Submitted:
11 September 2024
Posted:
12 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Research Questions
- How does Big Data capability impact SME's performance?
- What are the critical factors influencing the successful implementation of Big Data on SMEs?
- How can the awareness/comprehension of Big Data concerning SMEs be utilized to strengthen productivity?
- What are the potential implications and consequences of altering the form of information in the context of Big Data?
- What obstacles do SMEs encounter when they try to incorporate Big Data into their current systems and operations?
1.2. Rationale
1.3. Objectives
1.4. Research Contribution
- To analyze how BD capabilities affect SME performance, this paper conducts a detailed empirical study using structural equation modelling. Using data from SME studies, we show that advanced BD capabilities (technology itself as well as managerial support) have positive effects on SME performance thus indicating potential return-investment for improved business analytics in small and medium-sized enterprises.
- How knowledge management mediates the relationship between BD capabilities and SME performance is examined. We also highlight that the benefits of BD can be amplified by deploying KM practices, highlighting integration at a techno-human level in knowledge and learning processes are essential to realize performance improvements.
- The study further helps in theorizing BD by relating it with KM and performance outcomes. This theoretically comprehended study is a road map for using Big Data and offers implications for the practising owner/manager of an SME looking to improve competitive advantages through better data-driven knowledge.
1.5. Research Novelty
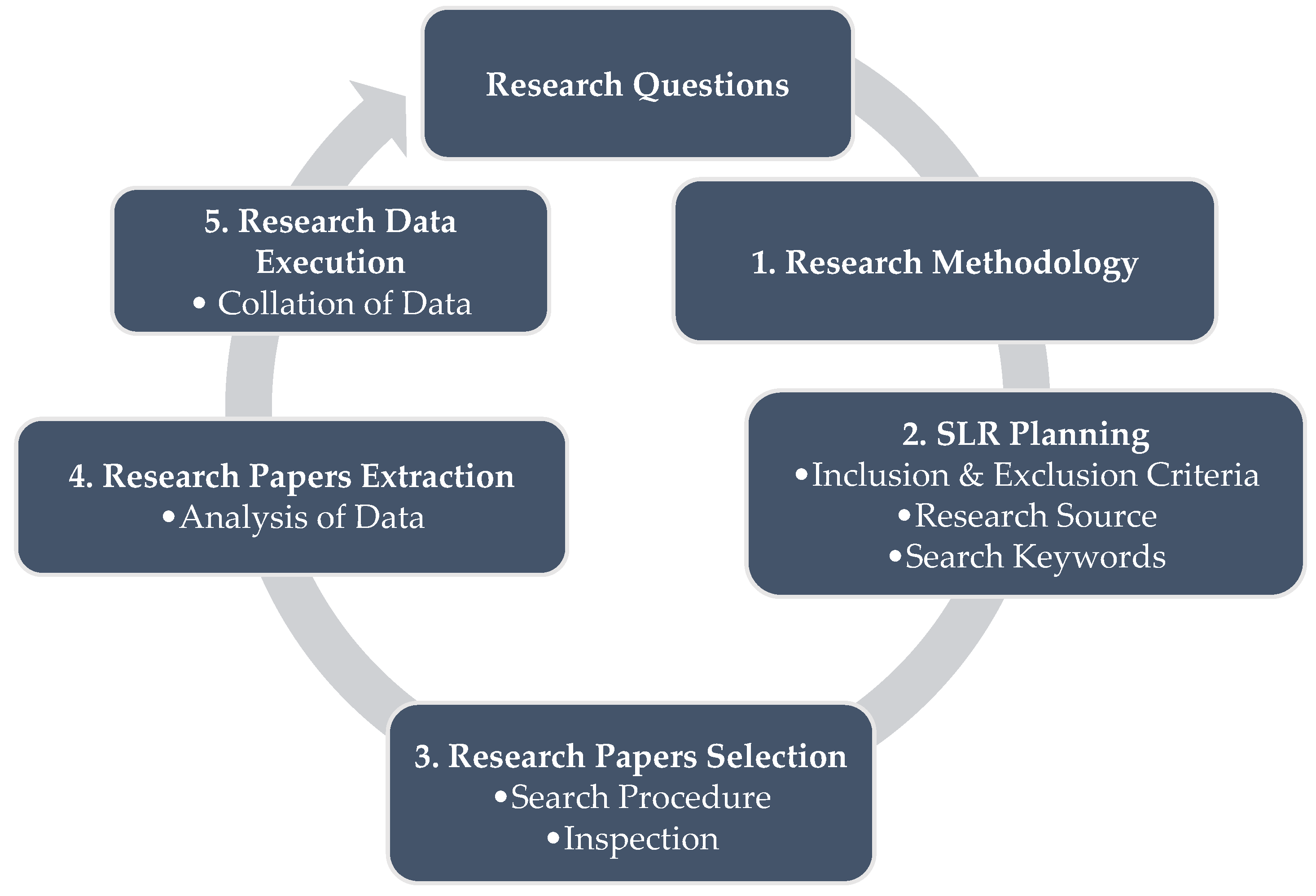
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Eligibility Criteria
2.2. Information Sources
2.3. Search Strategy
2.4. Selection Process
2.5. Data Collection Process
2.6. Data Items
2.6.1. Results and Data Collection
2.6.2. Contributor Characteristics
2.7. Study Risk of Bias Assessment
2.8. Effect Measures
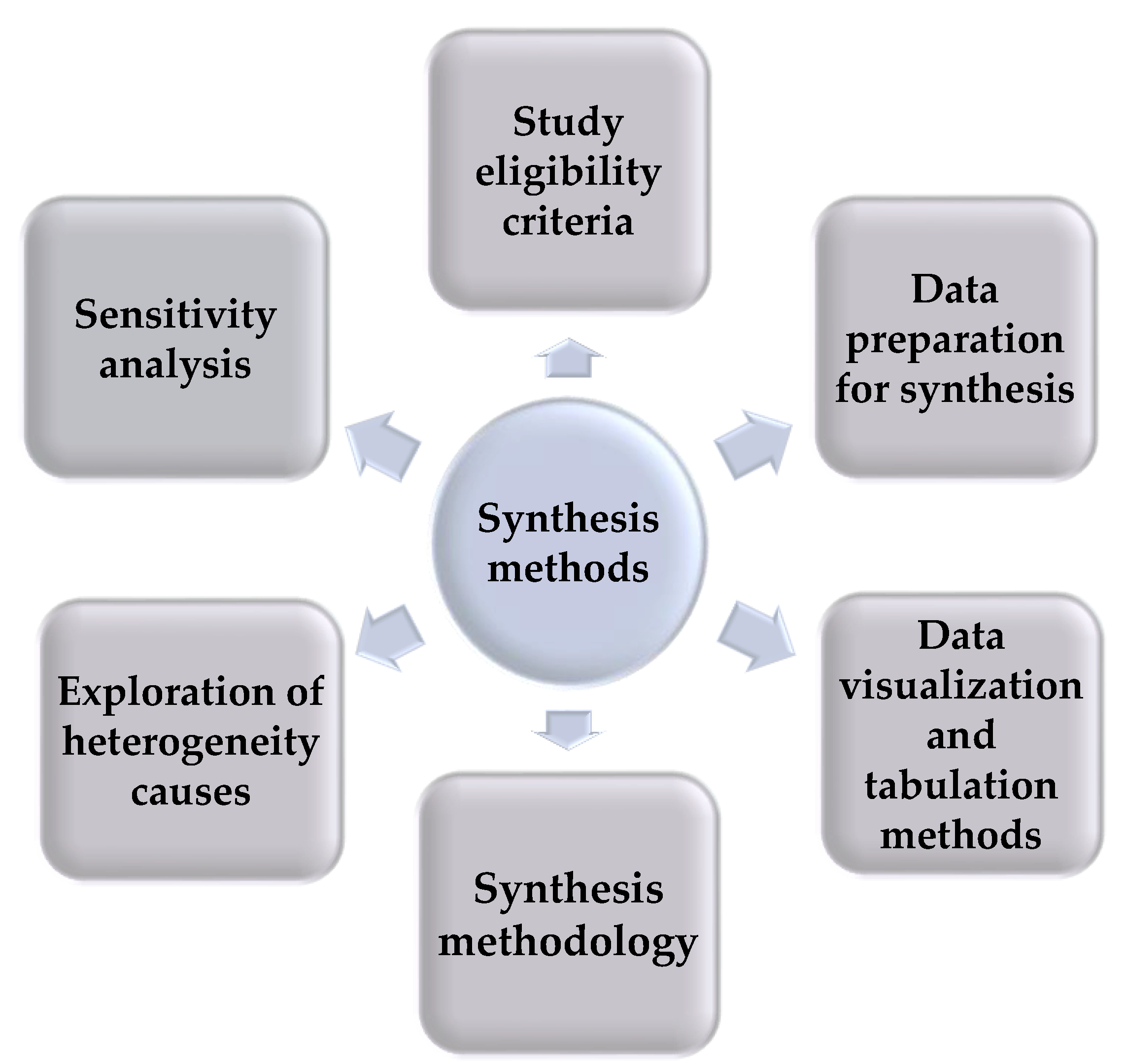
2.9. Synthesis Methods
2.9.1. Study Eligibility Criteria
2.9.2. Data Preparation for Synthesis
2.9.3. Data Visualization and Tabulation Methods
2.9.4. Synthesis Methodology
2.9.5. Exploration of Heterogeneity Causes
2.9.6. Sensitivity Analysis
2.10. Reporting Bias Assessment
2.11. Certainty Assessment
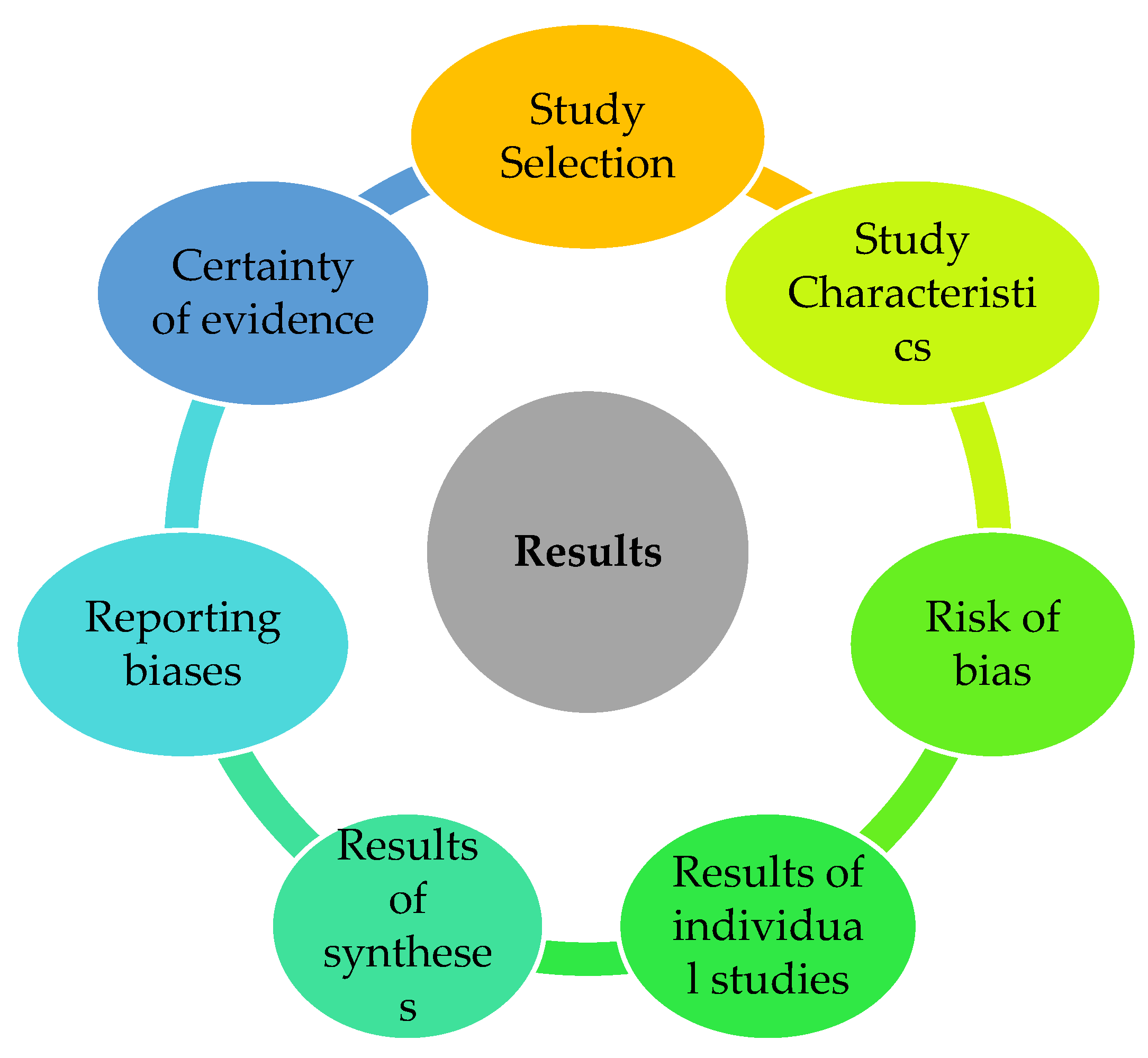
3. Results
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Study Characteristics
3.3. Risk of Bias
3.4. Results of Individual Studies
3.5. Results of Syntheses
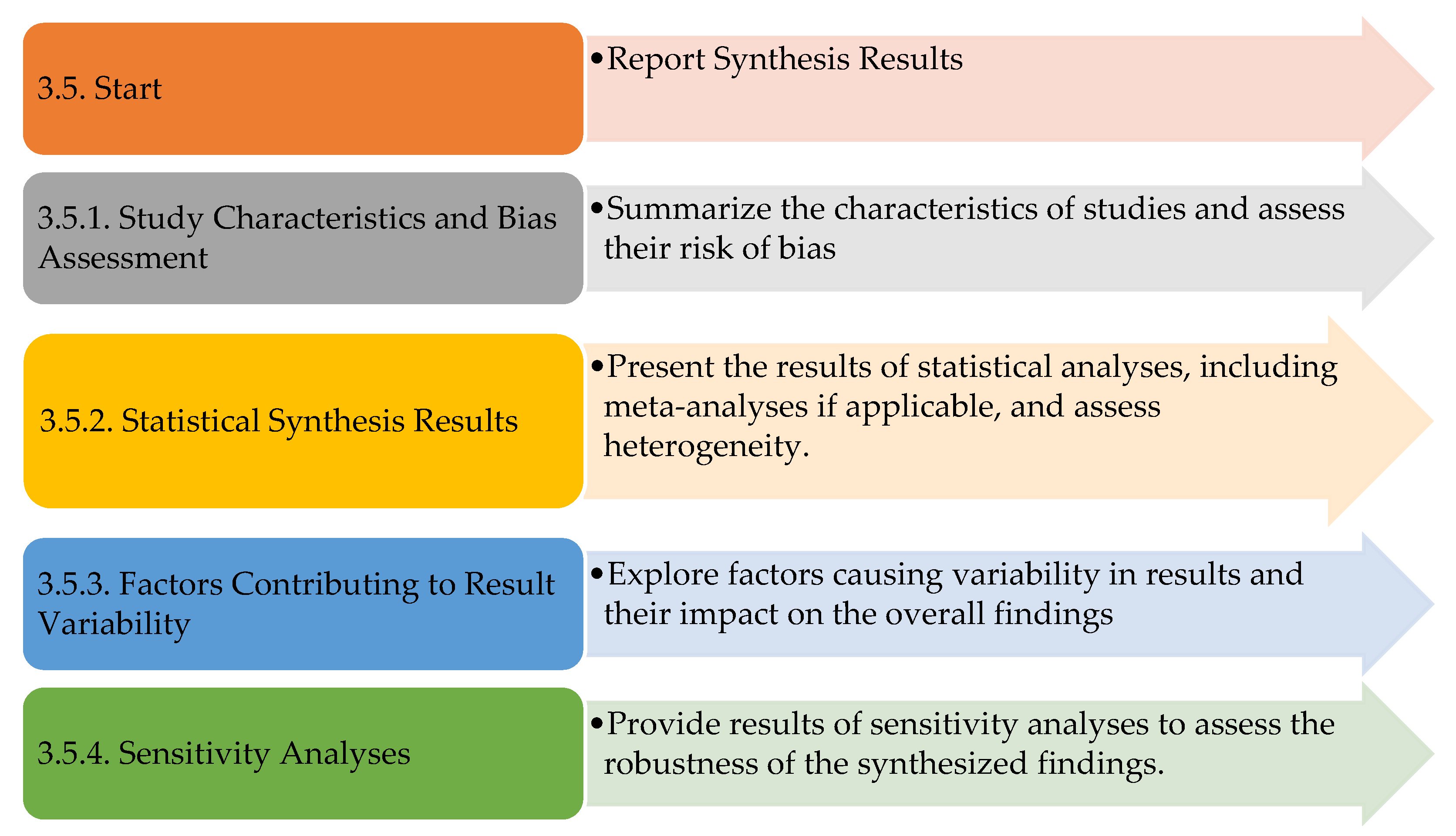
3.5.1. Study Characteristics and Bias Assessment
3.5.2. Statistical Synthesis Results
3.5.3. Factors Contributing to Result Variability
3.5.4. Sensitivity Analyses
3.6. Reporting Biases
3.7. Certainty of Evidence
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- W. Sun, Y. Zhao, and L. Sun, “Big data analytics for venture capital application: towards innovation performance improvement,” Int. J. Inf. Manage., vol. 50, pp. 557–565, 2020, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2018.11.017. [CrossRef]
- J. R. Saura, D. Palacios-Marqués, and D. Ribeiro-Soriano, “Digital marketing in SMEs via data-driven strategies: Reviewing the current state of research,” J. Small Bus. Manage., vol. 61, no. 3, pp. 1278–1313, 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/00472778.2021.1955127. [CrossRef]
- D. Q. Chen, D. S. Preston, and M. Swink, “How the use of big data analytics affects value creation in supply chain management,” J. Manag. Inf. Syst., vol. 32, no. 4, pp. 4–39, 2015, doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/07421222.2015.1138364. [CrossRef]
- S. Sedkaoui, “How data analytics is changing entrepreneurial opportunities?,” Int. J. Innov. Sci., vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 274–294, 2018, doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/IJIS-09-2017-0092. [CrossRef]
- S. Shan, Y. Luo, Y. Zhou, and Y. Wei, “Big data analysis adaptation and enterprises’ competitive advantages: the perspective of dynamic capability and resource-based theories,” Technol. Anal. Strat. Manag., vol. 31, no. 4, pp. 406–420, 2019, doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/09537325.2018.1516866. [CrossRef]
- Oecd-ilibrary.org. [Online]. Available: https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/economics/data-analytics-in-smes_1de6c6a7-en. [Accessed: 07-Sep-2024]. doi: https://doi.org/10.1787/f493861e-en. [CrossRef]
- S. Bag, P. Dhamija, D. J. Bryde, and R. K. Singh, “Effect of eco-innovation on green supply chain management, circular economy capability, and performance of small and medium enterprises,” J. Bus. Res., vol. 141, pp. 60–72, 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2021.12.011. [CrossRef]
- D. Vrontis, R. Chaudhuri, and S. Chatterjee, “Adoption of digital technologies by SMEs for sustainability and value creation: Moderating role of entrepreneurial orientation,” Sustainability, vol. 14, no. 13, p. 7949, 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/su14137949. [CrossRef]
- Econstor.eu. [Online]. Available: https://www.econstor.eu/handle/10419/168475. [Accessed: 07-Sep-2024]. doi:.
- S. D. Müller and P. Jensen, “Big data in the Danish industry: application and value creation,” Bus. Proc.management J., vol. 23, no. 3, pp. 645–670, 2017, doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/BPMJ-01-2016-0017. [CrossRef]
- Y. Zhang, S. Ren, Y. Liu, and S. Si, “A big data analytics architecture for cleaner manufacturing and maintenance processes of complex products,” J. Clean. Prod., vol. 142, pp. 626–641, 2017, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.07.123. [CrossRef]
- Y. Chen, J. Li, and J. Zhang, “Digitalisation, data-driven dynamic capabilities and responsible innovation: An empirical study of SMEs in China,” Asia Pac. J. Manag., 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10490-022-09845-6. [CrossRef]
- H. Oliff and Y. Liu, “Towards industry 4.0 utilizing data-mining techniques: A case study on quality improvement,” Procedia CIRP, vol. 63, pp. 167–172, 2017, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2017.03.311. [CrossRef]
- Y. Li, S. Arora, J. Youtie, and P. Shapira, “Using web mining to explore Triple Helix influences on growth in small and mid-size firms,” Technovation, vol. 76–77, pp. 3–14, 2018, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.technovation.2016.01.002. [CrossRef]
- K. Y. Chau, T. Huang, M. Moslehpour, W. Khan, Q. A. Nisar, and M. Haris, “Opening a new horizon in green HRM practices with big data analytics and its analogy to circular economy performance: an empirical evidence,” Environ. Dev. Sustain., vol. 26, no. 5, pp. 12133–12162, 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-023-03725-9. [CrossRef]
- S. H. Bhatti, A. Ahmed, A. Ferraris, W. M. Hirwani Wan Hussain, and S. F. Wamba, “Big data analytics capabilities and MSME innovation and performance: A double mediation model of digital platform and network capabilities,” Ann. Oper. Res., 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-022-05002-w. [CrossRef]
- L. J. Zheng, J. Z. Zhang, H. Wang, and J. F. L. Hong, “Exploring the impact of Big Data Analytics Capabilities on the dual nature of innovative activities in MSMEs: A Data-Agility-Innovation Perspective,” Ann. Oper. Res., 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-022-04800-6. [CrossRef]
- M. Kavre, B. Gardas, V. Narwane, N. Jafari Navimipour, and S. Yalcin, “Evaluating the effect of human factors on big data analytics and cloud of things adoption in the manufacturing micro, small, and medium enterprises,” IT Prof., vol. 24, no. 4, pp. 17–26, 01 July-Aug 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/MITP.2022.3156956. [CrossRef]
- P. M. Hartmann, M. Zaki, N. Feldmann, and A. Neely, “Capturing value from big data – a taxonomy of data-driven business models used by start-up firms,” Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manage., vol. 36, no. 10, pp. 1382–1406, 2016, doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/IJOPM-02-2014-0098. [CrossRef]
- A. Rajala and T. Hautala-Kankaanpää, “Exploring the effects of SMEs’ platform-based digital connectivity on firm performance – the moderating role of environmental turbulence,” J. Bus. Ind. Mark., vol. 38, no. 13, pp. 15–30, 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/JBIM-01-2022-0024. [CrossRef]
- S. Akter, S. F. Wamba, A. Gunasekaran, R. Dubey, and S. J. Childe, “How to improve firm performance using big data analytics capability and business strategy alignment?,” Int. J. Prod. Econ., vol. 182, pp. 113–131, 2016, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2016.08.018. [CrossRef]
- S. Verma and S. S. Bhattacharyya, “Perceived strategic value-based adoption of Big Data Analytics in emerging economy: A qualitative approach for Indian firms,” J. Enterp. Inf. Manag., vol. 30, no. 3, pp. 354–382, 2017, doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/JEIM-10-2015-0099. [CrossRef]
- Bartosik-Purgat, M. and Ratajczak-Mrożek, M.., “Big Data Analysis as a source of companies’ competitive advantage: A review,” Entrep. Bus. Econ. Rev., vol. 6, no. 4, pp. 197–215, 2018.
- N. A. K. Dam, T. Le Dinh, and W. Menvielle, “A systematic literature review of big data adoption in internationalization,” J. Mark. Anal., vol. 7, no. 3, pp. 182–195, 2019, doi: https://doi.org/10.1057/s41270-019-00054-7. [CrossRef]
- A. Retnowardhani, W. Sardjono, and Y. S. Triana, “Review study of business intelligence to support strategic decision making,” in 2019 International Conference on Electrical Engineering and Informatics (ICEEI), pp. 19–24, 2019, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICEEI47359.2019.8988820. [CrossRef]
- S. A. Mohd Selamat, S. Prakoonwit, and W. Khan, “A review of data mining in knowledge management: applications/findings for transportation of small and medium enterprises,” SN Appl. Sci., vol. 2, no. 5, 2020, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-020-2589-3. [CrossRef]
- A. Rumanti, A. F. Rizana, F. Ramadhan, and R. Reynaldo, “The impact of open innovation preparation on organizational performance: A systematic literature review,” IEEE Access, vol. 9, pp. 126952–126966, 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3111091. [CrossRef]
- Z. Inamdar, R. Raut, V. S. Narwane, B. Gardas, B. Narkhede, and M. Sagnak, “A systematic literature review with bibliometric analysis of big data analytics adoption from period 2014 to 2018,” J. Enterp. Inf. Manag., vol. 34, no. 1, pp. 101–139, 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/JEIM-09-2019-0267. [CrossRef]
- M. Koot, M. R. K. Mes, and M. E. Iacob, “A systematic literature review of supply chain decision making supported by the Internet of Things and Big Data Analytics,” Comput. Ind. Eng., vol. 154, no. 107076, p. 107076, 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2020.107076. [CrossRef]
- M. H. Chuah and R. Thurusamry, “Challenges of big data adoption in Malaysia SMEs based on Lessig’s modalities: A systematic review,” Cogent Bus. Manag., vol. 8, no. 1, 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/23311975.2021.1968191. [CrossRef]
- PhD Candidate, Putra Business School (AACSB-Accredited) University of Putra Malaysia (UPM) Malaysia, A. Islam, S. Abd Wahab, Professor (Director-Thesis Based Programme) University of Putra Malaysia (UPM) Putra Business School (AACSB-Accredited), A. S. Abdul Latiff, and Senior Lecturer University of Putra Malaysia (UPM) Putra Business School (AACSB-Accredited), “Annexing a smart sustainable business growth model for small and medium enterprises (SMEs),” World J. Entrep. Manag. Sustain. Dev., vol. 18, no. 2, pp. 22–46, 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.47556/J.WJEMSD.18.2.2022.2. [CrossRef]
- R. Jiwat and Z. (leo) Zhang, “Adopting big data analytics (BDA) in business-to-business (B2B) organizations – Development of a model of needs,” J. Eng. Technol. Manag., vol. 63, no. 101676, p. 101676, 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jengtecman.2022.101676. [CrossRef]
- C. Li, Y. Chen, and Y. Shang, “A review of industrial big data for decision making in intelligent manufacturing,” Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J., vol. 29, no. 101021, p. 101021, 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jestch.2021.06.001. [CrossRef]
- S. Aldossari, U. A. Mokhtar, and A. T. Abdul Ghani, “Factor influencing the adoption of Big Data Analytics: A systematic literature and experts review,” SAGE Open, vol. 13, no. 4, 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.1177/21582440231217902. [CrossRef]
- R. Mishra and R. K. Singh, “A systematic literature review on supply chain resilience in SMEs: learnings from COVID-19 pandemic,” Int. J. Qual. Reliab. Manag., vol. 40, no. 5, pp. 1172–1202, 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/IJQRM-03-2022-0108. [CrossRef]
- J. R. Saura, D. Palacios-Marqués, and D. Ribeiro-Soriano, “Digital marketing in SMEs via data-driven strategies: Reviewing the current state of research,” J. Small Bus. Manage., vol. 61, no. 3, pp. 1278–1313, 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/00472778.2021.1955127. [CrossRef]
- Ali, N. D. K. Nguyen, and S. Gupta, “A multi-disciplinary review of enablers and barriers to Cloud ERP implementation and innovation outcomes,” J. Enterp. Inf. Manag., vol. 36, no. 5, pp. 1209–1239, 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/JEIM-08-2022-0273. [CrossRef]
- R. Martínez-Peláez et al., “Role of digital transformation for achieving sustainability: Mediated role of stakeholders, key capabilities, and technology,” Sustainability, vol. 15, no. 14, p. 11221, 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/su151411221. [CrossRef]
- H. Y. Yeo and C. H. Ong, “Industry 4.0 competencies and sustainable manufacturing performance in the context of manufacturing SMEs: A systematic literature review,” SAGE Open, vol. 14, no. 3, 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.1177/21582440241271263. [CrossRef]
- R. R. Panigrahi, A. K. Shrivastava, and P. K. Kapur, “Impact of inventory management practices on the operational performances of SMEs: review and future research directions,” Int. J. Syst. Assur. Eng. Manag., vol. 15, no. 5, pp. 1934–1955, 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-023-02216-4. [CrossRef]
- N. S. Natrajan, R. Sanjeev, and R. U. Jain, “Sustainability in small and medium enterprises: A circular economy approach using cloud computing,” Bus. Strategy Dev., vol. 7, no. 2, 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/bsd2.370. [CrossRef]
- G. Narkhede, V. Dohale, and Y. Mahajan, “Darker side of industry 4.0 and its impact on triple-bottom-line sustainability,” Sustain. Dev., 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/sd.3009. [CrossRef]
- M. C. Solano and J. C. Cruz, “Integrating analytics in enterprise systems: A systematic literature review of impacts and innovations,” Adm. Sci., vol. 14, no. 7, p. 138, 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/admsci14070138. [CrossRef]
- A. M. Komolafe et al., “Harnessing business analytics for gaining Competitive Advantage in Emerging Markets: A systematic review of approaches and outcomes,” Int. j. manag. entrep. res, vol. 6, no. 3, pp. 838–862, 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.30574/ijsra.2024.11.2.0683. [CrossRef]
- A. Ferraris, A. Mazzoleni, A. Devalle, and J. Couturier, “Big data analytics capabilities and knowledge management: impact on firm performance,” Manag. Decis., vol. 57, no. 8, pp. 1923–1936, 2019, doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/MD-07-2018-0825. [CrossRef]
- M. F. Mubarak, F. A. Shaikh, M. Mubarik, K. A. Samo, S. Mastoi. “The impact of digital transformation on business performance: a study of Pakistani SMEs” Eng. Tech. App. Sci. Res., vol. 9, no. 6, pp. 5056-5061, 2019, doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.48084/etasr.3201. [CrossRef]
- T. Justy, E. Pellegrin-Boucher, D. Lescop, J. Granata, and S. Gupta, “On the edge of Big Data: Drivers and barriers to data analytics adoption in SMEs,” Technovation, vol. 127, no. 102850, p. 102850, 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.technovation.2023.102850. [CrossRef]
- M. K. A. Al-Azzam, M. A. M. Al-Alwan, M. M. Alqahtani, S. I. S. Al-Hawary, A. F. Alserhan. “Determinants of behavioral intention to use big data analytics (BDA) on the information and communication technologies (ICT) SMEs in Jordan.” DSL, vol. 12, pp. 605-616, 2023, doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5267/j.dsl.2023.4.004. [CrossRef]
- M. I. Baig, E. Yadegaridehkordi, and M. H. Nizam Bin Md Nasir, “Influence of big data adoption on sustainable marketing and operation of SMEs: a hybrid approach of SEM-ANN,” Manag. Decis., vol. 61, no. 7, pp. 2231–2253, 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/MD-06-2022-0778. [CrossRef]
- S. A. Mohd Selamat, S. Prakoonwit, and W. Khan, “A review of data mining in knowledge management: applications/findings for transportation of small and medium enterprises,” SN Appl. Sci., vol. 2, no. 5, 2020, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-020-2589-3. [CrossRef]
- Song et al., “The source of SMEs’ competitive performance in COVID-19: Matching big data analytics capability to business models,” Inf. Syst. Front., vol. 24, no. 4, pp. 1167–1187, 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-022-10287-0. [CrossRef]
- P. Maroufkhani, M.-L. Tseng, M. Iranmanesh, W. K. W. Ismail, and H. Khalid, “Big data analytics adoption: Determinants and performances among small to medium-sized enterprises,” Int. J. Inf. Manage., vol. 54, no. 102190, p. 102190, 2020, doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.elerap.2019.100921. [CrossRef]
- E. Yadegaridehkordi et al., “The impact of big data on firm performance in hotel industry,” Electron. Commer. Res. Appl., vol. 40, no. 100921, p. 100921, 2020, doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/09537325.2020.1772966. [CrossRef]
- M. Nasiri, J. Ukko, M. Saunila, T. Rantala, and H. Rantanen, “Digital-related capabilities and financial performance: the mediating effect of performance measurement systems,” Technol. Anal. Strat. Manag., vol. 32, no. 12, pp. 1393–1406, 2020, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2020.102190. [CrossRef]
- M. Nasrollahi, J. Ramezani, and M. Sadraei, “The impact of big data adoption on SMEs’ performance,” Big Data Cogn. Comput., vol. 5, no. 4, p. 68, 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc5040068. [CrossRef]
- A. M. Asiri, S. A. Al-Somali, and R. O. Maghrabi, “The integration of sustainable technology and big data analytics in Saudi Arabian SMEs: A path to improved business performance,” Sustainability, vol. 16, no. 8, p. 3209, 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/su16083209. [CrossRef]
- A.-R. H. Tawil, M. Mohamed, X. Schmoor, K. Vlachos, and D. Haidar, “Trends and challenges towards effective data-driven decision making in UK Small and Medium-sized Enterprises: Case studies and lessons learnt from the analysis of 85 Small and Medium-sized Enterprises,” Big Data Cogn. Comput., vol. 8, no. 7, p. 79, 2024, doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/bdcc8070079. [CrossRef]
- K. Mehmood, F. Jabeen, M. Rashid, S. M. Alshibani, A. Lanteri, and G. Santoro, “Unraveling the transformation: the three-wave time-lagged study on big data analytics, green innovation and their impact on economic and environmental performance in manufacturing SMEs,” Eur. J. Innov. Manag., 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/EJIM-10-2023-0903. [CrossRef]
- S. A. R. Khan, D. I. Godil, C. J. C. Jabbour, S. Shujaat, A. Razzaq, and Z. Yu, “Green data analytics, blockchain technology for sustainable development, and sustainable supply chain practices: evidence from small and medium enterprises,” Ann. Oper. Res., 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-021-04275-x. [CrossRef]
- WIBOWO, Sampurno, Yuyus SURYANA, S. A. R. I. Diana, and Umi KALTUM. "Marketing performance and big data use during the COVID-19 pandemic: A case study of SMEs in Indonesia." The Journal of Asian Finance, Economics and Business (JAFEB) 8, no. 7 pp. 571-578, 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-021-04275-x. [CrossRef]
- P. Maroufkhani, W. K. Wan Ismail, and M. Ghobakhloo, “Big data analytics adoption model for small and medium enterprises,” J. Sci. Technol. Policy Manag., vol. 11, no. 4, pp. 483–513, 2020, doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/JSTPM-02-2020-0018. [CrossRef]
- S. A. Mohd Selamat, S. Prakoonwit, R. Sahandi, W. Khan, and M. Ramachandran, “Big data analytics—A review of data-mining models for small and medium enterprises in the transportation sector,” Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Data Min. Knowl. Discov., vol. 8, no. 3, 2018, doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/widm.1238. [CrossRef]
- Q. Shabbir and S. B. W. Gardezi, “Application of big data analytics and organizational performance: the mediating role of knowledge management practices,” J. Big Data, vol. 7, no. 1, 2020, doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40537-020-00317-6. [CrossRef]
- J. Q. Dong and C.-H. Yang, “Business value of big data analytics: A systems-theoretic approach and empirical test,” Inf. Manag., vol. 57, no. 1, p. 103124, 2020, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.im.2018.11.001. [CrossRef]
- E. S. Kim, Y. Choi, and J. Byun, “Big Data analytics in government: Improving decision making for R&D investment in Korean SMEs,” Sustainability, vol. 12, no. 1, p. 202, 2019, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/su12010202. [CrossRef]
- D. Sen, M. Ozturk, and O. Vayvay, “An overview of big data for growth in SMEs,” Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci., vol. 235, pp. 159–167, 2016, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2016.11.011. [CrossRef]
- C. A. Ardagna, P. Ceravolo, and E. Damiani, “Big data analytics as-a-service: Issues and challenges,” in 2016 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data), pp. 3638–3644, 2016, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/BigData.2016.7841029. [CrossRef]
- S. Coleman, R. Göb, G. Manco, A. Pievatolo, X. Tort-Martorell, and M. S. Reis, “How can SMEs benefit from big data? Challenges and a path forward,” Qual. Reliab. Eng. Int., vol. 32, no. 6, pp. 2151–2164, 2016, doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/qre.2008. [CrossRef]
- R. S. Kalan and M. O. Unalir, “Leveraging big data technology for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs),” in 2016 6th International Conference on Computer and Knowledge Engineering (ICCKE), pp. 1–6, 2016, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCKE.2016.7802106. [CrossRef]
- R. Y. Zhong, S. T. Newman, G. Q. Huang, and S. Lan, “Big Data for supply chain management in the service and manufacturing sectors: Challenges, opportunities, and future perspectives,” Comput. Ind. Eng., vol. 101, pp. 572–591, 2016, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2016.07.013. [CrossRef]
- M. Asad, M. U. Asif, A. A. Khan, Z. Allam, and M. S. Satar, “Synergetic effect of entrepreneurial orientation and big data analytics for competitive advantage and SMEs performance,” in 2022 International Conference on Decision Aid Sciences and Applications (DASA), pp. 1192–1196, 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/DASA54658.2022.9765158. [CrossRef]
- T. Hongyun et al., “Navigating the digital landscape: examining the interdependencies of digital transformation and big data in driving SMEs’ innovation performance,” Kybernetes, 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/K-07-2023-1183. [CrossRef]
- T. T. Le, “Linking big data, sustainable supply chain management and corporate performance: the moderating role of circular economy thinking,” Int. J. Logist. Manag., vol. 34, no. 3, pp. 744–771, 2023, https://doi.org/10.1108/IJLM-01-2022-0011. [CrossRef]
- Asad, M. U. Asif, L. J. A. Bakar, and N. Altaf, “Entrepreneurial orientation, big data analytics, and SMEs performance under the effects of environmental turbulence,” in 2021 International Conference on Data Analytics for Business and Industry (ICDABI), pp. 144–148, 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDABI53623.2021.9655870. [CrossRef]
- A. Lutfi et al., “Drivers and impact of big data analytic adoption in the retail industry: A quantitative investigation applying structural equation modeling,” J. Retail. Consum. Serv., vol. 70, no. 103129, p. 103129, 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jretconser.2022.103129. [CrossRef]
- H. Song, M. Li, and K. Yu, “Big data analytics in digital platforms: how do financial service providers customise supply chain finance?,” Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manage., vol. 41, no. 4, pp. 410–435, 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/IJOPM-07-2020-0485. [CrossRef]
- H. Saleem, Y. Li, Z. Ali, M. Ayyoub, Y. Wang, and A. Mehreen, “Big data use and its outcomes in supply chain context: the roles of information sharing and technological innovation,” J. Enterp. Inf. Manag., vol. 34, no. 4, pp. 1121–1143, 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/JEIM-03-2020-0119. [CrossRef]
- A. I. Aljumah, M. T. Nuseir, and M. M. Alam, “Organizational performance and capabilities to analyze big data: do the ambidexterity and business value of big data analytics matter?” Bus. Proc.management J., vol. 27, no. 4, pp. 1088–1107, 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/BPMJ-07-2020-0335. [CrossRef]
- H. Han and S. Trimi, “Towards a data science platform for improving SME collaboration through Industry 4.0 technologies,” Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change, vol. 174, no. 121242, p. 121242, 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2021.121242. [CrossRef]
- S. Verma, V. Singh, and S. S. Bhattacharyya, “Do big data-driven HR practices improve HR service quality and innovation competency of SMEs,” Int. J. Organ. Anal., vol. 29, no. 4, pp. 950–973, 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/IJOA-04-2020-2128. [CrossRef]
- R. Dahiya, S. Le, J. K. Ring, and K. Watson, “Big data analytics and competitive advantage: the strategic role of firm-specific knowledge,” J. Strat. Manag., vol. 15, no. 2, pp. 175–193, 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/JSMA-08-2020-0203. [CrossRef]
- A. Behl, J. Gaur, V. Pereira, R. Yadav, and B. Laker, “Role of big data analytics capabilities to improve sustainable competitive advantage of MSME service firms during COVID-19 – A multi-theoretical approach,” J. Bus. Res., vol. 148, pp. 378–389, 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2022.05.009. [CrossRef]
- A. Bertello, A. Ferraris, S. Bresciani, and P. De Bernardi, “Big data analytics (BDA) and degree of internationalization: the interplay between governance of BDA infrastructure and BDA capabilities,” J. Manag. Gov., vol. 25, no. 4, pp. 1035–1055, 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10997-020-09542-w. [CrossRef]
- N. R. Vajjhala and E. Ramollari, “Big data using cloud computing - opportunities for small and medium-sized enterprises,” Eur. J. Econ. Bus. Stud., vol. 4, no. 1, p. 129, 2016, doi: https://doi.org/10.26417/ejes.v4i1.p129-137. [CrossRef]
- S. K. Mangla, R. Raut, V. S. Narwane, Z. (justin) Zhang, and P. Priyadarshinee, “Mediating effect of big data analytics on project performance of small and medium enterprises,” J. Enterp. Inf. Manag., vol. 34, no. 1, pp. 168–198, 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/JEIM-12-2019-0394. [CrossRef]
- A. Lutfi et al., “Antecedents of big data analytic adoption and impacts on performance: Contingent effect,” Sustainability, vol. 14, no. 23, p. 15516, 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/su142315516. [CrossRef]
- A. Lutfi et al., “Factors influencing the adoption of big data analytics in the digital transformation era: Case study of Jordanian SMEs,” Sustainability, vol. 14, no. 3, p. 1802, 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/su14031802. [CrossRef]
- P. Maroufkhani, M. Iranmanesh, and M. Ghobakhloo, “Determinants of big data analytics adoption in small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs),” Ind. Manag. Data Syst., vol. 123, no. 1, pp. 278–301, 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/IMDS-11-2021-0695. [CrossRef]
- T. Wessels and O. Jokonya, “Factors affecting the Adoption of Big Data as a Service in SMEs,” Procedia Comput. Sci., vol. 196, pp. 332–339, 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2021.12.021. [CrossRef]
- M. Iranmanesh, K. H. Lim, B. Foroughi, M. C. Hong, and M. Ghobakhloo, “Determinants of intention to adopt big data and outsourcing among SMEs: organisational and technological factors as moderators,” Manag. Decis., vol. 61, no. 1, pp. 201–222, 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/MD-08-2021-1059. [CrossRef]
- M. Sorger, B. J. Ralph, K. Hartl, M. Woschank, and M. Stockinger, “Big Data in the metal processing value chain: A systematic digitalization approach under special consideration of standardization and SMEs,” Appl. Sci. (Basel), vol. 11, no. 19, p. 9021, 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/app11199021. [CrossRef]
- S. Chatterjee, R. Chaudhuri, M. Shah, and P. Maheshwari, “Big data driven innovation for sustaining SME supply chain operation in post COVID-19 scenario: Moderating role of SME technology leadership,” Comput. Ind. Eng., vol. 168, no. 108058, p. 108058, 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2022.108058. [CrossRef]
- P. Chaudhary, B. B. Gupta, X. Chang, N. Nedjah, and K. T. Chui, “Enhancing big data security through integrating XSS scanner into fog nodes for SMEs gain,” Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change, vol. 168, no. 120754, p. 120754, 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2021.120754. [CrossRef]
- M. V. Ciasullo, R. Montera, and A. Douglas, “Building SMEs’ resilience in times of uncertainty: the role of big data analytics capability and co-innovation,” Transform. Gov. People Proc.Policy, vol. 16, no. 2, pp. 203–217, 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/TG-07-2021-0120. [CrossRef]
- D. Radicic and S. Petković, “Impact of digitalization on technological innovations in small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs),” Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change, vol. 191, no. 122474, p. 122474, 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2023.122474. [CrossRef]
- S. Wang and H. Wang, “Big data for small and medium-sized enterprises (SME): a knowledge management model,” J. Knowl. Manag., vol. 24, no. 4, pp. 881–897, 2020, doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/JKM-02-2020-0081. [CrossRef]
- A. Topalović and A. Azzini, “Data mining applications in SMEs: An Italian perspective,” Bus. Syst. Res. J., vol. 11, no. 3, pp. 127–146, 2020.
- S. Bag, L. C. Wood, L. Xu, P. Dhamija, and Y. Kayikci, “Big data analytics as an operational excellence approach to enhance sustainable supply chain performance,” Resour. Conserv. Recycl., vol. 153, no. 104559, p. 104559, 2020, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2019.104559. [CrossRef]
- H.-K. Kim, W.-H. So, and S.-M. Je, “A big data framework for network security of small and medium enterprises for future computing,” J. Supercomput., vol. 75, no. 6, pp. 3334–3367, 2019, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-019-02815-8. [CrossRef]
- S. Karim, A. Al-Tawara, E. Gide, and R. Sandu, “Is big data too big for SMEs in Jordan?,” in 2017 8th International Conference on Information Technology (ICIT), pp. 914–922, 2017, doi: 10.1109/ICITECH.2017.8079968. [CrossRef]
- M. Iqbal, S. H. A. Kazmi, A. Manzoor, A. R. Soomrani, S. H. Butt, and K. A. Shaikh, “A study of big data for business growth in SMEs: Opportunities & challenges,” in 2018 International Conference on Computing, Mathematics and Engineering Technologies (iCoMET), pp. 1–7, 2017, doi: 10.1109/ICOMET.2018.8346368. [CrossRef]
- G. Vitale, S. Cupertino, and A. Riccaboni, “Big data and management control systems change: the case of an agricultural SME,” J. Manag. Contr., vol. 31, no. 1–2, pp. 123–152, 2020, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00187-020-00298-w. [CrossRef]
- C. Vitari and E. Raguseo, “Big data analytics business value and firm performance: linking with environmental context,” Int. J. Prod. Res., vol. 58, no. 18, pp. 5456–5476, 2020, doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2019.1660822. [CrossRef]
- E. L. Tien, N. M. Ali, S. Miskon, N. Ahmad, and N. S. Abdullah, “Big data analytics adoption model for Malaysian SMEs,” in Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, Cham: Springer International Publishing, pp. 45–53, 2020, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-33582-3_5. [CrossRef]
- A. Soroka, Y. Liu, L. Han, and M. S. Haleem, “Big data driven customer insights for SMEs in redistributed manufacturing,” Procedia CIRP, vol. 63, pp. 692–697, 2017, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2017.03.319. [CrossRef]
- P. Del Vecchio, A. Di Minin, A. M. Petruzzelli, U. Panniello, and S. Pirri, “Big data for open innovation in SMEs and large corporations: Trends, opportunities, and challenges,” Creat. Innov. Manag., vol. 27, no. 1, pp. 6–22, 2018, doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/caim.12224. [CrossRef]
- L. I. U. Yadi, S. Yuning, Y. U. Jiayue, X. I. E. Yingfa, W. Yiyuan, and Z. Xiaoping, “Big-data-driven model construction and empirical analysis of SMEs credit assessment in China,” Procedia Comput. Sci., vol. 147, pp. 613–619, 2019, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2019.01.205. [CrossRef]
- Y. Liu, A. Soroka, L. Han, J. Jian, and M. Tang, “Cloud-based big data analytics for customer insight-driven design innovation in SMEs,” Int. J. Inf. Manage., vol. 51, no. 102034, p. 102034, 2020, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2019.11.002. [CrossRef]
- A. Muhammad, “A Novel Model of Software Process Improvements for Small and Medium Scale Enterprises by using the Big Data Analytics Approach,” Int. J. Multi. Sci. Eng., vol. 8, no. 3, 2017.
- M. Mohamed and P. Weber, “Trends of digitalization and adoption of big data & analytics among UK SMEs: Analysis and lessons drawn from a case study of 53 SMEs,” in 2020 IEEE International Conference on Engineering, Technology and Innovation (ICE/ITMC), pp. 1–6, 2020, doi: 10.1109/ICE/ITMC49519.2020.9198545. [CrossRef]
- R. C. Härting and A. Sprengel, “Cost-benefit considerations for data analytics - an SME-oriented framework enhanced by a management perspective and the process of idea generation,” Procedia Comput. Sci., vol. 159, pp. 1537–1546, 2019, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2019.09.324. [CrossRef]
- F. Azevedo and J. L. Reis, “Big data analysis in supply chain management in Portuguese SMEs ‘leader excellence,’” in Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, Cham: Springer International Publishing, pp. 621–632, 2019, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-16184-2_59. [CrossRef]
- S. Limpeeticharoenchot, N. Cooharojananone, T. Chanvanakul, N. Tuaycharoen, and K. Atchariyachanvanich, “Innovative mobile application for measuring Big Data maturity: Case of SMEs in Thailand,” pp. 87–106, 2020.
- A. F. Baharuden, O. Isaac, and A. Ameen, “Factors influencing Big Data & Analytics (BD&A) learning intentions with transformational leadership as moderator variable: Malaysian SME perspective,” International Journal of Management and Human Science, vol. 3, no. 1, pp. 10–20, 2019.
- M. Willetts, A. S. Atkins, and C. Stanier, “Barriers to SMEs adoption of big data analytics for competitive advantage,” in 2020 Fourth International Conference On Intelligent Computing in Data Sciences (ICDS), pp. 1–8, 2020, doi: 10.1109/ICDS50568.2020.9268687. [CrossRef]
- P. Upadhyay and A. Kumar, “The intermediating role of organizational culture and internal analytical knowledge between the capability of big data analytics and a firm’s performance,” Int. J. Inf. Manage., vol. 52, no. 102100, p. 102100, 2020, doi: 10.1109/ICDS50568.2020.9268687. [CrossRef]
- J. Choi et al., “Data mining-based variable assessment methodology for evaluating the contribution of knowledge services of a public research institute to business performance of firms,” Expert Syst. Appl., vol. 84, pp. 37–48, 2017, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2020.102100. [CrossRef]
- Scuotto, G. Santoro, S. Bresciani, and M. Del Giudice, “Shifting intra- and inter-organizational innovation processes towards digital business: An empirical analysis of SMEs,” Creat. Innov. Manag., vol. 26, no. 3, pp. 247–255, 2017, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2017.04.057. [CrossRef]
- D. Radicic and S. Petković, “Impact of digitalization on technological innovations in small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs),” Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change, vol. 191, no. 122474, p. 122474, 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/caim.12221. [CrossRef]
- W. Khan, Q. A. Nisar, M. A. Roomi, S. Nasir, U. Awan, and M. Rafiq, “Green human resources management, green innovation and circular economy performance: the role of big data analytics and data-driven culture,” J. Environ. Plan. Manag., vol. 67, no. 10, pp. 2356–2381, 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/09640568.2023.2189544. [CrossRef]
- A. Ciacci and L. Penco, “Business model innovation: harnessing big data analytics and digital transformation in hostile environments,” J. Small Bus. Enterp. Dev., vol. 31, no. 8, pp. 22–46, 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/JSBED-10-2022-0424. [CrossRef]
- T. Cadden, J. Weerawardena, G. Cao, Y. Duan, and R. McIvor, “Examining the role of big data and marketing analytics in SMEs innovation and competitive advantage: A knowledge integration perspective,” J. Bus. Res., vol. 168, no. 114225, p. 114225, 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2023.114225. [CrossRef]
- A. Trubetskaya, A. Ryan, and F. Murphy, “An implementation model for digitisation of visual management to develop a smart manufacturing process,” Int. J. Lean Six Sigma, vol. 15, no. 8, pp. 32–49, 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/IJLSS-07-2022-0156. [CrossRef]
- O. Troisi, A. Visvizi, and M. Grimaldi, “Digitalizing business models in hospitality ecosystems: toward data-driven innovation,” Eur. J. Innov. Manag., vol. 26, no. 7, pp. 242–277, 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/EJIM-09-2022-0540. [CrossRef]
- R. Figueiredo, J. J. Ferreira, M. E. Camargo, and O. Dorokhov, “Applying deep learning to predict innovations in small and medium enterprises (SMEs): the dark side of knowledge management risk,” VINE J. Inf. Knowl. Manag. Syst., vol. 53, no. 5, pp. 941–962, 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/VJIKMS-09-2022-0294. [CrossRef]
- A. Persaud and J. Zare, “Beyond technological capabilities: The mediating effects of analytics culture and absorptive capacity on big data analytics value creation in small- and medium-sized enterprises,” IEEE Trans. Eng. Manage., vol. 71, pp. 7147–7159, 2024, doi: 10.1109/TEM.2023.3249415. [CrossRef]
- T. Hautala-Kankaanpää, “Complementary and contingent value of SMEs’ data capability and supply chain capability in the competitive environment,” Ind. Manag. Data Syst., vol. 123, no. 8, pp. 2128–2149, 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/IMDS-01-2023-0013. [CrossRef]
- H. Bouwman, S. Nikou, and M. de Reuver, “Digitalization, business models, and SMEs: How do business model innovation practices improve performance of digitalizing SMEs?,” Telecomm. Policy, vol. 43, no. 9, p. 101828, 2019, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.telpol.2019.101828. [CrossRef]
- X. Li, Y. Ye, Z. Liu, Y. Tao, and J. Jiang, “FinTech and SME’ performance: Evidence from China,” Econ. Anal. Policy, vol. 81, pp. 670–682, 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eap.2023.12.026. [CrossRef]
- A. Riaz, G. Santoro, K. Ashfaq, F. H. Ali, S. U. Rehman, “Green competitive advantage and SMEs: Is big data the missing link?,” J. Competitiveness, vol. 15, no. 1, 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.7441/joc.2023.01.05. [CrossRef]
- R. Mishra, R. K. Singh, and J. A. Garza-Reyes, “Interplay between absorptive capacity, analytics competence and sustainable economic performance of MSMEs in supply chain: the mediating role of risk resilience,” Ann. Oper. Res., 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-023-05733-4. [CrossRef]
- A. Jalali, S. M. Al Riyami, M. R. Razzak, and H. Suleiman Alqam, “Linking extra-industry network and organization–stakeholder relationships to SMEs performance through absorptive capacity: interaction effect of outsourcing big data analytics,” Bus. Proc.management J., vol. 30, no. 2, pp. 411–434, 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/BPMJ-05-2023-0347. [CrossRef]
- S. Wang, H. Hu, and Z. Zhang, “Market development strategy and process performance of knowledge-intensive SMEs in the epidemic era: a process-oriented perspective,” Bus. Proc.management J., vol. 29, no. 4, pp. 1010–1030, 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/BPMJ-07-2022-0323. [CrossRef]
- B. i, Z. Xu, H. Wu, N. Hong, and M. Skare, “Open innovation: A research framework and case study of Huawei,” Technol. Econ. Dev. Econ., vol. 29, no. 1, pp. 278–306, 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.3846/tede.2023.17843. [CrossRef]
- S. Boubaker, T. D. Q. Le, T. Ngo, and R. Manita, “Predicting the performance of MSMEs: a hybrid DEA-machine learning approach,” Ann. Oper. Res., 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-023-05230-8. [CrossRef]
- Y. Kim et al., “Regional traffic event detection using data crowdsourcing,” Appl. Sci. (Basel), vol. 13, no. 16, p. 9422, 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/app13169422. [CrossRef]
- Kim, H. (2022), "Performance from building smart factories of small- and medium-sized enterprises: the moderating effects of product complexity and company size", International Journal of Operations & Production Management, Vol. 42 No. 10, pp. 1497-1520. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJOPM-10-2021-0654. [CrossRef]



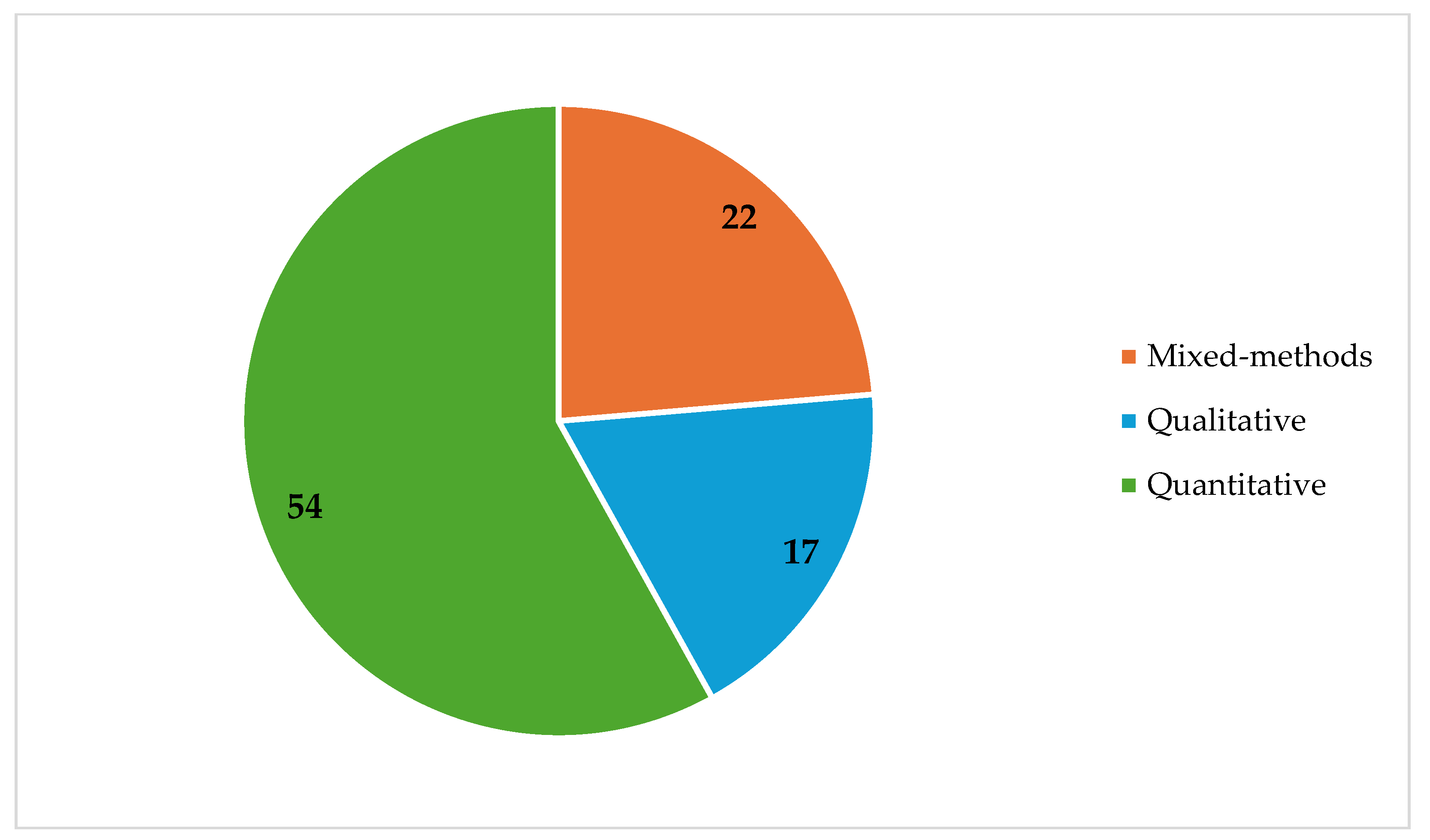
| Ref. | Cites | Year | Contribution | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [21] | 1583 | 2016 | Developed a Big Data Capabilities model integrating management, technology, and talent dimensions, validated through Delphi studies and surveys. | Highlights the importance of aligning analytics capabilities with business strategy; Provides a hierarchical model of Big Data Capabilities. | Lacks detailed empirical evidence on the direct impact of BDC on firm performance; Potentially limited generalizability of findings. |
| [22] | 233 | 2017 | Proposed a Big Data adoption model for Indian firms using PSV and TOE frameworks. | Insights into Big Data adoption in emerging economies; practical for managers. | Limited generalizability; small sample size. |
| [23] | 54 | 2018 | Review of Big Data as a source of competitive advantage | Identifies key benefits and sources of competitive advantage from Big Data; Practical implications for various industries | Requires managerial awareness for effective implementation; Focuses on conceptual benefits without in-depth empirical analysis |
| [24] | 50 | 2019 | The adoption of Big Data in international marketing is still in the early stages, especially in SMEs and developing countries. | Provides insights into the current state of Big Data adoption in internationalization and highlights future research directions, focusing on international marketing. | Limited research on Big Data adoption in international marketing, especially among SMEs and in developing countries. |
| [25] | 3 | 2019 | BI in Decision Support Systems | Enhances decision-making quality, supports strategic decisions, improves efficiency | Requires complex setup, can be costly, data integration challenges |
| [26] | 24 | 2020 | Review of DM and KM in small transport SMEs, proposing new assessment tool. | The framework highlights DM-KM benefits for SMEs, especially in transportation. | Limited empirical evidence on SMEs in transportation; research relies on literature. |
| [27] | 54 | 2021 | Comprehensive identification of the impact of open innovation on company performance through a systematic literature review. | Provides a clear picture of the importance of organizational readiness for open innovation. | Focuses primarily on the management domain, potentially limiting applicability to other fields |
| [28] | 108 | 2021 | Review and bibliometric analysis of Big Data adoption | A broad analysis of big data across sectors; Highlights research gaps and trends | Limited to English studies; May miss relevant research due to keyword selection |
| [29] | 159 | 2021 | IoT and Big Data in Supply Chain Decision-making: A review. | Promotes autonomous decision-making and distributed data processing. | Challenges in fully leveraging IoT-generated data for SCM decisions due to limited autonomy. |
| [30] | 15 | 2021 | A systematic review of Big Data adoption challenges in Malaysian SMEs. | Highlights Lessig's Four Modalities' relevance and SMEs' challenges insights. | Limited to Malaysian SMEs, focus on literature review rather than empirical data. |
| [31] | 25 | 2022 | Analyzed the impact of inventory management on SMEs' operational performance using bibliometric and systematic review methods. | Revealed trends and gaps in inventory management research. Identified emerging themes and technologies. | Limited to articles only in English and from Scopus; some papers only addressed IM or OP separately. |
| [32] | 11 | 2022 | Development of a Big Data Adoption Model in B2B, Four-Category Classification, Systematic Literature Review | Comprehensive, structured approach; Clarifies adoption motives; Broad view identifies research gaps | Lacks practical details, may miss contexts; Too theoretical, may miss nuances; May miss trends, lacks empirical validation |
| [33] | 246 | 2022 | Overview of Big Data in intelligent manufacturing; proposes a decision-making framework. | Provides theoretical basis and practical insights; highlights real-time dynamic perception. | Limited to one year; may not cover emerging technologies beyond 2021. |
| [34] | 3 | 2023 | Examined factors influencing the adoption of Big Data in SMEs, identifying 13 key factors. | Provides a thorough analysis with practical insights, enhances academic understanding, useful for SMEs. | Focuses mainly on SMEs and may overlook some emerging trends or factors. |
| [35] | 19 | 2023 | Analyzed COVID-19 impact on SMEs' supply chains | Provides current insights | Limited to a specific population |
| [36] | 111 | 2023 | Reviewed the use of data science in SMEs' digital marketing strategies. Identified seven state-of-the-art uses and proposed four future research directions. | Provides a comprehensive overview of current data science applications in SMEs; identifies gaps and future research areas. | Limited to existing literature; may not fully capture emerging trends in data science. |
| [37] | 9 | 2023 | A systematic review of Cloud ERP, linking enablers and barriers to innovation outcomes. | A thorough analysis of benefits and challenges, a useful framework, identifies future research areas. | Limited to literature up to February 2022; primarily based on Indian studies; lacks some empirical data. |
| [38] | 161 | 2023 | Identified initial steps for MSMEs in digital transformation | Empowers MSMEs, fosters innovation, and enhances reputation | Requires cultural change and stakeholder management |
| [39] | 0 | 2024 | The paper examines how Industry 4.0 skills impact sustainable manufacturing in SMEs, highlighting rational culture's moderating effect and stressing the need for these competencies to boost sustainability. | The study offers insight into how Industry 4.0 competencies can boost sustainable manufacturing for SMEs, identifies literature gaps, and underscores the moderating role of rational culture. | The study's focus on Malaysian SMEs may limit its broader applicability, and reliance on existing literature might overlook recent Industry 4.0 and sustainable manufacturing trends. |
| [40] | 6 | 2024 | Reviews the impact of inventory management practices on SMEs’ operational performance through bibliometric and systematic analysis. | Highlights key inventory management strategies, identifies research gaps, and provides a roadmap for future studies. | Focuses broadly on inventory management without in-depth analysis of specific practices or technologies. |
| [41] | 2 | 2024 | Examines cloud computing's role in the circular economy for SMEs using TOE and institutional isomorphism frameworks. | A comprehensive framework identifies research gaps and rigorous methodology. | Limited empirical data on cloud computing's impact, and complex framework. |
| [42] | 0 | 2024 | The paper explores the negative implications of Industry 4.0 on sustainability and presents a framework for addressing these issues. | It highlights Industry 4.0's negative impacts like job loss, wage gaps, and environmental issues, and suggests ways to address them. | The emphasis on negative impacts may overshadow Industry 4.0's benefits and relies mainly on Indian literature with limited empirical data. |
| [43] | 1 | 2024 | Systematic review of integrating analytics in Enterprise Information Systems (EISs) | A comprehensive review of global literature; Highlights adoption challenges and strategic impacts; Utilizes PRISMA 2020 and TOE framework | May overlook non-English studies; Limited by selected databases and search terms |
| [44] | 50 | 2024 | Systematic review of business analytics for competitive advantage in emerging markets | Comprehensive analysis of recent literature; Identifies key impacts and challenges | Excludes non-English and non-peer-reviewed sources; Limited to recent publications |
| Proposed systematic review |
Integrates research on Big Data applications for SMEs, and examines different setups, performance indicators, and sustainability for improving business outcomes. Also, introduces innovative regression models to assess various financial aspects of SME operations. | Comprehensive insight highlights research deficiencies, essential for future investigations. | |||
| Criteria | Inclusion | Exclusion |
|---|---|---|
| Topic | Articles must focus on the Impact of Big Data on SME Performance. | Articles unrelated to the Impact of Big Data on SME performance. |
| Research Framework | The articles must comprise a research framework for the Impact of Big Data on SME performance. | Articles with inadequate research framework focusing on the Impact of Big Data on SME performance. |
| Language | Papers written in English | Papers not written in English |
| Publication Period | Publications between 2014 and 2024 | Publications outside 2014 and 2024 |
| Search Terms | Data Bases | Fields | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Big Data OR Data Analytics OR Data Mining |
AND | SMEs OR Small and Medium Enterprises OR Small and Medium-sized Businesses |
AND | Performance OR Business Performance OR Organizational Performance |
AND | Impact OR Effect OR Influence OR Role |
Google Scholar Web of Science SCOPUS |
Title, Abstract Keywords |
| Fields | Description | Selections |
|---|---|---|
| Title | The name of the research article or paper. | None |
| Year | The publication year of the study. | None |
| Online database | The database where the article was sourced. | Google Scholar, SCOPUS, Web of Science |
| Journal name | Represents data as slices of a whole, ideal for showing proportional or percentage distribution of categories. | None |
| Research type | Shows parts of a whole, allowing multiple variables to be represented in the same category for easier comparison. | Article journal, conference paper, book chapter, dissertation, thesis |
| Cites | Plots individual data points on an X and Y axis to explore relationships or correlations between two variables. | None |
| Discipline or subject area | Uses colour coding to represent data intensity or frequency, useful for spotting patterns in large datasets. | Big Data, SME performance, Business Analytics |
| Industry Context | The industry or sector the research is focused on | SME’s, startups, small businesses |
| Geographic location | The region or country where the study was conducted or focused. | None |
| Economic context | The economic environment of the study | Developed, developing |
| Types of Big Data technologies | The specific Big Data technologies used in the research | Hadoop, Spark, NoSQL databases |
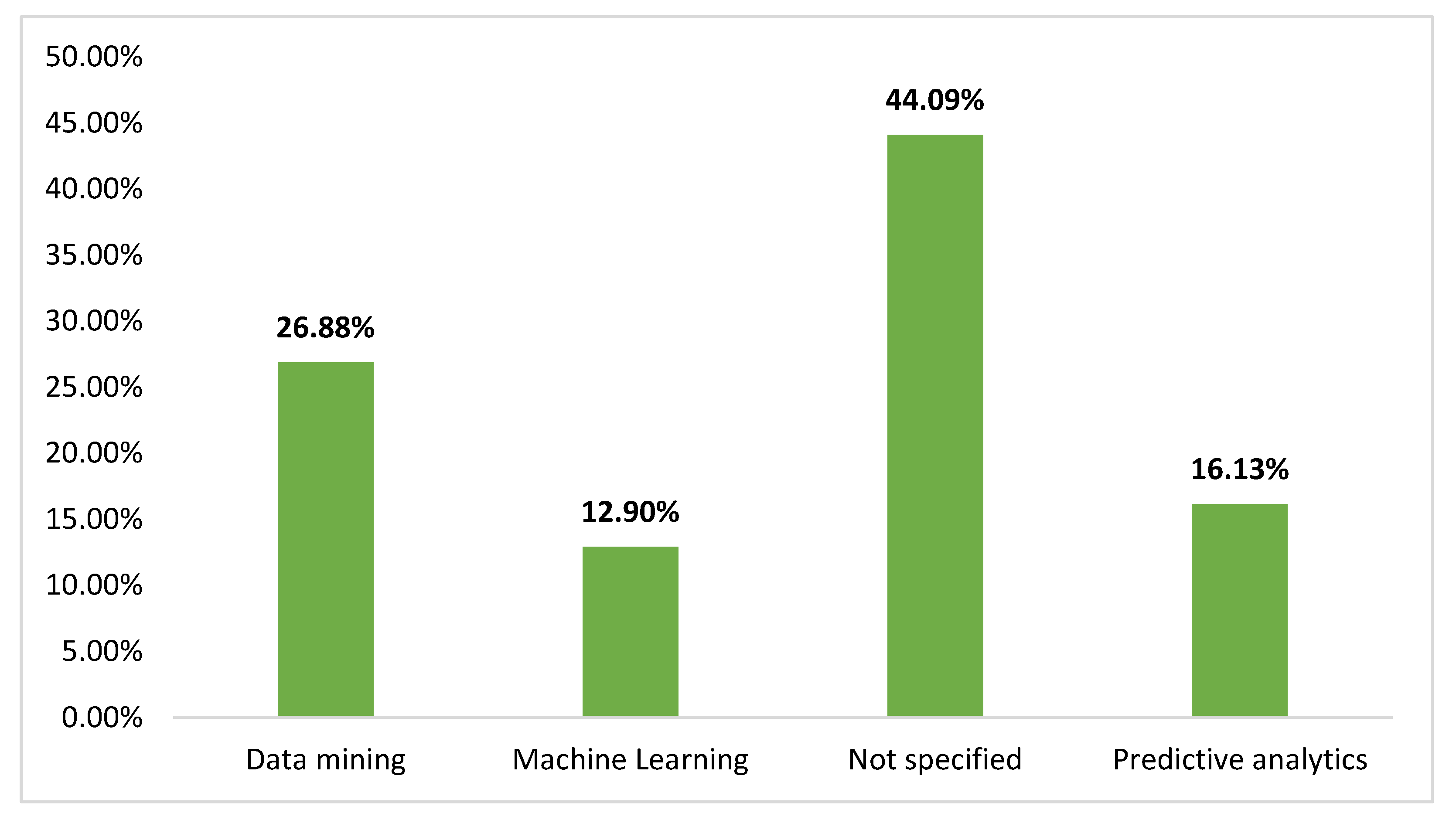
| Big Data analytics techniques | The analytical methods employed | Machine learning, data mining, predictive analytics |
| Technology providers | Companies or organizations providing the technology | Cloudera, Hortonworks, IBM, AWS |
| Technology implementation model | The mode of technology deployment | On-premises, cloud-based, hybrid |
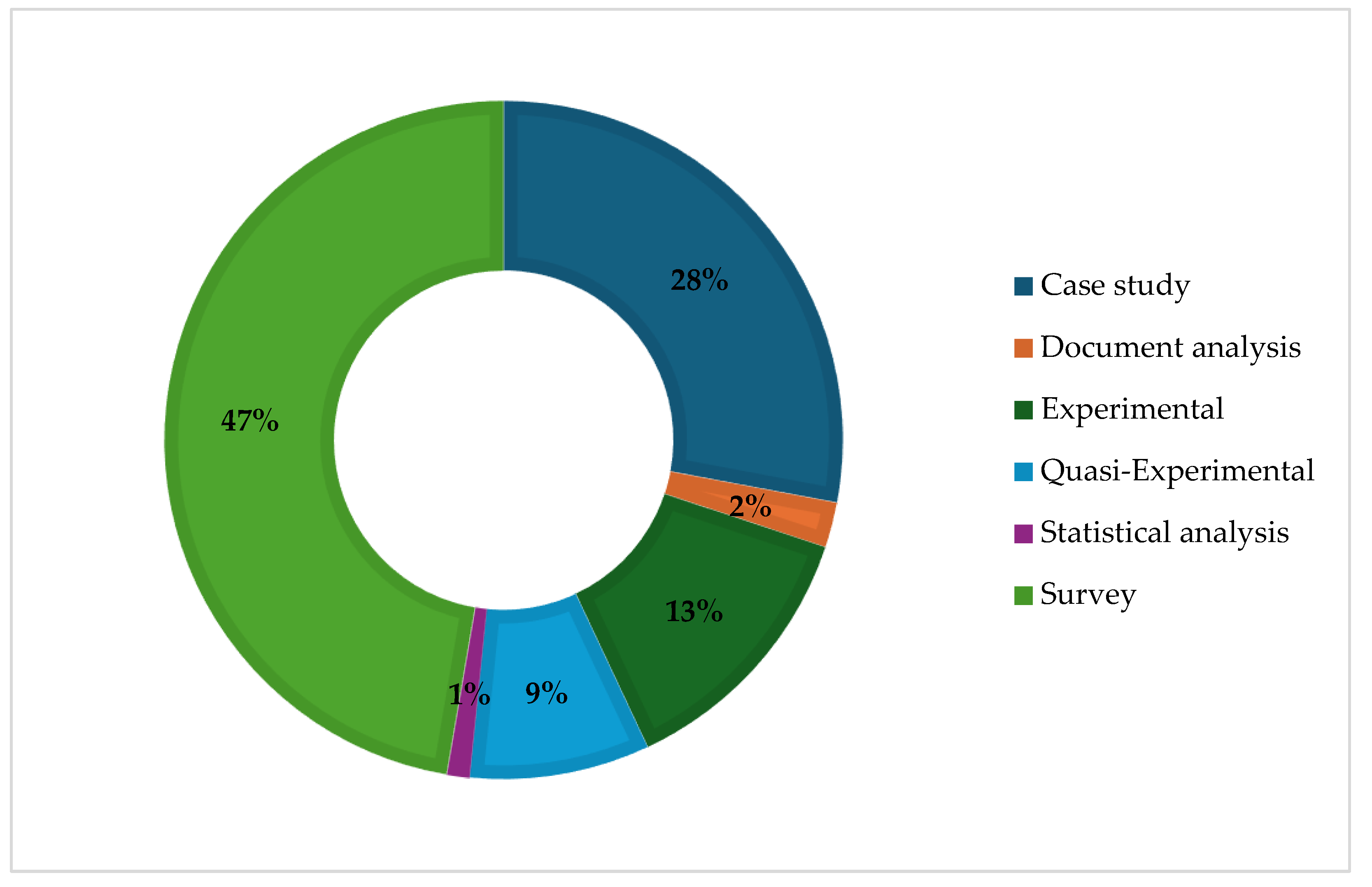
| Research design | The design of the study | Experimental, quasi-experimental, case study, survey |
| Type of Study | The methodology used | Qualitative, quantitative, and Mixed methods |
| Sample size | The number of participants or entities involved in the study. | None |
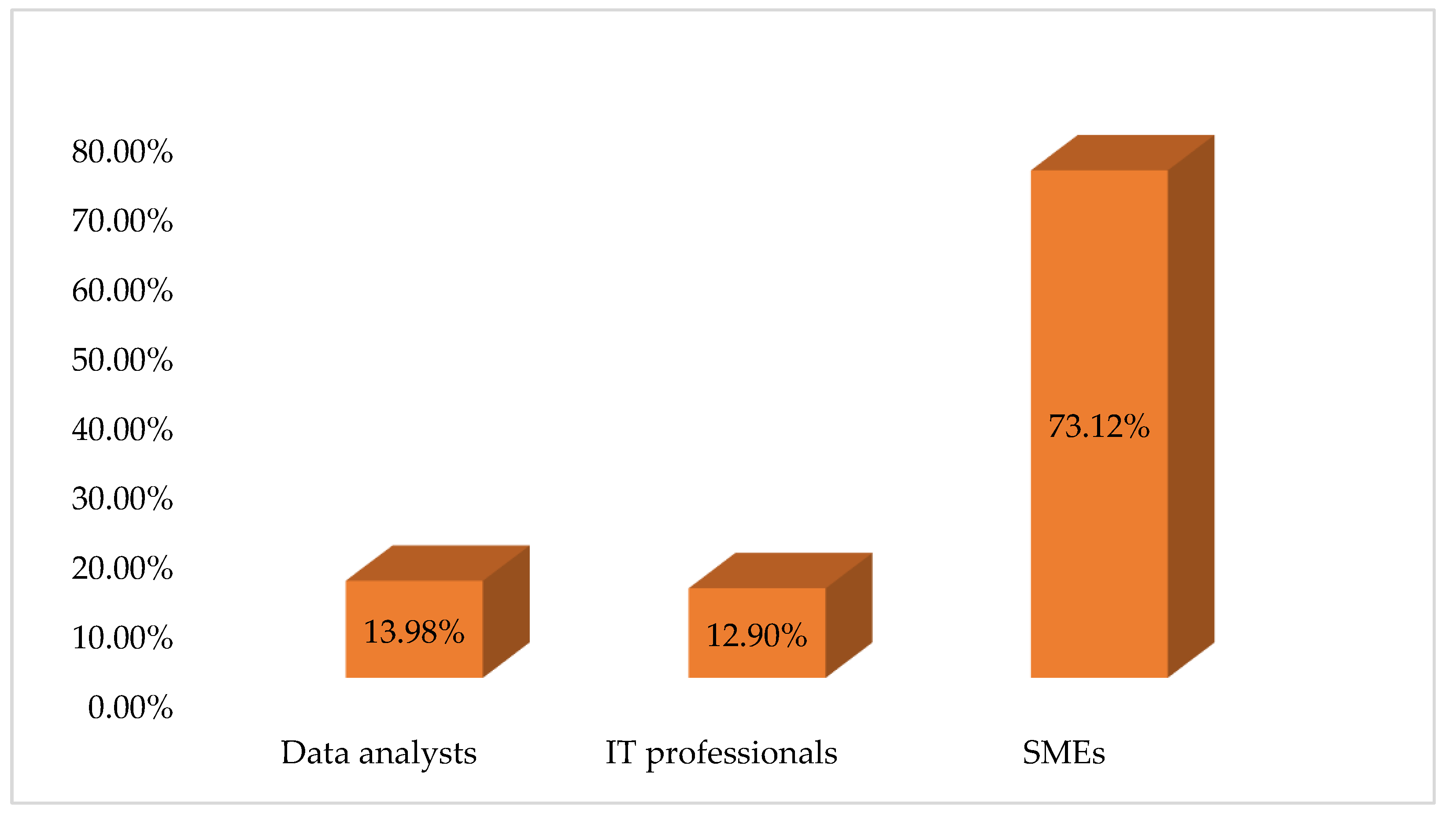
| Sample characteristics | Demographic or specific features of the sample | SME’s, Big Data, IT professionals |
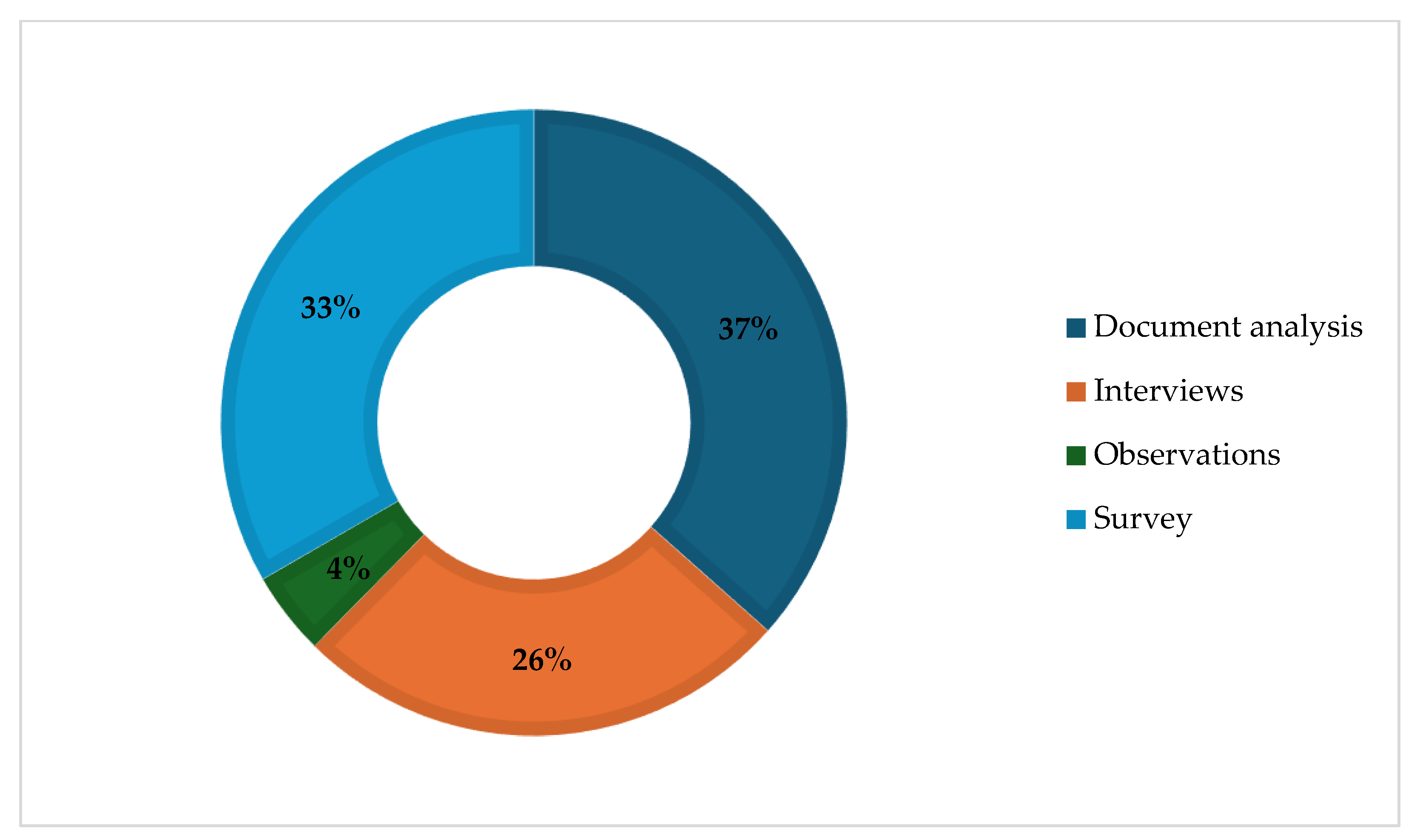
| Data collection methods | Techniques used to gather data | Interviews, surveys, observations, document analysis |
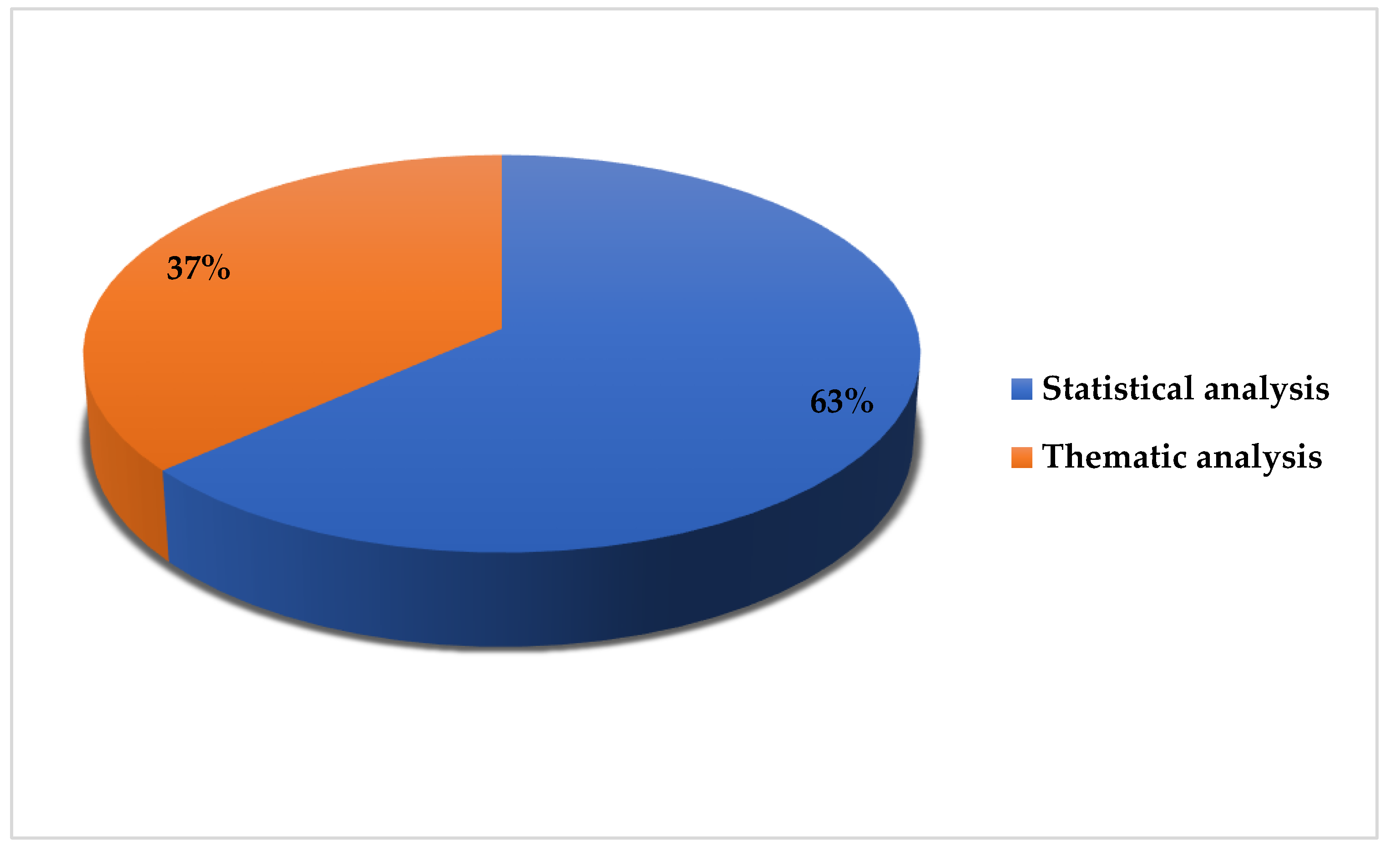
| Big Data techniques | Methods used to analyze the data | Statistical analysis, thematic analysis |
| IT performance metrics | Measures related to technological performance | Data processing speed, scalability, data accuracy |
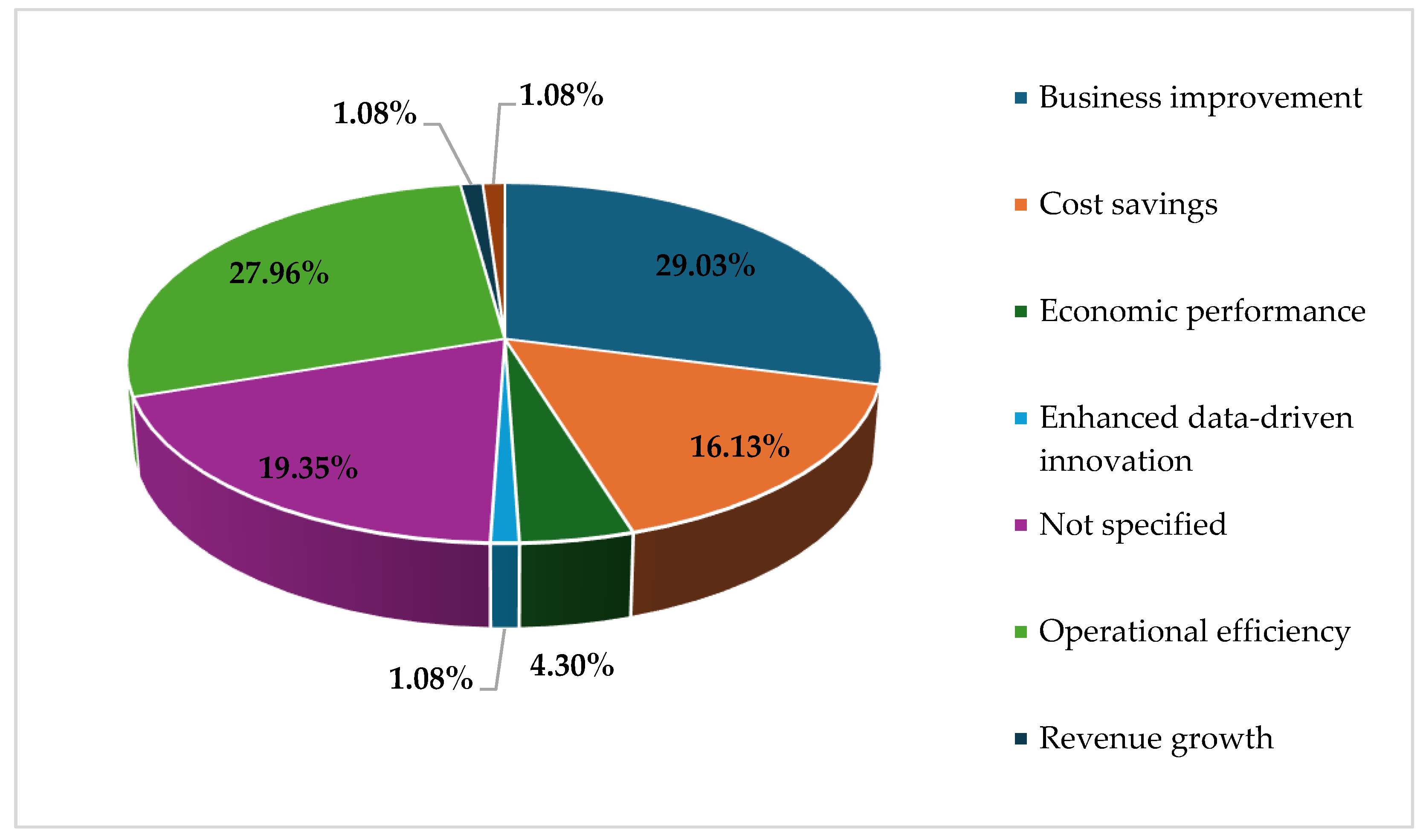
| Business performance | Measures of business outcomes | Operational efficiency, revenue growth, cost savings |
| Organizational outcomes | Results related to the organization | Employee satisfaction, customer satisfaction |
| Long-term impacts | The extended effects of the study findings | Business sustainability, competitive advantage |
| Ref. | Selection (0-4 stars) | Comparability (0-2 stars) | Outcome/Exposure (0-3) | Total Stars | Quality Rating |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [60,101,111] | ★★ | ★ | ★★ | 5 | Low |
| [62,66,68,82,93,98,100,107,109,126,129,135] | ★★ | ★★ | ★★ | 6 | Low-Moderate |
| [50,53,55,58,59,67,70,75,77,80,84,86,87,95,106,110,116,118,119,121,123,124,129,135] | ★★★ | ★★ | ★★ | 7 | Moderate |
| [45,47,48,52,54,56,57,61,63,64,69,71,74,80,85,87,88,93,96,97,104,106,109,113] | ★★★ | ★★ | ★★★ | 8 | Moderate-High |
| [46,49,51,65,72,73,76,78,81,83,92,94,99,102,104,108,115,117,124,130] | ★★★★ | ★★ | ★★★ | 9 | High |
| Chart Type | Purpose | Data Representation Format |
|---|---|---|
| Bar chart | Displays categorical data with rectangular bars, ideal for comparing different categories or variables in a dataset. | Numbers |
| Column chart | Similar to a bar chart, but with vertical bars, it is useful for comparing the frequency or amount of categories. | Numbers |
| Line chart | Shows trends over time by connecting data points with a continuous line. | Numbers |
| Pie chart | Represents data as slices of a whole, ideal for showing proportional or percentage distribution of categories. | Percentages (%) |
| Stacked bar chart | Shows parts of a whole, allowing multiple variables to be represented in the same category for easier comparison. | Numbers and Percentages (%) |
| Scatter plot | Plots individual data points on an X and Y axis to explore relationships or correlations between two variables. | Numbers |
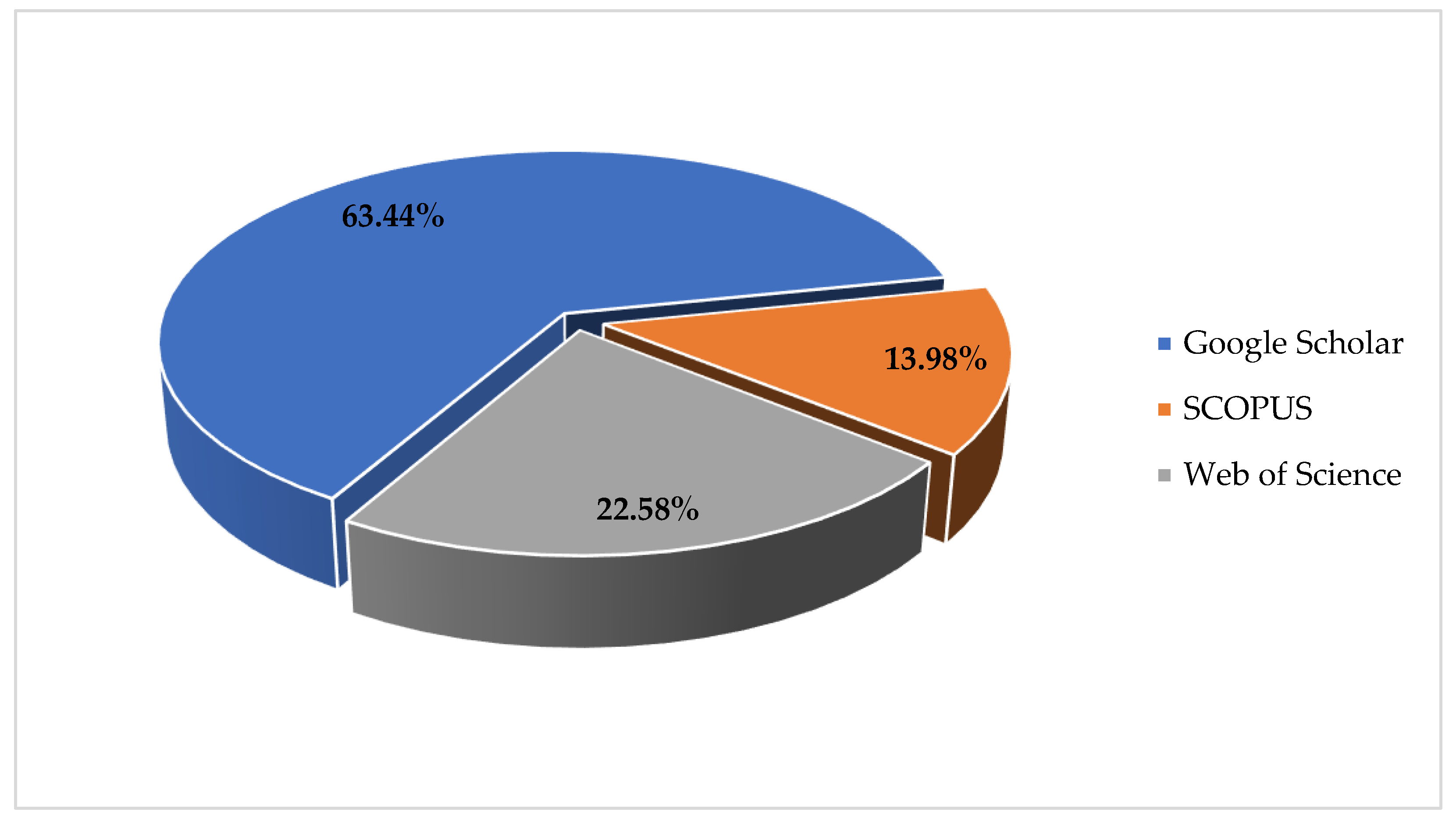
| No. | Online Repository | Number of results |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Google Scholar | 64 |
| 2 | Web of Science | 233 |
| 3 | Scopus | 13 |
| Total | 315 |
| Types of Big Data Technologies | Description |
|---|---|
| Hadoop | A framework developers can use for managing very large datasets in a distributed environment using simple programming models that span multiple clusters. It enables the expansion of additional machines in addition to the storage servers to a hundred thousand with a local processing unit and a local disk. |
| Spark | An analytics system that can process an entire Big Data stack in one tool which includes stream processing, SQL, machine learning, and graph computation processing engine. A particular processing framework that brings data into memory and processes it there instead of inputting data from disk every single time, therefore, it is appropriate for real-time analysis of data. |
| NoSQL Databases | This approach of database management systems is suitable for systems that require support for a variety of data formats such as relational, document, column-oriented, and graph databases. NoSQL databases are built with specific principles in mind, and they are most efficiently used in a Big Data environment with a great deal of data that is advancing in complexity. |
| Questions(Q) | Research Quality Questions |
|---|---|
| Q1 | Are the research objectives explicitly outlined and well-defined? |
| Q2 | Is the research methodology comprehensively detailed? |
| Q3 | Is the impact of Big Data on SME performance thoroughly and clearly analyzed? |
| Q4 | Are the methods for data collection comprehensively detailed and appropriate? |
| Q5 | Do the research findings add to the existing literature on the topic? |
| Ref. | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Q5 | Total | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [45,46,49,51,52,53,56,57,58,61,64,65,71,72,73,74,75,77,80,82,84,85,87,90,107,123,125,127,133] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 100% |
| [47,48,55,59,60,77,79,104,111,112,125,127,129,132] | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 1 | 1 | 4.5 | 90% |
| [54,63,80,92,95,96,97,98,99,100,101,102,103,105,109,124,134,137] | 1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 80% |
| [69,70,86,87,89,90,113,114,137,141] | 1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1 | 3.5 | 70% |
| [50,62,66,68,85,94,106,113,114,115,116,117,118,119,120,121,122,123] | 1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 60% |
| [67,82] | 1 | 0.5 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2.5 | 50% |
| Published Year | Conference Paper | Journal Article |
|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 3 | 2 |
| 2017 | 2 | 6 |
| 2018 | 1 | 2 |
| 2019 | 3 | 7 |
| 2020 | 3 | 13 |
| 2021 | 1 | 11 |
| 2022 | 2 | 10 |
| 2023 | 0 | 15 |
| 2024 | 0 | 12 |
| Category | Ref. | Contribution |
|---|---|---|
| Big Data (BD) and Firm Performance | [45,47,52,53,59,62,72,74,86,87,100,105,126,134] | BD enhances financial, growth, innovation, and environmental performance. Organizational readiness, top management support, and relative advantage are key drivers. Information sharing, competitive pressure, and compatibility influence BD adoption. SMEs in various sectors, including manufacturing, face challenges with adoption but see improved efficiency and effectiveness when overcome. BD-specific absorptive capacity and analytics culture mediate the relationship between technological and human capabilities and strategic business value. |
| Industry 4.0 and Digital Capabilities | [46,50,55,60,63,75,78,91,95,129,133] | The adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies improves operational, financial, and innovation performance, especially in manufacturing and SCM. Digital readiness, top management support, and firm-level R&D activities affect innovation outcomes in SMEs. Digital Twin Technology also shows increased Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE). |
| BD for Decision-Making and Knowledge Management | [48,51,66,67,69,81,96,101,108,109,125] | BD improves decision-making and knowledge management, leading to increased flexibility and productivity. Barriers include a lack of expertise and technological complexity. KM models enhance the strategic use of Big Data, guiding SMEs in effectively leveraging BD for process improvement. Integration of BD into software process improvements also enhances software quality and productivity. Deep learning identifies key factors in knowledge management that foster innovation. |
| BD and Competitive Advantage | [58,61,72,76,81,82,88,94,106,122] | BD enhances competitive advantage through better market performance and supply chain coordination. Entrepreneurial orientation, co-innovation, and environmental factors are important drivers. BD also enables resilience during crises, especially through supply chain optimization. Open innovation strategies and knowledge integration mechanisms also significantly impact competitive positioning and innovation. |
| Adoption Challenges and Barriers to BD | [93,101,113,114,126,135,136,161] | Common barriers include lack of understanding, financial constraints, and insufficient expertise. Technological, organizational, and environmental factors (TOE) influence BD and BDaaS adoption, and organizational readiness moderates adoption decisions. Cloud computing and maturity models can help SMEs overcome these challenges. Outsourcing BD is an emerging solution for smaller firms. |
| BD in Supply Chain Management | [71,75,78,87,92,98,112] | BD enhances supply chain efficiency through improved visibility, real-time adjustments, and sustainability. It is particularly impactful in logistics and during disruptions like COVID-19. Big Data management capabilities contribute to innovative green product development and sustainable supply chain outcomes. Data capability and supply chain capability (SCC) are crucial for leveraging BD effectively. |
| Cloud-Based BD and Scalability | [68,70,84,89,112,115] | Cloud computing offers scalable, cost-effective solutions for SMEs to access BD technologies, improving innovation, productivity, and profitability without heavy infrastructure investments. BDaaS and fog computing also address security and adoption challenges. A novel BDMM developed for SMEs in Thailand achieved positive user acceptance. |
| BD and HR Practices | [80,82] | Big Data improves HR service quality and innovation competency, particularly when organizations are open to change and focus on developing technical HR skills. |
| Big Data-Driven Innovation | [59,73,79,97,118,124] | BD enhances green innovation and performance, contributing to better economic and environmental outcomes. Digital readiness and collaboration in Industry 4.0 environments are key enablers. ICTs for intra- and inter-organizational innovation significantly enhance SMEs’ ability to generate new products and services. Data-driven business models in hospitality also foster innovation and value creation. |
| BD in Financial Services | [77,103,107,129] | BD helps financial services assess SMEs' credit, reduce information asymmetry, and facilitate financing by providing tailored support through digital platforms. The proposed framework integrating financial and non-financial data offers better credit assessments, especially for SMEs with poorer financial conditions. FinTech significantly improves SMEs’ performance by expanding financing scale and reducing financing costs. |
| BD and Project Performance | [85,135] | BD adoption positively influences project performance by mediating relationships between knowledge management, green purchasing, and operational capabilities, especially in manufacturing SMEs. A hybrid approach combining DEA with machine learning techniques improves performance prediction accuracy for MSMEs. |
| BD and Network Security | [93,99] | Security frameworks integrating BDA improve network reliability and data validity, helping SMEs address privacy concerns and prevent breaches using advanced techniques like fog computing and machine learning. |
| BD in Agriculture and SMEs | [102,104] | Big Data impacts both formal and informal management control systems (MCS). Leadership and managerial culture influence how Big Data stabilizes or changes MCS. BD supports sustainable operational practices in agricultural SMEs. |
| BD and Innovation Efficiency | [131,133] | Absorptive capacity directly affects sustainable economic performance and indirectly influences it through risk resilience. Big Data Capabilities (BDCs) positively regulate the relationship between market development strategy and product innovation efficiency. |
| BD in Traffic Systems | [136] | Crowdsourced traffic data combined with machine learning techniques enhances accuracy in traffic event detection, improving effectiveness and reducing costs compared to conventional methods. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





