1. Introduction
Candida albicans is a commensal fungus that integrates the microbiota of various mucous membranes in healthy individuals without causing disease. However, in immunocompromised hosts this species can become pathogenic. Thus, it has the ability to both coexist as a commensal and to predominate as a fungal pathogen in humans. Factors used for adaptation and virulence are the development of various polymorphisms, nutritional adaptation and biofilm production, among other factors [
1,
2,
3,
4].
Thus, the use of molecular biology based on the study of genetic material is what makes it possible not only to understand particular and fundamental characteristics, but also to detect these beings when present in other living beings. Thus, the isolation of genetic material is the initial milestone in the more detailed study of any being. Given that, regardless of complexity, they have the ability to synthesize macromolecules, such as nucleic acids and proteins, which contain all the information necessary for cellular functioning [
5,
6,
7].
For this reason, there are no single or fixed protocols for the extraction of genetic material, since the isolation of quality and quantity of genetic material requires a careful choice of extraction method, as they vary according to the samples used. In addition, adaptations to these methodologies aim to create less expensive and faster protocols that maintain the quality and yield of the isolated material [
8,
9,
10], making them valuable both for research purposes and for use in laboratory routines aimed at the molecular diagnosis of microorganisms.
Thus, methods that use silicon carbide (SiC) in their composition seek not only to assist in the rupture of cellular structures, but also to provide homogeneity to the samples. Thus, SiC granules are used as abrasive agents in the cell lysis stage, as they are stable and inert ceramic compounds produced industrially. Since structures composed of cell walls require more vigorous conditions for the release of cytoplasmic content, as they are more resistant compared to structures that only have a plasma membrane [
11,
12,
13,
14].
That way, the suitability is significant, as it seeks to optimize the process of extracting fungal genetic material, which is hindered by several factors, in addition to being the first step in the study of molecular biology, especially in small laboratories. Therefore, the objective of the study was to evaluate the yield, purity and integrity of the nucleic acids isolated by the adapted protocol for the joint extraction of DNA and RNA from Candida albicans, using a chemical method in conjunction with SiC from a few cells, followed by gradual additions to evaluate its effectiveness.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Materials
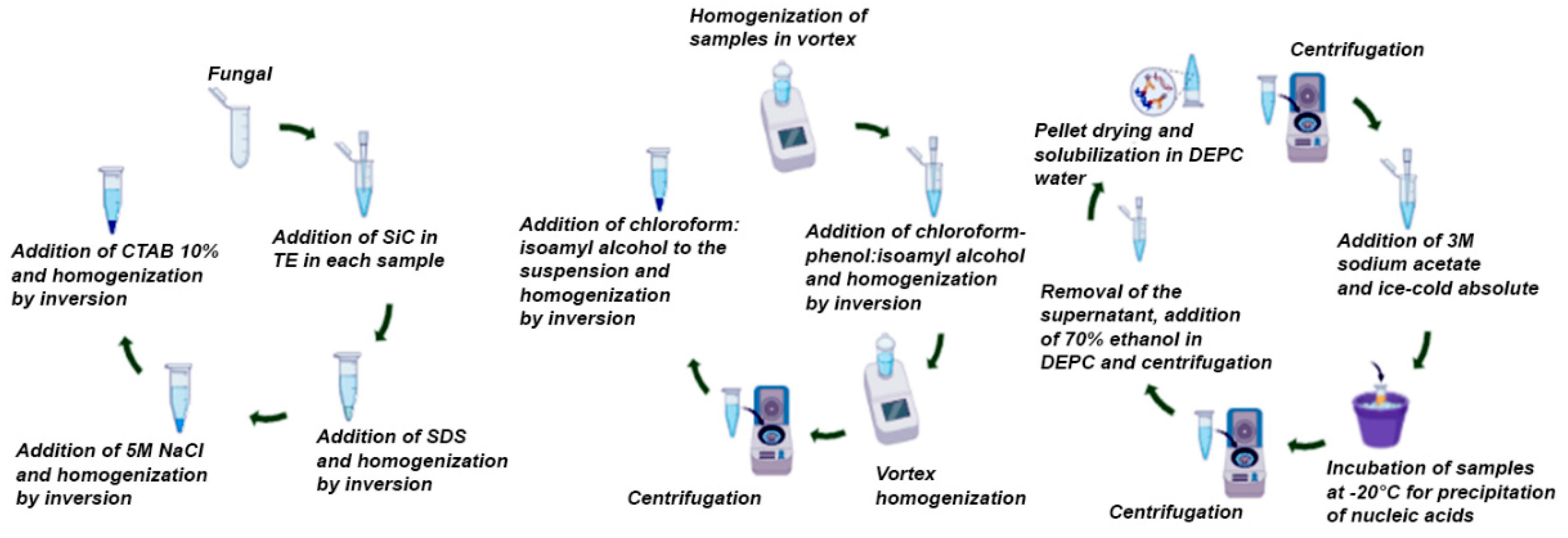
To perform the joint extraction of nucleic acids, the methodology used was the Oliveira et al. [
15] method, in which all solutions, including reagents, were prepared in deionized water treated with diethyl pyrocarbonade (DEPC) 1:1000 (v/v), at 37ºC for 24 hours, and autoclaved. The glassware and accessories used were also treated and those that were resistant were autoclaved at 120°C for 20 minutes and the plastics were ensured to be free of DNases and RNases.
2.2. Obtaining and Preparing Fungal Samples
To obtain fungal samples of the
Candida albicans species, two batches of a standard strain identified as NCP 3179 plated on Sabouraud Dextrose Agar obtained in collaboration with the Vicente Lemos Laboratory, located in Crato-CE, were inoculated both in approximately 60 mL of sterile Brain Heart Infusion (BHI) liquid medium and in solid Sabouraud Dextrose medium, prepared in two sterile plates. After that, the seeded BHI medium was incubated for 24 hours at 37°C, while the Sabouraud medium plates were kept in a humid chamber for approximately 2 weeks each. Then, aliquots were prepared from the seeded media (
Table 2). Thus, a total of 30 samples were prepared, 10 of which were obtained from aliquots taken from the BHI medium and transferred to sterile 15 mL Falcon tubes, called method 1. These were centrifuged at 3,500 rpm for 5 min to discard the BHI and then the cells were resuspended in 10 mL of saline.
Ten samples were also obtained from each Sabouraud plate, using colonies taken directly from the medium, called method 2 and method 3, which differ from each other due to adjustments in the nucleic acid extraction protocol. Thus, the maximum number of colonies on the plate was transferred to a sterile Falcon tube containing 10 mL of saline, then the suspension was vortexed until completely homogenized and separated into aliquots that were transferred to sterile 2.0 mL tubes, after removing 20µLeach sample for cell counting, as per
Table 2.
Cell counting was performed on the central hemocytometer of the Neubauer Chamber and the total number of cells per mL was estimated by calculating the cells contained in 10µL (
Table 2). Finally, the saline samples stored in 2.0 mL tubes were centrifuged again at 3,500 rpm for 5 min to discard the saline and stored at – 20°C until extraction.
2.3. Purification of Nucleic Acids
For the extraction of nucleic acids, method described by Oliveira et al. [
15] associated with the method of Rosa [
12], which used SiC with a particle size of around 320 mm with the aim of enhancing cell rupture due to its inert and abrasive nature. The reagents used in the extractions were kept refrigerated at 4°C and conditioned in an ice bath during the procedure, except for sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) and cetyltrimethylammonium sulfate (CTAB), since they precipitate at low temperatures.
Furthermore, the samples were preserved in an ice bath during the extraction process, except when the protocol recommended room temperature. The steps of agitation, centrifugation and precipitation time of nucleic acids described by Oliveira et al. [
15], were modified with the aim of reducing the protocol execution time (
Table 1) and in the recommended centrifugation steps at 4°C, the “non-refrigerated” centrifuge rotor was previously kept in the freezer to perform the centrifugations.
Initially, in a 15 mL DNase and RNase free Falcon tube containing TE (10 Mm Tris, 1 mM EDTA, pH 8.0) SiC (0.35 mg per sample) was added. The mixture was homogenized and from it 570 uL were transferred to each sterile and previously identified 2.0 mL polypropylene tube containing the fungal sample.
Then, 30 uL of 10% SDS was added to each tube and shaken for 10 seconds manually by inversion. After that,100 uL of 5 M NaCl/DEPC and stirred for 10 sec. also by inversion. Finally, 100 uL of the 10% CTAB solution (CTAB dissolved in 0.7 M NaCl) was added and stirred for 1 min. in vortex, however the vortex time was increased to 2 min throughout the protocol in method 3 (
Table 1).
Immediately afterwards, 600 uL (1:1) of phenol-chloroform:isoamyl alcohol (24:1) were added and homogenized for 5 min manually by inversion. However, in method 2, this step with phenol/chloroform was performed twice. Then, the samples were vortexed again. After that, the samples were centrifuged at 15,000 rpm for 15 min and the supernatant was transferred to another 2.0 mL microtube, observing the final volume for subsequent addition of 1 volume of chloroform:isoamyl alcohol (24:1) and homogenization by inversion for 5 min at room temperature.
The samples were then centrifuged at 15,000 rpm for 15 min and the supernatant transferred to another 2.0 mL microtube, observing the final volume for subsequent addition of 0.1 volumes of 3 M sodium acetate (pH 5.0) and two volumes of ice-cold absolute ethanol. After that, the samples were incubated at -20°C for 30 min to precipitate the nucleic acids. After this period, a new centrifugation was performed at 15,000 rpm for 15 min.
Finally, 1 mL of 70% ethanol in DEPC water 1:1000 (v/v) was added to the precipitate. Immediately afterwards, everything was centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 5 min. This step involved adding alcohol, discarding the supernatant and centrifuging twice. After the last wash, the pellet was dried for approximately 30 min by inversion on absorbent paper. After drying, the nucleic acids were solubilized in 50 uL of water/DEPC and the tubes were left to stand for 15 to 20 min for subsequent analysis of the integrity of the nucleic acids, as shown in
Scheme 1.
2.4. Integrity Analysis
To perform electrophoresis in 1% agarose gel, the step-by-step process was based on previously consolidated protocols of Sambrook and Russell [
16].
2.5. Quantification and Purity of Isolated Nucleic Acids
The evaluation of the degree of purity and quantification of the isolated nucleic acids was obtained in a microvolume spectrophotometer of Agilent Bio Tek Synergy LX Multimode Reader model Cytation 7 through the Take 3 plate andin collaboration with the Laboratory of Molecular Bioprospecting and Alternative Methods of URCA, located in Crato-CE. For this purpose, 2 µL of each sample was used. The purity and concentration obtained were A260/A280 (
Table 2).
3. Results
Below, the data obtained from the quantification of the samples, the yield and the purity index given by the A260/A280 ratio of methods 1, 2 and 3 are displayed in table form.
Table 2.
Concentration and purity of total nucleic acids isolated from Candida albicans.
Table 2.
Concentration and purity of total nucleic acids isolated from Candida albicans.
| |
|
|
|
Performance |
Purity |
| |
|
|
|
(ng/µL) |
(A260/A280) |
| Cultivation |
Sample |
Medium aliquot (mL) |
No. cells/mL
(x 106 CFU) |
DNA |
RNA |
DNA |
RNA |
Method 1
(BHI) |
1 |
0.1 |
0.025 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| 2 |
0.5 |
0.075 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| 3 |
1.0 |
0.115 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| 4 |
1.5 |
0.115 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| 5 |
2.0 |
0.160 |
24.8 |
- |
1.3 |
- |
| 6 |
2.5 |
0.260 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| 7 |
3.0 |
0.270 |
59.3 |
26.0 |
1.4 |
1.2 |
| 8 |
3.5 |
0.295 |
72.4 |
36.1 |
1.4 |
1.2 |
| 9 |
4.0 |
0.405 |
57.7 |
25.6 |
1.3 |
1.13 |
| 10 |
4.5 |
0.595 |
61.9 |
31.1 |
1.4 |
1.1 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Method 2
(Sabouraud) |
1 |
0.2 |
0.816 |
7.9 |
50.7 |
1.0 |
1.3 |
| 2 |
0.4 |
1,632 |
86.9 |
- |
1.4 |
- |
| 3 |
0.6 |
2,448 |
126.1 |
84.0 |
1.5 |
1.4 |
| 4 |
0.8 |
3.264 |
102.3 |
61.9 |
1.6 |
1.4 |
| 5 |
1.0 |
4.080 |
93.9 |
49.0 |
1.6 |
1.4 |
| 6 |
1,2 |
4,896 |
263.7 |
231.4 |
2.1 |
2.2 |
| 7 |
1.4 |
5.712 |
325.2 |
288.2 |
2.2 |
2.2 |
| 8 |
1.6 |
6,528 |
165.9 |
145.5 |
2.1 |
2.1 |
| 9 |
1.8 |
7,344 |
354.9 |
302.8 |
2.1 |
2.2 |
| 10 |
2.0 |
8.160 |
569.8 |
477.6 |
2.2 |
2.2 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Method 3
(Sabouraud) |
1 |
0.2 |
0.622 |
35.2 |
29.3 |
2.0 |
2.0 |
| 2 |
0.4 |
1,244 |
47.5 |
40.4 |
1.8 |
1.7 |
| 3 |
0.6 |
1,867 |
49.8 |
42.4 |
2.0 |
2.0 |
| 4 |
0.8 |
2,489 |
97.7 |
83.4 |
2.1 |
2.1 |
| 5 |
1.0 |
3.112 |
126.5 |
108.1 |
2.1 |
2.1 |
| 6 |
1,2 |
3,734 |
202.0 |
171.9 |
2.2 |
2.2 |
| 7 |
1.4 |
4,356 |
209.6 |
177.1 |
2.2 |
2.2 |
| 8 |
1.6 |
4,979 |
228.9 |
190.4 |
2.2 |
2.2 |
| 9 |
1.8 |
5.601 |
220.2 |
185.7 |
2.2 |
2.2 |
| 10 |
2.0 |
6.224 |
384.2 |
312.6 |
2.2 |
2.2 |
For extractions using method 1, the lowest number of fungal cells obtained was 0.025 x 106 CFU, and the maximum number was 0.595 x 10
6 CFU (
Table 2). As for the extractions of samples using methods 2 and 3, the greater number of cells obtained, as evidenced in the first samples of these methods, respectively 0.816 and 0.622 x 10
6 CFU, is mainly due to the greater growth of colonies in Sabouraud medium (
Table 2). Regarding cell number and yield, in method 1 the low concentration of DNA and RNA is correlated with the low number of cells. However, in some samples it is suggested that the low concentration of DNA and RNA is due to an inefficient rupture of the fungal cell wall, mainly in sample 1 of method 2 (
Table 2).
Regarding the yield and purity analysis, in method 3 an 'exponential' increase in the extracted nucleic acids in relation to the number of cells was observed, from sample 1 to sample 10, and a homogeneous purity between them. This did not happen in the samples of methods 1 and 2 (
Table 3), as there was a strong indication of the presence of contaminants, such as proteins and phenol. Although the yield did not surpass method 2 due to the number of cells, method 3 presented superior purity results (
Table 2).
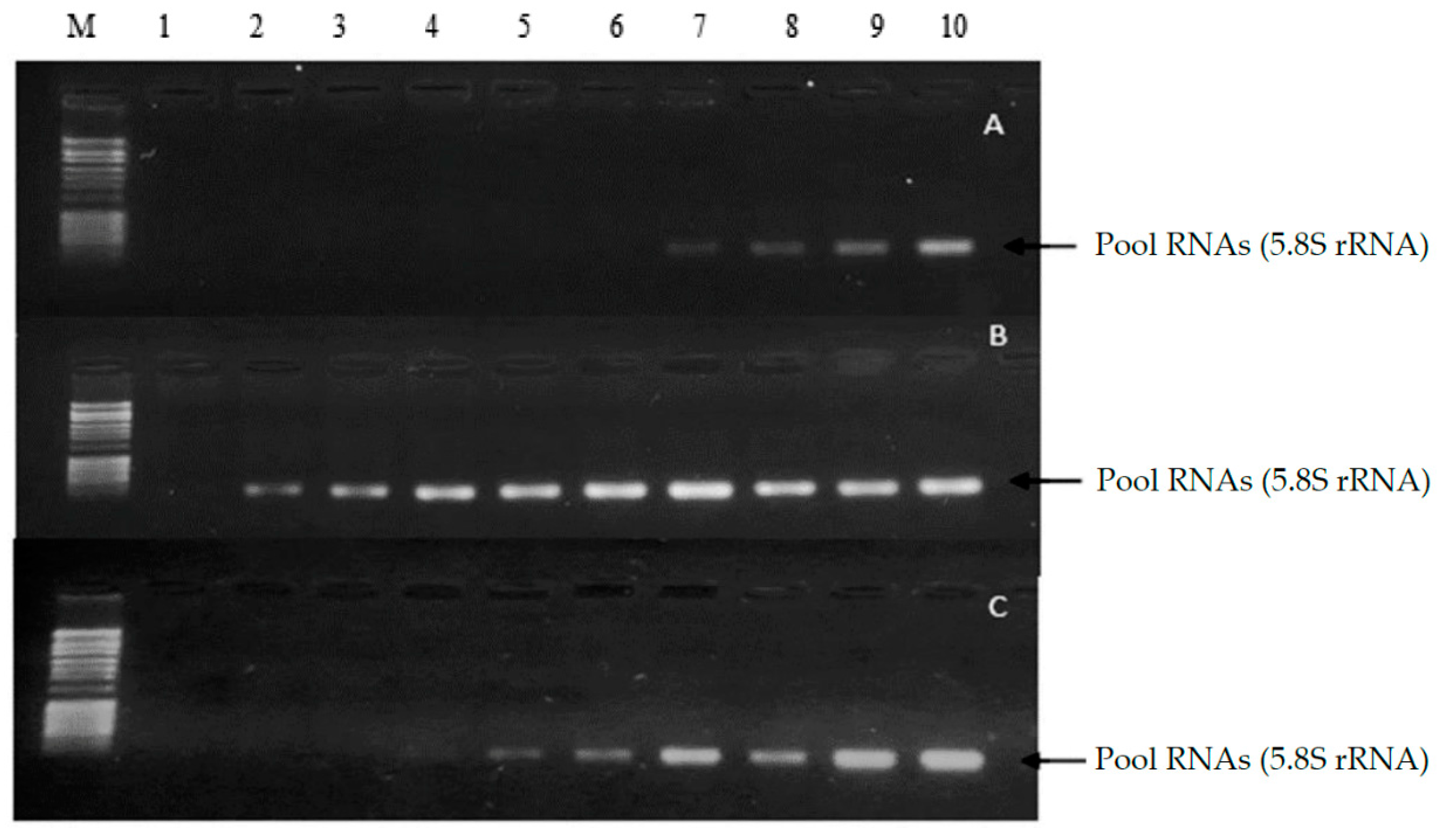
The results obtained through 1% agarose gel electrophoresis of the samples from methods 1, 2 and 3 are then displayed for comparison and subsequent integrity analysis (
Figure 1).
When assessing the integrity of the samples isolated by means of 1% agarose gel electrophoresis, it is possible to observe a small pool formed from samples 7 to 10 method 1, from 2 to 10 method 2 and from 4 to 10 in method 3. In addition, no traces were observed in the gels, suggesting degradation or deterioration, especially of the RNA. Thus, the electrophoresis suggests the integrity of the observed samples. Furthermore, it is verified in the samples that the pool formed corresponds to small RNAs compatible in base pair size with 5.8 S rRNA and tRNA (
Figure 1).
Below, the costs for performing both nucleic material extraction and 1% agarose gel electrophoresis per sample are set out in table form.
4. Discussion
Given this, the quantification of microorganism cells is relevant not only in areas such as microbiology, public health and the pharmaceutical industry, but also in molecular biology, since a minimum amount of biological sample is necessary to obtain DNA and/or RNA [
17,
18,
19,
20]. And it is reaffirmed by Silva [
21], given that for him a good quantity of cells regardless of the type of sample used is what enables the stability and good isolation of the genetic material.
Thus, it corroborates Valadares-Inglis and Melo [
22], since the success in isolation is influenced, above all, by cellular characteristics of the sample. Mainly, the fungal cellular composition, which differs from animal eukaryotic cells, due to the presence of a cell wall that provides resistance and protection [
23]. The partial lysis of the samples being confirmed by Sambrook and Russell [
16], when they mention obtaining 5,000 to 10,000 ng of RNA per 106 cells depending on the tissue. And evidenced by the maximum RNA yield obtained by the present study, which was 477.6 ng.
Despite the differences between the methods adapted in the present study in relation to the standard protocol, according to Beltrão et al. [
24] and Oliveira et al. [
15], A260/A280 ratios with values between 1.8 and 2.0 for DNA indicate the presence of a pure sample free from contamination by proteins, carbohydrates and phenolic compounds. Thus, ratios < 1.8 may be indicative of protein contamination, while values > 2.0 indicate contamination by reagents, such as phenol. However, in the SiC extraction method performed by Rosa [
12], DNA absorbance ratios between 1.55 and 1.78 were considered as good quality and with low protein concentrations.
Regarding RNA purity, values close to 2.0 are considered ideal [
25]. However, for Petrucelli [
26], ratios between 1.8 and 2.0 or even higher values, such as 2.1, are acceptable limits. Therefore, method 3 is the one that best encompasses samples considered pure of both DNA and RNA simultaneously, as is evident in samples 1, 2, and 3 of this method. Although for Mello et al. [
5], values higher than 30 ng/mL of genetic material, such as those obtained in almost all samples of methods 2 and 3, are already satisfactory for application in methodologies such as PCR.
Although the presence of the DNA molecule was not verified in the gels, the results obtained in the electrophoresis were promising. In addition to corroborating the yield and purity analyses obtained by spectrophotometry in the present study, it is worth considering the particularities of RNA, which, according to Devlin [
27], makes this molecule very unstable and easily degraded. For this reason, Dettogni and Louro [
28] confirm that RNA is so fragile that it deserves special attention during the extraction process. And methods optimized specifically for its protection due to the difficulty of laboratories in isolating this genetic material in some biological samples.
Regarding the cost-benefit analysis of using a manual protocol for the joint extraction of DNA/RNA and analysis of its integrity, it is possible to note that the adapted protocol has an excellent cost and allows for the performance of several extractions (
Table 3). This corroborates studies by Amaral et al. [
29] who, when comparing a phenol-chloroform extraction with other methodologies, including a commercial kit, classified this methodology as the most efficient because it obtains, at a low cost: good quality and concentration of the extracted genetic material in a time considered relatively fast compared to other methodologies.
5. Conclusions
The protocol adapted in the methods proved to be extremely promising for obtaining samples considered pure and complete, including for use in various molecular tools, in a shorter time. Thus, resulting in the development of a cheaper, faster and simpler method, in addition to obtaining excellent results using minimal quantities of biological sample, thus being an accessible methodology applicable to various laboratory infrastructures. Thus, it can range from its application in research in small laboratories to its use in laboratory routines.
Author Contributions
E.C.V.F.; M.R.V.L. and D.L.S.J. wrote the manuscript and compiled the data; F.A.S.; A.C.F.A.; P.R.F. and T.T.A.Y. carried out the microbiological and molecular biology experiments; M.K.N.S.L. coordinated the project and carried out tests; I.R.A.M. and H.D.M.C. took part in revising and finalizing the manuscript.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
We encourage all authors of articles published in MDPI journals to share their research data. In this section, please provide details regarding where data supporting reported results can be found, including links to publicly archived datasets analyzed or gener-ated during the study. Where no new data were created, or where data is unavailable due to privacy or ethical restrictions, a statement is still required. Suggested Data Availability State-ments are available in section “MDPI Research Data Policies” at
https://www.mdpi.com/ethics.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Dadar, M.; Tiwari, R.; Karthik, K.; Chakraborty, S.; Shahali, Y.; Dhama, K. Candida albicans-Biology, molecular characterization, pathogenicity, and advances in diagnosis and control–An update. Microb Pathog 2018, 117, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Liu, J.; Shao, J.; Da, W.; Shi, G.; Wang, T.; Wu, D.; Wang, C. Decreasing cell population of individual Candida species does not impair the virulence of Candida albicans and Candida glabrata mixed biofilms. Front Microbiol 2019, 10, 1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, F.L.; Wilson, D.; Hube, B. Candida albicans pathogenicity mechanisms. Virulence 2013, 4, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y. Looking into Candida albicans infection, host response, and antifungal strategies. Virulence 2015, 6, 307–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello, L.M.; Reiniger, L.S.; Meneghello, G.E.; Villela, F.A.; Mota, M.S. Isolamento de DNA genômico a partir de folhas secas de Erythrina crista-galli L., FABACEAE (Corticeira-do-banhado). Rev Thema. [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D.L.; Cox, M.M. Lehninger's Principles of Biochemistry, 7th ed. Porto Alegre: Artmed Editora LTDA, 2019.
- Pinho, M.D.S.L. Molecular biology research: how to do it? Rev Bras Colo-proctol 2006, 26, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrêa, A.A.P.; Unêda-Trevisoli, S.H.; Pazeto, M.S.R.; Vianna, V.F.; Mauro, A.D. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of DNA extraction in Jatropha. Científica (Jaboticabal), /: 235–245. Available in: https, 5555. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, S.D.S.O.; Barbosa, A.M. Metodologia de coleta e extração de DNA da Acariquara-Branca (Geissospermum urceolatum ah Gentry, 1984), no município de Manacapuru, km 60–comunidade Nova Esperança. Braz J Dev 2020, 6, 69130–69141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soouza, M.R.; Oliveira, G.D.; Santos, A.E.E.; Ságio, S.A. Comparação de métodos de extração de RNA aplicados a culturas amiláceas utilizadas na produção de etanol. Rev Desafios 2020, 7, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Görg, A.; Weiss, W.; Dunn, M.J. Current two-dimensional electrophoresis technology for proteomics. Proteomics 2004, 4, 3665–3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa, D.D. Método rápido de extração de DNA de bactérias. Summa Phytopathol 2008, 34, 259–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.C.D.R. Produção de carbeto de silício em escala piloto. Monograph (Undergraduate Degree in Mining Engineering) – Federal University of Ouro Preto, Brazil, 2018a. Available in: http://www.monografias.ufop.br/handle/35400000/1580.
- Stipp, L.C.L.; Monteiro-Hara, A.C.; Mendes, B.M.J. In vitro organogenesis of zucchini squash cv. Caserta. Hortic Bras 2012, 30, 274–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, W.G.; Lima, P.D.C.; Perinotto, C.M.; Campos, F.L. GelRedTM na coloração de DNA em Jatropha curcas L.(Euphorbiaceae). Rev Espacios, /: in: https, 1637. [Google Scholar]
- Sambrook, J.; Russell, D.W. Molecular Cloning, 4rd ed.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, 2001. Available in: https://www.cshlpress.com/pdf/sample/2013/MC4/MC4FM.pdf.
- Greghi, S.Q. Avaliação da eficiência de métodos rápidos usados para detecção de coliforme totais e coliforme fecais em amostras de água, em comparação com a técnica de fermentação em tubos múltiplos. Dissertation (Master's Degree in Food and Nutrition) – Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Araraquara Campus, São Paulo State University, 2005. Available in: http://hdl.handle.net/11449/88350.
- Ibrahim, R.I.H.A. modified CTAB protocol for DNA extraction from young flower petals of some medicinal plant species. Geneconserve, /: 165-182. Available in: http.
- Pessôa, G.; Magalhães, M.; Siqueira, A.; Wisniewski, C.; Tarley, C.; Luccas, P. Development of a Turbidimetric Flow Injection Analysis System for Cell Counting Original Paper. FIA 2008, 25, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, C.P.; Ramalhete, N.; Barbosa, A.; Silva Bito, R.A. , Candeias, A.; Gonçalves, J.; Pinheiro, A.; Teixeira, F.; Fitas, M. Microbiological control of parenteral dosage forms. BBR. [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.C.; Ekert, M.H.; Mazanek, M.L.; Miranda, C.S.; Santos, A.L.; Santos, A.R.; Monte, S.M.C.; Castro, S.G.; Souza, A.C. Ramalho-Neto, C.E. Alternative methodology for extraction of high-quality DNA from ancient bones by demineralization without pulverization. Forensic Sci Criminol. [CrossRef]
- Valadares-Inglis, M.C.; Melo, I.S. Métodos de extração de dna e sua aplicação em estudos genéticos e ecológicos. In: Ecologia Microbiana, Melo, I.S.; Azevedo, J.L. Jaguariúna: Embrapa-CNPMA, 1998 p. 187-204. Available in: https://www.alice.cnptia.embrapa.br/alice/bitstream/doc/13052/1/Melo-ecologia.pdf.
- Zaitz, C.; Campbell, I.; Marques, S.A.; Ruiz, L.R.B.; Framil, V.M.S. Compendium of Medical Mycology, Rio de Janeiro; Guanabara Koogan; 2 ed; 2015.
- Beltrão, F.A.S.; da Silva, D.S.; Lamoca-Zarate, R.M.; Felix, L.P.; Beltrão, A.E.S. Avaliação da diversidade genética através de rapd de acessos de maniçoba (manihot pseudoglaziovii pax & hoffm.) e de duas espécies afins de interesse forrageiro. Rev Caatinga, /: Available in: https.
- Barbas, C.F.; Burton, D.R.; Scott, J.K.; Silverman, G.J. Quantitation of DNA and RNA. Cold Spring Harbor Protocols, 2007, (11), pdb-ip47. Available in: https://cshprotocols.cshlp.org/content/2007/11/pdb.ip47.full/1000.
- Petrucelli, M.F.; Peronni, K.; Sanches, P.R.; Komoto, T.T.; Matsuda, J.B.; Silva Jr, W.A.D.; Beleboni, R.O.; Martinez-Rossi, N.M.; Marins, M.; Fachin, A.L. Dual RNA-Seq analysis of Trichophyton rubrum and HaCat keratinocyte co-culture highlights important genes for fungal-host interaction. Genes 2018, 9, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devlin, T.M. Testbook of biochemistry: with clinical correlations, 7th ed.; São Paulo: Blucher, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Dettogni, R.S.; Louro, I.D. Challenges of dengue virus RNA extraction (DNA binding and extraction: methods, applications and limitations). In: Resende, R.R. Biotechnology applied to Agro&Industry: fundamentals and applications, B: São Paulo, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, C.B.; Vieira, N.A.; Silva, R.A.R.; Santos, F.J.; Campos, B.A.; Oliveira, S.L.; Barufatti, G.A. Avaliação de protocolos para extração de DNA Genômico de sangue Bovino. J Selva Andina Res Soc, /: 95–103., 2072. [Google Scholar]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).