modulating immune reaction, apoptotic processes, and the decrease of inflammation in both local and systemic environments.
Several limitations were present in this study, with the most significant being the small sample size and monocentric design. Participants were recruited exclusively from a single hospital within Chinese racial groups, which may have restricted their representativeness and the generalizability of the results to a broader population. Future research should incorporate a larger sample size to introduce more significant findings, and examine subjects from diverse racial and geographical backgrounds. Another significant limitation pertains to the absence of investigation into the presence of GRP78/Bip in serum, SF, and synovium of healthy individuals due to ethical constraints, thus weakening the ability to establish a clear relationship between GRP78/Bip and the activity and progression of RA. Future research should aim to address these limitations by ensuring comprehensive data collection from both healthy individuals and RA patients to provide a more robust understanding of the role of GRP78/Bip in the disease process. Additionally, this was a cross-sectional study, thus the causalities between GRP78/Bip and RA remains unverified. Further validation is needed through more extensive prospective studies, such as longitudinal or cohort studies. Furthermore, the normal levels of GRP78/Bip in serum, SF, and synovium have not been definitively established, nor have we fully understood the significance of these levels. Various factors including age, sex, diet, ethnicity, physical activity, medication use, the method of estimating GRP78/Bip, and sample storage conditions all have the potential to influence GRP78/Bip levels. Further research is needed to establish a baseline for normal GRP78/Bip levels, understand its implications, and account for potential confounding variables that could affect measurements. By addressing these gaps in knowledge, we can improve our comprehension of the role of GRP78/Bip in different physiological processes and diseases. Last, exploring how interventions specifically targeted at intracellular or extracellular GRP78/Bip impact the activity and progression of RA in animal models or cell-based research was not within the scope of this study. It is recognized that further research is needed to assess the potential impact of interventions specifically aimed at intracellular or extracellular GRP78/BIP on the activity and progression of RA. This may involve exploring the mechanisms through which targeting GRP78/Bip can influence the pathogenesis of the disease and identifying potential therapeutic approaches that can modulate its expression or function. Overall, while this study did not directly investigate the effects of interventions targeting GRP78/Bip on RA, it highlights the need for future research in this area to better understand the role of GRP78/Bip in the pathophysiology of RA and to potentially identify novel treatment strategies for the disease.