1. Introduction
It is imperative to achieve precise and prompt mapping of urban land use and land cover through the utilization of a singular satellite dataset [
1]. Combining various data sources in remote sensing enhances the extraction of valuable insights beyond what single sources can achieve, resulting in substantially enhanced accuracy. [
2,
3]. The importance of data fusion techniques has grown significantly [
4], especially in enhancing the reliability and interpretability of remote sensing data. These techniques integrate data of various types, formats, spatial and temporal scales, and other characteristics to generate a cohesive perspective [
5]. Data fusion is increasingly utilized in multiple fields, including remote sensing [
6], robotics, surveillance, and medical science. One of the primary advantages of fusing remote sensing data is the ability to leverage the complementary strengths of different sources and modalities. This integrated approach can minimize noise, fill data gaps, address uncertainties, and generally enhance data quality. For instance, combining optical and radar satellite data can help overcome issues like cloud cover that affect optical data [
7].
In remote sensing, data fusion methods are typically classified into three levels: image, feature, and decision fusion. Image-level fusion involves combining pixel values from multiple images to produce a composite image [
8]. Feature-level fusion extracts relevant features from each data source and merges them into a unified representation before performing classification. Decision-level fusion keeps the features separate, classifies them individually, and then combines the classification results.
Several advanced methods based on Optical-SAR fusion [
9,
10,
11] are available, including Intensity-Hue-Saturation (IHS) Transformation, Principal Component Analysis (PCA), Wavelet Transform, Gram-Schmidt Spectral Sharpening, and Brovey Transform. Unlike Simple Layer Stacking (SLS), these methods involve various transformations, such as intensity, uncorrelated components, frequency bands, the use of panchromatic data, and ratio-based processing. These techniques offer advantages like spatial sharpening, multi-resolution analysis, and dimensionality reduction for specific remote sensing applications. However, applying advanced fusion techniques to urban areas can be challenging due to computational demands and inconsistencies in data.
Simple Layer Stacking (SLS) is a straightforward technique that avoids the need for data transformation or complex mathematical operations. It simply involves stacking layers from different sensors, such as SAR and optical data, to create a composite image. Several studies have examined the effectiveness of SLS in enhancing classification outcomes. For instance, research by [
12] demonstrated that using a simple layer stacking method for data fusion resulted in the highest mapping accuracy when integrating all spectral and backscattering bands, achieving an overall accuracy (OA) of 91.07%. Similarly, [
13] reported that an integrated layer stack of Sentinel radar and VNIR data performed exceptionally well when classified using the SVM algorithm. In another study, [
14] utilized SAR and simulated Sentinel-2 images, resampled and fused through layer stacking, with SVM for classification, though they did not compare their results with existing products. Additionally, [
15] employed SLS to fuse Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 data at the pixel level, highlighting its practical application.
These studies underscore the potential of data fusion, the various types and methods involved, and their advantages in improving classification accuracy. However, there remains a need for innovative approaches to fuse multi-sensor datasets on city, regional, and global scales. Consequently, the current research explores the application of SLS combined with the extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost) algorithm. This study introduces a novel framework that integrates Optical and SAR data through SLS and employs XGBoost to enhance classification accuracy. The innovative aspect of this research lies in the fusion of features extracted from Landsat-8 using modified indices and textures from Sentinel-1 SAR data, aimed at improving classification outcomes.
The study proposes an open-source framework utilizing a multi-sensor dataset to extract impervious surface information in densely populated urban areas. A key innovation in this approach is the integration of Simple Layer Stacking (SLS) with the XGBoost machine learning algorithm, which is designed to significantly enhance classification accuracy, particularly in urban land cover scenarios.
Moreover, while previous research has explored data fusion applications in urban mapping, a noticeable gap exists in comparing these methods with established land cover products. This study seeks to address two additional objectives: (1) to validate the obtained results against global products such as ESA and ESRI, thereby evaluating the effectiveness of the proposed approach, and (2) to analyze Land Surface Temperature (LST) and temperature trends in selected cities, providing valuable insights for future research applications.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Framework of MSFI
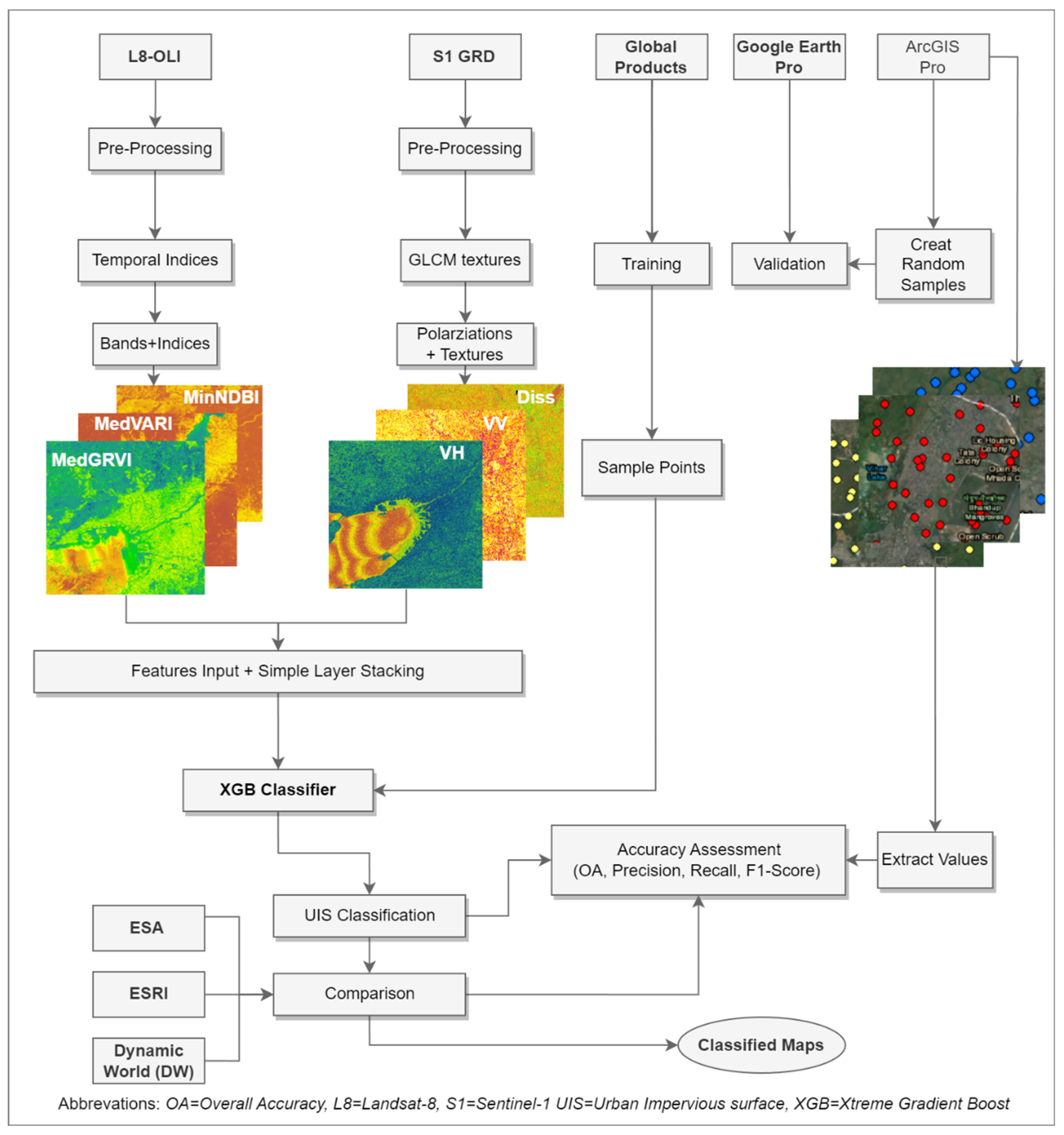
The suggested approach for fusing Optical and SAR data through a straightforward layer stacking (SLS) technique is outlined in (
Figure 1). The primary goal of this method was to integrate multi-sensor remote sensing datasets to extract urban impervious surface (UIS) with improved accuracy. The current approach combines multiple sensor data from Sentinel-1 (SAR) and Landsat 8 (optical), capturing urban areas through different spectral ranges and sensing modalities. For Landsat 8 data, modified indices were utilized temporally (based on all accessible images for the chosen year 2021) to capture the variations in surface characteristics.
Indices like the Visible Atmospherically Resistant Index (VARI) and the Normalized Difference Built-up Index (NDBI) offer valuable insights into land cover changes over time. For Sentinel-1 data, textural features such as local variance, dissimilarity, and entropy were extracted from SAR data to capture the spatial patterns and heterogeneity of urban surfaces.
The Simple Layer Stacking (SLS) method involves combining multiple layers, allowing for the effective capture of spectral characteristics related to impervious surfaces, including color, texture, and reflectance. This technique enables the extraction of meaningful features and offers a detailed view of impervious surfaces at the city scale. However, applying advanced data fusion techniques on a large scale introduces challenges, such as high computational demands and the need for diverse decision-making processes. To address these challenges, optical and SAR sensor data were combined using a simple layer-stacking technique. This process involved stacking the bands from both sensors into a single multi-band image, creating a comprehensive input dataset for subsequent classification.
An XGBoost machine learning classifier was then employed for the classification task, aiming to enhance the accuracy of Urban Impervious Surface (UIS) extraction. The results were assessed by comparing them with three well-established global data products: ESA, ESRI, and Dynamic World. Further details on the methodology and materials used are discussed in the following sections.
2.2. Study Area
Urban impervious surfaces, including roads, buildings, and parking lots, profoundly affect environmental processes, contributing to increased stormwater runoff, heightened flood risks, exacerbation of the UHI effect, and elevated levels of pollution [
16].
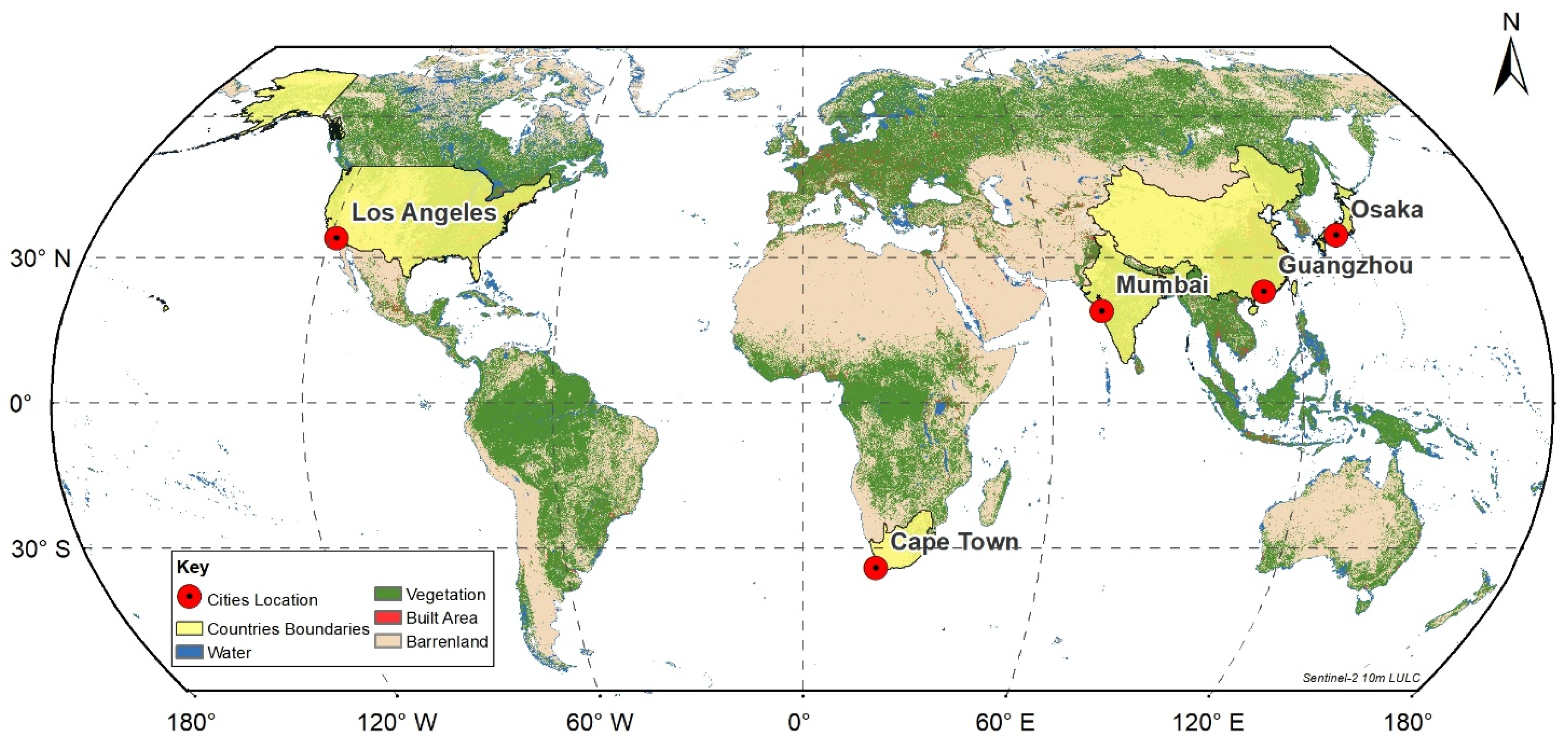
This study examines five cities: Mumbai, Osaka, Guangzhou, Los Angeles, and Cape Town, each characterized by unique climate conditions, population densities, and urbanization rates.
Table 1 presents the detailed profiles of these cities, including their respective climatic zones as classified by the Köppen-Geiger climate system [
17] and population in 2023.
Mumbai and Osaka, both densely populated cities, grapple with significant challenges related to stormwater runoff, flooding, and the urban heat island effect. In Mumbai, these issues are intensified by the city's dense population and vast impervious surfaces, which severely limit water infiltration. This underscores the critical need for comprehensive mapping and effective management strategies to address impervious surfaces in the region. Similarly, Osaka is affected by the urban heat island effect, where extensive impervious surface cover plays a key role in exacerbating the problem.
Guangzhou, a major city in southern China, faces significant air and water pollution challenges, largely due to its extensive impervious surface cover. It has been highlighted by [
18] that coastal regions, including Guangzhou, are experiencing rapid expansion of impervious surfaces. In Guangzhou, there is a strong focus on studying impervious surface dynamics to develop effective strategies for mitigating the urban heat island effect [
19].
Therefore, spatiotemporal patterns in impervious surfaces are vital for UHI and effective pollution management in this city. Los Angeles [
20] and Cape Town [
21], known for their Mediterranean climates, face issues related to air and water pollution, as well as concerns about stormwater runoff. Investigating impervious surfaces in Los Angeles and Cape Town provides valuable insights for addressing environmental challenges and effective water resource management in regions with similar climatic conditions.
This study, centered on five cities from diverse regions, aims to enhance our understanding of the impact of impervious surfaces on urban environments. By employing the SLS data fusion method in conjunction with XGBoost, the analysis achieves greater accuracy, providing important perspectives on eco-friendly urban development and environmental management. The study area map (
Figure 2) shows the locations of the study area.
2.3. Datasets
This study utilized SAR and optical satellite data, encompassing VV and VH polarizations, along with Landsat-8 OLI data, to delineate urban impervious surfaces. Integrating these datasets was crucial for overcoming challenges related to land use classes, building shadows, and cloud cover, resulting in improved accuracy of UIS mapping [
16,
22]. The inclusion of indices and textures improved the identification of urbanization trends and the mapping of impervious surfaces. Below,
Table 2 provides comprehensive details about the datasets and bands used in this study, along with their respective links in Google Earth Engine (GEE).
2.4. Methodology
In this research, the authors employed Landsat 8 multispectral imagery alongside Sentinel-1 synthetic aperture radar (SAR) data for their analysis. The Landsat 8 dataset included six key bands: blue, green, red, near-infrared, shortwave infrared 1, and shortwave infrared 2. These bands enabled the generation of various normalized indices, which the researchers further refined to compute annual statistical metrics such as minimum, median, maximum, and standard deviation.
The Sentinel-1 SAR dataset provided VV and VH polarizations, which were processed using the grey level co-occurrence matrix (GLCM) method to derive texture features within the Google Earth Engine (GEE) platform. These textures served as supplementary information in the analysis and were integrated with the modified indices.
The sampling datasets were enhanced through multiple sources, including Dynamic World (DW), the European Space Agency (ESA), ESRI datasets, and the GEE cloud platform. Sampling points were selected from over 50 urban and non-urban locations, as well as adjacent areas, based on a consensus regarding land use and land cover (LULC) classifications.
The selected sampling points included spectral bands, composite spectral-temporal indices, SAR polarizations, and texture features, which were merged into a cohesive dataset for classification. This dataset was then split into training, validation, and testing subsets using an 80-10-10 percentile division. This approach ensured that a significant portion of the data was used for training while keeping separate sets for performance evaluation. Following the classification, the authors carried out an accuracy assessment to measure the effectiveness of their methodology. This evaluation involved comparing the classifications generated by the model with ground truth data or reference datasets to assess the agreement between predicted and actual LULC categories. The accuracy assessment offered insights into the models' ability to accurately identify and classify different land use and land cover types.
The comprehensive methodology employed in this study—combining multispectral and SAR data alongside various data sources and cloud-based processing—illustrates a thorough approach to land use and land cover mapping. The results from the accuracy assessment can yield valuable insights for applications in land management, urban planning, and environmental monitoring.
2.4.1. XGB Ensemble Classifier
The XGBoost (Xtreme Gradient Boosting) algorithm is a highly efficient and powerful machine learning technique that has been shown to outperform other classifiers in various applications, including landslide susceptibility mapping and urban mapping [
23,
24]. A significant strength of XGBoost is its capability to handle noisy and imbalanced data, which are common challenges in complex classification tasks such as urban land cover mapping [
25].
The XGBoost algorithm works by iteratively building an ensemble of weak decision tree models, with each new tree attempting to correct the errors made by the previous ones. This process, known as gradient boosting, allows XGBoost to capture intricate patterns in the data and make highly accurate predictions.
The efficient and scalable nature of XGBoost also renders it highly effective for urban applications related to multi-sensor datasets and the need for real-time processing. This is particularly important in today's era of big data and the growing need for rapid, accurate, and responsive land cover monitoring and analysis.
The researchers implemented the XGBoost classifier following the approach outlined by [
26] utilizing equations (1-5) referenced in the original text. These equations represent the core components of the XGBoost algorithm, such as the decision function (1), the prediction function (2-3), the tree model representation (4), and the loss function optimization (5).
The researchers aimed to develop a robust and accurate land cover mapping solution that can effectively capture the complexity of urban environments and support various applications in urban planning, environmental monitoring, and decision-making.
2.4.2. Indices Developed
This research employed a diverse array of normalized difference indices derived from combinations of two bands selected from the six main Landsat bands, alongside four annual statistical composites. From an initial evaluation of 60 indices, the researchers identified six spectral and temporal features that demonstrated strong correlations with land use and land cover (LULC) classification.
The study introduced several modified indices (see
Table 3), including the Visible Atmospherically Resistant Index (VARI), Green Red Vegetation Index (GRVI), Normalized Difference Built-up Index (NDBI), Normalized Difference Tillage Index (NDTI), Soil Drought Index (SDUI), and Modified Normalized Difference Water Index (MNDWI).
By integrating both spectral and temporal-composite imagery, this approach significantly enhances the accuracy and comprehensiveness of the analysis, as incorporating the temporal aspect offers deeper insights into the dynamic and complex nature of urban environments. The modified indices, with their ability to leverage both spectral and temporal information, offer a more holistic and nuanced understanding of the land cover characteristics and transformations within the study area.
Additionally, the study utilized the minimum annual composition of the Normalized Difference Built-up Index (MinNDBI), which is effective in mapping high-density built-up areas, and the maximum annual composition of the Normalized Difference Tillage Index (MaxNDTI), which helps discriminate between urban and barren land. The standard deviation of the Normalized Difference Urban Index (SDUI) was also incorporated, which can help mitigate the impact of cloud cover. Lastly, the median composite of the Modified Normalized Difference Water Index (MedianMNDWI) was used, as it is highly accurate in mapping water resources.
By incorporating these modified indices, the study required to improve classification accuracy and offer a more in-depth understanding of land cover characteristics and their temporal dynamics within the study area. The innovation in these modified indices stems from their use of annual statistical composites derived from existing indices. By integrating both spectral information and temporal features, these indices effectively capture changes and patterns over time, enabling a more thorough analysis of land use and land cover dynamics.
2.4.3. SAR Texture Features
In this research, the authors utilized Sentinel-1 Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) data along with the grey level co-occurrence matrix (GLCM) texturing function available in Google Earth Engine (GEE) to enhance land use and land cover (LULC) classification.
Specifically, the study focused on extracting two key GLCM texture features from the SAR data: entropy and dissimilarity. Entropy, a measure of the randomness of the grey-level distribution, and dissimilarity, which quantifies the variability within the spatial neighborhood, were calculated for both the VV and VH polarizations using a one-pixel neighborhood [
36]. By incorporating these textural features, the researchers aimed to analyze and measure the spatial structure and variability within the SAR data, providing additional insights beyond the spectral information alone.
In total, the study utilized six SAR-derived features: 'VV', 'VH', 'VV_diss_30m', 'VV_ent_30m', 'VH_diss_30m', and 'VH_ent_30m'. These features were then used in the LULC classification analysis, which was evaluated using various performance metrics, including Overall Accuracy, F1 score, Precision, and Recall. The accuracy assessment considered both the results from the researchers' own methodology (MSFI) and three global LULC data products, allowing for a comprehensive evaluation of the classification performance.
By incorporating the textural information from the Sentinel-1 SAR data, the study aimed to enhance the accuracy and depth of the LULC classification, leading to a more comprehensive understanding of the land cover characteristics and their spatial patterns within the study area.
2.5. Accuracy Assessment, Confusion Matrix, and Correlation Matrix
2.5.1. Accuracy Assessment
To evaluate the accuracy of the proposed framework, the researchers performed a ground truth validation. They generated 525 random points for each of the five cities involved in the study, totaling 2,625 reference points across the entire area. A separate team manually verified these points using Google Earth Pro to provide the ground truth data.
Subsequently, the researchers used the "Extract Values to Points" tool in ArcGIS Spatial Analyst to retrieve classified raster values at each reference point location. This resulted in a dataset that included the reference point locations along with their corresponding extracted raster values, which was then exported as a comma-separated values (CSV) file.
The extracted CSV file was processed using a Python script in a Jupyter Notebook, facilitating statistical analysis and accuracy assessment. This method enabled a thorough evaluation of the framework's effectiveness, including calculations for overall accuracy, precision, F1 score, and recall.To ensure the reliability of the results, the researchers implemented a random sampling of the reference points and compared them with the ground truth data. This comparison provided a robust means of evaluating the accuracy and effectiveness of the classification methodology.
The formulas for calculating the aforementioned performance metrics, as described in [
37], were utilized to assess the classification model's accuracy, precision, and overall effectiveness. These equations (6-9) offer a standardized mathematical framework for evaluating the quality and reliability of the land use and land cover classification approach employed in the study.
By rigorously validating the classification results against ground truth data and calculating relevant performance metrics, the researchers were able to provide a wide-ranging assessment of the developed framework's accuracy and reliability, which is crucial for ensuring the credibility and robustness of the study's findings.
True Positives (TP) indicate the count of samples accurately identified as "positive." False Positives (FP) are the instances where samples are incorrectly classified as "positive" when they are actually "negative." True Negatives (TN) refer to the number of samples correctly classified as "negative." In contrast, False Negatives (FN) are the cases where samples are mistakenly labeled as "negative" despite being "positive."
The research findings demonstrate the accuracy assessment of individual satellite data and global products. The results indicate that the MSFI framework demonstrated enhanced classification performance compared to other data products. The MSFI approach achieved the highest overall accuracy value of 0.89, an F1 score of 0.84, a precision of 0.87, and a recall value of 0.86, indicating the best performance. On the other hand, the lowest values were observed for the Sentinel-1 dataset alone, with an accuracy of 0.67, an F1 score of 0.61, a precision of 0.68, and a recall value of 0.67.
Table 4 presents the comparative accuracy assessment of the MSFI framework against other data products, including Landsat-8, Sentinel-1, ESA, ESRI, and DW. The evaluation for the year 2021 utilized the same set of validation sample points for all data products, ensuring a fair and consistent comparison. The findings reveal that the MSFI framework demonstrates higher accuracy than the other established products, such as ESA, DW, and ESRI. This suggests that the MSFI method surpasses these well-known alternatives in terms of urban information system (UIS) classification accuracy and reliability.
2.5.2. Confusion Matrix (MSFI)
In
Table 5, the confusion matrix for the MSFI framework presents both the predicted and true values. It offers a detailed summary of both accurate and inaccurate predictions for each category. The confusion matrix is especially valuable for pinpointing classes that the model tends to confuse and misclassify, thereby highlighting potential errors. This matrix evaluates the model's classification accuracy across four distinct classes, demonstrating its effectiveness in correctly identifying samples. The confusion matrix reflects the overall performance across all five cities for the year 2021.
For the Water Bodies class, there were 300 true positive instances correctly identified. However, 4 Water Bodies were misclassified as Vegetation, and 3 were misclassified as Urban areas. The Vegetation class had 843 true positives. There were 5 false negatives, where Vegetation was mistakenly identified as Water Bodies, as well as 5 instances where Vegetation was misclassified as Urban areas. Barren Land demonstrated 217 true positive classifications. There was 1 false negative, where Barren Land was misclassified as Vegetation, and 3 instances where Barren Land was misclassified as Urban. The Urban areas class had the highest number of true positives, with 1873 instances correctly identified. However, there were some misclassifications, with 7 Urban areas being mistaken for Water Bodies, 8 as Vegetation, and 2 as Barren Land.
Overall, the classification results show strong performance, with high true positive rates across the different land cover types. The most common misclassifications were instances of Water Bodies, Vegetation, and Barren Land being identified as Urban areas, as well as a few cases of Vegetation and Barren Land being confused with each other or with Water Bodies.
2.5.3. Correlation Matrix
The correlation matrix is a square matrix that illustrates the correlation coefficients between pairs of variables. These coefficients indicate both the strength and direction of the relationship between two variables. By analyzing the values within the correlation matrix, one can evaluate the extent of correlation among different variables and identify whether these relationships are positive or negative.
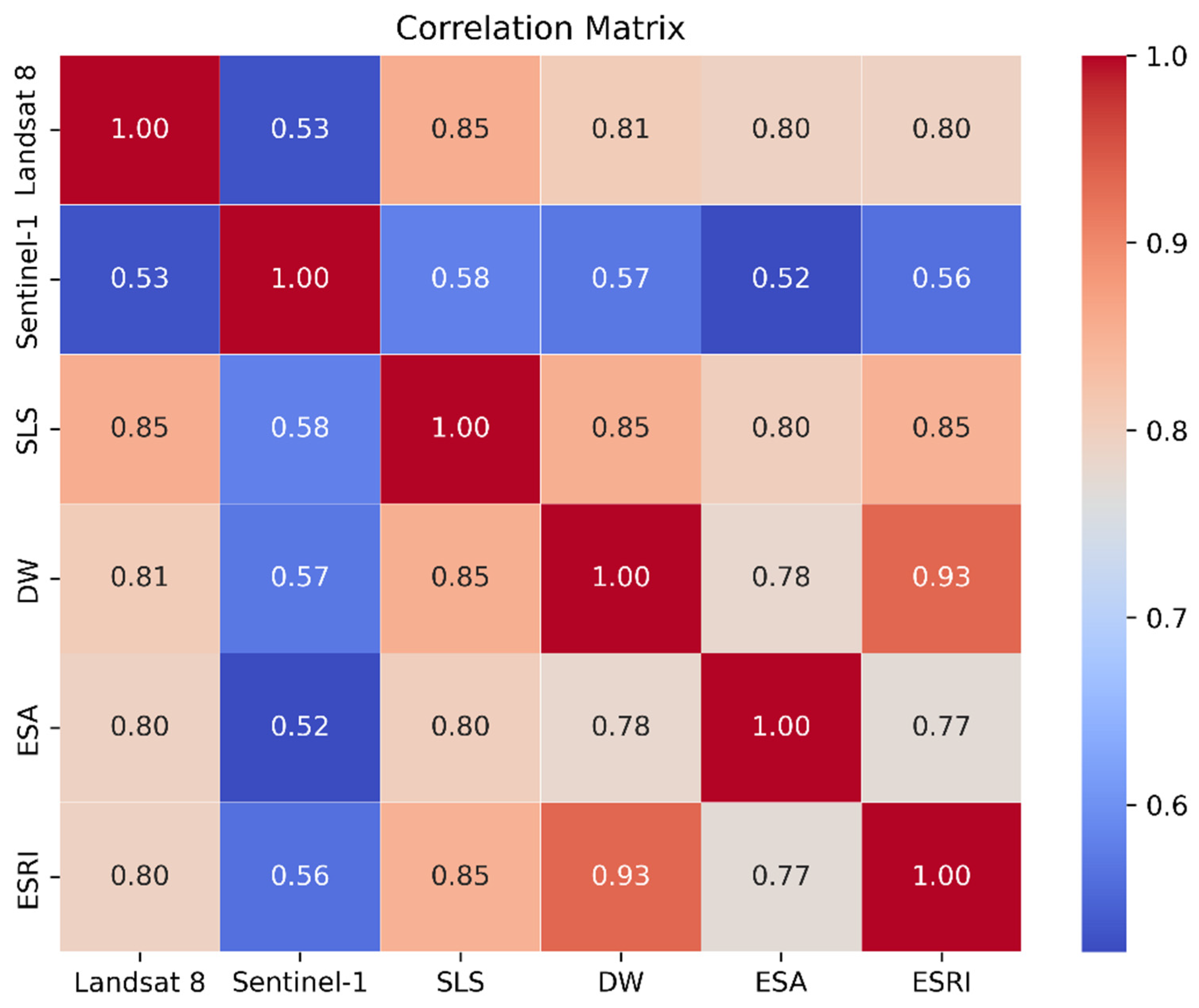
In this study, the researchers created a correlation matrix to investigate the relationships among the models utilized in their analysis, using consistent datasets. Additionally, they developed a separate correlation matrix, illustrated in
Figure 3, to assess the correlations and significance of various spectral bands. This matrix revealed the strongest associations, indicating high correlations between the SLS model and the Landsat-8, DW, and ESRI datasets, while demonstrating a weaker correlation with the ESA dataset. By quantifying these relationships, the correlation matrix offers valuable insights into the interconnections and relative significance of the different spectral bands in the analysis.
This correlation analysis serves as a valuable tool for understanding the underlying connections between the different datasets and spectral bands used in the study. It allows the researchers to identify the most influential and related variables, which can help inform the model selection and interpretation of the analysis results. The use of correlation matrices in this research helps to unveil the complex web of relationships between the datasets and spectral bands, offering a data-driven perspective on the relative significance of each component in the overall analysis.
3. Results
The research has successfully demonstrated the ability to extract UIS with high accuracy through the application of the MSFI fusion technique. This approach, as described in the methodology, combines multiple data sources and processing steps to achieve precise identification and delineation of impervious urban surfaces. The in-depth exploration of the results offers valuable insights into the nuances of the UIS extraction process. By unpacking the different components and their contributions, the researchers offer a thorough insight into the factors that enable the high-accuracy extraction of urban impervious surfaces.
Furthermore, the analysis delves into other relevant parameters that influence the performance and effectiveness of the MSFI fusion method. This additional information helps to contextualize the research findings and highlights the various considerations that must be taken into account when applying this approach in real-world scenarios.
3.1. Extraction of Urban Impervious Surface (UIS)
The methodology was implemented in five densely populated cities across the globe, each characterized by varied extents and heterogeneous landscapes.
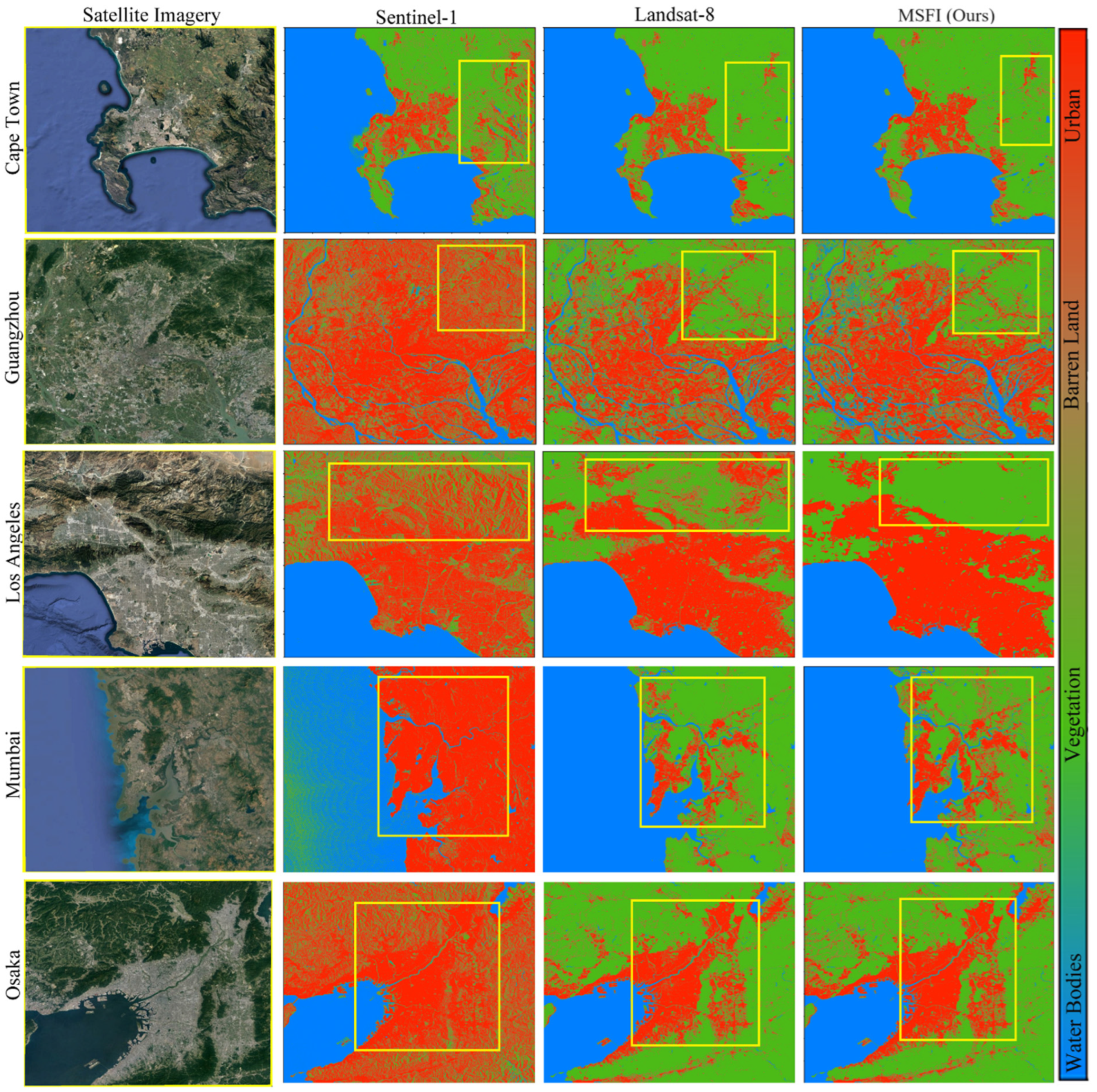
Figure 4 presents the classification outcomes for the cities, showcasing four distinct categories: urban impervious surfaces (UIS), water bodies, vegetation, and barren land. While the main goal of the method was to identify UIS, the training process included all four classes to ensure a thorough training experience and improve classification accuracy. The cities selected for this study include New York, Tokyo, Mumbai, São Paulo, and Cape Town, chosen for their diverse urban morphologies and significant variation in geographic and climatic conditions. This diversity allowed the methodology to be tested under a wide range of scenarios, ensuring its robustness and adaptability.
A land use and land cover classification was conducted in five cities utilizing three different mechanisms, including Sentinel-1 radar data, Landsat 8 optical data, and an ensemble of both datasets. The findings indicated significant differences in performance among these various approaches. Using Sentinel-1 radar data alone, the method tended to overestimate the area of urban impervious surfaces (UIS) in all cities except Cape Town, achieving an overall accuracy of 67%. This indicates that while Sentinel-1 can detect UIS, it may not be as reliable due to its tendency to overestimate these areas.
On the other hand, Landsat 8 optical data performed better than Sentinel-1, achieving an overall accuracy of 84%. Despite this improvement, Landsat 8 also showed a tendency to overestimate UIS, particularly in the city of Los Angeles. This suggests that while Landsat 8 provides more accurate UIS detection than Sentinel-1, it still has limitations in specific urban environments.
Combining the datasets from Sentinel-1 and Landsat 8 using a stacked approach that incorporated both indices and textural features led to a notable improvement in classification results across all cities. This stacked dataset attained the highest overall accuracy of 89%, surpassing the performance of the individual datasets. This enhancement illustrates that merging radar and optical remote sensing data through a stacked classification method results in more precise land use and land cover mapping. This approach capitalizes on the strengths of both sensors while alleviating the limitations associated with using each sensor in isolation.
3.2. Comparison of Results with three Established Global Data Products
The results were verified against three widely recognized state-of-the-art (SOTA) datasets. The classification outcomes were compared with global land use and land cover (LULC) products, including those from the European Space Agency (ESA), ESRI, and Dynamic World (DW). This cross-validation with established benchmark datasets offers an independent assessment of classification accuracy. These reference sources are regarded as authoritative due to their meticulous production processes and quality control measures. By comparing the study results with these reputable datasets, a strong and independent evaluation of classification accuracy was achieved.
The ESA's LULC product is known for its comprehensive global coverage and detailed thematic layers, while ESRI's dataset is highly regarded for its precision and integration with GIS applications. Dynamic World, on the other hand, offers real-time LULC data with high temporal resolution, making it an invaluable reference for dynamic and rapidly changing environments.
For example, ESA World Cover dataset [
38] is produced by the European Space Agency, an intergovernmental organization dedicated to space research. Similarly, the ESRI Land Cover dataset [
39], is developed by ESRI, a leading organization specializing in GIS-based software and products. The third dataset, Dynamic World, is a real-time land use and land cover (LULC) product created by Google in collaboration with the World Resources Institute, offering high temporal resolution data [
40].
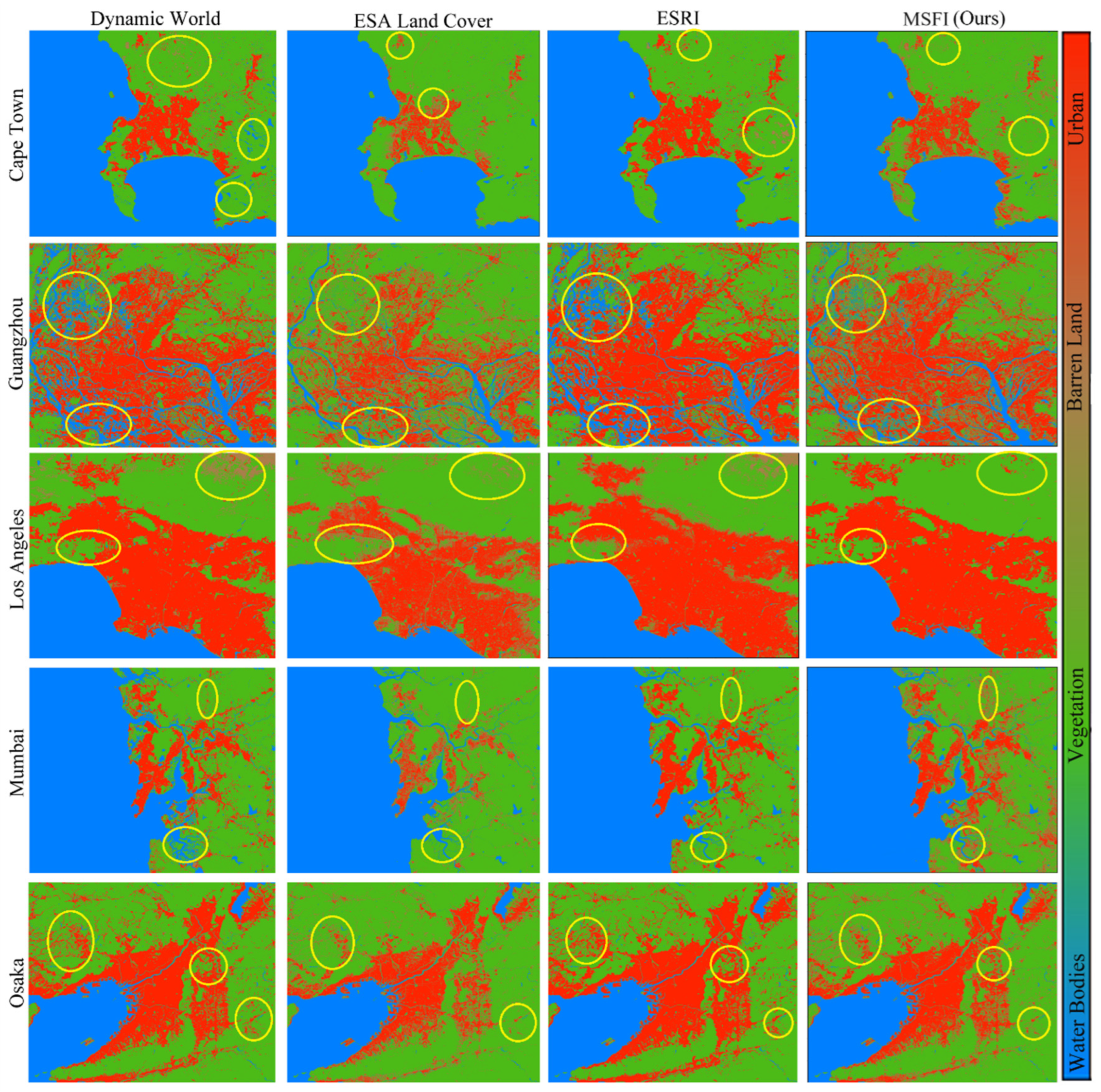
A comparison of all datasets with the results from the current approach is illustrated in
Figure 5, accompanied by the corresponding accuracy metrics in
Table 6. The map features five densely populated cities located in varied geographical contexts, highlighting the substantial impact of urbanization on urban impervious surfaces. To underscore the differences between the results from the three datasets and those from this study, specific regions within all five cities have been highlighted with yellow circles. These marked areas serve to emphasize the variations and discrepancies observed.
For Cape Town, all three datasets (ESA, ESRI, and Dynamic World) tended to mix barren land and vegetation within the highlighted circle. However, our research results provided a clearer delineation between barren land and vegetation. Furthermore, Cape Town showed the highest accuracy among the five cities, with the Optical-SAR fused method achieving an accuracy of 91% (
Table 4).
In Guangzhou, the ESRI and Dynamic World datasets overestimated the area of water bodies, while the ESA dataset misclassified water areas as vegetation. In contrast, our MSFI method yielded the best results for all classes in Guangzhou, achieving an overall accuracy of 88%. For Los Angeles, the Dynamic World, ESA, and ESRI datasets frequently confused barren land with impervious surfaces and vegetation, grouping these classes together. Our results, however, provided better separation and accuracy.
In Mumbai, the Dynamic World and ESA datasets misclassified impervious areas as water. While the ESRI dataset performed better, it still to some extent mixed vegetation with impervious surfaces. Our approach offered more precise results. Lastly, for Osaka, the Dynamic World and ESRI datasets overestimated impervious surfaces, whereas the ESA dataset underestimated them. Our method, however, delivered accurate delineation of impervious surfaces for this city.
Overall, our study shows enhanced performance relative to the other datasets, especially in differentiating between land cover classes and attaining greater accuracy across various cities. This highlights the effectiveness of our approach in providing more reliable and detailed land use/land cover classification.
3.3. LST Trends for Selected Cities
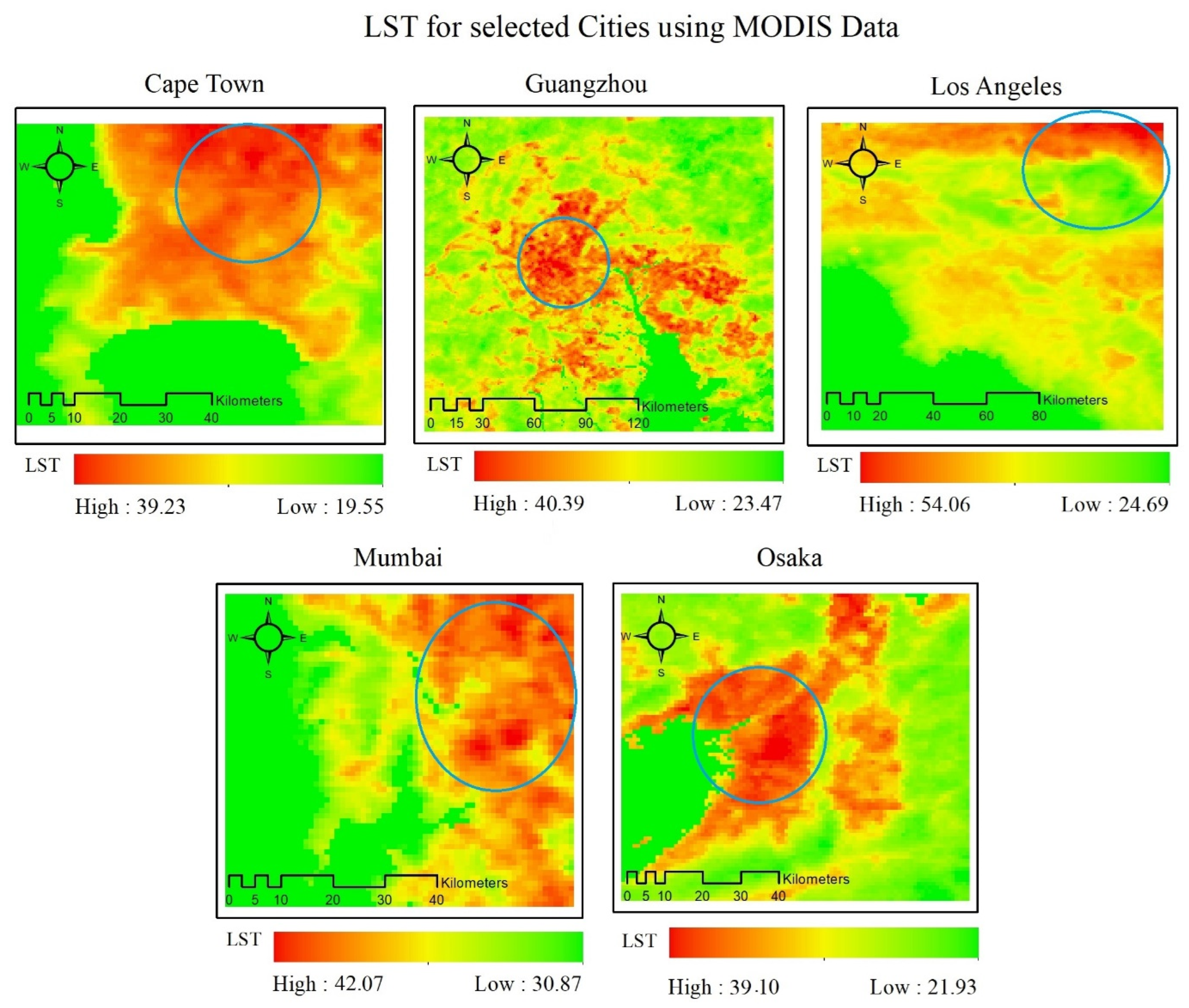
Urban impervious surface is related to the surface type that is more prone to high temperatures. Thus, an increase in UIS directly affects an increase in LST. Therefore, an LST analysis was performed using MODIS LST product of 1 km (MOD11A1 V6.1) through Google Earth Engine (GEE). Moreover, the TerraClimate dataset was used to compute monthly maximum, minimum, and mean ambient air temperature for the selected cities.
Figure 6, the analysis of satellite data reveals the presence of the highest Land Surface Temperature (LST) value in Los Angeles, reaching a peak of 54.6ºC. Notably, these elevated LST values are predominantly concentrated in close proximity to densely developed impervious areas within the city. The results demonstrate that cities with high levels of urbanization also tend to have high land surface temperatures. Based on the conducted analysis, the highest Land Surface Temperature (LST) values were recorded in all five cities. Cape Town recorded a maximum LST of 39.29ºC, Guangzhou had a maximum LST of 40.39ºC, Mumbai reached a maximum LST of 42.07ºC, and Osaka City had the lowest maximum LST of 39.1ºC among all the cities. These values correspond to the highest temperatures recorded in each respective city throughout the year 2021.
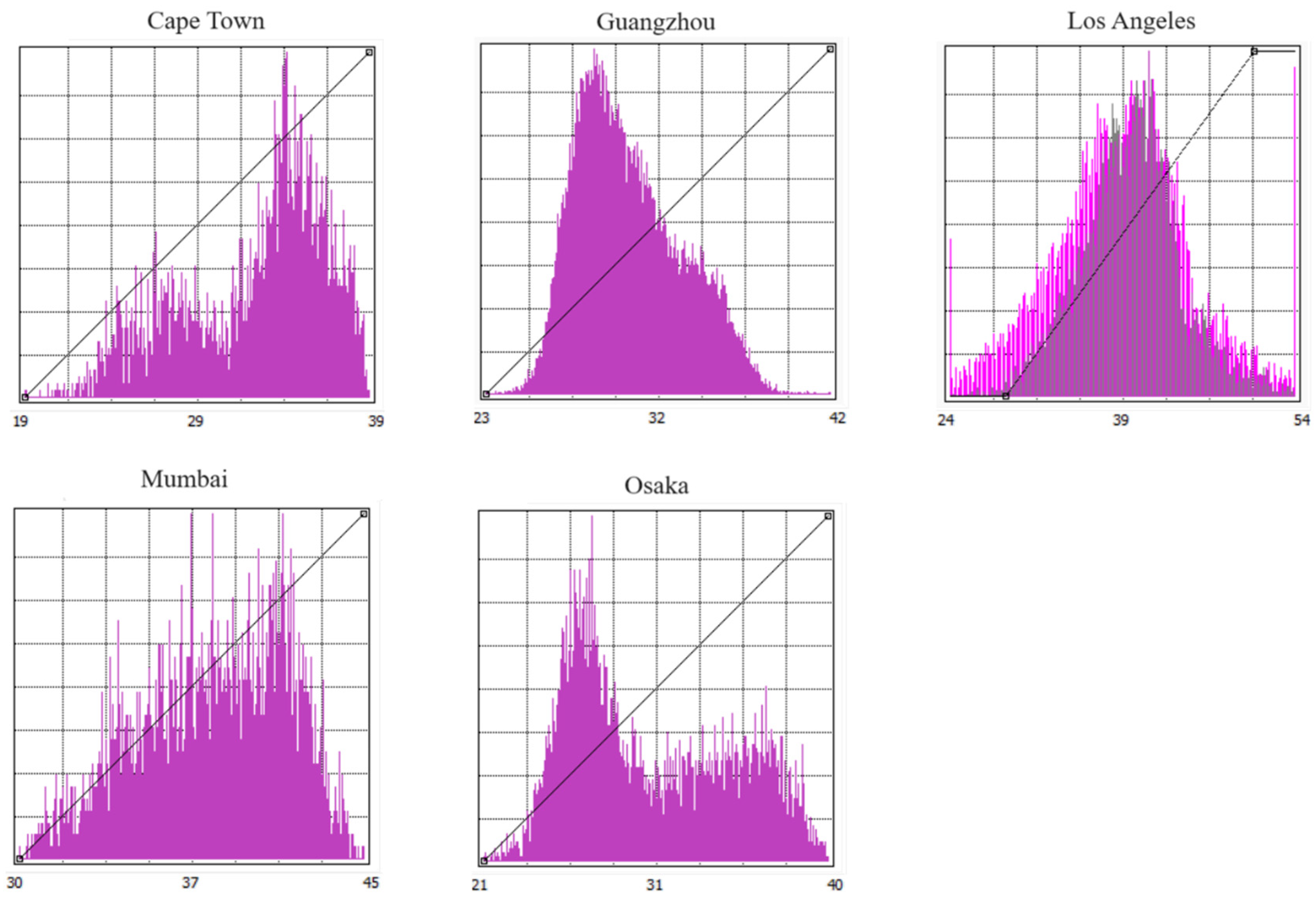
The histogram in
Figure 7 visually represents the distribution of Land Surface Temperature (LST) values for each city, showcasing the minimum, maximum, and median values. This graphical representation allows us to observe the predominant LST ranges and patterns within each city. From the histograms, it is evident that Cape Town and Osaka have a higher frequency of lower LST values, indicating a generally cooler temperature distribution in these cities. This cooler temperature distribution may be influenced by local climate conditions, such as proximity to the ocean in Cape Town and the temperate climate of Osaka.
Conversely, the histograms for Guangzhou, Los Angeles, and Mumbai show a higher occurrence of higher LST values, suggesting that these cities tend to experience warmer temperatures. This trend can be attributed to various factors, including urban heat island effects, local climatic conditions, and geographic location. These observations highlight the contrasting temperature characteristics among the cities, underscoring the influence of local climate and environmental factors on LST distribution. Understanding these temperature patterns is crucial for urban planning, climate adaptation strategies, and managing the impacts of urban heat on public health and infrastructure.
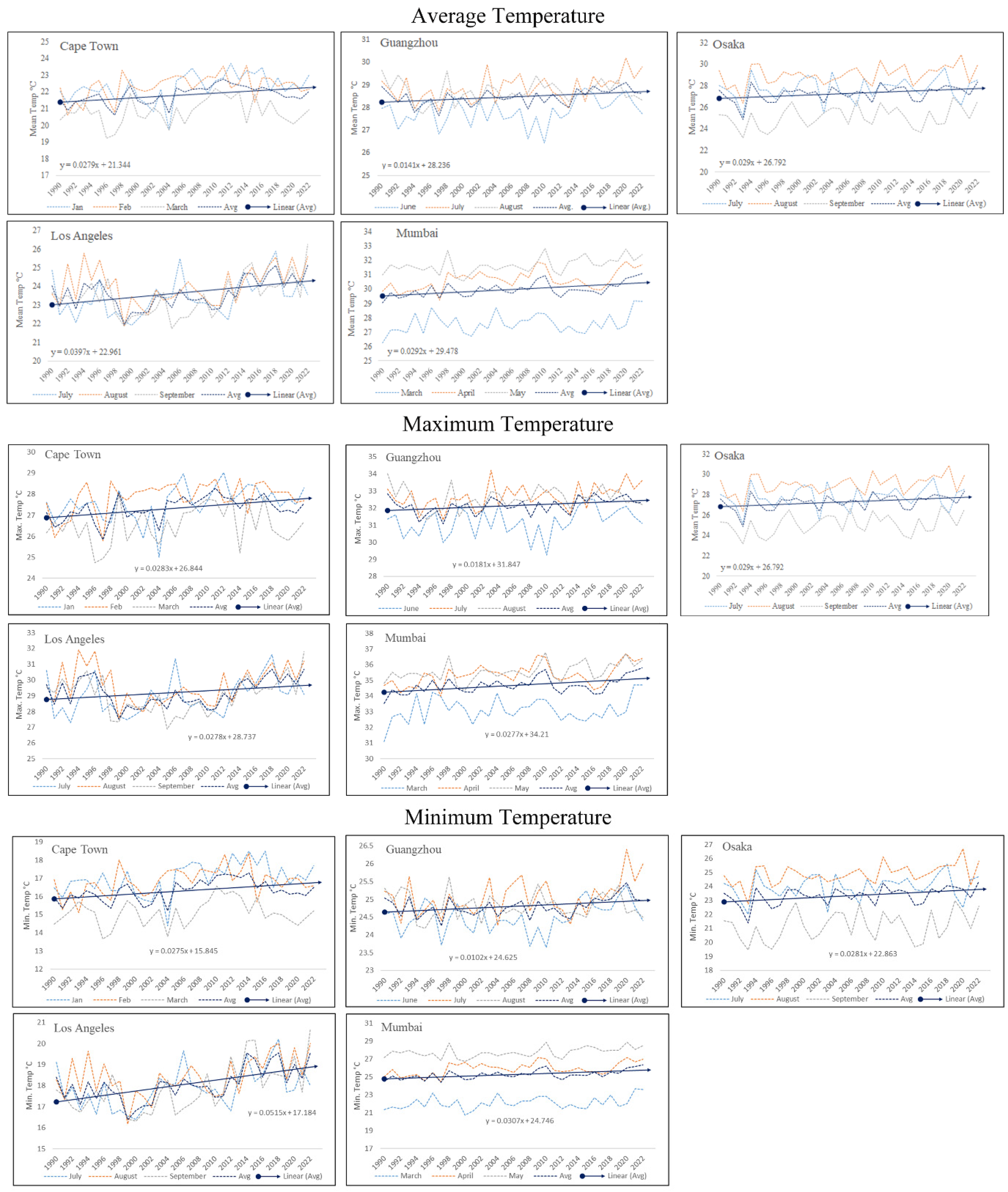
Additionally, the TerraClimate dataset was instrumental in computing the average, minimum, and maximum temperature trends for each city (
Figure 8). This dataset offered valuable insights into long-term temperature patterns and fluctuations, enabling a comprehensive understanding of temperature dynamics over time.
The analysis, covering the period from 1990 to 2022, allowed for the calculation of the percentile increase at the starting and ending points of the trend fit line for average max-temperature, average min-temperature, and average mean-temperature during the summer season. This analysis provided a detailed view of the relative changes in temperature trends over the specified timeframe, highlighting the magnitude of temperature variations during the summer season.
By examining these trends, we can better assess how temperatures have changed over the years, providing critical information for urban planning, climate adaptation strategies, and the management of heat-related impacts on public health and infrastructure.
This long-term analysis underscores the importance of monitoring and understanding temperature trends to mitigate the effects of climate change in urban environments. The TerraClimate dataset analysis considering increase in impervious surfaces provides a comprehensive view of how temperatures have changed over decades, offering critical information for planning and adaptation strategies in response to climate change.
4. Discussion
The main goal of this research is to improve the mapping accuracy of urban impervious surface (UIS). The findings underscore the significance of factors such as population growth and urbanization, which play crucial roles in influencing UIS. Additionally, the study highlights the impact of increasing Land Surface Temperature (LST) in selected cities, as UIS is closely related to various environmental factors. Urbanization, in particular, is a major driver of elevated LST levels, with higher urbanization correlating with increased land surface temperatures. Understanding these interconnected factors provides a more thorough perspective on UIS dynamics and their interaction with urban environments.
The findings indicate that merging optical and SAR remote sensing data greatly enhances UIS extraction accuracy compared to relying on individual datasets. By integrating texture and index features from Landsat-8 and Sentinel-1, the approach captured complementary spectral and spatial characteristics, resulting in improved classification performance. The XGBoost classifier adeptly modeled the complex relationships among land use classes based on the combined data, and accuracy assessments against recognized global products and validation points validated the superior performance of the proposed MSFI methodology.The land surface temperature analysis provided valuable insights into how increasing urbanization affects local climate patterns across different climatic zones. This integration of temperature and UIS data enriches the understanding of their relationship, offering a foundation for further research on urban environmental dynamics.
Nevertheless, applying the existing method alongside integrated multi-sensor open-source datasets offers certain challenges and limitations. Time series analysis is constrained by the paucity of historical satellite images, making it difficult to obtain consistent datasets for the same historical periods. While pre-processed imagery provided by data providers is beneficial, the presence of clouds can still impact classification accuracy despite the use of cloud removal algorithms. In certain cases, machine learning algorithms might incorrectly categorize clouds as different land cover types or even as a distinct class. Future research could benefit from applying this approach to high-resolution datasets, which may offer improved classification accuracy and more detailed insights into urban impervious surfaces.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion this research presents an Optical-SAR data fusion approach that integrates simple layer stacking with machine learning classification to improve the extraction of urban impervious surfaces. By combining texture, indices, and temporal features from both optical and radar datasets, the methodology offers a thorough characterization of land use patterns. The findings indicate that the fusion of multi-sensor SAR and optical data significantly enhances urban land cover classification compared to using either SAR or optical data independently. The proposed method achieved high overall accuracy, exceeding that of three established global products. Additionally, comparative temperature analysis highlighted the impact of impervious surfaces on local climate, emphasizing the advantages of multi-sensor data fusion for precise urban mapping applications. The application of XGBoost in this methodology proved to be highly effective, achieving an overall accuracy of 89%, an F1 score of 84%, and 87% precision. The inclusion of cities across diverse climate zones was strategically chosen to provide a broad basis for future research, enabling studies in various urban and climatic contexts using this approach. Linking the results to Land Surface Temperature (LST) analyses offers valuable insights into how impervious surfaces influence local climate change vulnerabilities. This research underscores the potential of multi-sensor data fusion for improving the accuracy and reliability of impervious surface mapping, contributing to more informed and sustainable urban development and environmental management practices in the face of changing climatic conditions.
Funding Support
This work was supported by an APC waiver from MDPI.
Disclosure Statement
The authors have no potential conflict of interest.
References
- Ban, Y.; Jacob, A. Fusion of multitemporal spaceborne SAR and optical data for urban mapping and urbanization monitoring. Multitemporal Remote Sens. Methods Appl. 2016, 107–123. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Yang, C.; Liu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Ye, Y. Comparative Analysis of Pixel-Level Fusion Algorithms and a New High-Resolution Dataset for SAR and Optical Image Fusion. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrian, J.; Sagan, V.; Maimaitijiang, M. Sentinel SAR-optical fusion for crop type mapping using deep learning and Google Earth Engine. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 175, 215–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagiannopoulou, A.; Tsertou, A.; Tsimiklis, G.; Amditis, A. Data fusion in earth observation and the role of citizen as a sensor: A scoping review of applications, methods and future trends. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Huang, Z.; Liu, J.; Yang, L. Multi-source data fusion and hydrodynamics for urban waterlogging risk identification. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, J.; Gong, P. ROBOT: A spatiotemporal fusion model toward seamless data cube for global remote sensing applications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 294, 113616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meraner, A.; Ebel, P.; Zhu, X.X.; Schmitt, M. Cloud removal in Sentinel-2 imagery using a deep residual neural network and SAR-optical data fusion. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 166, 333–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ounoughi, C.; Yahia, S.B. Data fusion for ITS: A systematic literature review. Inf. Fusion 2023, 89, 267–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karathanassi, V.; Kolokousis, P.; Ioannidou, S. A comparison study on fusion methods using evaluation indicators. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 2309–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Xie, G.; Zhou, S. Panchromatic and Multispectral Image Fusion Combining GIHS, NSST, and PCA. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, J.; Wang, X.; Xie, G.; Wei, L. Multiscale Fusion of Panchromatic and Multispectral Images Based on Adaptive Iterative Filtering. Remote Sens. 2023, 16, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, P.A.; Beltrão, N.E.S.; Guimarães, U.S.; Teodoro, A.C. Integration of sentinel-1 and sentinel-2 for classification and LULC mapping in the urban area of Belém, eastern Brazilian Amazon. Sensors 2019, 19, 1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clerici, N.; Calderón, C.A.V.; Posada, J.M. Fusion of Sentinel-1A and Sentinel-2A data for land cover mapping: a case study in the lower Magdalena region, Colombia. J. Maps 2017, 13, 718–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, J.; Ban, Y. Sentinel-1A SAR and sentinel-2A MSI data fusion for urban ecosystem service mapping. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2017, 8, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, D.H.; Mucsi, L. Comparison of layer-stacking and Dempster-Shafer theory-based methods using Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 data fusion in urban land cover mapping. Geo-spatial Inf. Sci. 2022, 25, 425–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Ahmad, M.N.; Javed, A.; Islam, F.; Jahangir, Z.; Ahmad, I. Expansion of Urban Impervious Surfaces in Lahore (1993–2022) Based on GEE and Remote Sensing Data. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2023, 89, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peel, M.C.; Finlayson, B.L.; McMahon, T.A. Updated world map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification. Hydrol. earth Syst. Sci. 2007, 11, 1633–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; et al. Exploring the variation trend of urban expansion, land surface temperature, and ecological quality and their interrelationships in Guangzhou, China, from 1987 to 2019. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Qu, K.; Darkwa, J.; Calautit, J.K. Evaluating urban heat island mitigation strategies for a subtropical city centre (a case study in Osaka, Japan). Energy 2022, 250, 123721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Papazoglou, E.G.; Cartalis, C.; Philippopoulos, K.; Vasilakopoulou, K.; Santamouris, M. On the mitigation potential and urban climate impact of increased green infrastructures in a coastal mediterranean city. Build. Environ. 2022, 221, 109264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brom, P.D.; Underhill, L.G.; Winter, K.; Colville, J.F. A mowing strategy for urban parks to support spring flowers in a mediterranean climate city in South Africa. Urban Ecosyst. 2023, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Guo, S.; Shao, Z.; Li, D. Urban Impervious Surface Extraction Based on Deep Convolutional Networks Using Intensity, Polarimetric Scattering and Interferometric Coherence Information from Sentinel-1 SAR Images. Remote Sens. 2023, 51, 1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, E.K. Assessing the predictive capability of ensemble tree methods for landslide susceptibility mapping using XGBoost, gradient boosting machine, and random forest. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Shen, W. A review of ensemble learning algorithms used in remote sensing applications. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.N.; Shao, Z.; Xiao, X.; Fu, P.; Javed, A.; Ara, I. A novel ensemble learning approach to extract urban impervious surface based on machine learning algorithms using SAR and optical data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2024, 132, 104013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavzoglu, T.; Teke, A. Predictive Performances of ensemble machine learning algorithms in landslide susceptibility mapping using random forest, extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost) and natural gradient boosting (NGBoost). Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2022, 47, 7367–7385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitelson, A.A.; Stark, R.; Grits, U.; Rundquist, D.; Kaufman, Y.; Derry, D. Vegetation and soil lines in visible spectral space: A concept and technique for remote estimation of vegetation fraction. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 2537–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motohka, T.; Nasahara, K.N.; Oguma, H.; Tsuchida, S. Applicability of green-red vegetation index for remote sensing of vegetation phenology. Remote Sens. 2010, 2, 2369–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fariz, T.R.; Faniza, V. Comparison of built-up land indices for building density mapping in urban environments. in AIP Conference Proceedings, AIP Publishing, 2023.
- Ahmad, M.N.; et al. Optical–SAR Data Fusion Based on Simple Layer Stacking and the XGBoost Algorithm to Extract Urban Impervious Surfaces in Global Alpha Cities. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osgouei, P.E.; Kaya, S.; Sertel, E.; Alganci, U. Separating built-up areas from bare land in mediterranean cities using Sentinel-2A imagery. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, M.; Jayamanna, S.; Tsujiko, Y. Quantitative evaluation of urbanization in developing countries using satellite data. Doboku Gakkai Ronbunshu 1997, 1997, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilchin, C.; et al. HIV transmission potential and sex partner concurrency: evidence for racial disparities in HIV risk among gay and bisexual men (MSM). AIDS Behav. 2022, 26, 709–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anusha, B.N.; Babu, K.R.; Kumar, B.P.; Kumar, P.R.; Rajasekhar, M. Geospatial approaches for monitoring and mapping of water resources in semi-arid regions of Southern India. Environ. Challenges 2022, 8, 100569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Ahmad, M.N.; Javed, A. Comparison of Random Forest and XGBoost Classifiers Using Integrated Optical and SAR Features for Mapping Urban Impervious Surface. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velichko, A.; Wagner, M.P.; Taravat, A.; Hobbs, B.; Ord, A. NNetEn2D: Two-dimensional neural network entropy in remote sensing imagery and geophysical mapping. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chicco, D.; Jurman, G. The advantages of the Matthews correlation coefficient (MCC) over F1 score and accuracy in binary classification evaluation. BMC Genomics 2020, 21, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanaga, D.; et al. ESA WorldCover 10 m 2021 v200. 2022.
- Venter, Z.S.; Barton, D.N.; Chakraborty, T.; Simensen, T.; Singh, G. Global 10 m Land Use Land Cover Datasets: A Comparison of Dynamic World, World Cover and Esri Land Cover. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.F.; et al. Dynamic World, Near real-time global 10 m land use land cover mapping. Sci. Data 2022, 9, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).