Submitted:
10 September 2024
Posted:
10 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
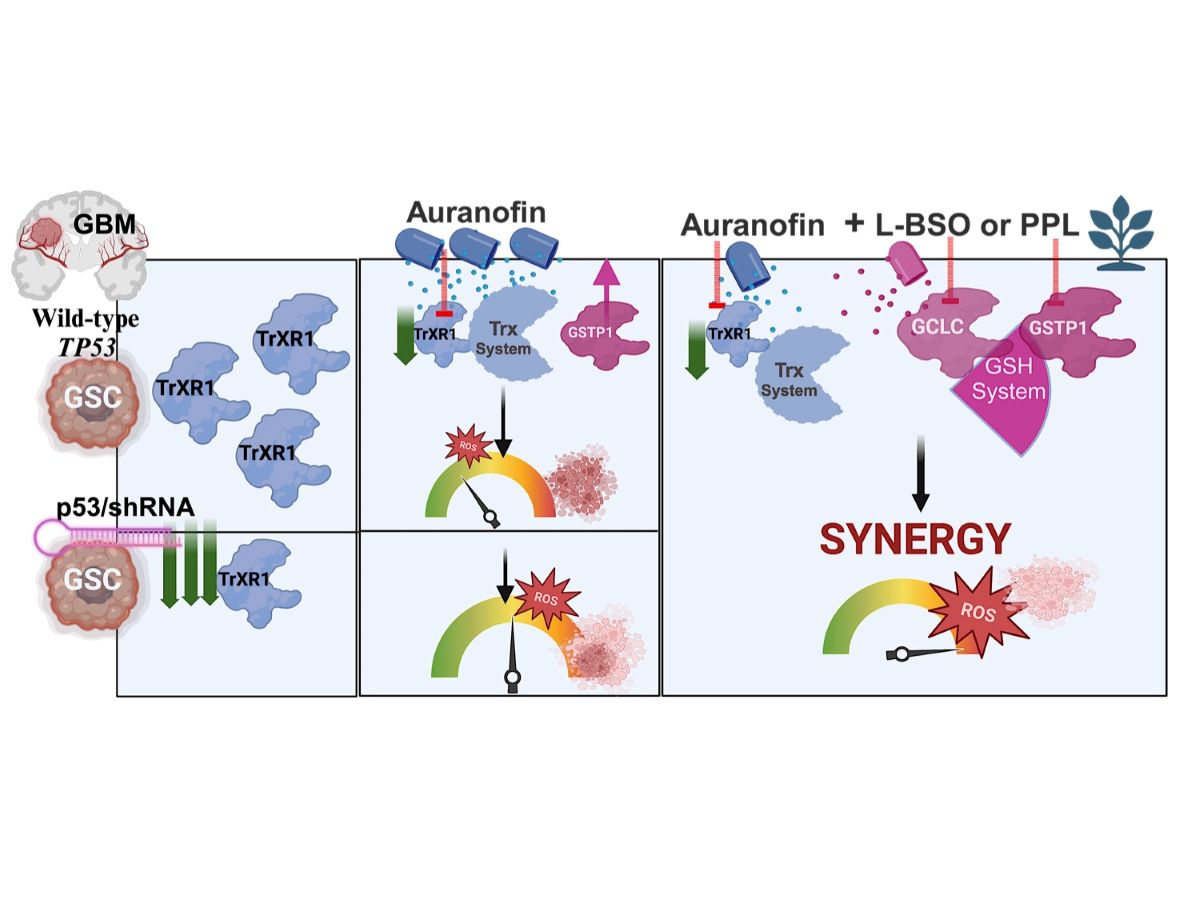
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. GBM Cell Lines and GSC Culture, Treatment and Transfection
2.2. MTT Cytotoxicity Assay
2.3. AlamarBlue Viability Assay
2.4. Clonogenic Assay
2.5. Neurosphere Formation Assay
2.6. Western Blot Analysis
2.7. Measurement of ROS Production
2.8. Gene Expression and Correlation Analysis in Publically Available Human Datasets
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
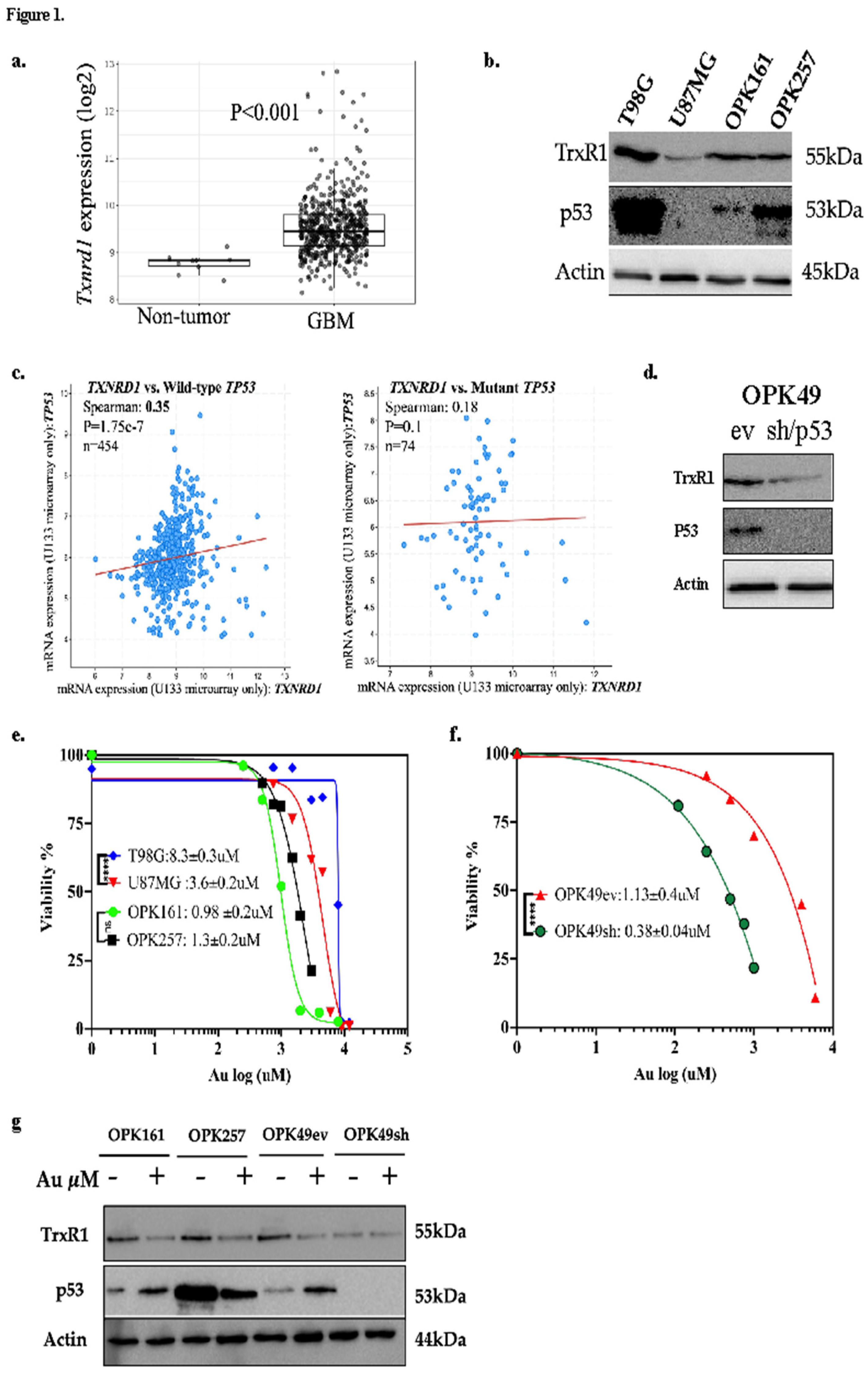
3.1. Au Decreased Viability of GBM Cell Lines and GSCs, with Enhanced Sensitivity in p53-Knockdown GSCs
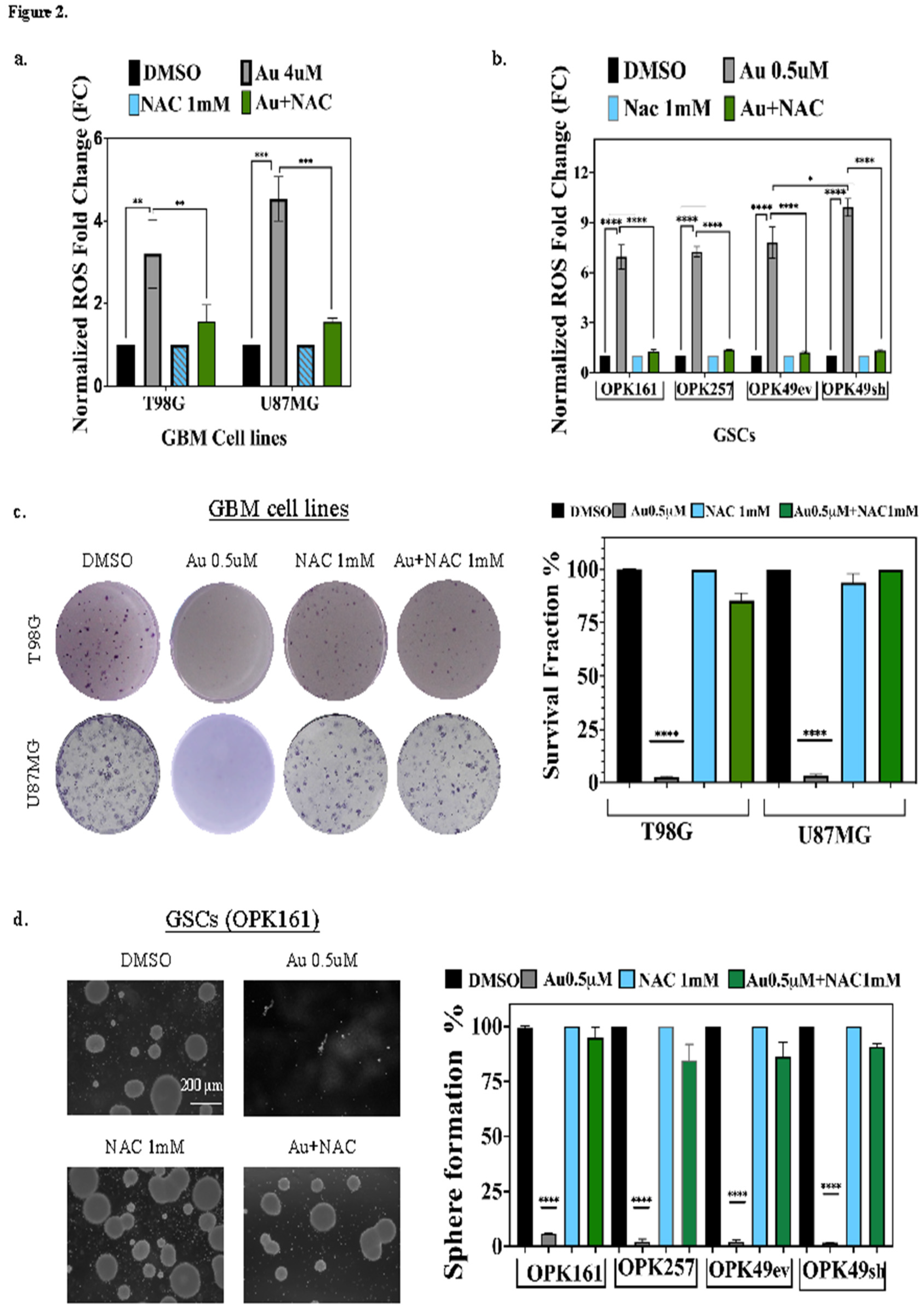
3.2. Au Induces ROS-Dependent Long-Term Cytotoxicity in GSCs and GBM Cell Lines with p53-Knockdown GSC Line Displaying the Highest ROS Increase
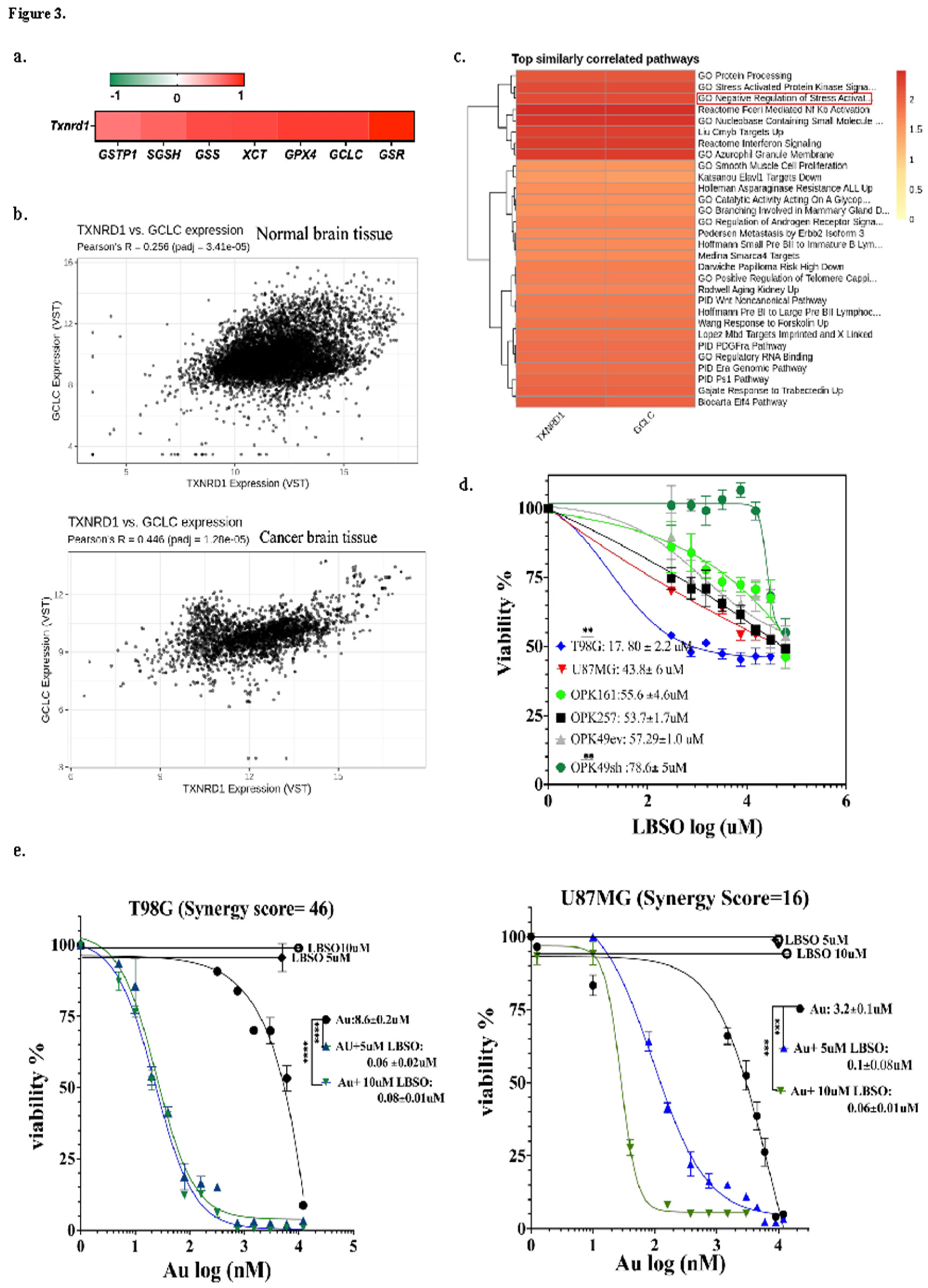
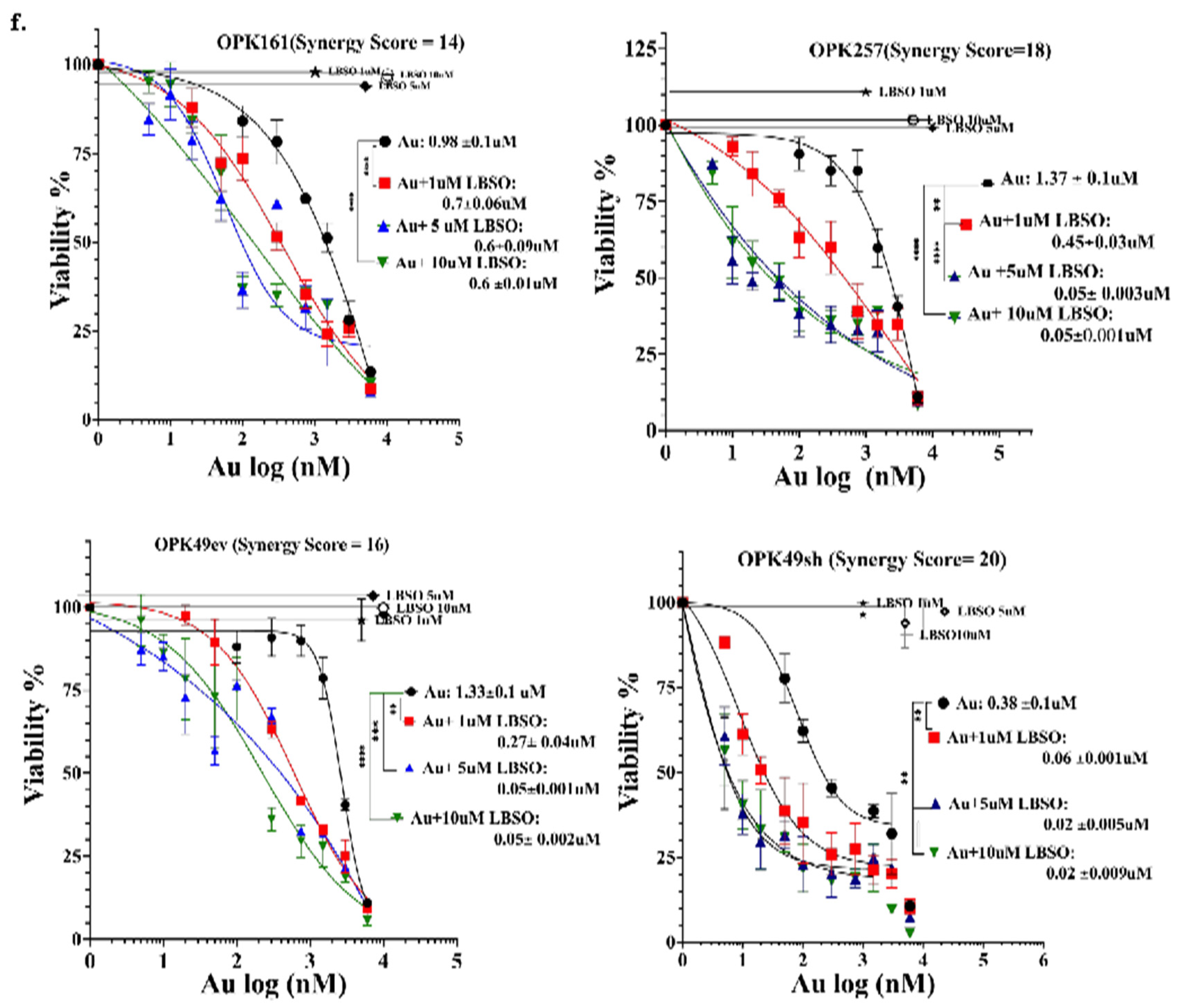
3.3. Correlation of GSH-Metabolizing Enzymes with Txnrd1 in GBM Datasets and Synergistic Cytotoxicity of Auranofin and L-BSO, a GSH Inhibitor
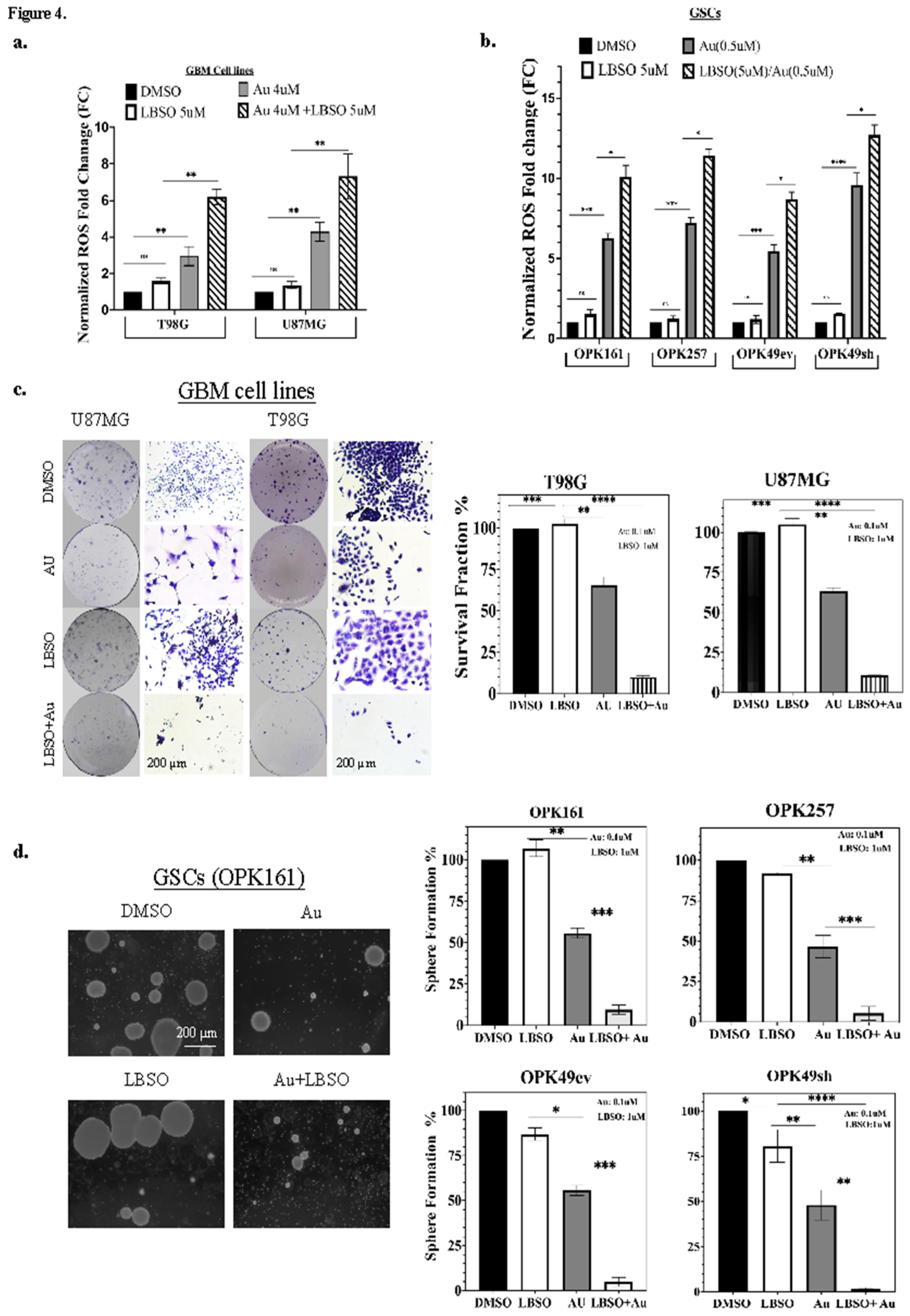
3.4. Combining Au with L-BSO Synergistically Increased ROS and Long-Term Cytotoxicity Compared to Each Drug Alone in GBM Cell Lines and GSCs
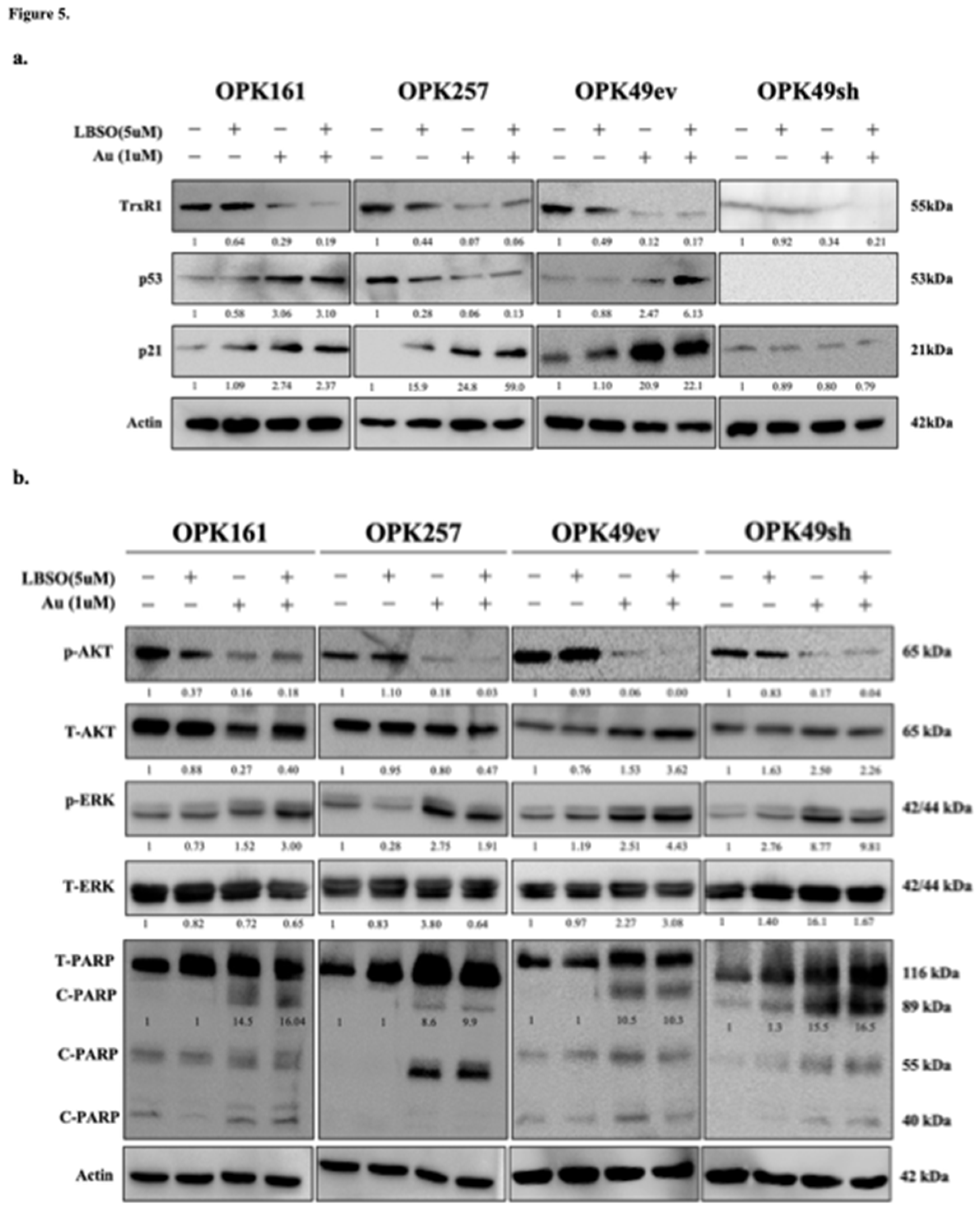
3.5. Combination of Au with L-BSO Decreased Cellular Survival Pathways and Induced Apoptosis in GSCs
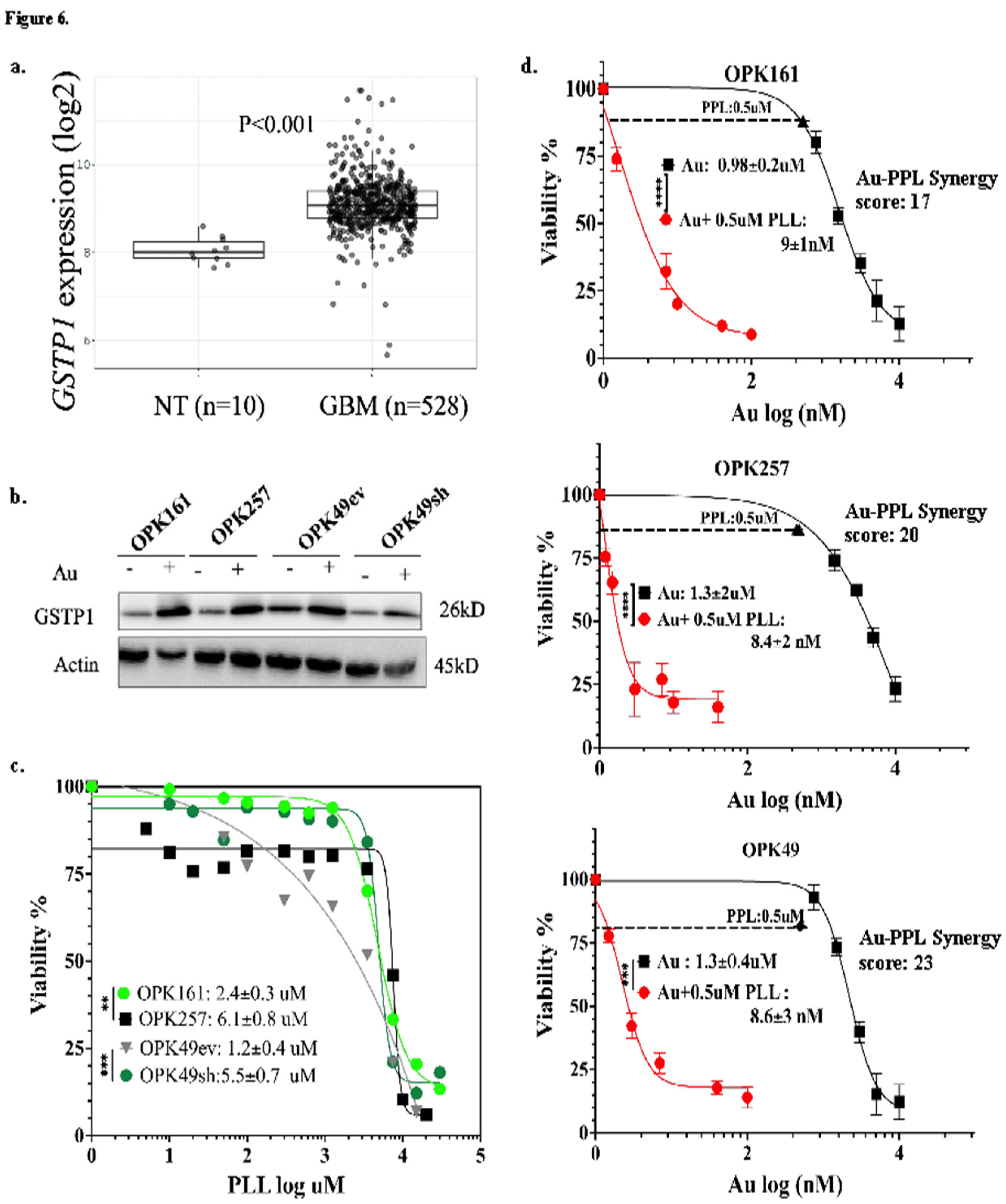
3.6. Auranofin Increased GSTP-1 While Piperlongumine (PPL) Induced Significant Cytotoxicity and a Strong Synergistic Effect within a Nanomolar Range in GSCs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Wesseling, P.; Brat, D.J.; Cree, I.A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Hawkins, C.; Ng, H.K.; Pfister, S.M.; Reifenberger, G.; et al. The 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A Summary. Neuro Oncol 2021, 23, 1231–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stupp, R.; Mason, W.P.; van den Bent, M.J.; Weller, M.; Fisher, B.; Taphoorn, M.J.B.; Belanger, K.; Brandes, A.A.; Marosi, C.; Bogdahn, U.; et al. Radiotherapy plus Concomitant and Adjuvant Temozolomide for Glioblastoma. New England Journal of Medicine 2005, 352, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Price, M.; Neff, C.; Cioffi, G.; Waite, K.A.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Other Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2016-2020. Neuro Oncol 2023, 25, IV1–IV99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, A.L.V.; Gomes, I.N.F.; Carloni, A.C.; Rosa, M.N.; da Silva, L.S.; Evangelista, A.F.; Reis, R.M.; Silva, V.A.O. Role of Glioblastoma Stem Cells in Cancer Therapeutic Resistance: A Perspective on Antineoplastic Agents from Natural Sources and Chemical Derivatives. Stem Cell Research & Therapy 2021 12:1 2021, 12, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.; Wu, Q.; McLendon, R.E.; Hao, Y.; Shi, Q.; Hjelmeland, A.B.; Dewhirst, M.W.; Bigner, D.D.; Rich, J.N. Glioma Stem Cells Promote Radioresistance by Preferential Activation of the DNA Damage Response. Nature 2006, 444, 756–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Hawkins, C.; Clarke, I.D.; Squire, J.A.; Bayani, J.; Hide, T.; Henkelman, R.M.; Cusimano, M.D.; Dirks, P.B. Identification of Human Brain Tumour Initiating Cells. Nature 2004, 432, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersh, A.M.; Gaitsch, H.; Alomari, S.; Lubelski, D.; Tyler, B.M. Molecular Pathways and Genomic Landscape of Glioblastoma Stem Cells: Opportunities for Targeted Therapy. Cancers (Basel) 2022, 14, 3743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, F.; Tai, G.; Wang, J.; Shang, J.; Zhang, B.; Wang, P.; Huang, B.; Du, J.; Yu, J.; et al. TIGAR Knockdown Radiosensitizes TrxR1-Overexpressing Glioma in Vitro and in Vivo via Inhibiting Trx1 Nuclear Transport. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 42928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, A.; Storr, S.J.; Al-hadyan, K.; Rahman, R.; Smith, S.; Grundy, R.; Paine, S.; Martin, S.G. Thioredoxin System Protein Expression Is Associated with Poor Clinical Outcome in Adult and Paediatric Gliomas and Medulloblastomas. Mol Neurobiol 2020, 57, 2889–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Zou, L.; Zhang, X.; Branco, V.; Wang, J.; Carvalho, C.; Holmgren, A.; Lu, J. Redox Signaling Mediated by Thioredoxin and Glutathione Systems in the Central Nervous System. Antioxid Redox Signal 2017, 27, 989–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.W.L.; Ghode, P.; Ong, D.S.T. Redox Regulation of Cell State and Fate. Redox Biol 2019, 25, 101056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Kim, S.M.; Lee, R.T. Thioredoxin and Thioredoxin Target Proteins: From Molecular Mechanisms to Functional Significance. Antioxid Redox Signal 2013, 18, 1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thioredoxin Reductase, a Redox-Active Selenoprotein, Is Secreted by Normal and Neoplastic Cells: Presence in Human Plasma1 | Cancer Research | American Association for Cancer Research. Available online: https://aacrjournals.org/cancerres/article/60/8/2281/507308/Thioredoxin-Reductase-a-Redox-active-Selenoprotein.
- Bjørklund, G.; Zou, L.; Wang, J.; Chasapis, C.T.; Peana, M. Thioredoxin Reductase as a Pharmacological Target. Pharmacol Res 2021, 174, 105854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, A.; Storr, S.J.; Al-hadyan, K.; Rahman, R.; Smith, S.; Grundy, R.; Paine, S.; Martin, S.G. Thioredoxin System Protein Expression Is Associated with Poor Clinical Outcome in Adult and Paediatric Gliomas and Medulloblastomas. Mol Neurobiol 2020, 57, 2889–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, L.; Sandhu, J.K.; Harper, M.-E.; Cuperlovic-Culf, M. Role of Glutathione in Cancer: From Mechanisms to Therapies. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Du, S.; Du, Y.; Ren, J.; Ying, G.; Yan, Z. Glutathione Reductase Mediates Drug Resistance in Glioblastoma Cells by Regulating Redox Homeostasis. J Neurochem 2018, 144, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Long, H.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Q.; Yuan, H.; Qu, Q.; Qu, J. Glutathione S-Transferase Genes Variants and Glioma Risk: A Case-Control and Meta-Analysis Study. J Cancer 2019, 10, 4679–4688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Shao, L.; Spitz, D.R. Reactive Oxygen Species in Normal and Tumor Stem Cells. In; 2014; pp. 1–67.
- Olivier, C.; Oliver, L.; Lalier, L.; Vallette, F.M. Drug Resistance in Glioblastoma: The Two Faces of Oxidative Stress. Front Mol Biosci 2021, 7, 620677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.L.; Laterra, J.; Lopez-Bertoni, H. Exploring Glioblastoma Stem Cell Heterogeneity: Immune Microenvironment Modulation and Therapeutic Opportunities. Front Oncol 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Chen, Y.; St. Clair, D.K. ROS and P53: A Versatile Partnership. Free Radic Biol Med 2008, 44, 1529–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Ni, X. ROS-Mediated DNA Methylation Pattern Alterations in Carcinogenesis. Curr Drug Targets 2015, 16, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksson, S.E.; Ceder, S.; Bykov, V.J.N.; Wiman, K.G. P53 as a Hub in Cellular Redox Regulation and Therapeutic Target in Cancer. J Mol Cell Biol 2019, 11, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redox Modulation of P53 Conformation and Sequence-Specific DNA Binding in Vitro1 | Cancer Research | American Association for Cancer Research. Available online: https://aacrjournals.org/cancerres/article/53/19/4469/499471/Redox-Modulation-of-p53-Conformation-and-Sequence.
- Butturini, E.; Butera, G.; Pacchiana, R.; de Prati, A.C.; Mariotto, S.; Donadelli, M. Redox Sensitive Cysteine Residues as Crucial Regulators of Wild-Type and Mutant P53 Isoforms. Cells 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Ma, X.; Lindner, D.J.; Karra, S.; Hofmann, E.R.; Reddy, S.P.M.; Kalvakolanu, D.V. Modulation of P53 Dependent Gene Expression and Cell Death through Thioredoxin-Thioredoxin Reductase by the Interferon-Retinoid Combination. Oncogene 2001 20:31 2001, 20, 4235–4248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadj Amor, I.Y.; Smaoui, K.; Chaabène, I.; Mabrouk, I.; Djemal, L.; Elleuch, H.; Allouche, M.; Mokdad-Gargouri, R.; Gargouri, A. Human P53 Induces Cell Death and Downregulates Thioredoxin Expression in Saccharomyces Cerevisiae. FEMS Yeast Res 2008, 8, 1254–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, H.-W.; Stephenson, L.; Cao, X.; Milas, M.; Pollock, R.; Ali-Osman, F. Identification and Functional Characterization of the Human Glutathione S-Transferase P1 Gene as a Novel Transcriptional Target of the P53 Tumor Suppressor Gene. Molecular Cancer Research 2008, 6, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, C.R.R.; Kajitani, G.S.; Quinet, A.; Fortunato, R.S.; Menck, C.F.M. NRF2 and Glutathione Are Key Resistance Mediators to Temozolomide in Glioma and Melanoma Cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 48081–48092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backos, D.S.; Fritz, K.S.; McArthur, D.G.; Kepa, J.K.; Donson, A.M.; Petersen, D.R.; Foreman, N.K.; Franklin, C.C.; Reigan, P. Glycation of Glutamate Cysteine Ligase by 2-Deoxy-d-Ribose and Its Potential Impact on Chemoresistance in Glioblastoma. Neurochem Res 2013, 38, 1838–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graczyk-Jarzynka, A.; Zagozdzon, R.; Muchowicz, A.; Siernicka, M.; Juszczynski, P.; Firczuk, M. New Insights into Redox Homeostasis as a Therapeutic Target in B-Cell Malignancies. Curr Opin Hematol 2017, 24, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benhar, M.; Shytaj, I.L.; Stamler, J.S.; Savarino, A. Dual Targeting of the Thioredoxin and Glutathione Systems in Cancer and HIV. J Clin Invest 2016, 126, 1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, P.K.; Schneider, M.; Kölle, P.; Kuhlencordt, P.; Förster, H.; Beck, H.; Bornkamm, G.W.; Conrad, M. Loss of Thioredoxin Reductase 1 Renders Tumors Highly Susceptible to Pharmacologic Glutathione Deprivation. Cancer Res 2010, 70, 9505–9514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Zhang, H.; Lu, J.; Holmgren, A. Glutathione and Glutaredoxin Act as a Backup of Human Thioredoxin Reductase 1 to Reduce Thioredoxin 1 Preventing Cell Death by Aurothioglucose. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2012, 287, 38210–38219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdalbari, F.H.; Telleria, C.M. The Gold Complex Auranofin: New Perspectives for Cancer Therapy. Discover Oncology 2021, 12, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashima, K.; Katoh, H. Expression of Gamma-Glutamyltransferase 1 in Glioblastoma Cells Confers Resistance to Cystine Deprivation–Induced Ferroptosis. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2022, 298, 101703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prejanò, M.; Marino, T.; Russo, N. On the Inhibition Mechanism of Glutathione Transferase P1 by Piperlongumine. Insight From Theory. Front Chem 2018, 6, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patyka, M.; Sharifi, Z.; Petrecca, K.; Mansure, J.; Jean-Claude, B.; Sabri, S. Sensitivity to PRIMA-1 MET Is Associated with Decreased MGMT in Human Glioblastoma Cells and Glioblastoma Stem Cells Irrespective of P53 Status. Oncotarget 2016 Sep 13; 7(37): 60245–60269. [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, Z.; Abdulkarim, B.; Meehan, B.; Rak, J.; Daniel, P.; Schmitt, J.; Lauzon, N.; Eppert, K.; Duncan, H.M.; Petrecca, K.; et al. Mechanisms and Antitumor Activity of a Binary EGFR/DNA–Targeting Strategy Overcomes Resistance of Glioblastoma Stem Cells to Temozolomide. Clinical Cancer Research 2019, 25, 7594–7608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godar, S.; Ince, T.A.; Bell, G.W.; Feldser, D.; Donaher, J.L.; Bergh, J.; Liu, A.; Miu, K.; Watnick, R.S.; Reinhardt, F.; et al. Growth-Inhibitory and Tumor- Suppressive Functions of P53 Depend on Its Repression of CD44 Expression. Cell 2008, 134, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipofectamine TM 3000 Reagent Protocol Protocol Outline. 2016.
- Kwolek-Mirek, M.; Zadrag-Tecza, R. Comparison of Methods Used for Assessing the Viability and Vitality of Yeast Cells. FEMS Yeast Res, 2014, n/a-n/a,. [CrossRef]
- Tada, H.; Shiho, O.; Kuroshima, K.; Koyama, M.; Tsukamoto, K. An Improved Colorimetric Assay for Interleukin 2. J Immunol Methods 1986, 93, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eilenberger, C.; Kratz, S.R.A.; Rothbauer, M.; Ehmoser, E.-K.; Ertl, P.; Küpcü, S. Optimized AlamarBlue Assay Protocol for Drug Dose-Response Determination of 3D Tumor Spheroids. MethodsX 2018, 5, 781–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franken, N.A.P.; Rodermond, H.M.; Stap, J.; Haveman, J.; van Bree, C. Clonogenic Assay of Cells in Vitro. Nat Protoc 2006, 1, 2315–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azari, H.; Louis, S.A.; Sharififar, S.; Vedam-Mai, V.; Reynolds, B.A. Neural-Colony Forming Cell Assay: An Assay To Discriminate Bona Fide Neural Stem Cells from Neural Progenitor Cells. Journal of Visualized Experiments 2011, 2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, R.L.; Wang, Q.; Carro, A.; Verhaak, R.G.W.; Squatrito, M. GlioVis Data Portal for Visualization and Analysis of Brain Tumor Expression Datasets. Neuro Oncol 2017, 19, 139–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bavarsad Shahripour, R.; Harrigan, M.R.; Alexandrov, A.V. N-acetylcysteine (NAC) in Neurological Disorders: Mechanisms of Action and Therapeutic Opportunities. Brain Behav 2014, 4, 108–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andringa, K.K.; Coleman, M.C.; Aykin-Burns, N.; Hitchler, M.J.; Walsh, S.A.; Domann, F.E.; Spitz, D.R. Inhibition of Glutamate Cysteine Ligase Activity Sensitizes Human Breast Cancer Cells to the Toxicity of 2-Deoxy-D-Glucose. Cancer Res 2006, 66, 1605–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffith, O.W. Mechanism of Action, Metabolism, and Toxicity of Buthionine Sulfoximine and Its Higher Homologs, Potent Inhibitors of Glutathione Synthesis. Journal of Biological Chemistry 1982, 257, 13704–13712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Wang, W.; Aldahdooh, J.; Malyutina, A.; Shadbahr, T.; Tanoli, Z.; Pessia, A.; Tang, J. SynergyFinder Plus: Toward Better Interpretation and Annotation of Drug Combination Screening Datasets. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics 2022, 20, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Kulesskiy, E.; Saarela, J.; Turunen, L.; Wennerberg, K.; Aittokallio, T.; Tang, J. Methods for High-Throughput Drug Combination Screening and Synergy Scoring. In Methods in molecular biology (Clifton, N.J.); Europe PMC Funders, 2018; Vol. 1711, pp. 351–398.
- Yadav, B.; Wennerberg, K.; Aittokallio, T.; Tang, J. Searching for Drug Synergy in Complex Dose–Response Landscapes Using an Interaction Potency Model. Comput Struct Biotechnol J 2015, 13, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Wennerberg, K.; Aittokallio, T. What Is Synergy? The Saariselkä Agreement Revisited. Front Pharmacol 2015, 6, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, R.; Satoh, R.; Takasaki, T. ERK: A Double-Edged Sword in Cancer. ERK-Dependent Apoptosis as a Potential Therapeutic Strategy for Cancer. Cells 2021, 10, 2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Vargas, J.M.; Ruiz-Magaña, M.J.; Ruiz-Ruiz, C.; Majuelos-Melguizo, J.; Peralta-Leal, A.; Rodríguez, M.I.; Muñoz-Gámez, J.A.; de Almodóvar, M.R.; Siles, E.; Rivas, A.L.; et al. ROS-Induced DNA Damage and PARP-1 Are Required for Optimal Induction of Starvation-Induced Autophagy. Cell Res 2012, 22, 1181–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatokun, A.A.; Dawson, V.L.; Dawson, T.M. Parthanatos: Mitochondrial-linked Mechanisms and Therapeutic Opportunities. Br J Pharmacol 2014, 171, 2000–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, H.H. L-S,R-Buthionine Sulfoximine: Historical Development and Clinical Issues. Chem Biol Interact 1998, 111–112, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Lima Moreira, F.; Habenschus, M.D.; Barth, T.; Marques, L.M.M.; Pilon, A.C.; da Silva Bolzani, V.; Vessecchi, R.; Lopes, N.P.; de Oliveira, A.R.M. Metabolic Profile and Safety of Piperlongumine. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 33646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, B.; Liao, W.; Wang, S. The Clinical Significance of Glutathione Peroxidase 2 in Glioblastoma Multiforme. Transl Neurosci 2021, 12, 032–039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strickland, M.; Stoll, E.A. Metabolic Reprogramming in Glioma. Front Cell Dev Biol 2017, 5, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Jaramillo, E.; Jamali, F.; Abdalbari, F.H.; Abdulkarim, B.; Jean-Claude, B.J.; Telleria, C.M.; Sabri, S. Pro-Oxidant Auranofin and Glutathione-Depleting Combination Unveils Synergistic Lethality in Glioblastoma Cells with Aberrant Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Expression. Cancers (Basel) 2024, 16, 2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdi, F.; Kaya, B.; Esen, H.; Karatas, Y.; Findik, S.; Keskin, F.; Feyzioglu, B.; Kalkan, E. New Clues in the Malignant Progression of Glioblastoma: Can Thioredoxin System Play a Role? Turk Neurosurg 2017, 28, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gencheva, R.; Arnér, E.S.J. Thioredoxin Reductase Inhibition for Cancer Therapy. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 2022, 62, 177–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kast, R.E.; Karpel-Massler, G.; Halatsch, M.-E. CUSP9* Treatment Protocol for Recurrent Glioblastoma: Aprepitant, Artesunate, Auranofin, Captopril, Celecoxib, Disulfiram, Itraconazole, Ritonavir, Sertraline Augmenting Continuous Low Dose Temozolomide. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 8052–8082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlenius, T.C.; Tonissen, K.F. Thioredoxin and Cancer: A Role for Thioredoxin in All States of Tumor Oxygenation. Cancers (Basel) 2010, 2, 209–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, B.; Schütte, L.; Wos-Maganga, M.; Weickhardt, S.; Timmer, M.; Eckstein, N. Thioredoxin Confers Intrinsic Resistance to Cytostatic Drugs in Human Glioma Cells. Int J Mol Sci 2018, 19, 2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mebratu, Y.; Tesfaigzi, Y. How ERK1/2 Activation Controls Cell Proliferation and Cell Death: Is Subcellular Localization the Answer? Cell Cycle 2009, 8, 1168–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, H.-J.; Kwon, H.-K.; Lee, J.-H.; Gui, X.; Achek, A.; Kim, J.-H.; Choi, S. Doxorubicin-Induced Necrosis Is Mediated by Poly-(ADP-Ribose) Polymerase 1 (PARP1) but Is Independent of P53. Sci Rep 2015, 5, 15798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fouquerel, E.; Goellner, E.M.; Yu, Z.; Gagné, J.-P.; Barbi de Moura, M.; Feinstein, T.; Wheeler, D.; Redpath, P.; Li, J.; Romero, G.; et al. ARTD1/PARP1 Negatively Regulates Glycolysis by Inhibiting Hexokinase 1 Independent of NAD + Depletion. Cell Rep 2014, 8, 1819–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaitanya, G.V.; Alexander, J.S.; Babu, P.P. PARP-1 Cleavage Fragments: Signatures of Cell-Death Proteases in Neurodegeneration. Cell Communication and Signaling 2010, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




