1. Introduction
As a result of the extensive use of concrete, the construction sector contributes 1.28 billion tons of CO
2 annually [
1]. The production of cement alone accounts for 5% to 8% of total global emissions [
2]. Concrete stands as the second most consumed material worldwide; its use surpasses the combined consumption of all other construction materials. Given the current global challenges associated with climate change, it is imperative to reduce our carbon footprint. The construction sector holds a pivotal role in this effort. One promising avenue for the concrete industry is the adoption of alternative concrete production technologies that offer a reduced environmental impact. Alkali activation stands out among these technologies; concrete produced through alkali activation has been shown to reduce CO
2 emissions by up to 80% [
3] compared to Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC).
Alkali-activated materials (AAM) are synthesized by activating an aluminosilicate precursor with an alkaline solution. Renowned for their outstanding durability, these materials exhibit stability at elevated temperatures and resist chemical attacks [
4]. The technology has found extensive application in the production of alkali-activated concrete (AAC). Various methodologies exist for AAC design, ranging from the adaptation of established prescriptive methods initially developed for Portland Cement Concrete (PCC) [
5] to the utilization of cutting-edge approaches like machine learning for optimizing mix proportions [
6].
Concrete mix design entails determining the optimal ratio between coarse granular materials and a matrix that both fills the voids between these particles and binds them together. In this study, the authors chose to devise an optimal concrete mix design utilizing a statistical tool known as Design of Experiments (DOE). Specifically, Mixture DOE, a response surface methodology (RSM), which facilitates the formulation of an optimal ingredient balance based solely on their respective proportions. Although DOE initially gained traction in the chemical, pharmaceutical, and food industries, its application in the construction sector has emerged more recently [
7]. A notable advantage of Mixture Design is its efficiency. Once a test matrix is defined and results are obtained, models can be developed to correlate performance indicators with ingredient proportions. Although the formulation of these models often necessitates the creation of numerous samples, the ability to establish a relationship between concrete characteristics and its constituents is invaluable. This relationship enables the generation of multiple mix designs tailored to optimize specific parameters.
A similar approach was previously used by Kharazi et al. [
8] who studied the optimal balance of cement, water, coarse aggregate, fine aggregate, and admixture content based on another type of DOE, factorial design. As the authors of this study, Kharazi et al. sought to optimize compressive strength and slump, and they found the methodology to be a simple and cost-effective approach for designing the optimal mix proportions for concrete. Simsek et al [
9], also utilized DOE, factorial design to develop a concrete mix design using as parameters the water to binder ratio, coarse aggregate total aggregate ratio, superplasticizer content, and fly ash content and found the technique effective to solve the mixture proportion optimization problem.
Dai et al. [
10] utilized RSM to optimize an alkali-activated slag concrete mix intended for backfills. The authors pinpointed the optimal combination of silica modulus, slag fineness, and alkaline activator concentration to achieve maximum compressive strength. Their findings underscored the reliability of this technique in synthesizing alkali-activated concrete (AAC). In a similar study, Gao et al. [
11] explored the effects of silica modulus, alkali activator concentration, and the liquid-to-solid ratio on the early mechanical performance of alkali-activated slag. Their results highlighted the significant influence of silica modulus and alkali activator concentration on early compressive strength, whereas the liquid-to-solid ratio exerted a comparatively minor impact.
Kanta et al. [
12] investigated the optimal combinations of slag content, slag/binder ratio, and fine aggregate/coarse aggregate ratio with the dual objectives of minimizing CO
2 emissions and maximizing concrete compressive strength. Their study demonstrated a close alignment (< 10% error) between the predictions of the Response Surface Methodology model and the experimental results.
Mendes et al. [
13] employed mixture DOE to determine the optimal proportions of chamotte, waste glass, and sand for manufacturing solid construction bricks. Their findings affirmed the efficacy of mixture DOE as a robust tool for analyzing and predicting the properties of alkali-activated construction materials. Similarly, Moseson et al. [
14] explored the potential of mixture DOE, utilizing granular limestone, ground granulated blast furnace slag, and sodium carbonate as alkali activators. Their research, akin to the present study, prioritized CO
2 emissions as a pivotal design parameter for alkali-activated concrete, achieving a remarkable 97% reduction compared to Portland Cement Concrete (PCC). Despite the existing body of literature on the application of RSM in concrete mix design, it is noteworthy that, at the time of the authors' research, no prior studies had specifically endeavored to develop an alkali-activated concrete mix tailored for high-temperature applications using Response Surface Methodology.
In this study, the authors utilized ferronickel slag—a readily available aluminosilicate source in northern Greece—to explore the formulation of a concrete mixture characterized by minimal environmental impact and enhanced durability, particularly under high-temperature conditions. Beyond employing ground ferronickel slag (GFNS) as a primary component of the concrete matrix, the authors incorporated coarse ferronickel slag (ranging from 0 mm to 4 mm) as a fine aggregate. The substantial utilization of ferronickel slag in this research aligns with the authors' commitment to advancing circular economy principles within the construction sector. In Greece, while the scarcity of sand is becoming a concern, approximately two million tons of ferronickel slag (FNS) are generated annually, with only 30% being recycled; the remainder is relegated to landfills or submerged in the sea [
15]. The mismanagement of FNS not only results in wastage but also incurs an annual disposal cost of €650,000 (based on 2007 metrics).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
Ground ferronickel slag served as the primary aluminosilicate source material, while sieved ferronickel slag was utilized as fine aggregate (ranging from 0 mm to 4 mm). The FNS was generously provided by The General Mining and Metallurgical Company SA in Larissa, Greece. As a supplementary silica source, silica fume with a silicon oxide content exceeding 85% was incorporated. The particle size distributions of both GFNS and silica fume (SF) were meticulously characterized using laser diffraction analysis via a Malvern Mastersizer 2000. The d50 and d90 values for GFNS were determined as 8.36 μm and 29.1 μm, respectively, while those for SF were 12.87 μm and 29.98 μm, respectively. Coarse limestone aggregates were employed in two distinct sizes: 4 mm - 8 mm and 8 mm - 16 mm. The alkaline solution was meticulously prepared by blending water with potassium silicate (KS) and potassium hydroxide (KOH). KS, acquired as a proprietary solution named Geosil® 14517, boasted a dry content of 45% and exhibited a modulus of 1.6. Meanwhile, KOH was sourced in pellet form with a purity level of 90%.
The chemical compositions of both GFNS and SF were analyzed using X-ray fluorescence (XRF) spectroscopy. This analysis encompassed the measurement of both major elements, including SiO2, Al2O3, CaO, MgO, MnO, Fe2O3, K2O, Na2O, P2O5, TiO2, as well as minor elements. For the analysis, 1.8 g of the dried ground sample was combined with 0.2 g of wax, which served as a binder. This mixture was subsequently mounted onto a 32 mm diameter circular powder pellet by pressing onto a base of boric acid. The XRF analysis was conducted using a RIGAKU ZSX PRIMUS II spectrometer, which was equipped with an Rh-anode operating at 4 kW, ensuring precise analysis of both major and trace elements. The spectrometer was outfitted with a range of diffracting crystals, including LIF (200), LIF (220), PET, Ge, RX-25, RX-61, RX-40, and RX-75, to facilitate comprehensive elemental analysis.
Table 1.
Ferronickel slag and silica fume chemical analysis through XRF, by weight*.
Table 1.
Ferronickel slag and silica fume chemical analysis through XRF, by weight*.
| Precursor |
SiO2 [%] |
Al2O3 [%] |
CaO [%] |
Fe2O3 [%] |
MgO [%] |
Na2O [%] |
P2O5 [%] |
K2O [%] |
TiO2 [%] |
MnO [%] |
LOI-Flux |
| GFNS |
36.9 |
3.61 |
4.18 |
32.8 |
7.41 |
0.15 |
0.02 |
0.48 |
0.19 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
| SF |
88.9 |
0.73 |
0.34 |
1.01 |
0.63 |
0.71 |
0.03 |
1.50 |
0.00 |
0.12 |
6.82 |
Binder was defined as the sum of GFNS, SF, KOH, and the dry part of KS. The optimal ratio of these ingredients was previously studied by the author [
16] and found to be 846.1 kg GFNS, 62.4 kg SF, 27.2 kg KOH and 64.4 kg KS for 1 ton of binder. These proportions were kept constant through all 20 mixes used for the calculation of the optimal mix. The binder was then combined with FNS sand (0 mm – 4 mm), faucet water, and 2 limestone aggregates (4 mm-8 mm, and 8 mm-16 mm). These five component proportions varied within the limits reported in
Table 2. Additionally, this table reports the on-carbon emissions and energy consumption of each component. CO
2-eq. emissions were calculated using SimaPro v8.5 software, Ecoinvent v3.4 database.
Outside the scope of optimum mix design, olivine aggregates were also tested to study their potentially better thermal compatibility with the GFNS matrix. The olivine aggregates used in this work were quarried in Northern Greece.
2.2. Concrete Production & Specimens’ Production
The aluminosilicate materials detailed in
Section 2.1 were activated using an alkaline solution formulated from KS and KOH. This solution was prepared approximately 24 hours prior to the casting of the concrete. To create the alkaline solution, water was first added to a deep container—this depth was crucial to prevent potential spills of the corrosive solution. Subsequently, Geosil® 14517 (a combination of KS and water) was introduced into the container, followed by the addition of KOH pellets. The mixture was then vigorously stirred using a long stirrer. Given that the dissolution of KOH pellets is exothermic, the solution was allowed to naturally cool for a period of 24 hours.
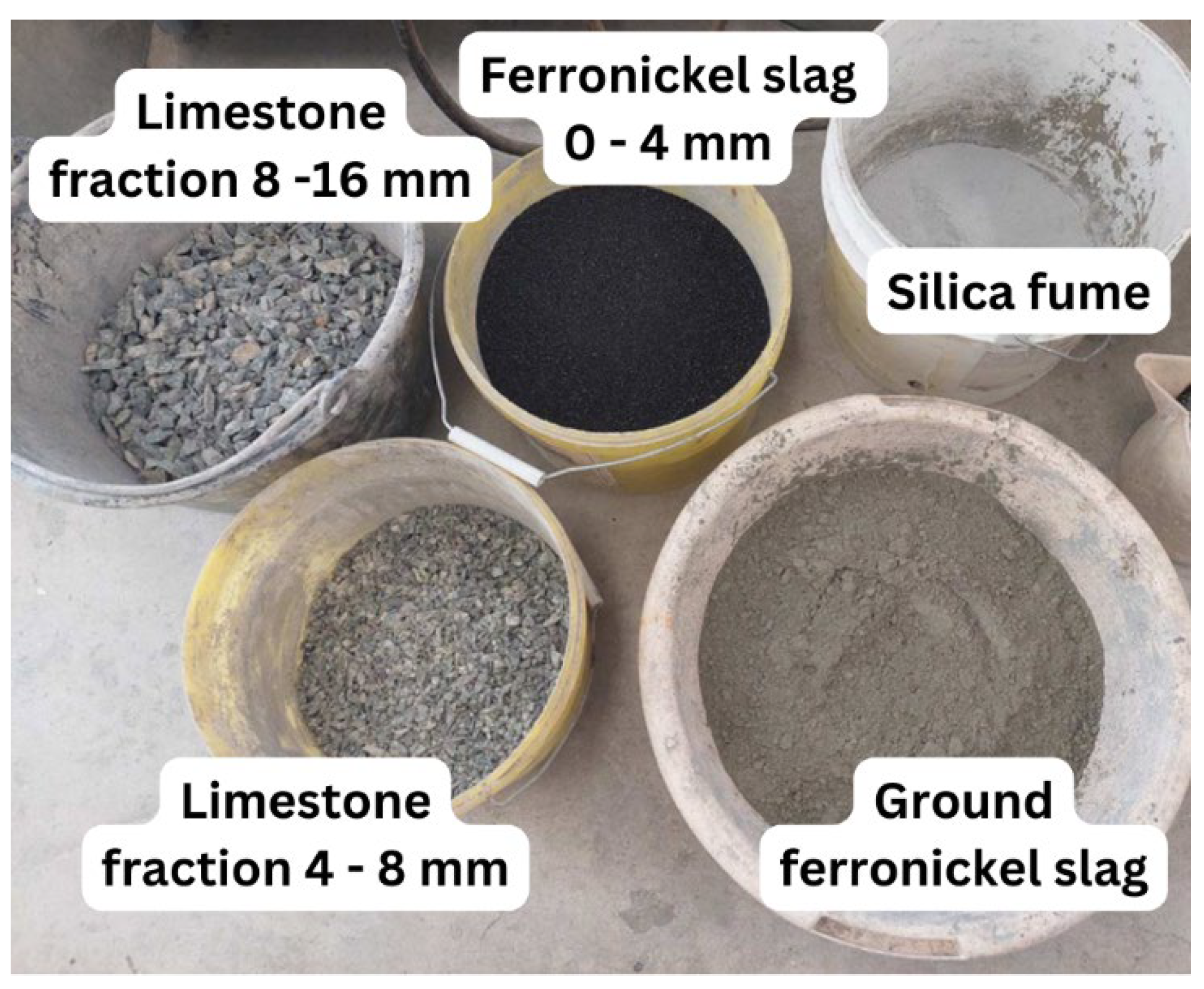
The limestone based ferronickel slag alkali activated concrete (L-FNS-AAC) specimens were produced in 60 kg batches using a 70 L electric pan-type concrete mixer. The process of production started with the addition of dry components (Fig 1) from the highest to the lowest size into the mixer. It was observed that this order facilitated the dry mixing process. Once all dry ingredients were placed, the electric mixer was used for 30 s, ensuring a homogeneous mixture. At this point, the activator solution (water + KOH + KS) was gradually added, and hand mixing followed (for approximately 20 s) to avoid splashing of the solution and promote absorption by the solid components. The final mixing phase involved operating the electric mixer for 10 minutes, with a pause after 5 minutes to scrape off any residual unmixed ingredients adhering to the mixer walls.
Figure 1.
Dry components of ferronickel slag alkali activated concrete.
Figure 1.
Dry components of ferronickel slag alkali activated concrete.
Each concrete batch was cast into six steel molds, each measuring 150 mm on each side. Following casting, the molds were subjected to vibration using a vibration table for a duration of 30 seconds to ensure optimal compaction. To minimize evaporation, the concrete cubes were then shielded with a thin plastic sheet. The demolding process was conducted the subsequent day.
2.3. Fresh- and Hardened-State Properties Tests
The slump test, in accordance with EN 12350-2 [
17], was conducted immediately upon the completion of the mixing process to assess the workability of the concrete. For the curing phase, the specimens were allowed to mature under laboratory conditions for a period of 28 days. These conditions were maintained at a temperature of 20 ± 2 °C and a relative humidity of 65%. Throughout the curing period, the specimens were wrapped in multiple layers of plastic foil to prevent moisture loss. No additional heat curing was employed.
For compressive strength evaluation, the concrete cubes were subjected to compression tests using a compression testing machine equipped with a maximum load capacity of 4000 kN. The application of load followed the guidelines specified in ASTM C 39 [
18], with a constant rate of 1 mm/min.
The residual compressive strength after unstressed heating conditions and cooling is typically considered to be lower than the compressive strength obtained at a ‘hot’ state after stressed or unstressed heating conditions [
19], [
20]. Hence, the residual compressive strengths reported in this work comprise a conservative lower bound for the material compressive strength during heating.
2.4. Design of Experiment (DOE)
The optimal proportions of the five components (A: binder, B: FNS sand, C: coarse aggregates 4-8 mm, D: coarse aggregates 8-16 mm, and E: faucet water) was investigated through Mixture Design of Experiment. Mixture DOE is used to find the optimal proportions of a mixture based on a multi-response desirability function. For the present study the selected responses were slump and compressive strength of the cubes, both unheated and heated.
To facilitate calculations the authors relied on Design Expert® v11.1.2.0. was selected. The optimization of components through mixture DOE starts with the selection of component constraints. The following constraints were considered: Water-to-binder ratio was set to range between 0.235 and 0.27; sand-to-binder ratio between 1 and 3; solid-to-liquid ratio from 13 to 17; aggregates 0-4 mm, and 8-16 mm were both restricted to range from 10% to 50% of mortar (the sum of water, binder, and FNS sand) content, by weight. These restrictions were selected based on preliminary experimental work (not presented here) and intended to produce concretes with neither excessive nor non-existent flow. The performance evaluation of each concrete mixture was conducted through slump tests and compressive strength tests, both pre- and post-heat exposure.
The D-optimality criterion was employed to formulate 20 distinct mix designs using Design Expert®, while adhering to the aforementioned constraints. For each mix design, six concrete cubes were fabricated from a singular batch. This setup facilitated the acquisition of three compressive strength measurements under ambient (unheated) conditions and an additional three under elevated (heated) conditions. Post-heating, the cubes were tested subsequent to cooling to ambient temperature. A singular slump value was determined immediately after the conclusion of the mixing process. A comprehensive summary of all mix designs, including their respective compositions per cubic meter, is delineated in
Table 3.
2.5. Heating Regime
For each mix design, three concrete cubes underwent thermal exposure in a controlled environment. These cubes were subjected to a temperature of 600°C within a 0.125 m3 electric furnace. The heating protocol was standardized, with the temperature increment set at 5°C/min until the desired temperature was attained. Upon reaching the target temperature, the heating was maintained for a duration of 2 hours. Subsequent to the 2-hour heating phase, the electric furnace was deactivated, allowing the specimens to undergo natural cooling over a span of approximately 24 hours, during which the furnace's shutter remained closed.
2.6. Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) Method
Adhering to the ISO 14040 LCA framework [
21], this analysis aimed to evaluate the environmental footprint associated with the proposed alkali-activated concrete mixes and offer a comparison to OPC-based concrete variants that exhibit comparable mechanical properties. The functional unit chosen for this assessment is 1 m
3 of concrete.
The system boundaries for the LCA encompass the environmental impacts stemming from the production and pretreatment stages of the constituent materials. To conduct this evaluation, the SimaPro 8.5 software was utilized. Life cycle inventories (LCIs) pertinent to the production processes of raw materials were sourced from the Ecoinvent v3.4 database.
The GFNS concrete developed in this study was evaluated under two distinct scenarios, based on the classification of the ferronickel slag: as a waste material and as an industrial by-product. In the former scenario, emissions attributable to the slag's production via the furnace process were not allocated to its manufacturing phase; only the pre-treatment stage was factored into the analysis. Conversely, in the latter scenario, an economic allocation approach was adopted [
16].
To quantify the global warming potential (GWP) of the proposed concrete mixes, the IPCC2013 life cycle impact assessment method was employed.
3. Results and Discussion
Table 4 presents the test results for both fresh and hardened states for the mixes described in
Table 3. For underscored values, refer to the next section.
3.1. DOE Models
The test results presented in
Table 4 were input into the Design Expert® software. Values underscored in the table indicate outliers, which were identified through various diagnostic plots generated by Design Expert®. These plots included normal plots, Cook's distance, and plots of Residual vs. Predicted values. After data curation, the refined dataset was used to develop regression models that correlate slump and compressive strength (both heated and unheated) with component’s proportions. These regression equations are listed in
Table 5. To use these equations for prediction, users can substitute the corresponding component contents (designated as A, B, C, D, E in
Table 2) in grams. The sum of all components corresponds to 60000 g (60 kg). (or 60 kg). The coefficients for each model (
Table 5) were selected by testing adjusted R
2 criteria, Akaike, and Bayesian information criteria (AIC and BIC), and selecting the criteria which resulted in the highest predicted R
2. This procedure was executed one by one for each model corresponding to one of the three studied responses.
Table 6 presents the fit statistics for each model, including mean values, standard deviation (Std. Dev.), and coefficient of variation (CoV). Three types of R
2 values are provided: the conventional R
2, as well as the adjusted and predicted R
2 values. The discrepancy between the predicted and adjusted R
2 values was found to be less than 20%, which is considered a reasonable level of agreement. Additionally, the adequate precision metric, which evaluates the signal-to-noise ratio, exceeded a value of 4 in all models. A value of 4 serves as a lower threshold, indicating an 80% probability that the predicted response is attributable to the influence of the ingredients rather than natural variation, also known as noise [
7].
3.2. Optimal Concrete Mix Design for High Temperature Applications
Upon deriving a regression equation for each of the three responses, all the required input to calculate an optimal mix was obtained. The objective was to identify the "sweet spot" where the component proportions would yield both slump values closely aligned with the S2-S3 classes and high compressive strengths. To achieve this, a desirability function, facilitated by the Design Expert® software, was employed. This function enabled the calculation of a desirability coefficient for each one of the multiple responses. Subsequently, these coefficients were combined to produce an overall desirability coefficient, reflecting the mix's overall performance. An importance factor ranging from 1 to 5 was assigned to each response to account for its relative significance in determining the optimal mix. In this study, slump and unheated compressive strength were assigned a factor of 4, while heated compressive strength was assigned a factor of 5.
Utilizing the desirability algorithm in conjunction with a hill-climbing algorithm, Design Expert® was used to identify the concrete mix design that yielded the highest desirability coefficient. The ingredient proportions for 1 m
3of this mix are detailed in
Table 7. A comparison between the predicted and measured values of slump and compressive strength in the table reveals a high level of agreement, with errors below approximately 3%. This level of error is notably lower than the discrepancies reported in other studies. For instance, Moseson et al. [
14] reported a difference of around 15% between expected and validated results when optimizing AAC mixtures for CO
2 emissions reduction using GGBFS activated with sodium carbonate through mixture design of experiments (DOE). Similarly, Kanta et al. [
12] observed a model prediction error of approximately 9% when predicting the mechanical properties of AAC based on steel slag and foundry sand, employing response surface methodology (RSM) and Minitab® software.
The GFNS AAC mix was further refined with the objective of adapting it for upscaled concrete castings, where a more fluid consistency would be advantageous. Consequently, an additional mix was formulated with the goal of increasing the slump to 200 mm. This modified mix design is detailed in
Table 7. As evident from the table, alterations in mix proportions were minimal, with the greatest change amounting to 6.3%. Special attention was devoted to maintaining the chemical activator content nearly constant to prevent a significant increase in CO
2 emissions associated with the modified mix. The resultant mix exhibited a slump of 210 mm and an unheated compressive strength nearly identical to that of the optimal DOE mix, but with a 30% lower heated strength, likely attributable to the increased water content. The mix demonstrated sufficient workability for up to 3 hours following mixing.
3.3. Olivine Aggregate Replacement in the Optimal Concrete Mix Design
In an attempt to enhance the residual compressive strength following heating, the limestone coarse aggregates reported in the upscaled mix design detailed in
Table 7 were replaced with olivine aggregates. The resulting olivine aggregate FNS-based AAC (O-FNS-AAC) exhibited a slump of 200 mm, which closely mirrors that of its limestone aggregate counterpart. Additionally, it demonstrated unheated and heated compressive strengths of approximately 65 MPa and 32 MPa, respectively, when heated to 600 °C for 2 hours. The reduction in unheated compressive strength compared to the limestone aggregate AAC is attributed to the flakiness of the olivine aggregates and their suboptimal grading. Notably, the relative residual compressive strength of O-FNS-AAC (expressed as a percentage of the unheated strength) surpassed that of limestone aggregate AAC by a factor of approximately 2. Furthermore, the absolute value of the residual compressive strength was greater for O-FNS-AAC than for the upscaled limestone-FNS-AAC mix. This higher absolute value suggests an improved mitigation of thermal strain mismatch between the matrix and aggregates.
3.4. Fresh State Properties: Slump
Many of the DOE mixes yielded zero slump, a condition likely attributable to the stringent limits set for water content (ranging from 5.6% to 6.3% by weight). Additionally, this outcome can be associated with the elevated silica modulus (1.6), which Law et al. [
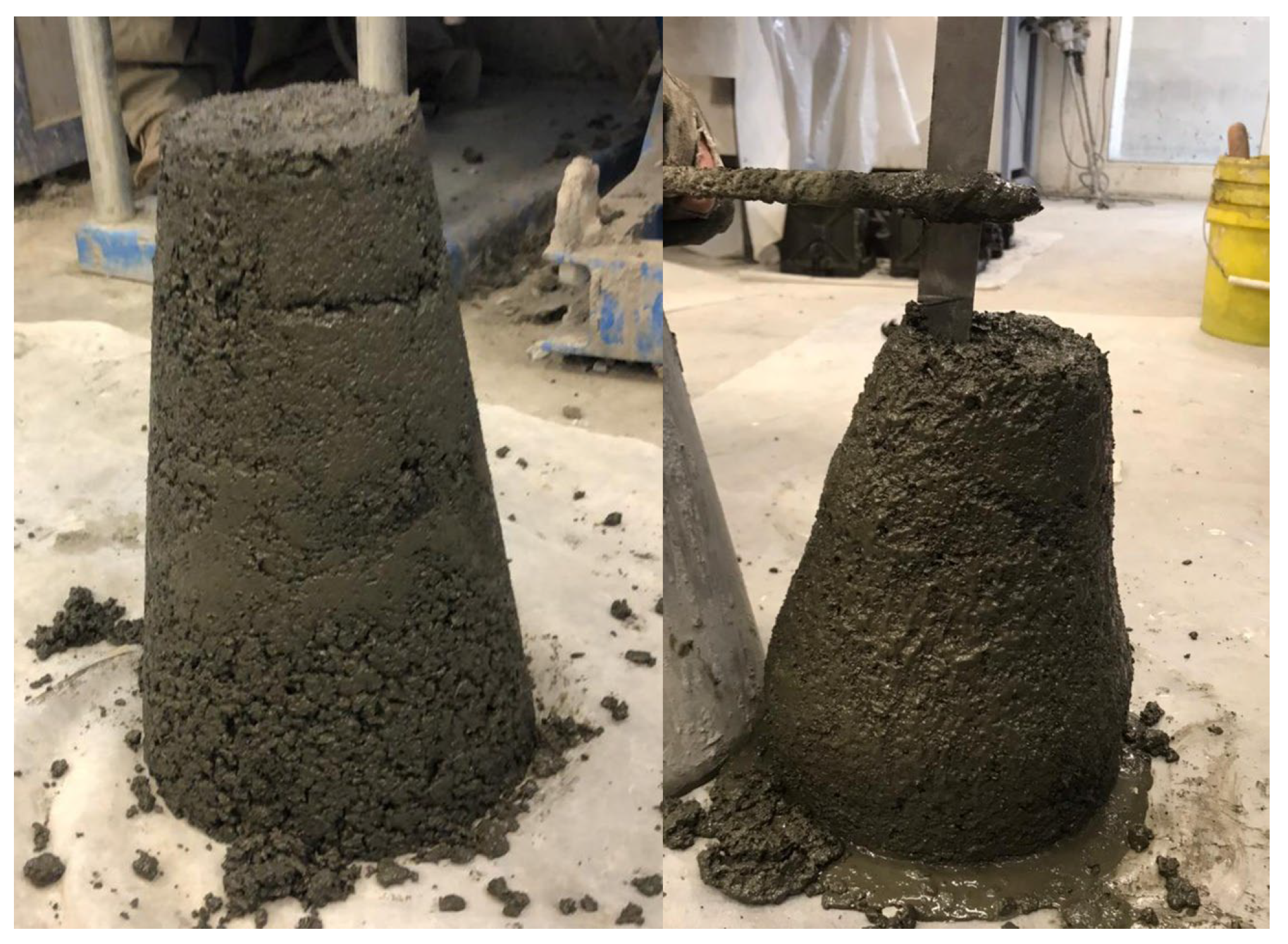
22] identified as a contributing factor to slump loss. Fig 2 illustrates an example of a zero-slump mix (mix 8), side to side with a mix exhibiting a 70 mm slump (mix 3).
Figure 2.
Slump test of fresh concrete for mixes 8 and 3.
Figure 2.
Slump test of fresh concrete for mixes 8 and 3.
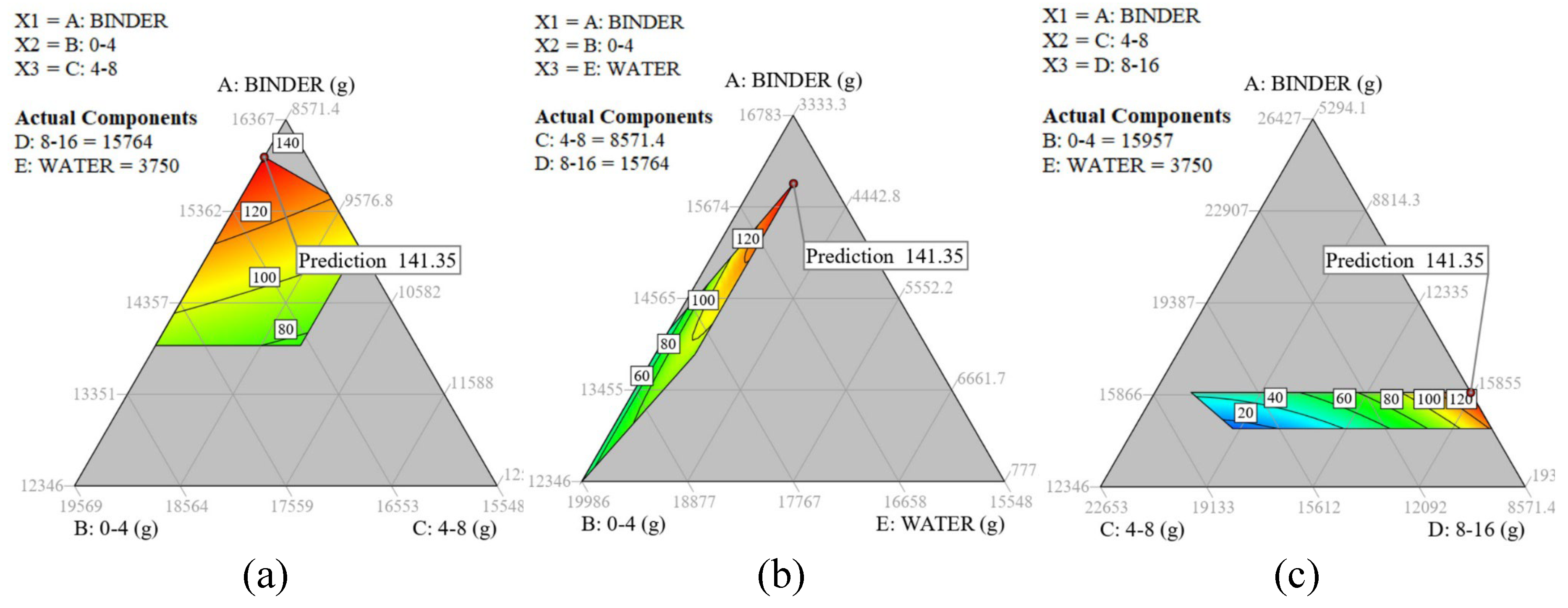
Fig 3 presents contour plots corresponding to the surfaces of the slump model outlined in
Table 5. In each plot, the quantities of all components are scaled to a 60 kg concrete batch, with each side representing a specific component and progressing in a clockwise direction around the plot. Within each plot, three components are subject to variation, while the remaining two are held constant. The optimal concrete mix is located in the upper corner of both Fig 3.a and Fig 3.b, suggesting that adjusting the original component limits to increase the binder content and decrease the aggregate fractions of 0-4 mm and 4-8 mm would likely enhance the concrete slump. This is expected as the reduction in the smaller sized fraction would result in less aggregate surface area to cover and therefore an increase in the amount of paste free to facilitate the flow of the mix.
A different trend emerges in Fig 3.c, where the water and sand contents are held constant. In this configuration, augmenting the binder content yields only a marginal increase in slump, while the quantity of coarse aggregates exerts the most significant influence on slump. Specifically, an increase in the amount of coarse aggregates leads to a more substantial slump. This behavior mirrors observations in conventional concrete, where augmenting the coarse aggregate fraction up to a certain threshold enhances flowability through the same mechanism previously described.
Figure 3.
2D ternary contour plots for slump as a function of three components: (a) A, B, C with fixed water and coarse aggregates 8 mm -16 mm; (b) A, B, E with all coarse aggregates fixed; (c) A, C, D with water and FNS sand content fixed.
Figure 3.
2D ternary contour plots for slump as a function of three components: (a) A, B, C with fixed water and coarse aggregates 8 mm -16 mm; (b) A, B, E with all coarse aggregates fixed; (c) A, C, D with water and FNS sand content fixed.
It was determined that a slump of 140 mm, as attained from the optimal concrete mix design, would be insufficient for practical applications. Consequently, as previously mentioned, the mix design was adjusted by increasing the content of the chemical activator solution until the concrete achieved a slump value of 200 mm (refer to
Table 7 for details on the upscaled mix). Additionally, the substitution of limestone with olivine aggregates did not result in a reduction in slump.
3.5. Compressive Strength
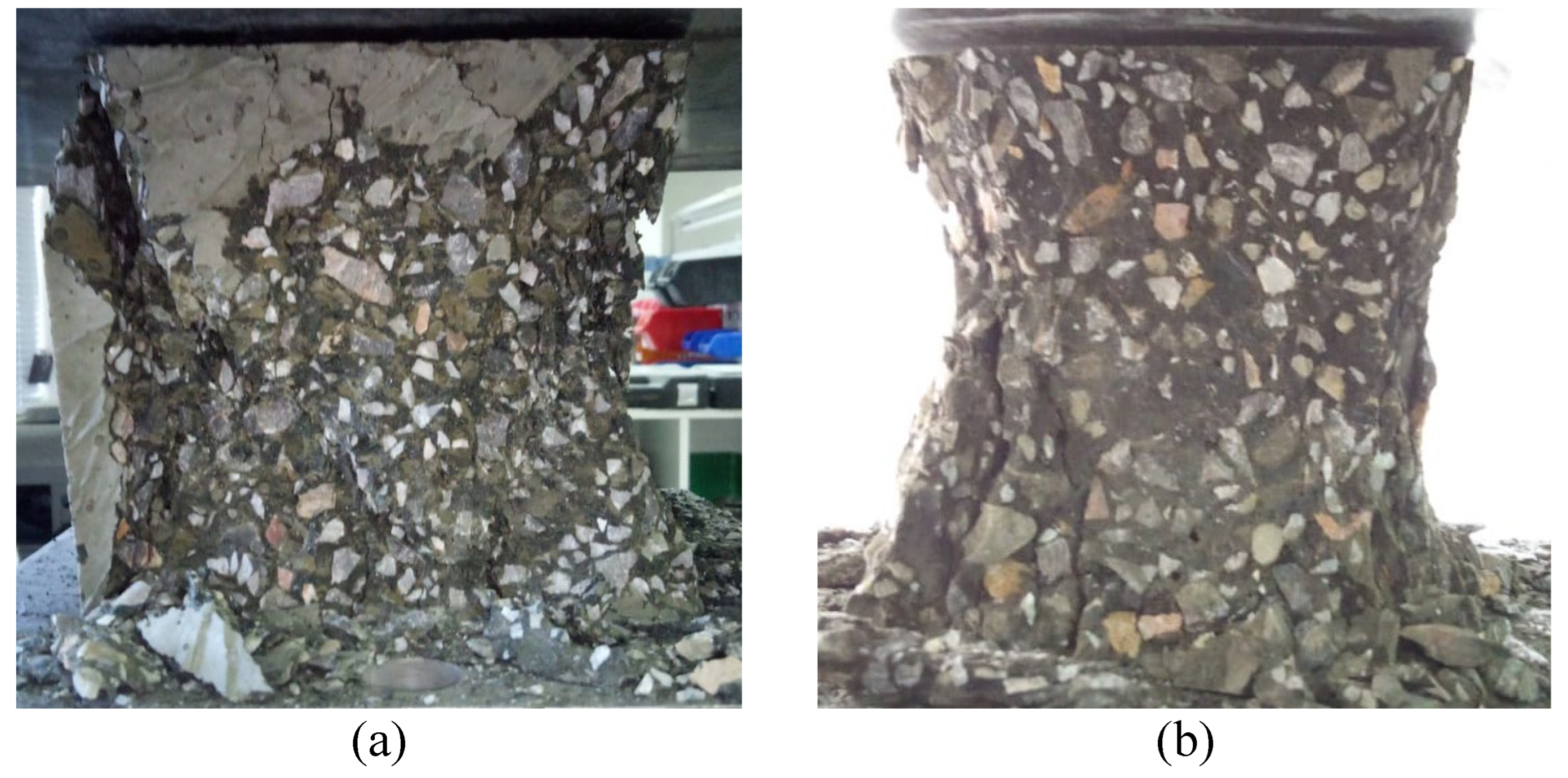
Fig 4 illustrates the typical conical failure mode observed in the L-FNS-AAC concrete cubes. All samples exhibited elevated mean 28-day unheated compressive strengths, ranging from 65.7 MPa to 87.9 MPa, in the absence of heat curing. On average, the residual compressive strength following heating at 600 °C for 2 hours amounted to approximately 35% of the unheated strength, with a range from 19% to 46%. The modification made to the DOE optimal mix to enhance slump (upscaled mix) resulted in reductions in both unheated and heated compressive strengths, by 2.7% and 30%, respectively. The decline in residual compressive strength, likely attributable to the increase in water content (increasing from 164.1 kg per m3 to 169.6 kg per m3), underscores the high sensitivity of the L-FNS-AAC concrete mixes to minor variations in water content.
Figure 4.
Post failure cube samples of L-FNS-AAC: (a) unheated; (b) heated samples.
Figure 4.
Post failure cube samples of L-FNS-AAC: (a) unheated; (b) heated samples.
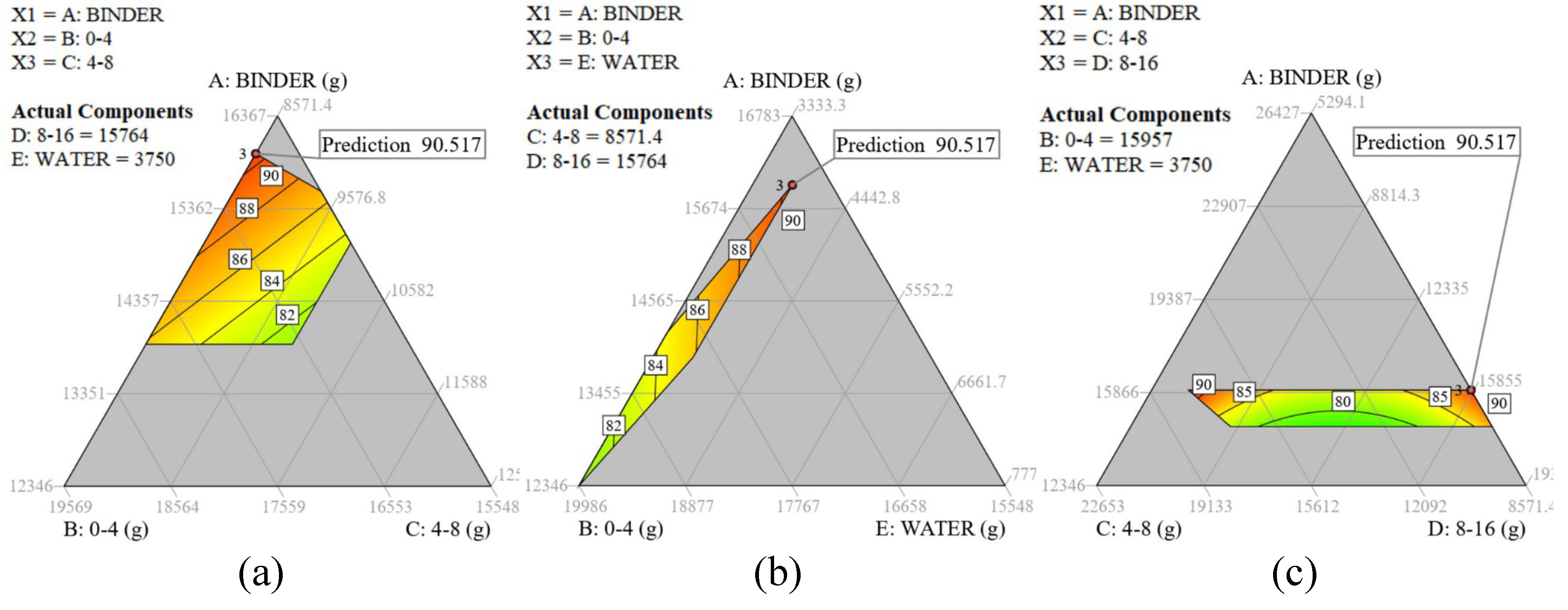
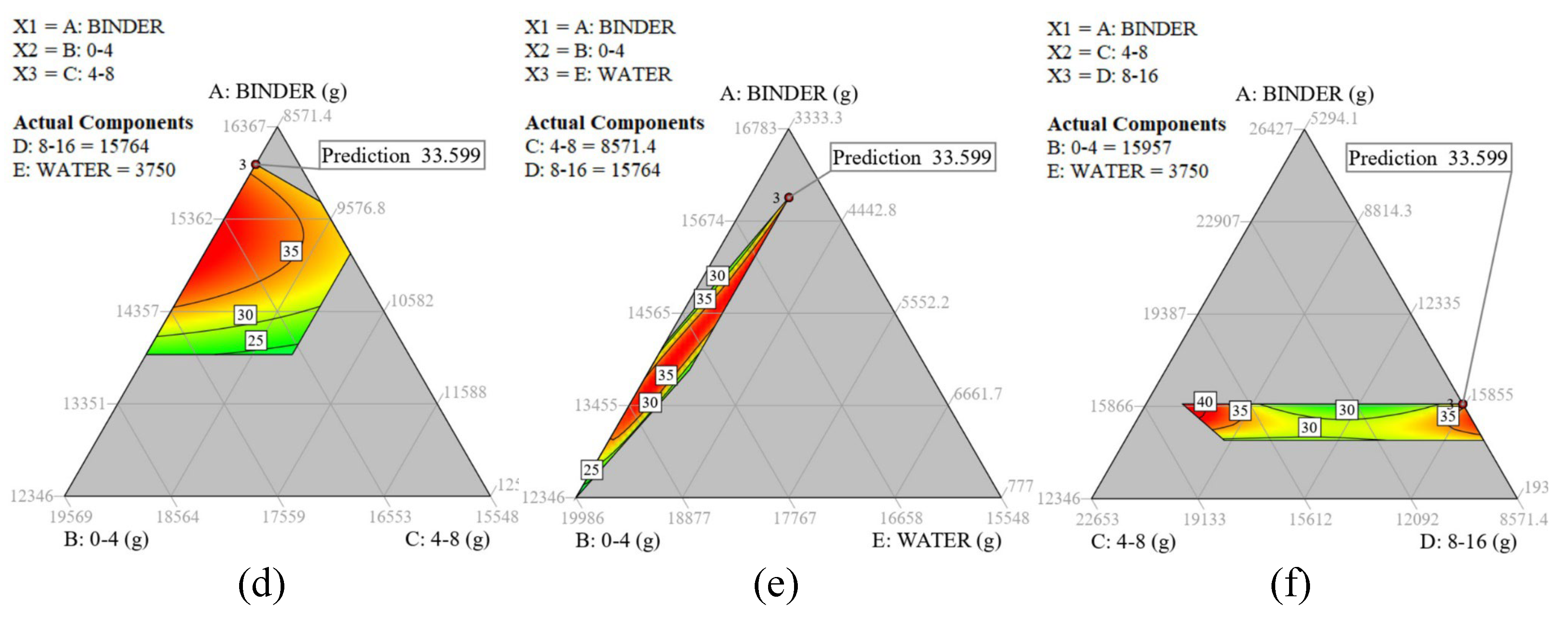
Fig 5 presents contour maps depicting the unheated (a-c) and heated (d-f) compressive strength. Fig 5.a and Fig 5.d illustrate that an increase in binder content leads to increased compressive strength both before and after heat exposure when water and aggregate 8-16 mm are held constant. The gradient observed in the contour plot of Fig 5.b suggests a linear relationship between binder content and unheated compressive strength, whereas the relationship appears nonlinear for the heated compressive strength as displayed in Fig 5.e. Fig 5.c and Fig 5.f elucidate the influence of coarse aggregates on the mix. The pronounced red regions on both extremes—left and right—indicate that the compressive strength of L-FNS-AAC benefits (with values ranging from 85 to 90 MPa) from aggregate contents near the lower or upper limit of the 8-16 mm fraction. In contrast, intermediate values yield diminished strength, falling below 80 MPa.
Figure 5.
2D ternary contour plots for compressive strength as a function of heat exposure [(a)-(c): unheated; (d)-(f) heated at 600 °C] and three components: (a) A, B, C with fixed water and coarse aggregates 8 mm -16 mm; (b) A, B, E with all coarse aggregates fixed; (c) A, C, D with water and FNS sand content fixed; (d) A, B, C with fixed water and coarse aggregates 8 mm -16 mm; (e) A, B, E with all coarse aggregates fixed; (f) A, C, D with water and FNS sand content fixed. All data is derived from L-FNS-AAC (DOE concrete mixes).
Figure 5.
2D ternary contour plots for compressive strength as a function of heat exposure [(a)-(c): unheated; (d)-(f) heated at 600 °C] and three components: (a) A, B, C with fixed water and coarse aggregates 8 mm -16 mm; (b) A, B, E with all coarse aggregates fixed; (c) A, C, D with water and FNS sand content fixed; (d) A, B, C with fixed water and coarse aggregates 8 mm -16 mm; (e) A, B, E with all coarse aggregates fixed; (f) A, C, D with water and FNS sand content fixed. All data is derived from L-FNS-AAC (DOE concrete mixes).
The observed decline in concrete strength can likely be attributed to the thermal incompatibility between the aggregates, in this case limestone, and the matrix. Alkali-activated matrices have a tendency to shrink at elevated temperatures, whereas aggregates tend to expand. This differential behavior results in internal stresses that, when exceeding the tensile capacity of the matrix, give rise to internal cracking, thereby compromising the concrete strength [
23], [
24], [
25]. Substituting limestone with olivine aggregates mitigated the thermal mismatch between the matrix and aggregates, leading to a partial recovery (an increment of 36%) in heated compressive strength, which increased from 23.5 MPa for the upscaled L-FNS-AAC to 32 MPa for the olivine-based ferronickel slag alkali-activated concrete, O-FNS-AAC. However, this improvement in heated compressive strength was accompanied by a reduction (23%) in unheated compressive strength, decreasing from 85 MPa to 65 MPa due to the change in coarse aggregate type.
The authors determined that the properties of O-FNS-AAC are more suitable for structural engineering applications, where a 65 MPa compressive strength after 28 days is generally adequate for most applications, and the heated value of 32 MPa would often suffice (and would be preferable to the 23 MPa achieved using limestone aggregates) to support loads until post-fire assessments and repair works can be carried out.
The O-FNS-AAC residual compressive strength (50%) is comparable to what has been reported by other studies on alkali activated concrete. For instance, Derinpinar et al. [
26] observed a residual compressive strength (after exposure to 600°C for 1 h,) that was approximately 50% of the original value (35 MPa) when activating blast furnace slag using sodium hydroxide. Although the percentage retention is similar to the value reports in the present study, the absolute residual compressive strength (~17 MPa) was considerably lower than that observed in the present study (~32 MPa).
Guerrieri et al.[
27] examined the residual compressive strength of three concrete mixtures: OPC-only, AAC based on slag, and a 50/50 blend of slag and OPC. All mixtures exhibited an unheated compressive strength of approximately 50 MPa after ambient curing for 28 days. Following exposure to 600°C for 1 h, the mixtures containing slag retained around 50% of their original strength, whereas the OPC-only concrete experienced a reduction of approximately 80% in its original strength. The enhanced retention of strength in alkali-activated concrete is attributed to the absence of calcium hydroxide which undergoes degradation at elevated temperatures, leading to diminished chemical stability in OPC-based concrete mixtures [
29].
Ramagiri et al. [
28] reported a strength retention of approximately 50% in AAC blends composed of slag and fly ash after subjecting the samples to a temperature of 538°C for 2 h. The author’s best performing blend, consisting of equal parts of slag and fly ash, exhibited compressive strengths of around 70 MPa and 35 MPa before and after heat exposure, respectively. These values align closely with those observed for the O-FNS-AAC mix evaluated in the present study. The decline in compressive strength is attributed to the degradation of the AAC matrix and the development of pore pressure, a damage mechanism corroborated by additional research [
29] on AAC subjected to high temperatures, which likely contributes to the observed reduction in strength for the O-FNS-AAC mix developed in this study.
3.6. Life Cycle Analysis
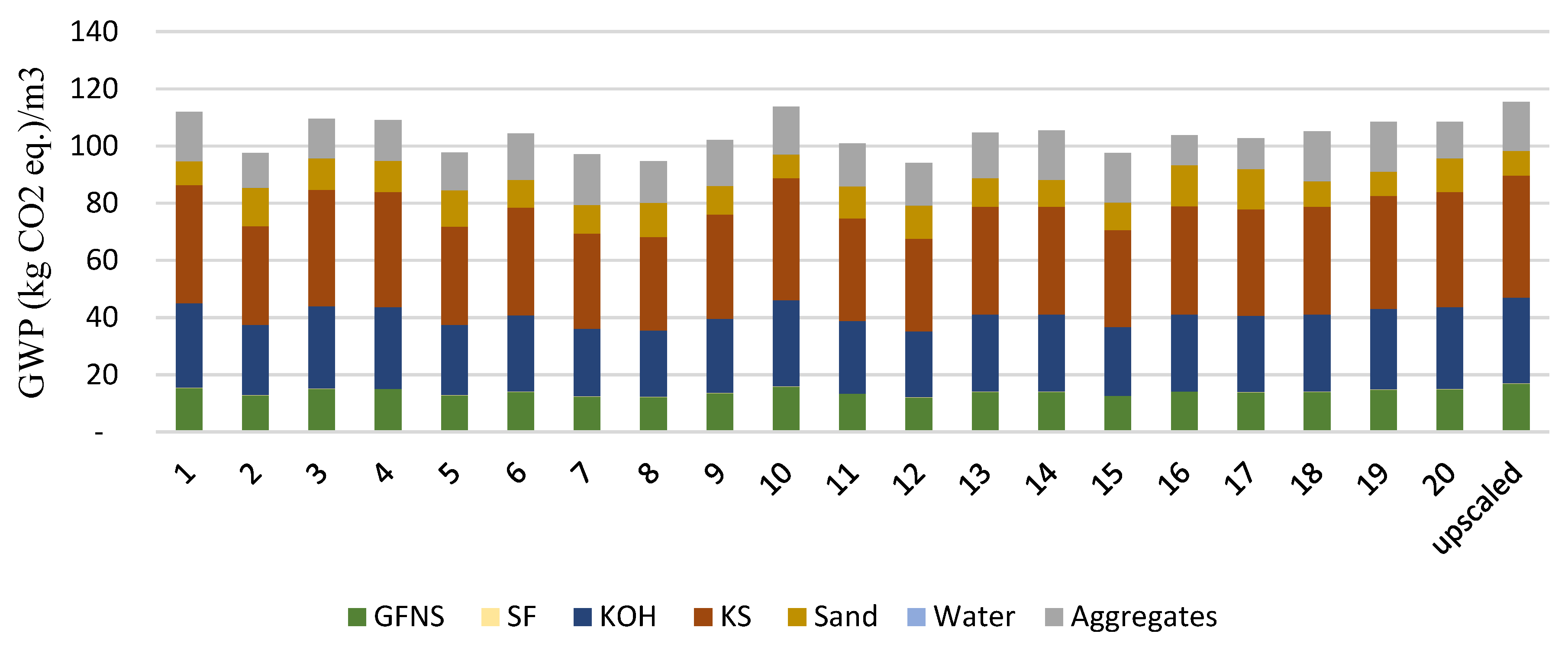
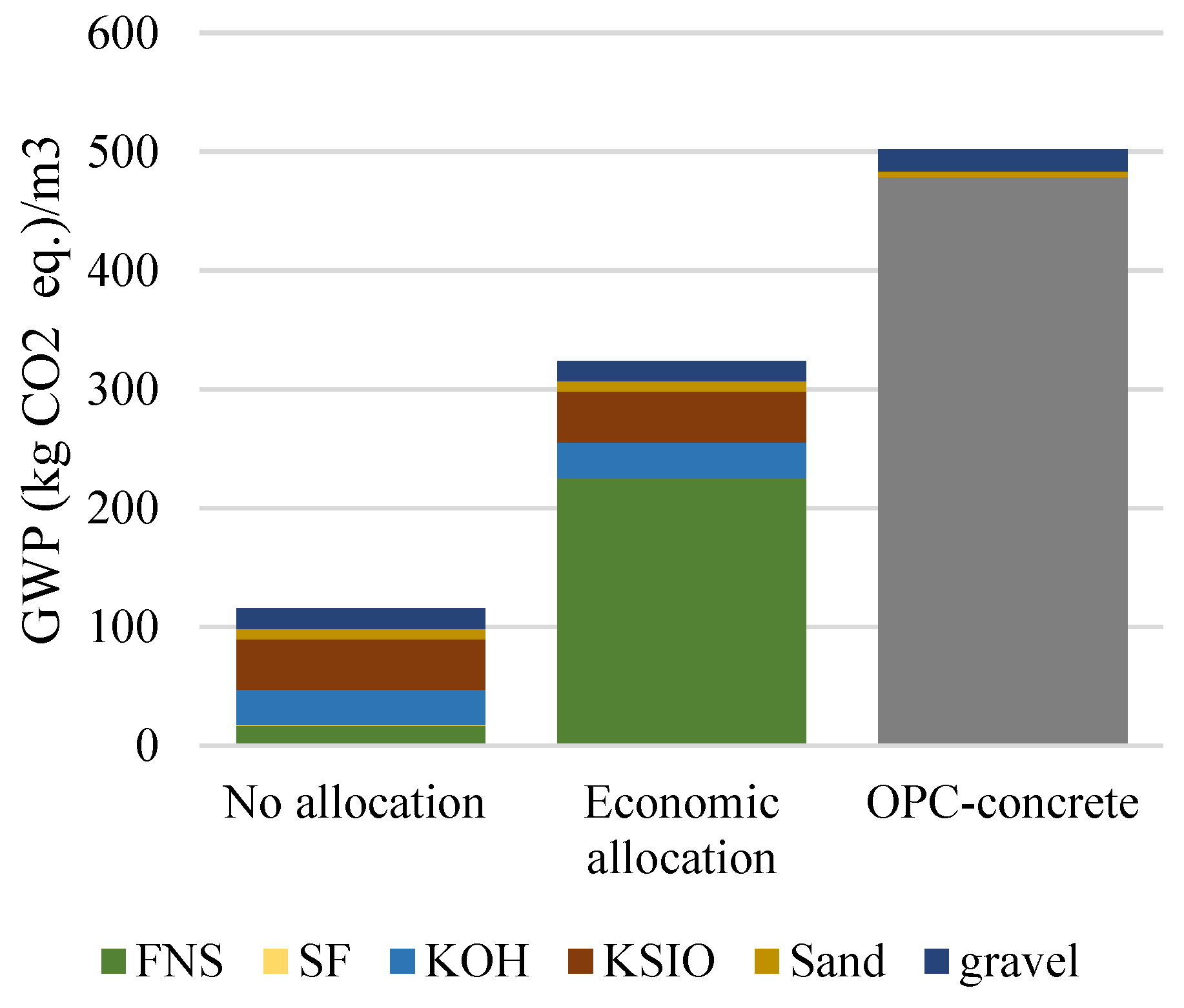
The global warming potential (GWP) associated with the optimal L-FNS-AAC mix was calculated to be 113.7 kg CO2_eq., while the upscaled mix resulted in 115.4 kg CO2_eq. The lowest emissions were observed for mix 12 (a mix with an overall poor performance), which is equal to 94 kg CO2_eq. per 1 m3 (Fig 6). In these calculations, emissions attributed to ferronickel slag (FNS) production were limited to those associated with the grinding process. Under this assumption, the contribution of FNS to the total GWP of the mixes was approximately 14%, whereas activators (specifically, KOH and KS) accounted for between 59% and 64% of the total GWP across all alkali-activated concrete mixes considered. When emissions are allocated based on the economic value of FNS, the optimal concrete mix and the upscaled L-FNS-AAC mix yield GWPs of 310 kg CO2_eq./ m3 and 324 kg CO2_eq./ m3, respectively. The upscaled AAC mix exhibited mechanical properties comparable to the high-strength (HS) OPC concrete mix developed by Chan et al. [
30], who also investigated the impact of high-temperature exposure on the residual strength of HS-OPC concrete. Given the high OPC content, the GWP associated with this concrete mix was 502 kg CO2_eq. Consequently, the upscaled L-FNS-AAC mix resulted in a 35% reduction in CO2_eq. emissions compared to an OPC-based concrete with equivalent unheated strength (Fig 7) when economic allocation is applied, considering FNS as an industrial by-product. This reduction increases to 77% when FNS is classified as waste.
Figure 6.
Global Warming Potential of L-FNS-AAC mixes (upscaled mix included), where no allocation is applied to FNS.
Figure 6.
Global Warming Potential of L-FNS-AAC mixes (upscaled mix included), where no allocation is applied to FNS.
Figure 7.
Impact of allocation method on total GWP of L-FNS-AAC (upscaled mix) compared to a strength-wise equivalent OPC-based concrete.
Figure 7.
Impact of allocation method on total GWP of L-FNS-AAC (upscaled mix) compared to a strength-wise equivalent OPC-based concrete.
5. Conclusions
This section is not mandatory but can be added to the manuscript if the discussion is unusually long or complex. This paper described a Mixture Design of Experiment procedure targeting the optimum mix design of an FNS-based alkali-activated concrete for high temperature applications.
Mixture design DOE can be used to accurately (less than 3.1% error in prediction) predict the compressive strength and slump of concrete mixes and thus is an effective mix design methodology for AAC.
The resulting (best-performing) GFNS-based AAC mix had the following ingredients’ proportions, per m3: 590.7 kg GFNS, 43.6 kg SF, 19 kg KOH, 45 kg KS, 698.1 kg FNS sand, 375 kg limestone aggregates 4-8mm, 689 kg limestone aggregates 8-16mm and 164.1 kg water. The mix developed a high 28d compressive strength when cured at (sealed) ambient conditions (~ 88 MPa) which suggests its applicability in conditions where high-strength concrete is required such as bridges, tunnels, and high-rise buildings.
The optimal mix was adjusted to achieve a workability and a retention thereof adequate for real-life (upscaled) castings (slump = 210 mm, retained for up to 3h post mixing). This upscaled mix achieved an unheated compressive strength almost identical to the optimal (lab-scaled) DOE mix while its heated compressive strength (after a 2h-heating at 600 °C) was reduced from approximately 34 MPa to 23.5 MPa.
Limestone aggregates were replaced with olivine aggregates to study the possible enhancement in residual compressive strength post high temperature exposure. The olivine based concrete mix resulted in lower unheated compressive strength, 65 MPa (23 % lower than the limestone-based equivalent) but higher residual compressive strength, 32 MPa (36% higher than its limestone based counterpart) while maintaining a slump of 200 mm.
The absolute values of slump, compressive strength before and after heat exposure suggest the potential utilization of the proposed olivine based mix in application where its fundamental to preserver the carrying load capacity after exposure to high thermal loads. The construction of the exposed layer of tunnels might be an application for this type of mix.
A Life Cycle Analysis was carried out to assess the Global Warming Potential of all L-FNS-AAC mixes. Assuming zero economic allocation for FNS (that is, regarding FNS as waste), it was found that the heaviest contributor to GWP (approx. 60%) are the chemicals used to comprise the alkali activator (namely, KOH and KS). Compared to an OPC-based concrete of equivalent unheated strength, the upscaled L-FNS-AAC mix, resulted in 35% or 77% lower CO2-eq. emissions depending on whether FNS (both finely ground and in its sand-like form) is perceived as an industrial by-product or a waste material, respectively.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing - Original Draft, Visualization Anastasija Komkova: Methodology, Formal analysis, Writing - Original Draft, Catherine G. Papanicolaou: Validation, Resources, Data Curation, Writing - Review & Editing, Visualization, Supervision, Project administration, Funding acquisition Thanasis C. Triantafillou: Writing - Review & Editing, Visualization, Supervision, Project administration, Funding acquisition.
Funding
This research was funded by the European Union’s H2020 MARIE SKODOWSKA-CURIE ACTIONS, grant agreement No. 813596 DuRSAAM. The APC was funded by the University of Patras.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
Acknowledgments
We thank the company LARCO for the kind donation of ferronickel slag. Special acknowledgement is given to the Laboratory of Sedimentology, and the Laboratory of Electron Microscopy and Microanalysis of the University of Patras.
Conflicts of Interest
authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- P. K. Mehta, “High-performance, high-volume fly ash concrete for sustainable development,” International Workshop on Sustainable Development and Concrete Technology, pp. 3–14, 2004.
- K. L. Scrivener and R. J. Kirkpatrick, “Innovation in use and research on cementitious material,” Cement and Concrete Research, vol. 38, no. 2, pp. 128–136, 2008, doi: 10.1016/j.cemconres.2007.09.025. [CrossRef]
- J. Davidovits, “Global warming impact on the cement and aggregates industries,” World Resource Review, 1994.
- C. Shi, P. V. Krivenko, and D. Roy, Alkali-Activated Cements and Concretes. in Alkali-Activated Cements and Concretes. New York: Taylor & Francis, 2006. doi: 10.4324/9780203390672. [CrossRef]
- N. T. Araújo Júnior, V. M.E. Lima, S. M. Torres, P. E.A. Basto, and A. A. Melo Neto, “Experimental investigation of mix design for high-strength alkali-activated slag concrete,” Construction and Building Materials, vol. 291, p. 123387, Jul. 2021, doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.123387. [CrossRef]
- R. Fernandes, S. Marathe, A. P. Rodrigues, Ł. Sadowski, and S. Akhila, “Smart modelling system for alkali-activated concrete pavements using machine learning techniques,” Asian J Civ Eng, vol. 24, no. 7, pp. 2193–2213, Nov. 2023, doi: 10.1007/s42107-023-00635-z. [CrossRef]
- M. J. Anderson, P. J. Whitcomb, and M. A. Bezener, Formulation simplified: Finding the sweet spot through design and analysis of experiments with mixtures. in Formulation Simplified: Finding the Sweet Spot through Design and Analysis of Experiments with Mixtures. 2018, p. 190. doi: 10.4324/9781315165578. [CrossRef]
- M. Kharazi, L. M. Lye, and A. Hussein, “Designing and optimizing of concrete mix proportion using statistical mixture design methodology,” Proceedings, Annual Conference - Canadian Society for Civil Engineering, vol. 3, no. January, pp. 2269–2278, 2013.
- B. Şimşek, Y. Tansel İç, and E. H.Şimşek, “A Full Factorial Design Based Desirability Function Approach for Optimization of Properties of C 40/50 Concrete Class,” MCA, vol. 18, no. 3, pp. 330–339, Dec. 2013, doi: 10.3390/mca18030330. [CrossRef]
- X. Dai, L. Ren, X. Gu, E. Yilmaz, K. Fang, and H. Jiang, “Strength Analysis and Optimization of Alkali Activated Slag Backfills Through Response Surface Methodology,” Front. Mater., vol. 9, p. 844608, Feb. 2022, doi: 10.3389/fmats.2022.844608. [CrossRef]
- Y. Gao, J. Xu, X. Luo, J. Zhu, and L. Nie, “Experiment research on mix design and early mechanical performance of alkali-activated slag using response surface methodology (RSM),” Ceramics International, vol. 42, no. 10, pp. 11666–11673, Aug. 2016, doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.04.076. [CrossRef]
- N. R. Kanta, M. R. Ponnada, and K. Mishra, “Application of response surface method for optimization of alkali activated slag concrete mix with used foundry sand as partial replacement of sand,” Sādhanā, vol. 47, no. 4, p. 269, Dec. 2022, doi: 10.1007/s12046-022-02040-9. [CrossRef]
- B. C. Mendes, L. G. Pedroti, C. M. F. Vieira, J. M. F. D. Carvalho, J. C. L. Ribeiro, and C. M. M. D. Souza, “Application of mixture design of experiments to the development of alkali-activated composites based on chamotte and waste glass,” Construction and Building Materials, vol. 379, p. 131139, May 2023, doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2023.131139. [CrossRef]
- J. Moseson, D. E. Moseson, and M. W. Barsoum, “High volume limestone alkali-activated cement developed by design of experiment,” Cement and Concrete Composites, vol. 34, no. 3, pp. 328–336, 2012, doi: 10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2011.11.004. [CrossRef]
- K. Komnitsas, D. Zaharaki, and V. Perdikatsis, “Geopolymerisation of low calcium ferronickel slags,” Journal of Materials Science, vol. 42, no. 9, pp. 3073–3082, 2007, doi: 10.1007/s10853-006-0529-2. [CrossRef]
- Arce, A. Komkova, J. V. D. Sande, C. G. Papanicolaou, and T. C. Triantafillou, “Optimal Design of Ferronickel Slag Alkali-Activated Material for High Thermal Load Applications Developed by Design of Experiment,” 2022.
- CEN/TC 104 Concrete ( performance, production, placing and compliance criteria ), EN 12350-2:2019 Testing fresh concrete - Part 2: Slump test, 2019.
- ASTM International, “ASTM C 39/C 39M – 03, Standard Test Method for Compressive Strength of Cylindrical Concrete Specimens.” 2003.
- L. Phan, “Fire Performance of High-Strength Concrete: A Report of the State-of-the-Art,” Fire Research, 1996.
- M. S. Abrams, “Compressive strength of concrete at temperatures to 1600F,” presented at the American Concrete Institute, ACI Special Publication, 1971.
- nternational Organization for Standardization, ISO 14040:2006 Environmental management — Life cycle assessment — Principles and framework, 2006. [Online]. Available: https://www.iso.org/standard/37456.html.
- D. W. Law, A. A. Adam, T. K. Molyneaux, and I. Patnaikuni, “Durability assessment of alkali activated slag (AAS) concrete,” Mater Struct, vol. 45, no. 9, pp. 1425–1437, Sep. 2012, doi: 10.1617/s11527-012-9842-1. [CrossRef]
- D. L. Y. Kong and J. G. Sanjayan, “Damage behavior of geopolymer composites exposed to elevated temperatures,” Cement and Concrete Composites, vol. 30, no. 10, pp. 986–991, 2008, doi: 10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2008.08.001. [CrossRef]
- N. Ranjbar, M. Mehrali, U. J. Alengaram, H. S. C. Metselaar, and M. Z. Jumaat, “Compressive strength and microstructural analysis of fly ash/palm oil fuel ash based geopolymer mortar under elevated temperatures,” Construction and Building Materials, vol. 65, pp. 114–121, 2014, doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2014.04.064. [CrossRef]
- S. A. Bernal, R. Mejía de Gutiérrez, F. Ruiz, H. Quiñones, and J. L. Provis, “Desempeño a temperaturas altas de morteros y hormigones basados en mezclas de escoria/metacaolín activadas alcalinamente,” Materiales de Construccion, vol. 62, no. 308, pp. 471–488, 2012, doi: 10.3989/mc.2012.01712. [CrossRef]
- N. Derinpinar, M. B. Karakoç, and A. Özcan, “Performance of glass powder substituted slag based geopolymer concretes under high temperature,” Construction and Building Materials, vol. 331, p. 127318, May 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.127318. [CrossRef]
- M. Guerrieri, J. Sanjayan, and F. Collins, “Residual compressive behavior of alkali-activated concrete exposed to elevated temperatures,” Fire and Materials, vol. 33, no. 1, pp. 51–62, Jan. 2009, doi: 10.1002/fam.983. [CrossRef]
- K. K. Ramagiri, D. R. Chauhan, S. Gupta, A. Kar, D. Adak, and A. Mukherjee, “High-temperature performance of ambient-cured alkali-activated binder concrete,” Innov. Infrastruct. Solut., vol. 6, no. 2, p. 71, Jun. 2021, doi: 10.1007/s41062-020-00448-y. [CrossRef]
- W. Tu and M. Zhang, “Behaviour of alkali-activated concrete at elevated temperatures: A critical review,” Cement and Concrete Composites, vol. 138, p. 104961, Apr. 2023, doi: 10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2023.104961. [CrossRef]
- S. Y. N. Chan, G. Peng, and J. K. W. Chan, “Comparison between high strength concrete and normal strength concrete subjected to high temperature,” vol. 29, no. December, pp. 616–619, 1996.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).