1. Introduction
Topology optimization is a method that can support the product developer in the lightweight design of structures and is therefore a central tool in product development to reduce
emissions from products. The most widespread method for topology optimization is density-based topology optimization, the development of which began with the publications by Bendsøe and Kikuchi [
1] and Bendsøe [
2]. In addition to the density-based topology optimization methods, there are many other topology optimization methods. These include, for example, the Optimization Criteria-based methods (), the Phase Field methods [
3] or the nature-mimicking Evolutionary Structural Optimization [
4,
5]. Another topology optimization method is based on the level set method and was primarily developed by Sethian and Wiegmann [
6], Wang et al. [
7] and Allaire et al. [
8]. In this method, the geometry is described during optimization using a discretized level set function. The geometry is evolved by applying the classical shape derivative to determine the front velocity and then by solving a Hamilton-Jacobi equation. [
8]
In addition to the level set-based topology optimization approach just described, there are other variants of using the level set method for topology optimization. An overview is given in [
9]. One such method is the Velocity Field Level Set method (VFLS) [
10]. It allows the use of mathematical programming methods, such as the Method of Moving Asymptotes (MMA) [
11] in combination with the level set method. Therby enabling the straightforward integration of several constraints into level set-based topology optimization. [
10]
Wang and Wang [
12] developed the so-called Color Level Set method for the optimization of multi-material systems. For this purpose, they refined a description of multi-material systems known from image processing for level set topology optimization. It allows the description of
materials using
n level set functions.
An alternative approach to optimizing multi-material systems is the Reconciled Level Set method (RCLS) [
13], in which each material is described by its own level set function. The individual level set functions are evolved independently of each other and any overlaps that arise are subsequently resolved using a correction process [
13]. Chen et al. [
14] applied the RCLS in the context of multi-material topology optimization of smart energy harvesters and Vogiatzis et al. [
15] used it for topology optimization of multi-material negative Poisson’s ratio metamaterials. Tian et al. [
16] combined the RCLS with the extended level set method to design ferromagnetic soft active structures using topology optimization.
There are three different approaches to represent the current design for the evaluation of the system response during level set-based topology optimization. In the first approach, a density field of a constant background Finite Element (FE) mesh is adjusted based on the values of the level set function. A smoothed heaviside function is usually used for the adjustment. This variant is similar to density-based topology optimization methods [
8]. The second approach applies immersed finite element methods, such as XFEM [
17] or CutFEM [
18] methods. These use a constant background mesh that is cut by the level set functions. The third approach is to adapt a mesh or remesh the level set function in each iteration [
19]. With this approach, the standard Finite Element Method (FEM) can be used.
Allaire et al. [
20] developed a level set topology optimization with iterative mesh adaptation. The unstructured mesh is iteratively adapted using classical mesh modification techniques such as edge collapse, vertex smoothing and edge swap. Li et al. [
21] combined this mesh adaptation algorithm with the reaction-diffusion equation based level-set method. It uses the topological derivative and a reaction-diffusion equation instead of the shape derivative and the Hamilton-Jacobi equation [
22]. Feppon [
23] optimized a heat exchanger using also this iterative mesh adaptation approach.
In this article, a multi-material topology optimization method based on RCLS and VFLS with iterative remeshing of the multi-material design is developed. The developed method is validated by two cases. In the developed method, the edge length of the FE mesh can be adjusted. The influence of the edge length and an additional filter radius parameter on the optimized design is investigated in two studies.
2. Methods
In the following, the boundary value problem of elastostatics, which is used in both single and multi-material cases, is introduced first. For the validation of the developed method, the single material optimization problem and the VFLS are then presented. In the next section, the multi-material optimization problem and the RCLS are introduced. Finally, an overview of the developed optimization method is given and its individual components are explained in detail.
2.1. Boundary Value Problem of Elastostatics
This article considers the quasi-static boundary value problem of elastostatics:
is the displacement field to be identified and
is the stress field of the domain
. For the Neumann boundary
with normal vector
, the force
is specified as a boundary condition. In addition, in this article the volume forces are assumed to be
and the displacements
on the Dirichlet boundary
.
To solve the boundary value problem
1, an additional constitutive law is required. For this purpose, Hook’s linear-elastic law is used:
The strain tensor
is given by
. In Equation (
2), the elasticity tensor
is a function that can be described in the single-material case by
and in the multi-material case by
. The indicator functions
of the i-th material each have the value 1 if the i-th material is present and 0 otherwise.
Using the constitutive law and the above simplification, the weak form of the boundary value problem can be derived:
Here denotes the space of the kinematically admissible displacement fields.
If one also introduces the two abbreviations
Equation (
3) can be written as
.
2.2. Single-Material
2.2.1. Optimization Problem
The optimization problem for the single material case is:
In Equation (
5), the weighted objective function of compliance and regularization term is considered, with the two weighting factors
and
. The latter ensures that a strut-like structure is created and also regularizes the optimization problem [
8]. The boundary value problem
3 in weak form exists as an equality constraint and the displacements
must satisfy this constraint at all times. The target volume fraction
of the material in relation to the volume of the design space
is specified as an inequality constraint. The design variables
are also constrained by the lower and upper bounds
and
. In the case of this article, the bounds are normal velocities, as the design variables in the VFLS are the normal velocities.
2.2.2. Velocity Field Level Set Method
The description of the part surface during optimization is done using the level set function
. An example of a level set function is depicted in
Figure 1. The level set function is positive inside the part, zero on the part surface and negative outside the part (in the rest of the design domain). In summary, the following applies:
In this article, a special form of the level set function, the so-called Signed Distance Function (SDF), is used to numerically stabilize the evolution of the surface described below [
8]. The function values of the SDF are the signed distances to the surface inside and outside the part. For example, in the part,
applies, whereby the function
d returns the distance between
and
. SDFs also have the property that
. [
24]
The evolution of the level set function and thus the surface (
) in a previously given or calculated normal velocity field
is described by the Hamilton-Jacobi equation [
24]:
The normal velocity field
is linked to the design variables
by linear interpolation in the topology optimization using VFLS [
10]:
Here,
is the global basis function of the linear FEM associated with node
i and
is the respective design variable. When discretizing the normal velocity field, other basis functions can be used in addition to the basis functions from the linear FEM. An overview of this is given in [
10].
The design variables are varied by the optimization algorithm based on previously calculated sensitivities. In the VFLS method, the derivation of the sensitivities is based on the shape derivative [
10]. The shape derivative of the compliance component of the objective function is based on the simplification described above (no volume forces and no variation of the Neumann and Dirichlet boundary) [
8,
10]:
and the shape derivative of the regularization component [
8]:
The mean curvature
of the surface
is defined as
[
8]. Using
, the derivative of the objective function with respect to the design variables
is given by [
10]:
Similarly, the following derivative for the volume constraint can be derived [
10]:
2.3. Multi-Material
2.3.1. Optimization Problem
The optimization problem for the multi-material case with two materials is as follows:
For the regularization in the multi-material case, the area of the interface between the two materials and their surface is used. The former regularization ensures that the optimization problem is solvable and the latter ensures strut-like structures in the result. The weighting is performed analogously to the single-material case with the weighting factors , and . In addition, there is another volume constraint for the volume fraction of the second material in the multi-material case compared to the single-material case.
2.3.2. Reconciled Level Set Method
This article applies the RCLS [
13] to describe the multi-material case. Each material is represented with its own level set function in the RCLS. Here, these are the two level set functions
and
(see
Figure 2).
The two level set functions are developed separately using the Hamilton-Jacobi Equation (
7). The sensitivities from the single material case are used to determine the normal velocity fields required for this (see Equations (
11) and (
12)). This is feasible because the RCLS is coupled with the VFLS method in this article. However, the elasticity tensor associated with the material (or the level set function) must be used for the compliance component of the sensitivity (e.g. for
).
In the multi-material case, the design variable vector takes the form .
Since the two level set functions are developed independently in RCLS, the individual level set functions may overlap during evolution (see
Figure 3). However, this problem can be solved using the Merriman-Bence-Osher (MBO) operator [
13]:
This means that the RCLS works like a predictor-corrector method. In the first step, the level set functions are further evolved in the respective existing velocity field without considering the overlap (predictor step). This results in the temporary level set functions
and
(predictor step). The overlaps are then removed using Equation (
14) (correction step). The described method is also depicted in
Figure 3.
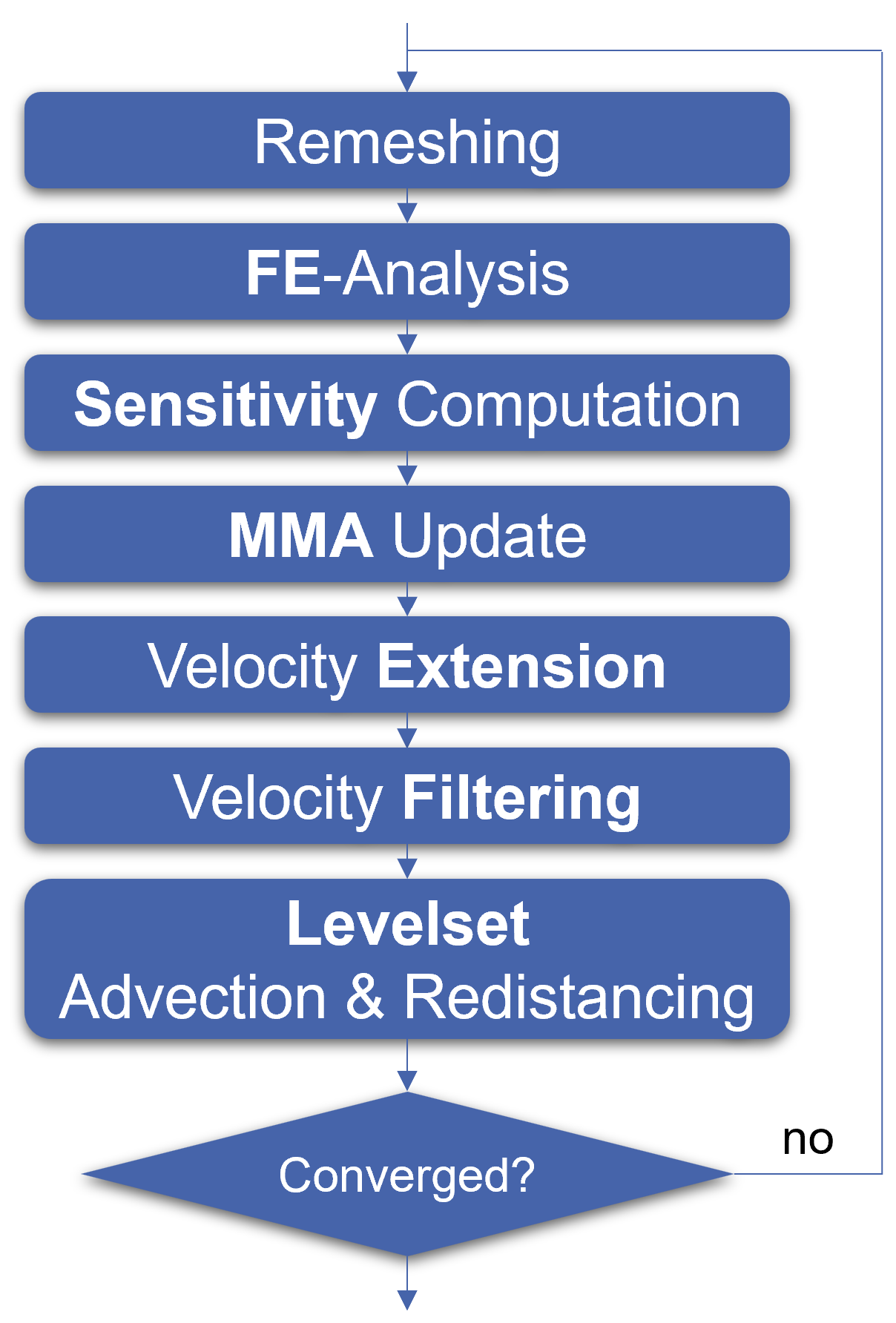
2.4. Optimization Method
The optimization loop of the developed method is shown in
Figure 4. At the beginning of each iteration, the current design, represented by the level set functions on the level set mesh, is remeshed with tetrahedra using the method described below in
Section 2.4.5. The result of the remeshing is the FE mesh of the current design. This is then used to determine the system response using linear FEM and to calculate the sensitivities (see
Section 2.2.2). The calculated sensitivities serve as input for the MMA [
11], which updates the design variables (normal velocities). The implementation of the MMA follows [
25]. Since the normal velocities are only non-zero in the immediate vicinity (on the surface) of the level set functions, they are extrapolated to the entire design domain (constant level set mesh) using the velocity extension method described in
Section 2.4.1. To stabilize the optimization method, the extrapolated normal velocities are then filtered using the Helmholtz equation (see
Section 2.4.2). The filtered normal velocities are then used to evolve the level set functions (see
Section 2.4.3). The evolved level set functions are then corrected using the MBO operator and subsequently their SDF property is restored using redistancing (see
Section 2.4.4).
2.4.1. Velocity Extension
The normal velocity field on the entire level set mesh is required for each level set function to be evolved. However, since the sensitivities are only non-zero in the vicinity of the zero level sets (surfaces) and consequently the normal velocities (design variables) updated by the optimizer are also non-zero, these must be extrapolated to the rest of the design domain (LS mesh).
For this purpose, a method is developed in this article with an analogous approach to the redistancing method described in [
26]. Extrapolation is carried out in the developed method in a two-stage process, which is outlined in
Figure 5. In the initialization phase, the surface described by the zero level set (
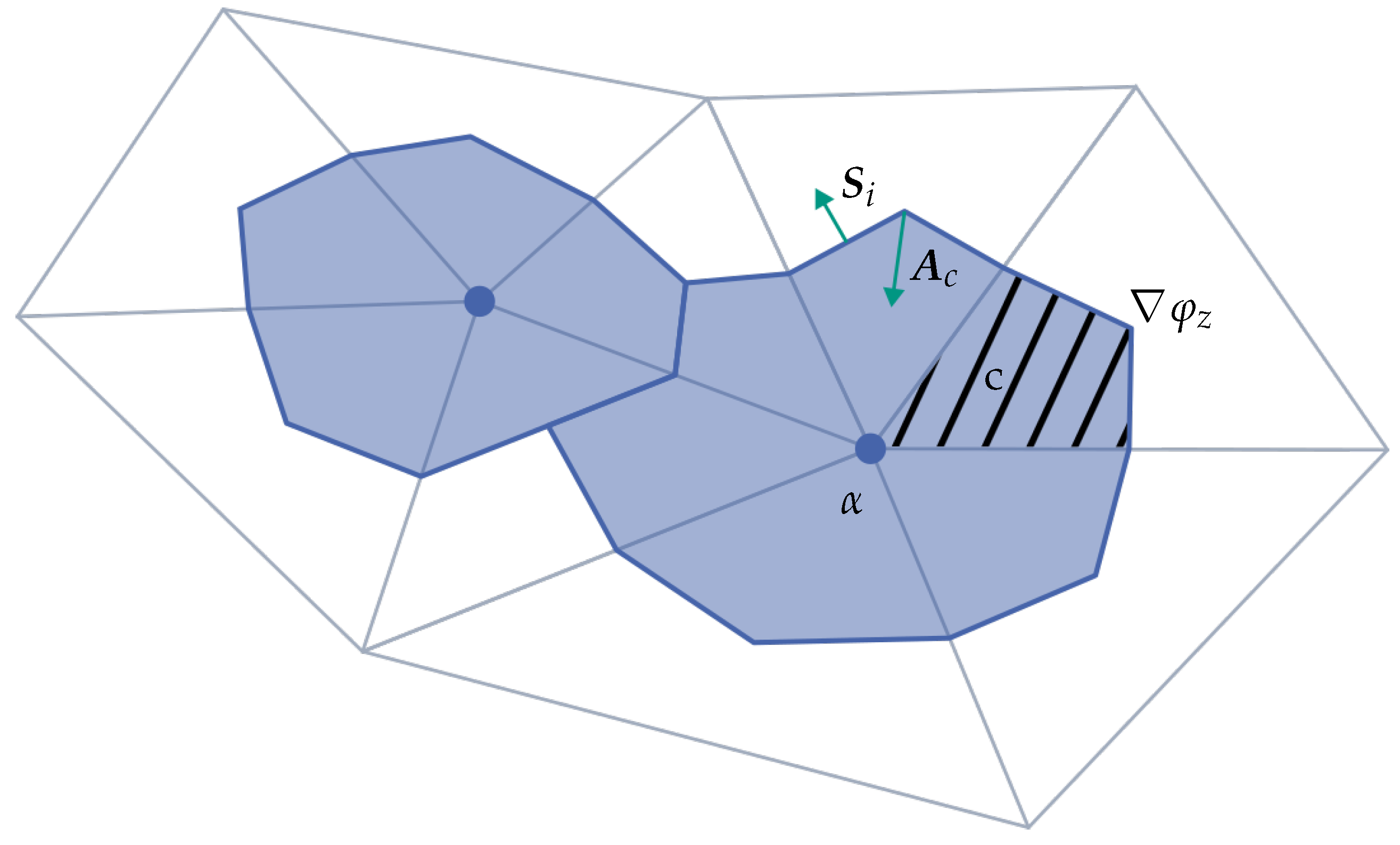
) is sampled. For this, the surface elements (triangles) belonging to the zero level set are derived from the FE mesh using the material ids. The values of the normal velocities are then determined for each node of the surface mesh using linear interpolation with the FE basis functions from the LS mesh.
The result of the initialization phase is a point cloud of the surface
analogous to [
26] with interpolated values and their adjacent triangles. The point cloud is also used to create a search data structure (kd tree).
In the extrapolation phase, the projection of each vertex of the level set mesh (design domain) is identified on the discretized level set surface mesh. The search data structure and the list of adjacency triangles are used for this purpose. At the identified point, the normal velocity is interpolated using linear interpolation and assigned to the original node in the level set mesh.
The two steps described can be parallelized straight-forward by means of multi-threading, since both the interpolation step in the initialization phase for each vertex of the surface mesh and the extrapolation step for each vertex of the LS mesh can be carried out independently of each other.
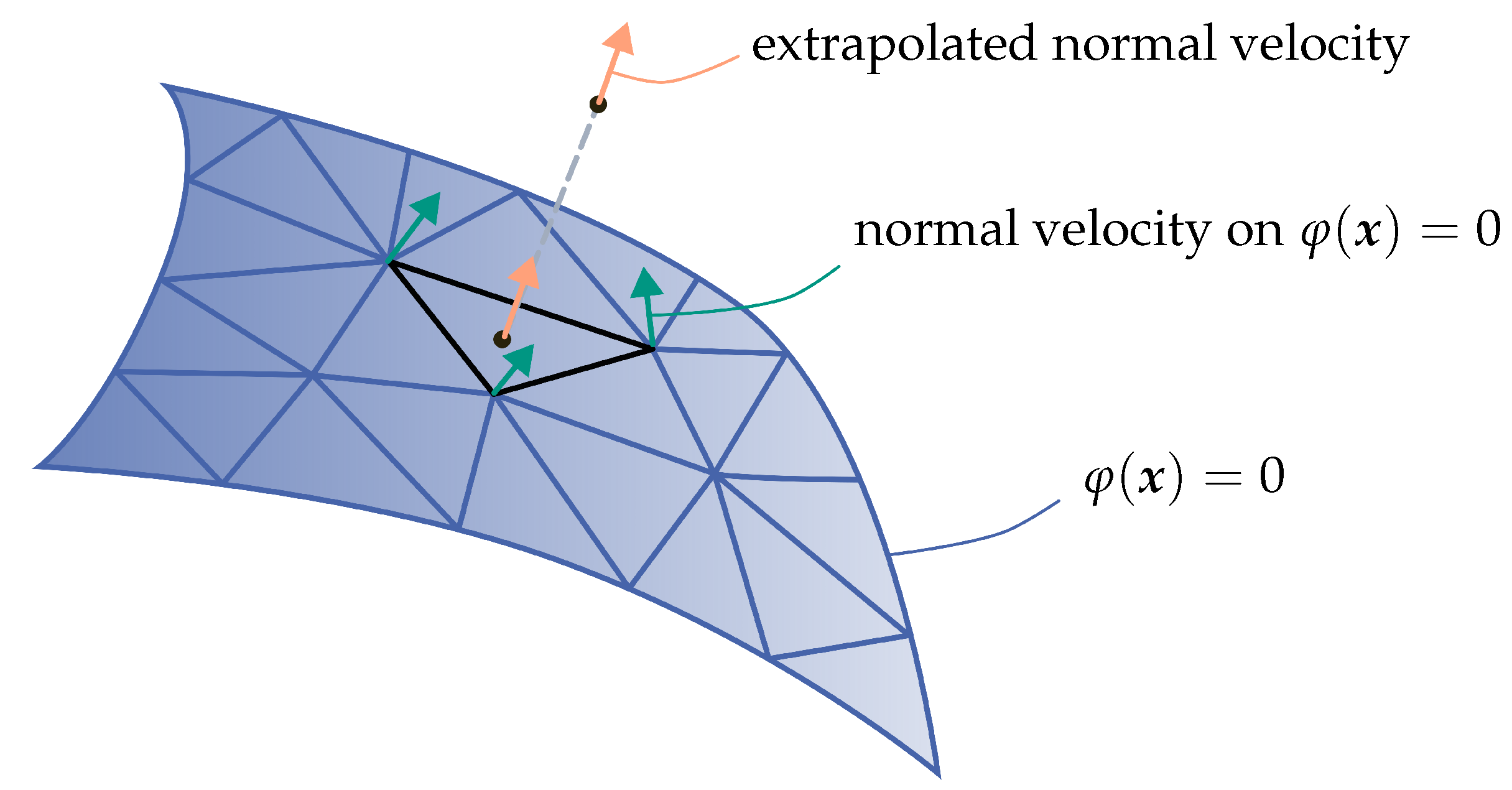
Figure 5.
Schematic representation of the velocity extension from the zero level set (blue) to the target vertex based on [
27]. For this purpose, the pole of the target vertex is determined on the zero level set and then the normal velocity of the target vertex (orange) is calculated from the normal velocities of the triangle (green) using linear interpolation.
Figure 5.
Schematic representation of the velocity extension from the zero level set (blue) to the target vertex based on [
27]. For this purpose, the pole of the target vertex is determined on the zero level set and then the normal velocity of the target vertex (orange) is calculated from the normal velocities of the triangle (green) using linear interpolation.
2.4.2. Velocity Filtering
After the normal velocities have been extrapolated into the entire design domain, a filter step is then performed. The filter is applied separately for the two normal velocity fields. The aim of filtering is to smooth the velocity field in order to stabilize the optimization process. The filter used is the one described in [
28], which is based on the Helmholtz-PDE and is well known in the field of homogenization-based topology optimization. The filter equation (Helmholtz PDE) is [
28]:
is the filtered normal velocity field that results as the solution of Equation (
15). The filter parameter
is a length parameter that describes the size of the filter mask, but not its explicit radius [
28].
To solve Equation (
15), its weak form is generated. The building blocks from the evaluation of the system response are used for evaluation the weak form. The weak form is solved on the LS mesh with homogeneous Neumann boundary conditions
and the unfiltered normal velocity field
as the right-hand side [
28].
The advantages of this filter approach over explicit filters are the reuse of the building blocks including their parallelization and the automatic consideration of non-convex design spaces (holes, undercuts) [
28].
2.4.3. Advection
In this section, the solution of the Hamilton-Jacobi Equation (
7) on tetrahedral meshes using the finite difference method is presented. The method described in [
29] is used for this purpose.
The Hamilton-Jacobi Equation (
7) can be written as [
29]:
The numerical solution of the equation using finite differences requires a stable and accurate upwind approximation of the Hamiltonian
[
29]. In the method for tetrahedral meshes developed in [
29], the approximation using an implicit mesh dual to the level set mesh (cf.
Figure 6) is applied as follows:
Here, the upwind approximation
is formed by weighting the cell-centered values
surrounding the node
with the corner weights
. These are calculated as [
29]:
In this case,
are the cell corner unit normals, which are derived by summation and normalization from the outward corner surface area normals
. The corner velocities in the case of normal advection are given as
. For the calculation of the corner velocities and the upwind approximation, the cell centered gradients are still required:
Here
denotes the volume of the current tetrahedron of the level set mesh,
means that all surfaces of the tetrahedron are summed up and
are the level set values associated with the surfaces
[
29].
The integration in time is carried out using the two-stage Runge-Kutta method. It is referred to as two-stage because the intermediate step
is calculated for the calculation of the
time step. [
29]
2.4.4. Redistancing
In the progress of the optimization, the signed distance property (
) of the level set functions disappears due to the evolution by means of the Hamilton-Jacobi Equation (
7) and after application of the MBO operator
14. However, this is essential for the stability of the optimization process, which is why it is restored by means of redistancing [
8,
14].
This article uses a two-step explicit method for redistancing. In the first step, the level set function is discretized using the Marching Tetrahedra (MT) method. For this purpose, all tetrahedra of the level set mesh are looped. For each tetrahedron, the intersection points of the edges with the zero level set function are determined and the respective MT case is identified based on the edge intersection pattern (see
Figure 7) [
30].
In the second step, the closest point on the discretized surfaces and the distance to this point are determined for each vertex of the level set mesh. The distance calculation is accelerated using an AABB tree. In addition to the distance, the sign is required, which is determined using the Fast-Windig-Number [
31].
2.4.5. Remeshing
This section describes the remeshing method and its implementation for resolving the current design in each iteration. A copy of the LS mesh serves as the starting point. Analogous to the redistancing method, all tetrahedra are looped and split based on the MT cases (see
Figure 7) and the individual tetrahedra are assigned the respective material id. The resulting mesh is then improved using the method described in [
32]. The method consists of the following four iterative phases [
32]:
split all edges with
collapse edges
swap edges of elements with
smooth all vertices
In the first phase, edges with a length greater than
are split by creating an additional vertex in the middle of the edge to be split. All tetrahedra adjacent to the updated edge are updated. In the second phase, all edges with a length less than
are collected and then all permissible collapses are performed. The first two phases of the remeshing method primarily ensure that the edge length converges in towards the target edge length
. In the third phase, all tetrahedra whose quality
q is less than
are identified. [
32] The volume-length measure [
33] is applied as quality measure. For the adjacent edges, all possible edge swaps are tested and the one with the best possible quality is performed. The edge swap phase is primarily used to improve the tetrahedral quality. In the fourth phase, all vertices are repositioned in a hierarchical smoothing. For this purpose, the vertices are divided into volume and boundary vertices and successively smoothed. The classification of the vertices is explained in more detail below. [
32] Smoothing the boundary vertices involves a projection step onto the surface, where we project onto the level set functions using Newton’s method instead of onto an Moving Least Square based geometric definition as in [
32].
In the phases listed above, many operations occur that are not permitted because they are not feature-preserving or because inverted tetrahedra are created during execution. For the former, a concise set of rules was established in [
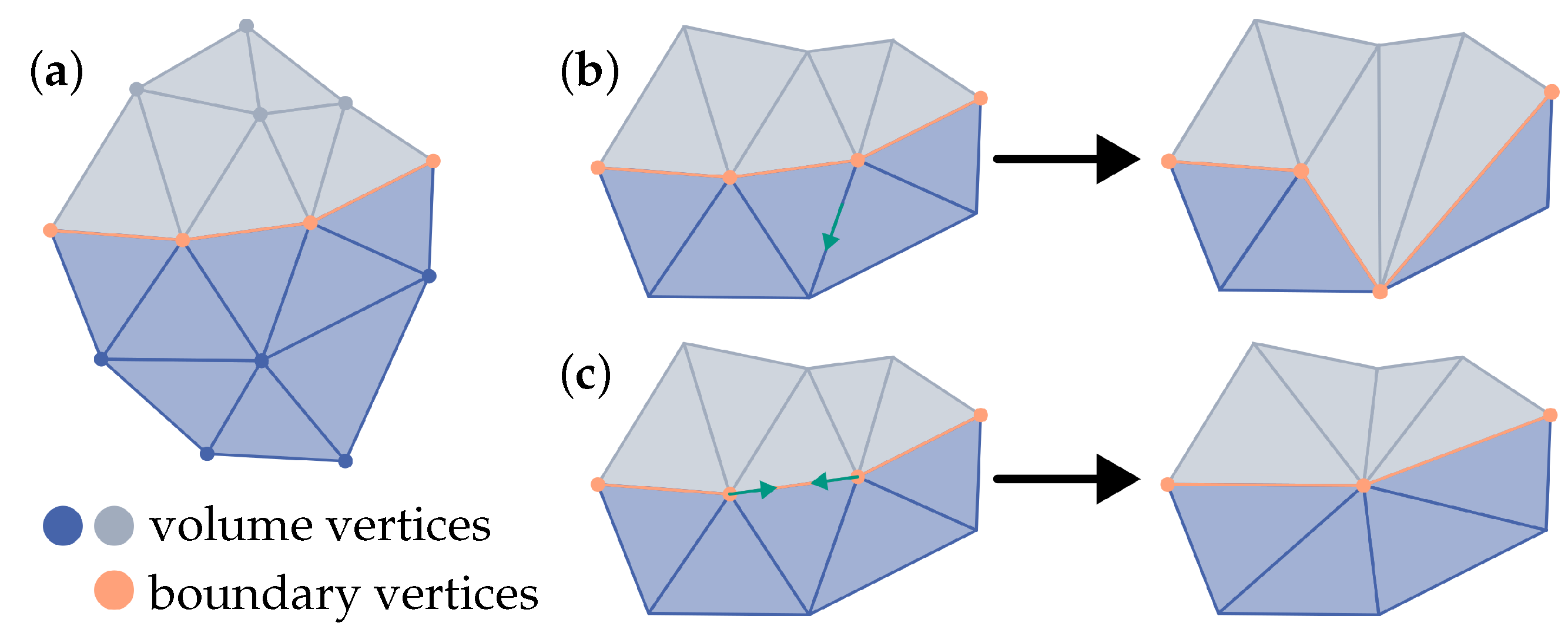
32], which is based on a classification of vertices, edges and tetrahedra as well as associated conditions. The classification uses the number of labels of the adjacent tetrahedra (here: #material ids). For vertices, for example, if there is exactly one material in the adjacent tetrahedra, it is a volume vertex and if there is more than one material, it is a boundary vertex (see
Figure 8a). The classification then allows rules to be defined that describe which mesh modifications are permitted. This is illustrated by the example of an edge collapse in
Figure 8b,c [
32].
The four phases described above are followed by a quality improvement phase, in which the last remaining tetrahedra with poor quality are eliminated [
32]. At this point, we also use the method described in [
34], which classifies the bad tetrahedra and then applies targeted operations depending on the type of tetrahedron.
For the implementation of the mesh modification (edge collapses, edge swap, ...) we use the unique cavity operator from [
35]. This allows the mesh modifications required for the phases described above to be represented using the same operator and therefore the same code. This can significantly reduce the implementation and maintenance effort for the mesh modification [
35].
The different operations can be implemented by different initialization and subsequent filling of the cavity [
35].
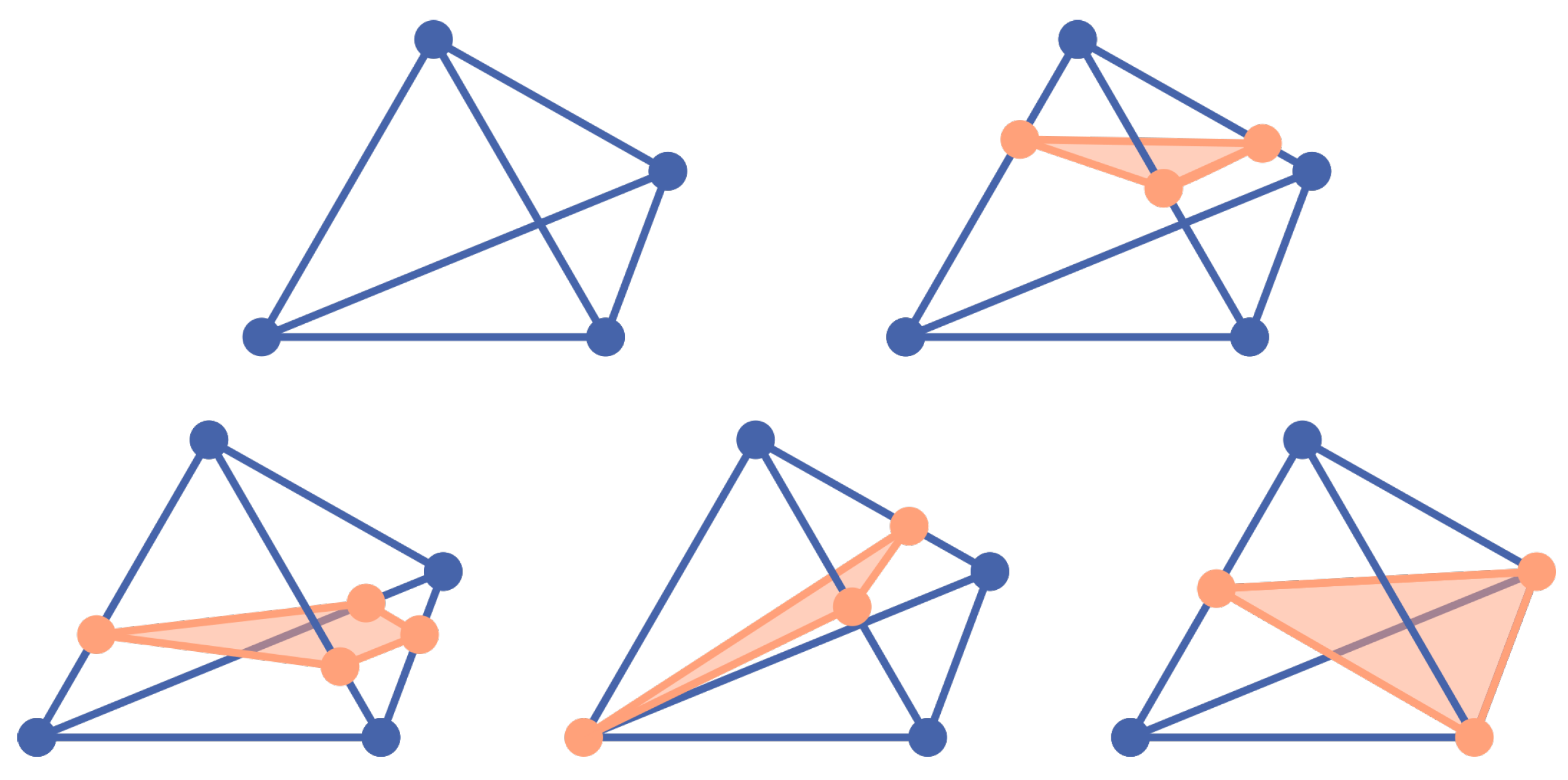
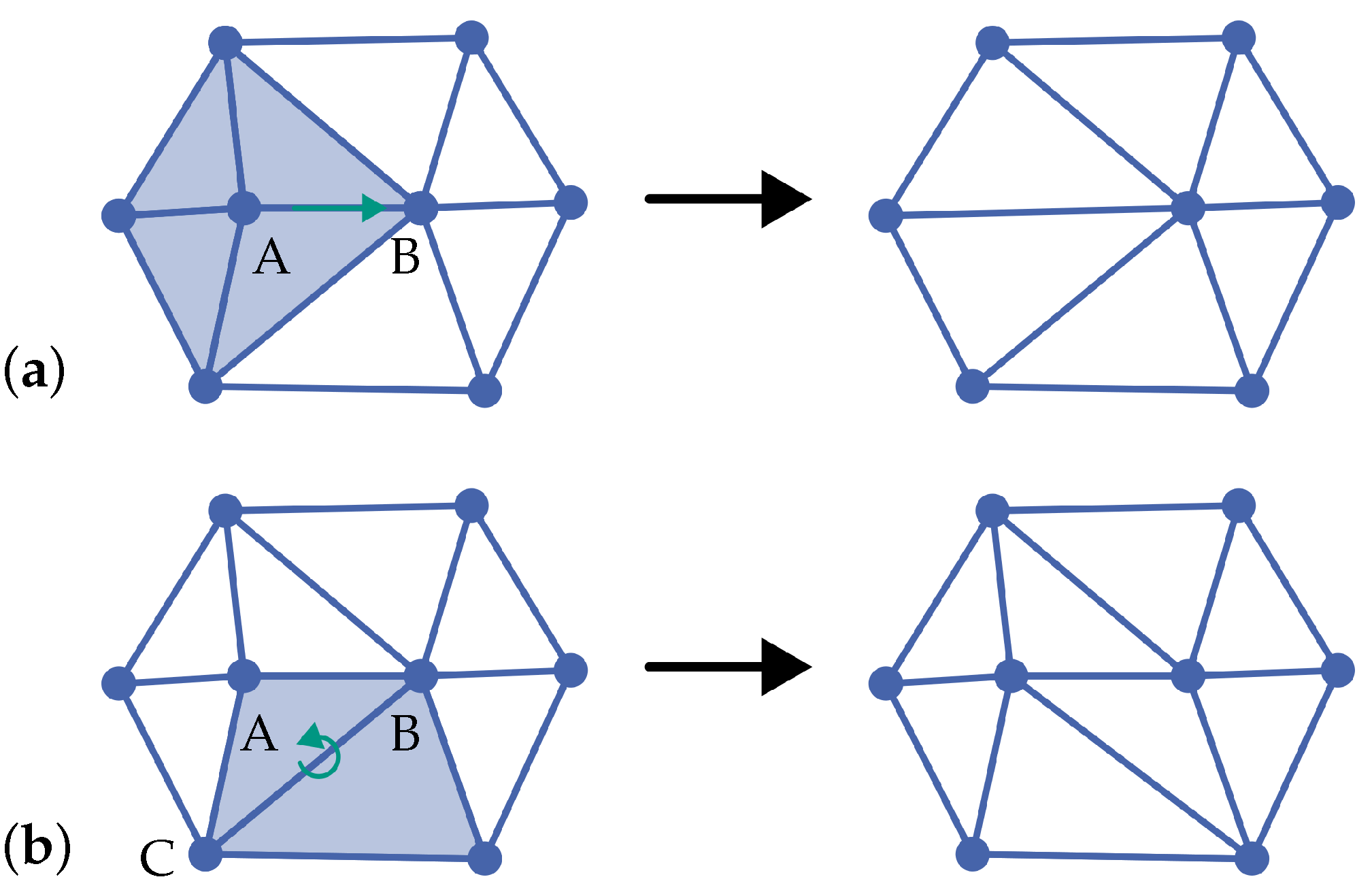
Figure 9 shows an edge collapse and an edge swap using a 2d triangle mesh. For the edge collapse
(
Figure 9a), all elements (tetrahedrons or triangles) are added to the cavity adjacent to vertex
A for the initialization, after which they are all deleted. The adapted mesh is obtained by connecting all surfaces of the cavity that do not contain vertex
B with target vertex
B.
In order to obtain a robust remeshing method, the first step is to test whether inverted tetrahedra are created during the filling process of the cavity operator. The filter-based orientation predicate described in [
36] is used for this purpose. Secondly, when initially cutting the mesh with the level set functions based on the MT cases, a vertex can be zero, negative or positive instead of only positive or negative.
A disadvantage of the cavity operator is the somewhat slower performance compared to explicitly implemented mesh operators. However, this disadvantage can be remedied by thread-based parallelization. In this paper, the vertex smoothing and the edge-collapse phase are parallelized. For the vertex smoothing phase, a heuristic graph coloring is used to identify independent cavities. The vertices of each color are then processed using #threads. After the vertices of a color have been smoothed, the threads are synchronized [
37].
The edge collapse phase is parallelized using the producer consumer pattern. We use #threads - 1 producer and 1 consumer. After the edges with too short a length have been identified, the producers test all the preconditions described above and then attempt to perform the collapse virtually. If a collapse is valid, it is entered in a queue. The consumer removes the pre-selected collapses and executes them with renewed preliminary checks. The latter is necessary, as the mesh in the vicinity of the edge may have changed in the time between insertion into the queue and execution of the collapse due to other collapses executed by the worker, meaning that the collapse may no longer be valid. The parallelization strategy is based on the fact that only about of the edge collapses per iteration are valid and can be executed.
The cavity operator described only works inside the volume and not at the boundary. Since no extra operator is implemented for the boundary region and the method described requires a convex region, a mesh preparation step is necessary [
32]. In the first step, the convex hull of the region is determined and an offset is then formed from this using the method described in [
38]. The resulting volume is filled with tetrahedra. We use the fTetWild algorithm [
39] for this. This preparation now makes it possible to apply the cavity operator described above to the entire area, as the filled offset means that the surface tetrahedra are surrounded by elements (see
Figure 10). [
32]
3. Numerical Experiments
The following section first presents the two cases that are used in the article to illustrate and validate the developed optimization method. In addition, a summary of the parameters that apply to all numerical examples is then provided. The parameters apply for as long as not directly stated otherwise. This is followed by two single-material optimization examples to validate the single-material case and then two multi-material examples to validated the multi-material case.
3.1. Cases
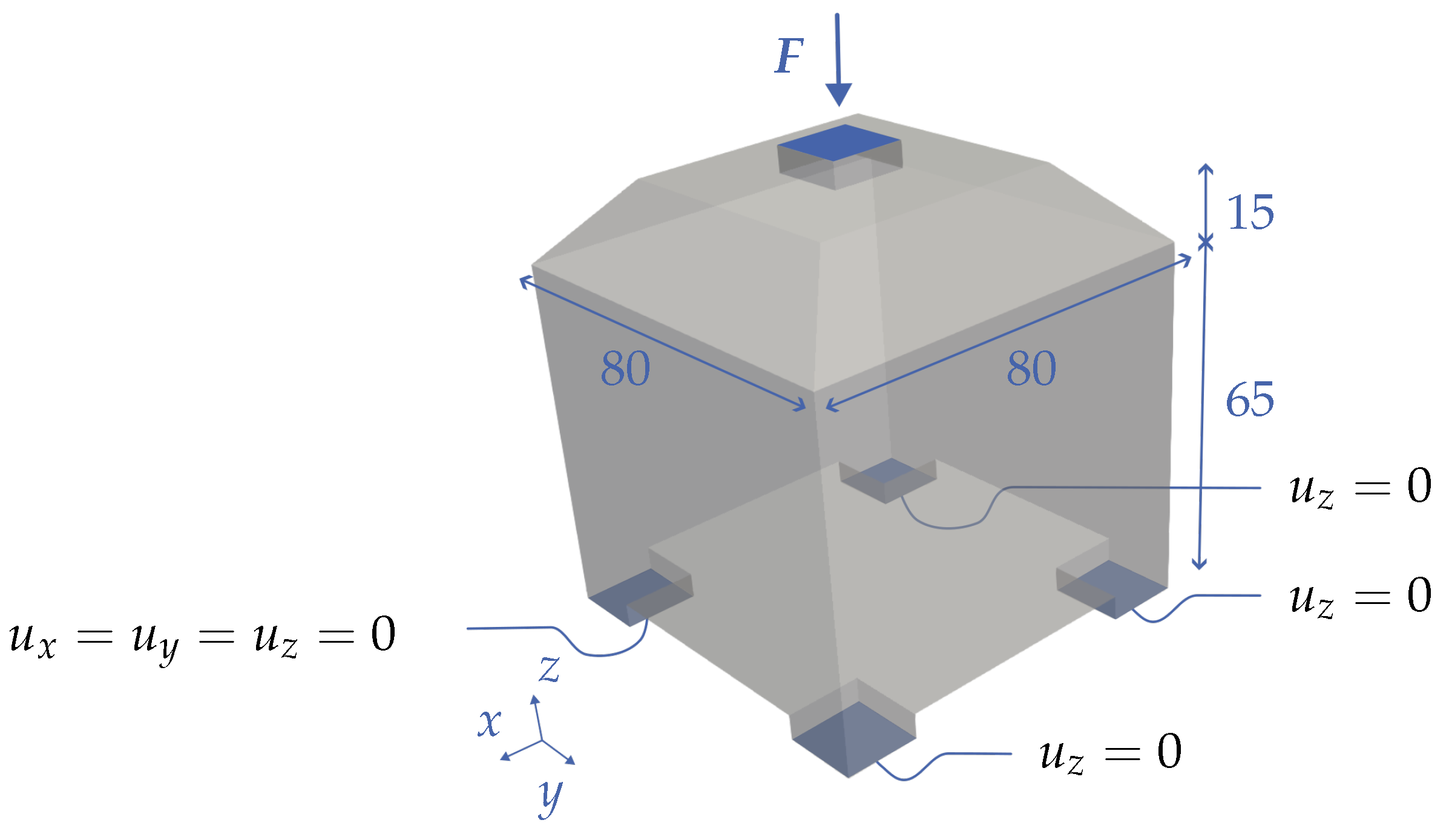
The first case is a cube with side length 80 with chamfered edges on the top (see
Figure 11). The case serves as an example for almost arbitrary design spaces of the optimization method. However, it can be compared at the same time with the classic example of the box without chamfering from the literature. The box is supported at four bearing points on the underside. The displacement of the vertices of one of these supports is restricted in all three spatial directions (
). The vertices of the other supports can move freely in the plane, but not in the z-direction (
). The square load application and constraint surfaces are slightly protruding. The first element layer adjacent to the surfaces is always considered as a non-design space in the optimization and cannot be modified.
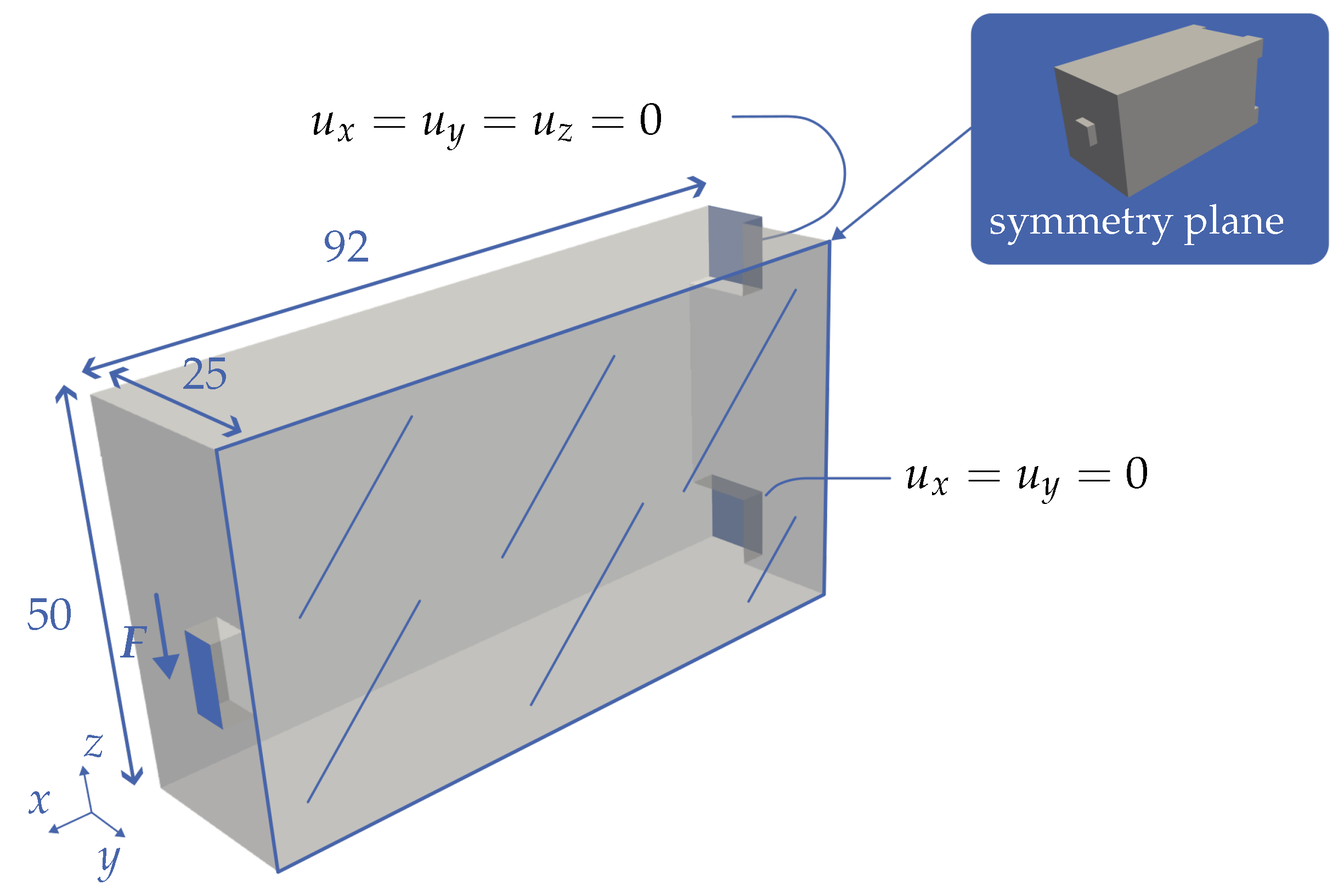
The second case is a cantilever clamped on one side (see
Figure 12), which is subjected to a force
F in the negative z-direction on the front surface. Two square surfaces with a side length of 15 length units are used for clamping. The vertices of the upper surface are completely fixed in all three spatial directions (
) and the vertices of the lower surface are only fixed in the x and y directions (
). Only half of the design domain is considered with an additional symmetry boundary condition so that the result of the optimization is a symmetrical design. The dimensions of the design domain can be taken from
Figure 12. As with the box, the load application and constraint surfaces are slightly protruding and the first element layer is a non-design space.
For both the single and multi-material cases, and are used. A normal velocity of is specified for the non-design spaces described above. The filter parameter is selected as times the average edge length and the target edge length is . The target volume fraction is set to of the design space. In the multi-material case, this is divided equally between the two materials so that and applies.
To determine the convergence of the optimization, a convergence criterion is evaluated after the optimization has been performed. This takes into account the 5 previous iterations in the sense of a moving average and uses this filtered value to calculate the percentage change between two points. In the single material case, the limit for the percentage change is set at and in the multi-material case.
3.2. Single-Material
For the two single material cases, we use the parameters described below in addition to those listed above. A Young’s modulus of and is used for the material. The weighting is selected as , for the box case and , for the cantilever. The regularization term is activated after iteration 30 to ensure that it does not dominate the optimization at the beginning.. The level set function is redistanced every 5 iterations. The c parameter of the MMA algorithm is increased from a starting value of 1.0 to 100.0 within 150 iterations by means of a linear ramp. The latter results in a slow and smooth volume reduction, which gives the optimization method sufficient time to shape the design according to the objective function.
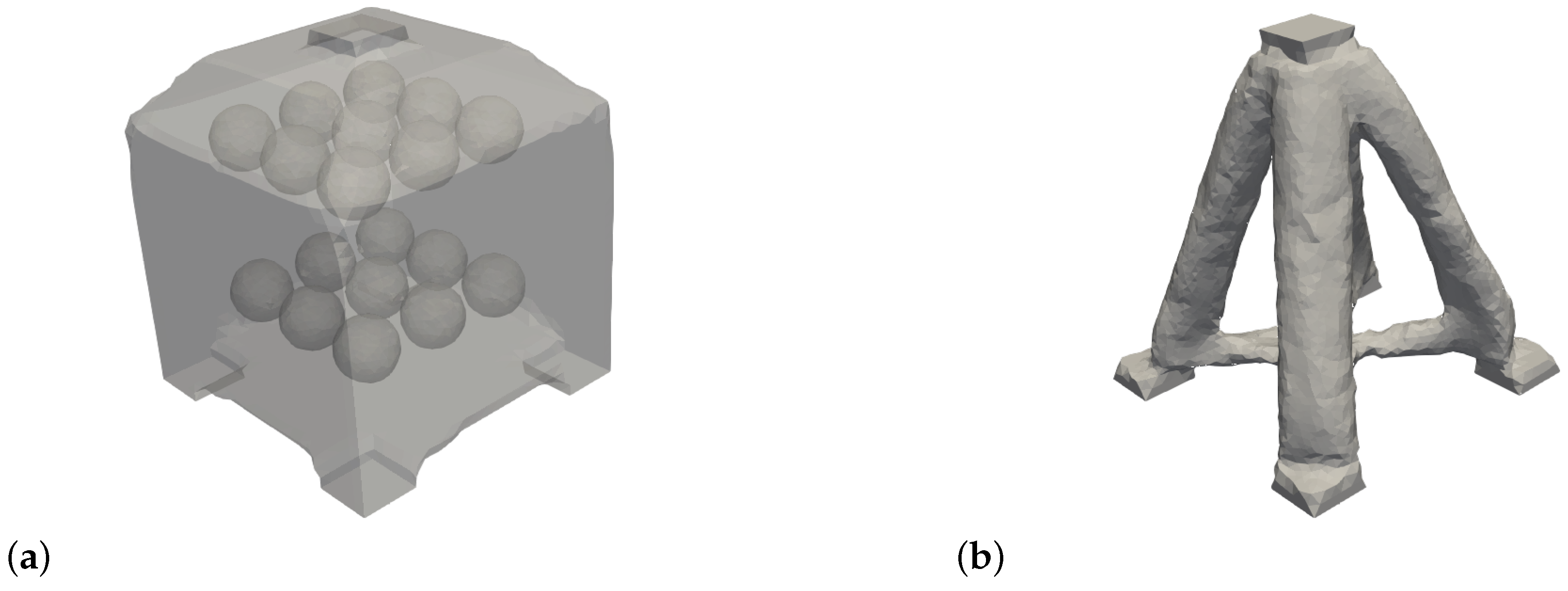
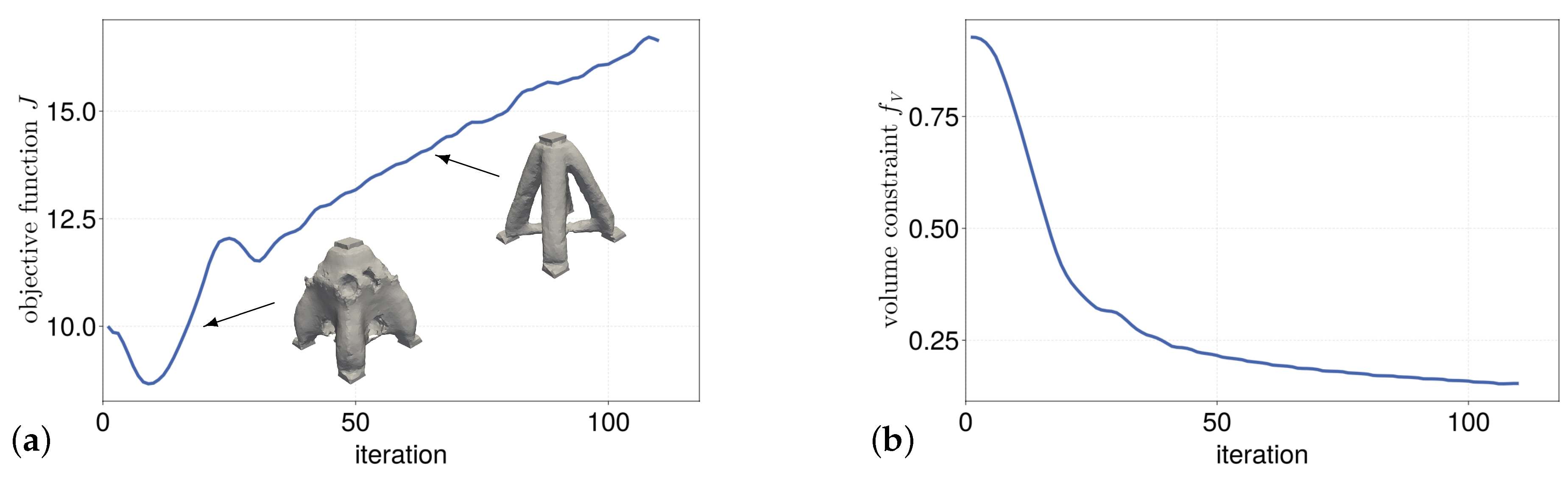
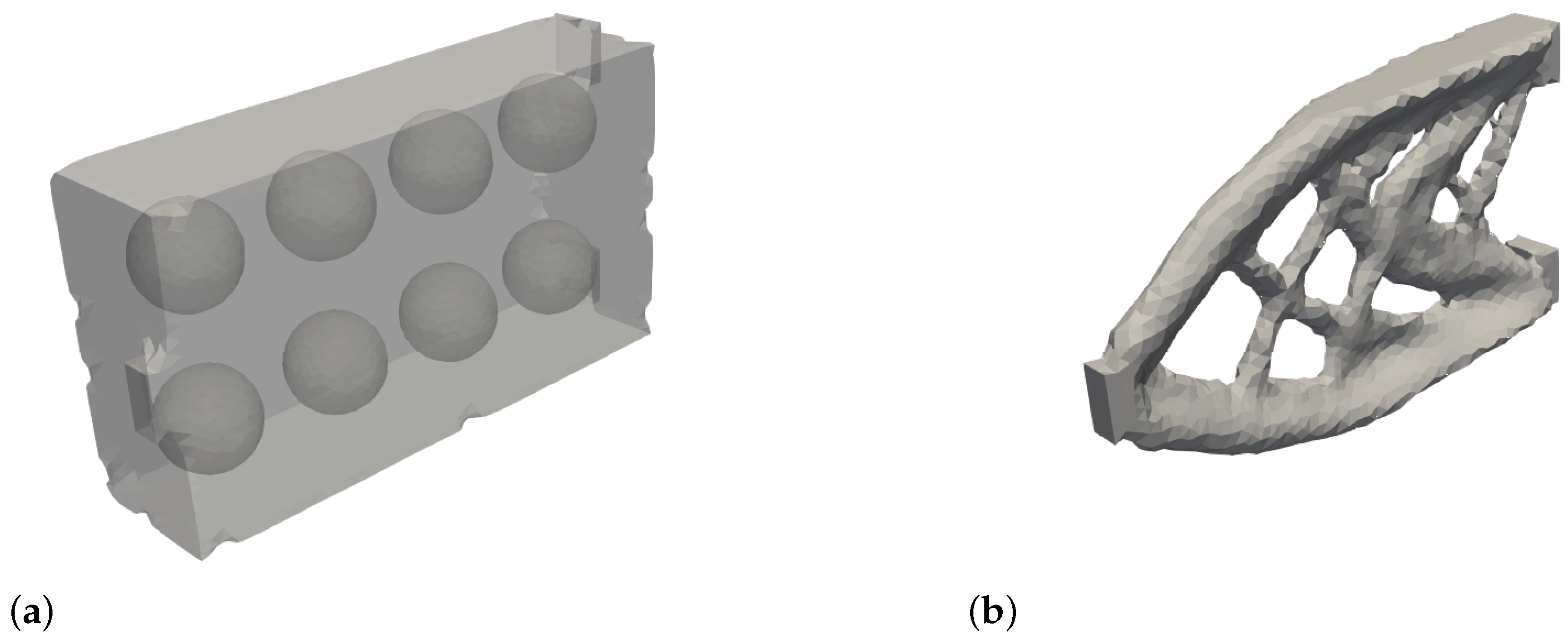
Figure 13a shows the initial hole structure used to initiate the level set function and
Figure 13b shows the corresponding optimization result at convergence at iteration 107 of the box in the single material case. It is evident that four main struts are formed to transfer the loads during the optimization process. These transfer the load directly from the point of application to the support points. In addition, cross struts develop in the form of a cross, which prevent the three floating supports from sliding sideways. The optimization result is in line with the state of the research (see e.g. Shape optimization book). However, it should be noted that depending on the optimization parameter (e.g. the
c parameter of the MMA algorithm), the optimization sometimes reaches a different local optimum. This results in a rectangular cross strut structure between the four main struts instead of the cross-shaped cross strut structure.
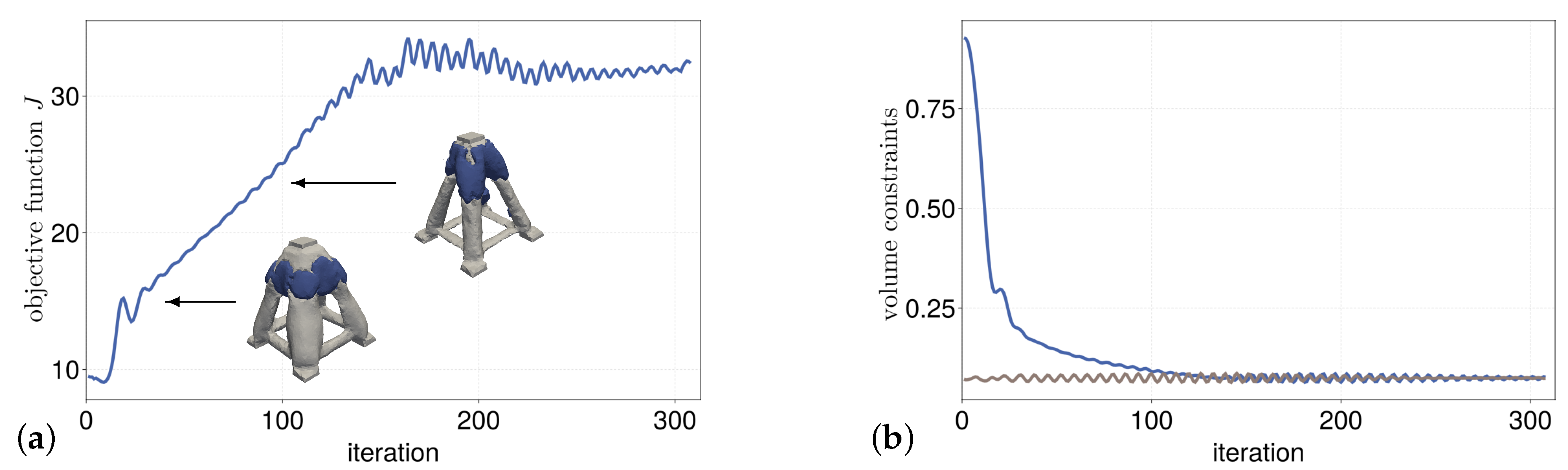
Figure 14a,b show the filtered history of the objective function and the volume constraint respectively. In order to filter out the numerical fluctuation introduced by the remeshing process, a moving-average filter is applied that takes into account the five past iterations. The history of the volume constraint shows the uniform decrease in volume over time.
Figure 15a shows the initial hole structure of the cantilever in the single-material case and
Figure 15b the resulting optimization result at iteration 60. The corresponding curves of the filtered objective function and volume constraint are shown in
Figure 16a resp. b.
The optimization result shows the usual truss structure consisting of triangles and agrees with the results from the state of research (see [
8]).
In summary, it can be said that the developed optimization method provides plausible results in the single material case, which are also consistent with the results from the current state of research. As a result, the developed method is considered validated for the single material case.
3.3. Multi-Material
Two isotropic materials with Young’s modulus of and are used for the multi-material cases. The Poisson’s ratio for the two materials is . The weighting is selected as , and for both cases. The two regularization terms are activated after iteration 30 to ensure that they do not dominate the optimization at the beginning.. Since the SDF property disappears when the MBO operator is applied, the two level set functions are redistanced in each iteration. The c parameter of the MMA algorithm is increased from a starting value of 0.1 to 400.0 within 250 iterations by means of a linear ramp.
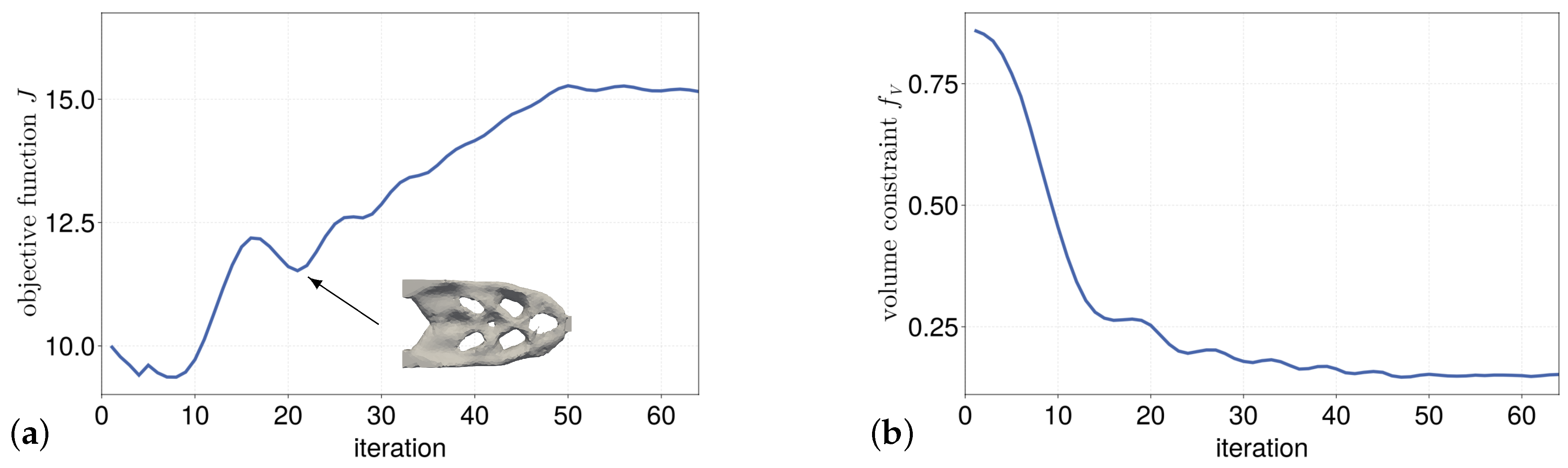
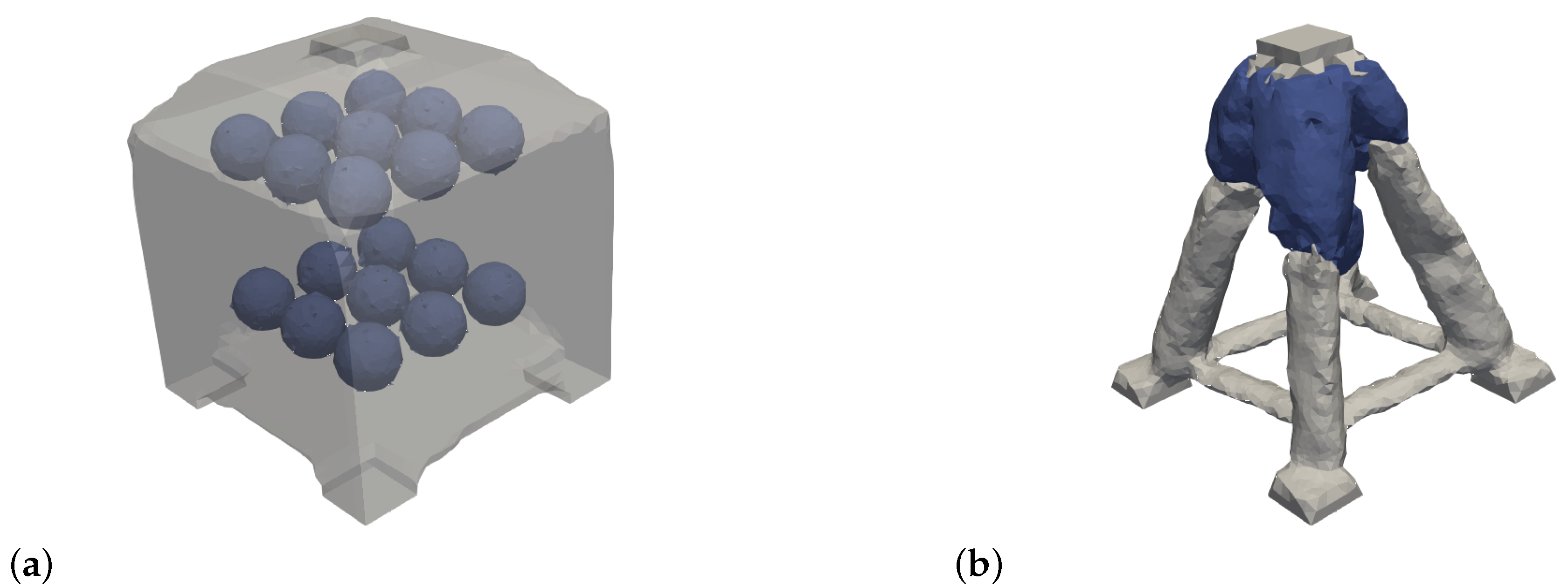
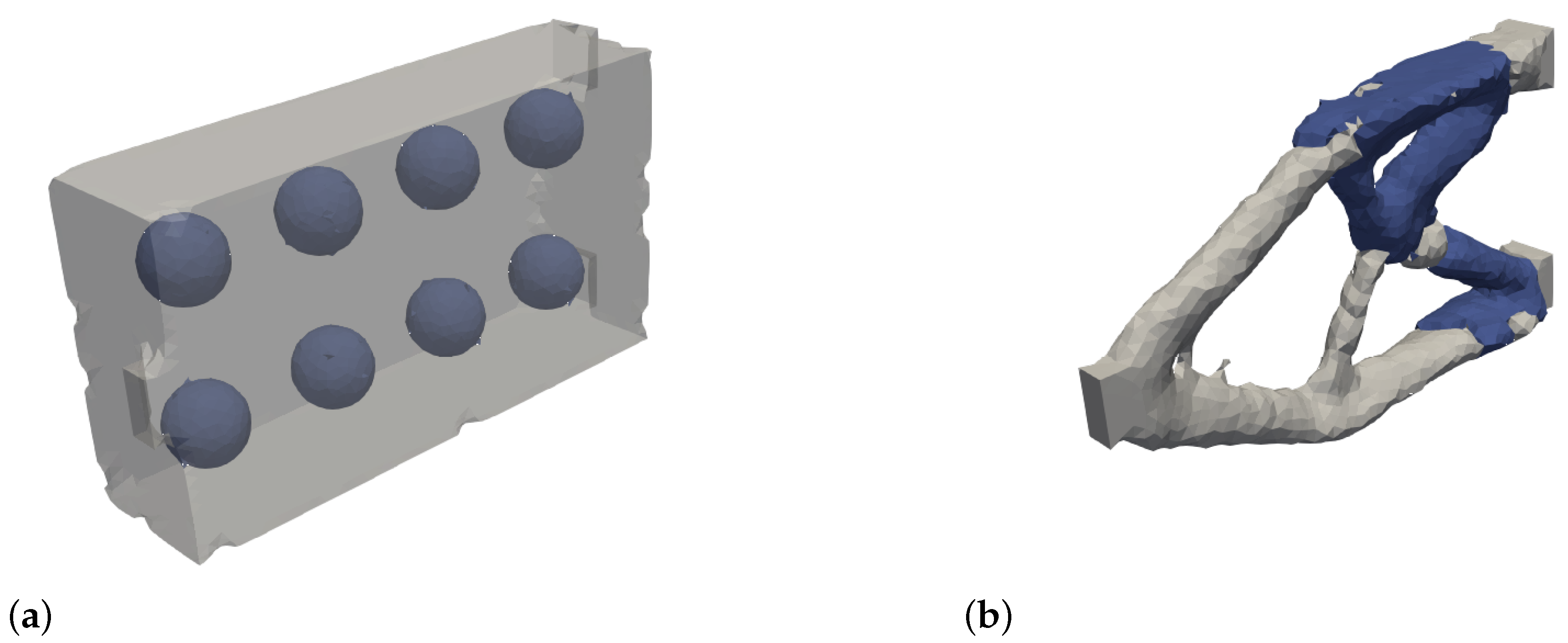
In
Figure 17a,b the initial hole structure for the multi-material case of the box as well as the optimization result is shown. The structure of the multi-material result is very similar to the single-material case. In this case, the square cross strut structure has formed. The less stiff material is shifted by the optimization near the load application.
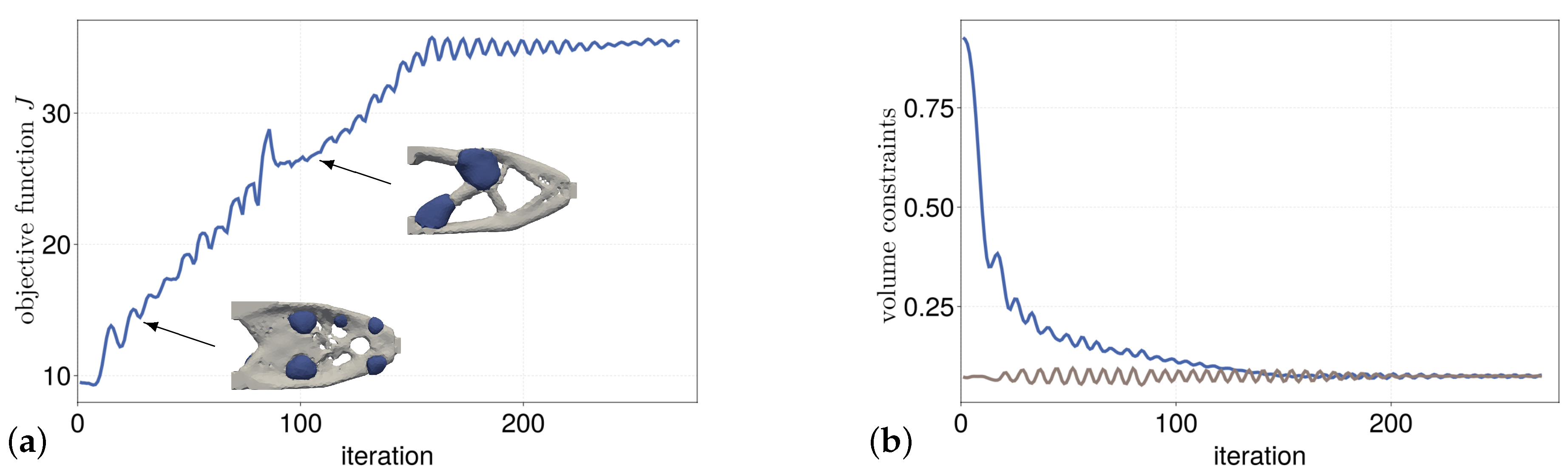
Figure 18a,b show the evolution of the objective function and the evolution of the two volume constraints.
In
Figure 19a,b the initial hole structure for the multi-material case of the cantilever and the resulting optimization result are shown. The optimization result is very similar to the single material result. The material with the lower stiffness is shifted to the rear part of the cantilever in particular. It is also clearly visible that the bars have a greater thickness in the areas of the less stiff material (blue) in order to compensate for the disadvantage of the lower Young’s modulus.
Figure 20a,b show the evolution of the objective function and the evolution of the two volume boundary conditions.
Since the developed optimization method for the multi-material case reuses the already validated components from the single-material case and the optimization results for the multi-material case are also plausible, the developed method is also considered validated for the multi-material case.
4. Sensitivity Studies
In the following, the influence of the two parameters element edge length ratio of the two meshes and filter radius on the optimization result is examined. One study is carried out for each parameter. In both cases, the symmetrical cantilever clamped on one side serves as the object of investigation for the studies. The values of the other parameters are selected analogously as above.
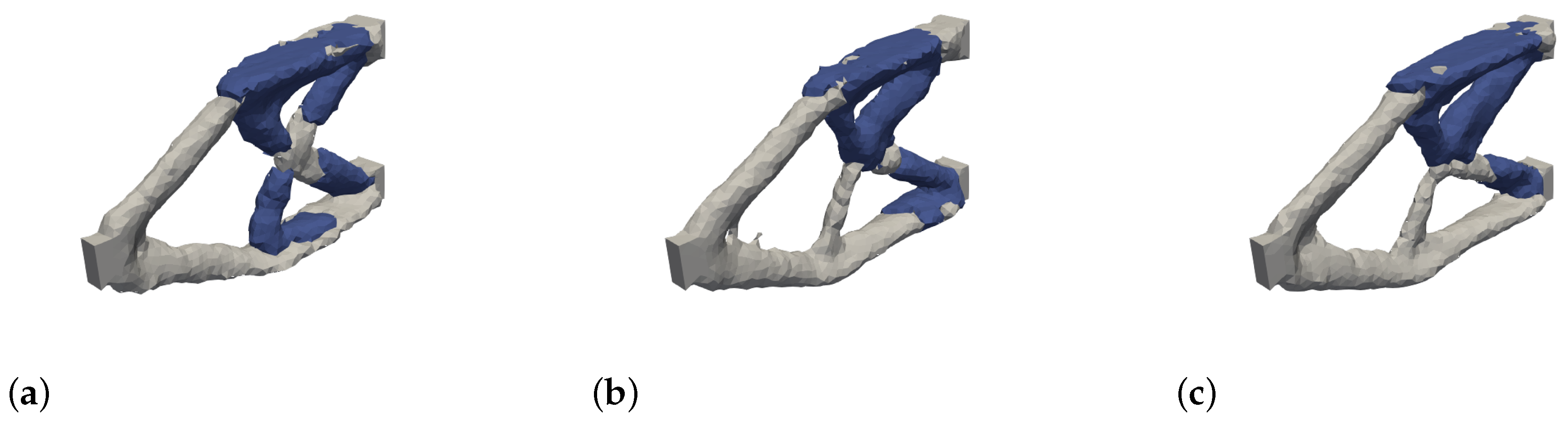
4.1. Edge Length Ratio
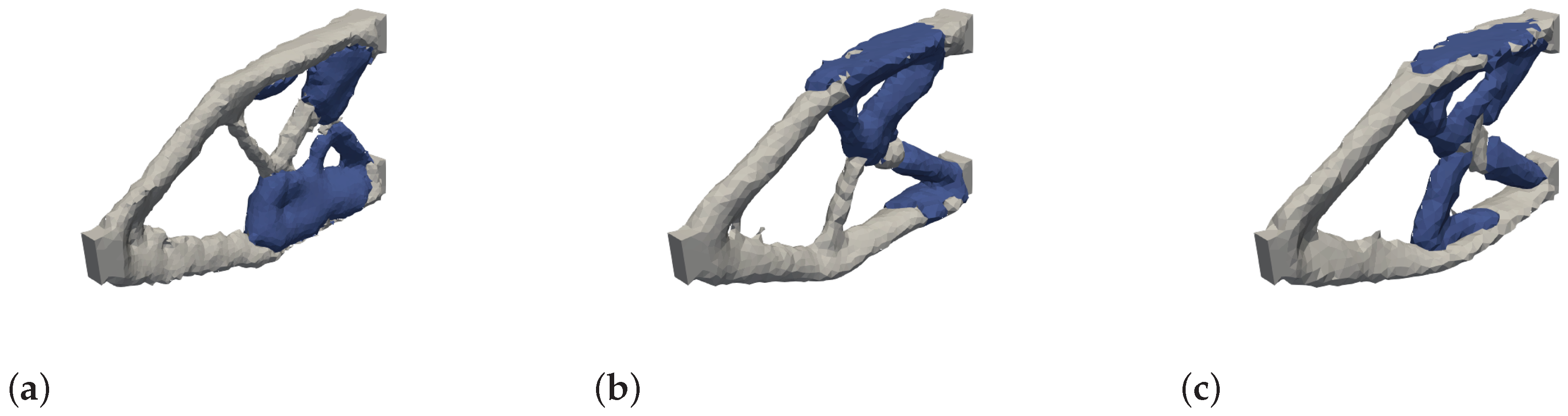
In
Figure 21, the optimization results are shown for different edge lengths of the FE mesh with a constant edge length of the level set mesh (change in ratio). It can be seen that the optimization runs in different local optima, but no systematic pattern can be identified. In addition, the local optima are very close to each other in terms of structure and material distribution.
Further numerical experiments have shown that satisfactory results can always be achieved with approximately the same edge length of the two meshes.
4.2. Filter Radius
In
Figure 22, the optimization results for three different filter parameters of the Helmholtz filter are listed. It can be seen that this has almost no influence on the final optimization result in the selected range. If the filter radius is increased further, it appears that the optimizer generates coarser features, but the two materials are separated during the optimization and it is therefore aborted.
5. Conclusions
In this article, a multi-material topology optimization method was developed to support the product developer for the development of structures in multi-material design. The method combines the Velocity Field Level set method with the Reconciled Level set method. The method uses a constant mesh for the development of the level set functions and a second adaptive mesh for the evaluation of the system response. For the validation of the method, it was first validated on two single-material and then on two multi-material examples.
The influence of the edge length ratio of the two meshes and the influence of the filter parameter on the optimization result were examined in two sensitivity studies. It was shown that the influence is low as long as the parameters are within a reasonable range.
The method forms the basis for further optimization problems that require an explicit resolution of the structures in the multi-material design during optimization. This includes the authors’ current research, in which the influence of the interfaces between the materials, as presented for the first time in [
27], is taken into account. The authors plan to publish their findings in the near future.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.R. and A.A.; methodology, R.R.; software, R.R.; validation, R.R. and A.A.; formal analysis, R.R.; investigation, R.R.; data curation, R.R.; writing—original draft preparation, R.R.; writing—review and editing, R.R.; visualization, R.R.; supervision, A.A.; funding acquisition, A.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this manuscript are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| FE |
Finite Element |
| FEM |
Finite Element Method |
| LS |
Level Set |
| MDPI |
Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute |
| MBO |
Merriman-Bence-Osher |
| MMA |
Method of Moving Asymptotes |
| RCLS |
Reconciled Level Set method |
| VFLS |
Velocity Field Level Set method |
References
- Bendsøe, M.P.; Kikuchi, N. Generating optimal topologies in structural design using a homogenization method. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering 1988, 71, 197–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendsøe, M.P. Optimal shape design as a material distribution problem. Structural Optimization 1989, 1, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.Y.; Zhou, S. Phase Field: A Variational Method for Structural Topology Optimization 2004.
- Xie, Y.; Steven, G. A simple evolutionary procedure for structural optimization. Computers & Structures 1993, 49, 885–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Querin, O.; Steven, G.; Xie, Y. Evolutionary structural optimisation (ESO) using a bidirectional algorithm. Engineering Computations 1998, 15, 1031–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethian, J.; Wiegmann, A. Structural Boundary Design via Level Set and Immersed Interface Methods. Journal of Computational Physics 2000, 163, 489–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.Y.; Wang, X.; Guo, D. A level set method for structural topology optimization. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering 2003, 192, 227–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allaire, G.; Jouve, F.; Toader, A.M. Structural optimization using sensitivity analysis and a level-set method. Journal of Computational Physics 2004, 194, 363–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dijk, N.P.; Maute, K.; Langelaar, M.; Van Keulen, F. Level-set methods for structural topology optimization: a review. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization 2013, 48, 437–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kang, Z. A velocity field level set method for shape and topology optimization. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering 2018, 115, 1315–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svanberg, K. The method of moving asymptotes—a new method for structural optimization. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering 1987, 24, 359–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.Y.; Wang, X. “Color” level sets: a multi-phase method for structural topology optimization with multiple materials. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering 2004, 193, 469–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merriman, B.; Bence, J.K.; Osher, S.J. Motion of Multiple Junctions: A Level Set Approach. Journal of Computational Physics 1994, 112, 334–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Gonella, S.; Chen, W.; Liu, W.K. A level set approach for optimal design of smart energy harvesters. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering 2010, 199, 2532–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogiatzis, P.; Chen, S.; Wang, X.; Li, T.; Wang, L. Topology optimization of multi-material negative Poisson’s ratio metamaterials using a reconciled level set method. Computer-Aided Design 2017, 83, 15–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Li, M.; Han, Z.; Chen, Y.; Gu, X.D.; Ge, Q.; Chen, S. Conformal topology optimization of multi-material ferromagnetic soft active structures using an extended level set method. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering 2022, 389, 114394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belytschko, T.; Xiao, S.P.; Parimi, C. Topology optimization with implicit functions and regularization. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering 2003, 57, 1177–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burman, E.; Elfverson, D.; Hansbo, P.; Larson, M.G.; Larsson, K. Shape optimization using the cut finite element method. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering 2018, 328, 242–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, S.H.; Cho, S. Level set based topological shape optimization of geometrically nonlinear structures using unstructured mesh. Computers & Structures 2008, 86, 1447–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allaire, G.; Dapogny, C.; Frey, P. A mesh evolution algorithm based on the level set method for geometry and topology optimization. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization 2013, 48, 711–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yamada, T.; Jolivet, P.; Furuta, K.; Kondoh, T.; Izui, K.; Nishiwaki, S. Full-scale 3D structural topology optimization using adaptive mesh refinement based on the level-set method. Finite Elements in Analysis and Design 2021, 194, 103561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T.; Izui, K.; Nishiwaki, S.; Takezawa, A. A topology optimization method based on the level set method incorporating a fictitious interface energy. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering 2010, 199, 2876–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feppon, F. Shape and topology optimization applied to Compact Heat Exchangers.
- Osher, S.; Fedkiw, R. Level set methods and dynamic implicit surfaces; Number 153 in Applied mathematical sciences, Springer: New York Berlin Heidelberg, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Aage, N.; Lazarov, B.S. Parallel framework for topology optimization using the method of moving asymptotes. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization 2013, 47, 493–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saye, R. High-order methods for computing distances to implicitly defined surfaces. Communications in Applied Mathematics and Computational Science 2014, 9, 107–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renz, R.; Frank, N.; Albers, A. Three-Dimensional Multi-Material Topology Optimization Considering Interface Behavior, 2023. Published: 15th World Congress of Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization (WCSMO 2023).
- Lazarov, B.S.; Sigmund, O. Filters in topology optimization based on Helmholtz-type differential equations. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering 2011, 86, 765–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, N.R.; Waltz, J.I. 3D level set methods for evolving fronts on tetrahedral meshes with adaptive mesh refinement. Journal of Computational Physics 2017, 336, 492–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagley, B.; Sastry, S.P.; Whitaker, R.T. A Marching-tetrahedra Algorithm for Feature-preserving Meshing of Piecewise-smooth Implicit Surfaces. Procedia Engineering 2016, 163, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barill, G.; Dickson, N.G.; Schmidt, R.; Levin, D.I.W.; Jacobson, A. Fast winding numbers for soups and clouds. ACM Transactions on Graphics 2018, 37, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraj, N.; Thiery, J.M.; Boubekeur, T. Multi-material adaptive volume remesher. Computers & Graphics 2016, 58, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthasarathy, V.; Graichen, C.; Hathaway, A. A comparison of tetrahedron quality measures. Finite Elements in Analysis and Design 1994, 15, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dassi, F.; Formaggia, L.; Zonca, S. Degenerate tetrahedra removal. Applied Numerical Mathematics 2016, 110, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loseille, A.; Menier, V. Serial and Parallel Mesh Modification Through a Unique Cavity-Based Primitive. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Meshing Roundtable; Sarrate, J.; Staten, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2014; pp. 541–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devillers, O.; Pion, S. Efficient Exact Geometric Predicates for Delaunay Triangulations. Technical Report RR-4351, INRIA, 2002.
- Shang, M.; Zhu, C.; Chen, J.; Xiao, Z.; Zheng, Y. A Parallel Local Reconnection Approach for Tetrahedral Mesh Improvement. Procedia Engineering 2016, 163, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holoch, J.; Lenhardt, S.; Renz, R.; Albers, A. Investigation on the Influence of Different Modeling of Multiple Surface Layers on a 3D Topology Optimization. 2021.
- Hu, Y.; Schneider, T.; Wang, B.; Zorin, D.; Panozzo, D. Fast tetrahedral meshing in the wild. ACM Transactions on Graphics 2020, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
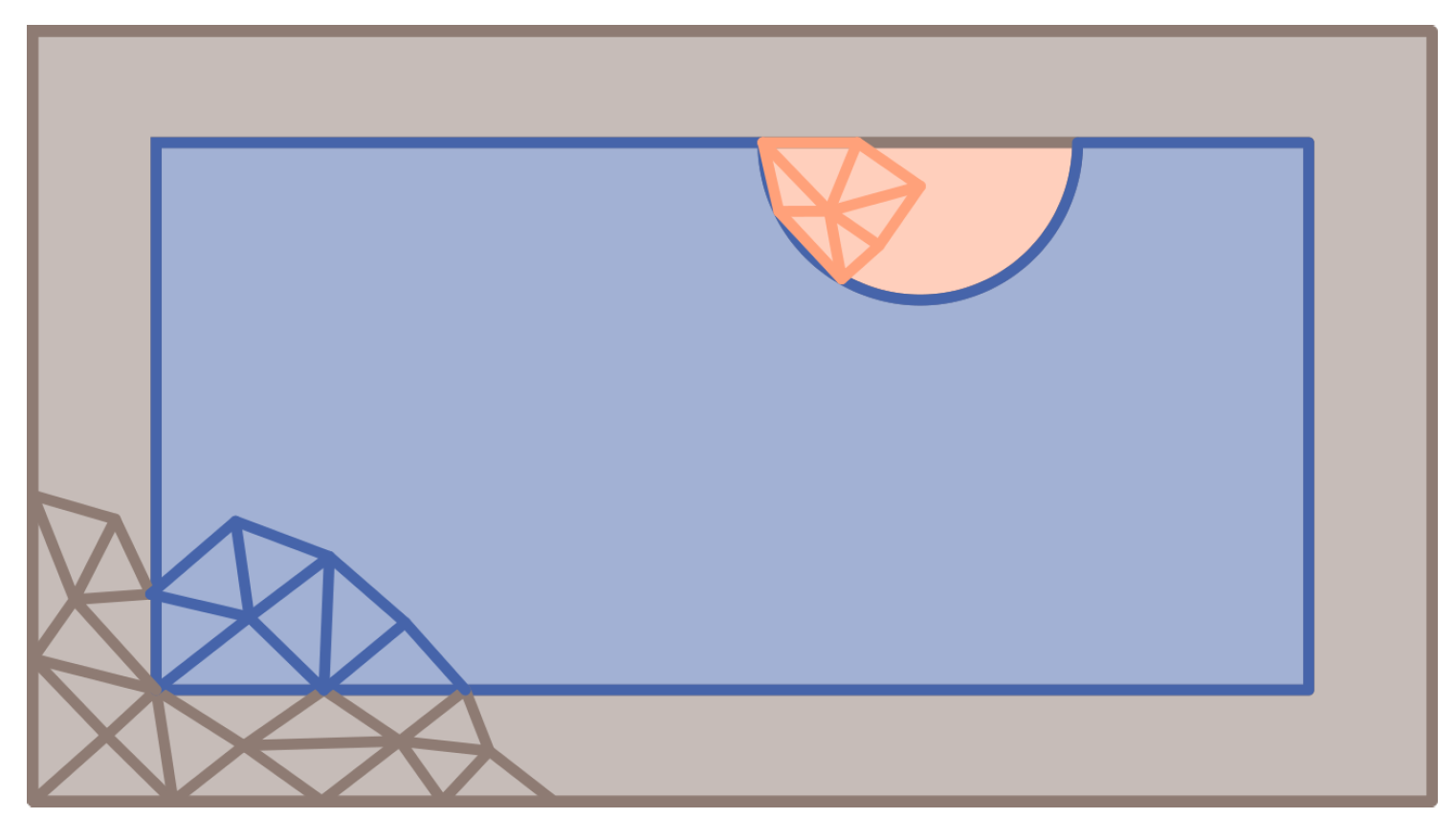
Figure 1.
(a) 2D level set function (blue), which represents a rectangle with two holes. The intersection between the level set function and the plane (green) results in the surface of the rectangle (orange). (b) Representation of the level set function and the corresponding part colored in blue.
Figure 1.
(a) 2D level set function (blue), which represents a rectangle with two holes. The intersection between the level set function and the plane (green) results in the surface of the rectangle (orange). (b) Representation of the level set function and the corresponding part colored in blue.
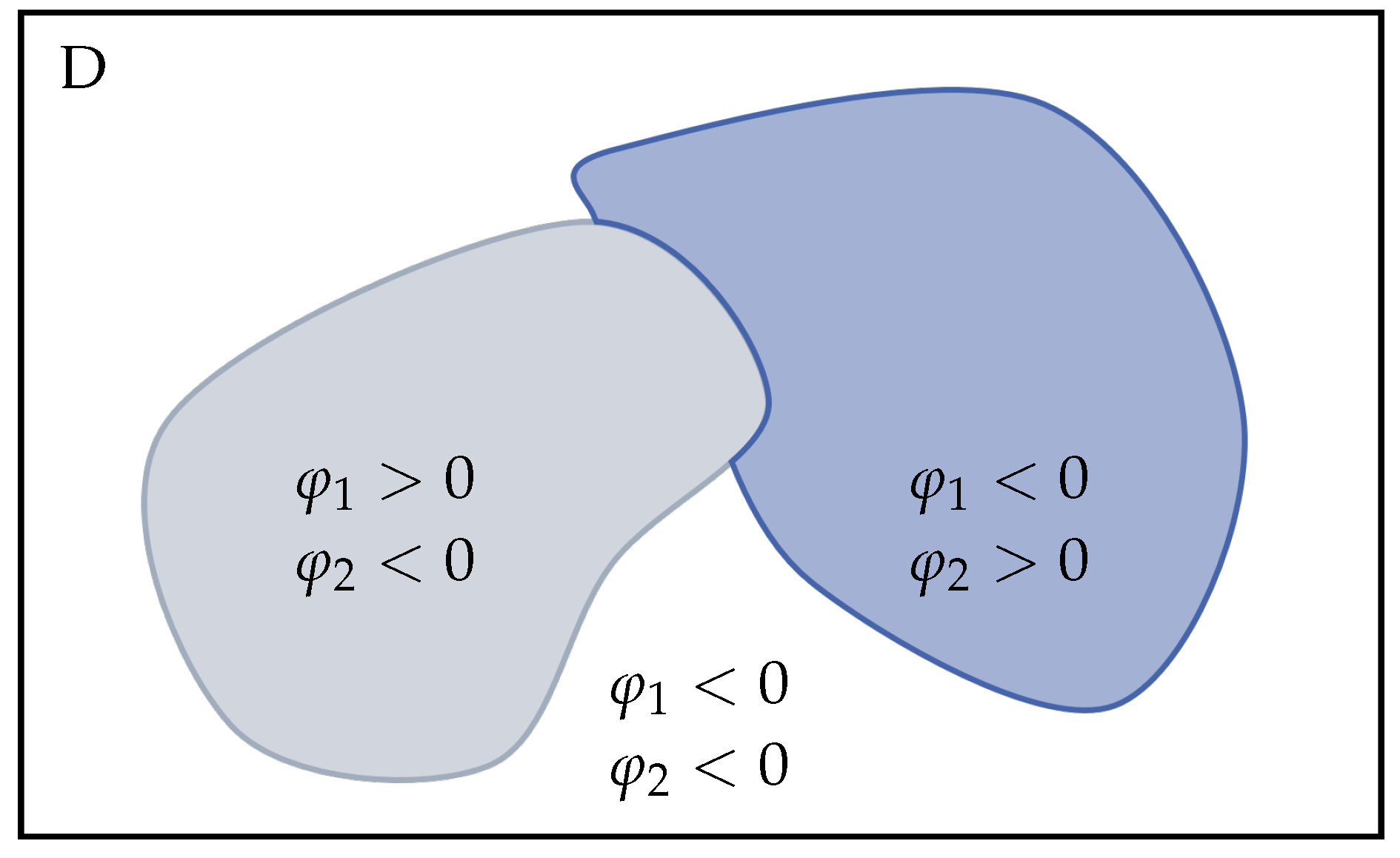
Figure 2.
Reconciled Level Set Method: The level set functions (gray) and (blue) each represent the boundaries of a material () in the design domain D.
Figure 2.
Reconciled Level Set Method: The level set functions (gray) and (blue) each represent the boundaries of a material () in the design domain D.
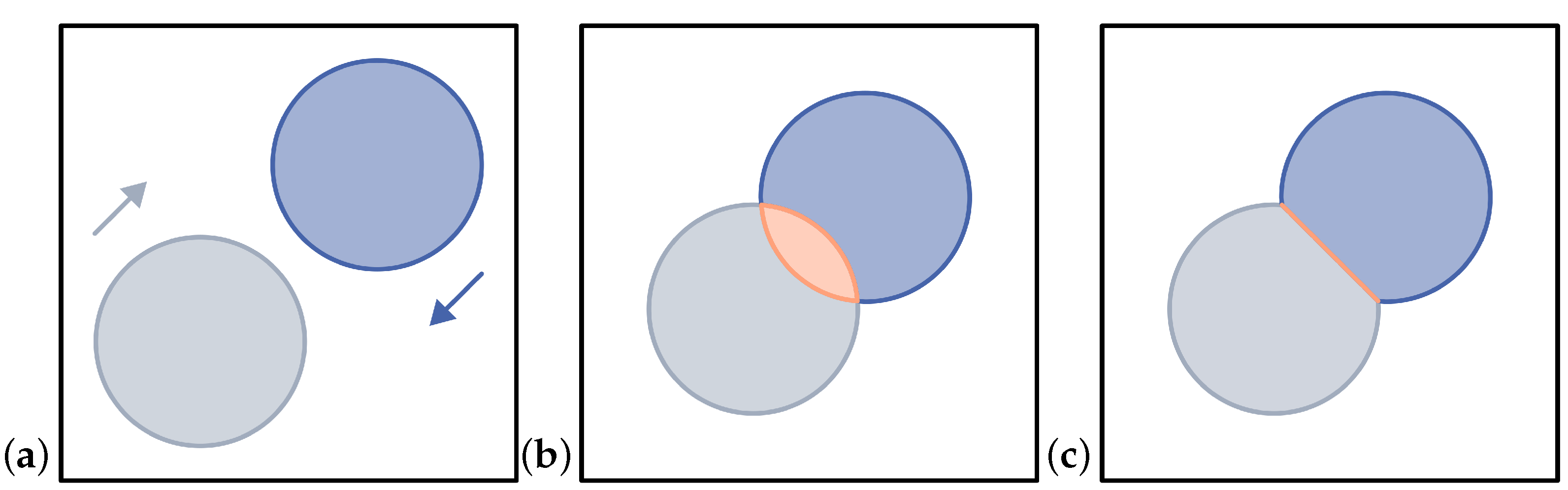
Figure 3.
Visualization of the MBO operator using two level set functions
(gray) and
(blue) moving towards each other based on [
15]. (
a)
and
are moving towards each other, there is no overlap. (
b)
and
overlap in the orange area. (
c) Correction of
and
by applying the MBO operator, there is no longer any overlap.
Figure 3.
Visualization of the MBO operator using two level set functions
(gray) and
(blue) moving towards each other based on [
15]. (
a)
and
are moving towards each other, there is no overlap. (
b)
and
overlap in the orange area. (
c) Correction of
and
by applying the MBO operator, there is no longer any overlap.
Figure 4.
Structure of the optimization loop with the individual components.
Figure 4.
Structure of the optimization loop with the individual components.
Figure 6.
Level set mesh (gray) and the dual mesh with corresponding cells (blue) based on [
29]. The dual mesh is used to develop an accurate upwind approximation of the Hamiltonian. A cellcorner c is shaded black.
Figure 6.
Level set mesh (gray) and the dual mesh with corresponding cells (blue) based on [
29]. The dual mesh is used to develop an accurate upwind approximation of the Hamiltonian. A cellcorner c is shaded black.
Figure 7.
Five unique marching tetrahedra cases based on [
30]. The resulting discretized interface consisting of triangles is shown in orange.
Figure 7.
Five unique marching tetrahedra cases based on [
30]. The resulting discretized interface consisting of triangles is shown in orange.
Figure 8.
(
a) Mesh with classification of vertices into volume and boundary vertices based on [
32]. (
b) Invalid edge collapse, since collapse does not preserve the interface position (non-feature preserving). (
c) Valid edge collapse, since collapse preserves the interface (feature preserving).
Figure 8.
(
a) Mesh with classification of vertices into volume and boundary vertices based on [
32]. (
b) Invalid edge collapse, since collapse does not preserve the interface position (non-feature preserving). (
c) Valid edge collapse, since collapse preserves the interface (feature preserving).
Figure 9.
Examples of cavity operations. (a) Edge collapse: the cavity is initialized with all adjacent elements (triangles or tetrahedra) of vertex A and vertex B serves as the target vertex for the meshing. (b) Edge swap: the cavity is initialized with all elements adjacent to edge BC and node A serves as the target node for meshing.
Figure 9.
Examples of cavity operations. (a) Edge collapse: the cavity is initialized with all adjacent elements (triangles or tetrahedra) of vertex A and vertex B serves as the target vertex for the meshing. (b) Edge swap: the cavity is initialized with all elements adjacent to edge BC and node A serves as the target node for meshing.
Figure 10.
Pre-processing step for remeshing the blue design area. Determination of the convex hull (orange), offset calculation of the convex hull (gray) with subsequent meshing.
Figure 10.
Pre-processing step for remeshing the blue design area. Determination of the convex hull (orange), offset calculation of the convex hull (gray) with subsequent meshing.
Figure 11.
Design space of a box with chamfered edges, which is supported at four locations in the z-plane and has a load application location on the surface with a force in the negative z-direction in the amount of F.
Figure 11.
Design space of a box with chamfered edges, which is supported at four locations in the z-plane and has a load application location on the surface with a force in the negative z-direction in the amount of F.
Figure 12.
Symmetrical design space of the cantilever beam with a fixed support (), a floating support () and a load application point on the front side with a force in the negative z-direction in the amount of F.
Figure 12.
Symmetrical design space of the cantilever beam with a fixed support (), a floating support () and a load application point on the front side with a force in the negative z-direction in the amount of F.
Figure 13.
(a) Initial hole structure of the box in the single-material case.(b) Optimization result for the box at iteration 107.
Figure 13.
(a) Initial hole structure of the box in the single-material case.(b) Optimization result for the box at iteration 107.
Figure 14.
(a) Objective function for the single material case of the box. (b) Volume constraint for the single material case of the box.
Figure 14.
(a) Objective function for the single material case of the box. (b) Volume constraint for the single material case of the box.
Figure 15.
(a) Initial hole structure of the cantilever in the single material case. (b) Optimization result for the cantilever at iteration 60.
Figure 15.
(a) Initial hole structure of the cantilever in the single material case. (b) Optimization result for the cantilever at iteration 60.
Figure 16.
(a) History of the objective function for the single material case of the cantilever. (b) History of the volume constraint for the single material case of the cantilever.
Figure 16.
(a) History of the objective function for the single material case of the cantilever. (b) History of the volume constraint for the single material case of the cantilever.
Figure 17.
(a) Initial hole structure of the box in the multi-material case. (b) Optimization result for the box at iteration 293.
Figure 17.
(a) Initial hole structure of the box in the multi-material case. (b) Optimization result for the box at iteration 293.
Figure 18.
(a) History of the objective function for the multi-material case of the box. (b) History of the volume constraints for the multi-material case of the box (blue material 1, brown material 2).
Figure 18.
(a) History of the objective function for the multi-material case of the box. (b) History of the volume constraints for the multi-material case of the box (blue material 1, brown material 2).
Figure 19.
(a) Initial hole structure of the cantilever in the multi-material case. (b) Optimization result of the cantilever at iteration 267.
Figure 19.
(a) Initial hole structure of the cantilever in the multi-material case. (b) Optimization result of the cantilever at iteration 267.
Figure 20.
(a) History of the objective function for the multi-material case of the cantilever. (b) History of the volume constraints for the multi-material case of the cantilever (blue material 1, brown material 2).
Figure 20.
(a) History of the objective function for the multi-material case of the cantilever. (b) History of the volume constraints for the multi-material case of the cantilever (blue material 1, brown material 2).
Figure 21.
Optimization results of the cantilever for the multi-material case for different average edge lengths of the FE mesh with constant edge length of the LS mesh (a) (iteration 230). (b) (iteration 267). (c) (iteration 163)
Figure 21.
Optimization results of the cantilever for the multi-material case for different average edge lengths of the FE mesh with constant edge length of the LS mesh (a) (iteration 230). (b) (iteration 267). (c) (iteration 163)
Figure 22.
Optimization results of the cantilever for the multi-material case for different values of the helmholtz filter parameter (a) (iteration 227). (b) (iteration 267). (c) (iteration 205).
Figure 22.
Optimization results of the cantilever for the multi-material case for different values of the helmholtz filter parameter (a) (iteration 227). (b) (iteration 267). (c) (iteration 205).
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).