Submitted:
10 September 2024
Posted:
10 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- This study introduces a unique data augmentation method utilizing Gaussian noise addition and signal stretching to generate synthetic data, effectively addressing the challenge of insufficient defect data in industrial environments. These traditional techniques simulate varied operating conditions and different rotational speeds, contributing to more robust fault diagnostics.
- The study further enhances the data augmentation process by integrating advanced techniques, including Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM), Autoencoder (AE), and Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs). This approach significantly improves the performance of diagnostic algorithms, reducing false positives and increasing fault detection rates, leading to a substantial boost in the accuracy and reliability of machine learning models for fault detection and classification.
- The study underscores the critical role of data augmentation in fault diagnostics, demonstrating how a well-augmented dataset can enhance predictive maintenance protocols. By ensuring the availability of diverse and representative data, the research paves the way for more effective and reliable fault detection, contributing to the efficient operation of industrial systems.
2. Backgrounds and Related Works
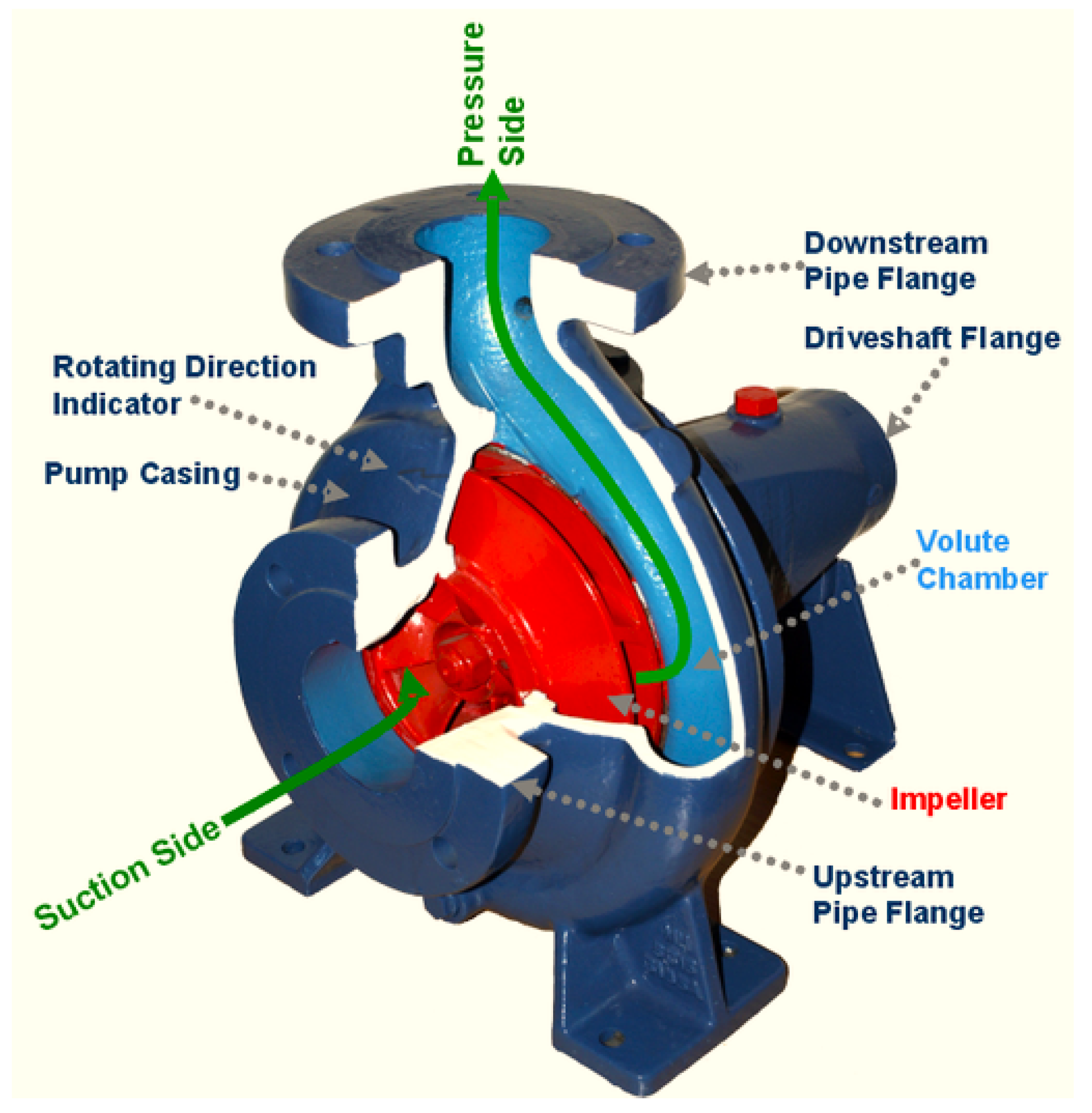
2.1. Fault Diagnostics under Vibration-Based AC Motor-Driven Centrifugal Pumps
2.2. Gaussian Noise and Signal Stretching
2.3. Machine Learning Classifier
2.4. Long Short-Term Memory Networks (LSTM)
2.5. Autoencoder Network
2.6. Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs
- Generator (G): The generator network takes as input a random noise vector z (often sampled from a uniform or normal distribution) and transforms it into a synthetic data sample . The generator is parameterized by , which are the weights of the neural network.
- Discriminator (D): The discriminator network takes as input a data sample x (which can be real or generated) and outputs a probability indicating whether the sample is real (close to 1) or generated (close to 0). The discriminator is parameterized by .
- Adversarial Loss: The training process of a GAN involves optimizing the following minimax objective:
- Training Process: Step 1: Update the discriminator by maximizing while keeping the generator fixed. This step improves the discriminator’s ability to distinguish between real and fake data. Step 2: Update the generator by minimizing while keeping the discriminator fixed. This step improves the generator’s ability to produce data that fools the discriminator.
- Convergence: Theoretically, a GAN reaches a Nash equilibrium when the discriminator cannot distinguish between real and generated data, meaning for all x. At this point, the generator has learned the underlying data distribution.
2.7. Time-Frequency Signal Processing Techniques
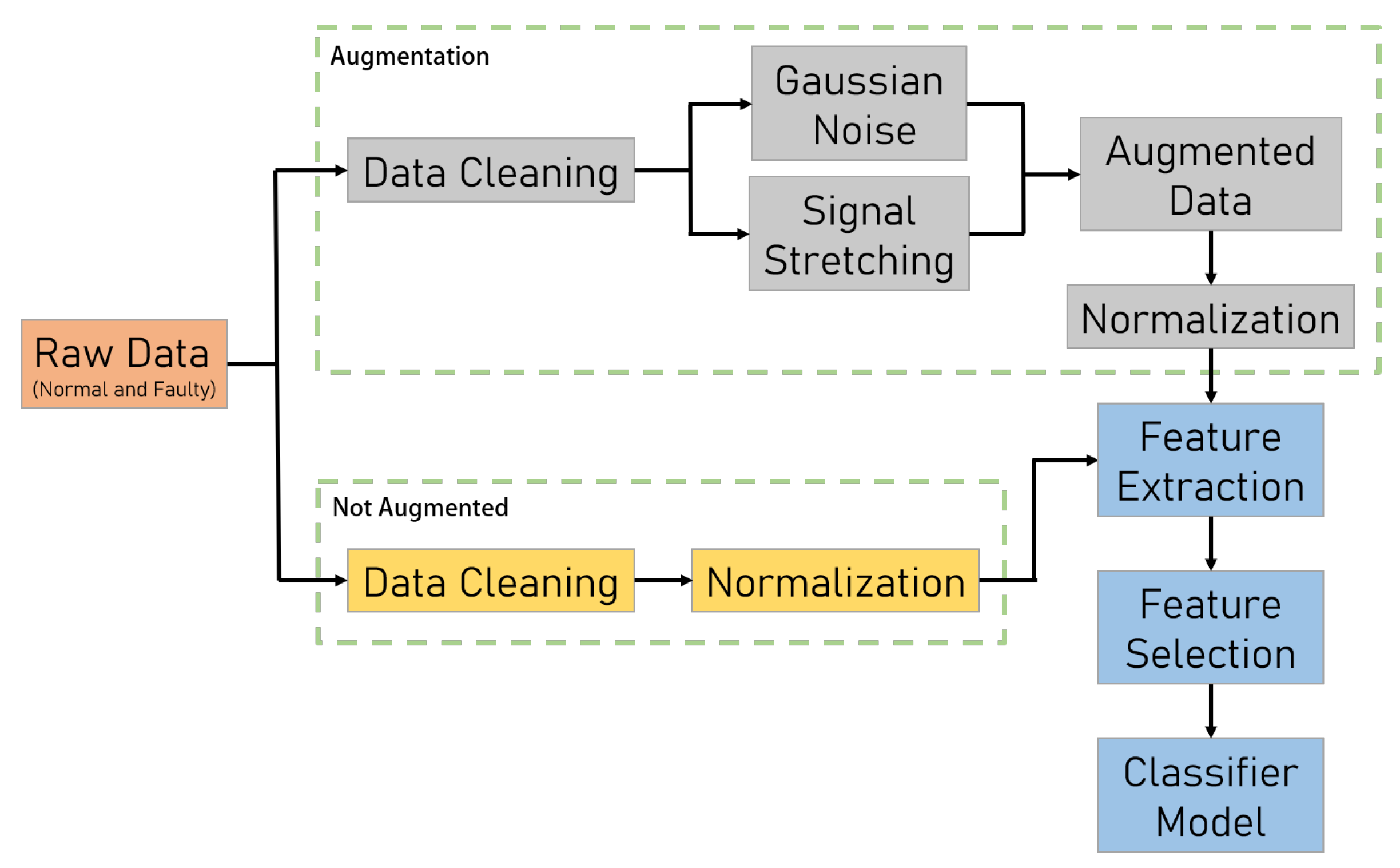
3. Methodology
3.1. Gaussian Noise and Signal Stretching
3.2. LSTM-AE-GAN for Anomaly Detection
3.3. Performance Metrics
4. Experimental Study
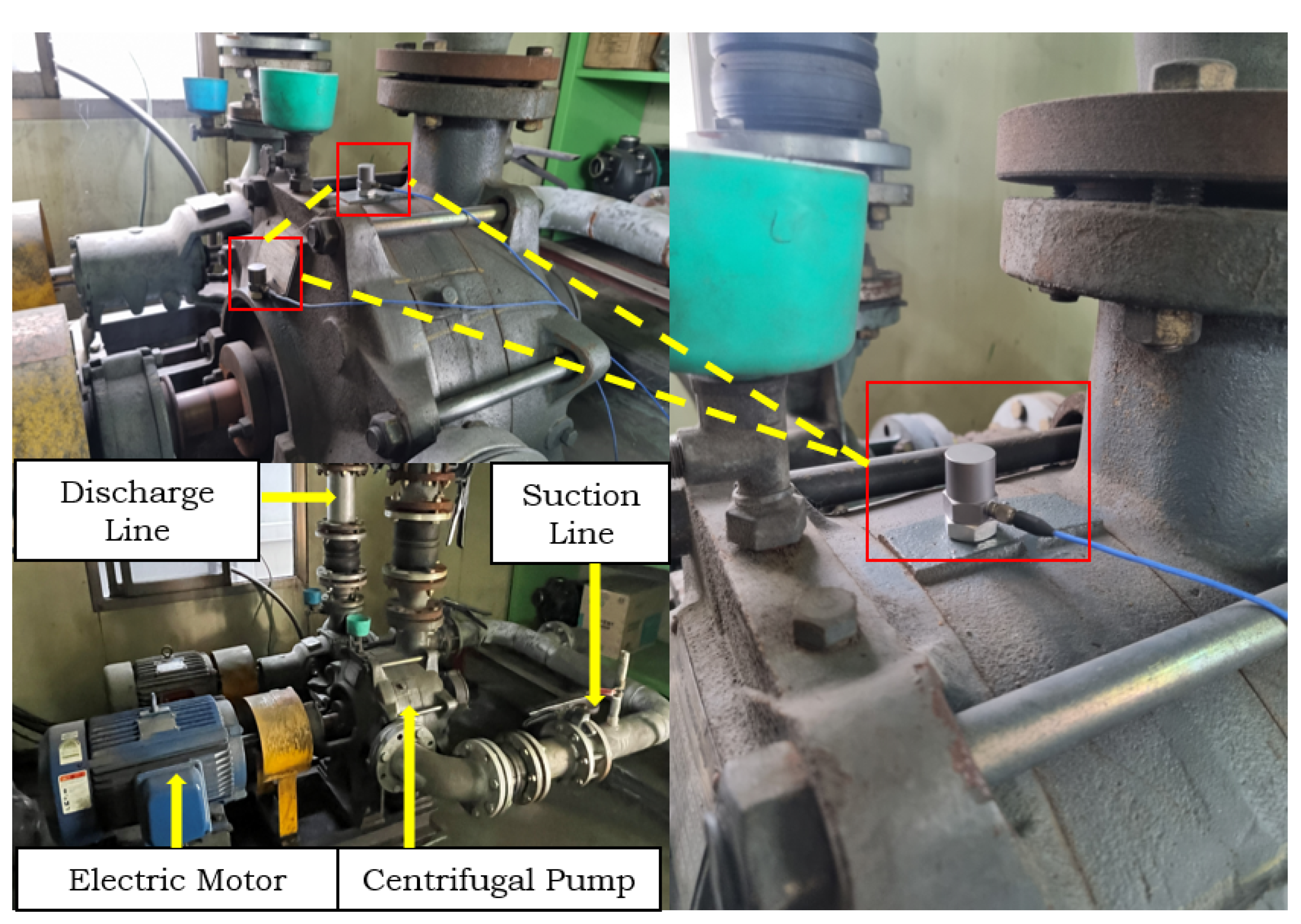
4.1. Data Collection and Preprocessing
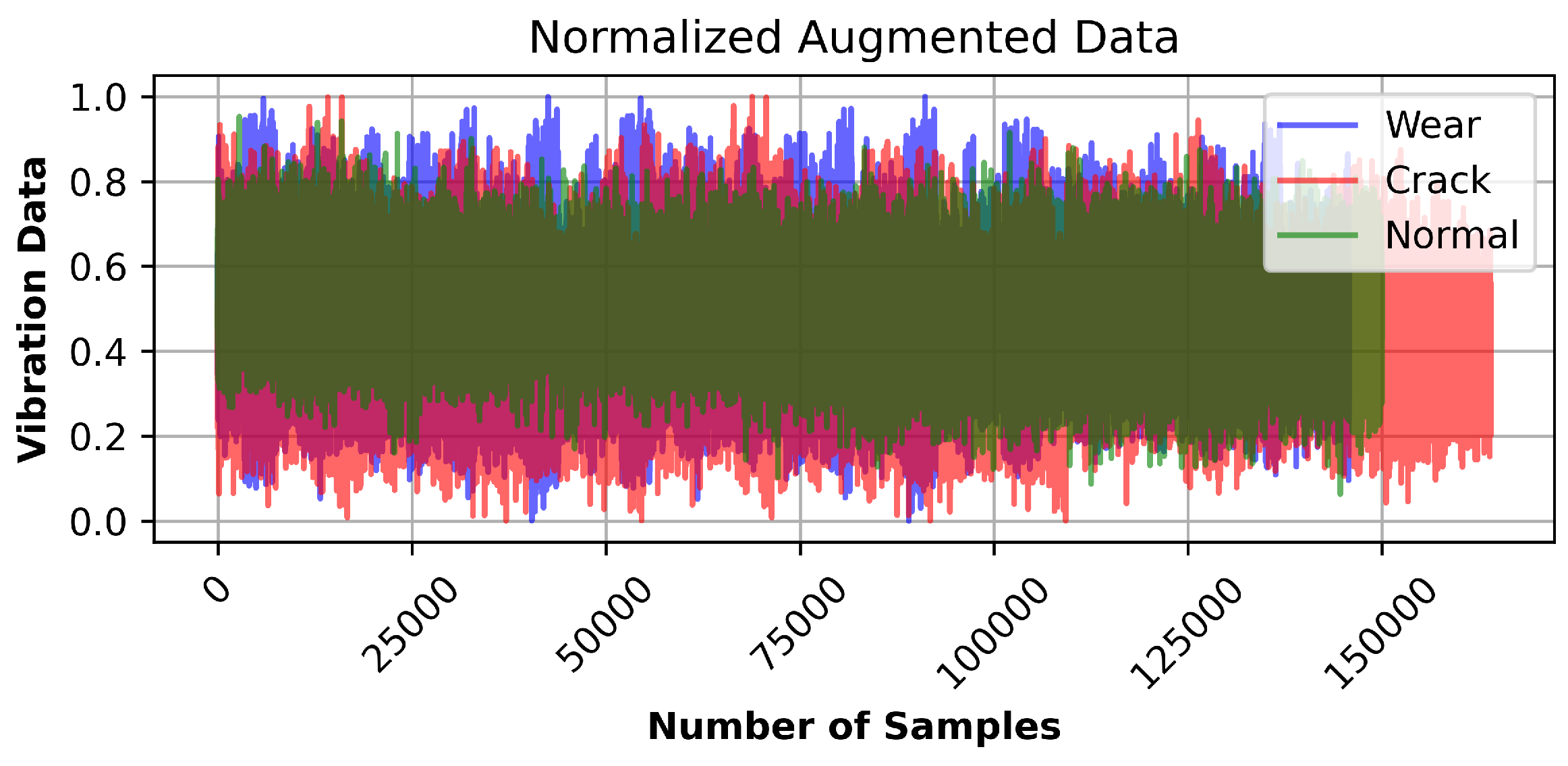
4.2. Data Augmentation and Implementation
5. Results and Discussion
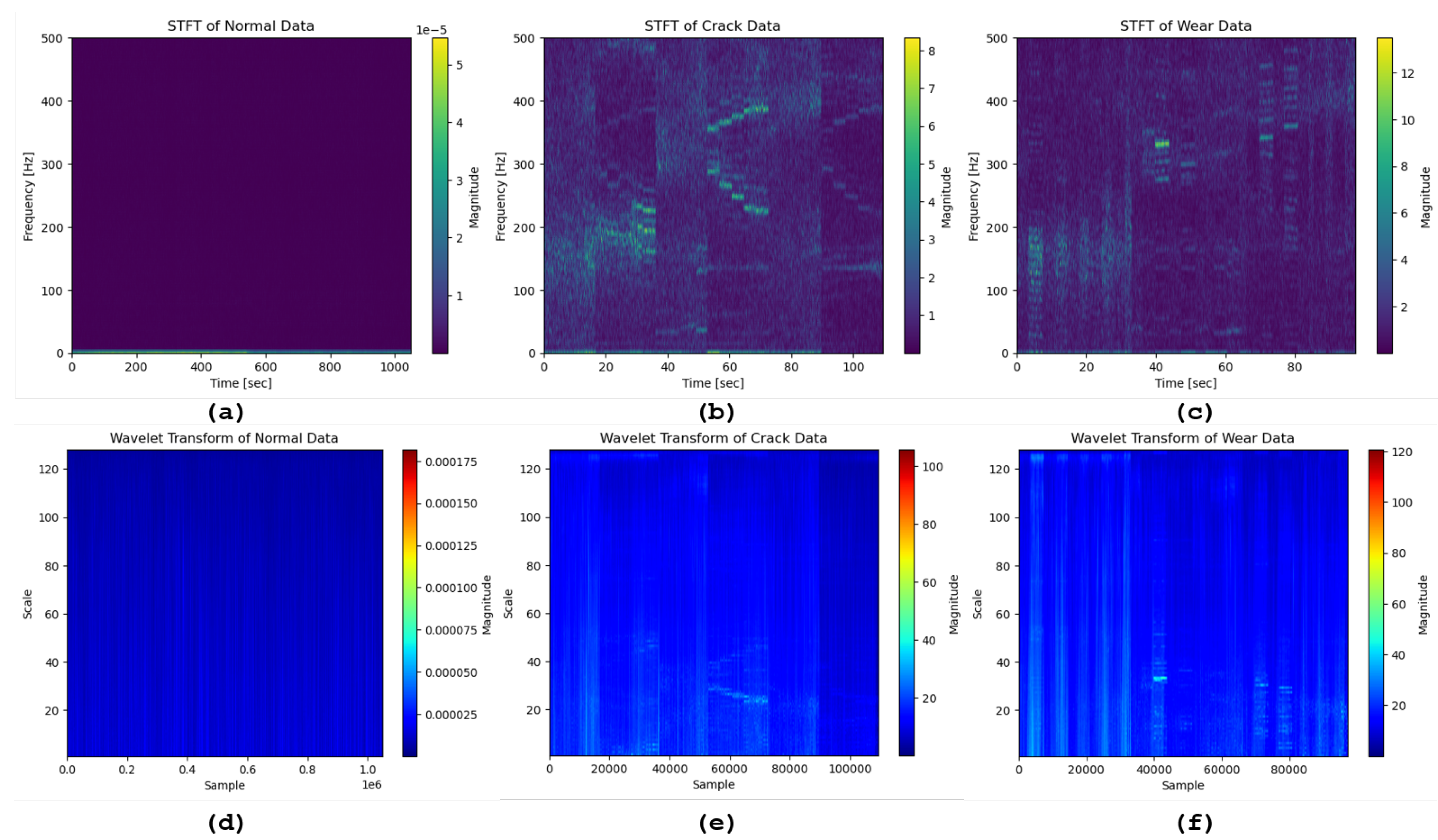
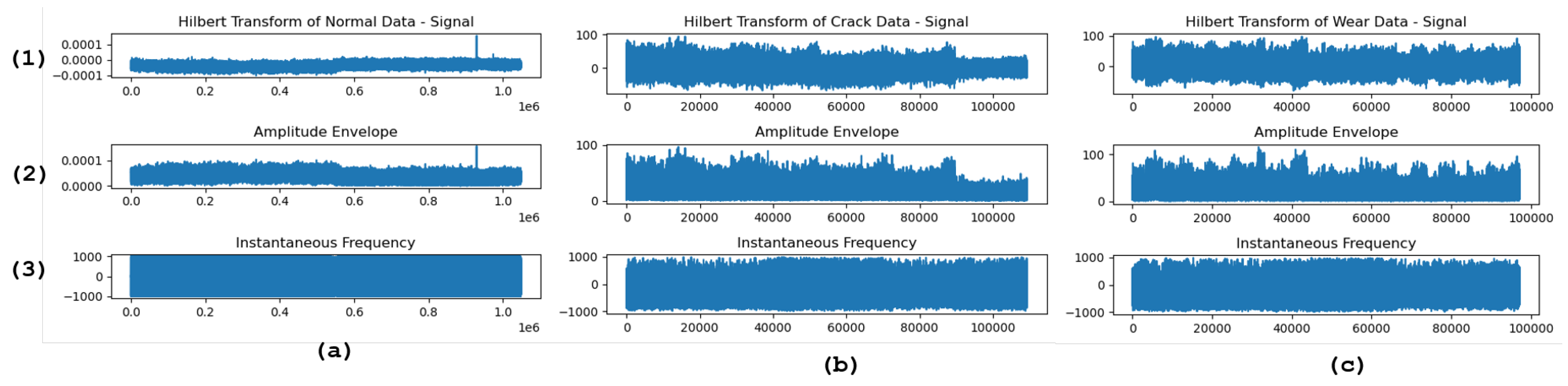
5.1. Time-frequency Signal Processing
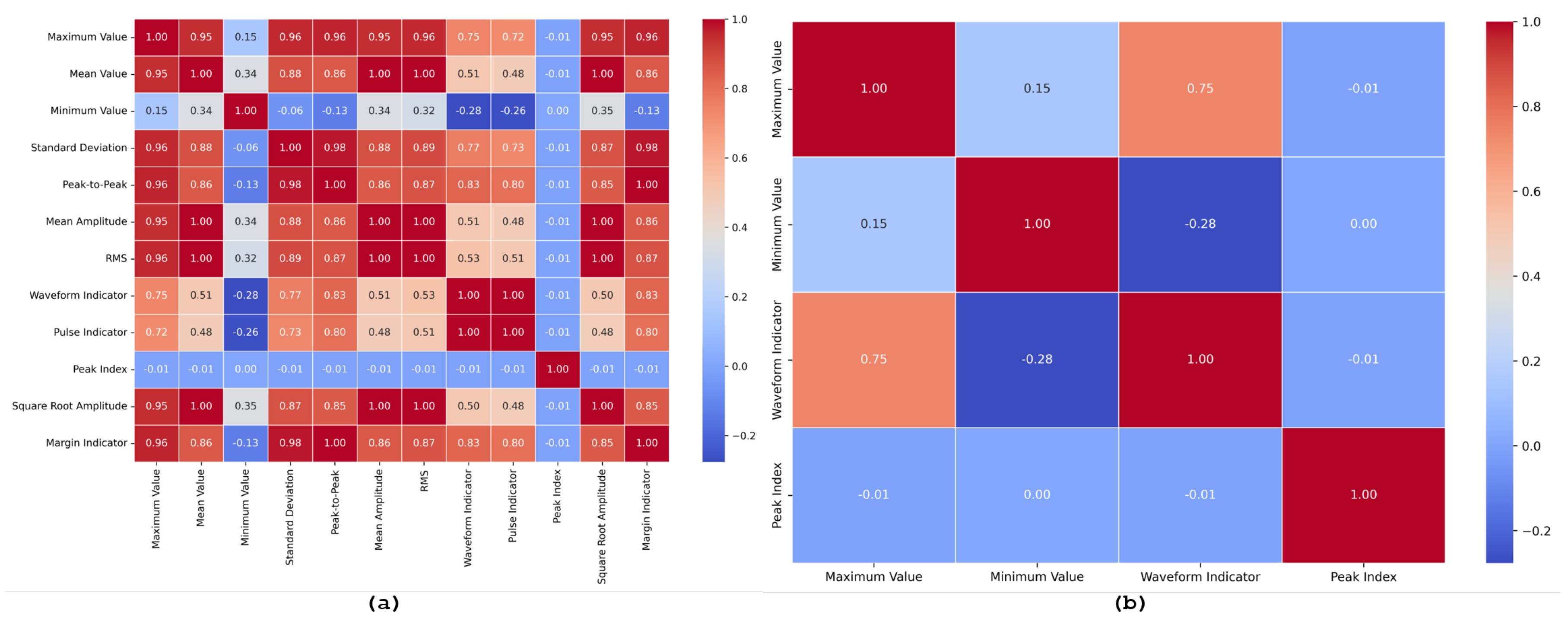
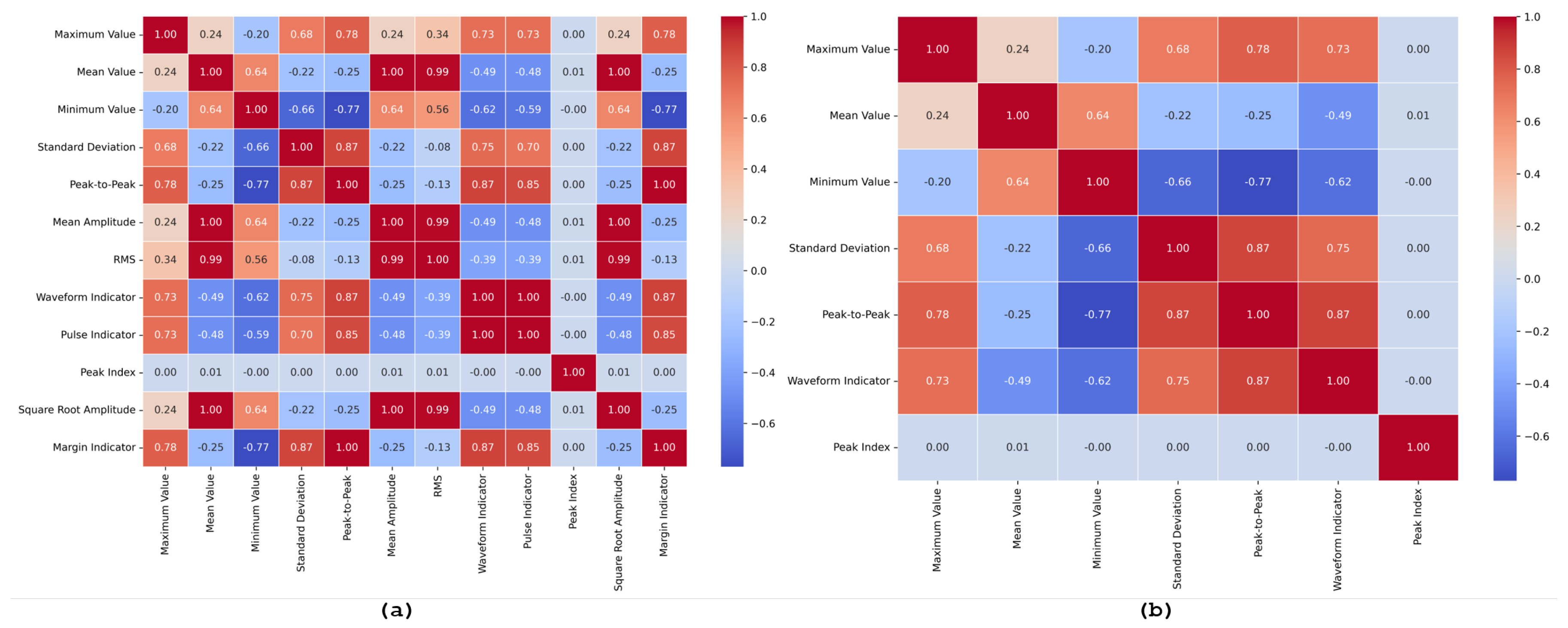
5.2. Statistical Feature Engineering
5.3. Gaussian Noise and Signal Stretching
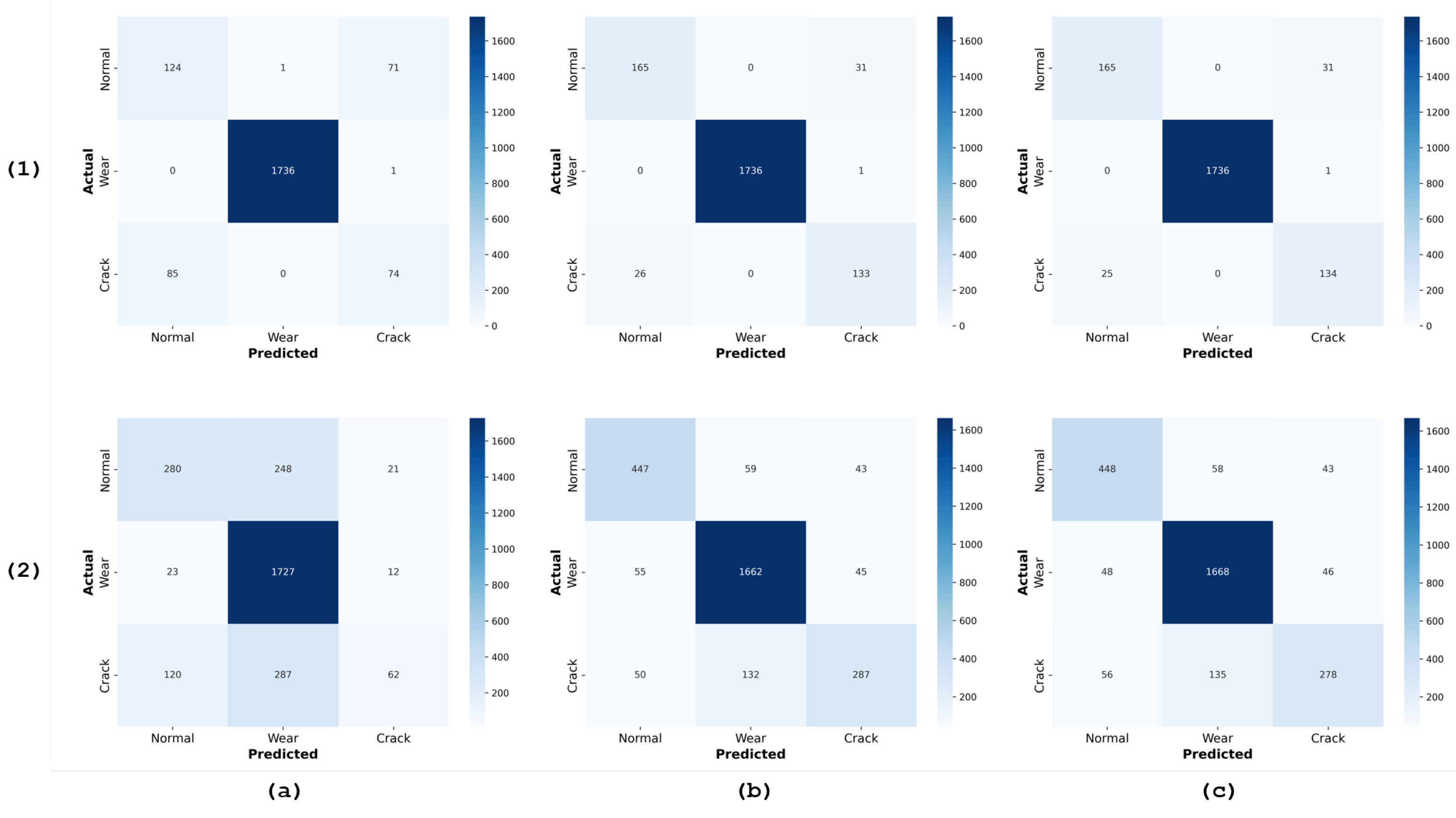
- Normal: Out of 196 samples, 124 were correctly predicted as usual, 71 were misclassified as crack, and only one misclassified as wear.
- Wear: Among 1737 samples, the model performed exceptionally well, correctly predicting 1736 as wear, with just one misclassified as crack.
- Crack: Out of 159 crack samples, 74 were correctly identified as crack, but a significant number (85) were misclassified as normal.
- Normal: The normal class saw a substantial increase in sample size to 549, with 280 correctly predicted as normal, though 248 were misclassified as wear and 21 as crack.
- Wear: Out of 1762 wear samples, 1727 were correctly identified, with a slight increase in misclassifications into the normal (23) and crack (12) classes.
- Crack: The crack class also benefited from augmentation, increasing to 469 samples. Here, 120 were misclassified as normal, 287 as wear, and 62 correctly identified as crack.
- Normal: Out of 196 normal samples, 165 were correctly classified, but 31 were misclassified as crack.
- Wear: The RF model performed excellently in the wear class, correctly classifying 1,736 out of 1,737 samples and misclassifying only one as a crack.
- Crack: For crack samples, 133 out of 159 were correctly identified, but 26 were incorrectly labeled as normal.
- Normal: Post-augmentation, the number of normal samples increased to 549, with 447 correctly predicted. This represents a significant improvement in the true positive rate for normal samples, a key benefit of data augmentation. However, the model now misclassified 59 samples as wear and 43 as crack, introducing more variability in misclassification.
- Wear: Among the 1,762 wear samples, 1,662 were correctly identified, showing a slight decline from the pre-augmentation performance. 55 were misclassified as normal, and 45 were classified as cracks.
- Crack: For crack samples, the model correctly classified 287 out of 469 samples. However, the increase in misclassifications, particularly into the wear category (132 samples), indicates that while the model’s ability to detect cracks improved, it also became more prone to confusion between similar classes.
- Normal: Out of 196 normal samples, 165 were correctly classified, with 31 misclassified as crack, similar to RF.
- Wear: The GB model performed almost flawlessly for the wear class, correctly classifying 1,736 out of 1,737 samples, with only one misclassification as crack.
- Crack: Among the crack samples, 134 out of 159 were correctly classified, with 25 misclassified as normal.
- Normal: The sample size for normal increased significantly, with 448 out of 549 samples correctly identified. The misclassification rates were 58 as wear and 43 as crack, showing an improvement in identifying normal samples but with similar misclassification patterns as RF.
- Wear: The GB model correctly identified 1,668 out of 1,762 wear samples, showing a slight decline in accuracy compared to the pre-augmentation results. This decline underscores the trade-offs involved in improving class representation through data augmentation.
- Crack: The model correctly classified 278 out of 469 crack samples. However, misclassifications increased, with 56 labeled as normal and 135 as wear, indicating a similar challenge in distinguishing cracks from other classes.
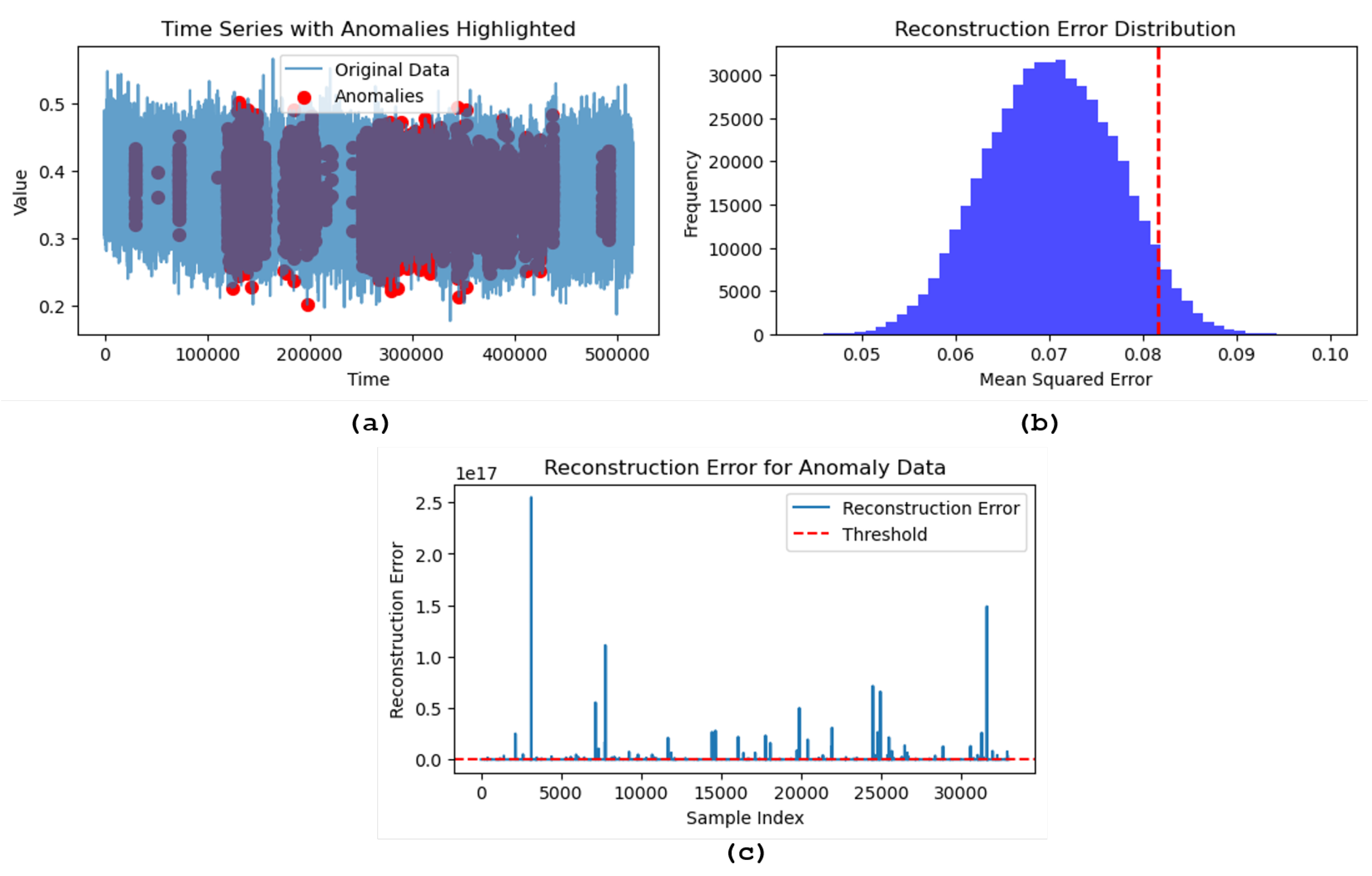
5.4. LSTM-AE-GAN
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Espina-Romero, L.; Guerrero-Alcedo, J.; Goñi Avila, N.; Noroño Sánchez, J.G.; Gutiérrez Hurtado, H.; Quiñones Li, A. Industry 5.0: Tracking Scientific Activity on the Most Influential Industries, Associated Topics, and Future Research Agenda. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mladineo, M.; Celent, L.; Milković, V.; Veža, I. Current State Analysis of Croatian Manufacturing Industry with Regard to Industry 4.0/5.0. Machines 2024, 12, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamwal, A.; Agrawal, R.; Sharma, M.; Giallanza, A. Industry 4.0 Technologies for Manufacturing Sustainability: A Systematic Review and Future Research Directions. Appl. Sci 2021, 11, 5725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinidis, F.K.; Myrillas, N.; Mouroutsos, S.G.; Koulouriotis, D.; Gasteratos, A. Assessment of Industry 4.0 for Modern Manufacturing Ecosystem: A Systematic Survey of Surveys. Machines 2022, 10, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webert, H.; Döß, T.; Kaupp, L.; Simons, S. Fault Handling in Industry 4.0: Definition, Process and Applications. Sensors 2022, 22, 2205 [CrossRef]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelopoulos, A.; Michailidis, E.T.; Nomikos, N.; Trakadas, P.; Hatziefremidis, A.; Voliotis, S.; Zahariadis, T. Tackling Faults in the Industry 4.0 Era—A Survey of Machine-Learning Solutions and Key Aspects. Sensors 2020, 20, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi, R.H.; Hady, H.N.; Hasan, A.M.; Al-Jodah, A.; Humaidi, A.J. Improved Fault Classification for Predictive Maintenance in Industrial IoT Based on AutoML: A Case Study of Ball-Bearing Faults. Processes 2023, 11, 1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.W.; Kong, J.H.; Lee, S.W.; et al. Recent Advances of Artificial Intelligence in Manufacturing Industrial Sectors: A Review. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2022, 23, 111–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldoseri, A.; Al-Khalifa, K.N.; Hamouda, A.M. Re-Thinking Data Strategy and Integration for Artificial Intelligence: Concepts, Opportunities, and Challenges. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 7082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, K.; Zhang, T.; Huang, J. Advanced Hybrid LSTM-Transformer Architecture for Real-Time Multi-Task Prediction in Engineering Systems. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 4890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Törngren, M.; Grogan, P.T. How to Deal with the Complexity of Future Cyber-Physical Systems? Designs 2018, 2, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Wang, J.; Lu, S.; Zhou, M.; Peng, X. A Review of Real-Time Fault Diagnosis Methods for Industrial Smart Manufacturing. Processes 2023, 11, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gültekin, Ö.; Cinar, E.; Özkan, K.; Yazıcı, A. Real-Time Fault Detection and Condition Monitoring for Industrial Autonomous Transfer Vehicles Utilizing Edge Artificial Intelligence. Sensors 2022, 22, 3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moshrefi, A.; Nabki, F. Advanced Industrial Fault Detection: A Comparative Analysis of Ultrasonic Signal Processing and Ensemble Machine Learning Techniques. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 6397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercorelli, P. Recent Advances in Intelligent Algorithms for Fault Detection and Diagnosis. Sensors 2024, 24, 2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mey, O.; Neufeld, D. Explainable AI Algorithms for Vibration Data-Based Fault Detection: Use Case-Adapted Methods and Critical Evaluation. Sensors 2022, 22, 9037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łuczak, D. Data-Driven Machine Fault Diagnosis of Multisensor Vibration Data Using Synchrosqueezed Transform and Time-Frequency Image Recognition with Convolutional Neural Network. Electronics 2024, 13, 2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senjoba, L.; Ikeda, H.; Toriya, H.; Adachi, T.; Kawamura, Y. Enhancing Interpretability in Drill Bit Wear Analysis through Explainable Artificial Intelligence: A Grad-CAM Approach. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 3621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Ma, W.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Feng, Z. The Performance Analysis of Time Series Data Augmentation Technology for Small Sample Communication Device Recognition. IEEE Transactions on Reliability 2023, 72(2), 574–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Ge, Z. Data Augmentation Classifier for Imbalanced Fault Classification. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering 2021, 18(3), 1206–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Wang, P.; Yan, R. Generative Adversarial Networks for Data Augmentation in Machine Fault Diagnosis. Computers in Industry 2019, 106, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Ding, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, C.; Ma, J.; Lu, C. An Interpretable Data Augmentation Scheme for Machine Fault Diagnosis Based on a Sparsity-Constrained Generative Adversarial Network. Expert Systems with Applications 2021, 182, 115234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, W.; Ding, Q.; Sun, J.-Q. Intelligent Rotating Machinery Fault Diagnosis Based on Deep Learning Using Data Augmentation. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing.
- Iwana, B.K.; Uchida, S. An Empirical Survey of Data Augmentation for Time Series Classification with Neural Networks. PLoS ONE 2021, 16(7), e0254841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Zou, K. EDA: Easy Data Augmentation Techniques for Boosting Performance on Text Classification Tasks. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and the 9th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (EMNLP-IJCNLP), Hong Kong, China, 2019; Association for Computational Linguistics. pp. 6382–6388. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, H.; Jeung, S.; Lee, H.; Kwon, J. BiVi-GAN: Bivariate Vibration GAN. Sensors 2024, 24, 1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stathatos, E.; Tzimas, E.; Benardos, P.; Vosniakos, G.-C. Convolutional Neural Networks for Raw Signal Classification in CNC Turning Process Monitoring. Sensors 2024, 24, 1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Ding, J.; Meng, G.; Lv, Z.; Feng, Y.; Wang, A.; Wan, X. Fault Diagnosis of Rolling Bearings in Primary Mine Fans under Sample Imbalance Conditions. Entropy 2023, 25, 1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Jin, Y.; Zhao, S.; Han, C.; Song, L. Remaining Useful Life Prediction Method Enhanced by Data Augmentation and Similarity Fusion. Vibration 2024, 7, 560–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, P.; Zhang, H.; Yu, W.; Liu, C. A Novel Model-Independent Data Augmentation Method for Fault Diagnosis in Smart Manufacturing. Procedia CIRP 2022, 107, 949–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramteke, D.S.; Parey, A.; Pachori, R.B. A New Automated Classification Framework for Gear Fault Diagnosis Using Fourier–Bessel Domain-Based Empirical Wavelet Transform. Machines 2023, 11, 1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Liu, H.; Tao, L.; Ma, J.; Cheng, Y. A Universal Feature Extractor Based on Self-Supervised Pre-Training for Fault Diagnosis of Rotating Machinery under Limited Data. Aerospace 2023, 10, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afridi, Y.S.; Hasan, L.; Ullah, R.; Ahmad, Z.; Kim, J.-M. LSTM-Based Condition Monitoring and Fault Prognostics of Rolling Element Bearings Using Raw Vibrational Data. Machines 2023, 11, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, Z.; Shi, W.; Li, W. Research on Fault Detection and Automatic Diagnosis Technology of Water Hammer in Centrifugal Pump. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 5606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Xu, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Bai, X.; Jing, L.; Ma, J.; Huang, J. The Fault Diagnosis of a Plunger Pump Based on the SMOTE + Tomek Link and Dual-Channel Feature Fusion. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 4785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanathan, C.; Venkatesh, S.N.; Dhanasekaran, S.; Mahanta, T.K.; Sugumaran, V.; Lakshmaiya, N.; Ramasamy, S.N. Deep Learning for Enhanced Fault Diagnosis of Monoblock Centrifugal Pumps: Spectrogram-Based Analysis. Machines 2023, 11, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, J.; Bogdan, M.; Classen, J.; Fricke, C. Support Vector Machine Classifiers Show High Generalizability in Automatic Fall Detection in Older Adults. Sensors 2021, 21, 7166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, R.; Watanobe, Y.; Islam, M.R.; Naruse, K.; Rahman, M.M. Unknown Object Detection Using a One-Class Support Vector Machine for a Cloud–Robot System. Sensors 2022, 22, 1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kareem, A.B.; Ejike Akpudo, U.; Hur, J.-W. An Integrated Cost-Aware Dual Monitoring Framework for SMPS Switching Device Diagnosis. Electronics 2021, 10, 2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadkarni, S.B.; Vijay, G.S.; Kamath, R.C. Comparative Study of Random Forest and Gradient Boosting Algorithms to Predict Airfoil Self-Noise. Eng. Proc. 2023, 59, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Cai, Y.; Tang, H.; Xu, P. Data-Driven Golden Jackal Optimization–Long Short-Term Memory Short-Term Energy-Consumption Prediction and Optimization System. Energies 2024, 17, 3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Ma, B.; Guo, X.; Chen, Y.; Xu, Y. A Hybrid ARIMA-LSTM Model for Short-Term Vehicle Speed Prediction. Energies 2024, 17, 3736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, Y.; Lee, Y.; Hwang, Y.; Jeong, J. Long Short-Term Memory Autoencoder and Extreme Gradient Boosting-Based Factory Energy Management Framework for Power Consumption Forecasting. Energies 2024, 17, 3666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, J.; Liu, F.-A. Multivariate Time Series Data Prediction Based on ATT-LSTM Network. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Shao, J.; Hussain, M.J.; Hao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L. DPG-LSTM: An Enhanced LSTM Framework for Sentiment Analysis in Social Media Text Based on Dependency Parsing and GCN. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Kim, J.; You, I. An Anomaly Detection Method Based on Multiple LSTM-Autoencoder Models for In-Vehicle Network. Electronics 2023, 12, 3543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, J.S.; Kareem, A.B.; Hur, J.-W. LSTM-Autoencoder for Vibration Anomaly Detection in Vertical Carousel Storage and Retrieval System (VCSRS). Sensors 2023, 23, 1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kareem, A.B.; Hur, J.-W. A Comparative Study of Deep-Learning Autoencoders (DLAEs) for Vibration Anomaly Detection in Manufacturing Equipment. Electronics 2024, 13, 1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Okwuosa, C.N.; Hur, J.-W. Extruder Machine Gear Fault Detection Using Autoencoder LSTM via Sensor Fusion Approach. Inventions 2023, 8, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-G.; Kim, D.-H.; Lee, J.H. Proactive Fault Diagnosis of a Radiator: A Combination of Gaussian Mixture Model and LSTM Autoencoder. Sensors 2023, 23, 8688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachekhab, F.; Benzaoui, M.; Tadjer, S.A.; Bensmaine, A.; Hamma, H. LSTM-Autoencoder Deep Learning Model for Anomaly Detection in Electric Motor. Energies 2024, 17, 2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.-W.; Kuo, W.-H.; Lan, J.-H.; Ding, C.-F.; Hsu, H.; Young, H.-T. Anomaly Detection Neural Network with Dual Auto-Encoders GAN and Its Industrial Inspection Applications. Sensors 2020, 20, 3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, Y.; Deng, X.; Liu, Z.; Lv, M.; Zhang, H. Dual Auto-Encoder GAN-Based Anomaly Detection for Industrial Control System. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 4986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avola, D.; Cannistraci, I.; Cascio, M.; Cinque, L.; Diko, A.; Fagioli, A.; Foresti, G.L.; Lanzino, R.; Mancini, M.; Mecca, A.; et al. A Novel GAN-Based Anomaly Detection and Localization Method for Aerial Video Surveillance at Low Altitude. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewert, P.; Wicher, B.; Pajchrowski, T. Application of the STFT for Detection of the Rotor Unbalance of a Servo-Drive System with an Elastic Interconnection. Electronics 2024, 13, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Chen, X.; Sun, K.; Xiong, C.; Song, D.; Lu, Y.; Huang, L.; He, S.; Zhang, X. A Wavelet Transform-Based Real-Time Filtering Algorithm for Fusion Magnet Power Signals and Its Implementation. Energies 2023, 16, 4091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lin, J.; Niu, G.; Wu, M.; Wei, X. A Hilbert–Huang Transform-Based Adaptive Fault Detection and Classification Method for Microgrids. Energies 2021, 14, 5040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, J.P.S.; Fruett, F.; Dalfré Filho, J.G.; Giesbrecht, M. Faults Detection and Classification in a Centrifugal Pump from Vibration Data Using Markov Parameters. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing 2021, 158, 107694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Yuan, S.; Luo, Y. Cyclic Spectral Analysis of Vibration Signals for Centrifugal Pump Fault Characterization. IEEE Sensors Journal 2018, 18(7), 2925–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakthivel, N.R.; Nair, B.B.; Elangovan, M.; Sugumaran, V.; Saravanmurugan, S. Comparison of Dimensionality Reduction Techniques for the Fault Diagnosis of Mono Block Centrifugal Pump Using Vibration Signals. Engineering Science and Technology, an International Journal 2014, 17(1), 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagiovanidis, M.; Pantazi, X.E.; Papamichail, D.; Fragos, V. Early Detection of Cavitation in Centrifugal Pumps Using Low-Cost Vibration and Sound Sensors. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Ahmad, Z.; Kim, J.-M. A Centrifugal Pump Fault Diagnosis Framework Based on Supervised Contrastive Learning. Sensors 2022, 22, 6448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| ML Model | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|
| SVC | gamma, C | scale, 90 |
| RF and GB | n estimators | 70 |
| Layer Type | Units | Activation | Output Shape |
|---|---|---|---|
| Input | - | - | (seq_length, n_features) |
| LSTM (Encoder) | 128 | ReLU | (seq_length, 128) |
| RepeatVector | - | - | (seq_length, 128) |
| LSTM (Decoder) | 128 | ReLU | (seq_length, 128) |
| Dense | n_features | - | (seq_length, n_features) |
| Layer Type | Units | Activation | Output Shape |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dense | 100 | LeakyReLU | (None, 100) |
| BatchNormalization | - | - | (None, 100) |
| Dense | seq_length × n_features | Tanh | (None, seq_length × n_features) |
| Reshape | - | - | (None, seq_length, n_features) |
| Layer Type | Units | Activation | Output Shape |
|---|---|---|---|
| LSTM | 128 | - | (seq_length, 128) |
| LSTM | 64 | - | (64) |
| Dense | 1 | Sigmoid | (1) |
| Statistical Feature | Description (Mathematical Expression) |
|---|---|
| Maximum Value | |
| Mean Value | |
| Minimum Value | |
| Standard Deviation | |
| Peak to Peak | |
| Mean Amplitude | |
| RMS | |
| Waveform Indicator | |
| Pulse Indicator | |
| Peak Index | |
| Square Root Amplitude | |
| Margin Indicator |
| Model | Fold | Before Augmentation | After Augmentation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-score | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-score | ||
| SVC | 1 | 0.9211 | 0.9158 | 0.9211 | 0.9175 | 0.7250 | 0.7123 | 0.7250 | 0.6616 |
| 2 | 0.9273 | 0.9246 | 0.9273 | 0.9231 | 0.7309 | 0.7340 | 0.7309 | 0.6678 | |
| 3 | 0.9293 | 0.9282 | 0.9293 | 0.9239 | 0.7147 | 0.7525 | 0.7147 | 0.6379 | |
| 4 | 0.9201 | 0.9144 | 0.9201 | 0.9169 | 0.7217 | 0.6930 | 0.7217 | 0.6690 | |
| 5 | 0.9159 | 0.9095 | 0.9159 | 0.9109 | 0.7247 | 0.6971 | 0.7247 | 0.6678 | |
| Averaged | 0.9227 | 0.9185 | 0.9227 | 0.9185 | 0.7234 | 0.7190 | 0.7234 | 0.6608 | |
| RF | 1 | 0.9590 | 0.9602 | 0.9590 | 0.9588 | 0.8621 | 0.8593 | 0.8621 | 0.8594 |
| 2 | 0.9590 | 0.9593 | 0.9590 | 0.9592 | 0.8620 | 0.8606 | 0.8620 | 0.8568 | |
| 3 | 0.9631 | 0.9631 | 0.9631 | 0.9631 | 0.8520 | 0.8483 | 0.8520 | 0.8475 | |
| 4 | 0.9579 | 0.9550 | 0.9549 | 0.9548 | 0.8589 | 0.8539 | 0.8590 | 0.8526 | |
| 5 | 0.9662 | 0.9661 | 0.9662 | 0.9661 | 0.8466 | 0.8423 | 0.8466 | 0.8424 | |
| Averaged | 0.9604 | 0.9607 | 0.9604 | 0.9604 | 0.8563 | 0.8529 | 0.8563 | 0.8517 | |
| GB | 1 | 0.9600 | 0.9618 | 0.9600 | 0.9598 | 0.8606 | 0.8575 | 0.8606 | 0.8579 |
| 2 | 0.9570 | 0.9576 | 0.9569 | 0.9571 | 0.8558 | 0.8532 | 0.8558 | 0.8489 | |
| 3 | 0.9549 | 0.9549 | 0.9549 | 0.9549 | 0.8481 | 0.8430 | 0.8481 | 0.8426 | |
| 4 | 0.9631 | 0.9631 | 0.9631 | 0.9631 | 0.8581 | 0.8528 | 0.8581 | 0.8508 | |
| 5 | 0.9579 | 0.9579 | 0.9579 | 0.9579 | 0.8427 | 0.8372 | 0.8427 | 0.8369 | |
| Averaged | 0.9586 | 0.9591 | 0.9586 | 0.9586 | 0.8531 | 0.8487 | 0.8531 | 0.8474 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




