1. Introduction
Diabetic foot sepsis (DFS) is the leading cause of hospital admission in individuals with diabetes mellitus (DM), and the two most feared complications of DFS are major amputation and death [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6]. An amputation of the lower extremity is considered major if it is proximal to the ankle joint [
2,
3,
4]. Around 20% of patients admitted with DFS end with a major amputation, and the in-hospital mortality is around 3-7% [
2,
4]. The inhospital is however higher in patients with co-morbidities like hypertension, coronary artery disease and chronic kidney disease [
1,
7,
8]. A state of chronic low-grade systemic inflammation from ongoing release of pro-inflammatory cytokines is characteristic of DM [
9]. Individuals with DM are likely to be overweight or obese, hypertensive and have coronary artery disease, which increase the risk of post-operative complications like surgical site infection (SSI) and acute kidney injury (AKI) [
10].
Individuals with DM are at high-risk of severe COVID-19, and among the features of severe COVID-19 disease is the over-exuberant systemic inflammatory response, the so-called “cytokine-storm”, which adds to a state of chronic low-grade inflammation that is prevalent in individuals with DM [
4,
11,
12]. The risk of a severe COVID-19 and associated mortality is higher in individuals older than 60 years of age who are obese or overweight with or without co-morbid conditions like CKD and DM [
9,
13,
14,
15,
16].
The rise COVID-19 cases led to the implementation of various stages of lock-down, which limited movements in some countries including South Africa [
17]. Access to healthcare establishment for emergency surgical services was limited [
17]. Routine pre-operative COVID-19 PCR testing became mandatory for patients who required surgical intervention at some of the hospitals. Some hospitals assigned one theatre for surgery on all patients who tested positive for COVID-19 who required emergency surgery regardless of the acuity or severity of the illness. Patients who required debridement or amputation of DFS were often not prioritized as DFS was regarded not immediately life threatening. Treatment of DFS is however time sensitive and delay in the initiation of treatment often lead to the spread of the infection and an increased possibility of major amputation or death.
The severity, and thus the likelihood of major amputation and mortality in patients with DFS are sometimes difficult to predict even when classification systems are used [[
19],Monteiro-Soares et al., 2014; [
20],Jalilian et al., 2020]. Recent studies have shown beneficial role of artificial intelligence (AI) for diagnosis, classification, treatment planning and prediction of outcome in patients with DFU and DFS [[
21],Qian, 2021; [
22],Binson et al., 2024; [
23],Guan et al., 2024]. Machine learning (ML) is the most basic form of AI. Machine learning algorithms may be supervised or unsupervised. The commonly used ML algorithms include Random Forest, Support Vector Machine and K-Nearest Neighbour for classificcation of categorical variables whereas Linear Regression, Decision Tree Regression and Support Vector Regression are for continous variable [[
24],Popa et al., 2023]. This study investigated the rate of major amputation and mortality in patients with DFS during the COVID-19 pandemic. Subsequently, the ability of ML algoritms to predict major amputation and death were studied.
2. Materials and Methods
This was a retrospective review of records of patients who were admitted and treated for DFS at a regional hospitals in the Ekurhuleni District of Gauteng Province of South Africa from 1st March 2020 to 30th October 2021. Participants were identified using hospital admission records and data were retrieved from in-hospital, theatre and laboratory findings. Extracted data were entered onto an excel spreadsheet. Review of the records was limited to the period from admission until death or discharge. Records of consecutive patients who were 18 years or older, and were admitted and treated for DFS were included but patients who required re-admission were excluded.
Data retrieved included demography, site and severity of DFS, co-morbidities, HIV and COVID-19 status, laboratory results, type of treatment, level of amputation and outcome. Blood test results retrieved included haemoglobin, white cell count (WCC), platelet count, C-reactive protein (CRP), potassium, urea, creatinine and glycosylated haemoglobin (HbA1c) levels. Post-operative complications and types of definitive treatment including the level of amputations were also captured. Demography and clinical findings were obtained from patient’s admission records and theatre notes, and blood test results from laboratory records.). The main outcome measures were major amputation and mortality. The main exposure variable was COVID-19 status and potential confounders were age, gender, HIV status and the level of haemoglobin and HbA1c. The effect modifiers included occurrence of post-operative complications including pneumonia, surgical site infection and acute kidney injury.
STATA© Statistics and Data Science 17.0 Standard Edition statistical package was used for statistical analysis. Actual numbers and percentages were used to summarize categorical data, which included gender, HIV and COVID-19 status, types of amputation, post-operative complications and the overall outcome. The association between the overall outcome and each of the categorical variables was tested using the two-sample proportions Pearson’s chi-squared test or Fisher’s exact test, with the later used when the count for one of the variables was less than 5%. We summarized continuous data using either the mean with standard deviation or median and interquartile range (IQR) if the data was parametric or non-parametric, respectively. Normally of distribution of continuous data was tested using the Shapiro-Wilk test.
Comparisons of two group means or medians for age and blood levels of potassium, haemoglobin and HbA1c of two groups of participants used the two-sided independent t-test as they were normally distributed. We used the Kruskal-Wallis test to compare medians of WCC, CRP, platelet count, urea and creatinine of 2 groups. Statistical significance was set at a p-value below 0.05. Multivariate logistic regression was done to evaluate factors that had a compounding effect on mortality due to DFS in patients who had COVID-19, and adopted the purposeful selection method to determine the variables to include in multivariate logistic regression [
18]. The cut-off used for inclusion in the logistic regression was a p-value below 0.26 following univariate analysis and less than 0.1 following multivariate logistic regression. We determined the odds of mortality with each unit change of the variables and reported it together with a 95% confidence interval. Subsequently, supervised ML algorithms were used to determine factors that had correlation with mortality. Factors that were significantly associated with mortality were matched and correlated using the ML algorithms. Performance of the ML algorithms were compared using the area under receiver operating characteristic curve. Finaly, Kaplan-Meier survival curve to compare the time to in-hospital mortality between COVID-19 negative and positive participants.
3. Results
There were 114 records for review, 48(42.1%) were females and the mean (SD) age of the entire group was 55(14) years. Leg sepsis was most prevalent diagnosis 79(69.3%) and right laterization 70(61%). There were 54(47.4%) who tested positive for COVID-19 and 41(36%) were HIV positive. Majority, 42(36.8%) had BKA surgery and major amputation was done in 79(69.3%) and 43(37.7%) of the patients admitted with DFS died. The median hospital stay was 11(6-16) days. Pneumonia and SSI developed in 63 (55.3%) and 64 (56.1%), respectively. Of the 41 patients who tested positive for HIV, 56.1% (23/41) were males. Fifty-four (47.4%:54/114) patients tested positive for COVID-19, 53.7% (29/54) of whom were males. The mean (SD) age of patients who tested positive for COVID-19 was 56 (12.3) years compared to 55.5 (15.7) years of the COVID-19 negative group. Concomitent HIV and COVID-19 positive status was recorded in 21.9% (25/114) of the cases. Blood test results showed median (IQR) haemoglobin of 10.3 (9.1-12.1)g/dl, HbA1c 11.2 (9.2-12.6) and potassium 4.6 (1.2-5.4), WCC was 15 (11.9-20.1), CRP 168 (86-238), platelets 401 (260-559), urea 7.8 (4.6-14.2) and creatinine 92µmml/l (63-192) (
Table 1).
Hundred and twelve (98.2%:112/114) of the patients had surgical intervention, comprising of amputations in 86.8% (97/112) and debridement in 11.4% (13/112). Thirty-seven (32.5%:37/114) of the patients ended up with an above knee while 36.8% (42/114) had below knee amputation, for a major amputation rate of 69.2% (79/114). Sixty-three (55.3%:63/114) and 26.3% (30/114) of the patients developed pneumonia and acute kidney injury, respectively during admission (
Table 2).
The median (IQR) length of stay of all the patients was 11 (7-17) days. Forty-three (37.7%:43/114) of the patients died, 62.8% (27/43) of whom were males. The influence of gender on mortality was however not statistically significant (p-value = 0.410). The patiens who died were significantly older at a mean (SD) age of 60.3 (15.5) years compared to 53 (12.6) years of those who were discharged (p-value = 0.007). Other parameters that were statistically significantly different in patients who died compared those who were discharged included HIV positive status of 37.2% versus 19.7% and COVID-19 infection rate of 83.7% versus 25.4%, and higher serum level of potassium (
Table 3).
Table 3.
Comparison of demographic characteristics and laboratory results of participants with DFS based on overall outcome of death or discharge.
Table 3.
Comparison of demographic characteristics and laboratory results of participants with DFS based on overall outcome of death or discharge.
| Variable |
Died |
Discharged |
p-value |
| Gender |
|
|
|
Male
Female |
27(62.8%)
16(37.2%) |
39(54.9%)
32(45.1%) |
0.410 |
| Age (SD) |
60(15) |
53(12.6) |
0.0067 |
| Nature of involvement |
Cellulitis
Foot sepsis
Gangrenous foot
Leg sepsis
Leg ulcer
Leg sepsis |
0(0%)
11(25.6%)
1(2.3%)
1(2.3%)
1(2.3%)
29(67.4%) |
1(1.4%)
15(21.1%)
0(0%)
3(4.2%)
2(2.8%)
50(70.4%) |
0.830 |
| Laterization |
Left
Right
Bilateral |
20(46.5%)
22(51.2%)
1(2.3%) |
23(32.4%)
48(67.6%)
0(0%) |
0.072 |
| Laboratory results |
| WCC |
17.2(13.45-21.33) |
14.54(11.6-18.37) |
0.0980 |
| CRP |
201(103-251) |
152(85-221) |
0.1874 |
| Haemoglobin |
9.8(8-11.3) |
10.9(9.6-12.6) |
0.0021 |
| Platelets |
315(201-559) |
417(298-561) |
0.0283 |
| Potassium |
5.1(4.4-5.9) |
4.5(4.1-5.1) |
0.0014 |
| Urea |
13(5.6-21.2) |
7.6(4.1-11.1) |
0.0038 |
| Creatinine |
176(66-302) |
89(55-128) |
0.0039 |
| HbA1c |
12.05(10.6-12.6) |
10.8(8.6-13.2) |
0.1353 |
| COVID-19 status |
No
Yes |
7(16.2%)
36(83.7%) |
53(74.6%)
18(25.4%) |
<0.000 |
| HIV status |
No
Yes |
16(37.2%)
27(62.8%) |
57(80.3%)
14(19.7%) |
<0.000 |
Table 4.
Comparison of treatement indstituted and outcomes between patients who died and those who were discharged.
Table 4.
Comparison of treatement indstituted and outcomes between patients who died and those who were discharged.
| Variable |
Died |
Discharged |
p-value |
| Extent of Surgery |
Above knee amputation
Below knee amputation
Debridement
None
Trans-metatarsal amputation
Toectomy |
15(34.9%)
19(44.2%)
4(9.3%)
1(2.3%)
3(6.9%)
1(2.3%) |
22(31%)
23(32.4%)
9(12.7%)
1(1.4%)
4(5.6%)
12(16.9%) |
0.178 |
| Major amputation |
No
Yes |
9(20.9%)
34(79.1%) |
26(36.6%)
45(63.4%) |
0.078 |
| Type of Anaesthesia |
|
|
|
General anaesthesia
Spinal anaesthesia
Not applicable |
11(25.6%)
31(72.1%)
1(2.3%) |
14(19.7%)
56(78.9%)
1(1.4%) |
0.619 |
| Surgical site infection |
No
Yes |
34(79.1%)
9(20.9%) |
19(26.8%)
52(73.2%) |
<0.0001 |
| Acute kidney injury |
No
Yes |
20(46.5%)
23(53.5%) |
64(90.1%)
7(9.9%) |
<0.0001 |
| Pneumonia |
|
|
|
No
Yes |
2(4.7%)
41(95.3%) |
49(69%)
22(31%) |
<0.0001 |
| Deep vein thrombosis |
No
Yes |
43(100%)
0(0%) |
70(98.6%)
1(1.4%) |
1.000 |
| Urinary tract infection |
No
Yes |
40(93%)
3(7%) |
42(59.2%)
29(40.8%) |
<0.0001 |
| Gastroenteritis |
|
|
|
No
Yes |
36(83.7%)
7(16.3%) |
64(90.1%)
7(9.9%) |
0.311 |
| Length of hospital stay |
7(5-16) |
12(8-16) |
0.0269 |
Although lower level of platelet count (p-value = 0.400) and raised serum potassium (p-value = 0.108), urea (p-value = 0.591) and creatinine (p-value = 0.653) were significantly associated with mortality on univariate analysis, their influence diminished following a multivarate analysis, unlike older age and concurrent COVID-19 and HIV infection(s) (
Table 3).
Table 5.
Results following multivariate logistic regression analysis for covariates and compounder that were predictive of mortality in patients who had DFS.
Table 5.
Results following multivariate logistic regression analysis for covariates and compounder that were predictive of mortality in patients who had DFS.
| Variable |
Odds ratio |
Standard error |
Z |
P>|z} |
95% CI |
| Age |
1.065 |
0.025 |
2.65 |
0.008 |
1.016-1.115 |
| Haemoglobin |
0.655 |
0.086 |
-3.20 |
0.001 |
0.506-0.849 |
| COVID-19 positive |
39.718 |
29.352 |
4.98 |
<0.001 |
9.332-169.053 |
| HIV positive |
12.698 |
8.499 |
3.80 |
<0.001 |
3.419-47.153 |
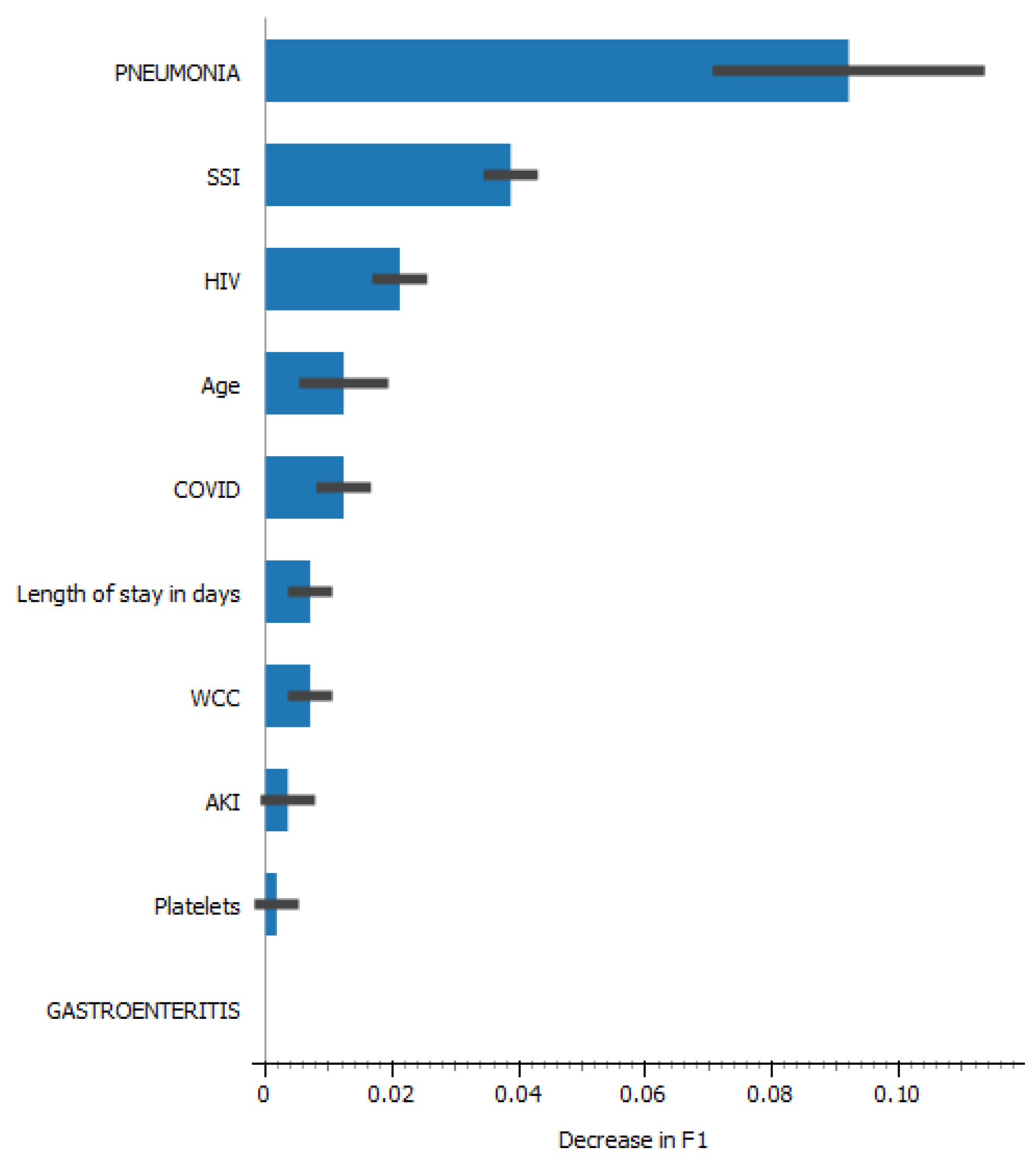
Among those who died the mean/median was 60(15) years for age, haemoglobin levels 9.8(8-11.3), platelets 315(201-559), potassium 5.1(4.4-5.9), urea 13(5.6-21.2), creatinine 176(66-302) and length of hospital stay was 7(5-16) days. The frequency amongst those who died was 36(84%) had positive covid results and 27(63%) were HIV positive. In relationship to information gain for our model the following variables were the top five predictors for the outcome (died/discharged) pneumonia, covid, SSI, AKI and creatinine with Information gain of 0.333, 0.248, 0.195, 0.166 and 0.15, respectively.
Based on the data provided, several models were evaluated to predict the outcomes (Died/Discharged) in DFU (Diabetic Foot Ulcer) patients. The models were assessed using various metrics, including AUC (Area Under the ROC Curve), CA (Classification Accuracy), F1 Score, Precision, Recall, and MCC (Matthews Correlation Coefficient). Random Forest (RF): The RF model demonstrated exceptional performance with an AUC of 0.965, a CA of 0.895, an F1 score of 0.893, and a high MCC of 0.775. These metrics suggest that the RF model has a strong ability to predict the outcome accurately, with balanced precision and recall.
Gradient Boosting also performed well, achieving an AUC of 0.947, a CA of 0.886, and an F1 score of 0.885. However, it was slightly less effective than the RF model, as indicated by its lower MCC of 0.755. Similarly, the Naïve Bayes had a commendable performance with an AUC of 0.931 and an F1 score of 0.868. However, it still lagged behind the RF model. Both the RF and Naïve Bayes faired much better compared to Logistic Regression, SVM, and Neural Network. Logistic Regression, SVM, and Neural Network had significantly lower AUC values, like 0.478 of Logistic Regression, indicating poor predictive capability for the given dataset (
Table 6).
The ensemble technique, referred to as “Stack,” outperformed all individual models, achieving the highest AUC of 0.966, CA of 0.904, and an F1 score of 0.903. Its MCC of 0.793 also indicates strong performance and generalizability. RF with Stratified 5-Fold Cross-Validation: The RF model was tested across multiple folds (RF4 through RF11), with consistent results across these folds. The AUC remained around 0.970, with a CA of 0.895 and an F1 score of 0.893. The consistency of these results across different folds confirms the robustness of the RF model (
Table 7).
Among all the models tested, the RF Stack ensemble technique performed the best, with the highest overall metrics across the board. However, if focusing on individual models, Random Forest 5 provided the most reliable performance, particularly in terms of AUC and MCC. These findings indicate that ensemble methods (Stack) or Random Forest can be highly effective in predicting clinical outcomes in DFU patients, offering reliable and robust predictions. The final models with favourable F1 scores were:
| |
AUC |
CA |
F1 |
Prec |
Recall |
MCC |
| RF5 |
0.967 |
0.895 |
0.919 |
0.883 |
0.958 |
0.775 |
Pneumonia and surgical site infection were the stronger predictors of mortality (
Figure 1).
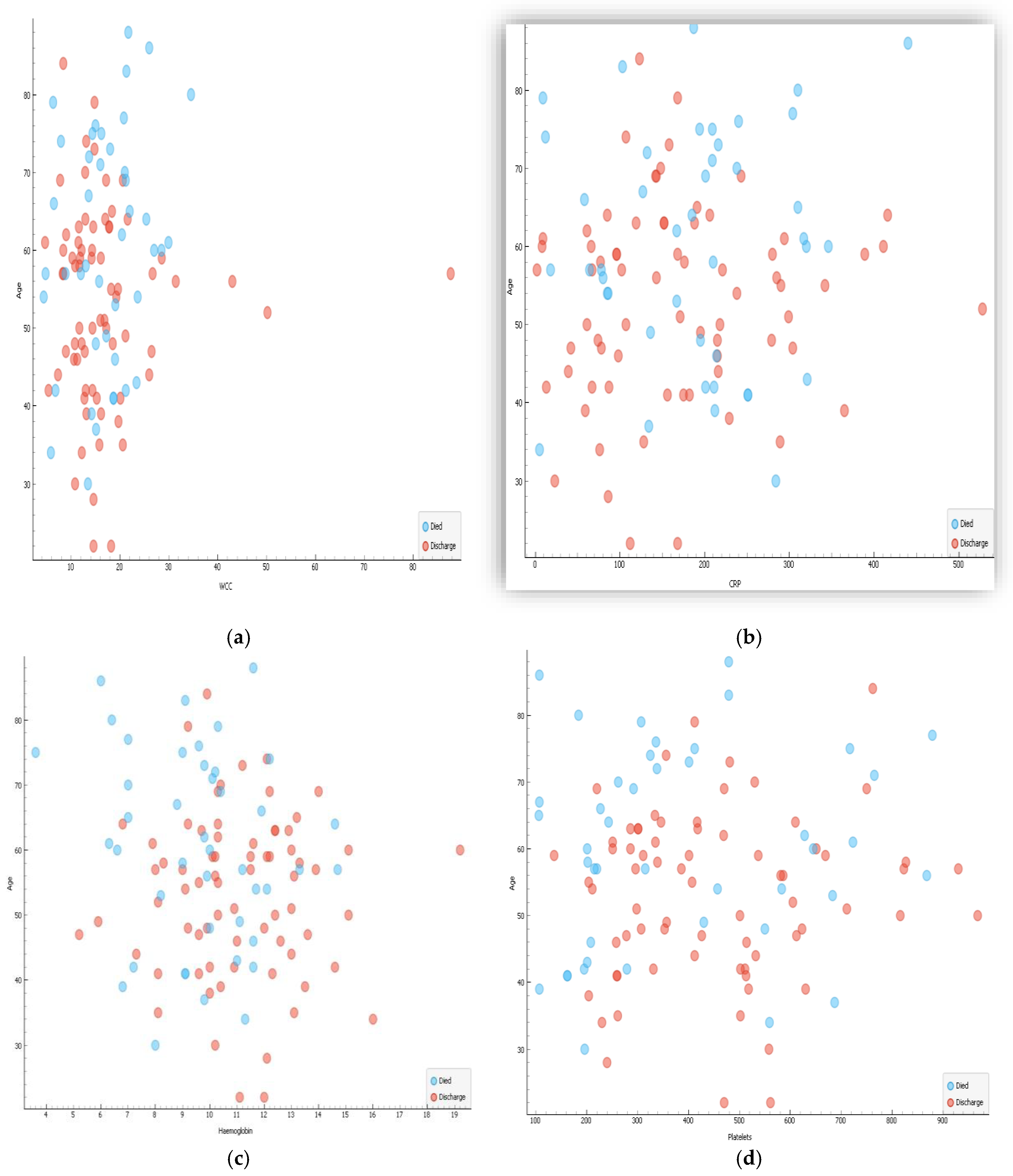
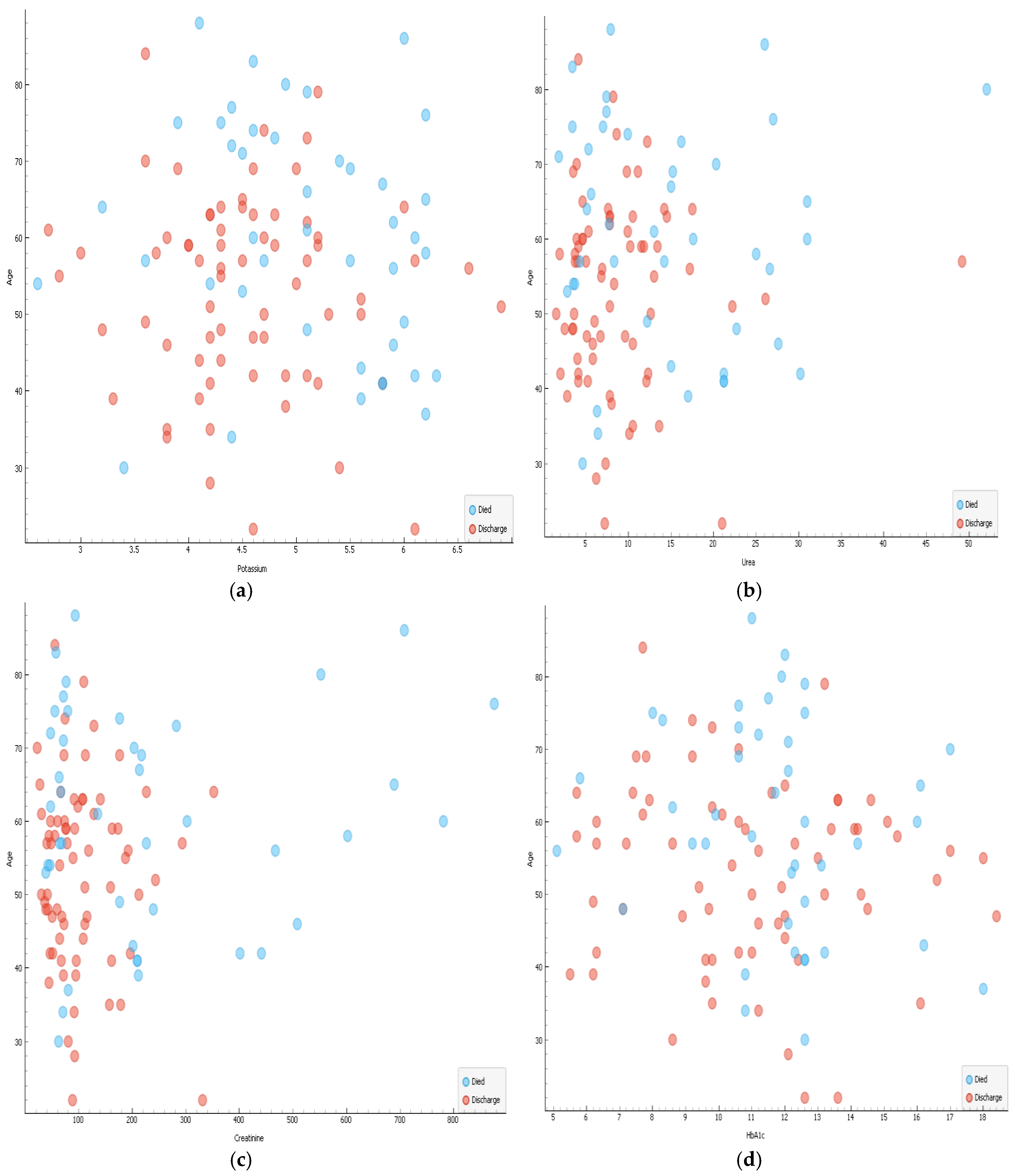
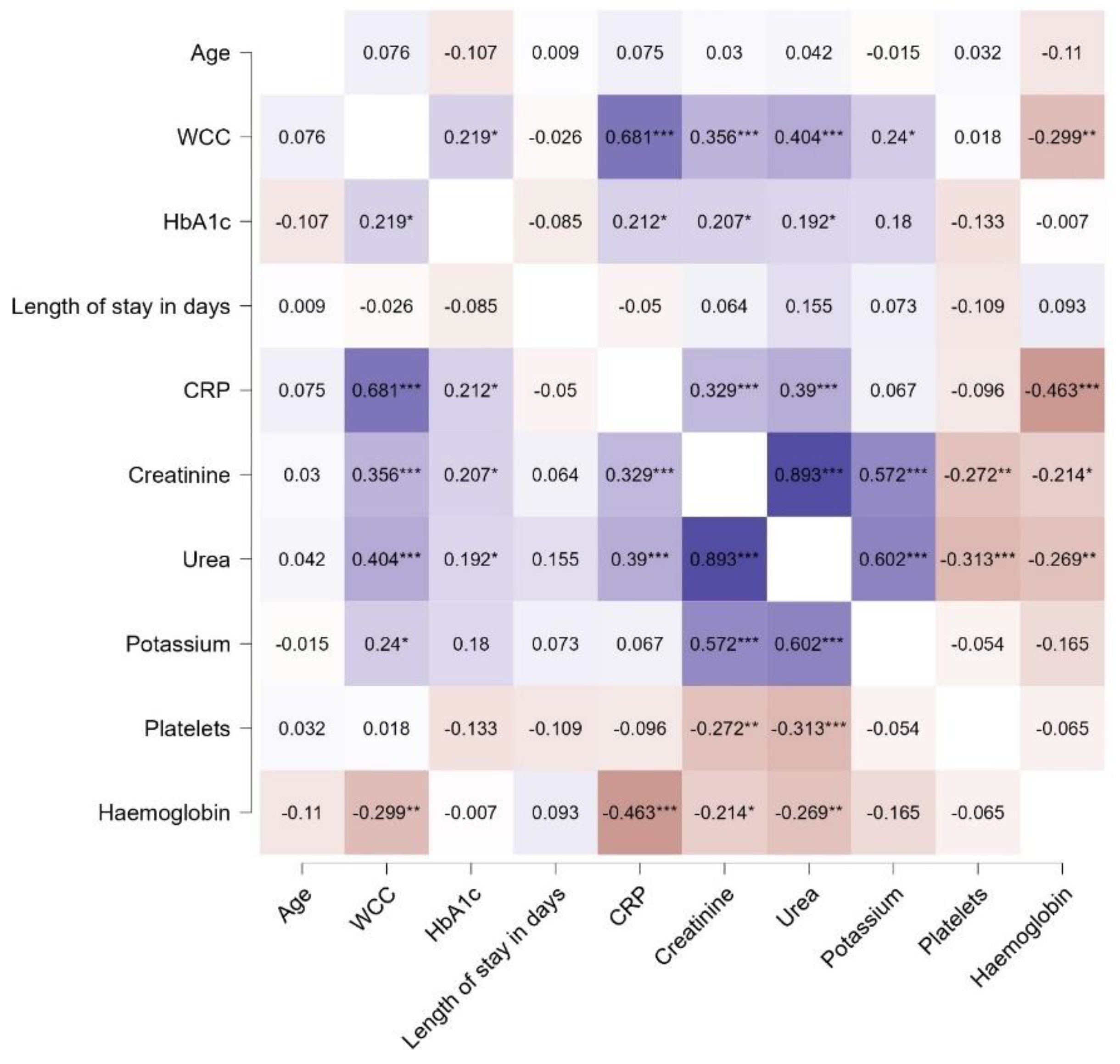
Correlations of age and biochemical results are shown in
Figure 2a–d whereas that of age and haematological parameters are shown in
Figure 3a–d.
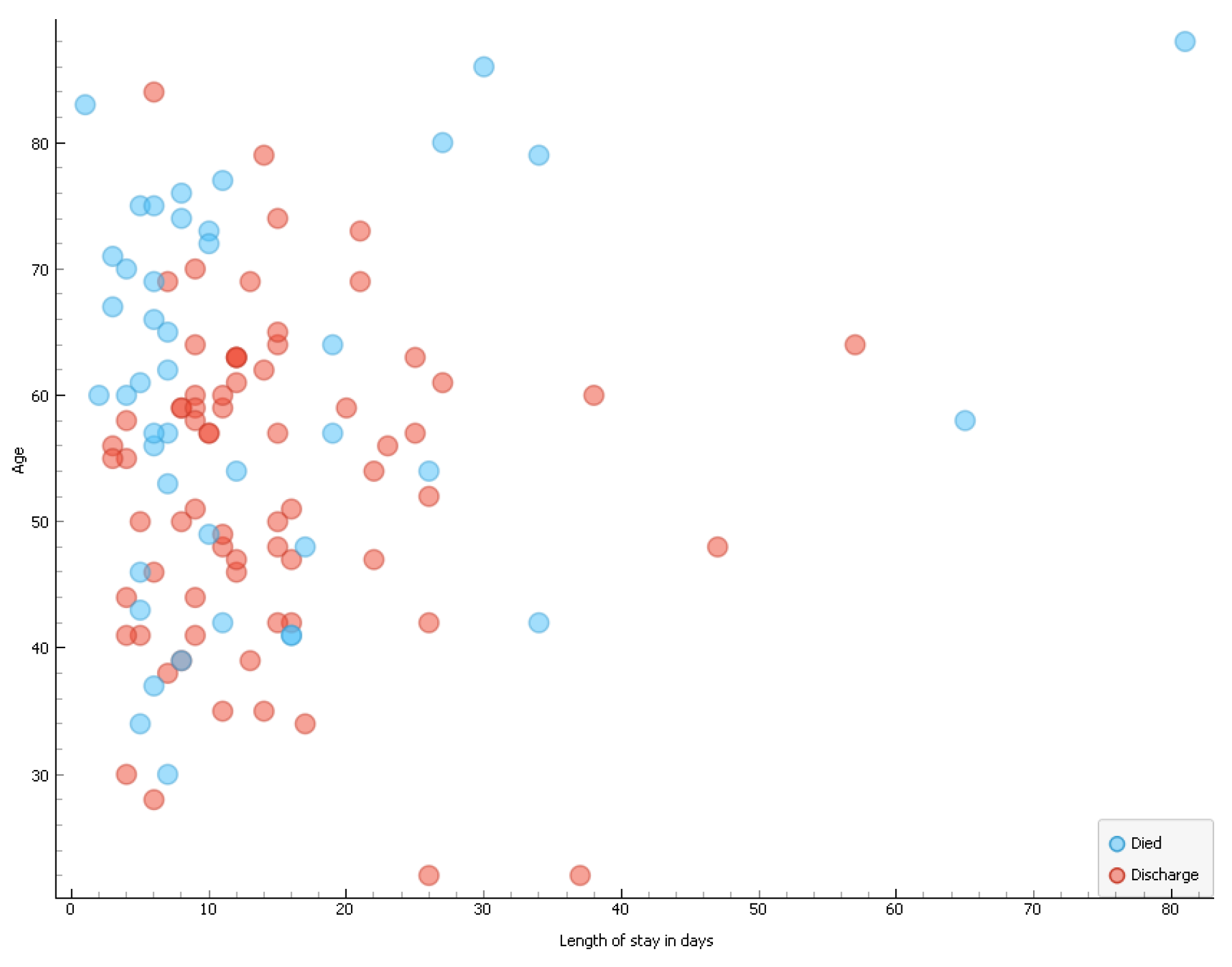
Majority of patients died or were discharged within 20 days (
Figure 4).
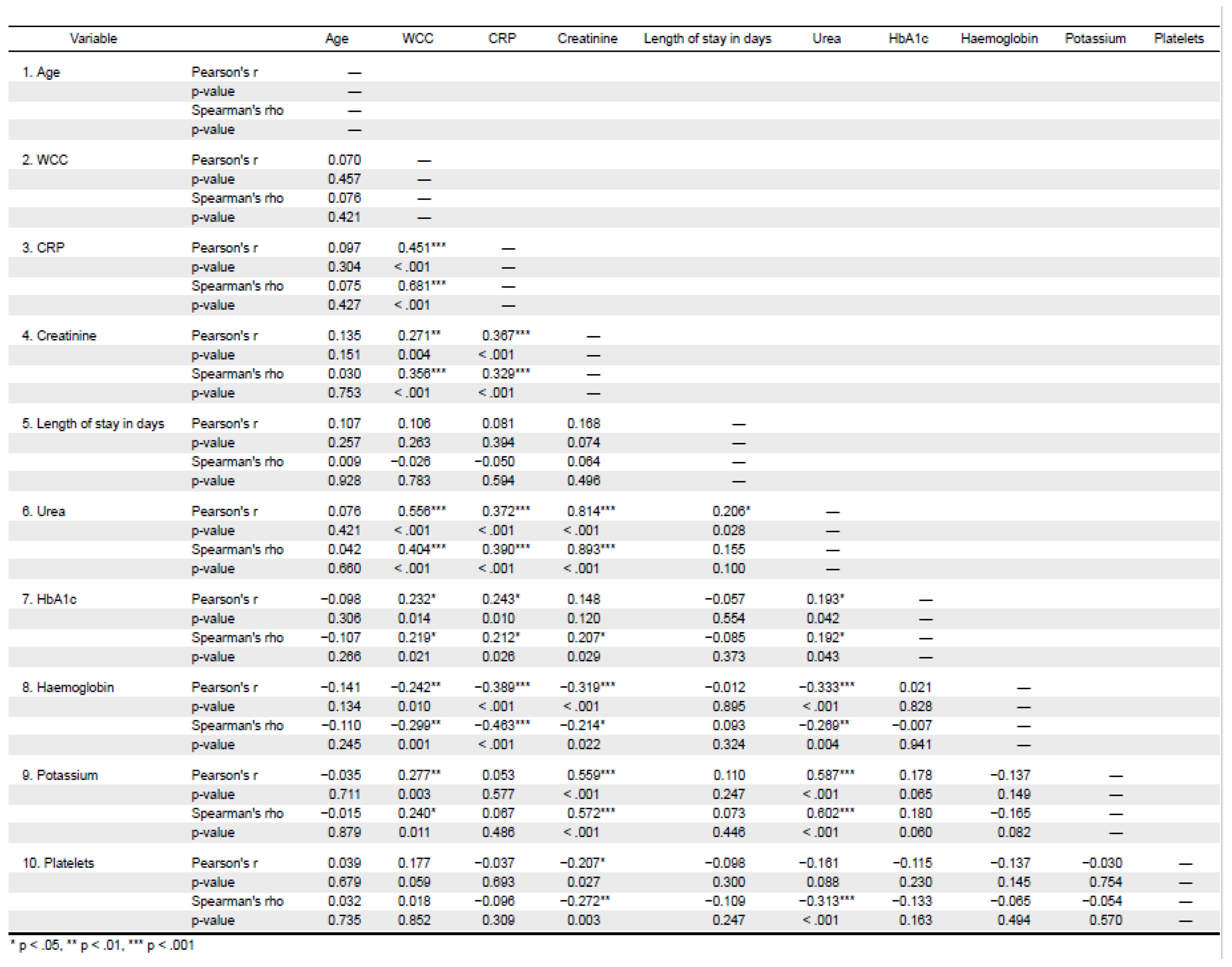
There was strong positive correlation for urea and creatinine r=0.893, CRP and WCC r=0.681 and urea and potassium r=0.602 (
Figure 5a,b)
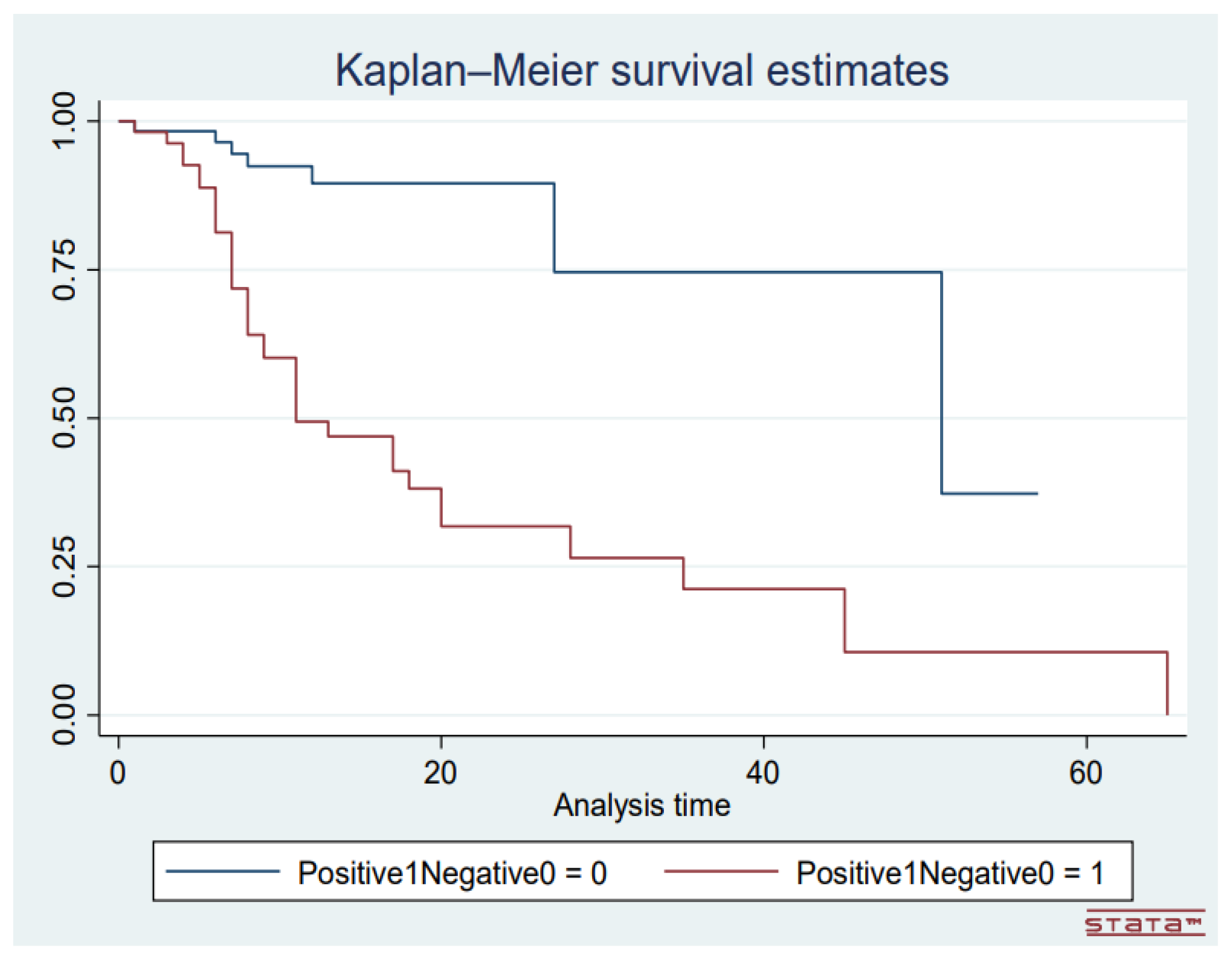
The median length of hospital stay of patients was statistically sighnificantly shorter than that of those who were discharged (p = 0.018). The length of hospital stay of the patients was however not influenced by gender (p = 0.2800) or COVID-19 status (p = 0.492). Majority of the deaths in patients who tested positive for COVID-19 occurred within the first 10 days following admission to the hospital (
Figure 6).
4. Discussion
Diabetic foot sepsis is responsible for the majority of hospital admissions of individuals with DM. Measures of outcome following admission of a patient with include the number of debridement, the need and level of amputation, length of hospital stay and the 30-day mortality [
5,
6]. This study was set out to investigate the influence of COVID-19 pandemic on the rate of major amputation and in-hospital mortality in patients who had DFS. Among the main findings were the high rate of COVID-19 infection in patients admitted with DFS, major amputation rate of 70% and the overall mortality rate of 38%. Additionally, majority of the patients who died were above the age of 60 years and 84% of the deaths were among patients who tested positive for COVID-19.
Complications of DM including DFS are more common in men as was also demonstrated in the current study [
25]. Furthermore, more men with DFS tested positive for COVID-19, which is in line with previous findings [
3,
26]. Among the plausible explanations for the high-rate of COVID-19 infection and mortality in men is a higher density of angiotensin converting enzyme receptors 2 (ACE2) in their hearts, lungs, kidneys, gastrointestinal tract and blood vessels compared to women [
27,
28]. Furthermore, men often delay seeking treatment, which might have also contributed to higher mortality [
6].
The mean age of the patients in the current study was 59 years, which is similar to findings from studies done in other countries [
3,
4,
6]. The mortality rate in our study was highest in patients who were older than 60 years, which was not surprising as the elderly are likely to have co-morbidities like coronary artery disease, hypertension and chronic kidney disease that increases the likelihood of postoperative death [
14,
26]. Some of the patients who concurrently were hypertensive might have been on ACE inhibitors. The use of ACE inhibitors can cause the up-regulation of ACE2 receptors, which increases the risk of COVID-19 infection, and the development of a severe disease [
11]. The likelihood of severe COVID-19 and its complications including death is higher in individuals above the age of 60 years [
11,
25].
Patients with DFS may be known or previously unknown with DM [
8]. Regardless of background history, the HbA1c in individuals with DM complicated by DFS is usually above 7.5%, as was the case in majority of the patients in the current study [
7]. Serum levels of potassium, urea and creatinine of the patients who died were markedly higher than of those who survived, which was not a surprise as severe sepsis due to DFS and cytokine storm of COVID-19 may lead to acute kidney injury [
9,
14,
15]. The likelihood of acute injury is especially higher in individuals who are already at an increased risk of renal dysfunction like patients with DM [
9,
14,
15]. The low levels of platelets count observed in patients who died is consistent with the expectations in severe sepsis and the cytokine storm of COVID-19.
The key priorities during management of a patient with DFS include fluid resuscitation, correction of electrolyte derangements, glycaemic control and early initiation of treatment with a broad-spectrum antibiotic [
20]. Acute kidney injury is among the common complications of DFS as demonstrated in the study [
14]. Acute care of a patient who has DFS is however labour intensive and requires hourly monitoring which might not have been feasible during the COVID-19 pandemic [
27]. Debridement and/or amputation of DFS is done in theatre following fluid resuscitation and when a patient’s hydration status, electrolyte derangements and acid base status have been corrected, and the level of blood glucose is below 15mmol/l [
4,
8]. The need for amputation depends on the severity of the infection, and patients with spreading necrotizing infection or wet gangrene require guillotine amputation [
4].
Of concern in the current study was the rate of major amputation of 70%, which was much higher than the 12.9% reported by Aulivola et al [
25]. Although high, the rate of major amputation in our study mirrors the findings by Cheddie and colleagues, in a study done in KwaZulu-Natal in South Africa [
3]. What was more concerning was the 47% of major amputations that were above the knee. Interestingly, neither concurrent HIV nor COVID-19 infection had an influence on the rate of major amputation, which is contrary to the findings by Chaudhary et al., 2021 [
4] and Zayed et al., 2022 [
16].
Patients with DM are immunocompromised and prone to local and systemic post-operative complications. The current study only focused on the final amputation and did not document the overall number of procedures done in each patient. The most common local complication following amputation for DFS is SSI, which often necessitates “salami” amputations [
7]. The other complications that are common in patients admitted for management of DFS with or without COVID-19 are pneumonia and acute kidney injured, which was also the case in the present study [
3,
8,
26]. The overall mortality in the study was 38%, which is four times higher than the 8.6% reported before the COVID-19 pandemic [
20]. Majority, 84% of the deaths in patients with DFS was among the patients who tested positive for COVID-19, which is keeping with the high-rate of severe COVID-19 and mortality in individuals with DM [
11]. Majority of the deaths in individuals who were above the age of 60 years, which is consistent with previous findings [
6]. Additionally, most of the mortalities occurred in the participants who had a major amputation, which is in keeping with findings from a previous studies [
7,
28,
29].
Recent studies have shown beneficial role of artificial intelligence (AI) for diagnosis, classification, treatment planning and prediction of outcome in patients with DFU and DFS [
21,
22,
23]. Machine learning (ML) is the most basic form of AI. Machine learning algorithms may be supervised or unsupervised. The commonly used ML algorithms include Random Forest, Support Vector Machine and K-Nearest Neighbour for classificcation of categorical variables whereas Linear Regression, Decision Tree Regression and Support Vector Regression are for continous variable [
22,
24]. The RF model demonstrated exceptional performance with an AUC of 0.965, and a strong ability to predict the outcome accurately, with balanced precision and recall.
Although there are limited tstudies on the role of ML-aided screeinng, diagnosis and decision making in the management of DFS, a lot is written on the role of AI in DM [
34,
35]. The use of AI for screening of DM-associated peripheral neuropathy has grown exponentially [
34]. Peripheral neuropathy is the commonest complication in patients with DM, and is the major risk factor of DFU [
34]. Majority of patients with DFS had had DFU, which did not heal. Once a neuropathic or neuroischaemic DFU has developed the focus should be to expedite healing and to prevent the development of DFS. Patients with DFS are lileky to end up with major amputation and subsequently die within 5 years [
31].
Patients with DFS require timeous and aggressive to prevent amputation or death. Knowing which patients are most at risk of death is important for tailoring of the aggression. In a study by Stefanopoulos et al using ML algorithms age above 40 years, gangrene, septic shock, low haemogobin level anaemia were among the factors that contributed significantly to the need for major amputation during admission [[
32],Stefanopoulos et al., 2024]. Similarly, following application of ML predictive models [Xie et al., (2021) found patients with DFS with elevated WCC and serum creatinine during admission; amongst other factors wer more likely to end up with a major amputation [
33]. Our study found that pneumonia, covid, SSI, AKI and creatinine strongly associated with mortality in patients with DFS. A study by Popa et al. (2023) combined categorical and continous variables and found that among others age of a patient, haemoglobin level, urea, creatinine, glomerular filtration rate and length of hospital stay were significantly associated with mortality from DFS [
34]. However, the aim of above study was to determine survival of patients with DFU over a 5 and 10 years period.
This study was retrospective, it is likely that we missed some records. The sample size is relatively small and the sample was not divided into training, testing and validation set as the size was small. A small sample size might have led to over-fitting. We did not investigate the influence of potential compounding factors such as the expertise involved in treatment decisions and waiting time for theatre, and the study was based at one facility and therefore the findings may not be generalizable.
5. Conclusions
The COVID-19 pandemic led to an increase in the rate of major amputation and mortality in patients with DFS. The COVID-19 status had no influence on the rate of amputation. The in-hospital mortality was higher in patients who older than 60 years old and tested positive for COVID-19. We recommend prioritization of patients with DFS for aggressive and timeous treatment during a pandemic, as they are at high-risk of major amputation and mortality.
Author Contributions
CM: TM, PM, AV, WM, MSM, TEL. Conceptualization, CM, TEL; protocol development, CM,TM,PM,AV,WM,TEL methodology, investigation, CM,TEL; resources, CM, TEL.; data curation, CM,TEL,MSM; writing—original draft preparation, CM,MSM,TEL.; writing—review and editing, CM, TM, PM, AV, WM, MSM, TEL X.; TEL. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Human Research Ethics Committee (Medical) of University of the Witwatersrand. Permission to conduct the study was also received from the CEO of Thelle Mogoerane Hospital and Research Review Board of Ehurrhuleni District.
Informed Consent Statement
Patient consent was waived as the study was retrospective and involved review of record.
Data Availability Statement
Anonymized data for the study will be made available on request.
Acknowledgments
We sincerely appreciate the support provided by members of staff at Patients Record Department of Thelle Mogoerane Hospital for their assistance during data collection.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Vuorlaakso, M.; Kiiski, J.; Salonen, T.; Karppelin, M.; Helminen, M.; Kaartinen, I. Major Amputation Profoundly Increases Mortality in Patients with Diabetic Foot Infection. Frontiers in Surgery 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkler, E.; Schoni, M.; Krähenbűhl, N.; Uҫkay, I.; Waibel, F.W.A. Foot Osteomyelitis Location and Rates of Primary or Secondary Major Amputations in Patients With Diabetes. Foot & Ankle International 2022, 43, 957–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheddie, S.; Mannel, C.G.; Pillay, B. Spectrum of disease and outcome of primary amputation for diabetic foot sepsis in rural Kwazulu-Natal. South African Journal of Surgery 2018, 56, 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, N.; Huda, F.; Roshan, R.; Basu, S.; Rajput, D.; Singh, S.K. Lower Limb Amputation Rates in Patients With Diabetes and an Infected Foot Ulcer: A Prospective Observational Study. Wound Management & Prevention 2021, 67, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyaraman, K.; Berhane, T.; Hamilton, M.; Chandra, A.P. Mortality in patients with diabetic foot ulcer: a retrospective study of 523 cases from a single Centre in the Northern Territory of Australia. BMC Endocrine Disorders 2019, 19, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adeleye, O.O.; Ugwu, E.T.; Gezawa, I.D.; Okpe, I.; Ezeani, I.; Enamino, M. Predictors of intra-hospital mortality in patients with diabetic foot ulcers in Nigeria: data from the MEDFUN study. BMC Endocrine Disorders 2020, 20, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amman, A.S.; Khalid, R.; Malik, U.; Zeb, M.; Abbas, H.M.; Khattak, S.B. Predictors of lower limb amputations in patients with diabetic foot ulcers presenting to a tertiary care hospital of Pakistan. JPMA. 2021, 71, 2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atosona, A.; Larbie, C. Prevalence and Determinants of Diabetic Foot Ulcers and Lower Extremity Amputations in Three Selected Tertiary Hospitals in Ghana. J Diabetes Res. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanelli, V.; Fiorentino, M.; Cantaluppi, V.; Gesualdo, L.; Stallone, G.; Ronco, C.; Castellano, G. Acute kidney injury in SARS-CoV-2 infected patients. Critical Care 2020, 24, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortington, L.V.; Geertzen, J.H.B.; van Netten, J.J.; Postema, K.; Rompers, G.M.; Dijkstra, P.U. Short and Long Term Mortality Rates after a Lower Limb Amputation. European Journal of Vascular & Endovascular Surgery 2013, 46, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Karakiulakis, G.; Roth, M. Are patients with hypertension and diabetes mellitus at increased risk for COVID-19 infection? Lancet Resp Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulton, A.J.M.; Vileiyte, L.; Ragnarson-Tennvall, G.; Apelqvist, J. The global burden of diabetic foot disease. Lancet 2005, 366, 1719-24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Channappanavar, R.; Perlman, S. Pathogenetic human coronavirus infections: causes and consequences of cytokine storm and immunopathy. Seminar in Immunopathology 2017, 39, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabarre, P.; Dumas, G.; Dupont, T.; Darmon, M.; Azoulay, E.; Zafrani, L. Acute kidney injury in critically ill patients with COVID-19. Intensive Care Medicine 2020, 46, 1339–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, R.C.W.; Holt, R.I.G. COVID-19 and diabetes. Diabet. Med. 2020, 37, 723–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zayed, H.; Musajee, M.; Thulasidasan, N.; Sayed, M.; Francia, F.; Green, M.; Arissol, M.; Lakhani, A.; Biasi, L.; Patel, S. Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on the Outcomes in Patients with Critical Limb Threatening Ischaemia and Diabetic Foot Infection. Annals of Surgery 2022, 275(6), 1037–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, D.; Diao, D.; Chandramohan, K.; Booth, C.M. Recommendations for Surgery During the Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19) Epi demic. Indian Journal of Surgery 2020, 82, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bursac Z, Gauss CH, Williams DK, Hosmer DW. Purposeful selection of variables in logistic regression. Source Code for Biology and Medicine 2008; 3: 17. [CrossRef]
- Monteiro-Soares, M., Martins-Mendes, D., Vaz-Carneiro, A., Sampio, S., Dinis-Ribeiro, M. Classification systems for lower extremity amputation prediction in subjects with active diabetic foot ulcer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2014; 30(7): 610-622. [CrossRef]
- Jililian, M., Sarbarzeh, P.A., Oubari, S. Factors Related to Severity of Diabetic Foot Ulcer: A Systematic Review. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2020; 13, 1835-1842. [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y. Exploration of machine algorithms based on deep learning model and feature extraction. Mathematical Biosciences and Engineering.18(6):7602-7618.
- Binson, VA, Thomas S, Subramoniam M, Arun J, Naveen S, Madhu S. A Review of Machine Learning Algorithms for Biomedical Applications. Annals of Biomedical Engineering (2024) 52:1159-1183.
- Guan H, Wang Y, Niu P, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Miao R, Fang X, Yin R, Zhao S, Liu J, Tian J. The role of machine learning in advancing diabetic foot: a review. DOI 10.3389/fendo.2024.1325434.
- Popa, A.D., Gavril, R.S., Iolanda Valentina Popa, Laura Mihalache, Andreea Gherasim, George Nita, Mariana Graur,Lidia Iuliana Arhire, Otilia Nita.Survival Prediction in Diabetic Foot Ulcers: A Machine Learning Approach. J.Clin.Med.2023,12,5816.
- Forlee, M. What is the diabetic foot? The rising prevalence of diabetes worldwide will mean an increasing prevalence of complication, SAMJ. 2010, 28(4), 152-157.
- Aulivola, B.; Helen, C.N.; Haldane, A.D.; Sheahan, M.G.; Veraldi, J.R.; Skillman, J.J.; Campbell, D.R.; Scovell, S.D.; LoGerfo, F.W.; Pomposelli Jr, F.B. Major lower extremity amputation: outcome of a modern series. [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Dai, Z.; Huang, C.; Chen, H.; Wang, X.; Li, X. Gastrointestinal Disease and COVID-19: A Review of Current Evidence. Dig Dis. 2022, 40(4), 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurbei, S. The renin-angiotensin system in COVID-19: Why ACE2 targeting by coronaviruses produces higher mortality in elderly hypertensive patients? Bioessays 2021; 43(3): e2000112. [CrossRef]
- Tuttolmondo A, Maida C, Pinto A. Diabetic foot syndrome: Immune-inflammatory features as possible cardiovascular markers in diabetes. World J Orthop 2015; 6(1): 62-76. [CrossRef]
- Panuda JS, Macalalad-Josue AA, Buenaluz-Sedurante M. Factors associated with In-Hospital Mortality with Diabetes Admitted for Lower Extremity Infections. Fed J ASEAN Endocr Soc. 2019; 34(1): 36-43. [CrossRef]
- Mokoala TC, Sididzha V, Molefe ED, Luvhengo TE. Life expectancy of patients with diabetic foot sepsis post-lower extremity amputation at a regional hospital in a South African setting. A retrospective cohort study. Surgeon 2023; S1479-666X(23)00143-9. [CrossRef]
- Stefanopoulos, S., Qiu, Q., Ren,G., Ahmed, A., Osman, M., Brunicardi, C.F., Nazzal, M. A Machine learning Model for Prediction of Amputation in Diabetics. Journal of Diabetis Science and Technology 2024, 18(4), 874-881. 4). [CrossRef]
- Xie, P., Li,Y., Deng, B., Chenzhen Du, C., Rui, S., Deng, W., Wang, M., Boey, J., Armstrong, D.G., Ma, Y., Deng, W. An explainable machine learning model for predicting in-hospital amputation rate of patients with diabetic foot ulcer. Int Wound j. 2022;19:910-918. [CrossRef]
- Radunovic, G., Velickkovic,Z., Pavlov-Dolijanovic, S., Janjic, S., Stojic, B., Velkova, I.J., Suljagic, N., Soldatovic, I. Wearable Movement Exploration Device with Machine Learning Algorithm for Screening and Rracking Diabetic Neuropathy – A Cross-Sectional, Diagnostic, Comparative Study. Biosensors (Basel), 14(4), 166. [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, G., Monge, J., Postolache, O., Pereira, J.M.D. A Novel AI Approach for Assessing Stress Levels in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Based on the Acquisition of Physiological Parameters Acquired during Daily Life. Sensors (Basel), 24(13), 4175. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).