2.1. Introduction
Supply chain sustainability is vital for long-term business success in a globalised economy. With the widespread adoption of ESG standards, integrating them into supply chain management is crucial for companies to improve competitiveness, reputation, and compliance. Focusing on ESG factors can enhance a company's risk resilience.
Sustainability ensures current needs met without harming future generations' economic, environmental, and social needs. Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) involves supplier diversity, promoting local and SME suppliers. Other aspects include Occupational Health and Safety, Business Ethics, Organisational and Individual Responsibility, Information Protection, and Social Responsibility. International Supply Management Association (ISM) advocates supply management professionals contribute to sustainability and social responsibility, primarily to their own organisations and then to others in the supply chain.
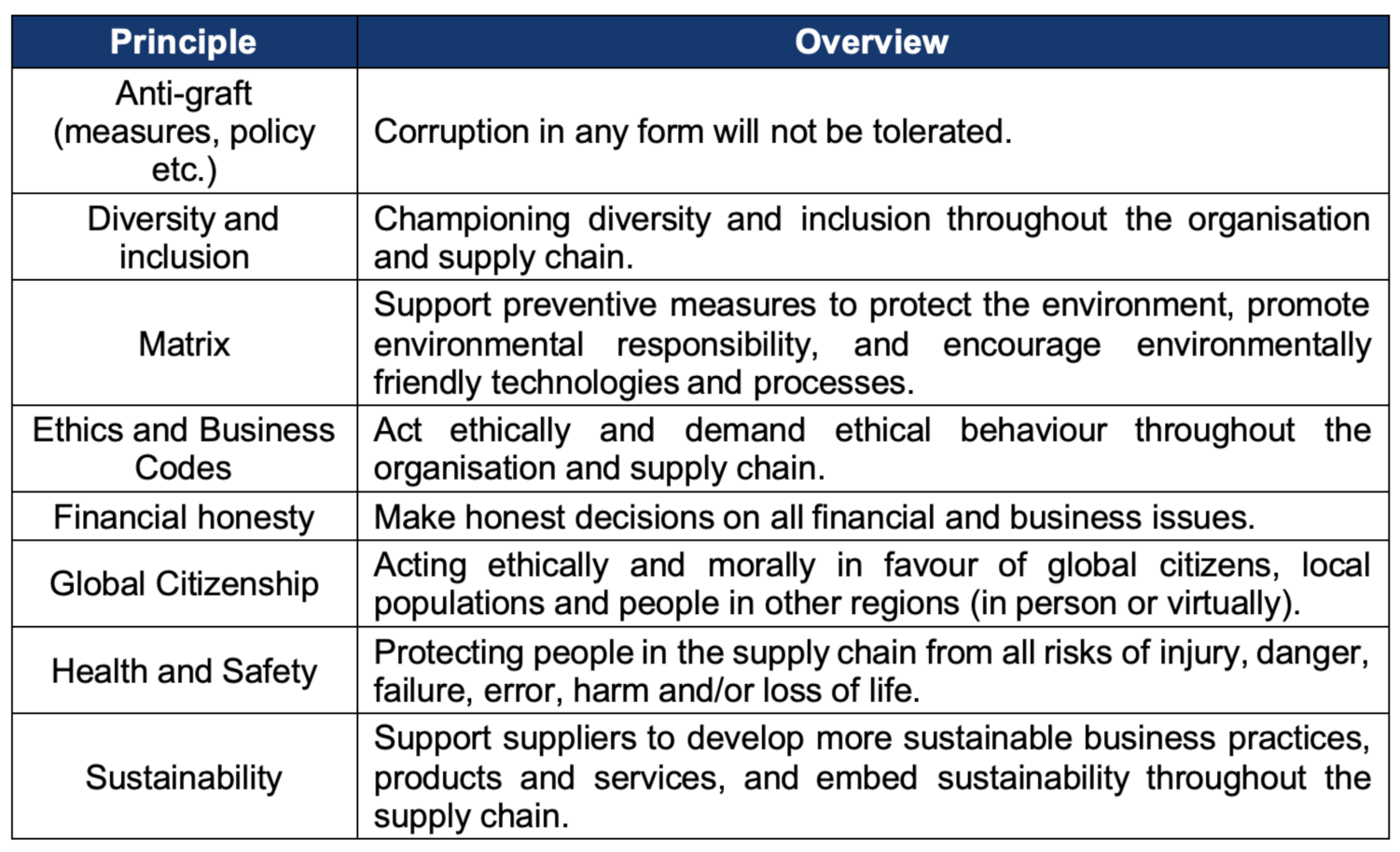
Table 1.
The institute for supply management's overview of ESG principles.
Table 1.
The institute for supply management's overview of ESG principles.
In addition, due to the complex and far-reaching nature of supply chains, it is important to balance local and global issues when making decisions that affect sustainability and social responsibility.
2.2. ESG-Related Studies
In recent years, ESG has been a popular research topic in both the financial and corporate worlds, with a large body of literature focusing on ESG investment and corporate ESG. ESG investment is the practice of ESG concepts and consideration of ESG factors in investors' investment decisions and activities[
7], and plays an important driving role in the ESG value chain. Corporate ESG is a constituent area of corporate sustainability strategy that defines and describes the non-financial outcomes that companies wish to achieve[
8]. Current corporate ESG research involves corporate ESG disclosure, ESG measurement and ratings, and ESG forensics, key ESG issues, and ESG management, among which the antecedent influencers and impact effects of corporate ESG performance are the hotspots of corporate ESG research.
From the perspective of antecedent factors, a number of studies have focused on the impact of country-level, domestic-level and firm-level factors on corporate ESG performance [
9]. ESG practices and performance of enterprises can be impacted at the national level by variations in the degree of economic growth, culture, institutional quality, and legal roots of various nations[
10]. Political affiliation and social capital have been found to be significant domestic determinants impacting the ESG performance and conduct of corporations[
11]. At the firm level, organisational resilience, firm digitisation, and mergers and acquisitions behaviours are among the operational and governance factors that have a major impact on firms' ESG performance [
12]. The former factor focusses on the characteristics of the executive team and shareholding. Regarding the impact effect, a lot of research has looked at how a firm's ESG performance affects several aspects of its performance, such as its employment, financial, and firm value [
13].
The early 1970s saw the beginning of research on the connection between corporate financial performance (CFP) and ESG norms. In their synthesis of the findings from over 2,000 previously published studies, Friede et al. [
14]observed that most of the studies (almost 90%) revealed a favourable connection between ESG-CFP. These results imply that ESG disclosure raises information return, which enhances future performance projections and clarifies expectations regarding firms' inherent risks. As a result, information risk is reduced, lowering firms' cost of capital [
15].
Disclosure can improve the effectiveness of monitoring, such as environmental performance assessment. In addition, it can lead firms to improve operational efficiency by reducing energy consumption, improving product quality or recruiting staff better [
16]. The argument suggests that publishing a comprehensive report that integrates ESG and financial data can even increase the market valuation of a firm's combined ESG and corporate governance performance economically and statistically significantly at no additional cost [
17]. Khan et al. [
18] reported that any given industry of the vast majority of ESG data is irrelevant to the investment performance of U.S. equities. Furthermore, while some literature suggests that investors use ESG data for financial rather than ethical reasons [
19], investors may be using ESG data for ethical rather than financial reasons. Although Edmans [
20] and Dorfleitner et al. [
21] cited that financial returns on ESG are positive in the case of long-term holdings of the respective shares, even if there are no additional returns, many investors consider social responsibility to be worthwhile.
There has been an ongoing debate about the relationship between ESG and CFP. Some scholars have attempted to explain the controversial results. For example, Drempetic et al. [
22] found a significant positive correlation between firm size and ESG scores and argued that capital does not flow to firms with higher ESG scores but rather to larger firms. Another study conducted by Amel-Zadeh and Serafeim [
19] showed that the importance of ESG information varies across countries , industry and even firm strategies differ systematically across firms, so the controversy may stem from differences in the samples. This observation inspires us to analyse the studies for heterogeneity.
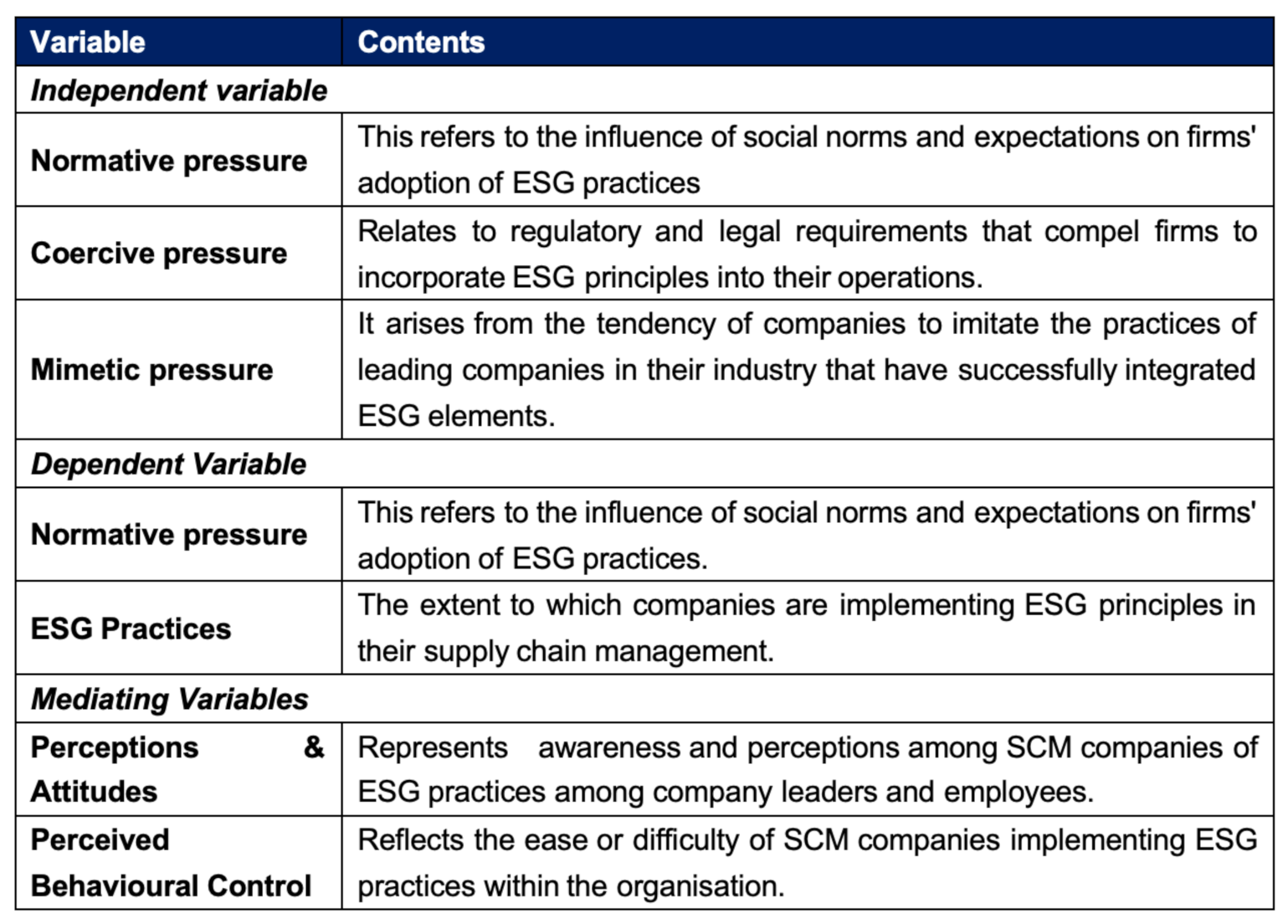
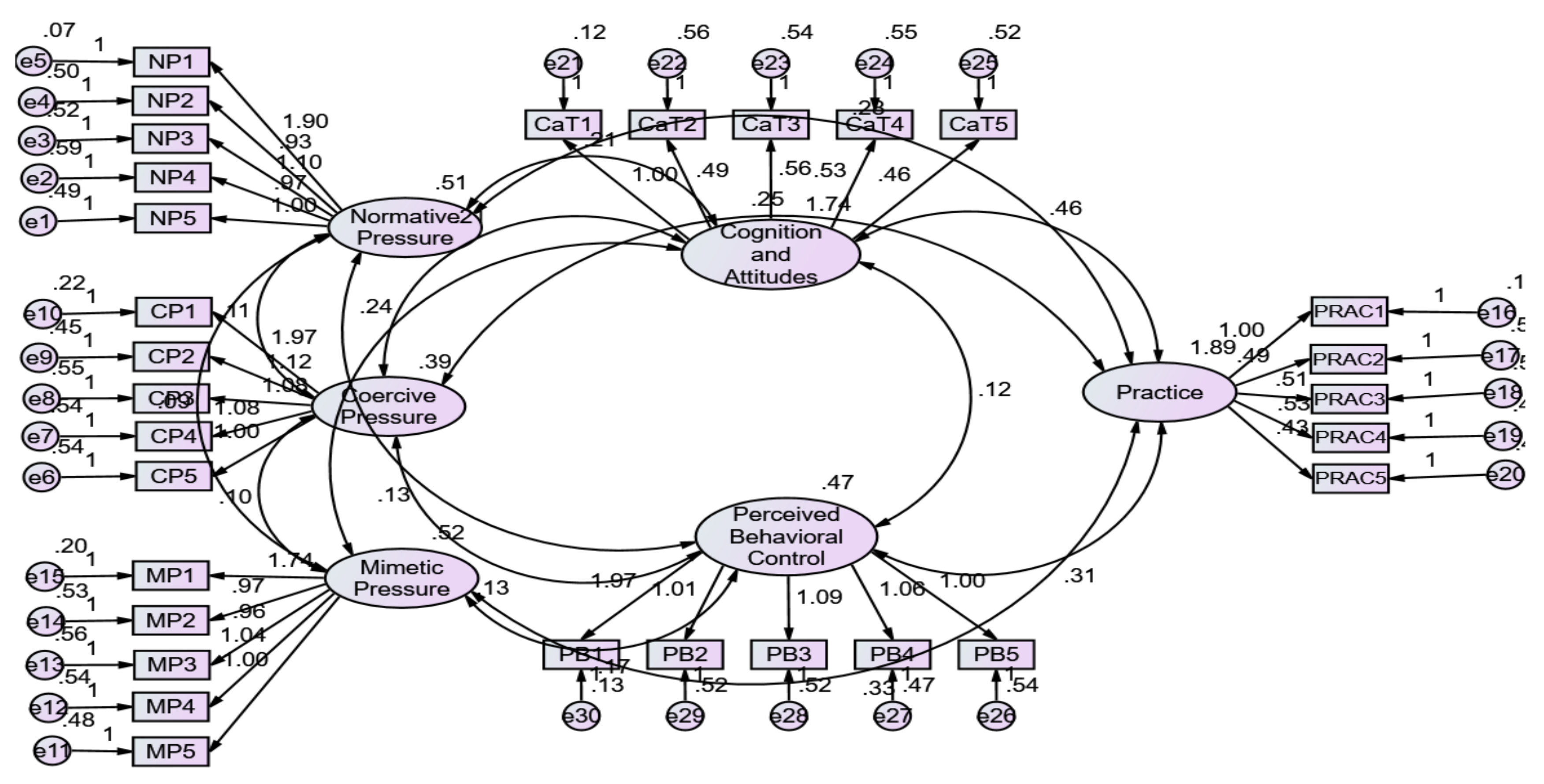
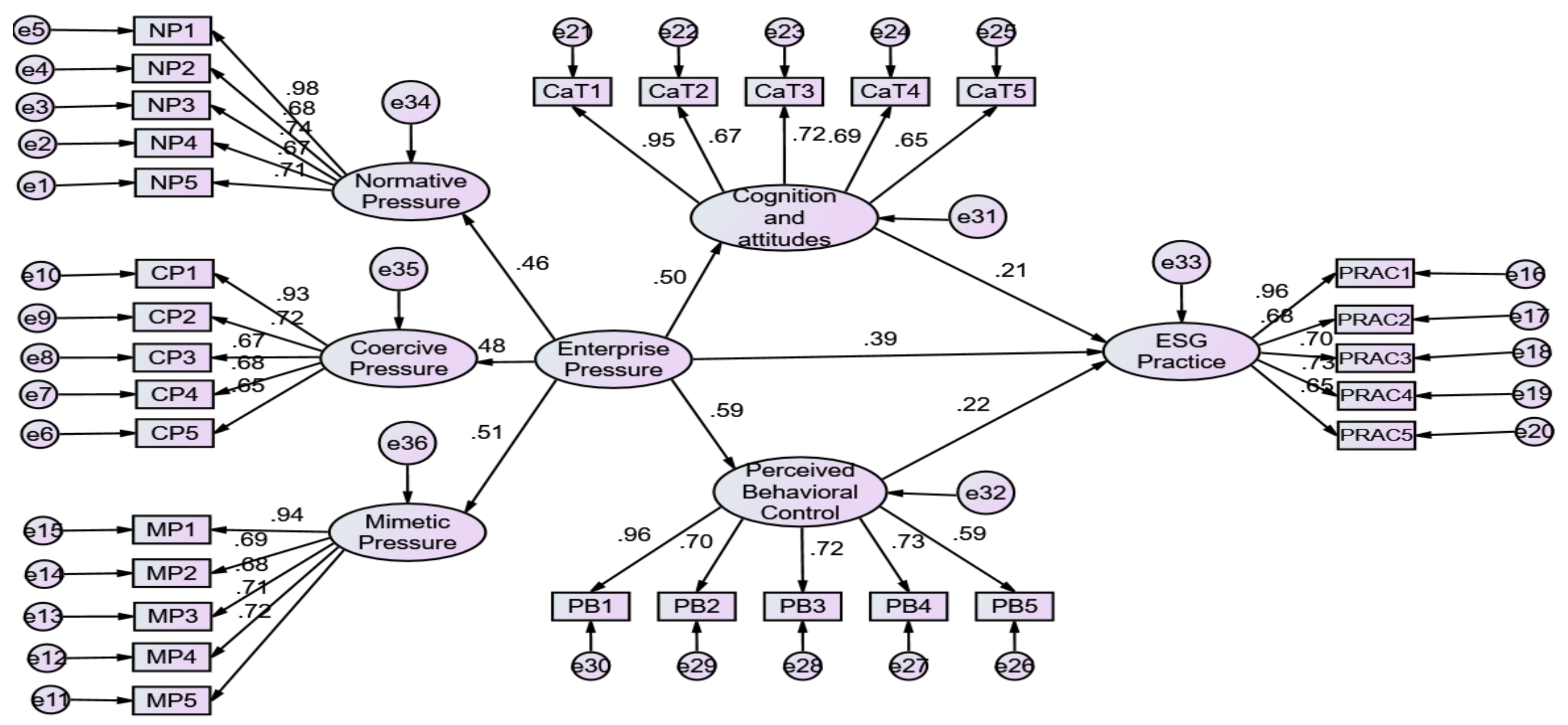
H1: There is a significant positive effect of Enterprise Pressure on Cognition and attitudes.
H2: There is a significant positive effect of Enterprise Pressure on Perceived Behavioral Control.
2.3. Technological Innovation and Sustainable Supply Chains
Zhang et al. [
23] found that open innovation has a positive effect on corporate ESG performance, and the higher the degree of innovation openness, the better the corporate ESG performance; the sub-dimensional test found that open innovation has the greatest effect on the promotion of environmental responsibility, followed by social responsibility, with corporate governance being the weakest; and compared with small and medium-sized enterprises, enterprises in regions with high degree of market openness, and non-state-owned enterprises, open innovation has a stronger effect on corporate ESG performance among large-sized enterprises, enterprises in regions with low degree of market openness, and state-owned enterprises. Ren and Isa [
24] found that ESG performance is positively correlated with the innovation level of enterprises through unbalanced panel data analysis of A-share listed companies in Shanghai and Shenzhen, and the analysis of the mechanism of ESG influencing corporate innovation shows that good ESG performance can reduce the risk of corporate innovation by reducing financing constraints. The analysis of the mechanism of ESG influence on corporate innovation shows that good ESG performance can promote corporate innovation by reducing financing constraints and obtaining more government subsidies, and ESG performance improves competitiveness by promoting enterprises to increase R&D investment [
25], and Zhang et al. [
26] suggested that ESG performance is positively related to green technology innovation, and the better the ESG performance of enterprises, the more green technology innovation activities they carry out. The better the ESG performance of the enterprise, the more green technology innovation activities the enterprise carries out.
It can be seen that technological innovation has promoted the development of sustainable supply chain, and the concept of sustainable development has penetrated into the whole process of supply chain, expanding the traditional supply chain management objectives from a single economic dimension to the triple bottom line of economic efficiency, social responsibility and environmental protection from a strategic height, or emphasising the social and environmental dimensions of supply chain management.
From the perspective of the relationship between customer firms and supplier firms, existing research on sustainable supply chains consists of two main types: firstly, research on customer firms' selection preferences for supplier firms' sustainability performance when choosing new suppliers. It has been found that customer firms consider their environmental or green performance, environmental standards, etc. and prefer socially responsible suppliers when selecting suppliers [
27]. The second category examines the impact of client firms on supplier sustainability. Early literature found that customer firms have a positive impact on supplier firms' sustainability, mainly through questionnaires. For example, Setyaningrum and Muafi [
28] found through a survey study that customer firms encourage supplier firms to implement green supply chain management and improve environmental performance. Some recent studies using empirical methods have also found this relationship from the perspective of supply chain diffusion or spillover and supply chain synergy. For example, Tang et al. [
29] found that the ESG performance of customer firms has spillover effects on the ESG performance of supplier firms.
H3: There is a significant positive effect of Cognition and attitudes on ESG Practice.
H4: There is a significant positive effect of Perceived Behavioral Control on ESG Practice.
H5: There is a significant positive effect of Enterprise Pressure on ESG Practice.
2.4. Digital Sustainable Supply Chains
The policy consensus and practical exploration of building digitally sustainable supply chains has triggered academic attention to the issue of digitisation contributing to supply chain sustainability, and there are two main categories of related research: the first is the impact of digitisation on the economic dimension of supply chain sustainability, which focuses on the changes brought about by the application of digital technologies to traditional supply chain activities and business processes, as well as on the new advantages generated by supply chain innovations [
30]. This category focuses on the impact of digitisation on the commercial activities and economic consequences of supply chains [
31] and does not address the impact of digitisation on the non-commercial activities and non-economic performance of supply chains, which is where most of the existing research falls. The second category, ‘The Impact of Digitisation on the Social and Environmental Aspects of Supply Chain Sustainability,’ examines how different digital technology applications have affected supply networks that are specifically characterised as sustainable [
32]. This category focusses on the direct and indirect effects of digitalisation on non-commercial activities and supply chains' non-economic performance [
33].
Regarding the relationship between digitisation and sustainable supply chains, existing research focuses on the impact of digitisation on sustainable supply chains, and the main ideas can be grouped into two categories: the first is that research has found that digitisation is a driver of sustainable supply chain practices. Xiao et al. [
34](2024) indicated that digitisation of customer firms to promote ESG performance of supplier firms helps to enhance supply chain resilience. Digital technology applications can provide decision-making information support for sustainable supply chain practices and are a key driver towards sustainable supply chain integration, which is critical for sustainable supply chain implementation [
35]. The second is that digitisation can directly or indirectly improve sustainable supply chain performance. In terms of direct impact effects, the adoption of digital technologies in supply chain management can positively affect environmental and social sustainability performance. The application of digital transformation, Industry 4.0 technologies has been found to significantly improve sustainable supply chain performance [
36]. However, some scholars' studies have also found that digitalisation has no direct effect on sustainable supply chain performance [
37]. In terms of indirect impact effects, the positive impacts of digitalisation on sustainable supply chain performance can be achieved by increasing efficiency, optimising operations, improving processes, enhancing agility, improving traceability and transparency, increasing accountability, and developing knowledge [
38].
H6: Cognition and attitudes play a mediating role in the effect of SCM Cognition and attitudes on ESG Practice.
There are three gaps in current research on the impact of digitisation on sustainable supply chains: first, there is a lack of research on the interactions between supply chain firms. Unlike the sustainable development of a single enterprise, the sustainable development of a supply chain focuses on the sustainable performance of upstream and downstream enterprises, so achieving the sustainable development of a supply chain is highly dependent on the interactions between upstream and downstream enterprises, especially the impacts of customer enterprises on supplier enterprises, and the role of digitisation in building a sustainable supply chain is no exception. Existing studies have explored the impact of digitisation on sustainable supply chain performance from the perspective of customer firms, and have almost always implicitly placed the 'sustainable supply chain' as a whole in the context of the sustainability of customer firms. As a result, the metrics are all based on customer perspectives that fall under the so-called sustainable supply chain enterprise performance [
39]. There is a lack of attention to the interaction between digitisation of the customer enterprise and the sustainability of upstream and downstream enterprises in the supply chain. Second, the ‘black box’ of the conditions and mechanisms by which digitalisation empowers supply chain sustainability has not yet been opened. While some studies have focused on the indirect effects of digitisation on supply chain sustainable performance and have begun to explore how digitisation can contribute to supply chain sustainability by increasing efficiency, optimising operations, improving processes, enhancing agility [
38], and developing knowledge [
37], these studies are are based on the perspective of customer firms and lack consideration of interactions between supply chain firms, as well as the interactions between customer firms and upstream and downstream supply chain firms. However, they are all based on the perspective of customer enterprises, lack of consideration of interactions between supply chain enterprises, and all imply the assumption of synchronous digitisation between customer enterprises and upstream and downstream supply chain, which actually turns into the role of digitisation of supply chain enterprises on their own sustainable development, rather than the role of empowerment of sustainable supply chain in the true sense, and the mechanism and conditions of digitisation of customer enterprises empowering upstream and downstream supply chain for sustainable development have not been effectively revealed. conditions have also not been effectively revealed. Third, there is a lack of large-sample empirical research. Current research on the impact of digitalisation on supply chain sustainability mainly adopts the qualitative method of case studies [
32] and the empirical method of questionnaire surveys [
39], which lacks large-sample empirical tests, while the latter can provide more accurate and reliable results.
H7: Perceived behavioural control mediates the effects of SCM cognition and attitudes on ESG practices.
2.5. ESG in Global Supply Chains
Since its introduction in a 2006 United Nations report, ESG has become the most widely accepted measure of corporate sustainability and governance. Similarly, supply chain operations have been impacted by ESG issues, with the majority of Fortune 250 companies in the United States setting various ESG targets through 2019. In addition, a publication of The European Parliament and the Council of the European Union [
40] indicated that, from January 2024, large European companies must regularly disclose information on their social and environmental impacts, increasing transparency on ESG matters and combating 'greenwashing'. It applies to all large European companies, banks and insurance companies, with the exception of micro-listed companies. Tellier [
41] noted that in 2021, Gartner introduced ESG-based inclusion criteria for the first time in the TOP SCM25, and in 2024, Gartner launched an assessment process that set a minimum S&P Global ESG score threshold for inclusion in the company list.
As the need for supply chain compliance has evolved, the standards for ESG due diligence have risen accordingly, with countries issuing important bills that address supply chain compliance for both domestic and extraterritorial companies. Legislation in this area can be analysed from three perspectives: (1) workers in the supply chain; (2) products in the supply chain; and (3) supplier behaviour. For workers in the supply chain, the main focus is on workers' rights and interests, such as the EU's Regulation on the Market for Products Prohibiting Forced Labour and the Law on Combating Forced and Child Labour in Supply Chains. For products in the supply chain, the focus is on the environmental impact throughout the life cycle, and representative laws include the EU Deforestation Regulation, the EU Batteries and Waste Batteries Act and the EU Carbon Boundary Adjustment Mechanism Act. In terms of supplier behaviour, whether suppliers comply with business ethics and whether there are violations is the focus, representative legislation includes the EU Proposal for a Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive and the German Corporate Supply Chain Due Diligence Act. [
40] China has also introduced some laws and regulations and recommended standards on supply chain, such as Supply Chain Risk Management Guidelines (GB/T 24420-2009), SCM (GB/T 26337), and Green Manufacturing - A Guide to Green Supply Chain Management for Manufacturing Enterprises (GB/T 33635-2017). Creating effective governance structures and legal systems that ensure the environmental, social and operational safety, transparency and accountability of global corporate supply chains is therefore key to development for governments worldwide.
In terms of modern ESG practices, modern ESG practices involved integrating sustainable development into core business strategies. This included setting clear sustainability goals, conducting life cycle assessments and adopting circular economy principles to reduce waste and resource consumption [
42]. Consequently, firms were increasingly focusing on developing dynamic capabilities to adapt and innovate in response to environmental challenges to ensure long-term sustainability and competitiveness [
43]. Murray et al. [
42] proposed the implementation of green manufacturing processes and the adoption of circular economy principles to reduce waste and resource consumption, and they focussed on the application of environmental sustainability in supply chain management. The study also concluded that recycling, remanufacturing and the use of sustainable materials help to reduce waste and resource consumption and that this approach improves resource efficiency and minimises the ecological footprint of the supply chain. Initially, companies have gradually adopted ESG frameworks, driven by regulatory pressure and public awareness. Early adopters such as Unilever and Patagonia set the benchmark by incorporating comprehensive sustainability practices into their operations. It was evident that ESG standards play a pivotal role in attracting socially responsible investors, and companies with sound ESG practices tend to enjoy better financing conditions and enhanced market reputation [
44].
2.6. Corporate ESG Practices
Investors are increasingly placing more weight on a company's CSR/ESG ratings due to the significant increase in socially conscious investors in CSR/ESG-oriented investment activities in recent decades. This has resulted in a sharp rise in demand for comprehensive CSR/ESG ratings and CSR/ESG performance scoring products from non-financial rating agencies.
The 2020 KPMG Sustainability Reporting Survey shows that 80 per cent of all large and medium-sized listed companies globally will have issued an ESG report by 2020, up from 12 per cent in 1993. ESG ratings play a key role in investors' assessment of company value and corporate sustainability [
45]. However, due to differences in ESG measurement standards, the diversity of data collected by different Non-Financial Reporting (NFR) agencies, and the opacity and heterogeneity of NFR agencies' rating methodologies, it is unclear whether ESG ratings from different rating agencies accurately and unbiasedly capture firms' ESG efforts and risks [
46]. In addition, policymakers around the world have expressed concerns that credit rating agencies may issue biased ratings for capital markets [
47]. Significant variations exist between the environmental, social, and corporate governance ratings assigned to an identical company by distinct rating agencies [
46].
Consider business procedures as an illustration. The well-known multinational corporation Apple has a strong track record in supply chain management. Apple used carbon offsets or renewable energy to reach zero emissions by 2020. More than 200 suppliers pledged to meet Apple's 2022 request for all of them to attain net zero emissions by 2030. The commitment letter has been signed by more than 200 vendors as of right now, including Foxconn, TSMC, and BYD.
In addition, IKEA has a sustainable procurement program. IKEA has a strict environmental policy that requires all wood used to come from sustainable forests certified by Forest Stewardship Council. By implementing this program, the company not only improves the environmental standards of its products, but also enhances customer trust.
Furthermore, Starbucks' supply chain sustainability program is also an example of how to use big data analysis and digital tools to optimize supply chain management, improve productivity, and track ESG performance in real time. This includes tracing the origin of raw materials through the use of blockchain technology and ensuring transparency and traceability of the supply chain. Starbucks guarantees ethical, social and environmental standards for coffee sourcing through the Coffee and Farmer Equity (C.A.F.E.) Practice Program. This strengthens the sustainability of the supply chain and enhances the company's reputation in the international market.
2.7. ESG Practices and Motivations for Chinese Companies in the Supply Chain
China's ESG standards are converging with international standards, and, ESG disclosure is progressing at a faster pace. The Corporate Sustainability Disclosure Guidelines 2024- Basic Guidelines issued by China's Ministry of National Finance further provides norms and guidance for corporate ESG disclosure. China worked closely with the European Union to launch the Common Classification Catalogue for Sustainable Finance, which will further promote China's corporate ESG to be globally aligned and facilitate international investors to participate in China's green bond market. As of 31 July 2023, a total of 347 of the 450 Chinese central state-owned enterprises (SOEs) that have been listed on the A-share market have disclosed their ESG social responsibility reports, a disclosure rate of 80.7%.
Chinese companies face challenges such as lack of unified ESG standards, the prevalence of greenwashing, and the need for enhanced ESG disclosure capabilities. However, motivations for adopting ESG practices include improving supply chain stability, gaining legitimacy, and accessing external resources.
According to this situation, Chinese companies are actively developing ESG practices and building a green logistics action system, focusing on key issues in three dimensions: environmental, social and governance, in order to achieve sustainable medium and long-term competitiveness. At the environmental level, logistics companies focus on indicators such as carbon emission reduction, park construction, waste disposal, and supply chain environmental costs to reduce negative environmental impacts. At the social level, ESG perspectives drive logistics companies to focus on employee safety, optimising supply chain operations, fulfilling social responsibilities and reducing negative incidents. At the corporate governance level, ESG pushes logistics companies to establish management systems, optimise compliance management, identify business risks, cultivate green talent, promote R&D and innovation, form sustainable long-term strategic goals, avoid short-term behaviours, and obtain better financing support.
Motivations for Chinese companies to adopt ESG in their supply chains include demand from international investors and national regulatory push. Supply chain relationship stability is an important factor in enhancing the level of resilience and security in industrial supply chains. Xin et al. [
48] showed that corporate ESG performance significantly affects the stability of supply chain relationships, particularly enhancing the stability of customer relationships, but has a weaker effect on the stability of supplier relationships.
Secondly, based on the organisational legitimacy theory, firms can obtain legitimacy at the institutional level and strategic level by virtue of ESG investments, thus gaining access to more external resources. Hertzel et al. [
49] argued that because of the cross-chain transmission of risk in the supply chain, firms will scrutinise the strategic decisions of their supply chain partners. When a firm fails to meet the social responsibility requirements of its supply chain partners, the supply chain partners are likely to terminate the co-operation. Aouadi and Marsat [
50] argued that when a firm has a large ESG problem, negative ESG events will make the legitimacy of the firm as well as the supply chain seriously challenged. Zimmerman and Zeitz [
51] cited that legitimacy is a resource that can help firms access resources. In practice, socially irresponsible behaviour of firms in the supply chain imposes significant costs on the entire supply chain. Social responsibility scandals of firms in the supply chain not only increase their own reputational risk, but also increase the reputational risk of other supply chain partners, thus creating a crisis of trust in the supply chain. Due to the interdependence of supply chain partners, there is a need for firms in the supply chain to work together on socially responsible activities [
52], and relationship performance can only be obtained by maintaining the trust of supply chain partners and sustaining long-term and stable cooperation [
53].
Thirdly, from the Resources-based view (RBV) theory, corporate ESG performance builds a positive information feedback system for upstream suppliers and downstream customers, i.e.; it increases the transparency of corporate ESG information; information transparency can bring about an improvement in the information governance effect, further enhancing the compliance of the system and the reliability of information disclosure [
54]. In fact, in the process of enterprise production and operation, the information interaction of partners in the supply chain can promote the high-quality development of enterprises [
55]. And enterprise ESG performance can convey signals to upstream suppliers and downstream customers about the enterprise's innovativeness and compliance in the production and operation process, reduce the information search cost of upstream suppliers and downstream customers [
54], and alleviate the information asymmetry problem in the supply chain. Therefore, enterprise ESG performance builds an effective information communication channel for the main bodies in the supply chain, which is conducive to the identification of the real value of the enterprise by upstream suppliers and downstream customers, and enhances the degree of trust of upstream suppliers and downstream customers to the enterprise, which leads to more upstream suppliers and downstream customers being willing to carry out long-term and continuous cooperation with the enterprise, and forming a stable trading relationship. Especially when the company is geographically distant from its upstream suppliers and downstream customers, i.e.; when the company faces a high threshold of legitimacy, the advantage of the information conveyed by the company's ESG performance to its upstream suppliers and downstream customers will be more obvious. For capital providers, they can not only reduce default and reputational risks by integrating ESG information from firms, but also enhance their reputation by presenting their ESG stance to the outside world by incorporating ESG information into their lending policies [
56]. This implies that better corporate ESG performance can help funders to be deeply involved in corporate governance activities, further curbing opportunistic behaviour, reducing agency problems and information asymmetry [
54], and lowering operational and default risks [
57]. Therefore, the better the ESG performance of an enterprise, the greater the possibility of financing given to the enterprise by the capital provider.