Background and Objectives
Budd-Chiari syndrome (BCS) is a rare but serious condition characterized by obstruction of the hepatic veins, leading to liver congestion, portal hypertension, and potentially life-threatening complications. The syndrome poses significant diagnostic and therapeutic challenges due to its varied etiologies, including thrombosis, malignancy, and other hematological disorders [
1]. Globally, BCS is a major concern in both developed and developing regions, with variations in prevalence and etiology observed across different populations. In Western countries, BCS is often associated with myeloproliferative disorders [
2,
3], whereas in Asia, particularly in countries like India and China, the condition is frequently linked to inferior vena cava obstruction [
4]. In Japan, BCS is designated as an intractable disease, reflecting the need for specialized care and a comprehensive understanding of its clinical management.
Despite advancements in diagnostic techniques and therapeutic interventions, the management of BCS remains complex, with substantial variability in clinical outcomes. The rarity of the syndrome and the need for specialized expertise highlight the importance of international collaboration and knowledge sharing among researchers. Co-authorship network analysis serves as a powerful tool to uncover the structure of scientific collaboration, identifying key contributors, research hubs, and the evolution of research networks over time. By analyzing co-authorship networks, this study aims to elucidate the patterns of collaboration among researchers in the BCS field, offering insights into how scientific contributions have shaped the understanding and management of this condition from 2000 to 2023.
Scope of the Study
This study examines publications related to BCS research indexed in the Web of Science (WoS) Core Collection database between 2000 and 2023. A total of 2,877 articles were selected for analysis, providing a comprehensive overview of the collaborative landscape within this specialized field over the past two decades. The dataset ensures the inclusion of the most recent publications (as of September 2024). The analysis will focus on constructing and evaluating co-authorship networks using macro-level indicators such as network density (the ratio of actual to possible connections), clustering coefficient (the degree to which nodes tend to cluster together), number of components (distinct connected subgroups within the network), and average path length (the average distance between nodes). At the micro-level, I will assess degree centrality (the number of direct connections each node has), closeness centrality (how close a node is to all other nodes), and betweenness centrality (the extent to which a node lies on the shortest path between other nodes). These metrics will help illuminate the structure and dynamics of researcher collaborations in this field.
Significance of the Study
This study holds significant value in the context of BCS research by offering a detailed exploration of the collaborative landscape within this field. Identifying major researchers and institutions involved in BCS research can help highlight leading contributors and emerging leaders. Furthermore, evaluating the progression of international collaborative research and its impact is essential for understanding how global partnerships contribute to advancements in this area. The analysis of network structures and their evolution over time can reveal critical trends, such as shifts in research focus or the emergence of new collaborative clusters.
By providing a clear picture of the current state of research and collaboration in BCS, this study not only enhances our understanding of existing networks but also sheds light on future directions and potential areas for new partnerships. The findings underscore the importance of international collaboration in addressing the complex challenges associated with BCS, highlighting the role of network analysis as a powerful tool for guiding future research strategies and fostering global cooperation.
Material and Methods
The present study investigates the co-authorship patterns in BCS research papers. I utilized the WoS Core Collection database, conducting a “Topic Search” with the keyword “Budd-Chiari syndrome” to analyze a total of 2,877 articles published between 2000 and 2023 (as of September 2024). In this analysis, I examined who collaborated with whom in co-authoring these papers. I conducted network analysis using the Python programming language (version 3.10.5) within the integrated development environment (IDE) PyCharm (software version 2022.1.3). This study employed methodology-established principles of social network analysis [
5]. I carried out the analysis in two main parts:
Macro-level Metrics:
Network Density: Calculated as the ratio of the number of edges to the maximum possible edges Between all nodes.
Clustering Coefficient: Measured the extent to which nodes form clusters by considering the number of edges among neighboring nodes and calculating the average.
Components: Identified and counted the number of subgraphs (components) where nodes are mutually connected.
Average Path Length: Evaluated the average “distance” between nodes by calculating the overall average path length in the network [6].
Micro-level Metrics:
Degree Centrality: Measured the importance of each node by counting the number of edges it has in the network.
Closeness Centrality: Defined as the inverse of the sum of the shortest path lengths from a node to all other nodes, measuring how close each node is to others in the network.
Betweenness Centrality: Assessed the extent to which a node lies on the shortest paths between other nodes, indicating its importance in information transmission within the network [
6,
7].
The significance of these macro-level metrics in understanding the structure of scientific collaboration networks and these micro-level centrality measures in scientific collaboration networks has been well documented and used [
6,
7]. Through these analyses, I can identify collaborative relationships and influential researchers in BCS research. This information may be useful for understanding research trends and planning future collaborative studies.
Results
The study analyzed the co-authorship network of researchers in BCS research, focusing on the periods from 2000 to 2023. The analysis was conducted using data from the WoS Core Collection and utilized both macro and micro-level network metrics to understand the evolution of collaborative networks in this field.
2000-2009. Network Analysis
During the 2000–2009 period, the co-authorship network for BCS research included a sparse and highly fragmented structure with a network density of 0.0017 (
Table 1), indicating that only 0.17% of all possible connections between authors were realized (
Figure 1). The average clustering coefficient was notably high at 0.926 (
Table 1), suggesting that when co-authorship occurred, it often formed tightly knit groups (
Figure 1). However, the network consisted of 533 components (
Table 1), reflecting many disconnected groups of researchers (
Figure 1). The average distance between nodes was infinite, highlighting the lack of a giant component that could connect most of the authors [
8].
At the micro level, the analysis of degree centrality identified Aurelie Plessier (0.0250), Dominique Valla (0.0207), and Harry L. A. Janssen (0.0175) as the top contributors by co-authorship frequency, indicating their central roles in BCS research during this period (
Table 2). For closeness centrality, which measures how quickly a researcher can connect to others in the network, G. Mentha (0.0293), HLA Janssen (0.0287), and Massimo Primignani (0.0287) were prominent (
Table 3). Betweenness centrality, which measures a node’s role in connecting different parts of the network, was led by G. Mentha (0.0027), G. Barosi (0.0026), and M. Primignani (0.0025), suggesting their influence in bridging otherwise disconnected groups (
Table 4).
2010-2019. Network Analysis
In the subsequent period from 2010 to 2019, the network showed slight improvements in density and cohesiveness. The network density was 0.0016 (
Table 1), marginally lower than the previous decade, indicating a slight decrease in the ratio of actual to possible connections (
Figure 2). The average clustering coefficient remained high at 0.928 (
Table 1), emphasizing the continued tendency for collaborative clusters among researchers (
Figure 2). The network’s fragmentation increased, as evidenced by 645 components (
Table 1), further demonstrating the absence of widespread collaborative integration (
Figure 2). The average distance between nodes remained infinite, pointing to continued fragmentation in the network [
8].
Aurelie Plessier (0.0349) and Dominique Valla (0.0281) continued to dominate in terms of degree centrality, solidifying their central positions in the BCS research landscape (
Table 2). Jonel Trebicka (0.0167) also emerged as a significant figure during this period. For closeness centrality, Aurelie Plessier (0.0757) and Dominique Valla (0.0735) remained top influencers, with Fanny Turon (0.0701) also playing a pivotal role in quickly connecting with others (
Table 3). In terms of betweenness centrality, which measures the potential of nodes to control information flow, Hui Chen (0.0207), Aurelie Plessier (0.0135), and Xingshun Qi (0.0127) were key intermediaries, suggesting their strategic importance in maintaining connectivity across the network (
Table 4).
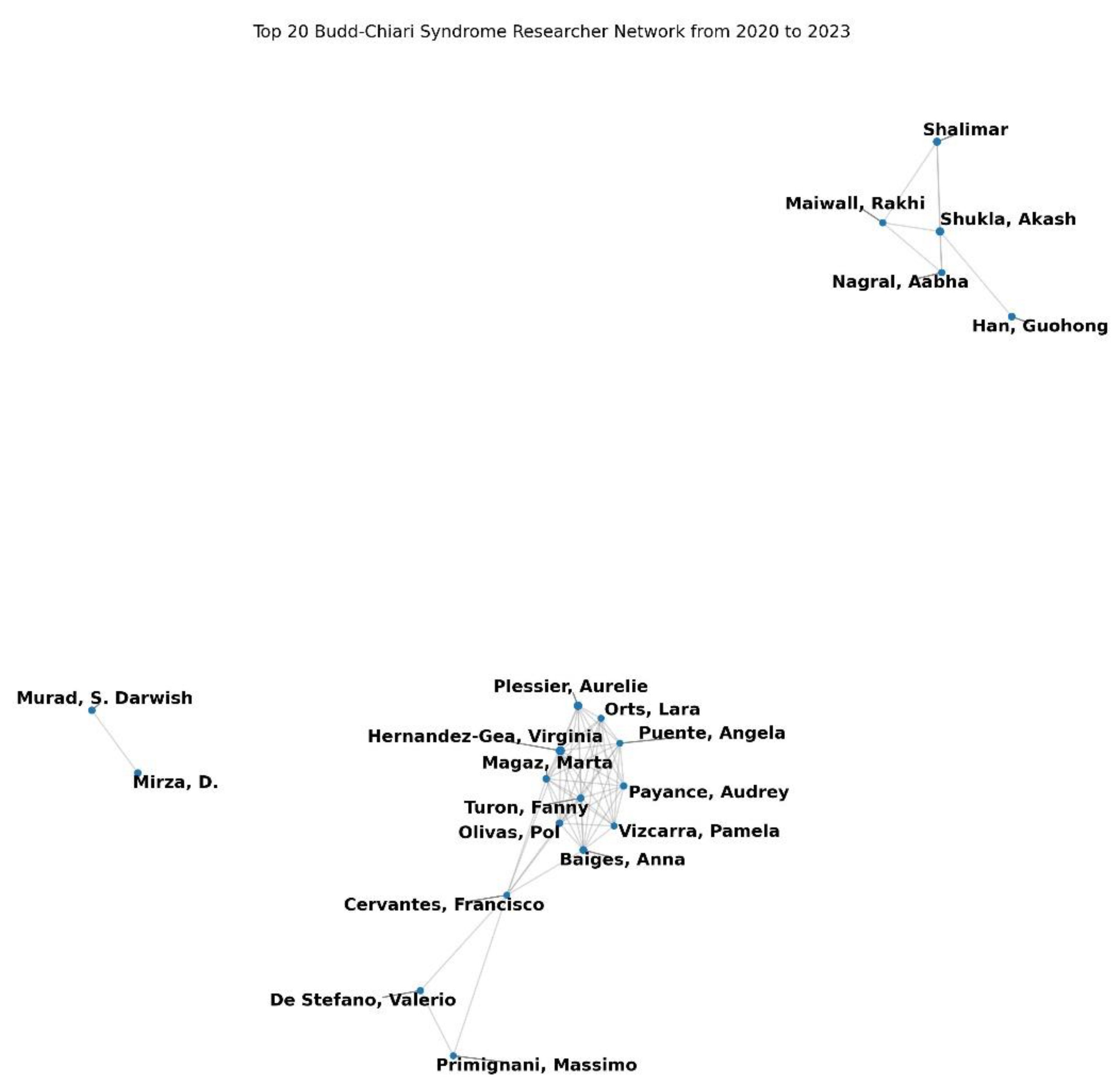
2020-2023. Network Analysis
During the 2020–2023 period, the co-authorship network for BCS research showed increased cohesiveness and integration, as reflected by a network density of 0.0032 (
Table 1), indicating that 0.32% of all possible co-authorship connections were realized (
Figure 3). The average clustering coefficient was 0.946 (
Table 1), suggesting a high tendency for authors to form closely knit groups, further emphasizing the network’s cohesive nature (
Figure 3). The number of components decreased to 376 (
Table 1), demonstrating a notable reduction in network fragmentation and suggesting improved collaborative integration among researchers (
Figure 3). Despite these improvements, the network still exhibited a lack of a giant component, as shown by an infinite average distance between nodes, highlighting continued challenges in achieving full connectivity across the network [
8].
At the micro level, degree centrality analysis identified Virginia Hernandez-Gea (0.0300), Aurelie Plessier (0.0254), and Akash Shukla (0.0245) as the most prominent figures based on co-authorship frequency, indicating their central roles in shaping the BCS research landscape during this period (
Table 2). Closeness centrality, which measures how efficiently a researcher can connect to others in the network, highlighted Valerie Paradis (0.0723), Aurelie Plessier (0.0694), and Audrey Payance (0.0679) as the most influential researchers, reflecting their pivotal positions in facilitating rapid connections within the network (
Table 3). In terms of betweenness centrality, which identifies nodes that act as critical bridges within the network, Valerie Paradis (0.0281), Xingshun Qi (0.0170), and Yuzheng Zhuge (0.0152) were key intermediaries, underscoring their strategic importance in connecting otherwise separate research clusters and enhancing the overall cohesiveness of the network (
Table 4).
Discussion
The analysis of the co-authorship network in BCS research from 2000 to 2023 reveals significant insights into the collaborative dynamics and evolution of scientific contributions in this field. By examining both macro and micro-level network metrics, we can better understand the structural changes and key contributors over the years, highlighting the impact of collaboration on research productivity and knowledge dissemination.
2000-2009 Period: During the initial period from 2000 to 2009, the co-authorship network was characterized by a sparse and highly fragmented structure. The network density was a mere 0.0017, indicating that only 0.17% of all possible connections between authors were realized. This low density reflects the nascent stage of collaboration in BCS research, where researchers were largely working in isolated groups. The high average clustering coefficient of 0.926 suggests that when collaborations did occur, they tended to form tightly knit groups. However, the presence of 533 components indicates a significant level of fragmentation, with many disconnected groups of researchers. The infinite average distance between nodes further highlights the lack of a giant component that could connect most authors, suggesting that the research community was highly segmented with limited inter-group communication.
At the micro level, degree centrality analysis identified Aurelie Plessier, Dominique Valla, and Harry L. A. Janssen as the top contributors by co-authorship frequency, underscoring their central roles in BCS research during this period. Closeness centrality highlighted G. Mentha, HLA Janssen, and Massimo Primignani, reflecting their ability to connect quickly with others in the network, thus facilitating knowledge flow. Betweenness centrality, which measures a node’s role in connecting different parts of the network, was led by G. Mentha, G. Barosi, and M. Primignani, suggesting their influence in bridging otherwise disconnected groups, which is crucial in a fragmented network.
2010-2019 Period: The subsequent period from 2010 to 2019 showed slight improvements in network density and cohesiveness. The network density was 0.0016, marginally lower than the previous decade, indicating a slight decrease in the ratio of actual to possible connections. Despite this, the average clustering coefficient remained high at 0.928, emphasizing the continued tendency for collaborative clusters among researchers. The network’s fragmentation increased, as evidenced by 645 components, further demonstrating the absence of widespread collaborative integration. The average distance between nodes remained infinite, pointing to continued fragmentation in the network. These findings suggest that while collaborative efforts were strong within specific groups, broader integration across the field remained limited, potentially hindering the overall progress of BCS research.
Aurelie Plessier and Dominique Valla continued to dominate in terms of degree centrality, solidifying their central positions in the BCS research landscape. Jonel Trebicka also emerged as a significant figure during this period. Closeness centrality highlighted Aurelie Plessier, Dominique Valla, and Fanny Turon as top influencers, reflecting their pivotal roles in quickly connecting with others. In terms of betweenness centrality, Hui Chen, Aurelie Plessier, and Xingshun Qi were key intermediaries, suggesting their strategic importance in maintaining connectivity across the network. Their roles underscore the importance of certain researchers not just as prolific contributors but as critical links that facilitate collaboration between otherwise disparate research clusters.
2020-2023 Period: The period from 2020 to 2023 marked a notable increase in network cohesiveness and integration. The network density rose to 0.0032, indicating that 0.32% of all possible co-authorship connections were realized, representing a positive trend towards increased collaboration. The average clustering coefficient increased to 0.946, suggesting a strong tendency for authors to form closely knit groups, further emphasizing the network’s cohesive nature. The number of components decreased to 376, demonstrating a reduction in network fragmentation and suggesting improved collaborative integration among researchers. Despite these improvements, the network still exhibited a lack of a giant component, as shown by an infinite average distance between nodes, highlighting continued challenges in achieving full connectivity across the network.
At the micro level, degree centrality analysis identified Virginia Hernandez-Gea, Aurelie Plessier, and Akash Shukla as the most prominent figures based on co-authorship frequency, indicating their central roles in shaping the BCS research landscape during this period. Closeness centrality highlighted Valerie Paradis, Aurelie Plessier, and Audrey Payance as the most influential researchers, reflecting their pivotal positions in facilitating rapid connections within the network. In terms of betweenness centrality, Valerie Paradis, Xingshun Qi, and Yuzheng Zhuge were key intermediaries, underscoring their strategic importance in connecting otherwise separate research clusters and enhancing the overall cohesiveness of the network.
Implications and Future Directions: Overall, the co-authorship network analysis of BCS research from 2000 to 2023 reveals a gradual evolution towards increased collaboration and integration among researchers. While the network has become more cohesive over time, challenges remain in achieving full connectivity, which is crucial for accelerating the pace of discovery and fostering innovation. The persistent fragmentation suggests that while collaborative pockets exist, the broader network still lacks integration, potentially limiting the dissemination of findings across the entire research community.
To address these challenges, efforts should focus on fostering broader collaborations, particularly through international partnerships and interdisciplinary approaches that can bridge the gaps between fragmented clusters. Initiatives such as global research consortia, targeted funding programs, and conferences that encourage cross-disciplinary collaboration could help enhance the integration and impact of BCS research. Additionally, leveraging digital platforms and social media to facilitate informal collaborations could further break down barriers and connect researchers across geographical and institutional boundaries.
In conclusion, while BCS research has made strides in collaborative integration, continued efforts are needed to build a more connected and cohesive research community that can effectively tackle the complex challenges posed by BCS.
Conclusion
The co-authorship network analysis of BCS research from 2000 to 2023 reveals important insights into the collaborative landscape within this field. Across the examined periods, the network displayed low overall cohesion, with only a small fraction of potential collaborations realized, reflecting the challenges inherent in fostering widespread cooperation among researchers in this rare disease domain. The macro-level indicators highlighted a network with generally low density and high fragmentation, as seen in the significant number of disconnected components and the persistent absence of a giant component throughout the analysis periods. These characteristics suggest that while researchers are forming collaborative clusters, the broader integration across the network remains limited.
From 2000 to 2009, the network was particularly sparse, with a density of just 0.17% and 533 components, indicating many isolated clusters of researchers. The high clustering coefficient of 0.926 within these clusters suggests that when collaborations occurred, they often did so within tightly knit groups, rather than forming broader connections across the network. Key contributors during this period, such as Aurelie Plessier (Hôpital Beaujon, Assistance Publique-Hôpitaux de Paris, France) and Dominique Valla (Université Paris-Cité, Assistance Publique-Hôpitaux de Paris, France), played central roles in co-authorship. Yet, the overall network structure lacked the cohesiveness necessary for efficient information dissemination.
In the 2010 to 2019 period, the network showed only marginal improvements in density, with the number of components increasing to 645, further emphasizing the continued fragmentation. Although the average clustering coefficient remained high, indicating strong local collaboration, the persistence of numerous disconnected components underscores the challenges of fostering widespread collaborative efforts. Influential researchers like Aurelie Plessier (Hôpital Beaujon, Assistance Publique-Hôpitaux de Paris, France) and Dominique Valla (Université Paris-Cité, Assistance Publique-Hôpitaux de Paris, France) maintained their central positions, but the network struggled to evolve beyond its fragmented state.
The 2020 to 2023 period witnessed modest gains in network integration, with the density rising to 0.32% and the number of components decreasing to 376, suggesting some improvement in collaborative integration. However, the network continued to lack a giant component, indicating that significant barriers to full connectivity remained. Prominent figures such as Virginia Hernandez-Gea (Hospital Clínic de Barcelona, Spain) and Valerie Paradis (Hôpital Beaujon, Assistance Publique-Hôpitaux de Paris, France) emerged as key contributors, reflecting a gradual shift towards a more interconnected research community, yet the overall pace of integration appears slow.
In conclusion, the co-authorship network of BCS research reflects a field that, while demonstrating pockets of strong local collaboration, remains characterized by a broader fragmentation that limits the flow of information and collaborative potential across the entire network. The persistence of multiple disconnected components suggests that efforts to enhance collaboration at an international level could be crucial in advancing the understanding and management of BCS. The identification of key contributors and research hubs underscores the potential for targeted strategies to bridge existing gaps and foster a more cohesive and productive research environment. Future initiatives aimed at enhancing international collaboration and integrating emerging leaders could play a pivotal role in overcoming the challenges identified in this analysis, ultimately contributing to more robust and impactful research outcomes in the study of Budd-Chiari syndrome.
Conflict of interest disclosure statement:
none
Ethics approval statement:
not applicable for this article.
Abbreviations
WoS, Web of Science; IDE, Integrated Development Environment; BCS, Budd-Chiari Syndrome.
References
- Martens, P.; Nevens, F. Budd-Chiari syndrome. United European Gastroenterol J. 2015, 3, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudo, M. Budd-Chiari syndrome and myeloproliferative disorder. Intern Med. 1996, 35, 837–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavriilidis, P.; Marangoni, G.; Ahmad, J.; Azoulay, D. State of the Art, Current Perspectives, and Controversies of Budd-Chiari Syndrome: A Review. J Clin Med Res. 2022, 14, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayanthi, V.; Udayakumar, N. Budd-Chiari Syndrome. Changing epidemiology and clinical presentation. Minerva Gastroenterol Dietol. 2010, 56, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wasserman, S.; Faust, K. Social network analysis: Methods and applications; Cambridge University Press, 1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, M. Scientific collaboration networks. II. Shortest paths, weighted networks, and centrality. Phys. Rev. E 2001, 64, 016132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, M.E. The structure of scientific collaboration networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001, 98, 404–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barabasi, A.L.; Albert, R. Emergence of scaling in random networks. Science. 1999, 286, 509–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).