1. Introduction
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a condition marked by damage to the lung's alveolar-capillary barrier, leading to the flooding of alveoli with protein-rich fluid and resulting in respiratory failure [
1]. ARDS comprises roughly 10% of all ICU admissions and continues to have a significant mortality rate of approximately 40%. Despite decades of research, there is still no effective approved medication for treating ARDS, and supportive care remains the primary management approach [
2,
3]. Although a wide range of conditions can result in ARDS, including acid aspiration, severe trauma, and repeated blood transfusions, sepsis and pneumonia are the main risk factors for the syndrome, with Streptococcus pneumoniae and Staphylococcus aureus being the most common bacteria causing pneumonia-induced ARDS [
1,
4,
5]. Alveolar epithelial cells (AEC), along with lung endothelial cells (EC), form the lung’s alveolar-capillary barrier, and are primary targets for bacteria and other respiratory pathogens. In acute lung injury (ALI), a series of events that include AEC and EC activation and production of pro-inflammatory mediators lead to lung barrier disruption and excessive immune cell recruitment [
1]. Strategies that inhibit these processes by preserving AEC and EC function following injury represent promising therapeutics for ARDS.
Phosphodiesterases (PDEs) are a family of enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) and cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), which are important intracellular second messengers regulating several signaling pathways and cellular functions [
6]. The PDE family consists of 11 groups, for which numerous specific inhibitors (PDEis) have been developed. Among these, PDE 3 and 4 inhibitors have attracted significant interest due to their cytoprotective and anti-inflammatory actions [
7,
8,
9,
10]. Several FDA-approved PDE3 or 4 inhibitors are clinically available to treat various conditions including chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), congestive heart failure, and peripheral artery disease [
11,
12,
13]. In ARDS, there has been particular interest in PDEs and how their modulation can impact the underlying pathogenetic mechanisms [
14]. This is due to extensive research demonstrating that inhibition of PDE 3 or 4 suppresses the increased endothelial permeability, epithelial dysfunction, inflammatory mediator release, and immune cell recruitment that characterize ALI [
14,
15,
16,
17]. Despite these promising effects, there has been no significant progress in assessing the efficacy of PDE 3 or 4 inhibitors in treating ARDS [
14].
Ensifentrine (RPL554) is a novel PDE inhibitor that was recently approved in June 2024 as a maintenance treatment for COPD [
18]. Ensifentrine has a novel mechanism of action by inhibiting both PDE 3 and 4, resulting in combined bronchodilator and anti-inflammatory actions [
19,
20]. Compared to other FDA-approved PDE inhibitors that selectively target either PDE3 or PDE4 and exhibit limited tolerability, ensifentrine demonstrates an exemplary clinical profile in terms of tolerability, safety, and efficacy [
21]. This makes it a highly promising therapeutic candidate for multiple indications, including ARDS. Our prior work has demonstrated that methicillin-resistant
Staph aureus (MRSA), an ALI-causing pathogen, is a potent inflammatory stimulus causing lung endothelial barrier disruption and inflammation [
22,
23]. Whether dual inhibition of PDE3 and 4 by ensifentrine can ameliorate MRSA’s injurious effects in the lung is unknown. Therefore, in the present study we aimed to investigate the effects of ensifentrine on lung endothelial and alveolar epithelial dysfunction caused by MRSA to explore the potential efficacy of this intervention in ARDS.
2. Materials and Methods
Cell culture and treatments. Human pulmonary artery endothelial cells (HPAEC, Cat#CC2539) and human lung microvascular endothelial cells (HLMVEC, Cat#CC2527) were obtained from Lonza (Walkersville, MD) and cultured in EBM-2 Basal Medium supplemented with EGM-2 SingleQuots supplements (Lonza) and 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS). A549 were grown in RPMI (with L-glutamine) supplemented with 5% FBS. Immortalized alveolar epithelial cells (iAEC, Cat# H-6053IM) and corresponding media (complete human epithelial cell medium, Cat# H6621) were purchased from CellBiologics (Chicago, IL). All cells were grown at 37°C in a 5% CO
2 incubator. Endothelial cells were used for experiments at passages 5-7. Before treatments, EC and epithelial cells (A549, iAEC) were incubated in 2% FBS media and FBS-free media, respectively, for 2 hours. A 10 mM stock of ensifentrine (Cat#HY-119708, MedChemExpress, Monmouth Junction, New Jersey) was made in DMSO, and aliquots were kept in -80°C for up to 1 month. Cells were treated with ensifentrine or DMSO for 1 hour (unless noted) followed by heat-killed MRSA treatment (2.5 x 10
8 CFU/ml). In separate experiments, cells were pretreated with ESI-08, an EPAC antagonist (HY-136172, MedChemExpress), prior to ensifentrine and MRSA. The USA300 CA-MRSA wild-type (LAC) strain used in this study was kindly provided by Dr. Jiwang Chen (UIC). Heat-killed bacteria (HK-MRSA) were prepared as described previously [
22,
23]. The HK-MRSA was diluted in PBS, aliquoted, and stored at -80°C until the day of the experiment.
Electric Cell-substrate Impedance Sensing (ECIS). EC monolayer barrier integrity was assessed using the ECIS assay (Applied Biophysics, Troy, NY, USA), as we have described previously [
22]. Briefly, ECs were seeded into 8-well ECIS arrays and grown to confluency before indicated treatments. Transendothelial electrical resistance (TER) values were measured over time. For data analysis, normalized TER was plotted versus time. To quantify changes, the area under the curve (AUC) was calculated for each condition for the time period of 2-20 hours, or as indicated. For each independent experiment, AUC values of treated conditions were normalized to control.
XPerT permeability Assay. Gap formation in endothelial monolayers was assessed using the XPerT permeability Assay as described [
23,
24,
25] with some modifications. Briefly, confluent HPAEC grown on biotinylated gelatin coated 12-well plates were pre-treated with ensifentrine (5 μM) or DMSO for 1 hour, followed by HK-MRSA treatment (2.5 x 10
8 CFU/ml). 20 hours later, FITC-conjugated avidin (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Skokie, IL) was added to the media (7.5 μg/ml) for 2 minutes. Cells were washed quickly in pre-warmed 3.7% paraformaldehyde, and then fixed in 3.7% paraformaldehyde for 15 minutes. Images were taken with a REVOLVE microscope (Discover Echo Inc, San Diego, CA) with a 20x Olympus objective. Gap formation was defined by green fluorescence signal (matrix bound FITC-avidin), and Image J (National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland, USA) was used to quantify the area of green immunofluorescence as we have described previously [
25].
Western blotting. Following indicated treatments, cells were washed in ice-cold PBS and then lysed with RIPA buffer (Millipore Sigma, St Louis, MO) containing protease and phosphatase inhibitors (Millipore Sigma). Protein lysates collected after high-speed centrifugation were mixed with 6x SDS-sample buffer (Boston BioProducts, Milford, MA) and boiled for 5 minutes. Protein samples were loaded into 12-20% SurePAGE gels (GenScript, Piscataway, NJ) and transferred onto PVDF membranes (Millipore Sigma). The BLUEstain Protein Ladder (11-245 kDa) from GoldBio (St. Louis, MO) was used to identify the molecular weights. Membranes were then immunoblotted with primary antibodies ICAM-1 (Cat#A5597, ABclonal, Woburn, MA), VCAM-1 (Cat#sc-8304, Santa Cruz Biotech, Dallas, TX) phospho-NFkB (Cat#3033, Cell signaling, Danvers, MA) at 4°C (overnight) followed by secondary anti-rabbit antibody conjugated to HRP from Cell Signaling (room temperature, 1 hour). Membranes were then incubated with HRP-conjugated β-actin monoclonal antibody (Cat#HRP-60008, Proteintech, Rosemont, IL) as loading control. For membrane stripping, we used the Restore PLUS western blot stripping buffer (Cat#46430, Thermo Fisher) according to manufacturer’s instructions. Protein expression was detected with Pierce ECL western blotting substrate (Cat#32106, Thermo Fisher) on HyBlot CL film (Thomas Scientific, Swedesboro, NJ). Blots were analyzed using ImageJ software.
Immunofluorescence. Cells were grown on 8-well glass slides (Millicell EZ slide; Millipore Sigma) until confluency. Following the indicated treatments, cells were fixed in 3.7% paraformaldehyde (Boston BioProducts) for 15 min at room temperature. After washing in PBS, cells were permeabilized in 0.1% triton-X in PBS for 4 minutes followed by blocking in 3% BSA/PBS for 1 hour. Then cells were incubated for 10 min in room temperature with a Fc receptor blocking solution (Trustain FcX, Biolegend, San Diego, CA) to block non-specific binding from MRSA [
26]. Trustain was diluted in 1% BSA/PBS. Primary antibody (VE-cadherin F8; Santa Cruz Biotech) was then added to the cells (without the removal of the Fc receptor blocking solution) at 1:150 at 4°C overnight. After washing in PBS, cells were incubated with anti-mouse AlexaFluor-488 secondary antibody from Thermo Fisher (1:500, 4°C, 1 hour in the dark). After washing, cells were mounted with ProLong DAPI (ThermoFisher). Imaging was performed using the REVOLVE microscope and a 20x Olympus objective.
Cell viability. Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) activity was measured in cell supernatants using the Roche Cytotoxicity detection kit (Cat# 11644793001, Millipore Sigma). After collection, cell supernatants were centrifuged at 2,000 x g for 10 min and immediately analyzed for LDH. Absorbance was measured in the microplate reader Spectramax M2e (Molecular Devices, San Jose, CA) at 490 nm with a reference wavelength of 600 nm for 20 minutes and ΔOD was calculated.
ELISA. Human IL-6 and IL-8 levels were measured in cell supernatants using ELISA MAX Deluxe set kits from Biolegend (San Diego, CA) according to manufacturer’s instructions.
Data analysis and statistics. Experiments were performed at least 3 independent times, and results are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD). Data graphing and statistics were conducted using GraphPad Prism software (version 10). Comparisons between groups were made using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey’s post-hoc test. P values <0.05 were considered statistically significant.
4. Discussion
Our study characterized for the first time the effects of ensifentrine, a dual PDE 3/4 inhibitor, on lung endothelial and alveolar epithelial cell dysfunction caused by MRSA. MRSA is a gram-positive pathogen that can cause severe pneumonia or sepsis-induced ARDS [
5,
33]. Here we demonstrate that ensifentrine exerts endothelial barrier protective properties pre- or post- MRSA treatment. Notably, the preservation of endothelial cell barrier integrity by ensifentrine was accompanied by suppressed inflammation in both lung EC and alveolar epithelial cells. Optimal lung health is dependent on a functional alveolar-capillary barrier, making strategies that protect both the lung endothelium and the epithelium from inflammatory insults advantageous and more promising.
There has been a sustained and long-term interest in phosphodiesterase 3 and 4 inhibitors and their therapeutic potential. Cilostazol and milrinone (PDE3i), along with roflumilast and apremilast (both PDE4i) are among the FDA-approved inhibitors developed for the treatment of various conditions [
10]. Cilostazol is primarily used for peripheral arterial disease, milrinone for short-term treatment of acute decompensated heart failure, while roflumilast and apremilast are FDA-approved for COPD and psoriasis, respectively [
10]. These approved inhibitors, along with several other investigational selective PDE3 or 4 inhibitors, have been considered as potential therapeutics for additional indications, including treatment of ALI [
14] and neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s [
34].
Specifically for ALI, numerous pre-clinical studies have generated substantial evidence to demonstrate that specific inhibition of PDE3 or 4 (as well as other PDE subtypes) suppresses lung inflammation, edema formation, lung epithelial and endothelial injury, and reduces platelet activation (reviewed in detail in [
14]). There have been numerous clinical trials investigating the therapeutic potential of non-selective PDE inhibitors in ARDS (reviewed in [
14]), with some of those showing promising results. However, there have been no clinical studies to test specific PDE4 inhibitors, and only two clinical studies have assessed the effects of PDE3i by milrinone in ARDS-related conditions [
14]. The first study enrolled pediatric patients with non-hyperdynamic septic shock, and the second recruited severe sepsis patients [
35,
36]. Although data from both studies were positive, there has been limited interest in their widespread clinical use in ARDS, potentially due to their several adverse side effects, as discussed below.
Ensifentrine (RLP554) is a novel dual inhibitor of PDE3 and PDE4 that was recently (June 2024) approved by the FDA as maintenance treatment for patients with COPD [
18,
37]. By targeting both PDE3 and 4 enzymes, ensifentrine has been shown to relax the airway smooth muscles and suppress the release of pro-inflammatory mediators [
18]. In addition, ensifentrine stimulates the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) in
in vitro studies, which can improve mucociliary clearance by reducing mucus viscosity and pathogens from the respiratory track [
37,
38]. In addition to COPD, ensifentrine is being considered for the treatment of asthma [
39], cystic fibrosis, and non-cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis.
Despite its excellent therapeutic profile, there are only a few pre-clinical studies exploring the effects of ensifentrine on lung cell function. This present study aimed to determine the role of dual PDE3/4 inhibition by ensifentrine using an
in vitro model of lung injury. Increased endothelial permeability is a critical step in the development and progression of ARDS [
28]. Extensive research has demonstrated that phosphodiesterases and cyclic nucleotide second messengers (cAMP and cGMP) regulate endothelial barrier function [
15]. cAMP and cGMP exhibit differential effects on endothelial permeability; however, the majority of evidence indicates that increased cAMP levels due to PDE inhibition results in activation of PKA (protein kinase A) and EPAC signaling that mediate barrier enhancement and protection [
15]. Indeed, several studies have demonstrated that individual inhibition of PDE3 or 4, or their combination, leads to barrier protection. For example, selective inhibition of PDE4 (by roflumilast) or PDE3 (by motapizone) reduced thrombin-induced macromolecule permeability in HUVEC, while their combination completely prevented it [
17]. Early studies also demonstrated that an experimental PDE3/4 inhibitor, zardaverine, protected against thrombin and
Escherichia coli hemolysin-induced lung endothelial barrier disruption [
40]. In agreement with these prior observations, we present evidence that ensifentrine exhibits potent barrier enhancing properties and barrier-protective effects against MRSA when given pre- or post-treatment (
Figure 1 and
Figure 2). These responses appear to be mediated by protection of the VE-cadherin junctions, which are cell-cell junctions that stabilize the endothelial monolayer but are disrupted by MRSA treatment, as we have previously shown [
22]. Increased cell death, such as apoptosis and necroptosis, can compromise the integrity of the endothelial barrier [
41,
42]. MRSA causes a mild decrease in cellular viability as measured by LDH levels, which was inhibited in the presence of ensifentrine (
Figure 3B). It is therefore possible that dual inhibition of PDE3/4 leads to barrier protection by preserving the inter-endothelial junctions and preventing cellular death.
The potent anti-inflammatory properties of PDEi are well-established [
43,
44]. In agreement with the literature, ensifentrine reduces pro-inflammatory signaling in lung EC in the current study. Specifically, this compound completely prevented VCAM-1 upregulation after MRSA and decreased the levels of ICAM-1 in endothelial cells (
Figure 4). VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 are adhesion molecules, which are up-regulated upon endothelial activation from inflammatory insults and mediate pro-inflammatory signaling and immune cell recruitment [
45]. Strategies that reduce their expression mitigate ALI [
46]. Prior research has shown that PDE3i by cilostazol down-regulates VCAM-1 in the endothelium of diabetic rats [
47], while PDE4i by apremilast reduces VCAM-1 but not ICAM-1 expression in TNF-α-treated HUVEC [
48]. Combining a PDE3 inhibitor, Org9935, and the PDE4 inhibitor, rolipram, resulted in a synergistic reduction of VCAM-1 following TNF-α treatment in HUVEC. However, in that study the combination did not affect ICAM-1 levels [
49]. Our studies also demonstrated that IL-6 levels were significantly reduced following ensifentrine treatment in endothelial cells, consistent with existing literature showing decreased inflammatory cytokine release following PDE3 or 4 inhibition [
8,
50].
In this study, MRSA causes upregulation of ICAM-1, activation of NF-kB, and increased release of IL-8 in alveolar epithelial cells, all of which were reduced in the presence of ensifentrine (
Figure 5 and
Figure 6). In one of the few published studies exploring the role of ensifentrine
in vitro, it was demonstrated that in well-differentiated bronchial epithelial cells that express a CFTR mutation (in vitro model of cystic fibrosis), ensifentrine reduced IL-1β-induced MCP1 and GM-CSF production, while it had no effect on IL-8 [
20]. The anti-inflammatory properties of ensifentrine in this study were shown to be mediated by inhibition of PDE4, and this is consistent with extensive literature studying the role of PDE4 and not PDE3 in epithelial cells, with a focus on bronchial epithelial cells. Less is known about PDE4 inhibition specifically in the alveolar epithelium, which is a primary site of ALI pathogenesis. One study showed that PDE4 inhibition by roflumilast decreases the production of IL-8, MCP-1, and CXCL1 induced by neutrophil elastase in A549 cells [
51].
While our studies clearly demonstrate that ensifentrine exerts potent barrier protective and anti-inflammatory properties, its efficacy
in vivo to treat ARDS remains to be determined. Important considerations for animal experiments are the dose and route of administration, which are especially important when using PDE inhibitors. It is well established that systemic administration of PDEi is associated with several side effects that have limited their use, such as gastrointestinal issues [
14]. Clinical trials testing inhaled ensifentrine for its safety and tolerability show that it is well-tolerated, with side effects comparable to those of a placebo [
21]. In addition, our results demonstrate that endothelial cells require slightly lower doses of ensifentrine compared to epithelial cells. Therefore, delivery of the medication by inhalation could potentially achieve higher concentrations in the alveoli compared to the vasculature and therefore efficiently target both cell types. Future studies will investigate ensifentrine’s efficacy in treating ALI when given systemically versus directly in the respiratory system.
Further research is also required to explore the mechanisms by which ensifentrine mediates its potent effects. EPAC is directly activated by cAMP, and it is a downstream effector of PDEi [
52]. A recent study demonstrated that EPAC activation by 8CPT in lung endothelial cells stimulated with extracellular histones led to superior barrier enhancing and protective properties, and it caused dramatic decreases in several inflammatory markers including VCAM-1, ICAM-1 and pro-inflammatory cytokines [
32]. In agreement with this, our data (
Figure 7) suggest that EPAC activation at least partially mediates ensifentrine’s protective effects on both lung EC and AEC. However, additional studies are needed to elucidate the specific signaling pathways involved.
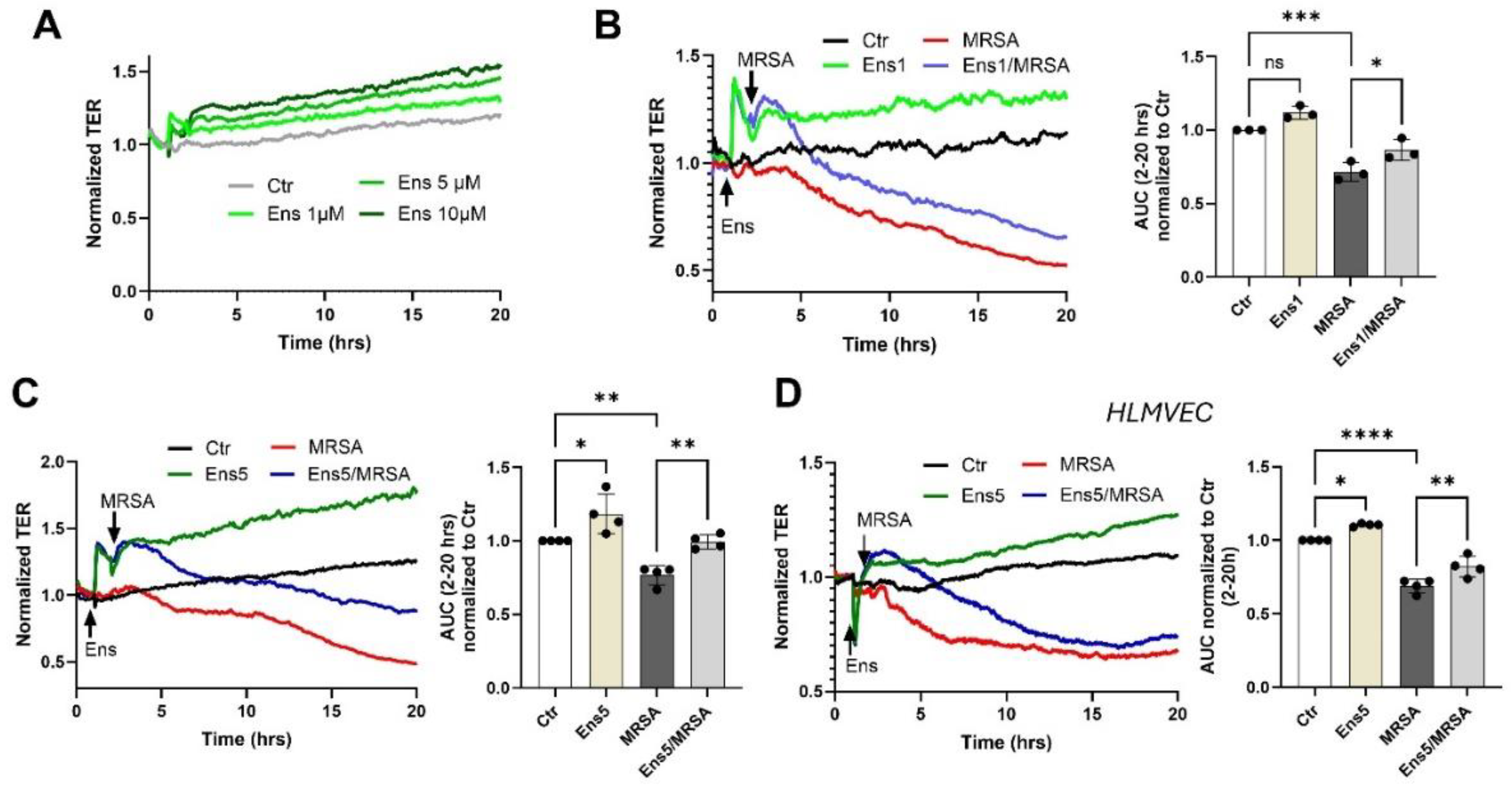
Figure 1.
Ensifentrine exhibits barrier enhancing and barrier protective properties against MRSA. Human pulmonary artery endothelial cells (HPAEC) (A-C) or human lung microvascular endothelial cells (HLMVEC) (D) were pre-treated with ensifentrine or vehicle (DMSO) for 1 hour prior to HK-MRSA challenge (2.5 x108/ml). EC barrier was assessed with the ECIS assay. (A) Representative TER tracings over time of HPAEC treated with various doses of ensifentrine (1-10 μM) in control cells. (B-C) Representative TER tracings over time of HPAEC pre-treated with 1 and 5 μM ensifentrine prior to HK-MRSA. The area under the curve was calculated for each condition and normalized to untreated cells. (D) Representative TER tracings over time of HLMVEC pre-treated with 5 μM ensifentrine prior to MRSA and corresponding quantification. N=3-4 independent experiments. Data were analyzed using one-way Anova, *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.****p<0.0001.
Figure 1.
Ensifentrine exhibits barrier enhancing and barrier protective properties against MRSA. Human pulmonary artery endothelial cells (HPAEC) (A-C) or human lung microvascular endothelial cells (HLMVEC) (D) were pre-treated with ensifentrine or vehicle (DMSO) for 1 hour prior to HK-MRSA challenge (2.5 x108/ml). EC barrier was assessed with the ECIS assay. (A) Representative TER tracings over time of HPAEC treated with various doses of ensifentrine (1-10 μM) in control cells. (B-C) Representative TER tracings over time of HPAEC pre-treated with 1 and 5 μM ensifentrine prior to HK-MRSA. The area under the curve was calculated for each condition and normalized to untreated cells. (D) Representative TER tracings over time of HLMVEC pre-treated with 5 μM ensifentrine prior to MRSA and corresponding quantification. N=3-4 independent experiments. Data were analyzed using one-way Anova, *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.****p<0.0001.
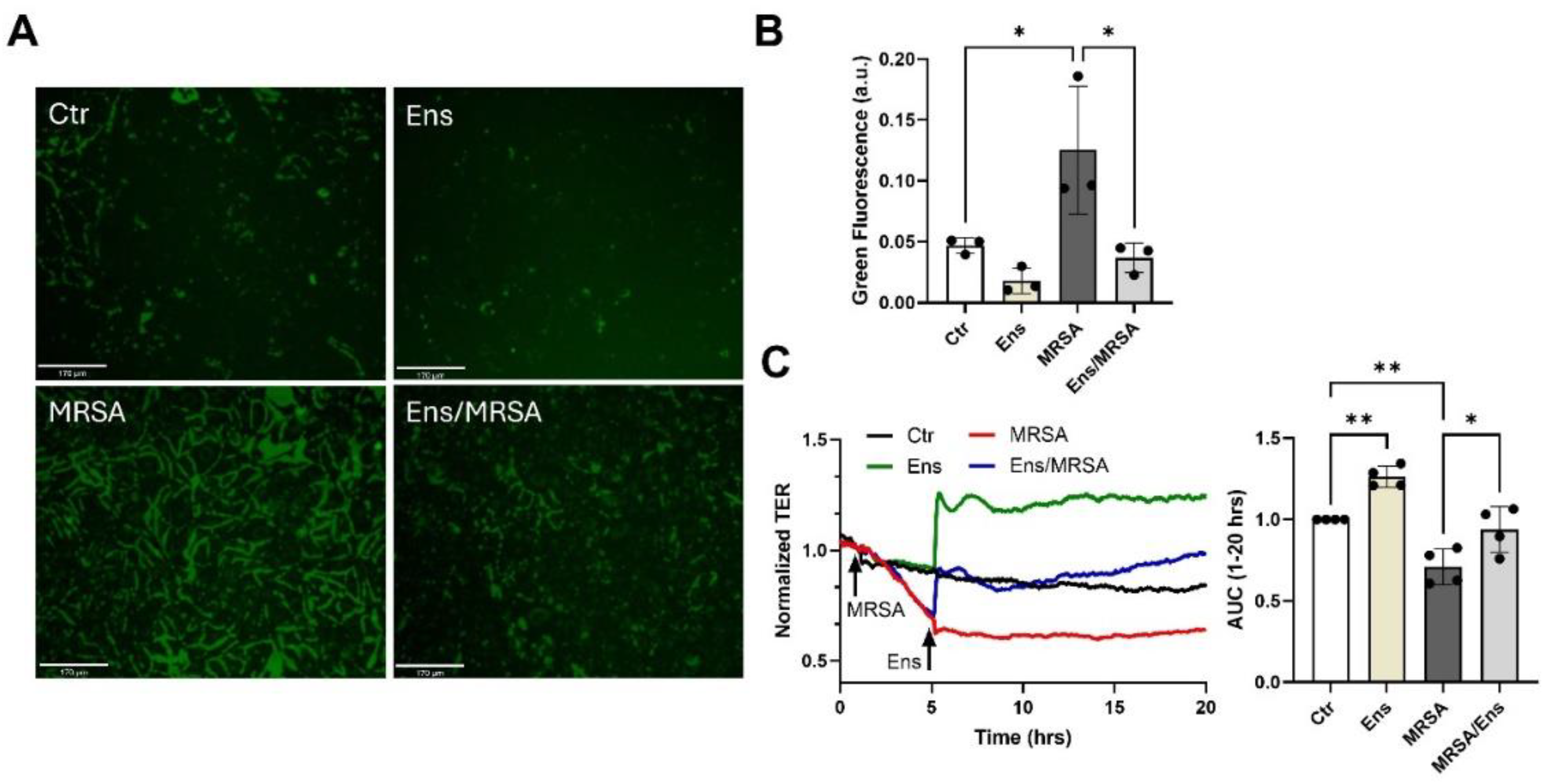
Figure 2.
Ensifentrine inhibits MRSA-induced gap formation and restores barrier integrity. (A-B) XperT permeability assay. HPAEC grown on biotinylated gelatin-coated dishes were pre-treated with ensifentrine (5 μΜ) or vehicle (DMSO) for 1 hour prior to HK-MRSA challenge (2.5 x108/ml). 20 hours later, FITC-avidin was added and pictures were taken at 20x. Increased FITC signal indicates gap formation. Scale bar= 170 μm. (B) Quantification of green fluorescence using ImageJ. (C) HPAEC were treated with HK-MRSA (2.5 x108/ml), and 4 hours later ensifentrine (5 μΜ) or vehicle (DMSO) was added. Depicted are representative TER tracings over time. The area under the curve was calculated for each condition for the period 1-20 hours. N=3-4 independent experiments. Data were analyzed using one-way Anova. *p<0.05, **p<0.01.
Figure 2.
Ensifentrine inhibits MRSA-induced gap formation and restores barrier integrity. (A-B) XperT permeability assay. HPAEC grown on biotinylated gelatin-coated dishes were pre-treated with ensifentrine (5 μΜ) or vehicle (DMSO) for 1 hour prior to HK-MRSA challenge (2.5 x108/ml). 20 hours later, FITC-avidin was added and pictures were taken at 20x. Increased FITC signal indicates gap formation. Scale bar= 170 μm. (B) Quantification of green fluorescence using ImageJ. (C) HPAEC were treated with HK-MRSA (2.5 x108/ml), and 4 hours later ensifentrine (5 μΜ) or vehicle (DMSO) was added. Depicted are representative TER tracings over time. The area under the curve was calculated for each condition for the period 1-20 hours. N=3-4 independent experiments. Data were analyzed using one-way Anova. *p<0.05, **p<0.01.
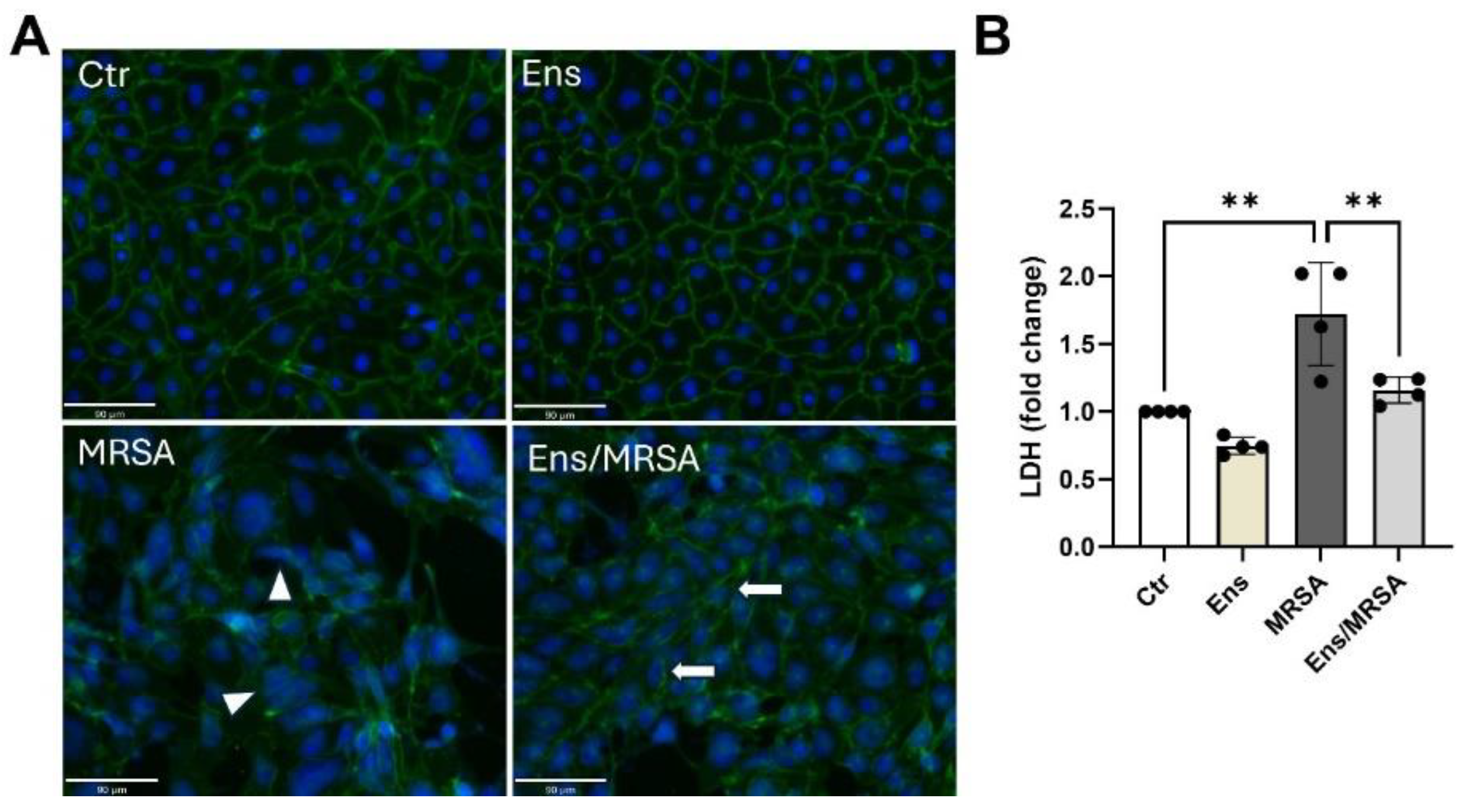
Figure 3.
Ensifentrine attenuates MRSA-induced VE-cadherin disruption and cell death. HPAEC were pre-treated with ensifentrine (5 μM) or vehicle (DMSO) for 1 hour prior to HK-MRSA challenge (2.5 x108/ml, 20 hrs). (A) EC were fixed and processed for VE-cadherin staining using an alexa-488 secondary antibody. Nuclei were stained using DAPI (blue). Images were taken at 20x. (Scale bar=90 μm). Depicted are representative images. White arrows indicate VE-cadherin staining at cell junctions, and triangles indicate VE-cadherin bond disruption. (B) Extracellular LDH levels were measured in the conditioned media. N=3-4 independent experiments. Data were analyzed using one-way Anova, **p<0.01.
Figure 3.
Ensifentrine attenuates MRSA-induced VE-cadherin disruption and cell death. HPAEC were pre-treated with ensifentrine (5 μM) or vehicle (DMSO) for 1 hour prior to HK-MRSA challenge (2.5 x108/ml, 20 hrs). (A) EC were fixed and processed for VE-cadherin staining using an alexa-488 secondary antibody. Nuclei were stained using DAPI (blue). Images were taken at 20x. (Scale bar=90 μm). Depicted are representative images. White arrows indicate VE-cadherin staining at cell junctions, and triangles indicate VE-cadherin bond disruption. (B) Extracellular LDH levels were measured in the conditioned media. N=3-4 independent experiments. Data were analyzed using one-way Anova, **p<0.01.
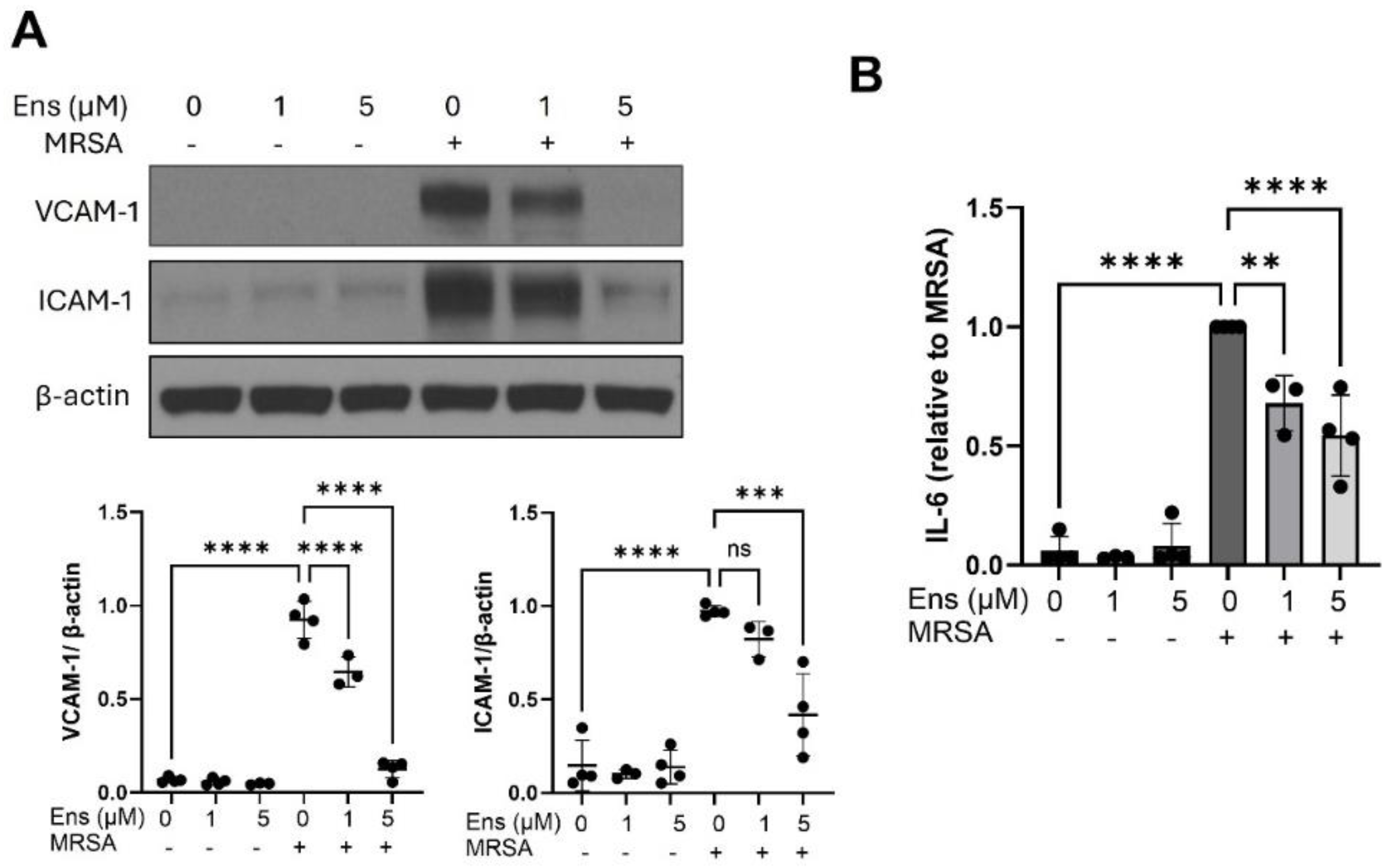
Figure 4.
Ensifentrine inhibits MRSA-induced pro-inflammatory signaling in lung endothelial cells. HPAEC were pre-treated with ensifentrine (5 μM) or vehicle (DMSO) for 1 hour prior to HK-MRSA challenge (2.5 x108/ml, 20 hrs). (A) Representative western blots and pooled densitometric analyses of EC lysates are shown for VCAM-1, ICAM-1, and β-actin expression. (B) IL-6 levels were measured in EC supernatants. N=3-4 independent experiments. Data were analyzed using one-way Anova, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001.
Figure 4.
Ensifentrine inhibits MRSA-induced pro-inflammatory signaling in lung endothelial cells. HPAEC were pre-treated with ensifentrine (5 μM) or vehicle (DMSO) for 1 hour prior to HK-MRSA challenge (2.5 x108/ml, 20 hrs). (A) Representative western blots and pooled densitometric analyses of EC lysates are shown for VCAM-1, ICAM-1, and β-actin expression. (B) IL-6 levels were measured in EC supernatants. N=3-4 independent experiments. Data were analyzed using one-way Anova, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001.
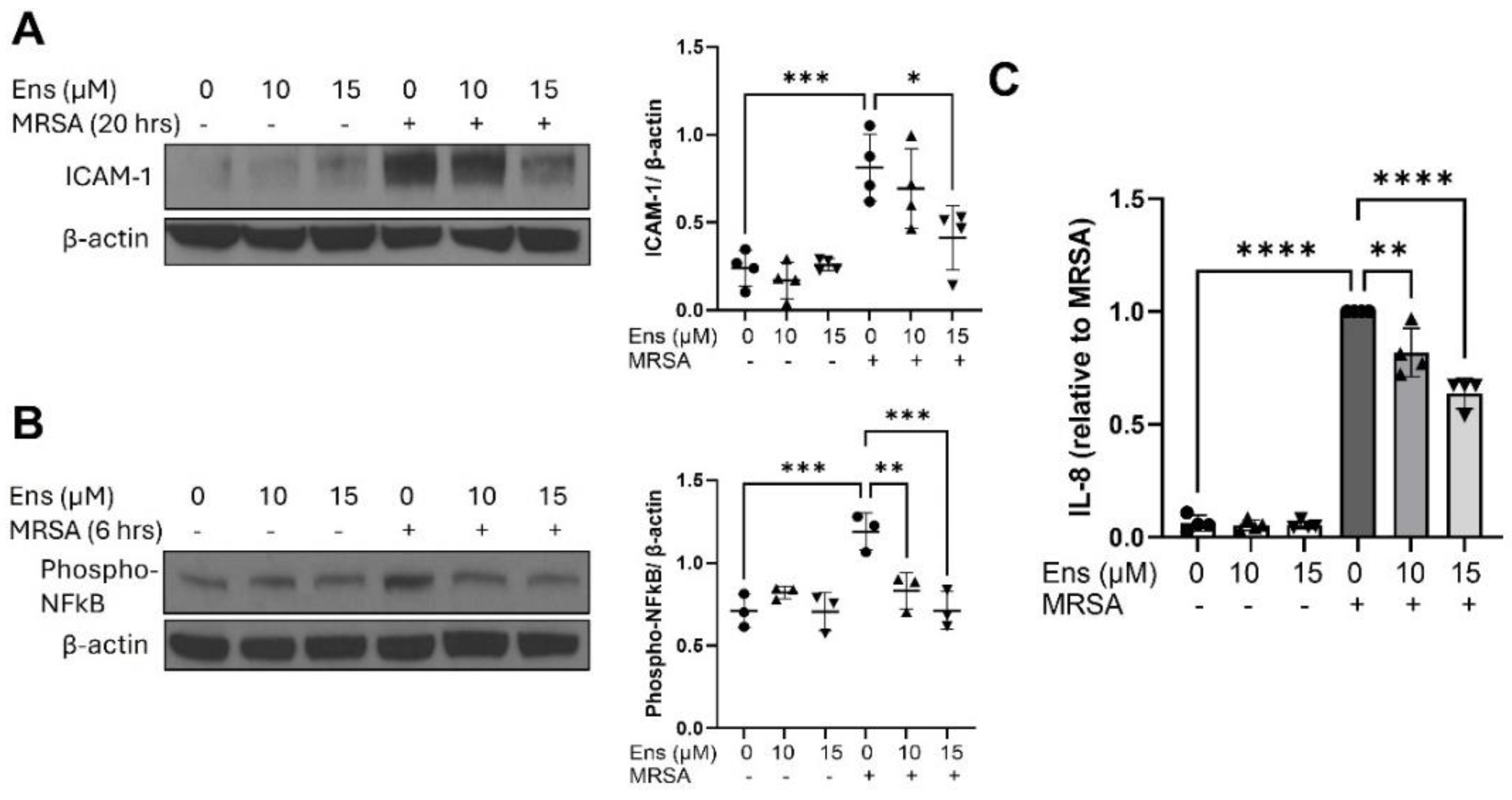
Figure 5.
MRSA-induced inflammatory signaling in A549 is decreased by ensifentrine. A549 were pre-treated with ensifentrine (10 or 15 μM) or vehicle (DMSO) for 1 hour prior to HK-MRSA challenge (2.5 x108/ml). Representative western blots of cell lysates are shown for (A) ICAM-1 expression (20 hours of MRSA), and (B) phospho-NFkB (6 hours of MRSA). Densitometric analysis was performed by normalizing to β-actin levels. (C) IL-8 levels were measured in cell supernatants. N=3-4 independent experiments. Data were analyzed using one-way Anova, *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001.
Figure 5.
MRSA-induced inflammatory signaling in A549 is decreased by ensifentrine. A549 were pre-treated with ensifentrine (10 or 15 μM) or vehicle (DMSO) for 1 hour prior to HK-MRSA challenge (2.5 x108/ml). Representative western blots of cell lysates are shown for (A) ICAM-1 expression (20 hours of MRSA), and (B) phospho-NFkB (6 hours of MRSA). Densitometric analysis was performed by normalizing to β-actin levels. (C) IL-8 levels were measured in cell supernatants. N=3-4 independent experiments. Data were analyzed using one-way Anova, *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001.
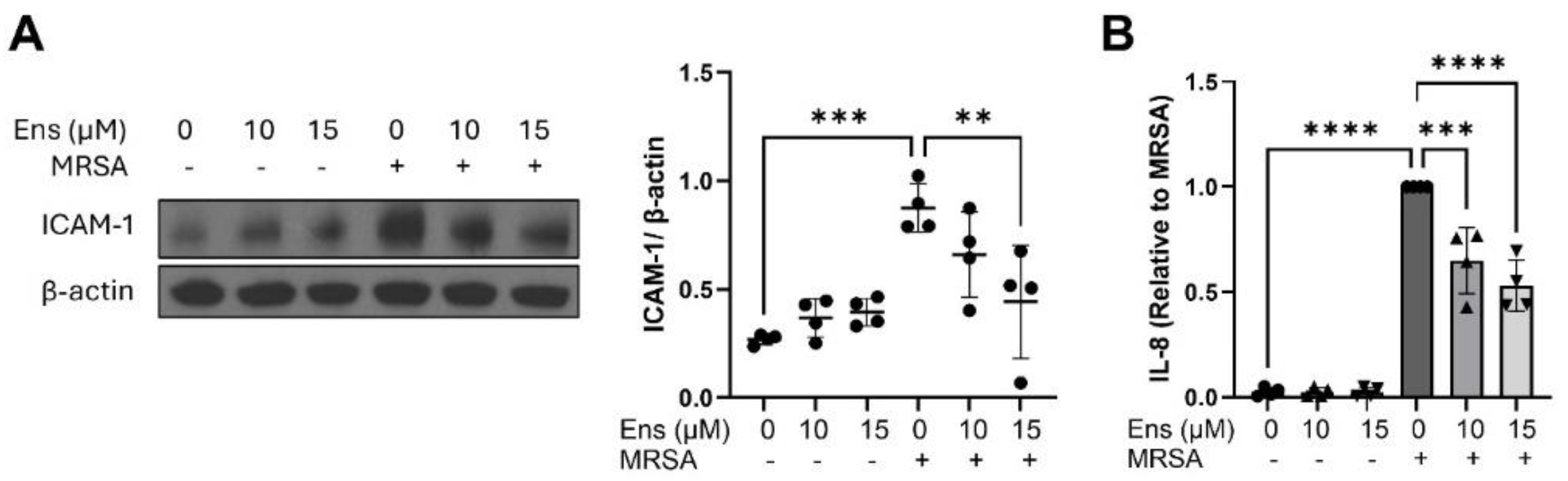
Figure 6.
MRSA-induced inflammatory signaling in immortalized alveolar epithelial cells is decreased by ensifentrine. Immortalized AEC were pre-treated with ensifentrine (10 or 15 μM) or vehicle (DMSO) for 1 hour prior to HK-MRSA challenge (3 x108/ml, 20 hrs). (A) Representative western blots and pooled densitometric analyses of cell lysates are shown for ICAM-1 expression and β-actin. (B) IL-8 levels were measured in cell supernatants. N=4 independent experiments. Data were analyzed using one-way Anova, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001.
Figure 6.
MRSA-induced inflammatory signaling in immortalized alveolar epithelial cells is decreased by ensifentrine. Immortalized AEC were pre-treated with ensifentrine (10 or 15 μM) or vehicle (DMSO) for 1 hour prior to HK-MRSA challenge (3 x108/ml, 20 hrs). (A) Representative western blots and pooled densitometric analyses of cell lysates are shown for ICAM-1 expression and β-actin. (B) IL-8 levels were measured in cell supernatants. N=4 independent experiments. Data were analyzed using one-way Anova, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001.
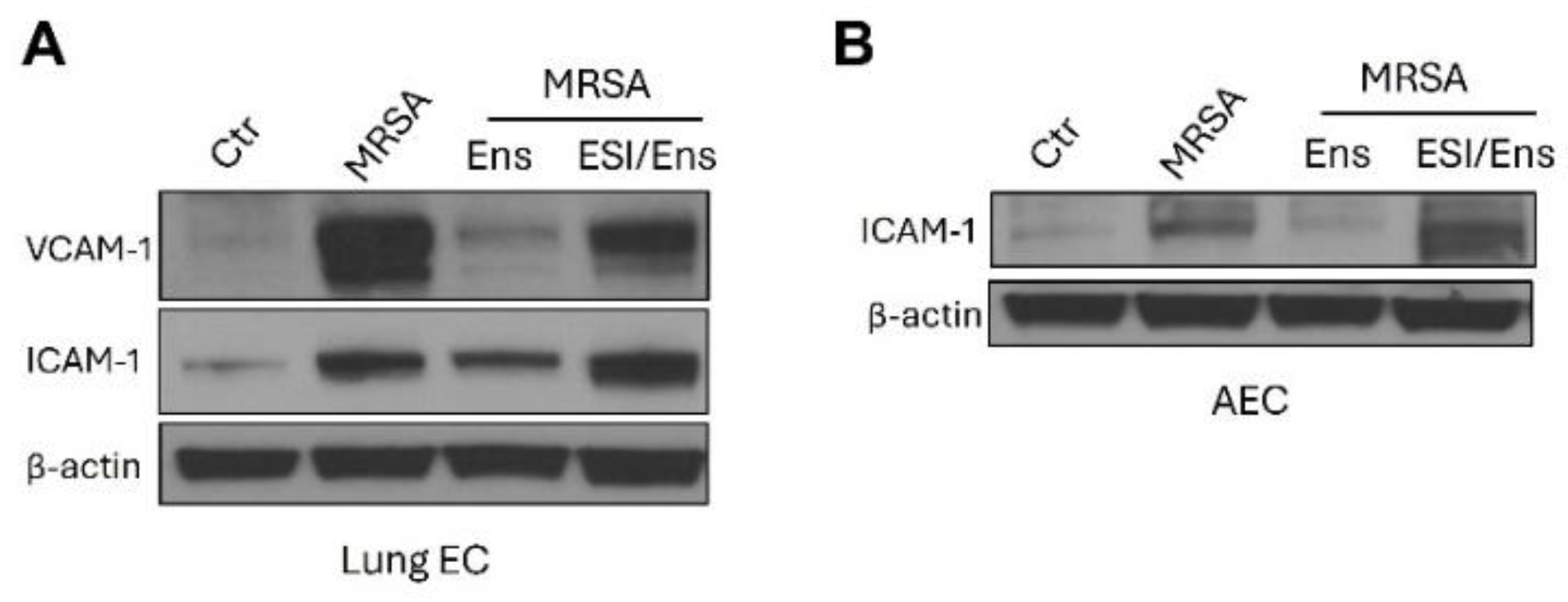
Figure 7.
Ensifentrine reduces the expression of inflammatory adhesion molecules in lung EC and AEC in an EPAC-dependent manner. HPAEC and A549 were pre-treated with 20 μΜ or 5 μΜ ESI-08 (EPAC antagonist) respectively. After 1 hour, ensifentrine was added (5 μM for HPAEC and 15 μΜ for A549). Cells were treated with HK-MRSA 1 hour later (2.5 x108/ml, 20 hrs). Representative western blots are shown for (A) VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 expression and β-actin in HPAEC, and (B) ICAM-1 expression and β-actin in A549. N=3 independent experiments.
Figure 7.
Ensifentrine reduces the expression of inflammatory adhesion molecules in lung EC and AEC in an EPAC-dependent manner. HPAEC and A549 were pre-treated with 20 μΜ or 5 μΜ ESI-08 (EPAC antagonist) respectively. After 1 hour, ensifentrine was added (5 μM for HPAEC and 15 μΜ for A549). Cells were treated with HK-MRSA 1 hour later (2.5 x108/ml, 20 hrs). Representative western blots are shown for (A) VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 expression and β-actin in HPAEC, and (B) ICAM-1 expression and β-actin in A549. N=3 independent experiments.